Rapid Morphological Measurement Method of Aortic Dissection Stent Based on Spatial Observation Point Set
Abstract
1. Introduction
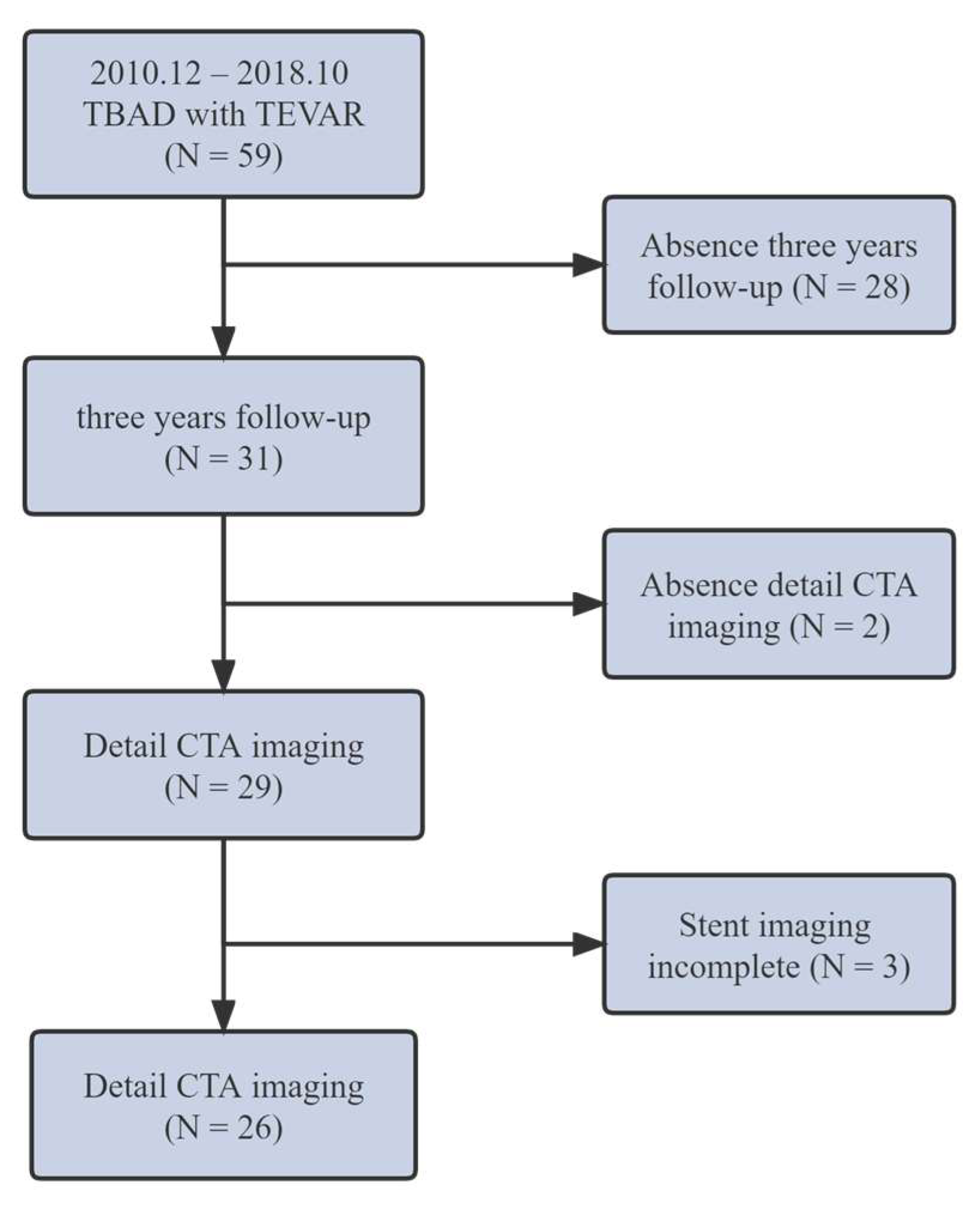
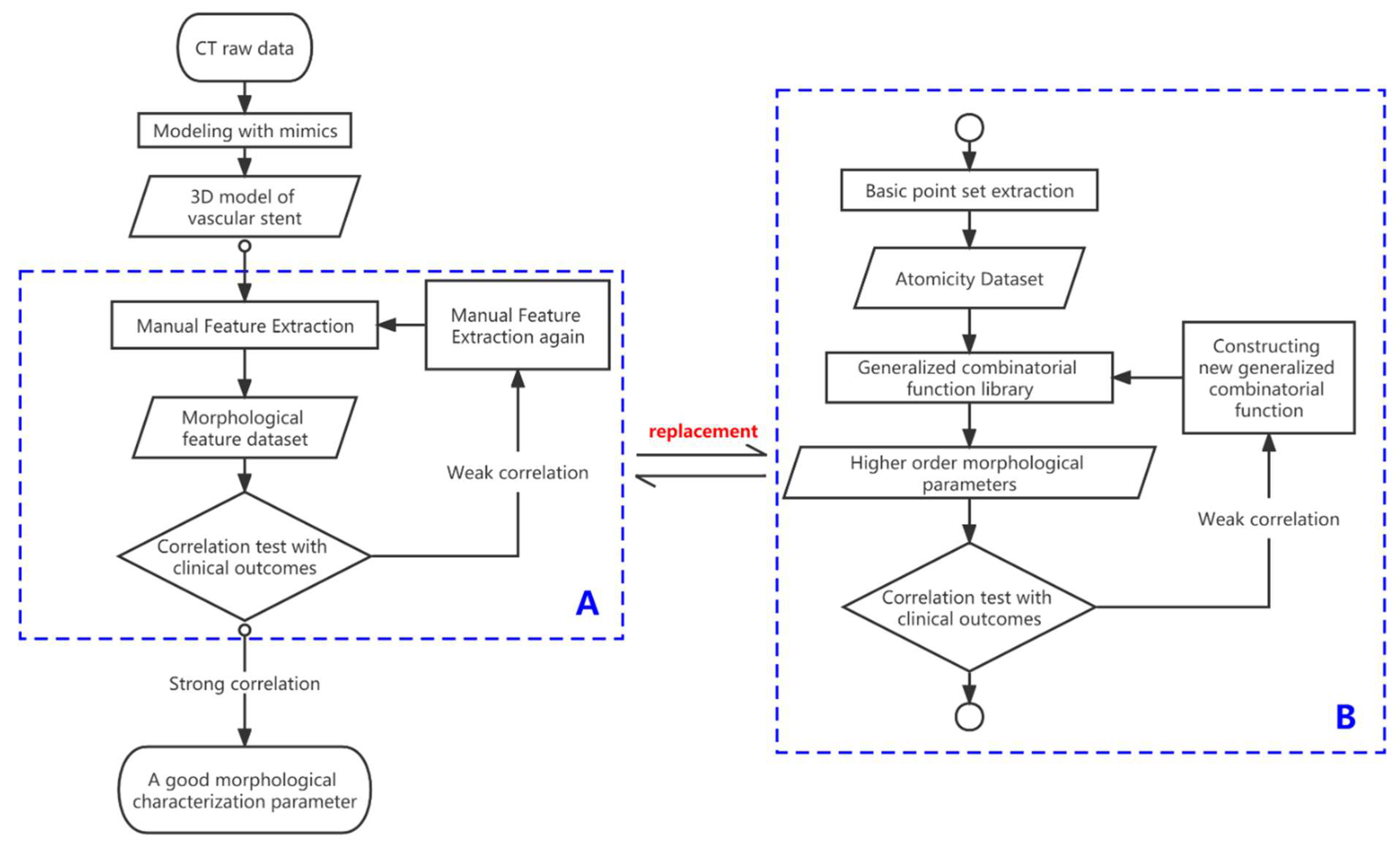
2. Methods
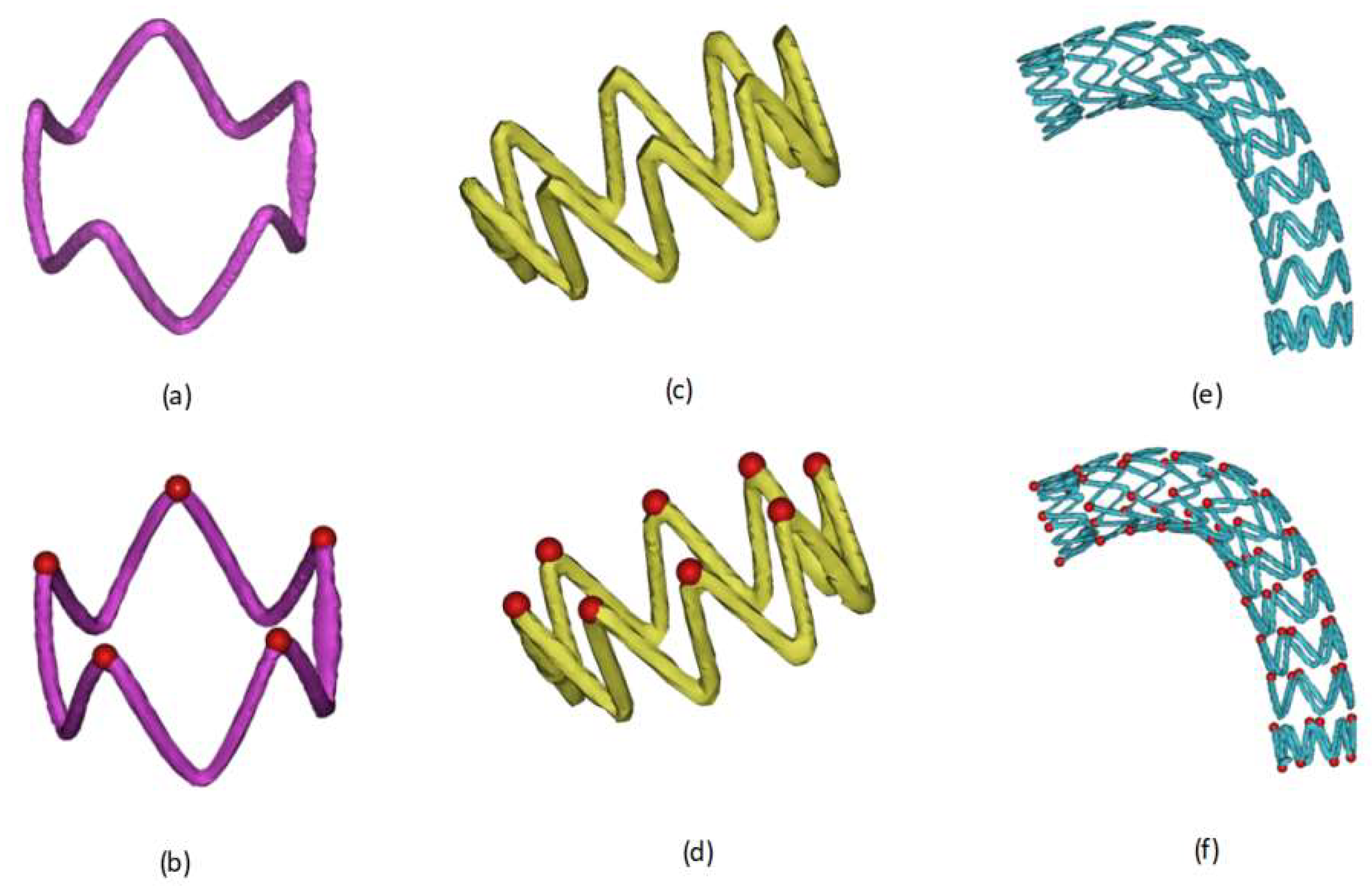
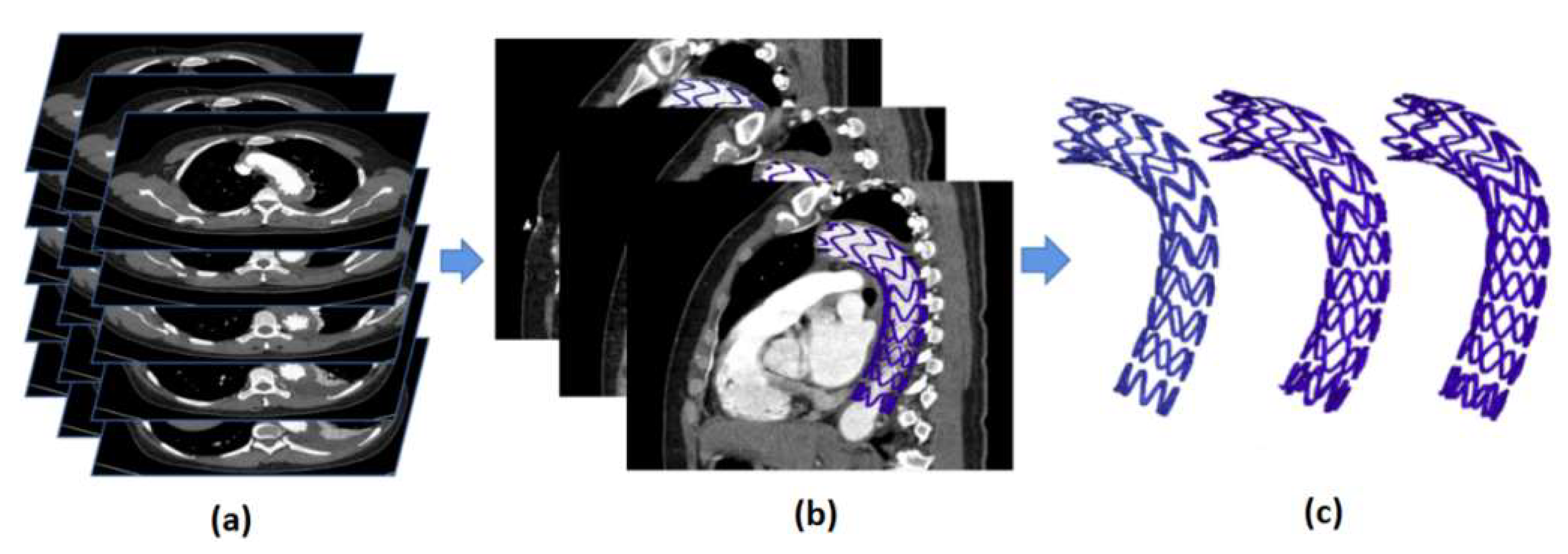
