Implementation of Fluorescent-Protein-Based Quantification Analysis in L-Form Bacteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Culture Conditions
2.3. Plasmid Constructions
2.4. Microplate Reader Measurement
2.5. Confocal Microscopy Observation
2.6. Imaging Flow Cytometry (IFC) Analysis
3. Results
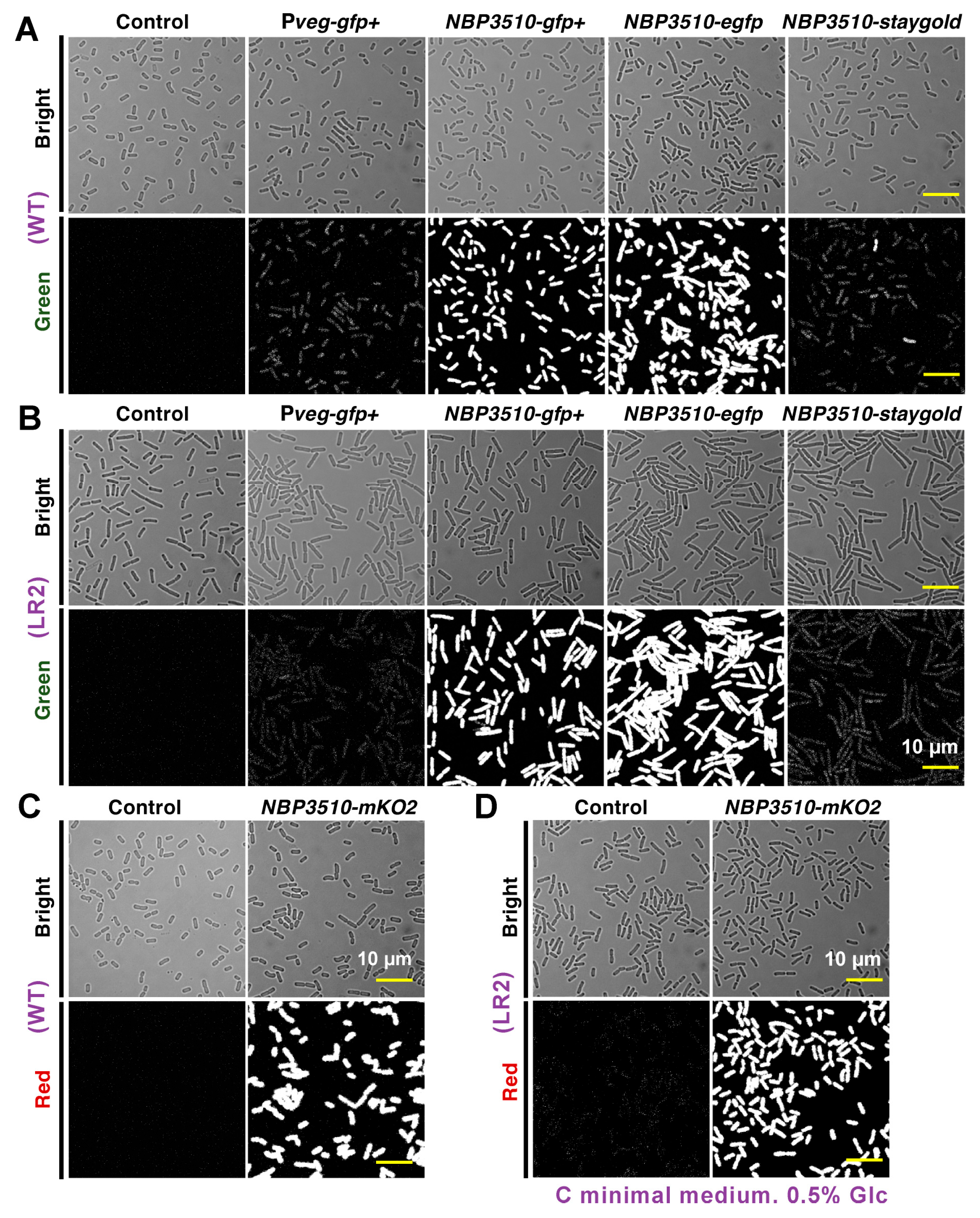
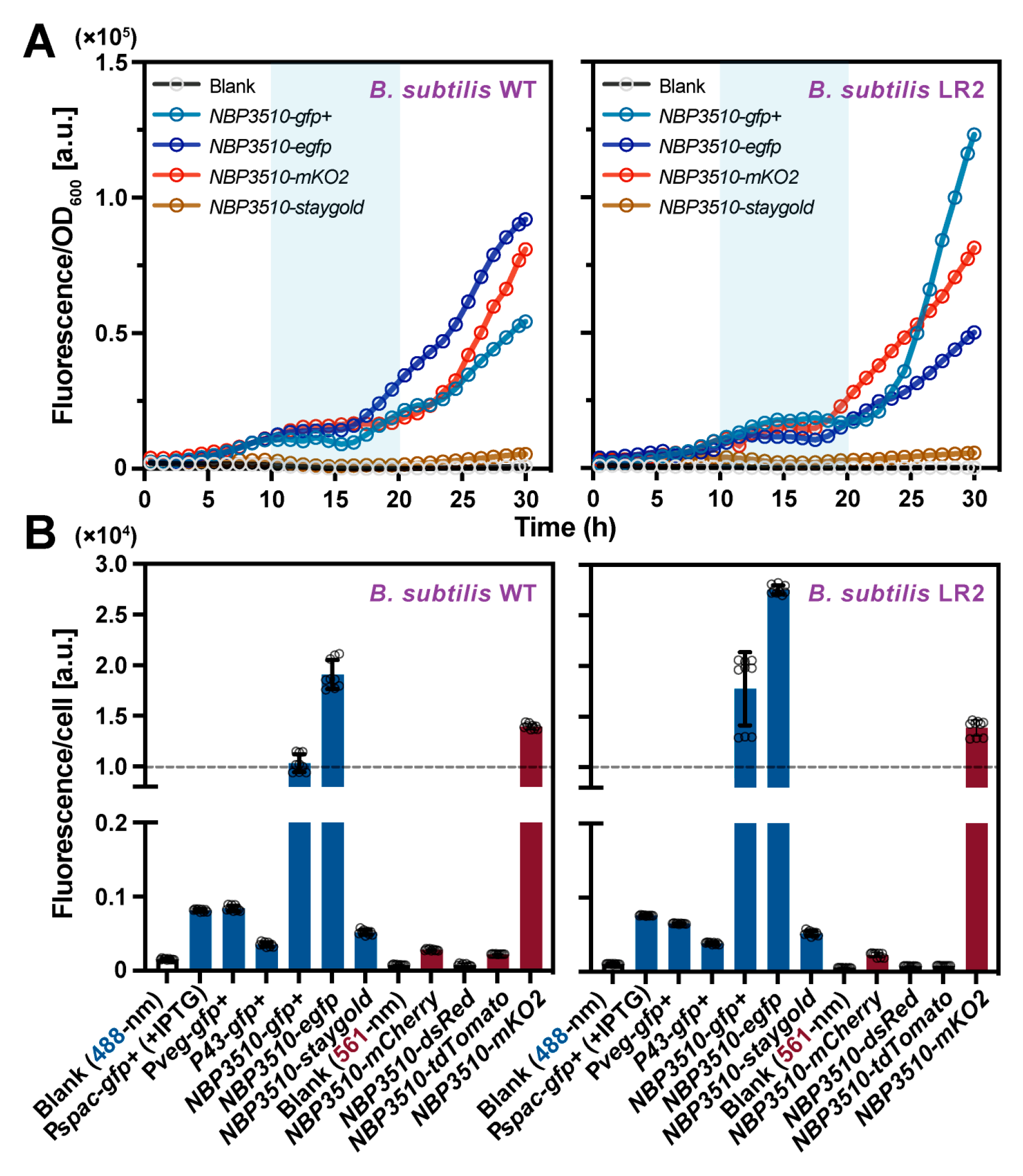
3.1. Evaluation of the Fluorescent Protein Expressions in B. subtilis WT and LR2
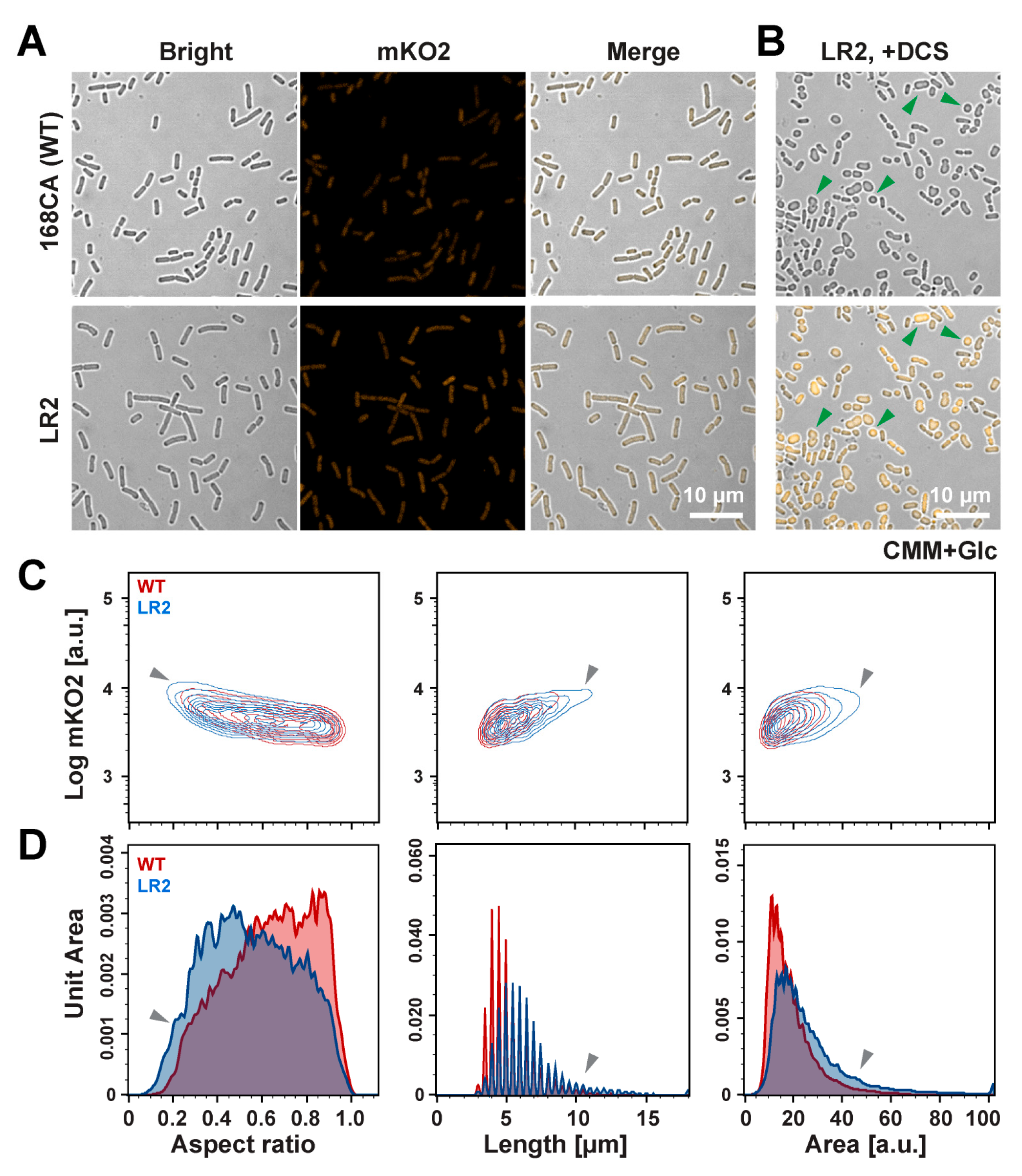
3.2. Fluorescent Protein mKO2-Based Quantification Analysis in B. subtilis WT and L-Form Cells
3.3. NBP3510 Promoter Is Also Active in E. coli Strains
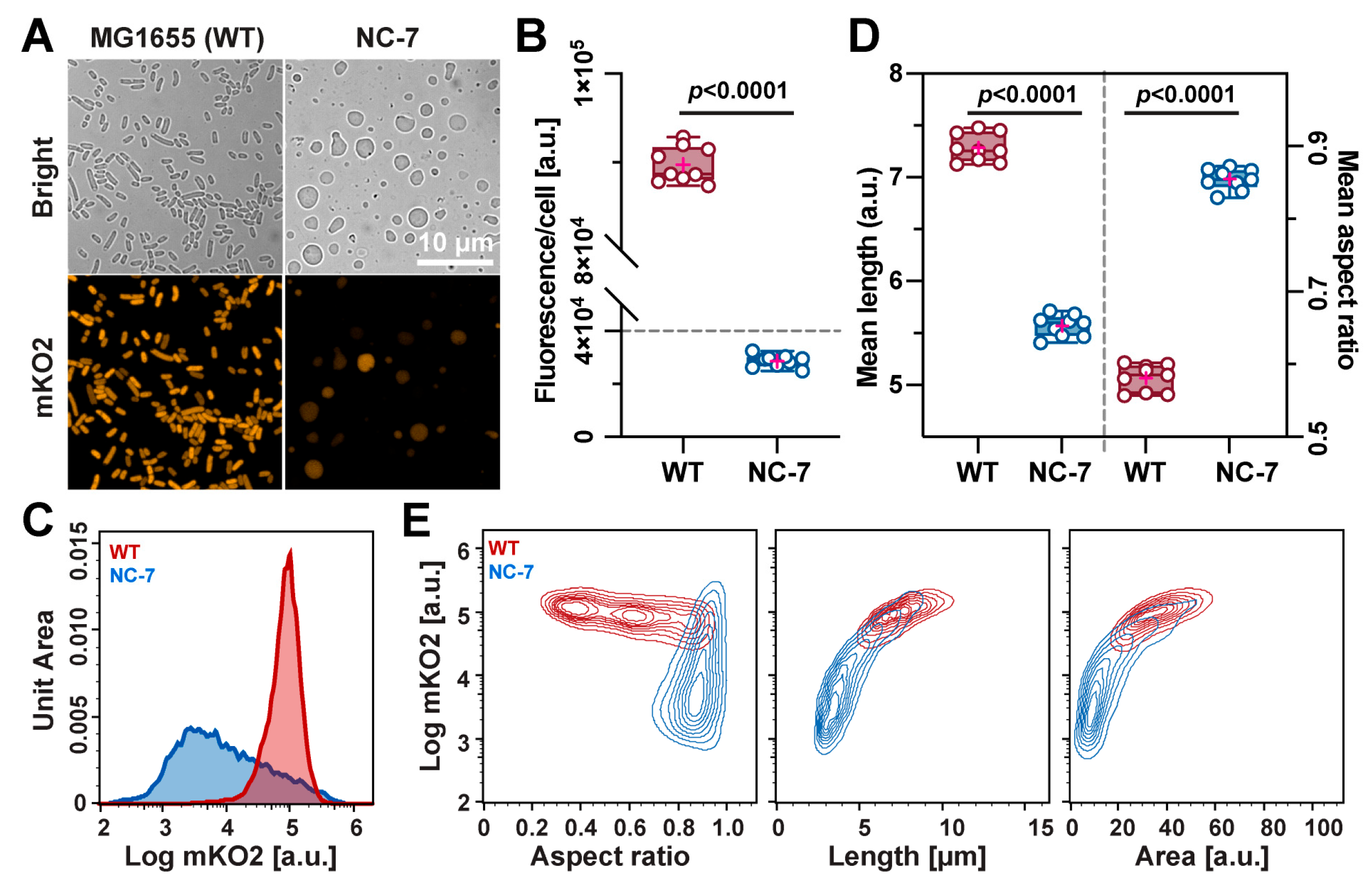
3.4. Quantification Analysis in the E. coli WT and NC-7 L-Form Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allan, E.J.; Hoischen, C.; Gumpert, J. Bacterial L-forms. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 68, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markova, N.; Slavchev, G.; Michailova, L.; Jourdanova, M. Survival of Escherichia coli under lethal heat stress by L-form conversion. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 6, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlfarth, J.C.; Feldmuller, M.; Schneller, A.; Kilcher, S.; Burkolter, M.; Meile, S.; Pilhofer, M.; Schuppler, M.; Loessner, M.J. L-form conversion in Gram-positive bacteria enables escape from phage infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattman, L.H. Cell Wall Deficient Forms: Stealth Pathogens; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Osawa, M.; Erickson, H.P. L form bacteria growth in low-osmolality medium. Microbiology 2019, 165, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducret, A.; Quardokus, E.M.; Brun, Y.V. MicrobeJ, a tool for high throughput bacterial cell detection and quantitative analysis. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sycuro, L.K.; Rule, C.S.; Petersen, T.W.; Wyckoff, T.J.; Sessler, T.; Nagarkar, D.B.; Khalid, F.; Pincus, Z.; Biboy, J.; Vollmer, W. Flow cytometry-based enrichment for cell shape mutants identifies multiple genes that influence Helicobacter pylori morphology. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 90, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubacher, M.E.; Melquist, A.L.; Chandramohan, L.; Young, K.D. Cell sorting enriches Escherichia coli mutants that rely on peptidoglycan endopeptidases to suppress highly aberrant morphologies. