Palmitic Acid Upregulates CD96 Expression to Mediate Maternal–Foetal Interface Immune Tolerance by Inhibiting Cytotoxic Activity and Promoting Adhesion Function in Human Decidual Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
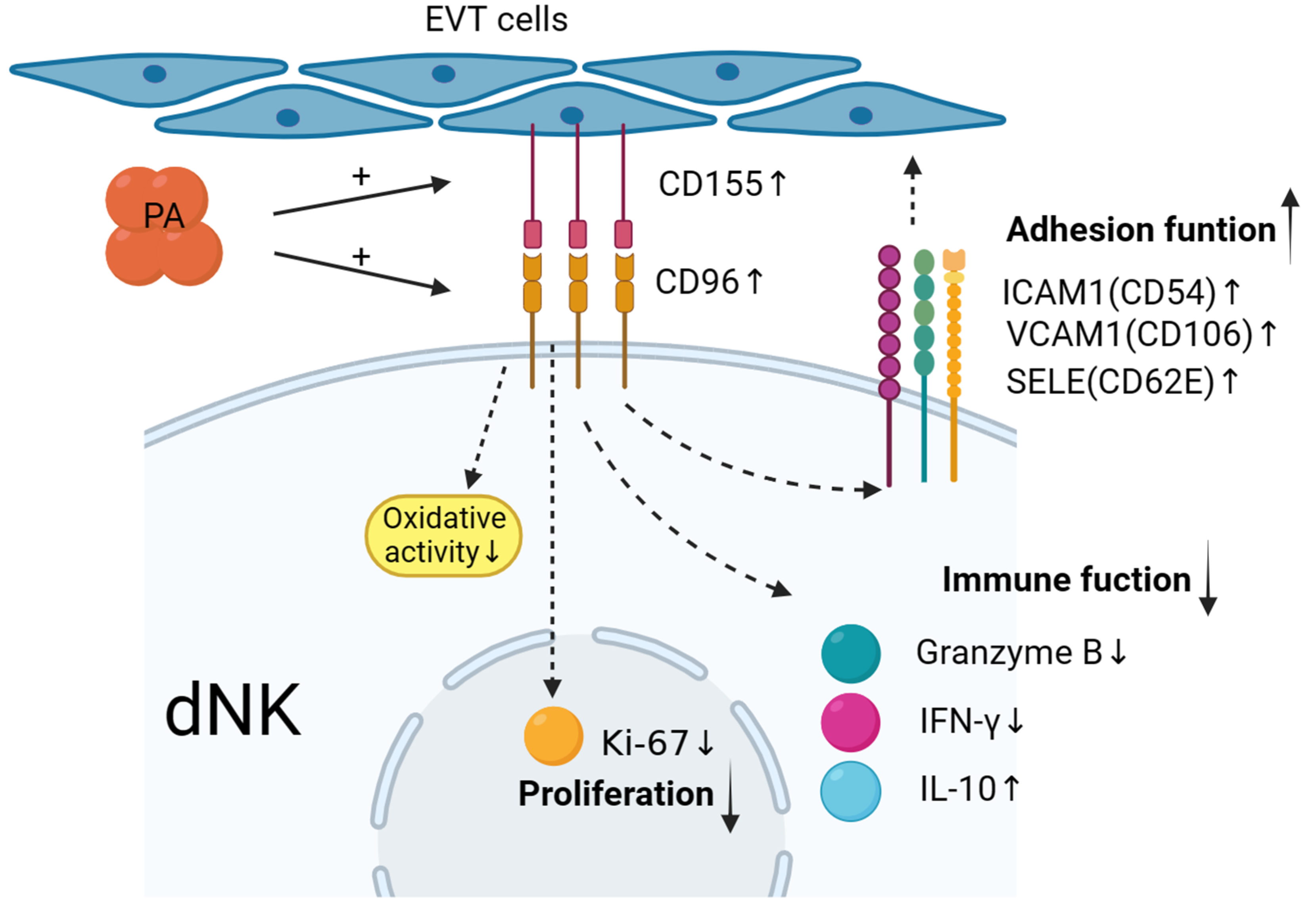
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissues
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Lysis of Erythrocytes
2.4. Flow Cytometry Assays
2.5. Paraffin Section Preparation
2.6. Immunofluorescence in Paraffin Sections
2.7. Cell Adhesion Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
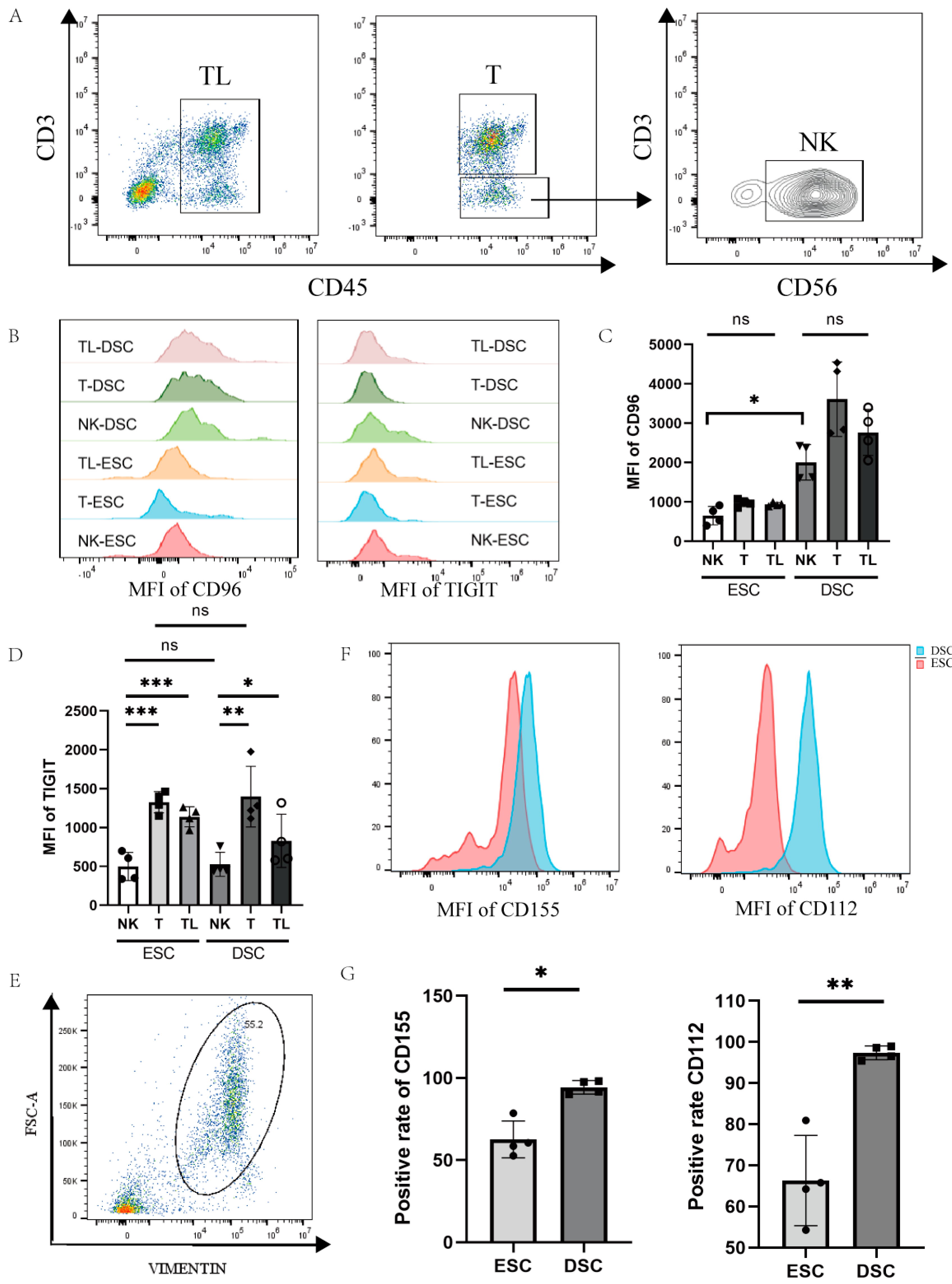
3.1. CD96 Is Enriched in the Maternal–Foetal Interface during Pregnancy
3.2. CD96 Is Highly Expressed in Normal Gestational Decidual NK Cells, While There Is No Difference in the Expression of TIGIT in the Endometrium and Normal Pregnancy Decidual NK Cells
3.3. Phenotype and Characteristics of CD96+ dNK Cells
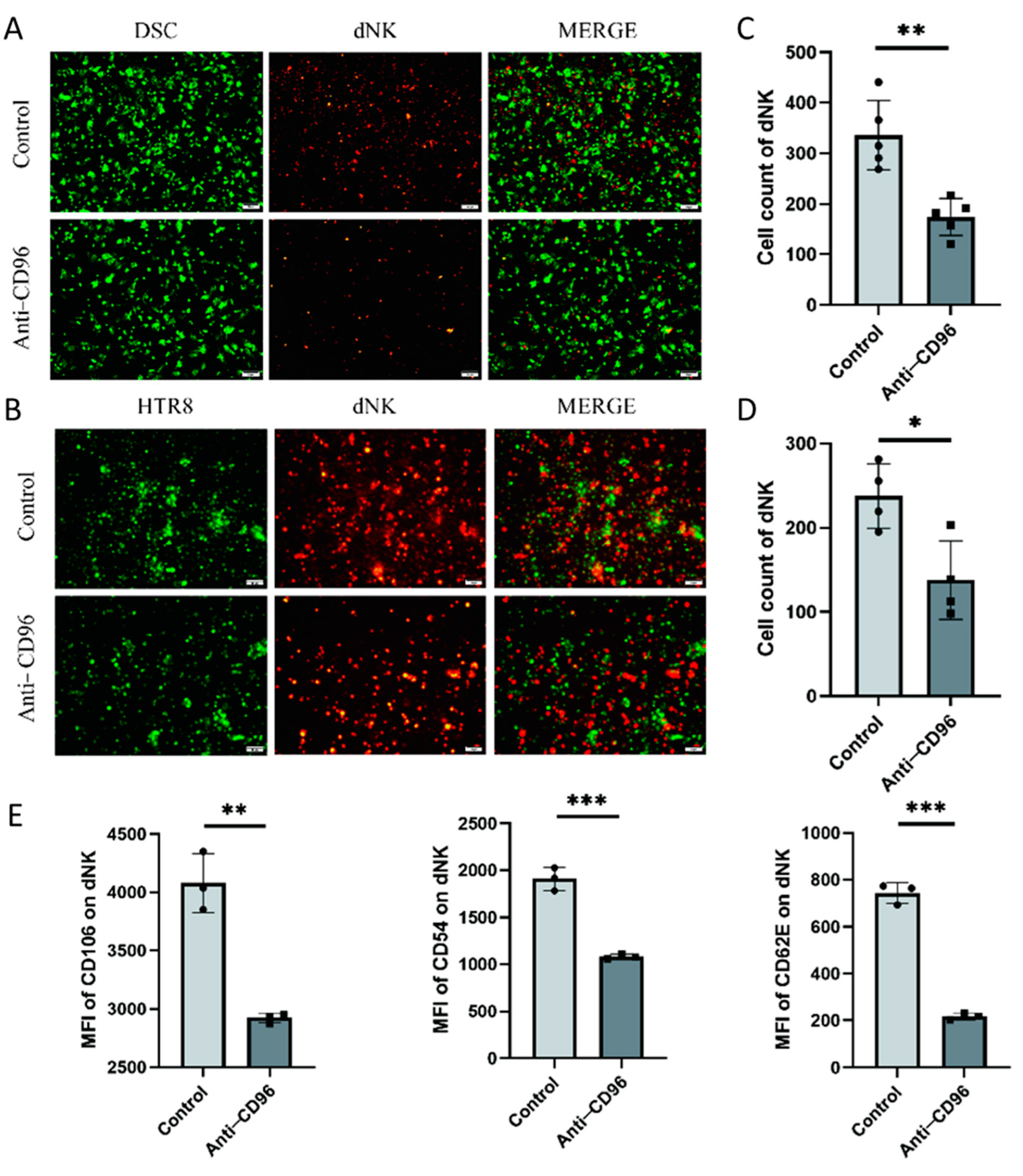
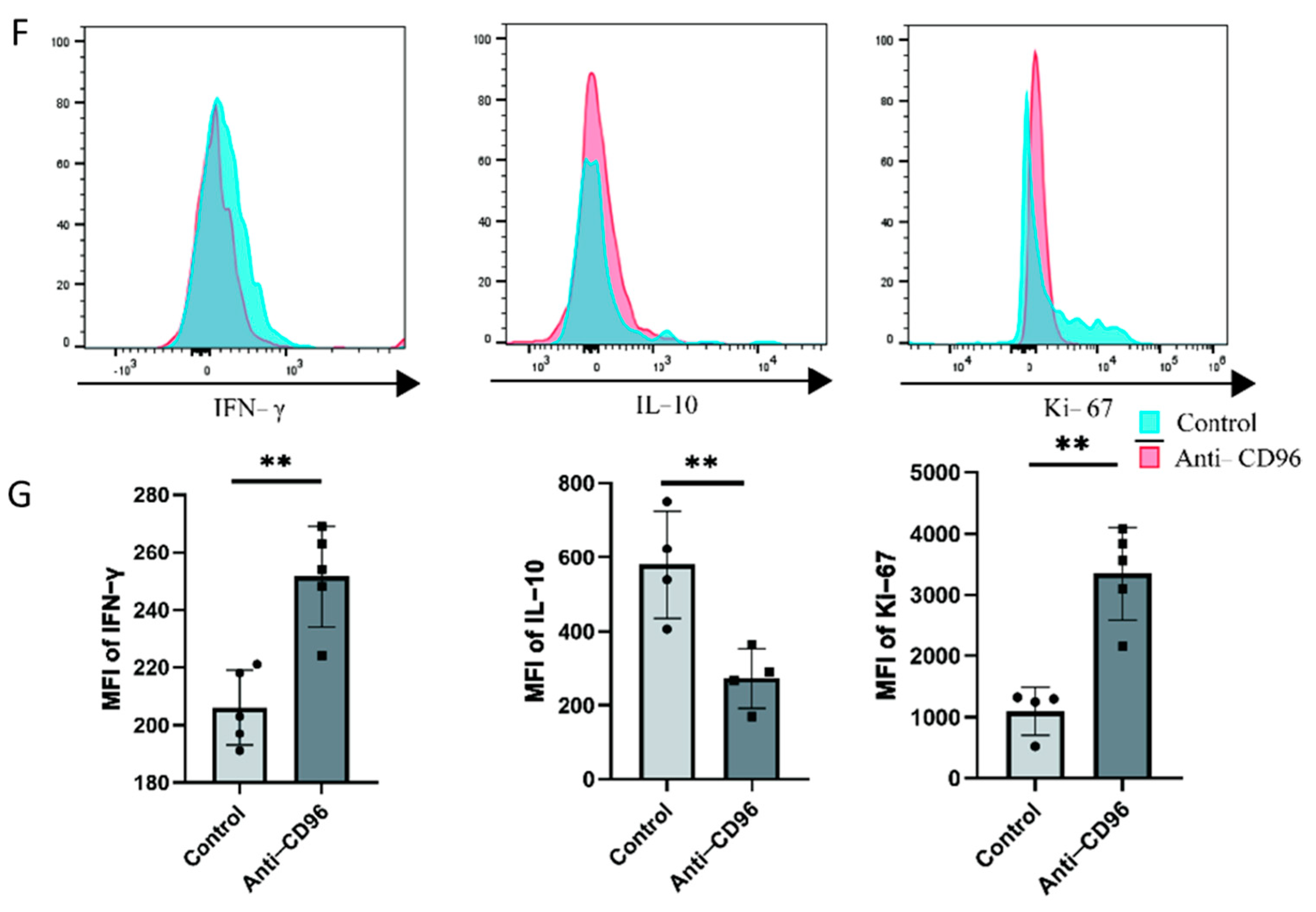
3.4. After CD96 Antagonists Block NK Cells, the Adhesion of NK Cells to Stromal Cells and Trophoblasts Decreases
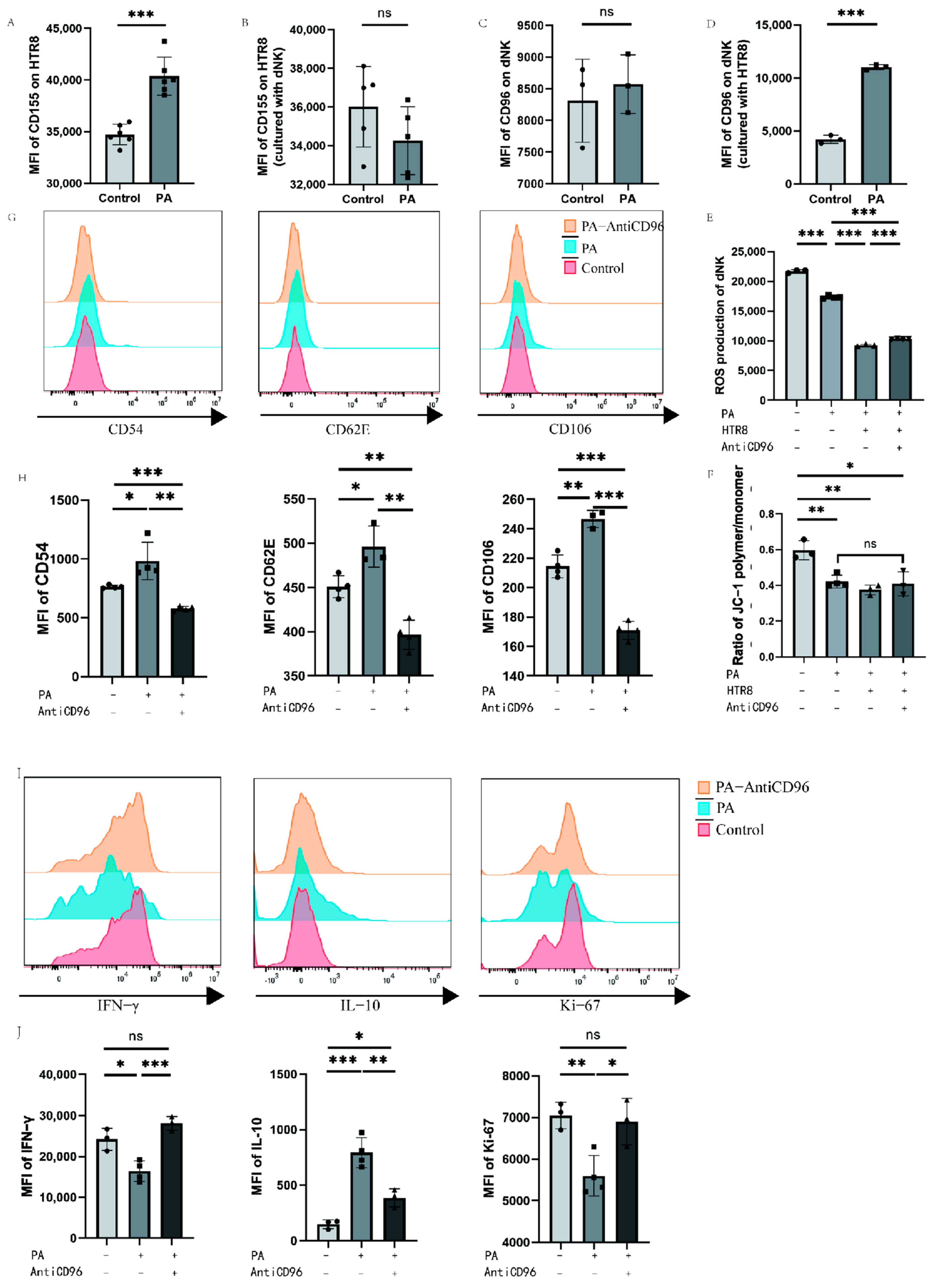
3.5. Low-Dose Palmitic Acid Can Regulate CD96 Expression, Thereby Affecting Cellular Oxidative Function
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, N.; Li, J. Human Uterine Decidual NK Cells in Women with a History of Early Pregnancy Enhance Angiogenesis and Trophoblast Invasion. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6247526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.-Q.; Zhou, W.-J.; Li, D.-J.; Li, M.-Q. Innate Lymphoid Cells at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Human Pregnancy. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Sun, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Cui, L.; Qian, J.