A Novel Phytogenic Formulation, EUBIO-BPSG, as a Promising One Health Approach to Replace Antibiotics and Promote Reproduction Performance in Laying Hens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Media
2.2. Animal Study
2.3. DNA Extraction and NGS Analysis of the Gut Microbiome [28]
2.4. Growth, Counting, and AR Measurement of Fecal Bacteria [29]
2.5. MAC, MIC, IC50, and Disc Diffusion Assays
2.6. Measurement of HGT, Conjugation, and Recombination Frequency
2.7. PI Staining and TEM Analysis [33]
2.8. Quantification of SCFA in Chicken Feces Using LC-MS/MS
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. BP Increases Egg Production and Probiotics and Reduces Mortality, Antibiotic Resistance, and Pathogens in Aged Laying Hens
3.2. BP Differentially Regulates Fecal Bacterial Genera in Aged Laying Hens
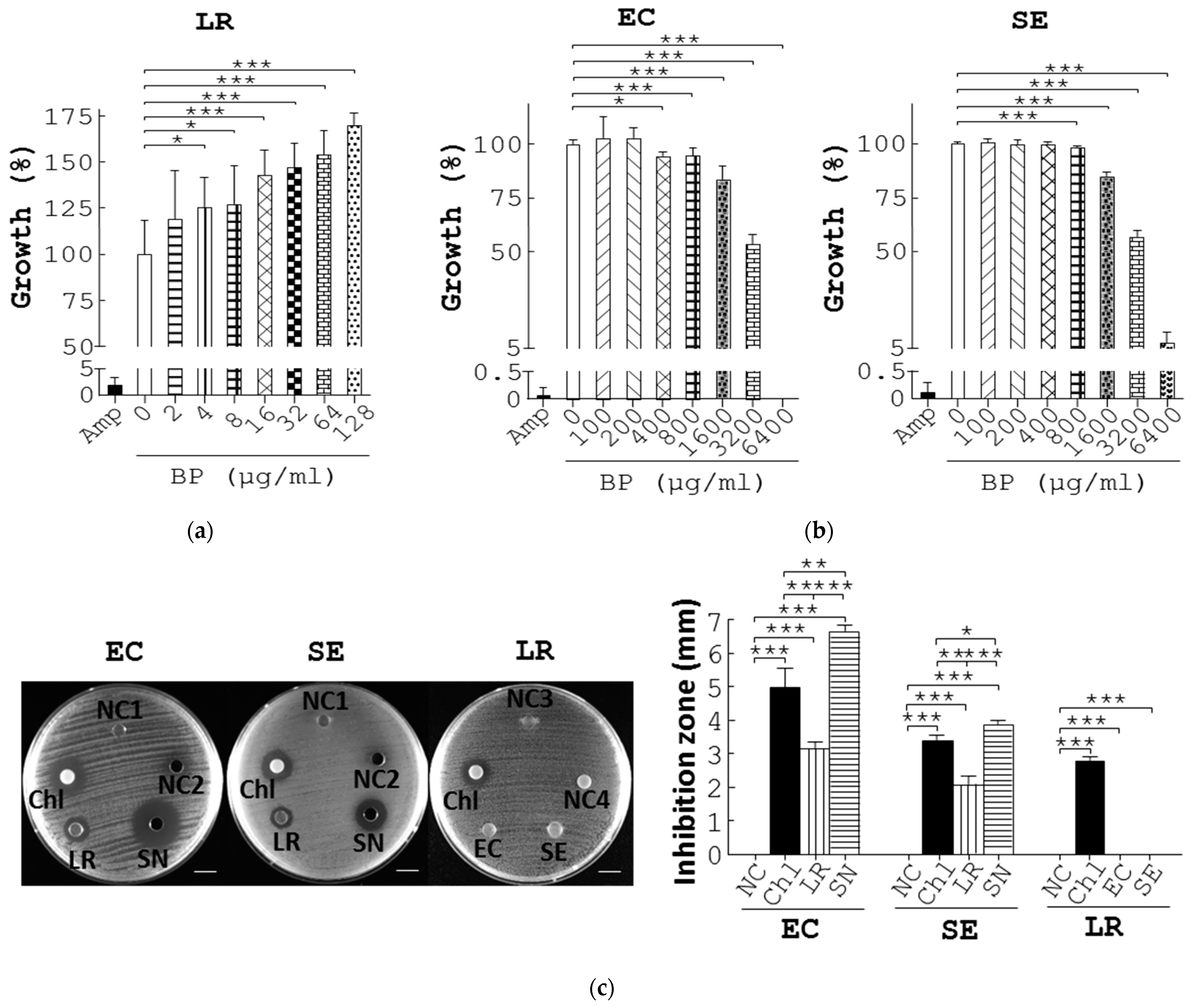
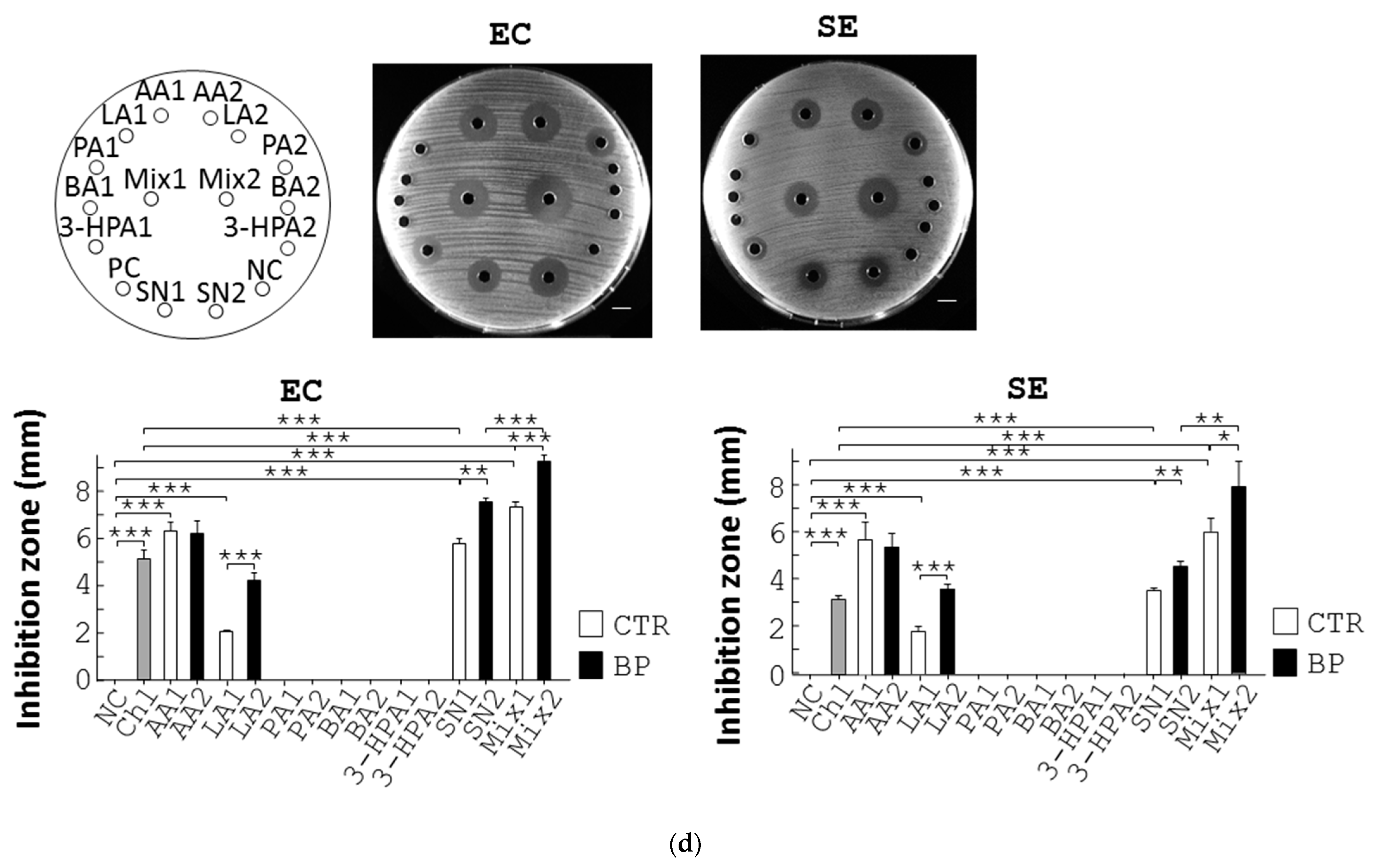
3.3. Promotion of Probiotics and Inhibition of Pathogenic Bacteria by BP In Vitro
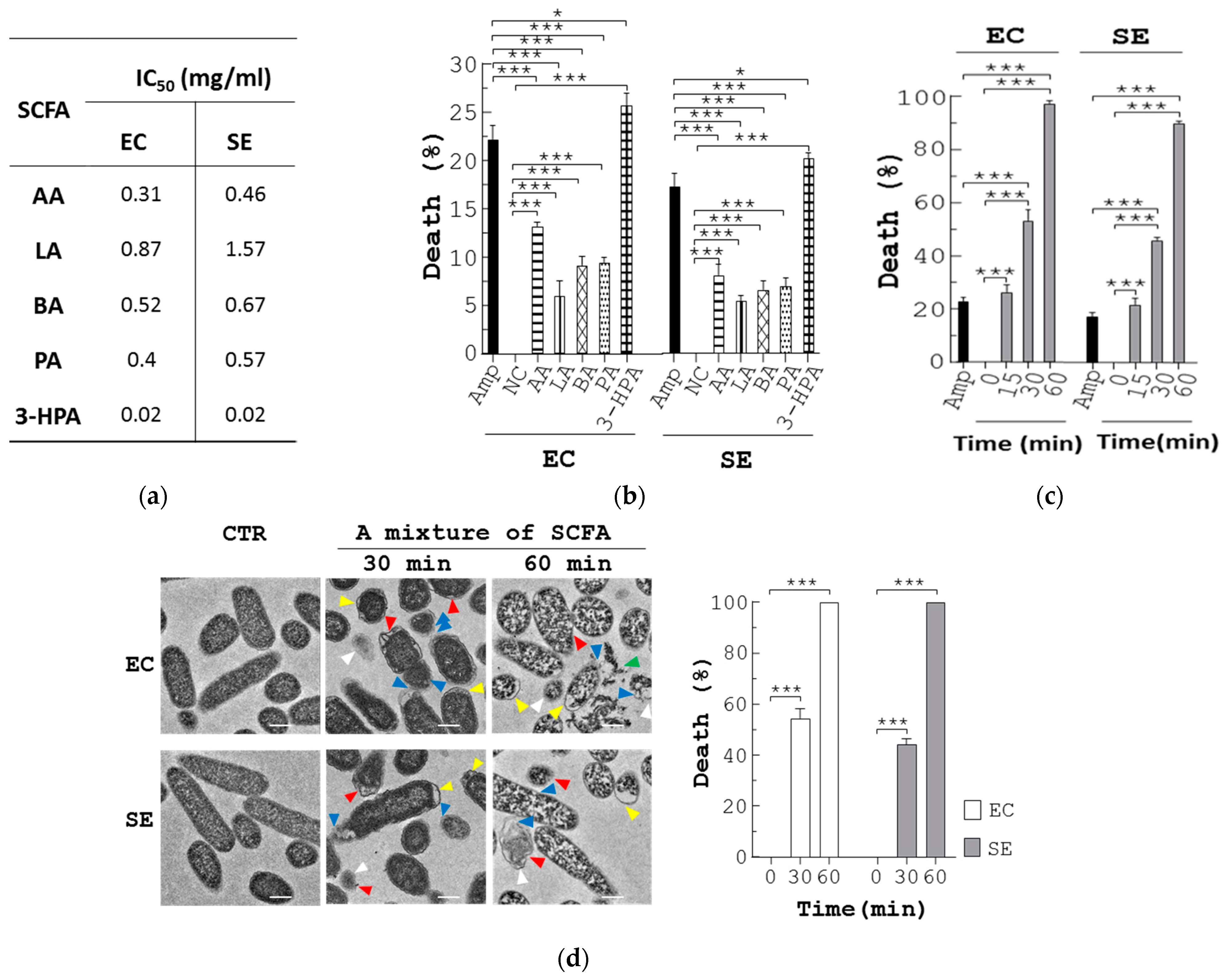
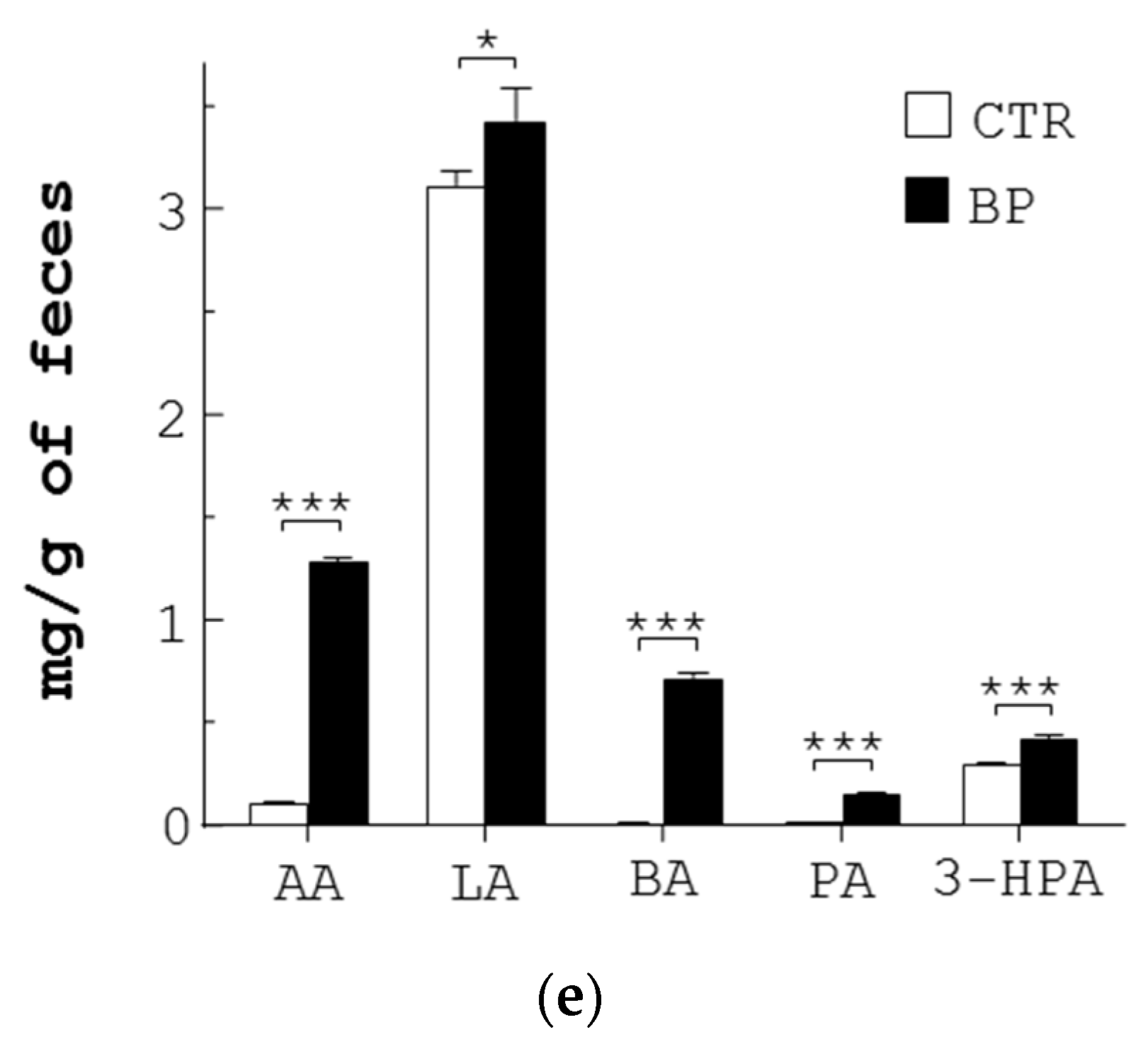
3.4. BP Inhibits Pathogenic Bacteria through Upregulation of SCFA in L. reuteri
3.5. SCFA Suppress Growth of Pathogenic Bacteria via Membrane Destruction
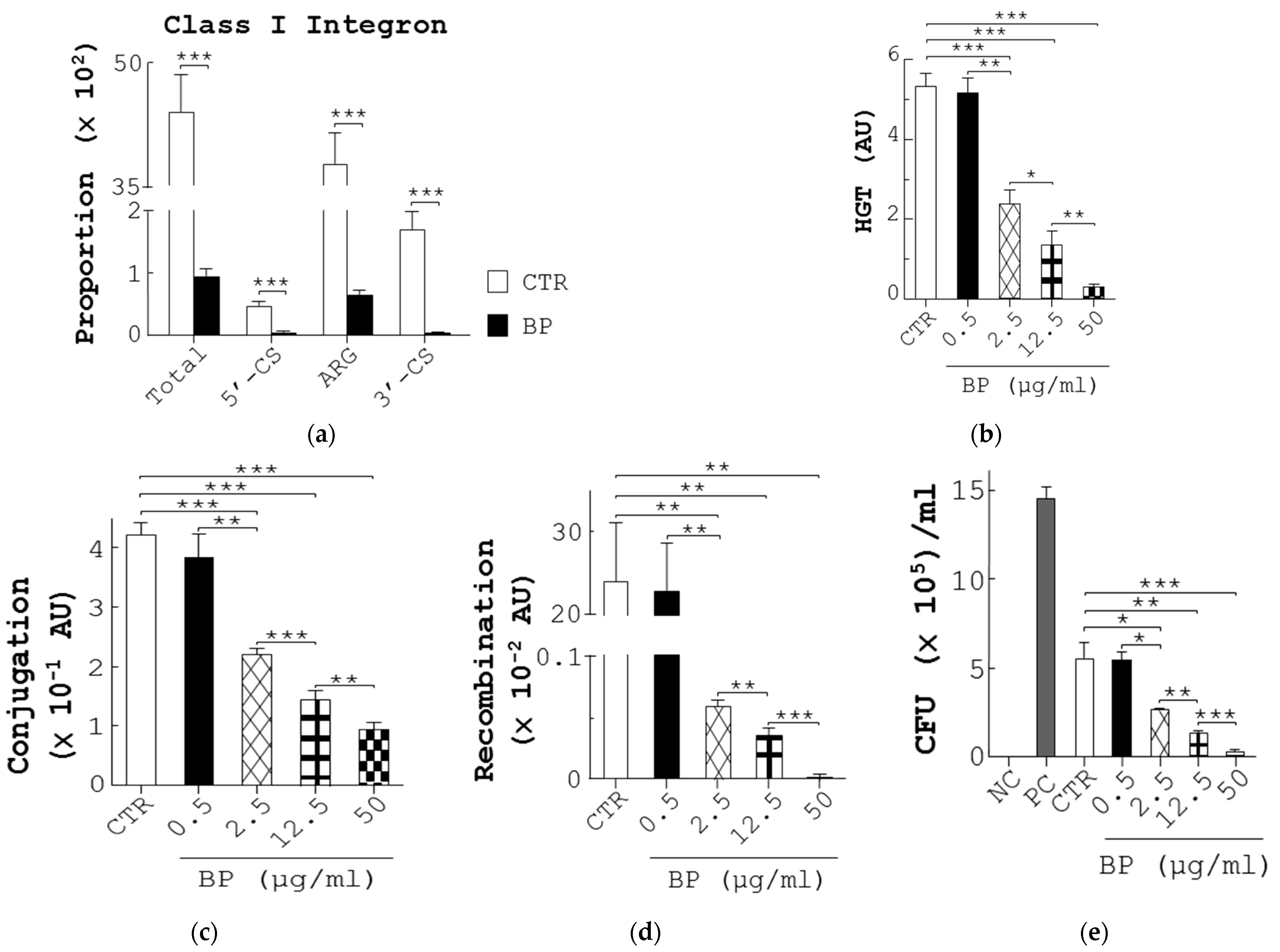
3.6. BP Decreases ARG in Fecal Bacteria and Conjugation and Recombination in E. coli
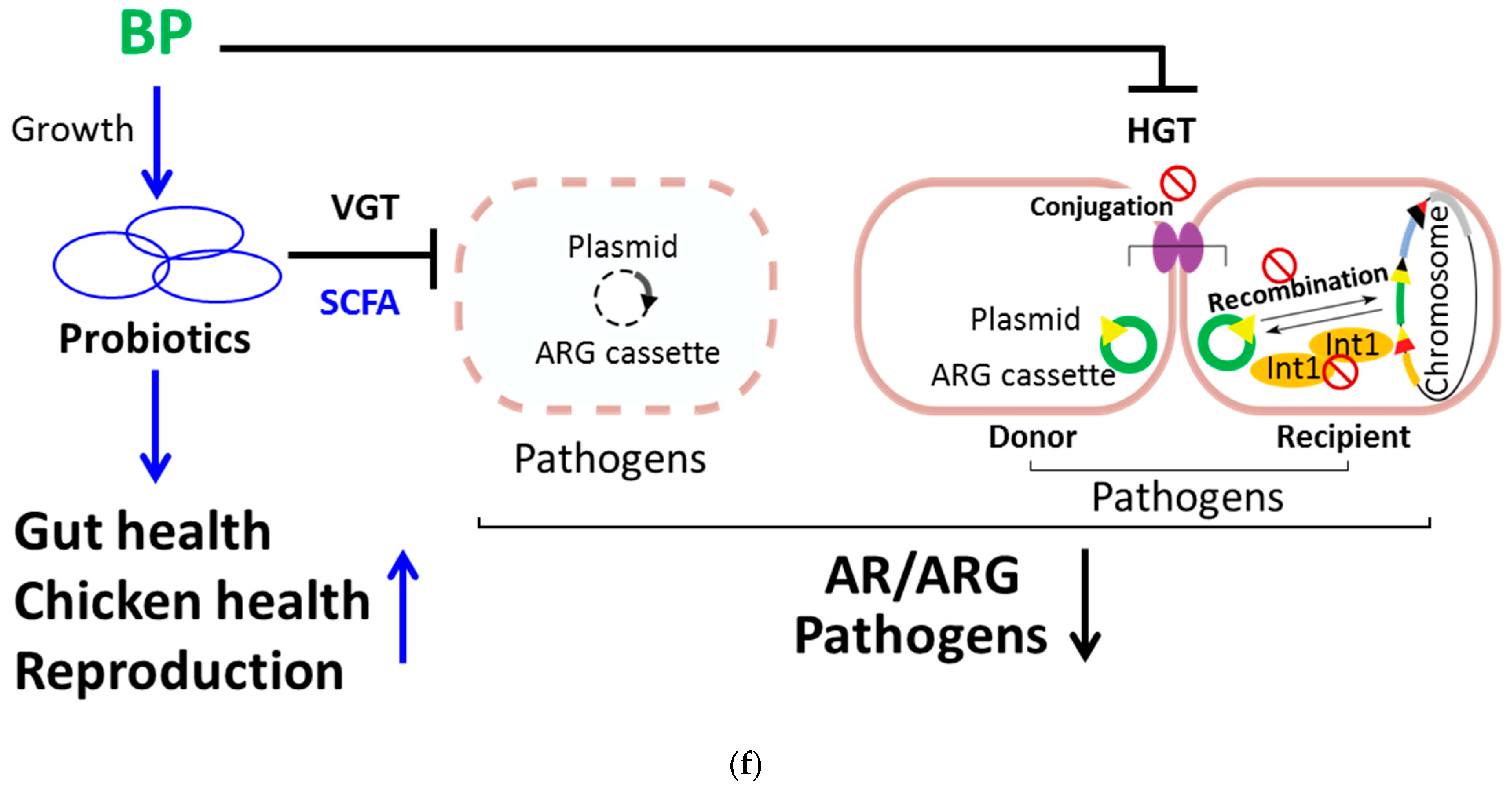
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An insight into gut microbiota and its functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 473–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, I.; Gibson, G.; Heinken, A.; Scott, K.; Swann, J.; Thiele, I.; Tuohy, K. Gut microbiota functions: Metabolism of nutrients and other food components. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syngai, G.G.; Gopi, R.; Bharali, R.; Dey, S.; Lakshmanan, G.A.; Ahmed, G. Probiotics—The versatile functional food ingredients. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yao, X.; Yang, Y.; Cao, G.; Yi, G. In vitro digestibility and fermentability profiles of wheat starch modified by chlorogenic acid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 215, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boesmans, L.; Valles-Colomer, M.; Wang, J.; Eeckhaut, V.; Falony, G.; Ducatelle, R.; Van Immerseel, F.; Raes, J.; Verbeke, K. Butyrate producers as potential next-generation probiotics: Safety assessment of the administration of Butyricicoccus pullicaecorum to healthy volunteers. mSystems 2018, 3, e00094-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, K.; Drouillard, J.; de Aguiar Veloso, V.; Huynh, G.; Trinetta, V.; Gragg, S.E. The use of probiotic Megasphaera elsdenii as a pre-harvest intervention to reduce Salmonella in finishing beef cattle: An in vitro model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Moore, R.; Stanley, D.; Chousalkar, K. The gut microbiota of laying hens and its manipulation with prebiotics and probiotics to enhance gut health and food safety. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00600-00620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, B.; Bian, C.; Han, Y.; Qiao, H. Fermented Astragalus in diet improved laying performance, egg quality, antioxidant and immunological status and intestinal microbiota in laying hens. AMB Express 2020, 10, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Vollenweider, S.; Lacroix, C.; Zurich, E. The potential of reuterin produced by Lactobacillus reuteri as a broad spectrum preservative in food. In Protective Cultures, Antimicrobial Metabolites and Bacteriophages for Food and Beverage Biopreservation; Lacroix, C., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 129–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lamas, A.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C.M. Short chain fatty acids commonly produced by gut microbiota influence Salmonella enterica motility, biofilm formation, and gene expression. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, A.A.; El-Antrawy, M.A.; El-Ganiny, A.M. Impact of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) on antimicrobial activity of new β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combinations and on virulence of Escherichia coli isolates. J. Antibiot. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajati, H. Application of organic acids in poultry nutrition. Int. J. Avian Wildl. Biol. 2018, 3, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athalye-Jape, G.; Patole, S. Probiotics for preterm infants—Time to end all controversies. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ailioaie, L.M.; Litscher, G. Probiotics, photobiomodulation, and disease management: Controversies and challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Nelson, C.D.; Driver, J.D.; Elzo, M.A.; Peñagaricano, F.; Jeong, K.C. Host genetics exerts lifelong effects upon hindgut microbiota and its association with bovine growth and immunity. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2306–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, A.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress, depression, diet, and the gut microbiota: Human-bacteria interactions at the core of psychoneuroimmunology and nutrition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 28, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.; Guarner, F.; Bustos Fernandez, L.; Maruy, A.; Sdepanian, V.L.; Cohen, H. Antibiotics as Major Disruptors of Gut Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 572912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirdham, O. Global Egg Market Size, Major Players and Overview; EIN Presswire: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.einnews.com/pr_news/488638048/global-egg-market-size-major-players-and-overview (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Shahbandeh, M. Global Egg Production from 1990 to 2019 (in 1000 Metric Tons)*; Statista: New York, NY, USA. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/263972/egg-production-worldwide-since-1990/ (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Chang, C.; Chung, C.; Kuo, C.; Kuo, T.; Yang, C.; Yang, W. Beneficial effect of Bidens pilosa on body weight gain, food conversion ratio, gut bacteria and coccidiosis in chickens. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, S.; Sun, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. Age-related variations in intestinal microflora of free-range and caged hens. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curabay, B.; Sevim, B.; Cufadar, Y.; Ayasan, T. Effects of adding Spirulina platensis to laying hen rations on performance, egg quality, and some blood parameters. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2021, 72, 2945–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A. Tackling antimicrobial resistance in the shadow of COVID-19. mBio 2021, 12, e0047321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, S.H.; Li, X.; Rashid, A.; Su, J.; Xu, J.; Brejnrod, A.D.; Su, J.-Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Zhou, S.G.; et al. Co-selection of antibiotic resistance genes, and mobile genetic elements in the presence of heavy metals in poultry farm environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufarelli, V.; Baghban-Kanani, P.; Azimi-Youvalari, S.; Hosseintabar-Ghasemabad, B.; Slozhenkina, M.; Gorlov, I.; Seidavi, A.; Ayaşan, T.; Laudadio, V. Effects of horsetail (Equisetum arvense) and spirulina (Spirulina platensis) dietary supplementation on laying hens productivity and oxidative status. Animals 2021, 11, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, A.; Villaseñor, I.; Yang, W. Bidens pilosa L. (Asteraceae): Botanical properties, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 340215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiavari-Frederico, M.; Barbosa, L.; Carvalho Dos Santos, I.; Ratti da Silva, G.; Fernandes de Castro, A.; de Campos Bortolucci, W.; Barboza, L.; Campos, C.; Gonçalves, J.; Menetrier, J.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of Asteraceae species against bacterial pathogens isolated from postmenopausal women. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzi, F.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; Manfreda, G.; Remondini, D.; De Cesare, A. Comparison between 16S rRNA and shotgun sequencing data for the taxonomic characterization of the gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, G.