ARISE—The Accuracy Evaluation of a Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Biopsy System Based on MRI Data: A Cadaveric Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Body Donation
2.2. Preparation
2.3. Clinical Imaging
2.3.1. MR Imaging
2.3.2. CT Imaging
2.4. Virtual Target Planning
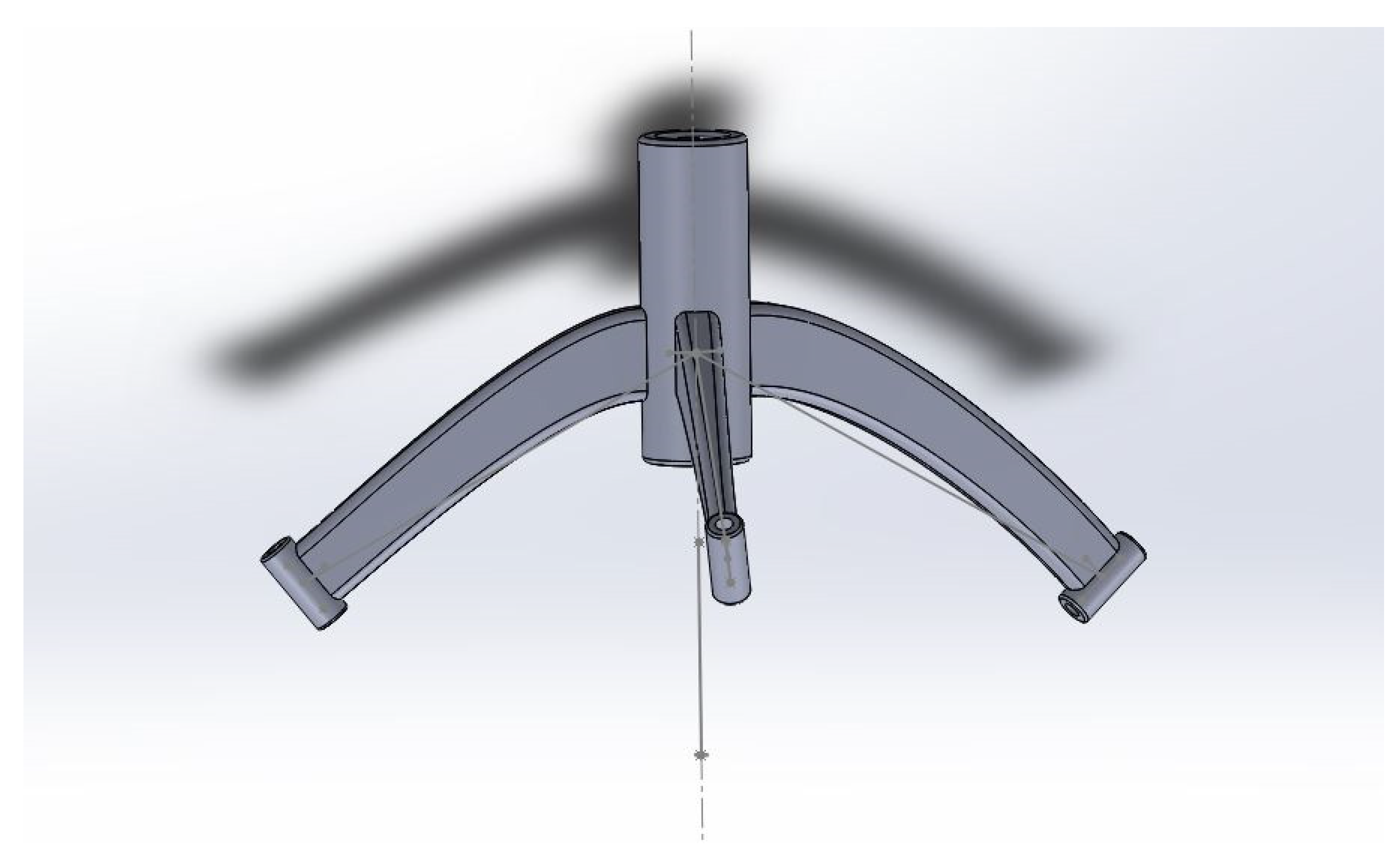
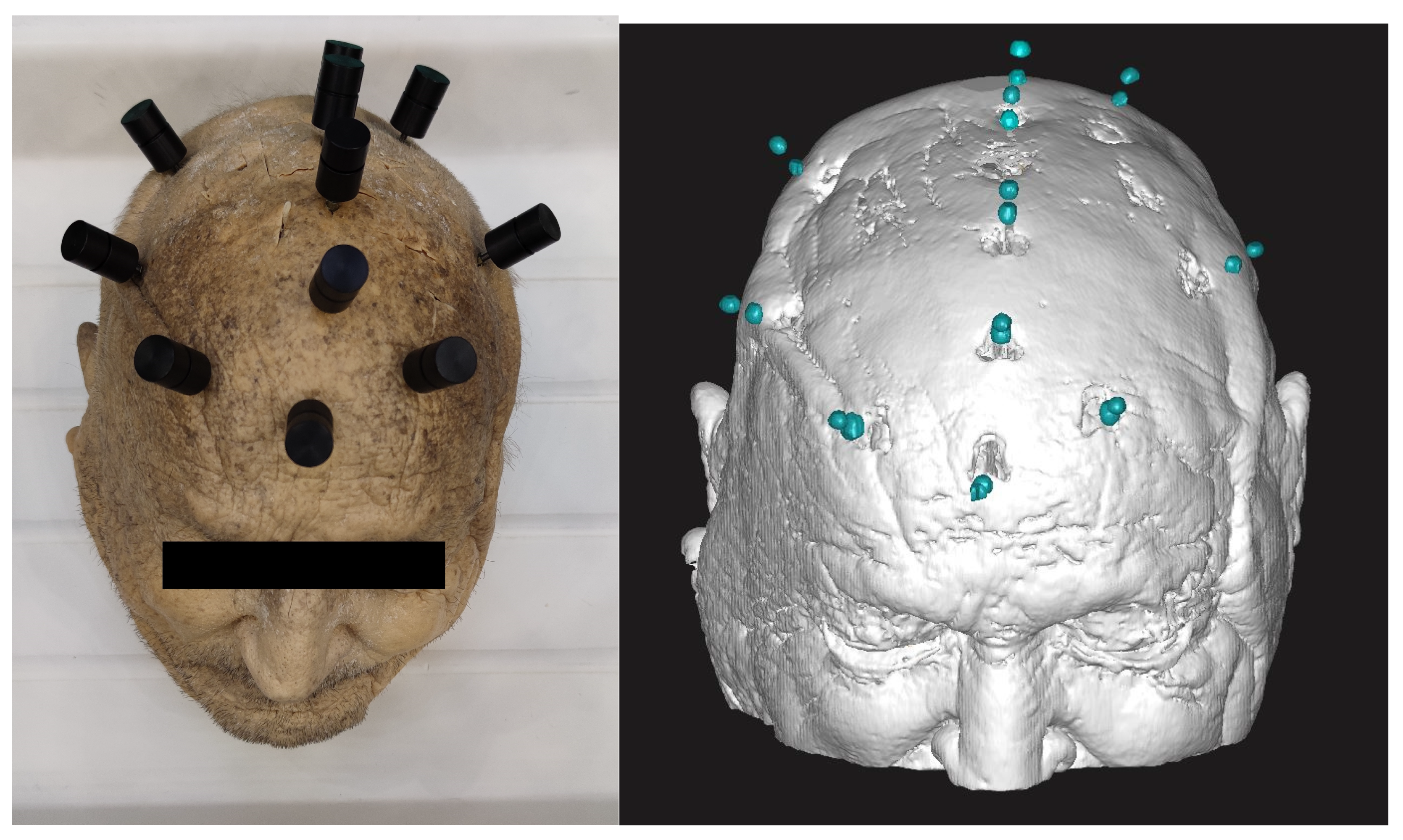
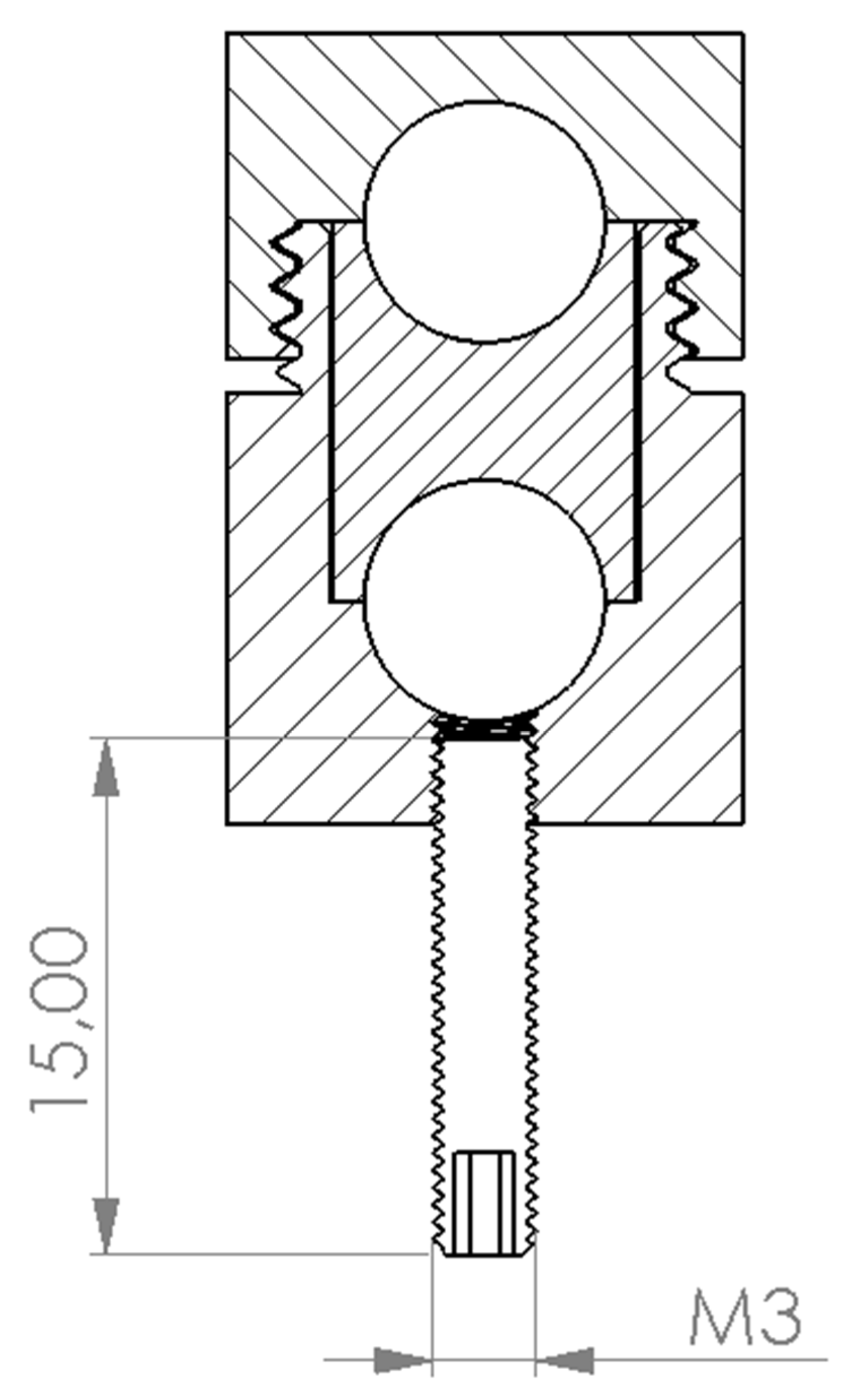
2.5. Three-Dimensional Printing
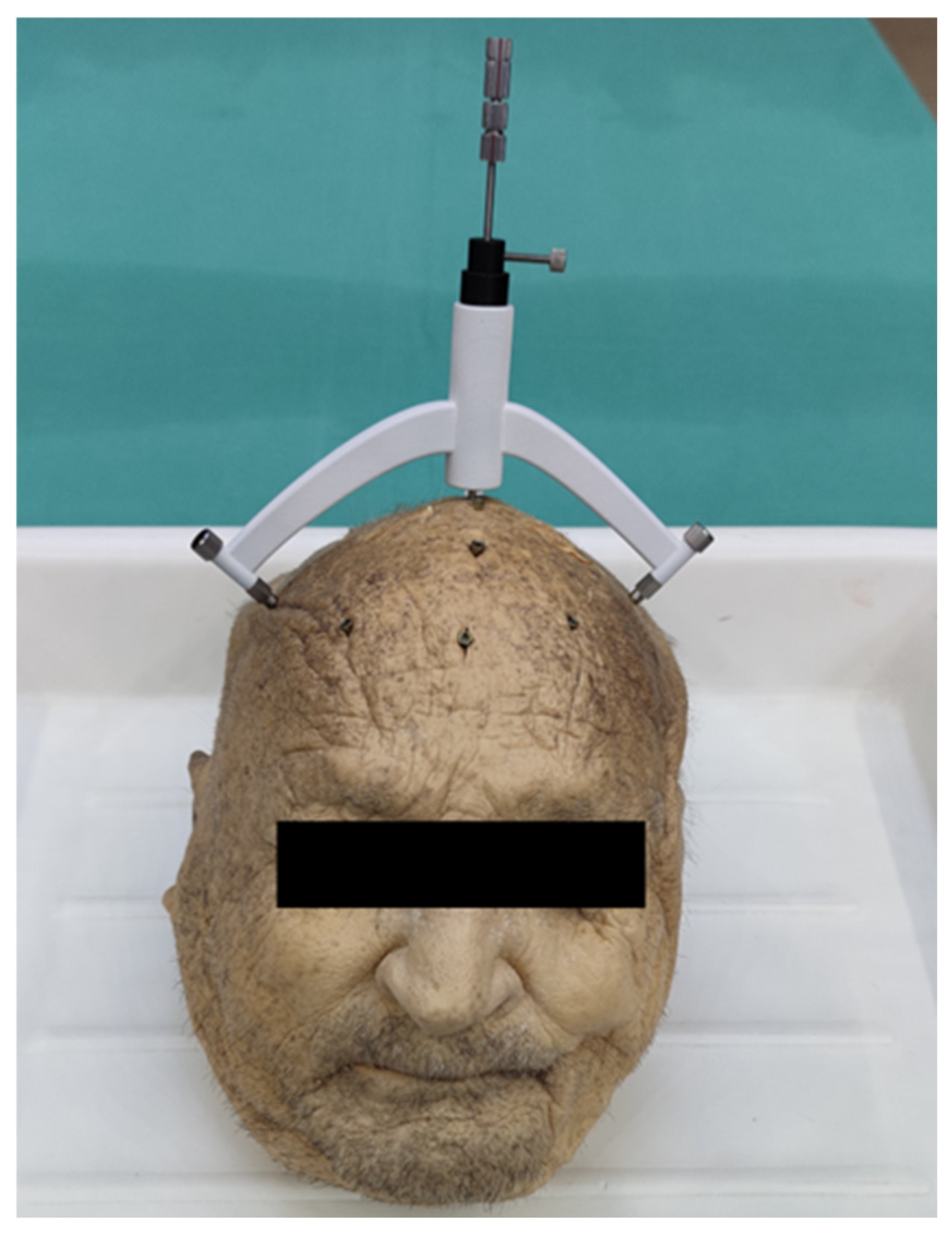
2.6. Intraoperative Implementation
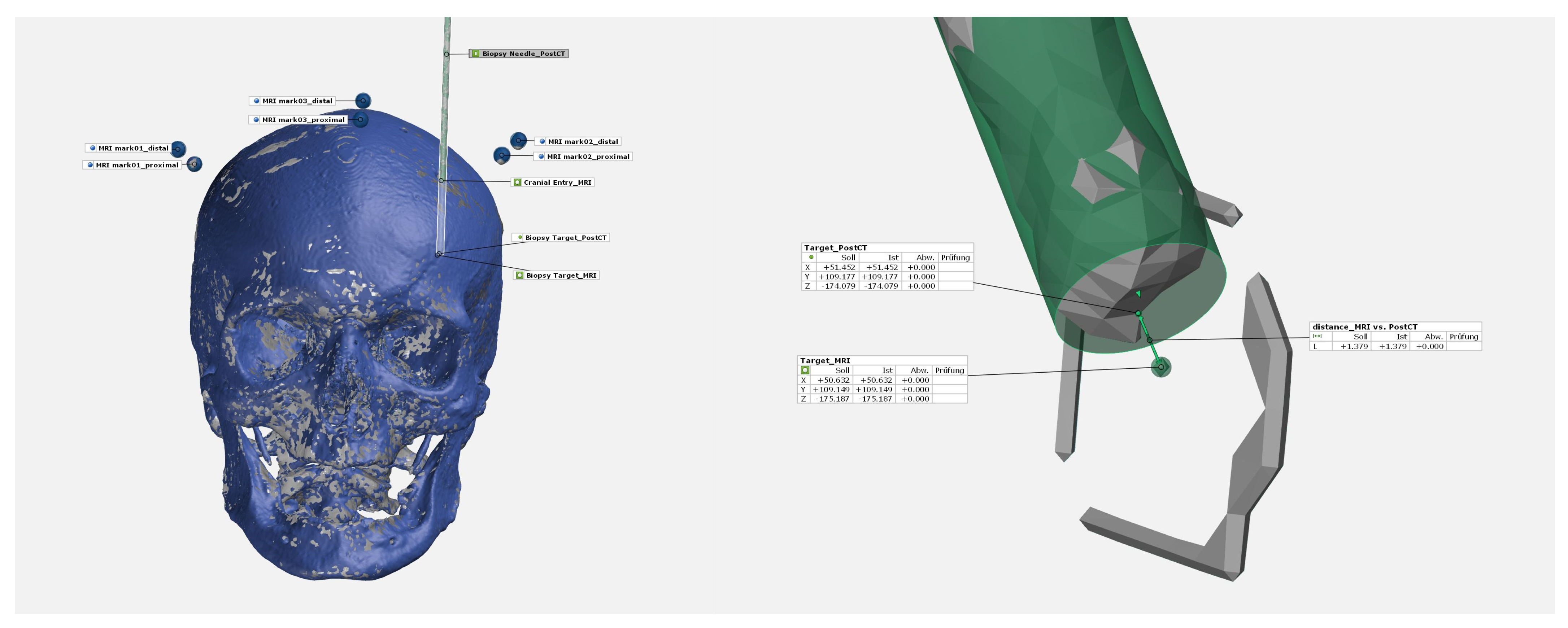
2.7. Accuracy Evaluation
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Accuracy Target Points
3.2. Brain Hemispheres and Lesion Depth
3.3. Manufacturing Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krieger, M.D.; Chandrasoma, P.T.; Zee, C.S.; Apuzzo, M.L. Role of stereotactic biopsy in the diagnosis and management of brain tumors. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1998, 14, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cai, P.; Zhang, H.; Adilijiang, A.; Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Che, S.; Lan, F.; Liu, C. A Comparation Between Frame-Based and Robot-Assisted in Stereotactic Biopsy. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 928070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alptekin, O.; Gubler, F.S.; Ackermans, L.; Kubben, P.L.; Kuijf, M.L.; Kocabicak, E.; Temel, Y. Stereotactic accuracy and frame mounting: A phantom study. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Hu, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sang, L.; Shao, X.; Zhang, K. A comparison between robot-guided and stereotactic frame-based stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) electrode implantation for drug-resistant epilepsy. J. Robot. Surg. 2023, 17, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gempt, J.; Buchmann, N.; Ryang, Y.M.; Krieg, S.; Kreutzer, J.; Meyer, B.; Ringel, F. Frameless image-guided stereotaxy with real-time visual feedback for brain biopsy. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabian, A.; Vinke, S.; Candelario-Mckeown, J.; Milabo, C.; Salazar, M.; Nizam, A.K.; Salloum, N.; Hyam, J.; Akram, H.; Joyce, E.; et al. Accuracy, precision, and safety of stereotactic, frame-based, intraoperative MRI-guided and MRI-verified deep brain stimulation in 650 consecutive procedures. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 138, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Shinya, Y.; Aono, T.; Hasegawa, H.; Kawashima, M.; Shin, M.; Takami, H.; Takayanagi, S.; Umekawa, M.; Ikemura, M.; et al. The Role of Stereotactic Frame-Based Biopsy for Brainstem Tumors in the Era of Molecular-Based Diagnosis and Treatment Decisions. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 4558–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennlund, A.; Jakola, A.S.; Skoglund, T.; Ljungqvist, J. A single-centre study of frame-based stereotactic brain biopsies. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 36, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, S.; He, Y.