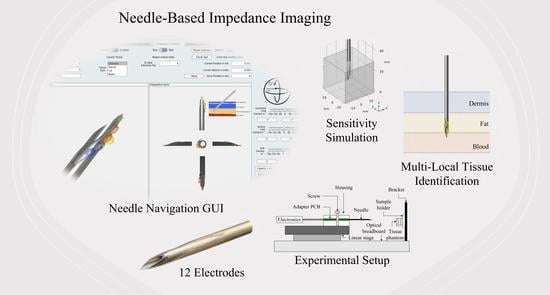
Needle-Based Electrical Impedance Imaging Technology for Needle Navigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sensor Development
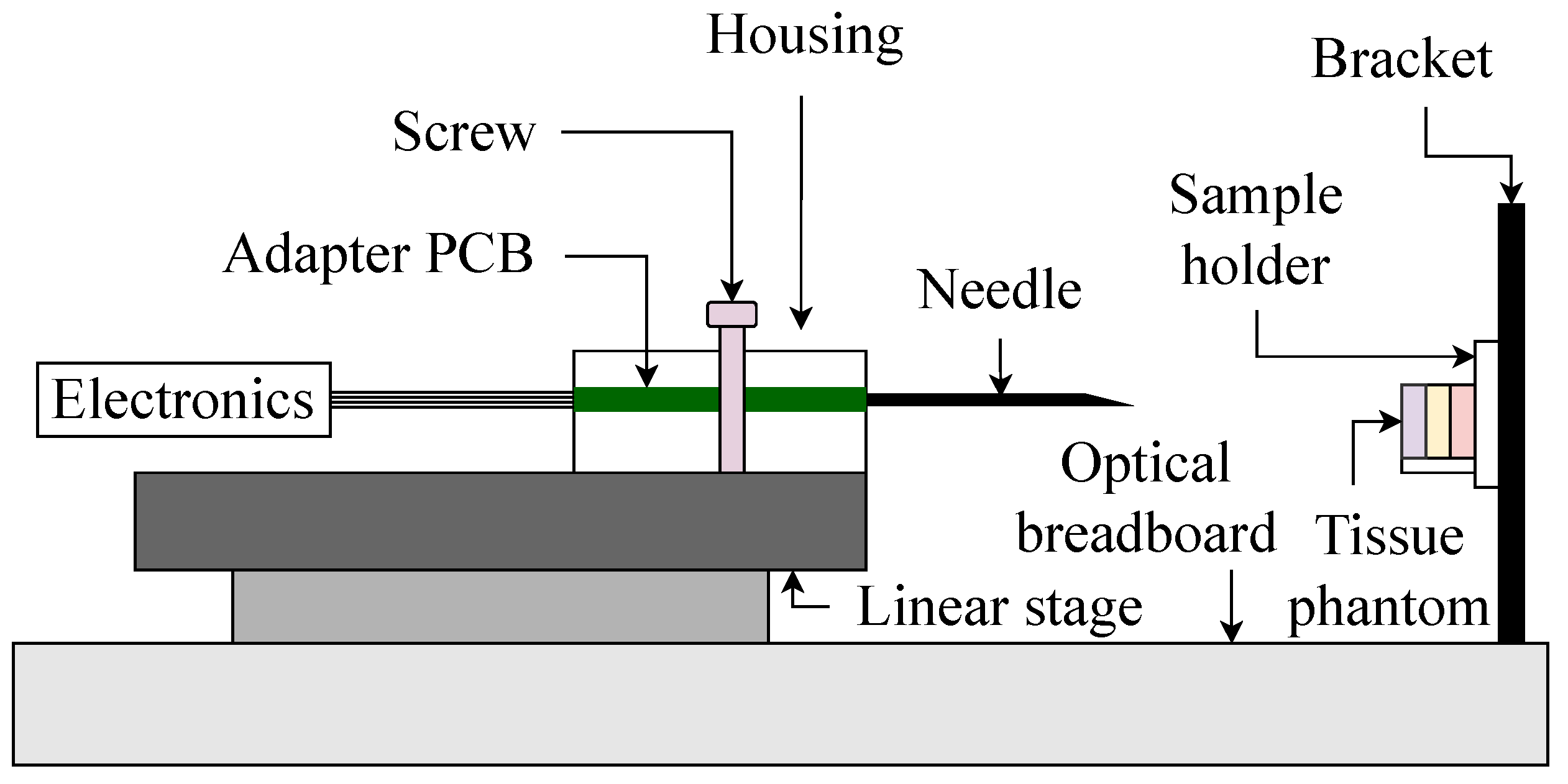
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Simulation
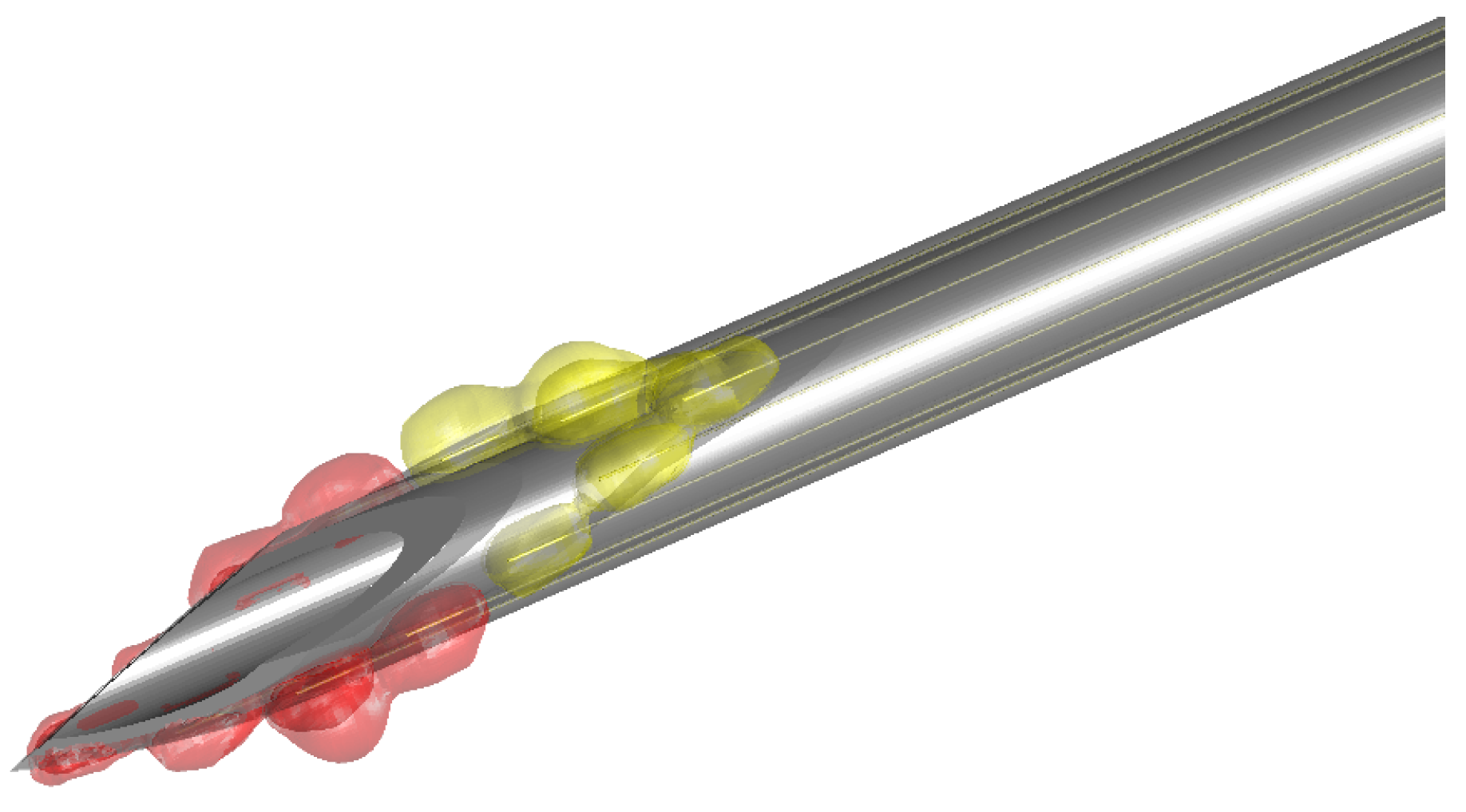
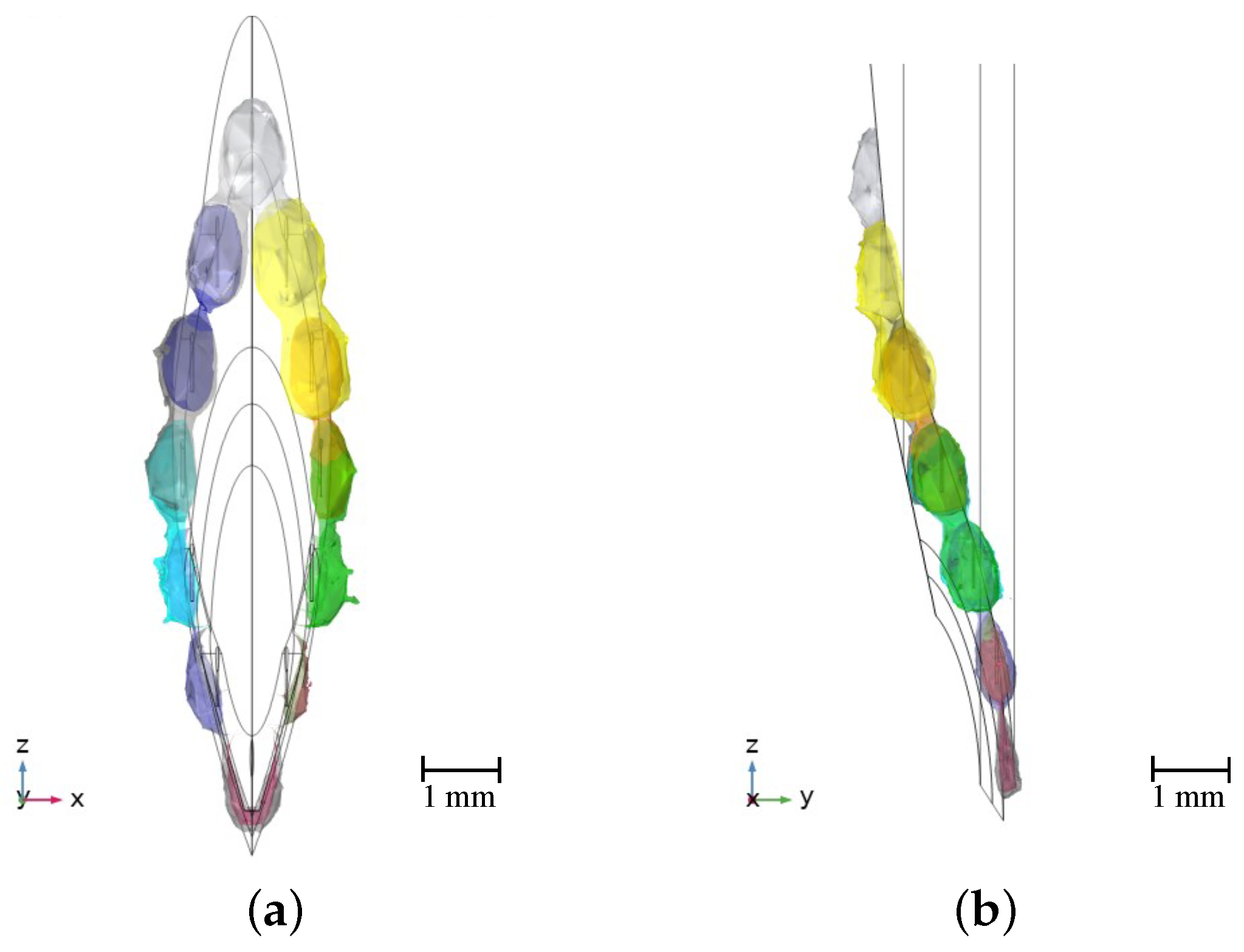
2.3.1. Geometry
2.3.2. Material Properties
2.3.3. Boundary Conditions
2.3.4. Meshing
2.3.5. Post-Processing
2.4. Software Architecture
2.5. Needle Navigation Software
3. Results
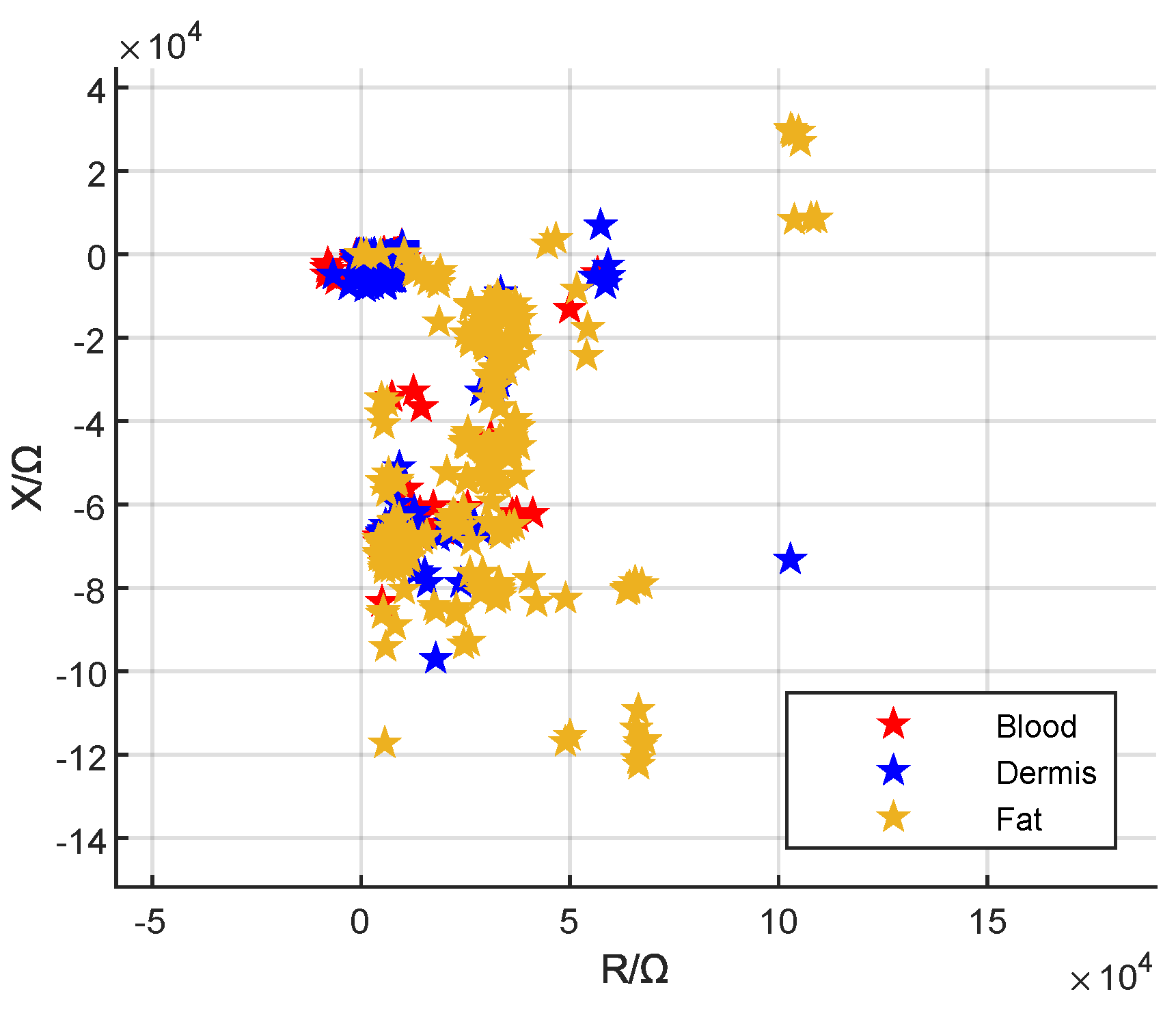
3.1. Local Visualization
3.2. Global Visualization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC/DC | Alternating Current/Direct Current |
| ASCII | American Standard Code for Information Interchange |
| CAD | Computer-Aided Design |
| CC | Current-Carrying |
| COM | Communication Port |
| EC | Electric Current |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| FEM | Finite Element Method |
| G | Gauge |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| IA | Impedance Analyzer |
| IDE | Integrated Development Environment |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| ML | Machine-Learning |
| PCB | Printed Circuit Board |
| PIVC | Peripheral Intravenous Catheter |
| PU | Pick-Up |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol |
References
- Rickard, C.M.; Webster, J.; Wallis, M.C.; Marsh, N.; McGrail, M.R.; French, V.; Foster, M.R.; Gallagher, P.; Gowardman, J.R.; Zhang, L.; et al. Routine versus clinically indicated replacement of peripheral intravenous catheters: A randomised controlled equivalence trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrou, E.; Ray-Barruel, G.; Carr, P.J.; Frost, S.; Inwood, S.; Higgins, N.; Alberto, L.; Mermel, L.; Rickard, M. International