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H.; Wang, C.; Li, R.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, K.; Hou, C. Occurrence and antibacterial resistance of culturable antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the Fildes Peninsula, Antarctica. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 162, 111829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Daim, A.; Hassouna, N.; Hafez, M.; Ashor, M.; Aboulwafa, M. Antagonistic activity of Lactobacillus isolates against Salmonella typhi in vitro. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 680605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vit, C.; Loot, C.; Escudero, J.; Nivina, A.; Mazel, D. Integron identification in bacterial genomes and cassette recombination assays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2075, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigo, J.-M. Natural conjugative plasmids induce bacterial biofilm development. Nature 2001, 412, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridges, D.F.; Lacombe, A.; Wu, V.C.H. Integrity of the Escherichia coli O157:H7 cell wall and membranes after chlorine dioxide treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lin, K.; Sequeira, C.; Borchers, C.H. An isotope-labeled chemical derivatization method for the quantitation of short-chain fatty acids in human feces by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 854, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torki, M.; Mohebbifar, A.; Mohammadi, H. Effects of supplementing hen diet with Lavandula angustifolia and/or Mentha spicata essential oils on production performance, egg quality and blood variables of laying hens. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jia, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Wu, S.; Qi, G. Supplemental plant extracts from Flos lonicerae in combination with Baikal skullcap attenuate intestinal disruption and modulate gut microbiota in laying hens challenged by Salmonella pullorum. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaligh, F.; Sadeghi, G.; Karimi, A.; Vaziry, A. Evaluation of different medicinal plants blends in diets for broiler chickens. J. Med. Plant Res. 2011, 5, 1971–1977. [Google Scholar]