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Alattar, A.A.; Chen, C.C. Comparison of Frame-Based Versus Frameless Intracranial Stereotactic Biopsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 607–616.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutmann, S.; Winkler, D.; Müller, M.; Möbius, R.; Fischer, J.P.; Böttcher, P.; Kiefer, I.; Grunert, R.; Flegel, T. Accuracy of a magnetic resonance imaging-based 3D printed stereotactic brain biopsy device in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.; Winkler, D.; Möbius, R.; Sauerstein, T.; Scholz, S.; Gutmann, S.; Flegel, T.; Meixensberger, J.; Drossel, W.G.; Grunert, R. A concept for a 3D-printed patient-specific stereotaxy platform for brain biopsy—A canine cadaver study. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 124, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.; Achten, D.; Launhardt, M. Kunststoff-Wissen für die Additive Fertigung: Eigenschaften, Verarbeitung und Einsatzgebiete von Thermoplasten. 1. Auflage; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: München, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Marasso, S.L.; Cocuzza, M. High Resolution Manufacturing from 2D to 3D/4D Printing: Applications in Engineering and Medicine; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Anderhofstadt, R.; Disselkamp, M. Disruptive 3D Printing; Hanser: Munich, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Narváez-Martínez, Y.; García, S.; Roldán, P.; Torales, J.; Rumià, J. Estereoelectroencefalografía mediante el uso de O-Arm® y brazo articulado pasivo Vertek®: Nota técnica y experiencia de un centro de referencia de epilepsia. Neurocirugia 2016, 27, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, G.; Schullian, P.; Ortler, M.; Bale, R. Frameless stereotactic targeting devices: Technical features, targeting errors and clinical results. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. MRCAS 2012, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shi, S. Accuracy and Feasibility Analysis of SEEG Electrode Implantation using the VarioGuide Frameless Navigation System in Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021, 82, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baarsen, K.M.; Woodley, D.E.A.; Slot, K.M.; Woerdeman, P.A.; Han, K.S.; Hoving, E.W. Robotic alignment system Cirq (Brainlab) for navigated brain tumor biopsies in children. Child’s Nerv. Syst. ChNS Off. J. Int. Soc. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2023, 40, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joris, V.; Ribeiro-Vaz, J.G.; Finet, P.; El Tahry, R.; Elkaim, L.M.; Raftopoulos, C.; Ferrao-Santos, S. Stereoelectroencephalography Implantation Using Frameless Neuronavigation and Varioguide: Prospective Analysis of Accuracy and Safety in a Case Series of 11 Patients. World Neurosurg. 2023, 174, e62–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjartmarz, H.; Rehncrona, S. Comparison of accuracy and precision between frame-based and frameless stereotactic navigation for deep brain stimulation electrode implantation. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2007, 85, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradac, O.; Steklacova, A.; Nebrenska, K.; Vrana, J.; de Lacy, P.; Benes, V. Accuracy of VarioGuide Frameless Stereotactic System Against Frame-Based Stereotaxy: Prospective, Randomized, Single-Center Study. World Neurosurg. 2017, 104, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, J.O.; Cook, P.; Brandmeir, N.J. Awake Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery Without Intraoperative Imaging Is Accurate and Effective: A Case Series. Oper. Neurosurg. 2022, 23, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, L.; Nachum, O.; Zibly, Z.; Wohl, A.; Harel, R.; Attia, M.; Spiegelmann, R.; Zaubermann, J.; Feldman, Z.; Knoller, N.; et al. Comparison of Frame-Based Versus Frameless Image-Guided Intracranial Stereotactic Brain Biopsy: A Retrospective Analysis of Safety and Efficacy. World Neurosurg. 2022, 164, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiopoulos, M.; Ellul, J.; Chroni, E.; Constantoyannis, C. Efficacy, Safety, and Duration of a Frameless Fiducial-Less Brain Biopsy versus Frame-based Stereotactic Biopsy: A Prospective Randomized Study. J. Neurol. Surg. Part A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2018, 79, 31–38. [Google Scholar]

| Donor ID | Sex | Age | Height | Weight | Cause of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [years] | [cm] | [kg] | |||
| 121-2019 | male | 89 | 171 | 77.0 | Cardiovascular failure |