prevalence of the use of peripheral intravenous catheters. J. Hosp. Med. 2015, 10, 530–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balter, M.L.; Chen, A.I.; Maguire, T.J.; Yarmush, M.L. The System Design and Evaluation of a 7-DOF Image-Guided Venipuncture Robot. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 41, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buowari, O.Y. Complications of venepuncture. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galena, H.J. Complications occurring from diagnostic venipuncture. J. Fam. Pract. 1992, 34, 582–584. [Google Scholar]
- Bölenius, K.; Brulin, C.; Graneheim, U.H. Personnel’s Experiences of Phlebotomy Practices after Participating in an Educational Intervention Programme. Nurs. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 538704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiszewska, E.; Pasicz, K.; Grabska, I.; Skrzyński, W.; Ślusarczyk-Kacprzyk, W.; Bulski, W. Evaluation of Imaging Parameters of Ultrasoand Scanners: Baseline for Future Testing. Pol. J. Radiol. 2017, 82, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, S.J.; Kanal, K.; Bhargava, P.; Vaidya, S.; Dighe, M.K. Ultrasoand artifacts: Classification, applied physics with illustrations, and imaging appearances. Ultrasound Q. 2014, 30, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, G.A.; Johnson, D.; Bodenham, A.R. Visualisation of needle position using ultrasonography. Anaesthesia 2006, 61, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyum, P.; Kalvøy, H.; Martinsen, Ø.G.; Grimnes, S. A finite element model of needle electrode spatial sensitivity. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 1369–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki, S.; Kari, J.; Ahonen, P.; Elomaa, T.; Annus, P.; Kronström, K. Biopsy Needle Including Bioimpedance Probe with Optimized Sensitivity Distribution. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 2015, 17, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Trebbels, D.; Fellhauer, F.; Jugl, M.; Haimerl, G.; Min, M.; Zengerle, R. Online tissue discrimination for transcutaneous needle guidance applications using broadband impedance spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalvøy, H. Needle Guidance in Clinical Applications Based on Electrical Impedance. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physics, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Choy, Y.B.; Tsai, J.Z.; Vorperian, V.R.; Webster, J.G. Using electrical impedance to predict catheter-endocardial contact during RF cardiac ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kalvøy, H.; Frich, L.; Grimnes, S.; Martinsen, Ø.G.; Hol, P.K.; Stubhaug, A. Impedance-based tissue discrimination for needle guidance. Physiol. Meas. 2009, 30, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalamagas, P.P.; Sapia, M.A. Method to Sense the Tissue for Injection from a Hypodermic Needle. U.S. Patent 5 271 413, 21 December 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, H.; Miyajima, K.; Kudo, H.; Mitsubayashi, K. A computer controlled venepuncture system for blood test. In Proceedings of the SENSOR+TEST Conferences, Nuremberg, Germany, 26–28 May 2009; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Tsui, B.C.H.; Pilly, J.J.; Chu, K.T.; Dillane, D. Electrical impedance to distinguish intraneural from extraneural needle placement in porcine nerves during direct exposure and ultrasoand guidance. Anesthesiology 2008, 109, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Bouayad, H.; Schned, A.; Hartov, A.; Heaney, J.; Halter, R.J. A