- Hafeez, A.; Shah, S.A.A.; Khan, R.U.; Ullah, Q.; Naz, S. Effect of diet supplemented with phytogenics and protease enzyme on performance, serum biochemistry and muscle histomorphology in broilers. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2020, 48, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiroleslami, M.; Torki, M. Egg quality characteristics and productive performance of laying hens fed diets supplemented by Echinacea purpurea extract, immunofin and vitamin E. Glob. Vet. 2011, 7, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Saravana Kumar, M.; Brindhalakshmi, B.; Ramasamy, S.; Prashanth, D.S. Modulation of chicken cecal microbiota by a phytogenic feed additive, stodi®: A metagenomic analysis. Pharmacogn. Res. 2019, 11, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeuas, V.V.; Mountzouris, K.C. Modulation of broiler gut microbiota and gene expression of Toll-like receptors and tight junction proteins by diet type and inclusion of phytogenics. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2220–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokapirnasari, W.P.; Pribadi, T.B.; Al Arif, A.; Soeharsono, S.; Hidanah, S.; Harijani, N.; Najwan, R.; Huda, K.; Wardhani, H.C.P.; Rahman, N.F.N.; et al. Potency of probiotics Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus casei to improve growth performance and business analysis in organic laying hens. Vet. World 2019, 12, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobierecka, P.A.; Wyszyńska, A.K.; Aleksandrzak-Piekarczyk, T.; Kuczkowski, M.; Tuzimek, A.; Piotrowska, W.; Górecki, A.; Adamska, I.; Wieliczko, A.; Bardowski, J.; et al. In vitro characteristics of Lactobacillus spp. strains isolated from the chicken digestive tract and their role in the inhibition of Campylobacter colonization. Microbiologyopen 2017, 6, e00512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connerton, P.L.; Timms, A.R.; Connerton, I.F. Using