| Target Device ID (Brain Hemi-Sphere) | Device Weight [g] | Intracranial Lesion Depth [mm] | Segmented Needle Length [mm] | Segmented Needle Diameter [mm] | Deviation Planned vs. Real [mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x-Plane | y-Plane | z-Plane | Total | |||||
| 01 (right) | 57.3 | 51.06 | 141.06 | 2.49 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 0.21 | 0.24 |
| 01 (left) | 22.34 | 112.33 | 2.56 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.80 | 0.91 | |
| 02 (right) | 65.4 | 53.67 | 143.67 | 2.59 | 0.81 | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.96 |
| 02 (left) | 53.16 | 143.16 | 2.68 | 0.17 | 0.33 | 0.39 | 0.54 | |
| 03 (right) | 70.1 | 54.00 | 144.00 | 2.60 | 0.89 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 1.23 |
| 03 (left) | 44.61 | 134.61 | 2.69 | 0.37 | 0.70 | 0.17 | 0.81 | |
| 04 (right) | 69.9 | 64.25 | 154.25 | 2.84 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.53 | 0.73 |
| 04 (left) | 37.18 | 127.18 | 2.87 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.53 | |
| 05 (right) | 66.4 | 33.72 | 123.72 | 2.63 | 0.27 | 0.20 | 0.78 | 0.85 |
| 05 (left) | 27.28 | 117.28 | 2.69 | 0.06 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.30 | |
| 06 (right) | 50.8 | 31.29 | 121.29 | 2.54 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.38 | 0.41 |
| 06 (left) | 26.95 | 116.95 | 2.68 | 0.90 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 0.95 | |
| 07 (right) | 59.2 | 42.45 | 143.10 | 3.01 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.28 | 1.27 |
| 07 (left) | 40.82 | 142.26 | 2.95 | 0.63 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.83 | |