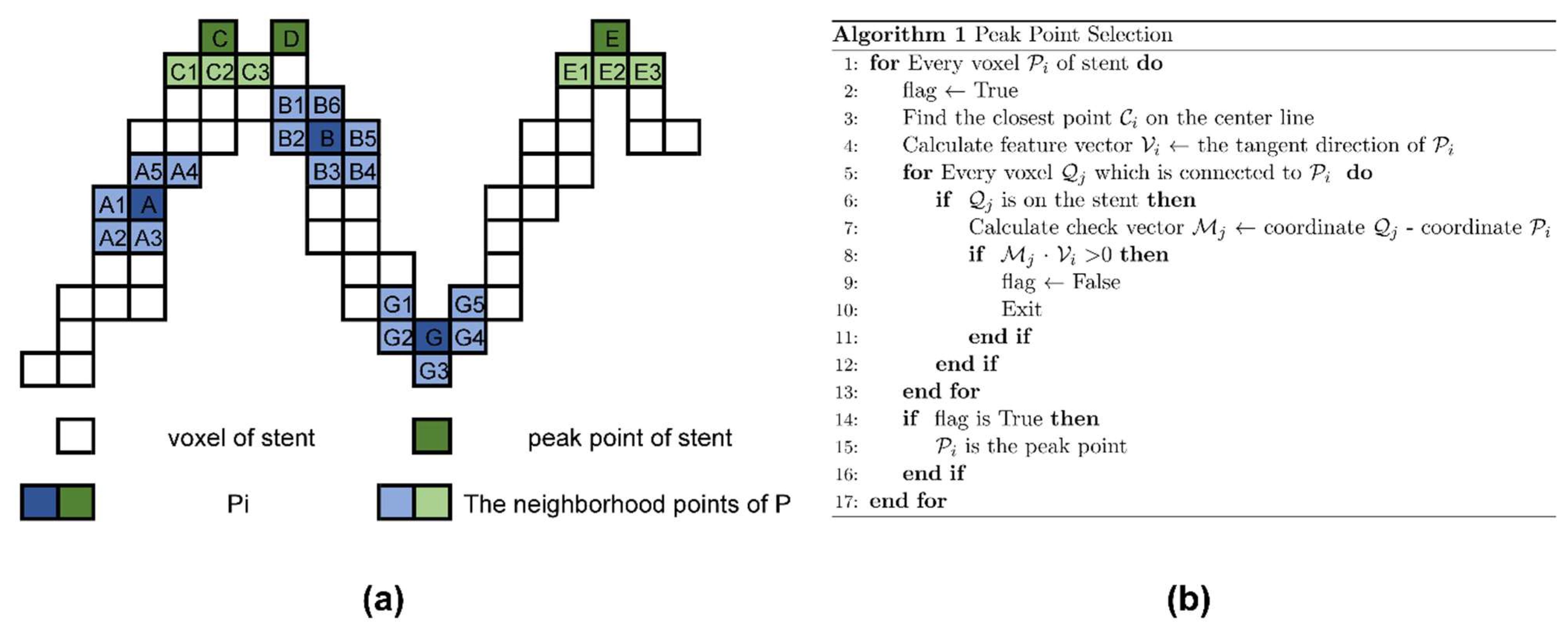
2.1. Definition and Extraction of Basic Observation Points of Vascular Stents