antimicrobial cultures, bacteriocins and bacteriophages to reduce carriage of food-borne bacterial pathogens in poultry. In Protective Cultures, Antimicrobial Metabolites and Bacteriophages for Food and Beverage Biopreservation; Lacroix, C., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 181–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Abbas, M.; Rehman, M.U.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Gong, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, A. Dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) via integrons in Escherichia coli: A risk to human health. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinacci, P.; Mevissen, M.; Ayrle, H.; Maurer, V.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Melzig, M.F.; Walkenhorst, M. Medicinal plants for prophylaxis and therapy of common infectious diseases in poultry–a systematic review of in vivo studies. Planta Med. 2022, 88, 200–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, T.; Khanh, T. Chemistry and pharmacology of Bidens pilosa: An overview. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 46, 91–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, C.; Hall, J.P.; Harrison, E.; Wood, A.; Brockhurst, M.A. Gene mobility promotes the spread of resistance in bacterial populations. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1930–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillings, M.R.; Gaze, W.H.; Pruden, A.; Smalla, K.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhu, Y.-G. Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabezón, E.; de la Cruz, F.; Arechaga, I. Conjugation inhibitors and their potential use to prevent dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokai-Kun, J.F.; Roberts, T.; Coughlin, O.; Sicard, E.; Rufiange, M.; Fedorak, R.; Carter, C.; Adams, M.H.; Longstreth, J.; Whalen, H.; et al. The oral β-lactamase syn-004 (ribaxamase) degrades ceftriaxone excreted into the intestine in phase 2a clinical studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02197-02116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gunzburg, J.; Ducher, A.; Modess, C.; Wegner, D.; Oswald, S.; Dressman, J.; Augustin, V.; Feger, C.; Andremont, A.; Weitschies, W.; et al. Targeted adsorption of molecules in the colon with the novel adsorbent-based medicinal product, DAV132: A proof of concept study in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 55, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran Nguyen Minh, H.; Kuo, T.-F.; Lin, W.-Y.; Peng, T.-C.; Yang, G.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chang, T.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Ho, C.-H.; Ou, B.-R.; et al. A Novel Phytogenic Formulation, EUBIO-BPSG, as a Promising One Health Approach to Replace Antibiotics and Promote Reproduction Performance in Laying Hens. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030346
Tran Nguyen Minh H, Kuo T-F, Lin W-Y, Peng T-C, Yang G, Lin C-Y, Chang T-H, Yang Y-L, Ho C-H, Ou B-R, et al. A Novel Phytogenic Formulation, EUBIO-BPSG, as a Promising One Health Approach to Replace Antibiotics and Promote Reproduction Performance in Laying Hens. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(3):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030346
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran Nguyen Minh, Hieu, Tien-Fen Kuo, Wen-Yu Lin, Tzu-Chia Peng, Greta Yang, Chih-Yu Lin, Ting-Hsiang Chang, Yu-Liang Yang, Cheng-Hsun Ho, Bor-Rung Ou, and et al. 2023. "A Novel Phytogenic Formulation, EUBIO-BPSG, as a Promising One Health Approach to Replace Antibiotics and Promote Reproduction Performance in Laying Hens" Bioengineering 10, no. 3: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030346
APA StyleTran Nguyen Minh, H., Kuo, T.-F., Lin, W.-Y., Peng, T.-C., Yang, G., Lin, C.-Y., Chang, T.-H., Yang, Y.-L., Ho, C.-H., Ou, B.-R., Yang, C.-W., Liang, Y.-C., & Yang, W.-C. (2023). A Novel Phytogenic Formulation, EUBIO-BPSG, as a Promising One Health Approach to Replace Antibiotics and Promote Reproduction Performance in Laying Hens. Bioengineering, 10(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10030346