| 08 (right) | 55.2 | 47.84 | 131.65 | 2.88 | 0.41 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.41 |
| 08 (left) | 47.41 | 132.78 | 2.82 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.47 | 0.62 | |
| 09 (right) | 56.7 | 56.52 | 141.52 | 2.93 | 0.30 | 0.52 | 0.27 | 0.66 |
| 09 (left) | 39.40 | 124.40 | 2.96 | 0.71 | 0.15 | 0.92 | 1.18 | |
| 10 (right) | 60.6 | 30.00 | 128.70 | 2.95 | 0.76 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.84 |
| 10 (left) | 29.11 | 126.92 | 2.90 | 0.34 | 0.95 | 0.80 | 1.28 | |
| 11 (right) | 61.9 | 33.30 | 122.99 | 2.92 | 0.59 | 0.92 | 0.02 | 1.09 |
| 11 (left) | 37.85 | 128.27 | 2.85 | 0.04 | 0.27 | 0.45 | 0.53 | |
| 12 (right) | 63.2 | 62.19 | 161.90 | 3.20 | 0.30 | 0.18 | 0.61 | 0.71 |
| 12 (left) | 67.57 | 167.90 | 3.15 | 1.81 | 0.94 | 0.42 | 2.09 | |
| 13 (right) | 62.9 | 42.05 | 121.73 | 3.24 | 0.45 | 1.46 | 0.27 | 1.55 |
| 13 (left) | 81.25 | 160.94 | 3.21 | 2.13 | 0.74 | 0.82 | 2.40 | |
| 14 (right) | 67.5 | 51.05 | 138.00 | 3.08 | 0.20 | 2.27 | 0.59 | 2.36 |
| 14 (left) | 39.46 | 126.64 | 2.87 | 0.29 | 1.82 | 0.87 | 2.04 | |
| 15 (right) | 58.4 | 37.11 | 137.11 | 3.20 | 0.30 | 0.58 | 0.35 | 0.74 |
| 15 (left) | 52.58 | 152.58 | 3.18 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 0.36 | 0.70 | |
| 16 (right) | 73.6 | 64.48 | 149.48 | 3.32 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.81 | 1.47 |
| 16 (left) | 66.31 | 158.31 | 3.08 | 2.00 | 1.47 | 0.43 | 2.52 | |
| meantotal | 62.4 | 45.88 | 136.77 | 2.89 | 0.56 | 0.60 | 0.45 | 1.05 |
| SDtotal | 6.0 | 13.86 | 14.19 | 0.23 | 0.53 | 0.53 | 0.24 | 0.63 |