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Du, M. Tim-3+ decidual Mφs induced Th2 and Treg bias in decidual CD4+T cells and promoted pregnancy maintenance via CD132. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.; Chen, X.; Qiu, H.; He, W.; Zhou, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, A. Insights into the immunomodulatory regulation of matrix metalloproteinase at the maternal-fetal interface during early pregnancy and pregnancy-related diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1067661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, Q.; Jin, L. Dynamic Function and Composition Changes of Immune Cells During Normal and Pathological Pregnancy at the Maternal-Fetal Interface. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trippella, G.; Ciarcià, M.; Ferrari, M.; Buzzatti, C.; Maccora, I.; Azzari, C.; Dani, C.; Galli, L.; Chiappini, E. COVID-19 in Pregnant Women and Neonates: A Systematic Review of the Literature with Quality Assessment of the Studies. Pathogens 2020, 9, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebmann, V.; da Silva Nardi, F.d.S.; Wagner, B.; Horn, P.A. HLA-G as a Tolerogenic Molecule in Transplantation and Pregnancy. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 297073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, M.; Fan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Beejadhursing, R.; Feng, L.; Deng, D. Impaired Gal-9 Dysregulates the PBMC-Induced Th1/Th2 Imbalance in Abortion-Prone Matings. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 9517842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siewiera, J.; El Costa, H.; Tabiasco, J.; Berrebi, A.; Cartron, G.; Le Bouteiller, P.