Encrypt with Your Mind: Reliable and Revocable Brain Biometrics via Multidimensional Gaussian Fitted Bit Allocation
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to encode intracortical brain signals into reliable long keys.
- In this paper, we propose a novel approach called multidimensional Gaussian fitted bit allocation (MGFBA) to encode brain signals into digitalized keys.
- We found that with the proposed MGFBA, the average effective key length using the intracortical brain signals of 10 rats was 938 bits, and we achieved high authentication accuracy of 88.1% at a false acceptance rate of 1.9%, which is a significant improvement over conventional EEG-based approaches.
- Our MGFBA-based keys can be conveniently revoked using different motor behaviors. The experimental results demonstrate the potential of using intracortical brain signals for reliable authentication and other security applications.
2. Methods
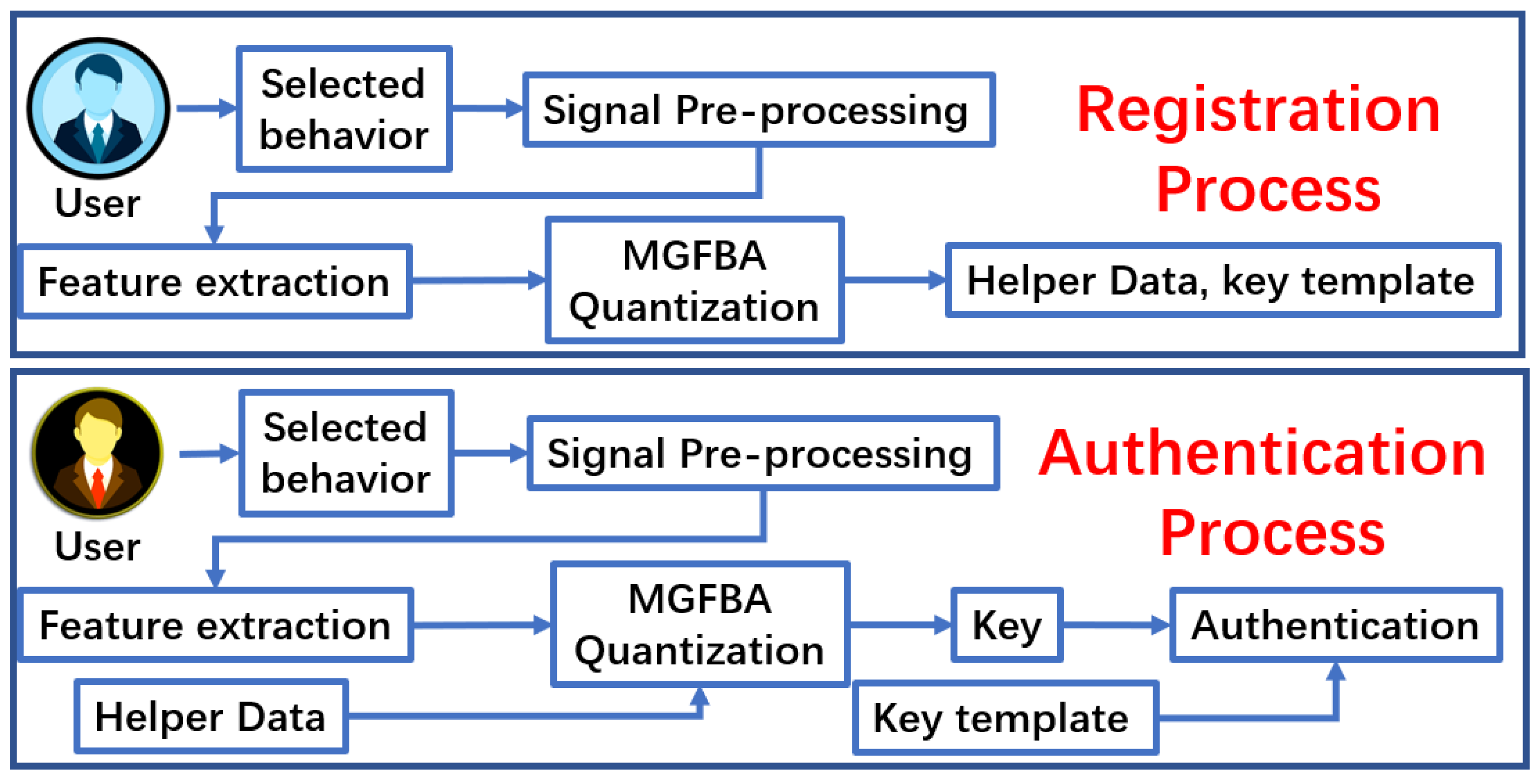
2.1. Overview
2.2. Signal Preprocessing and Feature Extraction
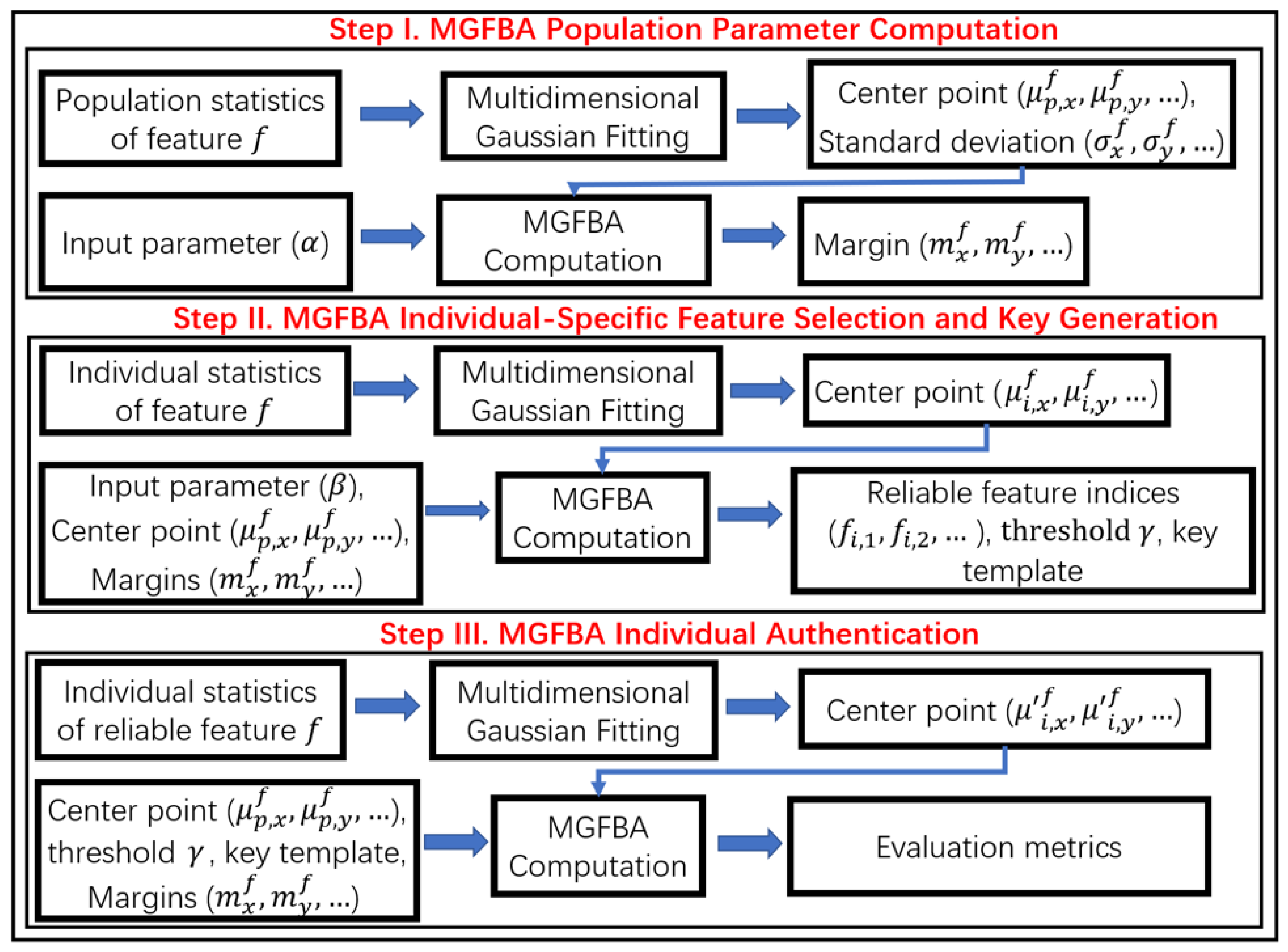
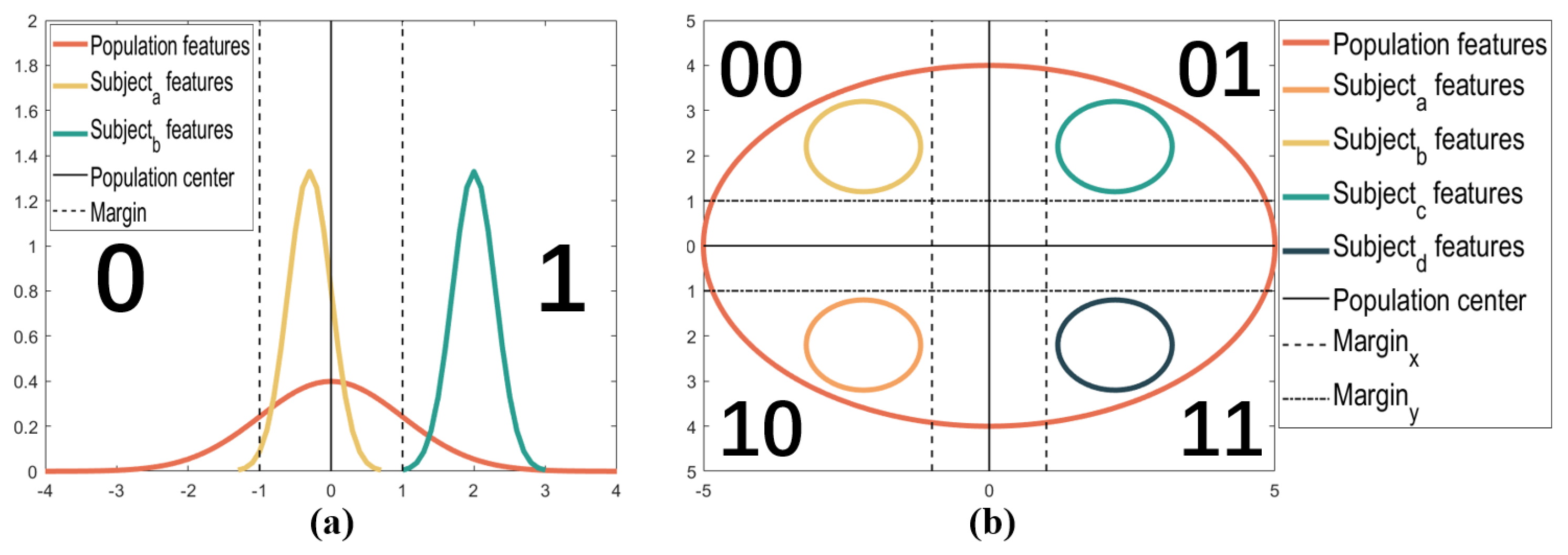
2.3. MGFBA Quantization
| Algorithm 1. MGFBA Population Parameter Computation |
Input: , population statistics
|
| Algorithm 2. MGFBA Feature Selection and Key Generation |