| meanright | 47.18 | 137.76 | 2.90 | 0.47 | 0.60 | 0.40 | 1.14 | |
| meanleft | 44.58 | 135.78 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 0.59 | 0.50 | 0.97 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Möbius, R.; Winkler, D.; Kropla, F.; Müller, M.; Scholz, S.; Güresir, E.; Grunert, R. ARISE—The Accuracy Evaluation of a Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Biopsy System Based on MRI Data: A Cadaveric Study. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11101013
Möbius R, Winkler D, Kropla F, Müller M, Scholz S, Güresir E, Grunert R. ARISE—The Accuracy Evaluation of a Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Biopsy System Based on MRI Data: A Cadaveric Study. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(10):1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11101013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMöbius, Robert, Dirk Winkler, Fabian Kropla, Marcel Müller, Sebastian Scholz, Erdem Güresir, and Ronny Grunert. 2024. "ARISE—The Accuracy Evaluation of a Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Biopsy System Based on MRI Data: A Cadaveric Study" Bioengineering 11, no. 10: 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11101013
APA StyleMöbius, R., Winkler, D., Kropla, F., Müller, M., Scholz, S., Güresir, E., & Grunert, R. (2024). ARISE—The Accuracy Evaluation of a Patient-Specific 3D-Printed Biopsy System Based on MRI Data: A Cadaveric Study. Bioengineering, 11(10), 1013. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11101013