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N. Human cytomegalovirus infection elicits new decidual natural killer cell effector functions. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Oliveras, R.; Mendoza, M.; Capote, S.; Pratcorona, L.; Esteve-Valverde, E.; Cabero-Roura, L.; Alijotas-Reig, J. Immunological and physiopathological approach of COVID-19 in pregnancy. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 304, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.J.; Searle, R.F.; Robson, S.C.; Innes, B.A.; Bulmer, J.N. Decidual leucocyte populations in early to late gestation normal human pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2009, 82, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Cao, C.; Lv, S.; Wei, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; et al. The Immune Atlas of Human Deciduas With Unexplained Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 689019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, E.Y.; Almeida, P.E.; Nagata, D.E.A.; Bowles, K.H.; Du, X.; Chitre, A.S.; Banta, K.L.; Kwon, Y.; McKenzie, B.; Mittman, S.; et al. CD96 functions as a co-stimulatory receptor to enhance CD8+ T cell activation and effector responses. Eur. J. Immunol. 2020, 50, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Correa, B.; Valhondo, I.; Hassouneh, F.; Lopez-Sejas, N.; Pera, A.; Bergua, J.M.; Arcos, M.J.; Bañas, H.; Casas-Avilés, I.; Durán, E.; et al. DNAM-1 and the TIGIT/PVRIG/TACTILE Axis: Novel Immune Checkpoints for Natural Killer Cell-Based Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinato, D.J.; Guerra, N.; Fessas, P.; Murphy, R.; Mineo, T.; Mauri, F.A.