Input: , individual statistics, population center point, margin
|
| Algorithm 3. MGFBA Individual Authentication |
Input: , individual statistics, population center point, margin, reliable feature index of individuals, similarity threshold of individuals, key template of individuals
|
3. Experimental Setup and Results
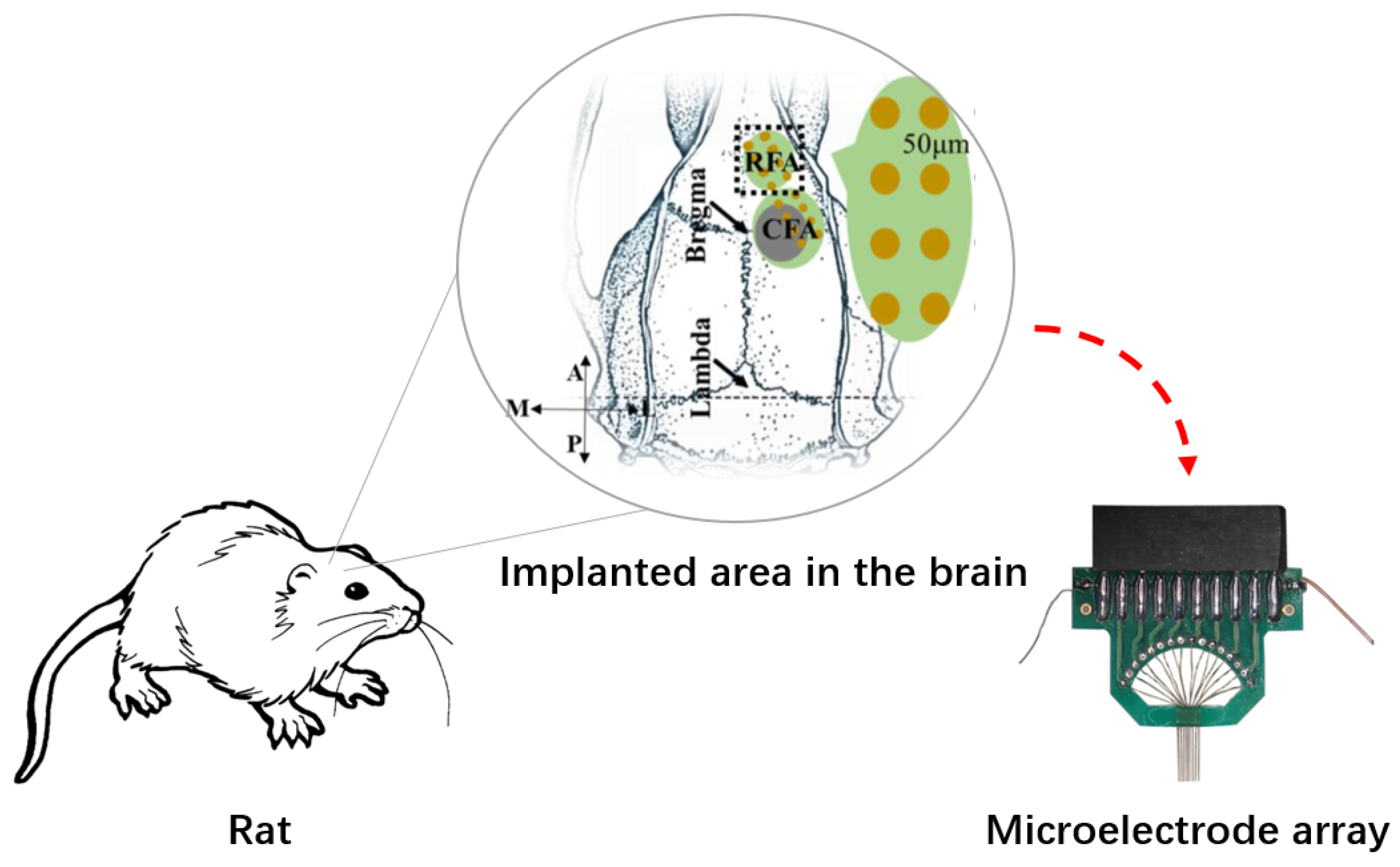
3.1. Data Acquisition
3.2. Evaluation Metrics
3.3. Performance of Brain-Based Authentication
3.4. Revocability
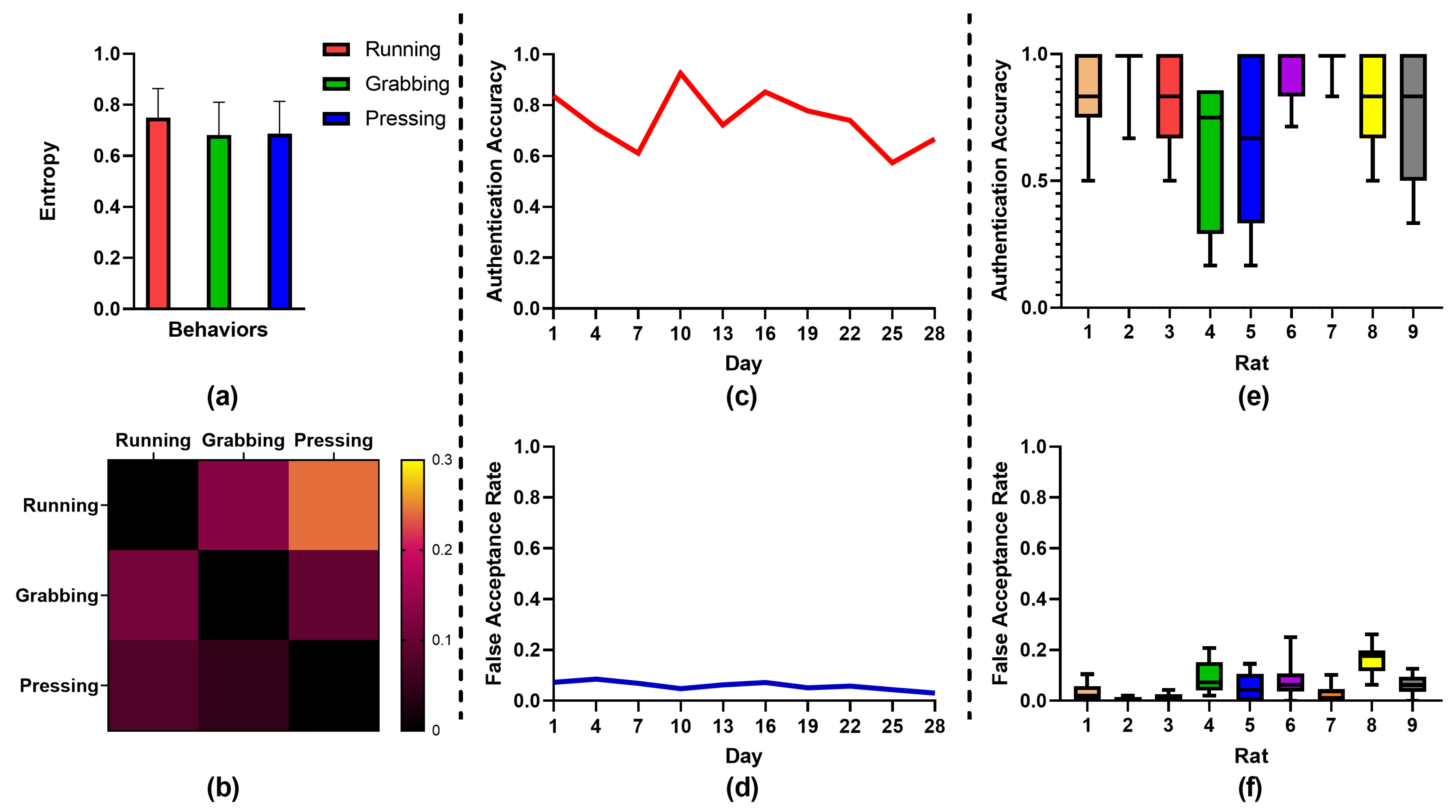
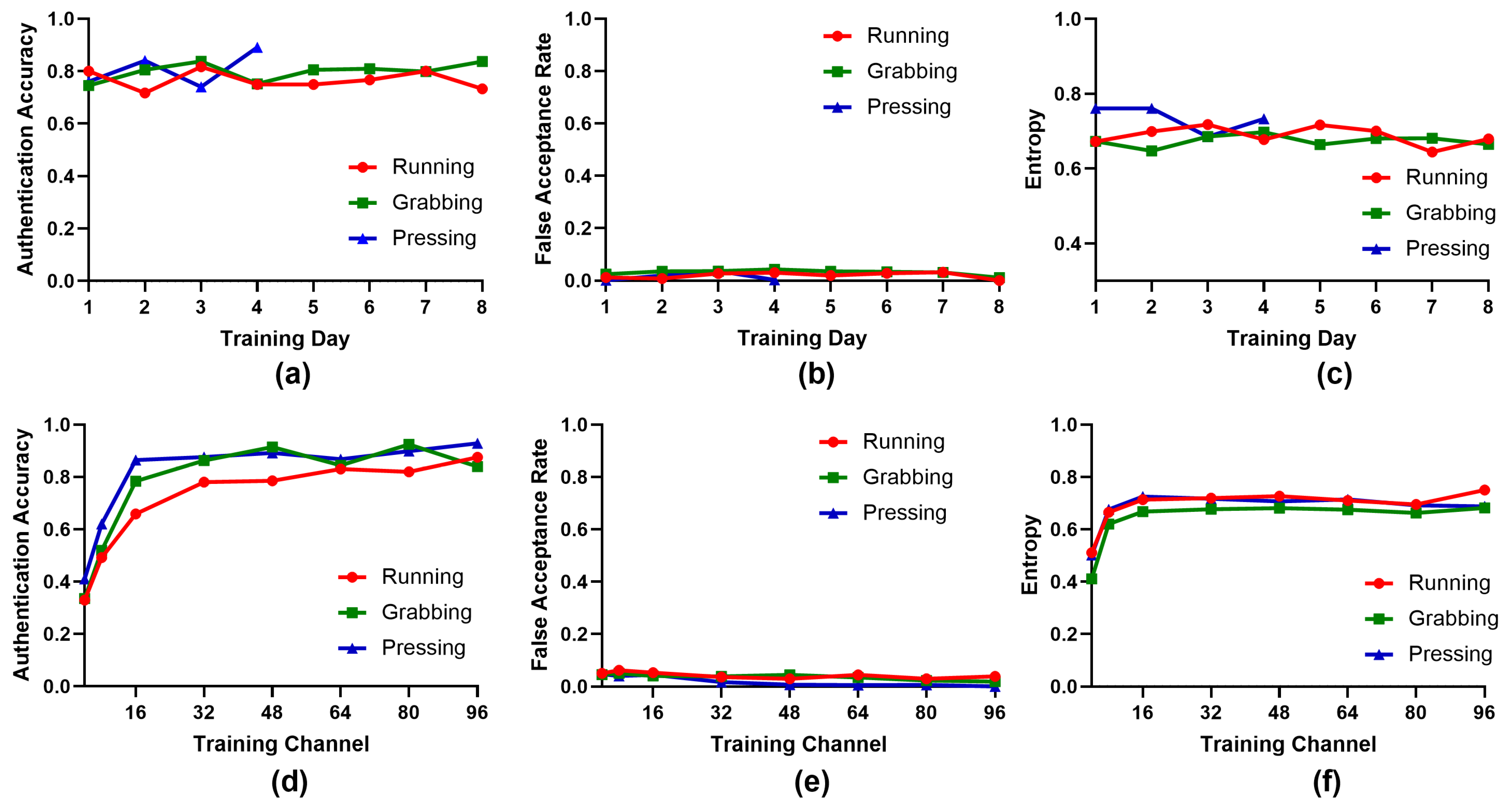
3.5. Long-Term Stability
3.6. Influence of Parameters
3.6.1. Training Size
3.6.2. Number of LFP Channels
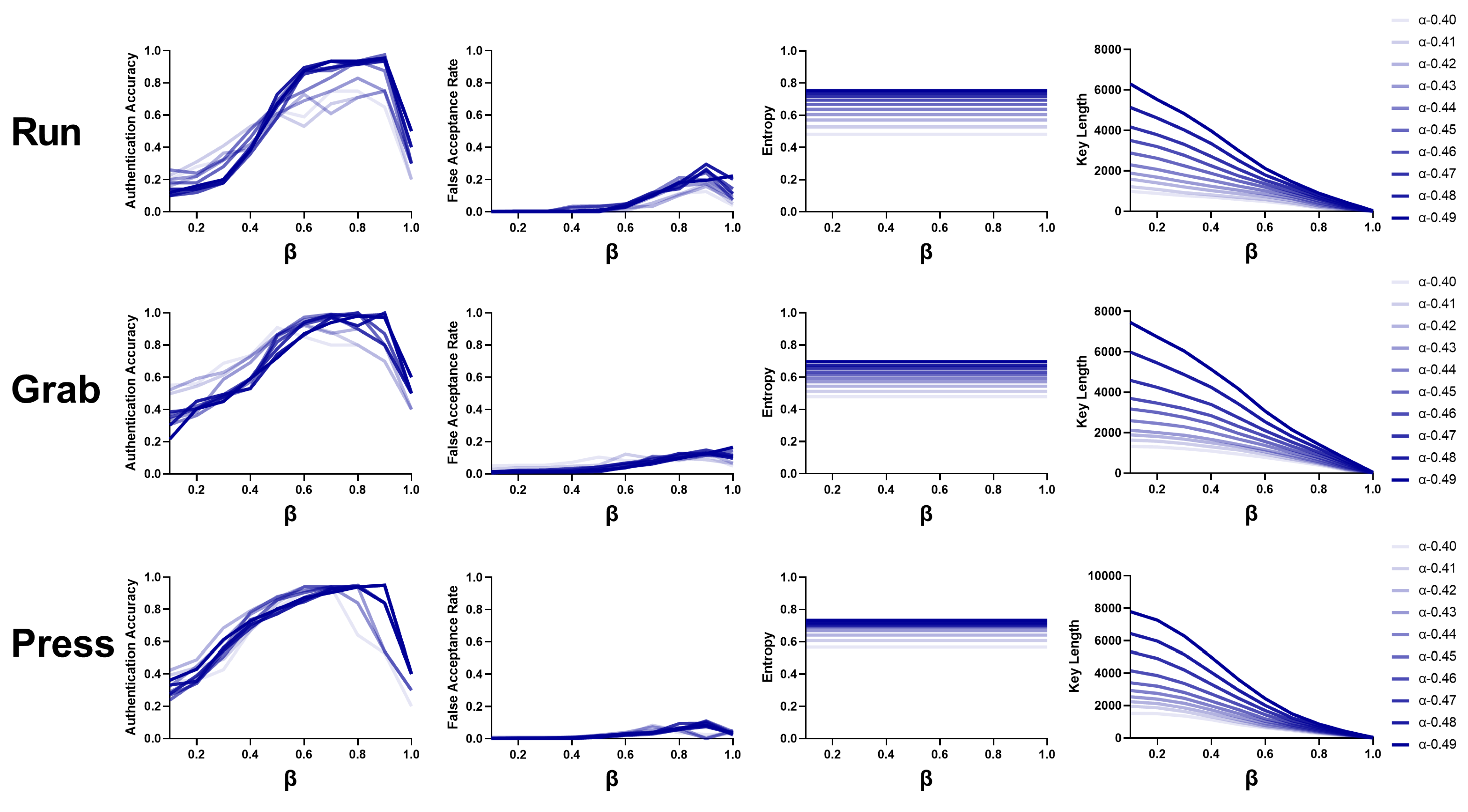
3.6.3. Parameter
3.6.4. Parameter
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tatlı, E.I. Cracking more password hashes with patterns. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, U.; Pankanti, S.; Prabhakar, S.; Jain, A.K. Biometric cryptosystems: Issues and challenges. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Ross, A.; Pankanti, S. Biometrics: A tool for information security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2006, 1, 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Teoh, A.B.J.; Goi, B.-M.; Tay, Y.-H. Biometric cryptosystems: A new biometric key binding and its implementation for fingerprint minutiae-based representation. Pattern Recognit. 