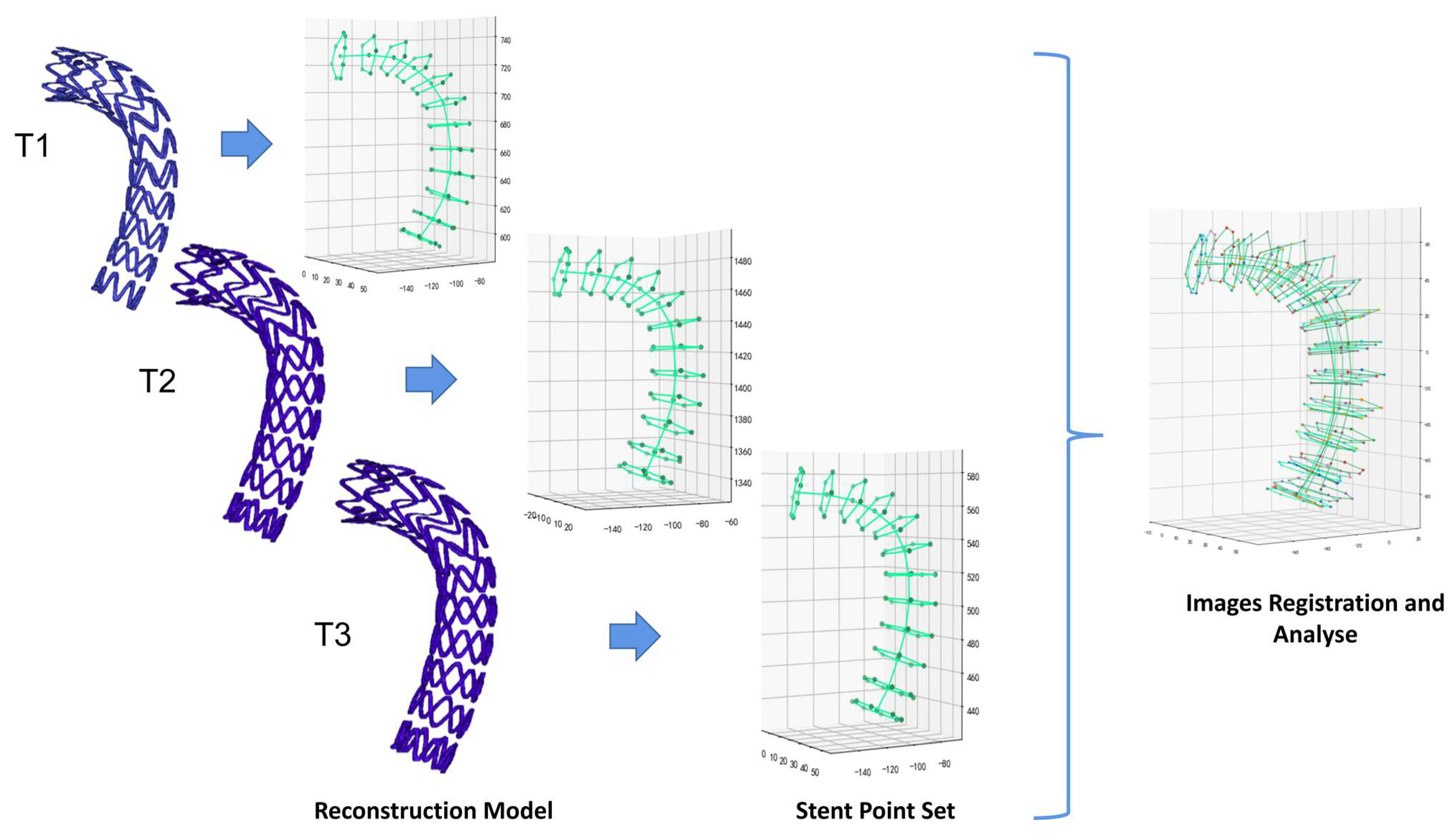
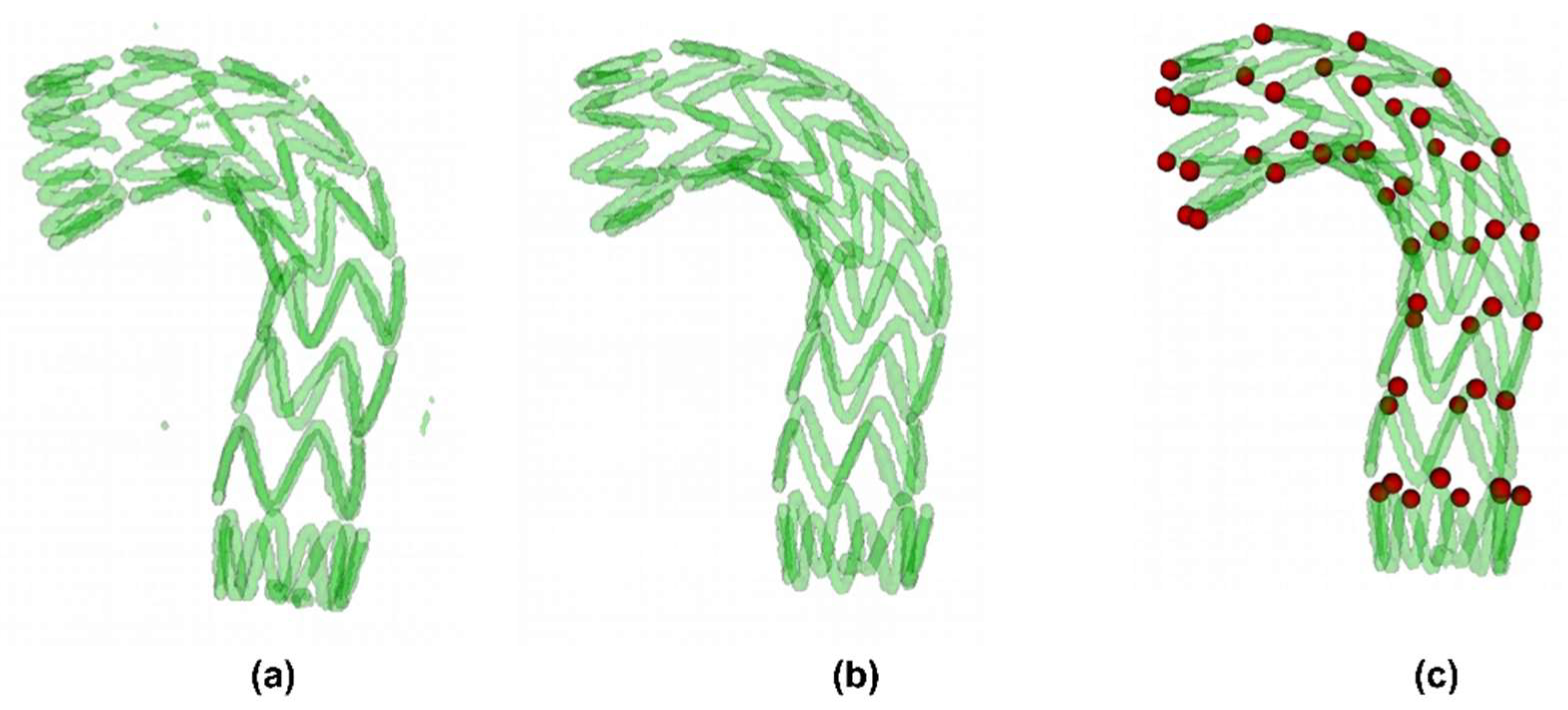
2.2. Automatic Stent Segmentation and Observation Point Extraction Method