real-time electrical impedance sensing biopsy needle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 3327–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halonen, S.; Kari, J.; Ahonen, P.; Kronström, K.; Hyttinen, J. Real-Time Bioimpedance-Based Biopsy Needle Can Identify Tissue Type with High Spatial Accuracy. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Davies, B.L.; Caldwell, D.G.; Mattos, L.S. A venipuncture detection system for robot-assisted intravenous catheterization. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), Singapore, 26–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Göhring, C.; Pott, P.P. Integration of a Hollow, Bipolar Needle Electrode into a Handheld Impedance Measurement Device for Tissue Identification. In Proceedings of the 2021 13th Biomedical Engineering International Conference (BMEiCON), Ayutthaya, Thailand, 19–21 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kronström, K.; Ahonen, P.; Mäki, S.; Elomaa, T.; Kari, J. Biopsy Needle for Biopsy Sampling, Biopsy Device, and Methods of Manufacturing a Biopsy Needle or a Biopsy Device. U.S. Patent WO 2016 198910 A1, 15 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Helen, L.; O’Donnell, B.D.; Messina, W.; O’Mahony, C.; Ahmed, O.M.A.; Moore, E.J. Impedance Sensor to Detect Substance Change at the Needle Tip. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shcherbachev, A.V.; Bychkov, E.A.; Kudashov, I.A.; Volkov, A.K. Research coaxial needle electrode characteristics for the automated vein puncture control system. In Proceedings of the 2018 Ural Symposium on Biomedical Engineering, Radioelectronics and Information Technology, Yekaterinburg, Russia, 7–8 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stoianovici, D.