2016, 56, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratha, N.K.; Chikkerur, S.; Connell, J.H.; Bolle, R.M. Generating cancelable fingerprint templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2007, 29, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, S.; Hu, Y.; Niyogi, P.; Zhang, H.-J. Face recognition using laplacianfaces. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 328–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wildes, R.P. Iris recognition: An emerging biometric technology. Proc. IEEE 1997, 85, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Ross, A.; Prabhakar, S. An introduction to biometric recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2004, 14, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, E.; Ross, A. A survey on antispoofing schemes for fingerprint recognition systems. ACM Comput. Surv. 2014, 47, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T.; Matsumoto, H.; Yamada, K.; Hoshino, S. Impact of artificial “gummy” fingers on fingerprint systems. In Optical Security and Counterfeit Deterrence Techniques IV; Electronic Imaging: San Jose, CA, USA, 2002; Volume 4677, pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- Galbally, J.; Ross, A.; Gomez-Barrero, M.; Fierrez, J.; Ortega-Garcia, J. From the iriscode to the iris: A new vulnerability of iris recognition systems. Black Hat Briefings USA 2012, 1, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Leier, A.; Richter, C.; Banzhaf, W.; Rauhe, H. Cryptography with DNA binary strands. Biosystems 2000, 57, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odinaka, I.; Lai, P.-H.; Kaplan, A.D.; O’Sullivan, J.A.; Sirevaag, E.J.; Rohrbaugh, J.W. ECG biometric recognition: A comparative analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2012, 7, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimian, N.; Guo, Z.; Tehranipoor, M.; Forte, D. Highly reliable key generation from electrocardiogram (ECG). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 64, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monrose, F.; Reiter, M.K.; Wetzel, S. Password hardening based on keystroke dynamics. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 2002, 1, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Feng, H.; Wah, C.C. Private key generation from on-line handwritten signatures. Inf. Manag. Comput. Secur. 2002, 10, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielhauer, C.; Steinmetz, R. Handwriting: Feature correlation analysis for biometric hashes. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2004, 2004, 389304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire-Santos, M.; Fierrez-Aguilar, J.; Ortega-García, J. Cryptographic key generation using handwritten signature. In Biometric Technology for Human Identification III; Defense and Security Symposium: Orlando (Kissimmee), FL, USA, 2006; Volume 6202, pp. 225–231. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Cho, K.W.; Song, C.; Jin, Z.; Xu, W. Exploring a brain-based cancelable biometrics for smart headwear: Concept, implementation, and evaluation. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2019, 19, 2774–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; El-Fiqi, H.; Hu, J.; Abbass, H.A. Convolutional neural networks using dynamic functional connectivity for EEG-based person identification in diverse human states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2019, 14, 3259–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Fan, C.; Fu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, X. Measuring and computing cognitive statuses of construction workers based on electroencephalogram: A critical review. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 9, 1644–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaheri, H.; Muhammad, G.; Alsulaiman, M.; Amin, S.U.; Altuwaijri, G.A.; Abdul, W.; Bencherif, M.A.; Faisal, M. Deep learning techniques for classification of electroencephalogram (EEG) motor imagery (MI) signals: A review. Neural Comput. Applic 2023, 35, 14681–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Cai, W.; Gao, M.; Jiang, Y.; Ning, X.; Qian, P. Multi-Source domain transfer discriminative dictionary learning modeling for electroencephalogram-based emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 9, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Jin, F.; Kong, W.; Nie, F.; Lu, B.-L.; Cichocki, A. OGSSL: A semi-supervised classification model coupled with optimal graph learning for EEG emotion recognition. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2022, 30, 1288–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, Q.; Ruiz-Blondet, M.V.; Laszlo, S.; Jin, Z. A survey on brain biometrics. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2019, 51, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorana, E.; Campisi, P. Longitudinal evaluation of EEG-based biometric recognition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2017, 13, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinger, J.L.; Wodlinger, B.; Downey, J.E.; Wang, W.