2.3. Representative Morphological Parameters of Stent
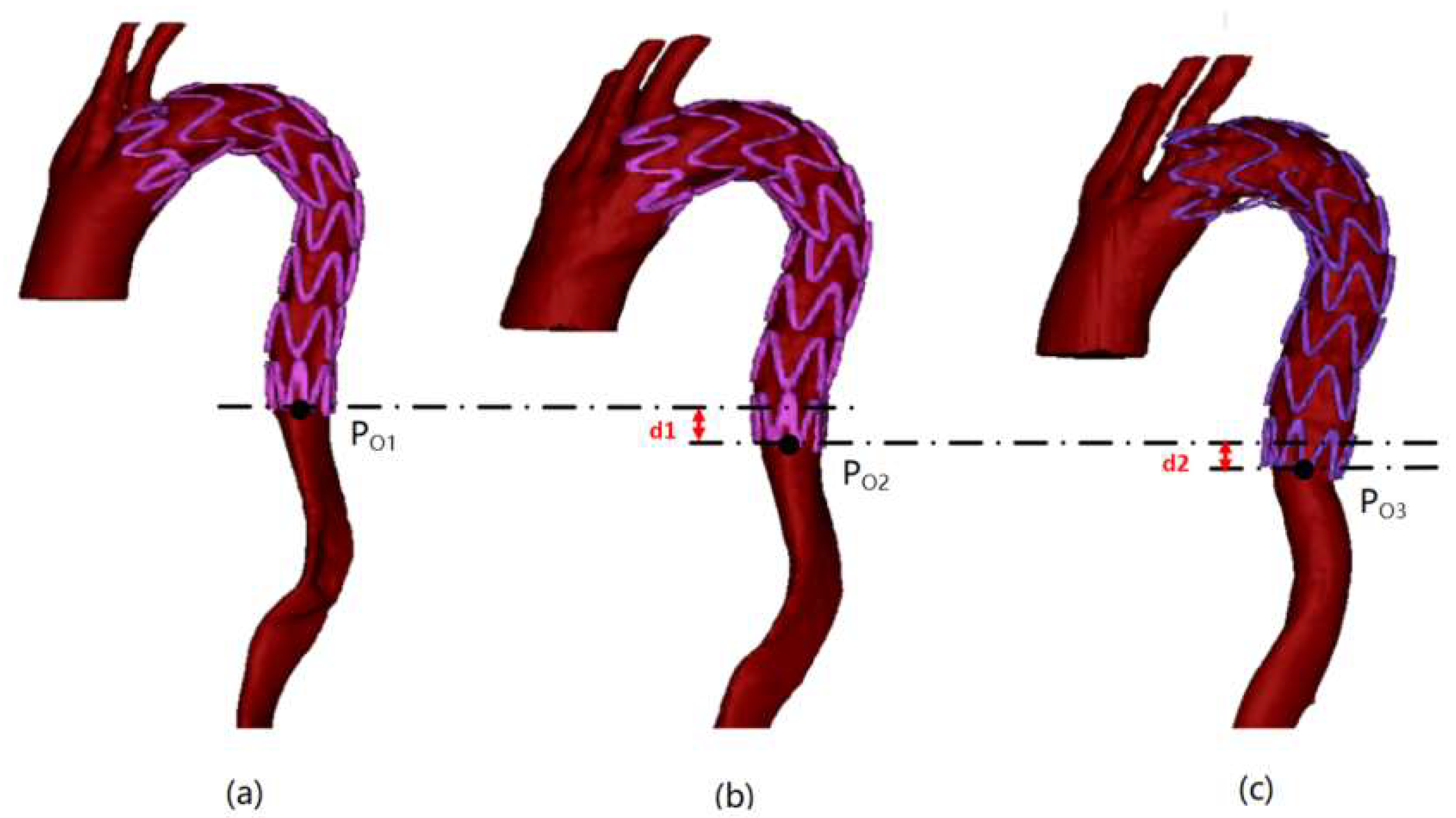
2.3.1. Stent End-Slip Vector
