Effect of 3-Dimensional Robotic Therapy Combined with Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Function and Cerebral Cortex Activation in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
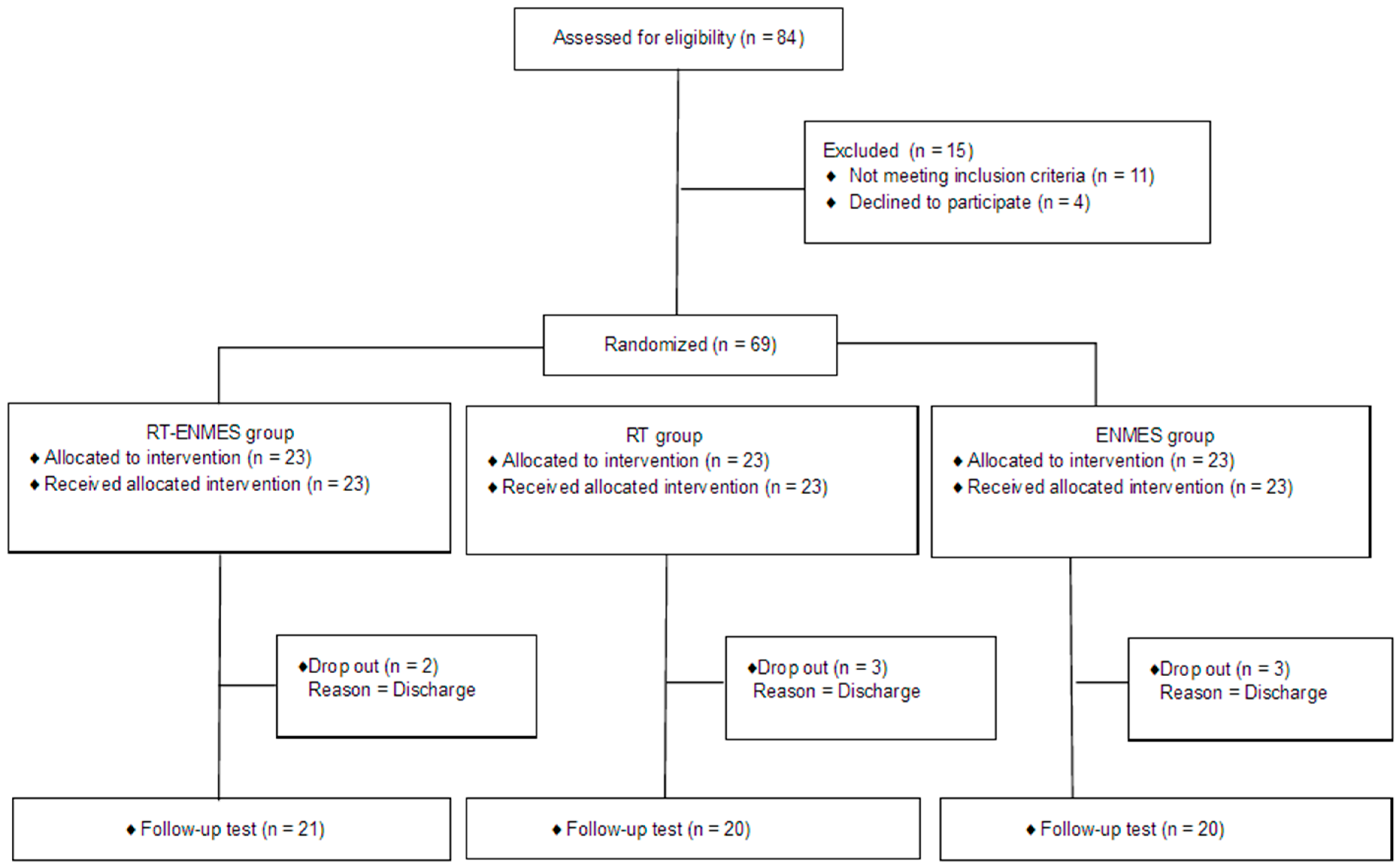
2.2. Study Procedure
2.3. Intervention
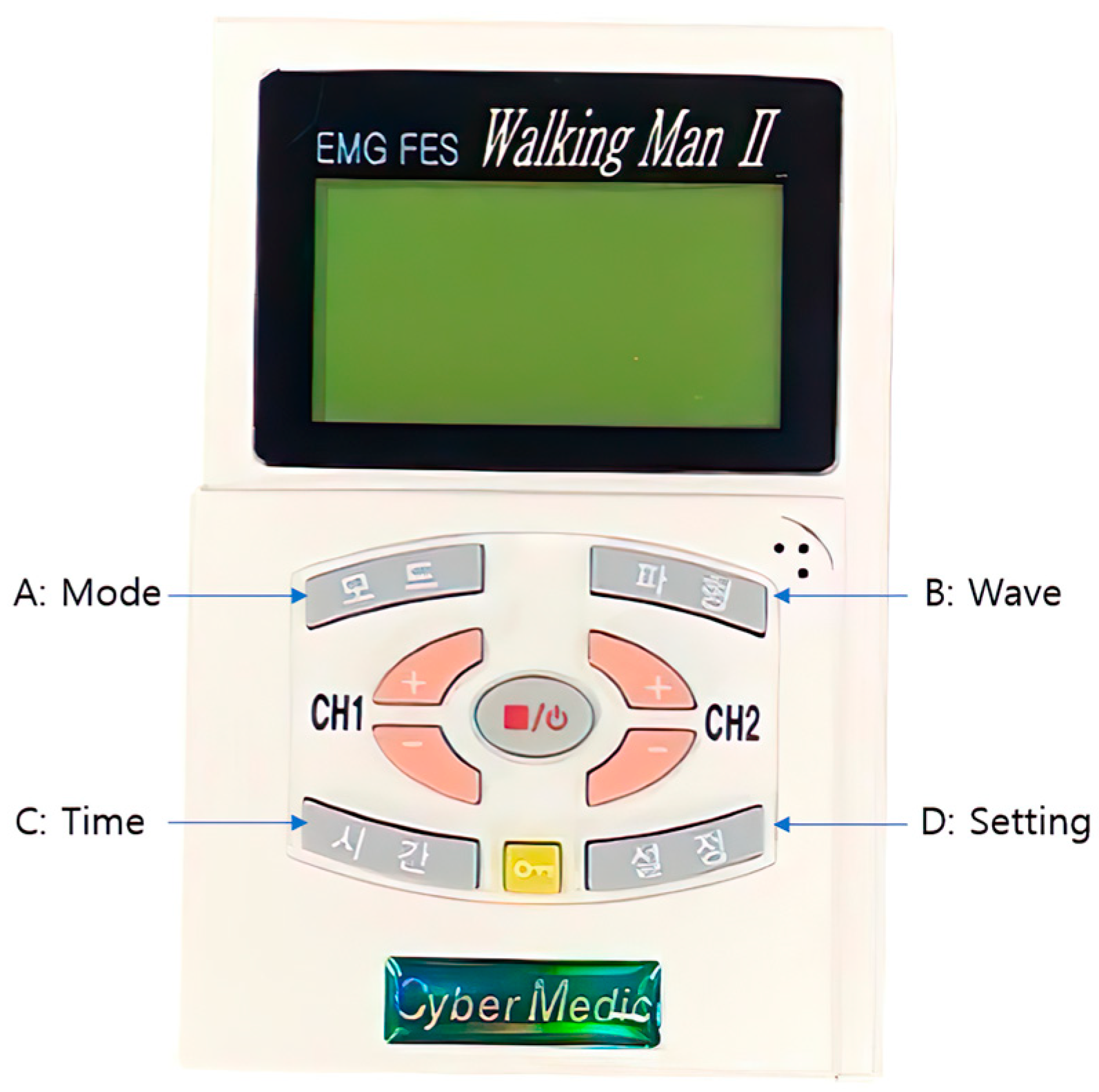
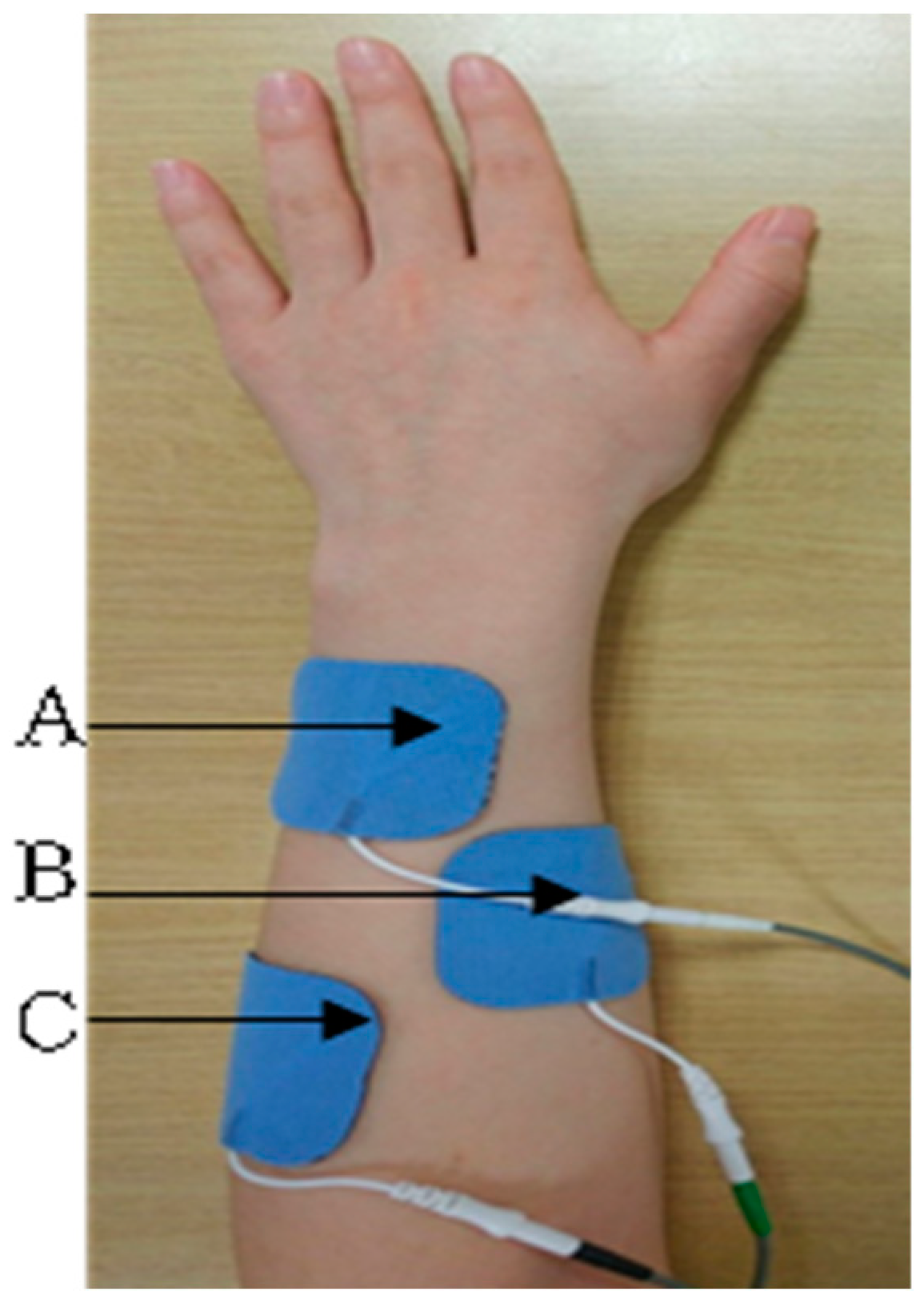
2.3.1. Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (ENMES)
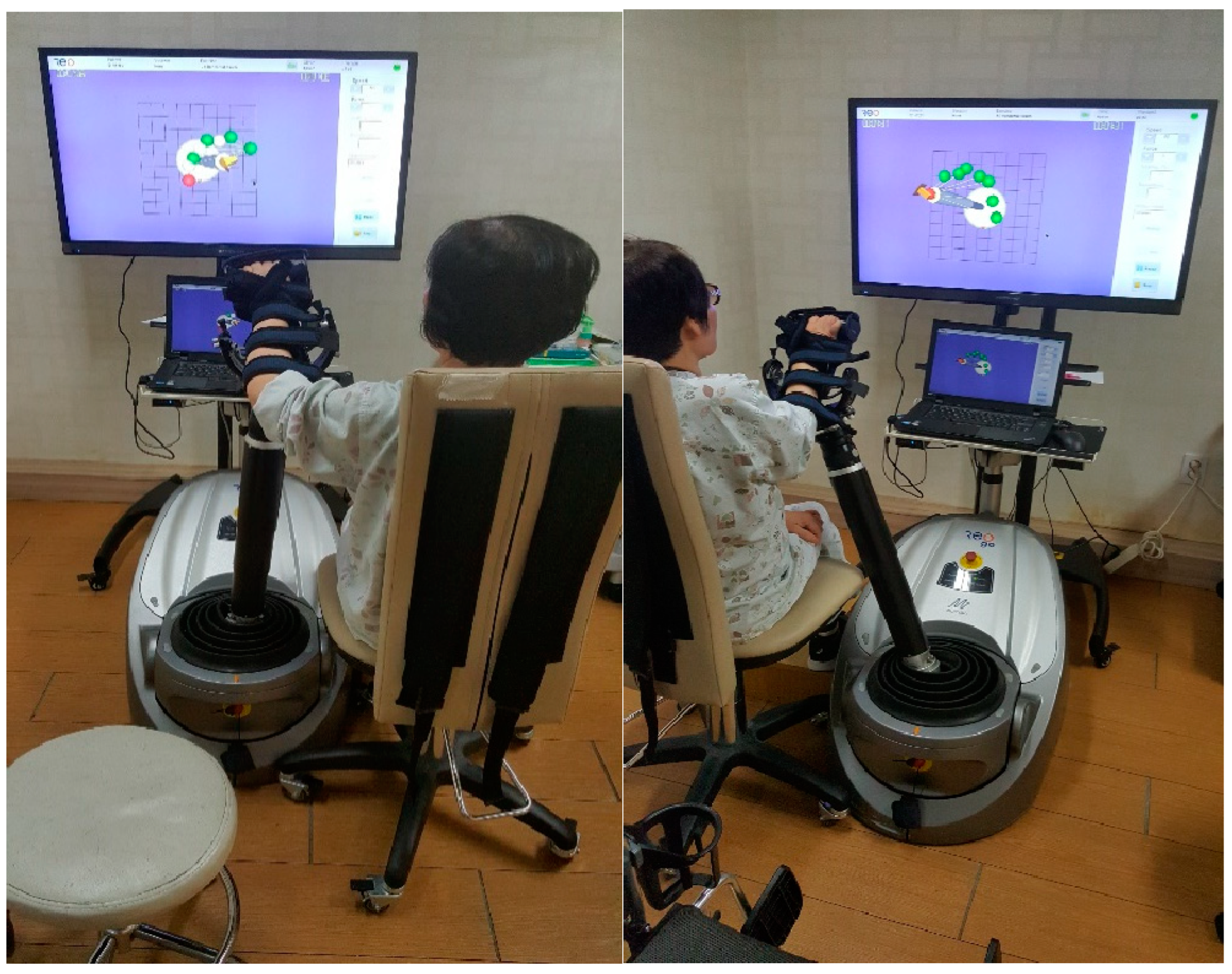
2.3.2. 3D-Based Robotic Therapy (RT)
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.4.1. Fugl–Meyer Assessment for Upper Extremity (FMA-UE)
2.4.2. Wolf Motor Function Test (WMFT)
2.4.3. Action Research Arm Test (ARAT)
2.4.4. Motor-Evoked Potential (MEP) Amplitude
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
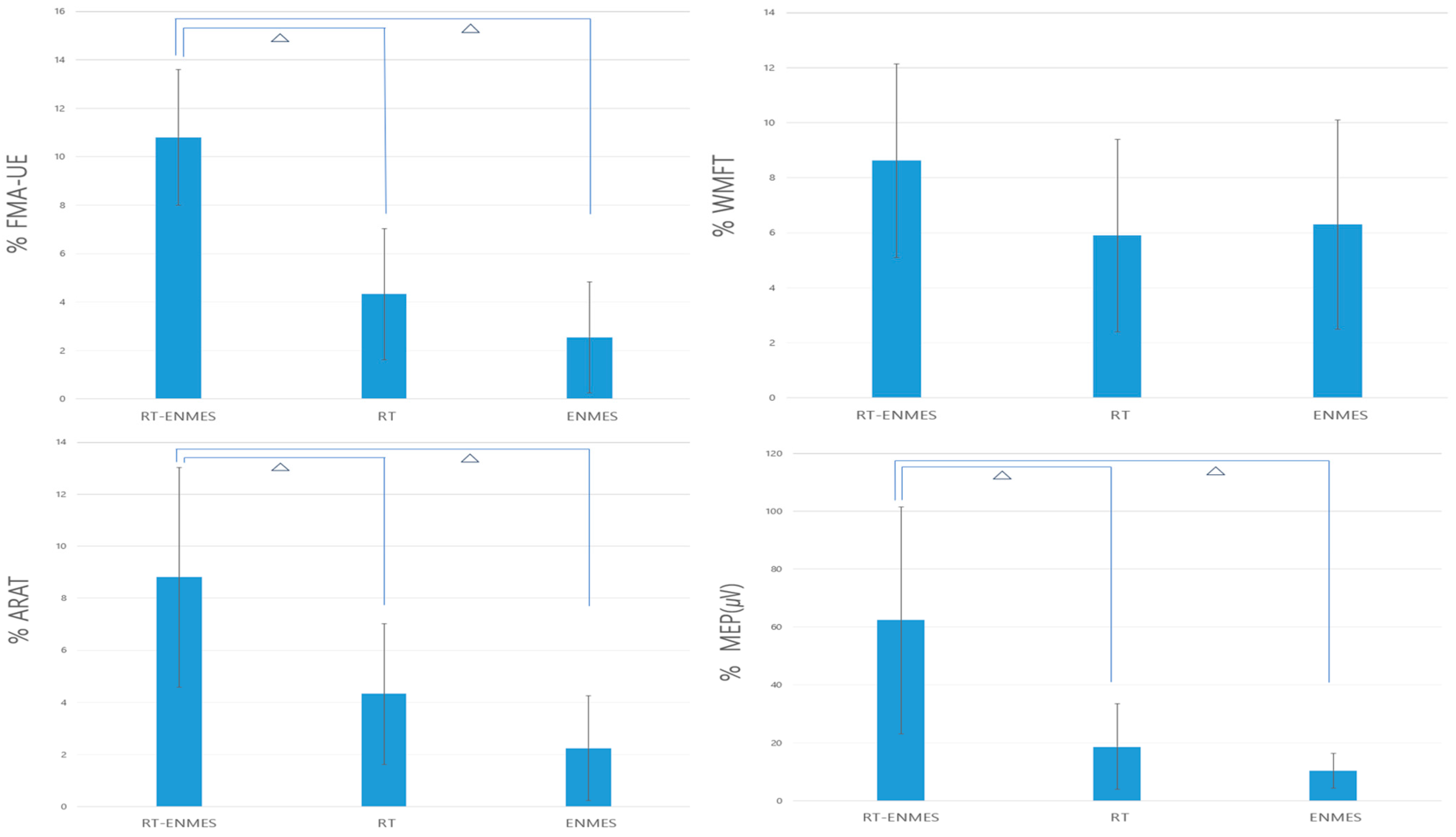
3.2. Comparison between the Experimental and Control Groups
3.3. Changes in the Groups before and after Intervention
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Zarahn, E.; Riley, C.; Speizer, A. Inter-individual variability in the capacity for motor recovery after ischemic stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair. 2008, 22, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwakkel, G.; Kollen, B.J. Predicting activities after stroke: What is clinically relevant? Int. J. Stroke 2013, 8, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, K.; Barker, R.; Brauer, S. Interventions to promote upper limb recovery in stroke survivors with severe paresis: A systematic review. Disabil. Rehabil. 