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Allaf, M.; Jackman, S. Surgical Needle Probe for Electrical Impedance Measurements. U.S. Patent 6 337 994, 8 January 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, D.J.; Sinkov, V.A.; Roberts, W.W.; Allaf, M.E.; Patriciu, A.; Jarrett, T.W.; Kavoussi, L.R.; Stoianovici, D. Measurement of bio-impedance with a smart needle to performe percutaneous kidney access. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, H.-I.; Lee, J.-H. Electrical impedance spectroscopy on a needle for safer Veress needle insertion during laparoscopic surgery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 250, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Davies, B.L.; Caldwell, D.G.; Barresi, G.; Xu, Q.; Mattos, L.S. A hand-held robotic device for peripheral intravenous catheterization. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 2017, 231, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Choi, W.-M.; Kim, K.; Jeong, W.-I.; Seo, J.-B.; Park, I. Biopsy Needle Integrated with Electrical Impedance Sensing Microelectrode Array towards Real-time Needle Guidance and Tissue Discrimination. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.; Cristina, J.F.D.; Rutkove, S.B.; Sanchez, B. Recording characteristics of electrical impedance-electromyography needle electrodes. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 055005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Park, I. Development of multi-spot impedance sensing biopsy needle based on attachable and flexible sensor film. In Proceedings of the 2016 38th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 16–20 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkove, S.B.; Kwon, H.; Guasch, M.; Wu, J.S.; Sanchez, B. Electrical impedance imaging of human muscle at the microscopic scale