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Thursz, M.; Wong, C.N.; Sharma, R.; et al. Immune-based therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 3620–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Iizumi, T.; Mashima, K.; Abe, T.; Suzuki, N. Roles and Regulation of Ketogenesis in Cultured Astroglia and Neurons Under Hypoxia and Hypoglycemia. ASN Neuro 2014, 6, 1759091414550997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.A.; Kasahara, D.I.; Cho, Y.; Bell, L.N.; Gunst, P.R.; Karoly, E.D.; Shore, S.A. Effect of acute ozone exposure on the lung metabolomes of obese and lean mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Li, X.Y.; Li, Z.; He, L.N.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, K.; Zhou, Z.G. Octanoylated Ghrelin Inhibits the Activation of the Palmitic Acid-Induced TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in THP-1 Macrophages. ISRN Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 237613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Shimazaki, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Karasawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Ohkuchi, A.; Takahashi, H.; Kurosawa, A.; Torii, Y.; Iwata, H.; et al. Palmitic acid activates NLRP3 inflammasome and induces placental inflammation during pregnancy in mice. J. Reprod. Dev. 2020, 66, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.-Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.-J.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.-W.; Yang, H.-L.; Xie, F.; Chen, W.-D.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, C.; et al. Single-cell transcriptome profiling of the human endometrium of patients with recurrent implantation failure. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6527–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, H.-L.; Zhou, W.-J.; Lai, Z.-Z.; Qiu, X.-M.; Fu, Q.; Zhao, J.-Y.; Wang, J.; Li, D.