2010, 32, 197–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhorne, J.; Bernhardt, G. Stroke rehabilitation. Lancet 2011, 377, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, L.; Thomas, H.J.; Coupe, L. Repetitive task training for improving functional ability after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 8, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, J.; Zhao, X.; van Praag, H.; Wodtke, K. Effects of voluntary exercise on synaptic plasticity and gene expression in the dentate gyrus of adult mal Sprague–Dawley rats in vivo. Neuroscience 2004, 124, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Kilgore, K.; Triolo, R.; Yu, D. Neuromuscular stimulation for motor neuroprosthesis in hemiplegia. Crit. Rev. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2000, 12, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Yu, D. Neuromuscular stimulation for motor relearning in hemiplegia. Crit. Rev. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 1999, 11, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, J.H.; Ladouceur, M. Clinical and therapeutic applications of neuromuscular stimulation: A review of current use and speculation into future developments. Neuromodulation 2001, 4, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Hara, J.; Oba, H.; Hotta, F.; Tsuji, T. Effectiveness of hybrid assistive neuromuscular dynamic stimulation therapy in patients with subacute stroke: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2011, 25, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alan, F.L.; Alon, G.; McCarthy, P.A. Functional electrical stimulation enhancement of upper extremity functional recovery during stroke rehabilitation: A pilot study. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2007, 21, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralj, A.R.; Bajd, T. Functional Electrical Stimulation: Standing and Walking after Spinal Cord Injury; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Bertani, R.; Melegari, C.; De