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Caliari, A.; Lu, H.; Xia, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Yomo, T. Cell Sorting-Directed Selection of Bacterial Cells in Bigger Sizes Analyzed by Imaging Flow Cytometry during Experimental Evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felip, M.; Andreatta, S.; Sommaruga, R.; Straskrabova, V.; Catalan, J. Suitability of flow cytometry for estimating bacterial biovolume in natural plankton samples: Comparison with microscopy data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 4508–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.R.; Hands, C.L.; Coello-Garcia, T.; Sani, B.S.; Ott, A.I.G.; Smith, S.J.; Davenport, R.J. A flow cytometry method for bacterial quantification and biomass estimates in activated sludge. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 160, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, F.; McGoverin, C.; Swift, S.; Vanholsbeeck, F. Absolute bacterial cell enumeration using flow cytometry. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 464–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alba, C.; Marin, A.C.; McNicholl, A.G.; Montalban-Arques, A.; Mora-Gutierrez, I.; Sanchez-Arroyo, A.J.; Soler, T.; Garcia-Fresnadillo, D.; Gisbert, J.P.; Alarcon, T.; et al. A quick flow cytometry protocol to assess Helicobacter pylori viability. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 177, 106043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayana, S.K.; Mallick, S.; Siegumfeldt, H.; van den Berg, F. Bacterial flow cytometry and imaging as potential process monitoring tools for industrial biotechnology. Fermentation 2020, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, A.L.; Barber, D.G.; Groenhof, S.R.M.; Wagley, S.; Liu, P.; Parker, D.A.; Love, J. The Application of Imaging Flow Cytometry for Characterisation and Quantification of Bacterial Phenotypes. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 716592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreatta, S.; Wallinger, M.M.; Piera, J.; Catalan, J.; Psenner, R.; Hofer, J.S.; Sommaruga, R. Tools for discrimination and analysis of lake bacterioplankton subgroups measured by flow cytometry in a high-resolution depth profile. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 36, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; Chung, J.; Yin, J.; Yoon, J. Recent progress in fluorescent probes for bacteria. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7725–7744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Fluorescent proteins of the EosFP clade: Intriguing marker tools with multiple photoactivation modes for advanced microscopy. RSC Chem. Biol. 2021, 2, 796–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Genetically encodable fluorescent protein markers in advanced optical imaging. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2022, 10, 042002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, H.; Yang, Y.; Yoon, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular Antibacterial Materials for Combatting Antibiotic Resistance. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1805092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giepmans, B.N.; Adams, S.R.; Ellisman, M.H.; Tsien, R.Y. The fluorescent toolbox for assessing protein location and function. Science 2006, 312, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpe, K. Overview of bacterial expression systems for heterologous protein production: From molecular and biochemical fundamentals to commercial systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calero, P.; Nikel, P.I. Chasing bacterial chassis for metabolic engineering: A perspective review from classical to non-traditional microorganisms. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 98–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yansura, D.G.; Henner, D.J. Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavsar, A.P.; Zhao, X.; Brown, E.D. Development and characterization of a xylose-dependent system for expression of cloned genes in Bacillus subtilis: Conditional complementation of a teichoic acid mutant. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, T.T.; Nguyen, H.D.; Schumann, W. Novel plasmid-based expression vectors for intra- and extracellular production of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 46, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.T.; Schumann, W. A novel cold-inducible expression system for Bacillus subtilis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2007, 53, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.T.; Schumann, W. Development of a glycine-inducible expression system for Bacillus subtilis. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 128, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Ogasawara, N.; Sekiguchi, J. Transcriptional, functional and cytochemical analyses of the veg gene in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biochem. 2003, 133, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.L.; Liu, H.; Yang, M.M.; Gong, Y.S.; Chen, H. Assay and characterization of a strong promoter element from B. subtilis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Cui, Z.L.; Hong, Q.; Li, S.P. High-level expression and secretion of methyl parathion hydrolase in Bacillus subtilis WB800. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4101–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Pan, J.G.; Park, S.H.; Choi, S.K. Development of a stationary phase-specific autoinducible expression system in Bacillus subtilis. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 149, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.; Cui, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, J.; Hu, X.; Xiao, G.; Zhou, Z. Construction and development of an auto-regulatory gene expression system in Bacillus subtilis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, C.; Cui, W.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z. Development of an efficient autoinducible expression system by promoter engineering in Bacillus subtilis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Chu, X.; Wang, P.; Tian, J.; Wu, N.; Fan, Y. Identification of a highly efficient stationary phase promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, B.; Cheng, S.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Yan, X. Promoter engineering enables overproduction of foreign proteins from a single copy expression cassette in Bacillus subtilis. Microb. Cell Fact. 2019, 18, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, J.; Valle, F.; Bolivar, F.; Merino, E. Construction of protein overproducer strains in Bacillus subtilis by an integrative approach. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 55, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijland, R.; Lindner, C.; van Hartskamp, M.; Hamoen, L.W.; Kuipers, O.P. Heterologous production and secretion of Clostridium perfringens beta-toxoid in closely related Gram-positive hosts. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 127, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, R.; Vasheghani-Farahani, E.; Shojaosadati, S.A.; Bambai, B. Auto-inducible expression system based on the SigB-dependent ohrB promoter in Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Biol. 2014, 48, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leaver, M.; Dominguez-Cuevas, P.; Coxhead, J.; Daniel, R.; Errington, J. Life without a wall or division machine in Bacillus subtilis. Nature 2009, 457, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Mercier, R.; Wu, L.J.; Domínguez-Cuevas, P.; Oshima, T.; Errington, J. Cell growth of wall-free L-form bacteria is limited by oxidative damage. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 1613–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, Y.; Mickiewicz, K.; Errington, J. Lysozyme Counteracts beta-Lactam Antibiotics by Promoting the Emergence of L-Form Bacteria. Cell 2018, 172, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errington, J. L-form bacteria, cell walls and the origins of life. Open Biol. 2013, 3, 120143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, R.; Kawai, Y.; Errington, J. Excess membrane synthesis drives a primitive mode of cell proliferation. Cell 2013, 152, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoda, T.; Oshima, A.; Nakano, S.; Matsuno, A. Morphology, growth and reversion in a stable L-form of Escherichia coli K12. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1987, 133, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faires, N.; Tobisch, S.; Bachem, S.; Martin-Verstraete, I.; Hecker, M.; Stulke, J. The catabolite control protein CcpA controls ammonium assimilation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 1, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.J.; Marston, A.L. GFP vectors for controlled expression and dual labelling of protein fusions in Bacillus subtilis. Gene 1999, 227, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltwasser, M.; Wiegert, T.; Schumann, W. Construction and application of epitope- and green fluorescent protein-tagging integration vectors for Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mercier, R.; Kawai, Y.; Errington, J. General principles for the formation and proliferation of a wall-free (L-form) state in bacteria. Elife 2014, 3, e04629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cornilleau, C.; Muller, R.R.; Meier, D.; Flores, P.; Guerin, C.; Wolf, D.; Fromion, V.; Carballido-Lopez, R.; Mascher, T. Comprehensive and Comparative Transcriptional Profiling of the Cell Wall Stress Response in Bacillus subtilis. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M.; Ando, R.; Shimozono, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Takeda, N.; Kurokawa, H.; Deguchi, R.; Endo, K.; Haga, K.; Takai-Todaka, R. A highly photostable and bright green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veening, J.W.; Smits, W.K.; Hamoen, L.W.; Jongbloed, J.D.; Kuipers, O.P. Visualization of differential gene expression by improved cyan fluorescent protein and yellow fluorescent protein production in Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 6809–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastalla, I.; Chim, K.; Cheung, G.Y.; Pomerantsev, A.P.; Leppla, S.H. Codon-optimized fluorescent proteins designed for expression in low-GC gram-positive bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortineau, N.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Gaillot, O.; Pellegrini, E.; Berche, P.; Gaillard, J.-L. Optimization of green fluorescent protein expression vectors for in vitro and in vivo detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Res. Microbiol. 2000, 151, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, T.; Skretas, G.; Georgiou, G. Strain engineering for improved expression of recombinant proteins in bacteria. Microb. Cell Fact. 2011, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaner, N.C.; Patterson, G.H.; Davidson, M.W. Advances in fluorescent protein technology. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 4247–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulatowski, L.M.; Whitmore, K.L.; Romigh, T.; VanderWyden, A.S.; Satinover, S.M.; Drumm, M.L. Strain-specific variants of the mouse Cftr promoter region reveal transcriptional regulatory elements. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 1933–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guan, C.; Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Huang, X.; Su, J.; Chen, D.; Lu, Z.; Li, Q.; Gu, R. Broad-host-range application of the srfA promoter from Bacillus subtilis in Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 168, 105798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J.; Mickiewicz, K.; Kawai, Y.; Wu, L.J. L-form bacteria, chronic diseases and the origins of life. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, J.C.; Patil, K.R.; Rocha, I. Systems biology perspectives on minimal and simpler cells. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 487–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, C.; Tian, D.; Lu, H.; Xu, B.; Xia, Y.; Kashiwagi, A.; Westermann, M.; Hoischen, C.; et al. Comparative genomics hints at dispensability of multiple essential genes in two Escherichia coli L-form strains. Biosci. Rep. 2023, 43, BSR20231227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, C.M.; Booth, N.A.; Allan, E.J. An ELISA for the detection of Bacillus subtilis L-form bacteria confirms their symbiosis in strawberry. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2000, 31, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mickiewicz, K.M.; Kawai, Y.; Drage, L.; Gomes, M.C.; Davison, F.; Pickard, R.; Hall, J.; Mostowy, S.; Aldridge, P.D.; Errington, J. Possible role of L-form switching in recurrent urinary tract infection. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejman, D.; Livyatan, I.; Fuks, G.; Gavert, N.; Zwang, Y.; Geller, L.T.; Rotter-Maskowitz, A.; Weiser, R.; Mallel, G.; Gigi, E.; et al. The human tumor microbiome is composed of tumor type-specific intracellular bacteria. Science 2020, 368, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Yomo, T. Implementation of Fluorescent-Protein-Based Quantification Analysis in L-Form Bacteria. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010081
Tian D, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Xia Y, Xu B, Xu J, Yomo T. Implementation of Fluorescent-Protein-Based Quantification Analysis in L-Form Bacteria. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Di, Yiyuan Liu, Yueyue Zhang, Yunfei Liu, Yang Xia, Boying Xu, Jian Xu, and Tetsuya Yomo. 2024. "Implementation of Fluorescent-Protein-Based Quantification Analysis in L-Form Bacteria" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010081
APA StyleTian, D., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., Xia, Y., Xu, B., Xu, J., & Yomo, T. (2024). Implementation of Fluorescent-Protein-Based Quantification Analysis in L-Form Bacteria. Bioengineering, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010081