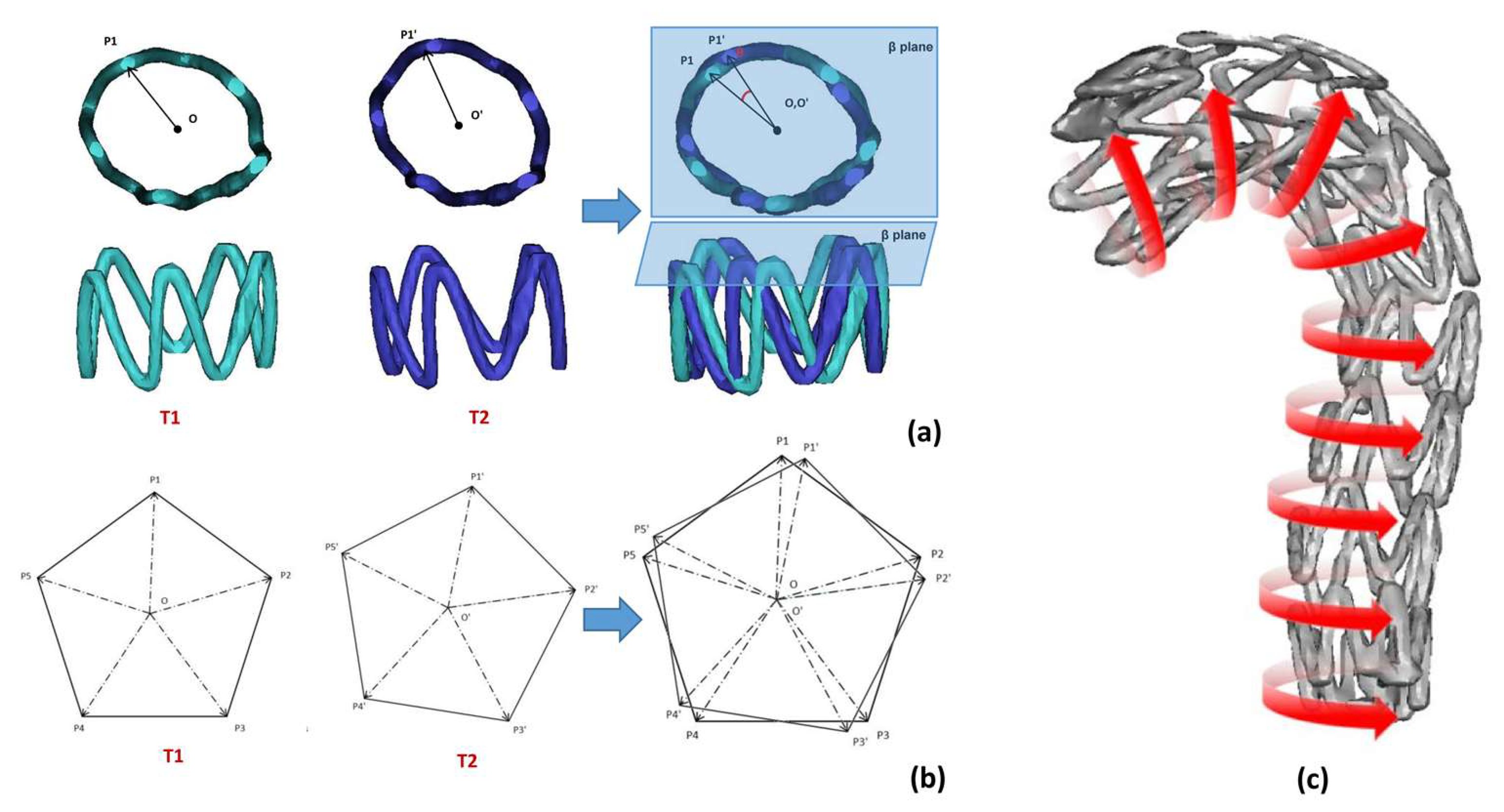
2.3.2. Radial Characteristic Diameter Change of Support Ring
2.3.3. Stent Ring Deflection Angle
3. Results