-J.; Li, M.-Q. Rapamycin prevents spontaneous abortion by triggering decidual stromal cell autophagy-mediated NK cell residence. Autophagy 2020, 17, 2511–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habets, D.H.J.; Schlütter, A.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Spaanderman, M.E.A.; Al-Nasiry, S.; Wieten, L. Natural killer cell profiles in recurrent pregnancy loss: Increased expression and positive associations with TACTILE and LILRB1. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 88, e13612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, H.; Ravens, I.; Papadogianni, G.; Bernhardt, G. Coming of Age: CD96 Emerges as Modulator of Immune Responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Qu, X.; Ma, L.; Yi, L.; Cheng, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Che, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. CD155 expression impairs anti-PD1 therapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2022, 208, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Paniccia, A.; Schulick, A.C.; Chen, W.; Koenig, M.R.; Byers, J.T.; Yao, S.; Bevers, S.; Edil, B.H. Identification of CD112R as a novel checkpoint for human T cells. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.-X.; Yang, S.-L.; Li, M.-Q.; Wang, H.-Y. Autophagy suppression of trophoblast cells induces pregnancy loss by activating decidual NK cytotoxicity and inhibiting trophoblast invasion. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, F.; Yue, J.; Li, L.; Mei, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y. Narrative review of the relationship between the maternal-fetal interface immune tolerance and the onset of preeclampsia. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, V.; Grebenkina, P.; Khokhlova, E.; Davydova, A.; Salloum, Z.; Tyshchuk, E.; Zagainova, V.; Markova, K.; Kogan, I.; Selkov, S.; et al. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Context of NK Cell–Trophoblast Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarousseau, A.-C.; Thibault, G.; Reverdiau, P.; Rodriguez, A.-M.; Lacord, M.; de Russe, J.; Watier, H.; Degenne, D.; Lebranchu, Y.; Gruel, Y.; et al. Adhesive Properties of Choriocarcinoma Cells toward Lymphocytes Activated or Not by Interleukin-2. Cell. Immunol. 1994, 157, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, K.; Li, X.; Zhong, J.; Ng, E.H.Y.; Yeung, W.S.B.; Lee, C.L.; Chiu, P.C.N. Placenta-Derived Exosomes as a Modulator in Maternal Immune Tolerance During Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 671093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veljkovic Vujaklija, D.; Sucic, S.; Gulic, T.; Dominovic, M.; Rukavina, D. Cell death mechanisms at the maternal-fetal interface: Insights into the role of granulysin. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 180272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, D.; Sharma, N.R.; Kancharla, S.; Kolli, P.; Tripathy, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Singh, S.; Kumar, S.; Mohanty, A.K.; Jena, M.K. Role of Natural Killer Cells during Pregnancy and Related Complications. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Tong, F. Global trends in research of immune cells associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy: A 20-year bibliometric analyses (from 2001 to 2021). Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1036461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skliutė, G.; Baušytė, R.; Ramašauskaitė, D.; Navakauskienė, R. Characterization of Epigenetic and Molecular Factors in Endometrium of Females with Infertility. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticconi, C.; Pietropolli, A.; Di Simone, N.; Piccione, E.; Fazleabas, A. Endometrial Immune Dysfunction in Recurrent Pregnancy Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yang, X. The central role of natural killer cells in preeclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1009867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.-Y.; Li, Z.-Y.; Fang, W.-N.; Song, Z.-H.; Yang, D.-D.; Li, D.-D.; Yang, Y.; Peng, J.-P. Cytochrome P450 26A1 modulates natural killer cells in mouse early pregnancy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 21, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson-Gregg, F.J.; Krepel, S.A.; Anderson, S.K. Tuning of human NK cells by endogenous HLA-C expression. Immunogenetics 2020, 72, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, A.J.; Moore, R.E.; Townsend, S.D.; Gaddy, J.A.; Aronoff, D.M. The Influence of Obesity and Associated Fatty Acids on Placental Inflammation. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antibody | Fluorescence | Manufactory | Clone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-human CD45 antibody | BV510 | Biolegend | 2D1 |
| Anti-human CD3 antibody | AF700 | Biolegend | SK7 |
| Anti-human CD56 antibody | PE/Cy7 | Biolegend | HCD56 |
| Anti-human TIGIT antibody | PE | Biolegend | A15153G |
| Anti-human CD96 antibody | BV421 | Biolegend | NK92.39 |
| Anti human CD96 antibody | AO | Abcam | NK92.39 |
| Anti human CD155 antibody | PE | Biolegend | TX24 |
| Anti human CD112 antibody | APC | Biolegend | TX31 |
| Anti-human Vimentin antibody | AF488 | BD | RV202 |
| Anti-human Granzyme B antibody | APC | Biolegend | QA18A28 |
| Anti-human CD54 antibody | FITC | Biolegend | HA58 |