Cola, M.C. Effects of robot-assisted upper limb rehabilitation in stroke patients: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, B.T.; Ferraro, M.; Lynch, D.; Christos, P. Robotics and other devices in the treatment of patients recovering from stroke. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2004, 6, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duret, A.G.; Grosmaire, H.I. Robot-assisted therapy in upper extremity hemiparesis: Overview of an ev idence-based approach. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehle, A.; Stuerner, J.; Hassa, T.; Spiteri, S.; Schoenfeld, M.A.; Liepert, J. Behavioral and neurophysiological effects of an intensified robot-assisted therapy in subacute stroke: A case control study. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 2021, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, H.I.; Hogan, N. Robotic therapy. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 91, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, C.D.; Der-Yeghiaian, L.V.; Le, R.R. Robot-based hand motor therapy after stroke. Brain 2008, 2, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrholz, J.; Pohl, M.; Platz, T.; Kugler, J. Electromechanical and robot-assisted arm training for improving activities of daily living, arm function, and arm muscle strength after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, V.S.; Krakauer, J.W. Robotic neurorehabilitation: A computational motor learning perspective. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L. The effects of electromechanical wrist robot assistive system with neuromuscular electrical stimulation for stroke rehabilitation. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, J.P.; Dohring, M.E.; Marsolais, E.B.; Rogers, J. Feasibility of combining gait robot and multichannel functional electrical stimulation with intramuscular electrodes. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2008, 45, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauraugh, J.; Light, K.; Kim, S.; Thigpen, M. Chronic motor dysfunction after stroke: Recovering wrist and finger extension by electromyography-triggered neuromuscular stimulation. Stroke 2000, 31, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israel, J.F.; Campbell, D.D.; Kahn, J.H.; Hornby, T.G. Metabolic costs and muscle activity patterns during robotic- and therapist-assisted treadmill walking in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Domen, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Toshima, M. The efficacy of upper extremity robotic therapy in subacute post-stroke hemiplegia: An exploratory randomized trial. Stroke 2016, 47, 1385–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, T. Robot-assisted training as self-training for upper-limb hemiplegia in chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Stroke 2022, 53, 2182–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.; Moreland, J.; Swanson, L.R.; Stratford, P.W. Reliability of the Fugl-Meyer Assessment for testing motor performance in patients following stroke. Phys. Ther. 1993, 73, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodics, T.M.; Nakatsuka, K.; Upreti, B.; Alex, A.; Smith, P.S.; Pezzullo, J.C. Wolf Motor Function Test for characterizing moderate to severe hemiparesis in stroke patients. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2012, 93, 1963–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.L.; Hsueh, I.P.; Chiang, F.M. Inter-rater reliability and validity of the action research arm test in stroke patients. Age Ageing 1998, 27, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yozbatiran, N.; Der-Yeghiaian, L.; Cramer, S.C. A standardized approach to performing the action research arm test. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 22, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borich, M.R.; Wheaton, L.A.; Brodie, S.M.; Lakhani, B. Evaluating interhemispheric cortical responses to transcranial magnetic stimulation in chronic stroke: A TMS-EEG investigation. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 618, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicciari, M.C.; Bonni, S.; Ponzo, V.; Cinnera, A.M. Dynamic reorganization of TMS-evoked activity in subcortical stroke patients. NeuroImage 2018, 175, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, P.M.; Barker, A.T.; Berardelli, A.; Caramia, M.D. Non-invasive electrical an magnetic stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: Basic principles and procedures for routine clinical application. Report of an IFCN committee. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1994, 91, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombly, C.A.; Quintana, L.A. The effects of exercise on finger extension of CVA patients. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 1983, 37, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ambrosini, E.; Gasperini, G.; Zajc, J.; Immick, N. A robotic system with emg-triggered functional eletrical stimulation for restoring arm functions in stroke survivors. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2021, 35, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armagan, O.; Tascioglu, F.; Oner, C. Electromyographic biofeedback in the treatment of the hemiplegic hand: A placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 82, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, D.A.; Cauraugh, J.H.; Hausenblas, H.A. Electromyogram-triggered neuromuscular stimulation and stroke motor recovery of arm/hand functions: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 223, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudo, R.J.; Wise, B.M.; SiFuentes, F.; Milliken, G.W. Neural substrates for the effects of rehabilitative training on motor recovery after ischemic infarct. Science 1996, 272, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebayashi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Okita, Y.; Kubo, H. Impact of the robotic-assistance level on upper extremity function in stroke patients receiving adjunct robotic rehabilitation: Sub-analysis of a randomized clinical trial. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, K.C.; Hsieh, C.J.; Liu, J.S.; Wang, T.N.; Ou-Yang, P. Psychometric comparison of the shortened Fugl-Meyer Assessment and the streamlined Wolf Motor Function Test in stroke rehabilitation. Clin. Rehabil. 2012, 26, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabadi, M.H.; Rabadi, F.M. Comparison of the action research arm test and the Fugl-Meyer assessment as measures of upper-extremity motor weakness after stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 962–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshiyuki, F.; Yuko, K.; Kaoru, H.; Yoshihiro, M.; Tetsuya, T.; Rieko, O. Motor improvement and corticospinal modulation induced by hybrid assistive neuromuscular dynamic stimulation (HANDS) therapy in patients with chronic stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Straudi, S.; Baroni, A.; Mele, S.; Craighero, L. Effects of a robot-assisted arm