Wearable Electromyography Classification of Epileptic Seizures: A Feasibility Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
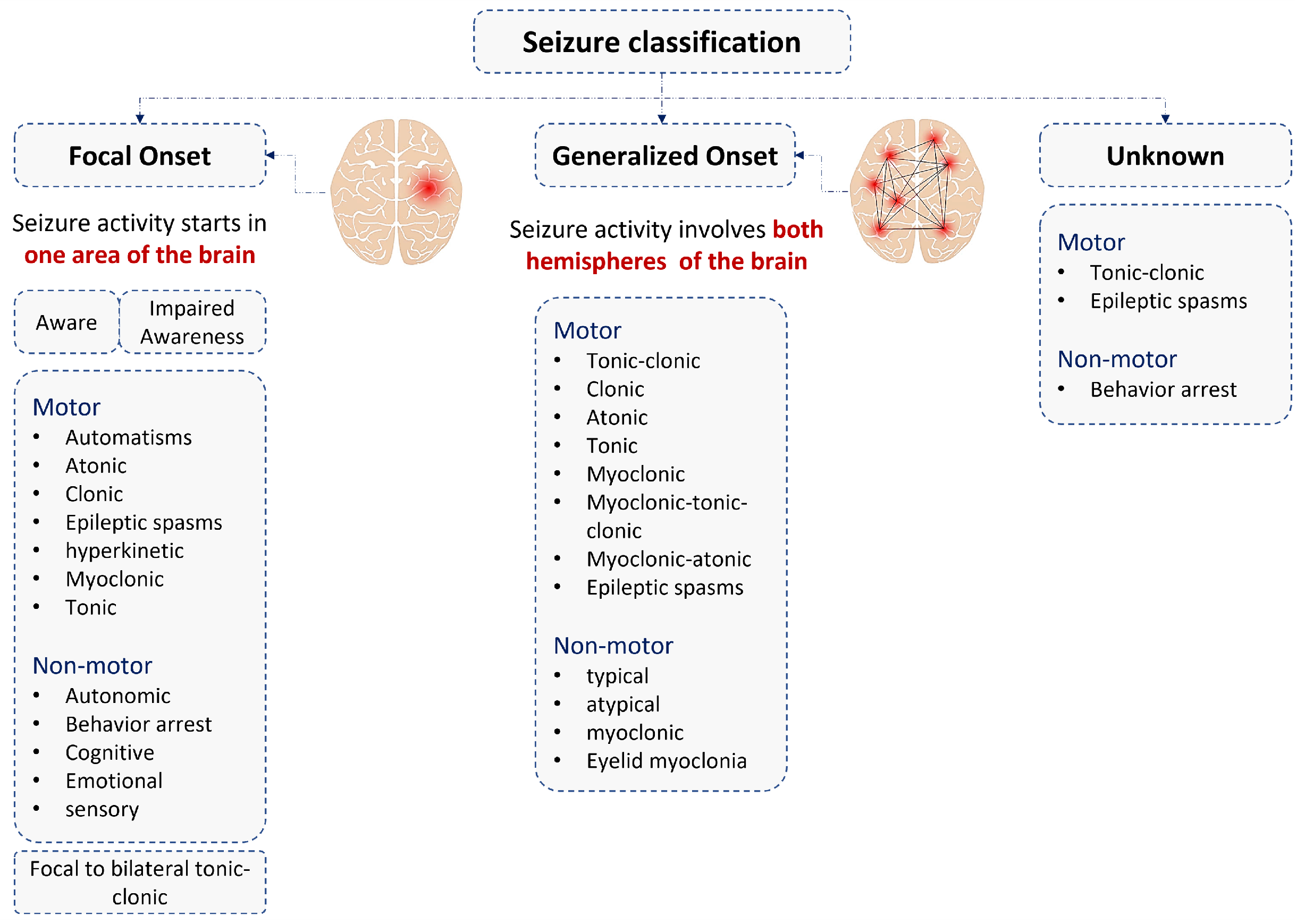
2. Epileptic Seizure Types and Sensors Used for the Diagnosis
2.1. Epileptic Myoclonic Seizure
2.2. Epileptic Tonic Seizure
2.3. Surface Electromyography (sEMG) and Quantity Analysis
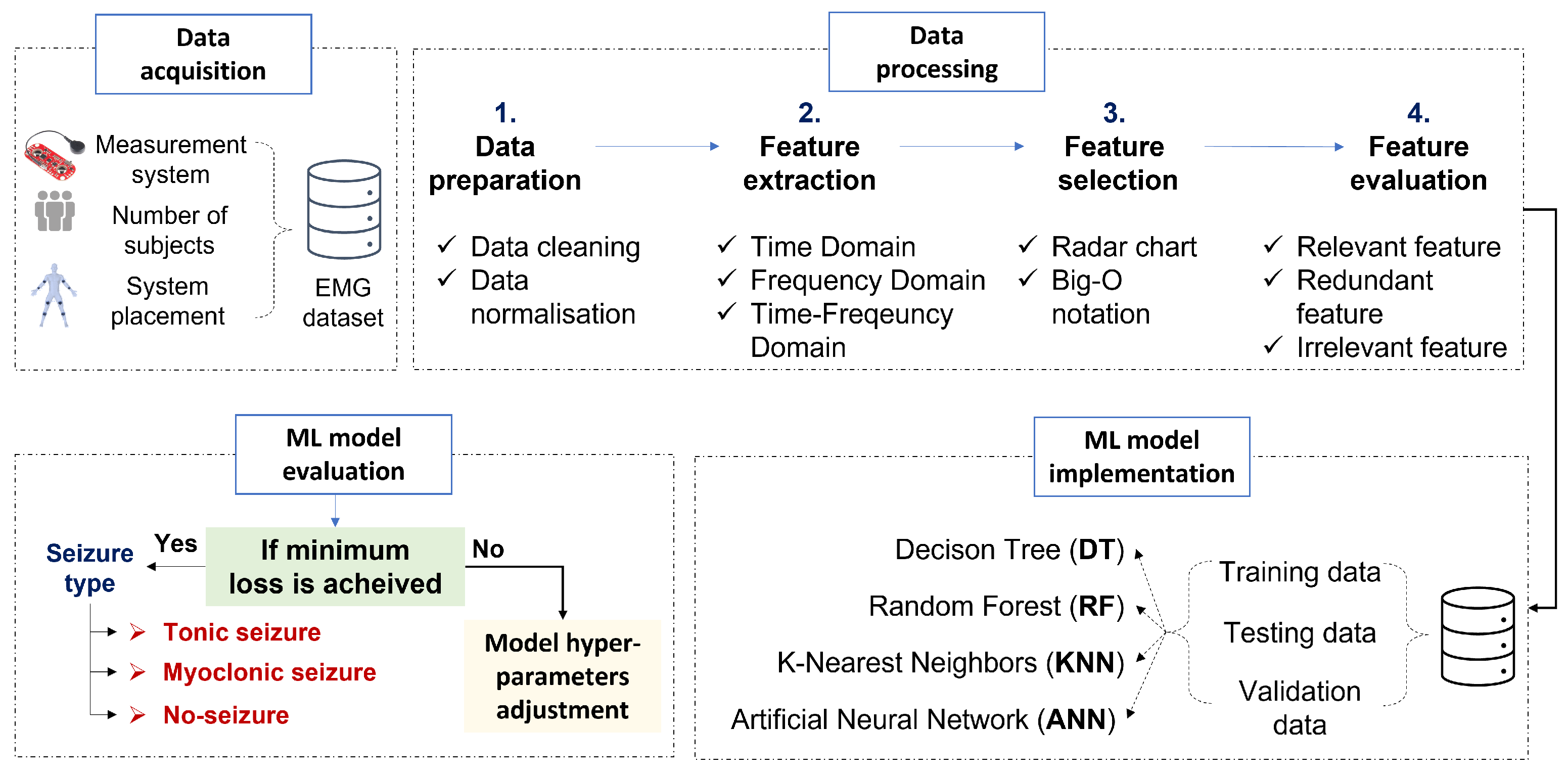
3. Materials and Methods
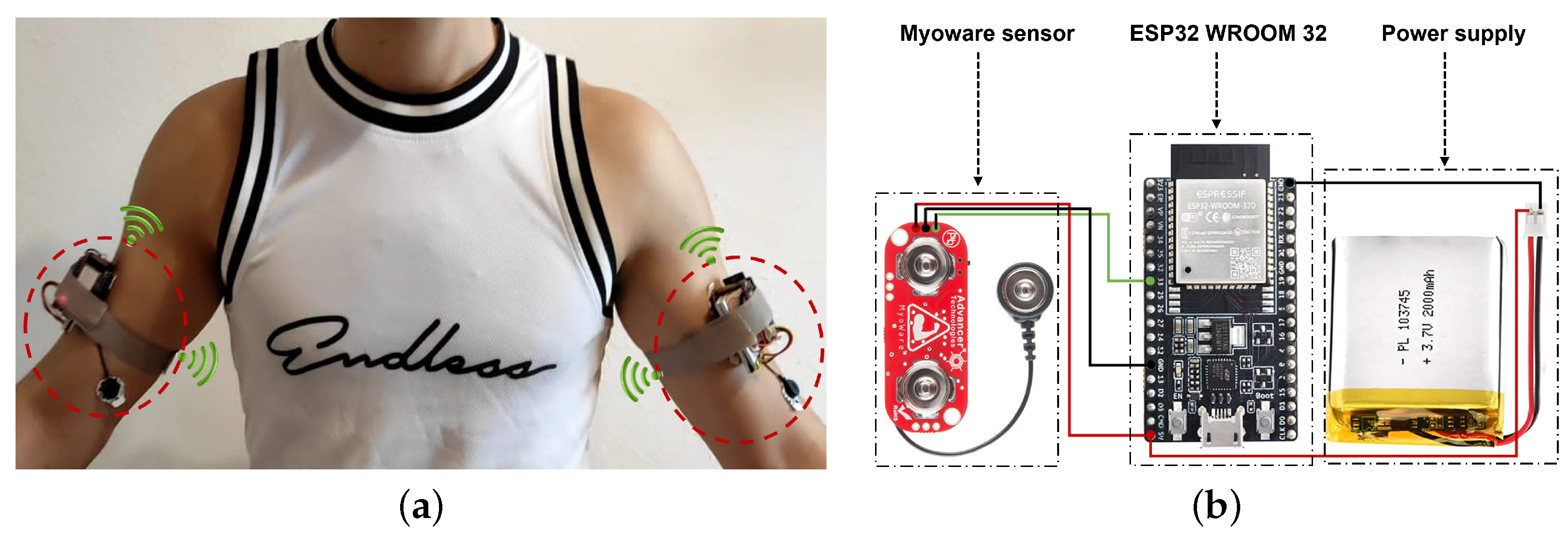
3.1. System Design
3.2. sEMG Electrodes Placement
3.3. sEMG Dataset Description
4. Data Processing
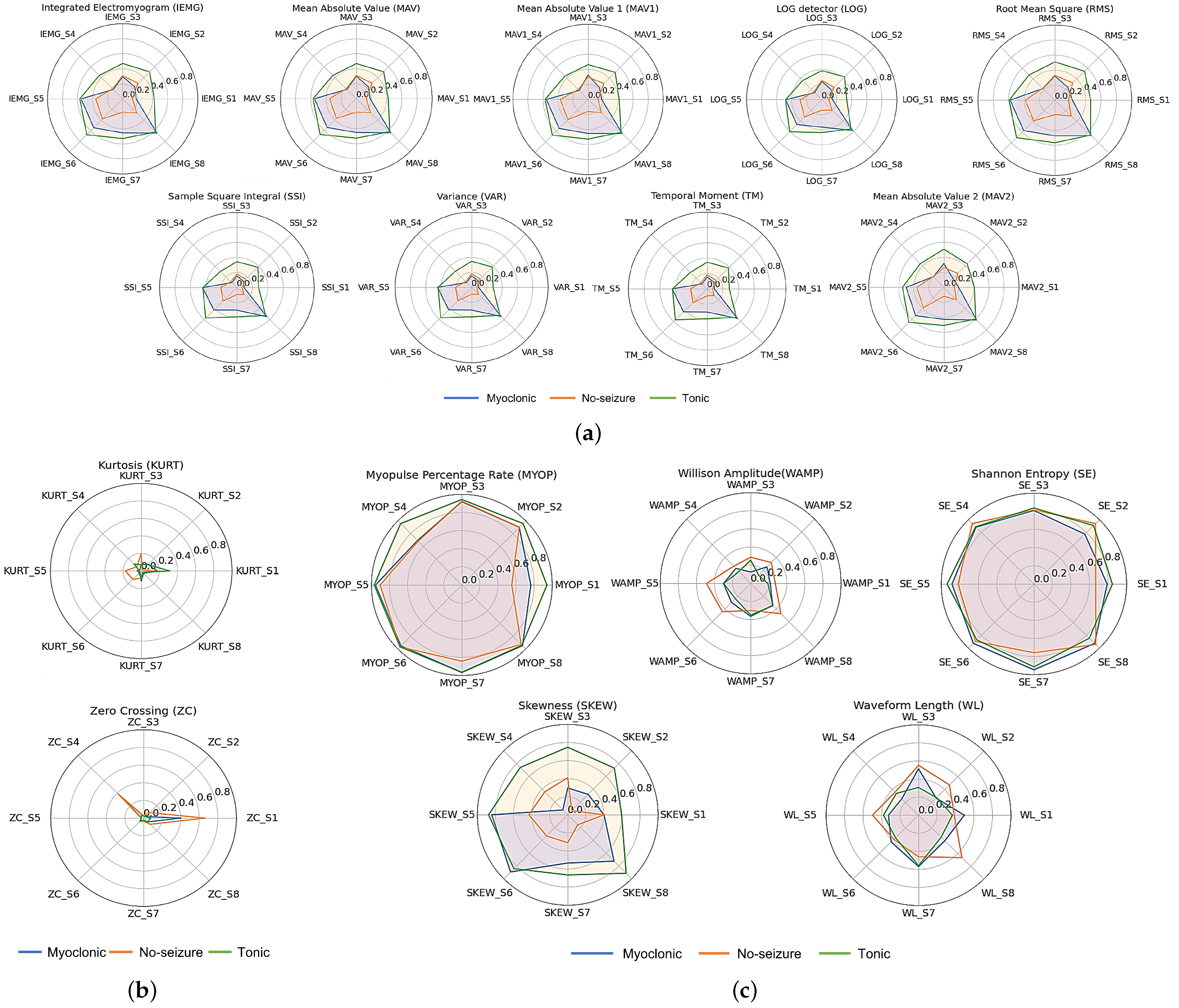
4.1. Feature Extraction
4.2. Feature Selection
5. Epileptic Movement Classification Based on Machine Learning Algorithms
5.1. Models Hyperparameter Setup
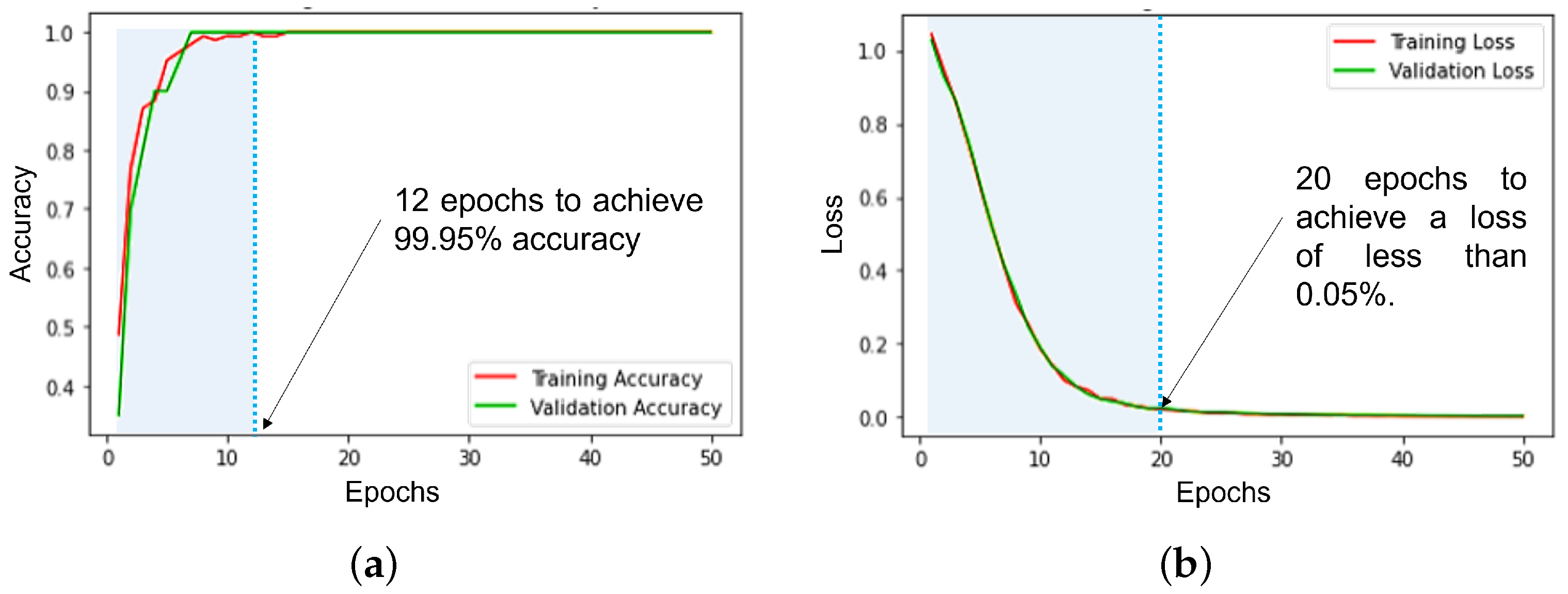
5.2. Machine Learning Models Evaluation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulate-Campos, A.; Coughlin, F.; Gaínza-Lein, M.; Fernández, I.S.; Pearl, P.; Loddenkemper, T. Automated seizure detection systems and their effectiveness for each type of seizure. Seizure 2016, 40, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beghi, E.; Giussani, G.; Nichols, E.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; Abraha, H.N.; Adib, M.G.; Agrawal, S.; Alahdab, F.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of epilepsy, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oto, M.M. The misdiagnosis of epilepsy: Appraising risks and managing uncertainty. Seizure 2017, 44, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniczky, S.; Wiebe, S.; Jeppesen, J.; Tatum, W.O.; Brazdil, M.; Wang, Y.; Herman, S.T.; Ryvlin, P. Automated seizure detection using wearable devices: A clinical practice guideline of the International League Against Epilepsy and the International Federation of Clinical Neurophysiology. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsen, I.; Beniczky, S.; Wolf, P.; Jennum, P.; Sorensen, H.B. Evaluation of novel algorithm embedded in a wearable sEMG device for seizure detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 2048–2051. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, E.; Viana, P.F.; Sperling, M.R.; Richardson, M.P. Seizure detection at home: Do devices on the market match the needs of people living with epilepsy and their caregivers? Epilepsia 2020, 61, S11–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmire, L.; Voyles, S.; Cardenas, D.; Cavazos, J. Diagnostic Utility of Continuous sEMG Monitoring in a Home Setting-Real-world use of the SPEAC®System (P4.5-012). Neurology 2019, 92, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Beniczky, S.; Conradsen, I.; Henning, O.; Fabricius, M.; Wolf, P. Automated real-time detection of tonic-clonic seizures using a wearable EMG device. Neurology 2018, 90, e428–e434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Sharma, V.; Mujawar, M.; Mishra, Y.K.; Kaushik, A.; Ghosal, A. Biosensors for epilepsy management: State-of-art and future aspects. Sensors 2019, 19, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaiby, T.N.; Alshebeili, S.A.; Alotaibi, F.M.; Alrshoud, S.R. Epileptic seizure prediction using CSP and LDA for scalp EEG signals. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2017, 2017, 1240323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, M.M. Overview of drugs used for epilepsy and seizures: Etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 392. [Google Scholar]
- Obeid, I.; Picone, J. Machine learning approaches to automatic interpretation of EEGs. In Signal Processing and Machine Learning for Biomedical Big Data; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 271–300. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Truong, N.D.; Nikpour, A.; Zhou, L.; Kavehei, O. Epileptic seizure classification with symmetric and hybrid bilinear models. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2844–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; French, J.A.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; Peltola, J.; Roulet Perez, E.; et al. Operational classification of seizure types by the International League Against Epilepsy: Position Paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Asif, U.; Tang, J.; Harrer, S. Seizure type classification using EEG signals and machine learning: Setting a benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 5 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Panayiotopoulos, C. Optimal use of the EEG in the diagnosis and management of epilepsies. In The Epilepsies: Seizures, Syndromes and Management; Bladon Medical Publishing: Oxfordshire, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Albaqami, H.; Hassan, G.M.; Datta, A. Wavelet-Based Multi-Class Seizure Type Classification System. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemal, A.; Bouchaala, D.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Artifacts Removal From Epileptic EEG Signal Based on Independent Components Analysis Method. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Application (MeMeA), Messina, Italy, 22–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Japaridze, G.; Loeckx, D.; Buckinx, T.; Armand Larsen, S.; Proost, R.; Jansen, K.; MacMullin, P.; Paiva, N.; Kasradze, S.; Rotenberg, A.; et al. Automated detection of absence seizures using a wearable electroencephalographic device: A phase 3 validation study and feasibility of automated behavioral testing. Epilepsia 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzichristos, C.; Swinnen, L.; Macea, J.; Bhagubai, M.; Van Paesschen, W.; De Vos, M. Multimodal detection of typical absence seizures in home environment with wearable electrodes. Front. Signal Process. 2022, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, R.S.; Cross, J.H.; D’souza, C.; French, J.A.; Haut, S.R.; Higurashi, N.; Hirsch, E.; Jansen, F.E.; Lagae, L.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. Instruction manual for the ILAE 2017 operational classification of seizure types. Epilepsia 2017, 58, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmast, S.T.; Abdullahi, A.M.; Jahan, N. Current classification of seizures and epilepsies: Scope, limitations and recommendations for future action. Cureus 2020, 12, e10549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviness, J.N. Treatment of myoclonus. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanty, N.; Jones, J.; Tonner, F. Adjunctive levetiracetam in children, adolescents, and adults with primary generalized seizures: Open-label, noncomparative, multicenter, long-term follow-up study. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrutha, N.; Arul, V. A Review on Noises in EMG Signal and its Removal. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 2017, 7, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, R.; Ni, Y.; Jing, X.; Gao, S. A Review of EMG-, FMG-, and EIT-Based Biosensors and Relevant Human–Machine Interactivities and Biomedical Applications. Biosensors 2022, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaweera, H.K.P.Y. Design and Implementation of Electromyography (EMG) Based Real-Time Pattern Recognition Model for Prosthetic hand Control. 2021. Available online: https://osf.io/rd2cf/ (accessed on 10 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Daud, W.M.B.W.; Yahya, A.B.; Horng, C.S.; Sulaima, M.F.; Sudirman, R. Features extraction of electromyography signals in time domain on biceps brachii muscle. Int. J. Model. Optim. 2013, 3, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniczky, S.; Conradsen, I.; Moldovan, M.; Jennum, P.; Fabricius, M.; Benedek, K.; Andersen, N.; Hjalgrim, H.; Wolf, P. Quantitative analysis of surface electromyography during epileptic and nonepileptic convulsive seizures. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E. EMG pattern recognition in the era of big data and deep learning. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2018, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiewak, C.; Islam, M.; Zaman, A.; Rahman, M.H. A comprehensive study on EMG feature extraction and classifiers. Open Access J. Biomed. Eng. Biosci. 2018, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Perez, D.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Gómez-Loenzo, R.A. A study of computing zero crossing methods and an improved proposal for EMG signals. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 8783–8790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Martínez, D.; Alfaro-Ponce, M.; Pogrebnyak, O.; Aldape-Pérez, M.; Argüelles-Cruz, A.J. Hand movement classification using burg reflection coefficients. Sensors 2019, 19, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waris, A.; Kamavuako, E.N. Effect of threshold values on the combination of EMG time domain features: Surface versus intramuscular EMG. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2018, 45, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradsen, I.; Moldovan, M.; Jennum, P.; Wolf, P.; Farina, D.; Beniczky, S. Dynamics of muscle activation during tonic–clonic seizures. Epilepsy Res. 2013, 104, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M.; DelRosso, L.M.; Elble, R.; Ferri, R.; Horak, F.B.; Lehericy, S.; Mancini, M.; Matsuhashi, M.; Matsumoto, R.; Muthuraman, M.; et al. Evaluation of movement and brain activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2608–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barioul, R.; AlQudah, A.; Atitallah, B.B.; Bouchaala, D.; Kanoun, O. Surface electrical impedance myography measurements for recognition of numbers in american sign language. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA), Tunis, Tunisia, 22–24 June 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, P.; Shi, X. Evaluation of feature extraction and classification for lower limb motion based on sEMG signal. Entropy 2020, 22, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A.; Khushaba, R.N.; Scheme, E. Feature extraction and selection for myoelectric control based on wearable EMG sensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, R.H.; Reaz, M.B.; Ali, M.A.B.M.; Bakar, A.A.; Chellappan, K.; Chang, T.G. Surface electromyography signal processing and classification techniques. Sensors 2013, 13, 12431–12466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinyomark, A.; Khushaba, R.N.; Ibáñez-Marcelo, E.; Patania, A.; Scheme, E.; Petri, G. Navigating features: A topologically informed chart of electromyographic features space. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, X. A novel feature selection algorithm based on damping oscillation theory. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, O.; Hagiwara, Y.; Hong, T.J.; Lih, O.S.; Acharya, U.R. Deep learning for healthcare applications based on physiological signals: A review. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Min, J.Y.; Byun, S. Electromyogram-based classification of hand and finger gestures using artificial neural networks. Sensors 2021, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, S.; Sun, Y. A Muscle Fatigue Classification Model Based on LSTM and Improved Wavelet Packet Threshold. Sensors 2021, 21, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y. Deep learning for EMG-based human-machine interaction: A review. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 8, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djemal, A.; Bouchaala, D.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Epileptic Seizure Motion Classification based on sEMG and Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Workshop on Impedance Spectroscopy (IWIS), Chemnitz, Germany, 29 September–1 October 2021; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Djemal, A.; Bouchaala, D.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Tonic-Myoclonic Epileptic Seizure Classification based on Surface Electromyography. In Proceedings of the 2021 18th International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices (SSD), Monastir, Tunisia, 22–25 March 2021; pp. 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Di Nardo, F.; Nocera, A.; Cucchiarelli, A.; Fioretti, S.; Morbidoni, C. Machine Learning for Detection of Muscular Activity from Surface EMG Signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.; Withanachchi, G.P.; Yihun, Y. Performance of forearm FMG for estimating hand gestures and prosthetic hand control. J. Bionic Eng. 2019, 16, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasi, A.; Alharbi, L.; Madani, R.; Qaisar, S.M. Surface EMG based classification of basic hand movements using rotation forest. In Proceedings of the 2018 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET), Dubai, Sharjah, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 6 February–5 April 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, K. Hand gesture recognition based on concentric circular scan lines and weighted K-nearest neighbor algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jmal, A.; Barioul, R.; Meddeb Makhlouf, A.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. An embedded ANN raspberry PI for inertial sensor based human activity recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics, Hammamet, Tunisia, 24–26 June 2020; pp. 375–385. [Google Scholar]