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Weber, D.J.; McMorl, A.J.; Velliste, M.; Boninger, M.L.; Schwartz, A.B. High-performance neuroprosthetic control by an individual with tetraplegia. The Lancet 2013, 381, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouton, C.E.; Shaikhouni, A.; Annetta, N.V.; Bockbrader, M.A.; Friedenberg, D.A.; Nielson, D.M.; Sharma, G.; Sederberg, P.B.; Glenn, B.C.; Mysiw, W.J.; et al. Restoring cortical control of functional movement in a human with quadriplegia. Nature 2016, 533, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| RUNNING | Rat-1 | Rat-2 | Rat-3 | Rat-4 | Rat-5 | Rat-6 | Rat-7 | Rat-8 | Rat-9 | Rat-10 | Avg |
| Authentication Accuracy | 1.00 | 0.75 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.88 |
| False Acceptance Rate | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0.08 | 0 | 0.04 |
| Key Length | 1114 | 338 | 488 | 248 | 938 | 3780 | 740 | 112 | 30 | 1134 | 892 |
| GRABBING | Rat-1 | Rat-2 | Rat-3 | Rat-4 | Rat-5 | Rat-6 | Rat-7 | Rat-8 | Rat-9 | Rat-10 | Avg |
| Authentication Accuracy | 0.23 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.84 |
| False Acceptance Rate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0 | 0.02 |
| Key Length | 2110 | 134 | 140 | 358 | 250 | 4222 | 2858 | 234 | 148 | 1636 | 1209 |
| PRESSING | Rat-1 | Rat-2 | Rat-3 | Rat-4 | Rat-5 | Rat-6 | Rat-7 | Rat-8 | Rat-9 | Rat-10 | Avg |
| Authentication Accuracy | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.89 | 0.40 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.93 |
| False Acceptance Rate | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Key Length | 642 | 48 | 360 | 150 | 32 | 4412 | 650 | 366 | 60 | 408 | 713 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Qi, Y.; Pan, G. Encrypt with Your Mind: Reliable and Revocable Brain Biometrics via Multidimensional Gaussian Fitted Bit Allocation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080912
Li M, Qi Y, Pan G. Encrypt with Your Mind: Reliable and Revocable Brain Biometrics via Multidimensional Gaussian Fitted Bit Allocation. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(8):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080912
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ming, Yu Qi, and Gang Pan. 2023. "Encrypt with Your Mind: Reliable and Revocable Brain Biometrics via Multidimensional Gaussian Fitted Bit Allocation" Bioengineering 10, no. 8: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080912
APA StyleLi, M., Qi, Y., & Pan, G. (2023). Encrypt with Your Mind: Reliable and Revocable Brain Biometrics via Multidimensional Gaussian Fitted Bit Allocation. Bioengineering, 10(8), 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10080912