training plus hand functional electrical stimulation on recovery after stroke: A randomized clinical trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, S.; Katsuhiro, M.; Michiyuki, K.; Osamu, T. Neuromuscular electrical stimulation-enhanced rehabilitation is associated with not only motor but also somatosensory cortical plasticity in chronic stroke patients: An interventional study. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2019, 10, 2040622319889259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | RT–ENMES Group (n = 21) | RT Group (n = 20) | ENMES Group (n = 20) | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year), mean ± SD | 61.10 ± 7.66 | 63.38 ± 8.34 | 63.10 ± 8.57 | 0.483 | 0.619 |
| Gender (male/female) | 10/11 | 12/9 | 10/10 | 0.197 | 0.821 |
| Type of stroke (Hemorrhage/Infarction) | 7/14 | 9/12 | 9/11 | 0.964 | 0.387 |
| Side of stroke (Right/Left) | 11/10 | 8/13 | 11/9 | 0.669 | 0.516 |
| Time since onset of stroke months, mean ± SD | 3.48 ± 1.12 | 3.67 ± 1.23 | 3.60 ± 1.31 | 0.130 | 0.878 |
| RT–ENMES Group | RT Group | ENMES Group | p | Post hoc Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Treatment | After Treatment | Before Treatment | After Treatment | Before Treatment | After Treatment | |||
| FMA UE | 16.76 (3.80) | 27.57 (4.99) ** | 15.33 (4.85) | 19.67 (4.83) ** | 15.95 (3.94) | 18.50 (4.60) ** | 0.000 † | P1 = 0.000 ᅀ P2 = 0.000 ᅀ P3 = 0.710 |
| WMFT | 15.14 (5.24) | 23.76 (4.63) ** | 16.05 (6.62) | 22.10 (6.92) ** | 16.60 (7.49) | 22.90 (6.04) ** | 0.293 | |
| ARAT | 10.43 (3.37) | 19.24 (3.16) ** | 10.90 (2.99) | 15.24 (3.92) ** | 10.74 (3.33) | 13.15 (4.34) ** | 0.000 † | P1 = 0.004 ᅀ P2 = 0.000 ᅀ P3 = 0.259 |
| MEP (μV) | 132.10 (53.02) | 194.47 (60.11) ** | 138.28 (40.57) | 157.31(49.14) ** | 126.92 (49.62) | 137.43(53.28) ** | 0.002 † | P1 = 0.011 ᅀ P2 = 0.003 ᅀ P3 = 0.847 |