- Djemal, A.; Hellara, H.; Barioul, R.; Atitallah, B.B.; Ramalingame, R.; Fricke, E.; Kanoun, O. Real-Time Model for Dynamic Hand Gestures Classification based on Inertial Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications (CIVEMSA), Chemnitz, Germany, 15–17 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Veer, K.; Sharma, T. A novel feature extraction for robust EMG pattern recognition. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2016, 40, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashikant, R.; Chetankumar, P. Predictive model of cardiac arrest in smokers using machine learning technique based on Heart Rate Variability parameter. Appl. Comput. Inform. 2020. ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Subject | Gender | Age | Weight (kg) | High (m) | Subject | Gender | Age | Weight (kg) | High (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | male | 23 | 63 | 1.83 | 11 | female | 26 | 66 | 1.68 |
| 2 | male | 24 | 70 | 1.85 | 12 | female | 24 | 92 | 1.86 |
| 3 | male | 27 | 63 | 1.75 | 13 | female | 24 | 62 | 1.64 |
| 4 | male | 25 | 84 | 1.78 | 14 | female | 25 | 65 | 1.70 |
| 5 | male | 25 | 81 | 1.77 | 15 | female | 25 | 61 | 1.64 |
| 6 | male | 25 | 74 | 1.83 | 16 | female | 24 | 58 | 1.72 |
| 7 | male | 25 | 82 | 1.78 | 17 | female | 27 | 75 | 1.71 |
| 8 | male | 24 | 97 | 1.80 | 18 | female | 27 | 62 | 1.68 |
| 9 | male | 27 | 63 | 1.83 | 19 | female | 24 | 53 | 1.62 |
| 10 | male | 26 | 89 | 1.82 | 20 | female | 26 | 58 | 1.76 |
| Abbreviation | Feature | Equation |
|---|---|---|
| IEMG | Integrated EMG | , Here N denotes the length of the signal and represents the sEMG signal in a segment. |
| MAV | Mean Absolute Value | |
| MAV 1 | Mean Absolute Value 1 | , |
| MAV 2 | Mean Absolute Value 2 | , |
| SSI | Simple Square Integral | |
| VAR | Variance | |
| TM | Temporal Moment | |
| RMS | Root Mean Square | |
| LOG | LOG detector | |
| WL | Waveform Length | |
| ZC | Zero Crossing | , |
| MYOP | Myopulse Percentage Rate | , |
| WAMP | Willison Amplitude | , |
| KURT | Kurtosis | |
| SKEW | Skewness | |
| SE | Shannon Entropy |
| Predictive Model | Hyperparameter | Tuned to |
|---|---|---|
| DT | Criterion | Gini, Entropy |
| Depth of trees | 4 | |
| RF | Criterion | Gini, Entropy |
| Decision trees | 2 | |
| Maximum features | Auto | |
| KNN | K-neighbour | K = 3 |
| Distance | Euclidean | |
| ANN | Batch size | 20 |
| Epochs | 50 | |
| Hidden layers | 1 | |
| Neurons | 64 | |
| Activation function | Softmax | |
| Learning rate | ||
| Optimizer | Adam | |
| Loss rate | Categorical Crossentropy | |