using a multi-electrode needle device: A simulation study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2018, 129, 1704–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Goehring, C.; Schiele, F.; Moeller, K.; Pott, P.P. Fabrication and Experimental Evaluation of Simple Tissue-Mimicking Phantoms with Realistic Electrical Properties for Impedance-Based Sensing. IJIE 2021, 13, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, S.; Lau, R.W.; Gabriel, C. The dielectric properties of biological tissues: II. Measurements in the frequency range 10 Hz to 20 GHz. Phys. Med. Biol. 1996, 41, 2251–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasgall, P.A.; Neufeld, E.; Gosselin, M.C.; Klingenböck, A.; Kuster, N.; Kuster, N.; Hasgall, P.; Gosselin, M. IT’IS Database for Thermal and Electromagnetic Parameters of Biological Tissues. Version 4.1. 22 February 2022. Available online: https://itis.swiss/database (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Yamamoto, T.; Yamamoto, Y. Electrical properties of the epidermal stratum corneum. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 1976, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, B.; Xue, H.; Birgersson, E.; Ollmar, S.; Birgersson, U. Dielectrical Properties of Living Epidermis and Dermis in the Frequency Range from 1 kHz to 1 MHz. J. Electr. Bioimpedance 2019, 10, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimnes, S.; Martinsen, Ø.G. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics, 3rd ed.; Elsevier Science: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Atmaca, Ö.; Ly, T.J.; Pott, P.P. Numerical Sensitivity Analysis of Microelectrodes for Multi- Local Impedance Measurements on Needles. In Proceedings of the 9th GMM-Workshop, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 May 2022; pp. 