| Anti-human CD62E antibody | PE | Biolegend | HAE-1f |
| Anti-human CD106 antibody | APC | Biolegend | STA |
| Anti-human IL10 antibody | APC | Biolegend | JES3-9D7 |
| Anti-human Ki67 antibody | APC | Biolegend | Ki-67 |
| Anti-human Ki67 antibody | FITC | Biolegend | 11F6 |
| Anti-human IFN-γ antibody | AF700 | Biolegend | 4S.B3 |
| Anti-human IFN-γ antibody | BV421 | Biolegend | 4S.B3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Palmitic Acid Upregulates CD96 Expression to Mediate Maternal–Foetal Interface Immune Tolerance by Inhibiting Cytotoxic Activity and Promoting Adhesion Function in Human Decidual Natural Killer Cells. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091008
Wang Y, Wang Y. Palmitic Acid Upregulates CD96 Expression to Mediate Maternal–Foetal Interface Immune Tolerance by Inhibiting Cytotoxic Activity and Promoting Adhesion Function in Human Decidual Natural Killer Cells. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(9):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091008
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yingjie, and Yun Wang. 2023. "Palmitic Acid Upregulates CD96 Expression to Mediate Maternal–Foetal Interface Immune Tolerance by Inhibiting Cytotoxic Activity and Promoting Adhesion Function in Human Decidual Natural Killer Cells" Bioengineering 10, no. 9: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091008
APA StyleWang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2023). Palmitic Acid Upregulates CD96 Expression to Mediate Maternal–Foetal Interface Immune Tolerance by Inhibiting Cytotoxic Activity and Promoting Adhesion Function in Human Decidual Natural Killer Cells. Bioengineering, 10(9), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10091008