| Regularizer | L2 regularizer |
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Measure of the model’s correct predictions. |
| Precision | Determine the classifier’s ability to deliver accurate positive predictions. |
| Recall | Probability of a positive test, conditioned on truly being positive. |
| F1-score | Weighted average of precision and recall. |
| Predictive Model | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%) | Recall (%) | F1-Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DT | 91.67 | 91.90 | 91.67 | 91.72 |
| RF | 91.67 | 92.13 | 91.67 | 91.65 |
| KNN | 93.75 | 94.36 | 93.75 | 93.66 |
| ANN | 99.95 | 99.43 | 99.56 | 99.63 |
| Sensors Combination | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | S7 | S8 | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | x | x | 85.51 | ||||||
| x | x | 87.75 | |||||||
| x | x | 88.50 | |||||||
| x | x | 91.83 | |||||||
| 4 | x | x | x | x | 90.00 | ||||
| x | x | x | x | 92.40 | |||||
| x | x | x | x | 93.64 | |||||
| x | x | x | x | 93.82 | |||||
| x | x | x | x | 94.27 | |||||
| x | x | x | x | 94.60 | |||||
| 6 | x | x | x | x | x | x | 93.84 | ||
| x | x | x | x | x | x | 94.21 | |||
| x | x | x | x | x | x | 95.59 | |||
| x | x | x | x | x | x | 96.05 | |||
| 8 | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | 99.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Djemal, A.; Bouchaala, D.; Fakhfakh, A.; Kanoun, O. Wearable Electromyography Classification of Epileptic Seizures: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060703
Djemal A, Bouchaala D, Fakhfakh A, Kanoun O. Wearable Electromyography Classification of Epileptic Seizures: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(6):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060703
Chicago/Turabian StyleDjemal, Achraf, Dhouha Bouchaala, Ahmed Fakhfakh, and Olfa Kanoun. 2023. "Wearable Electromyography Classification of Epileptic Seizures: A Feasibility Study" Bioengineering 10, no. 6: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060703
APA StyleDjemal, A., Bouchaala, D., Fakhfakh, A., & Kanoun, O. (2023). Wearable Electromyography Classification of Epileptic Seizures: A Feasibility Study. Bioengineering, 10(6), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10060703