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bayer, C.F.; Baer, E.; Waltrich, U.; Malipaard, D.; Schletz, A. Simulation of the electric field strength in the vicinity of metallization edges on dielectric substrates. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2015, 22, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Tissue Type | Ingredients (% w/w) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distilled Water | Sodium Chloride | Agar | Gelatine | Propylene Glycol | 5 M NaCl Solution | |
| Skin | 75.40 | 0.30 | 3.77 | 1.88 | 18.72 | - |
| Fat | 95.24 | - | 4.76 | - | - | - |
| Blood | - | - | - | - | 70.00 | 30.00 |
| Entity | Material | (S/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Needle | Stainless Steel 410 Annealed | 1 | |
| Insulation | PVDF | 8.1 | |
| Wires | Gold | 1 | |
| Tissue | Blood | 0.7 | 5120.02 |
| Fat | 101.49 | ||
| Dermis | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Atmaca, Ö.; Pott, P.P. Needle-Based Electrical Impedance Imaging Technology for Needle Navigation. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050590
Liu J, Atmaca Ö, Pott PP. Needle-Based Electrical Impedance Imaging Technology for Needle Navigation. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(5):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050590
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jan, Ömer Atmaca, and Peter Paul Pott. 2023. "Needle-Based Electrical Impedance Imaging Technology for Needle Navigation" Bioengineering 10, no. 5: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050590
APA StyleLiu, J., Atmaca, Ö., & Pott, P. P. (2023). Needle-Based Electrical Impedance Imaging Technology for Needle Navigation. Bioengineering, 10(5), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10050590