| RT–ENMES Group | RT Group | ENMES Group | p | Post hoc Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMA UE | 10.81 (2.80) | 4.33 (2.70) | 2.55 (2.44) | 0.000 † | P1 = 0.000 ᅀ P2 = 0.000 ᅀ P3 = 0.257 |
| WMFT | 8.62 (3.52) | 5.90 (3.74) | 6.30 (3.88) | 0.056 | |
| ARAT | 8.81 (4.22) | 4.33 (2.70) | 2.25 (2.07) | 0.000 † | P1 = 0.002 ᅀ P2 = 0.000 ᅀ P3 = 0.081 |
| MEP (μV) | 62.36 (39.18) | 18.80 (14.64) | 10.50 (6.09) | 0.000 † | P1 = 0.000 ᅀ P2 = 0.000 ᅀ P3 = 0.798 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.-W.; Ma, S.-R.; Choi, J.-B. Effect of 3-Dimensional Robotic Therapy Combined with Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Function and Cerebral Cortex Activation in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010012
Yang S-W, Ma S-R, Choi J-B. Effect of 3-Dimensional Robotic Therapy Combined with Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Function and Cerebral Cortex Activation in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Seo-Won, Sung-Ryong Ma, and Jong-Bae Choi. 2024. "Effect of 3-Dimensional Robotic Therapy Combined with Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Function and Cerebral Cortex Activation in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Bioengineering 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010012
APA StyleYang, S.-W., Ma, S.-R., & Choi, J.-B. (2024). Effect of 3-Dimensional Robotic Therapy Combined with Electromyography-Triggered Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Upper Limb Function and Cerebral Cortex Activation in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Bioengineering, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11010012