3.1. Automatic Stent Segmentation and Observation Point Extraction
3.2. Vascular Stent End-Slip Volume
3.3. Radial Characteristic Diameter Change of Support Ring
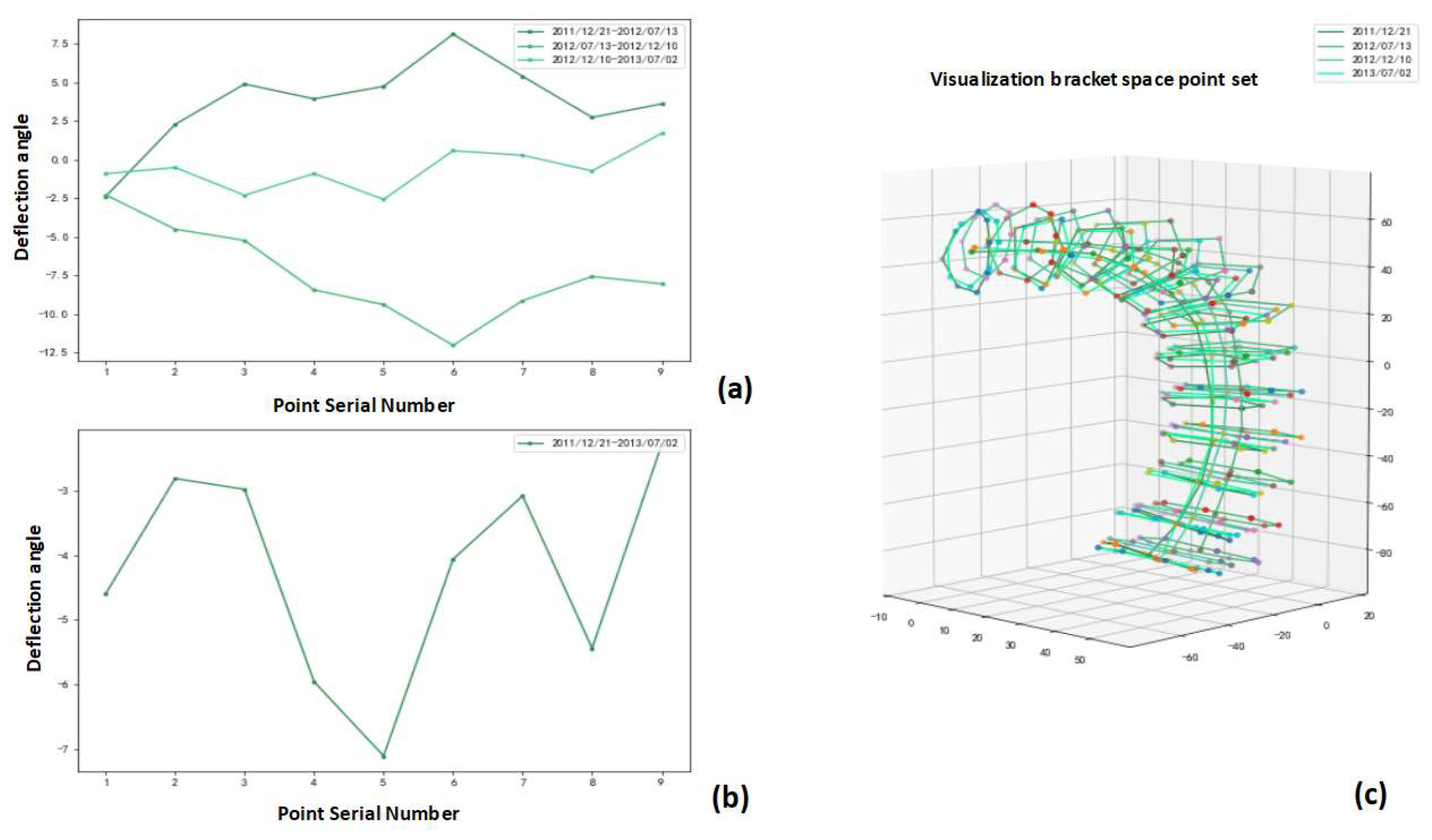
3.4. Stent Ring Deflection Angle
4. Discussion
- (1)
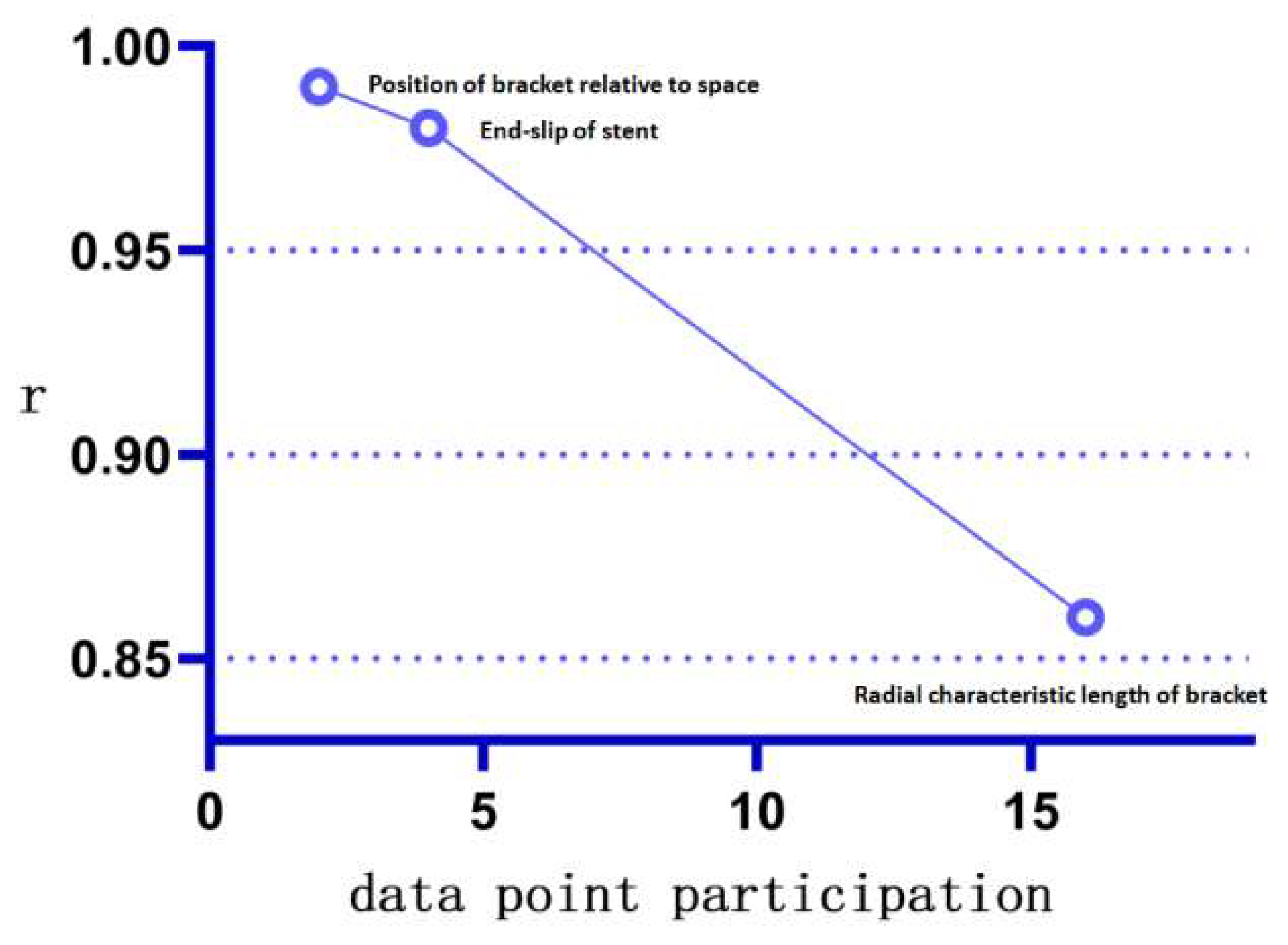
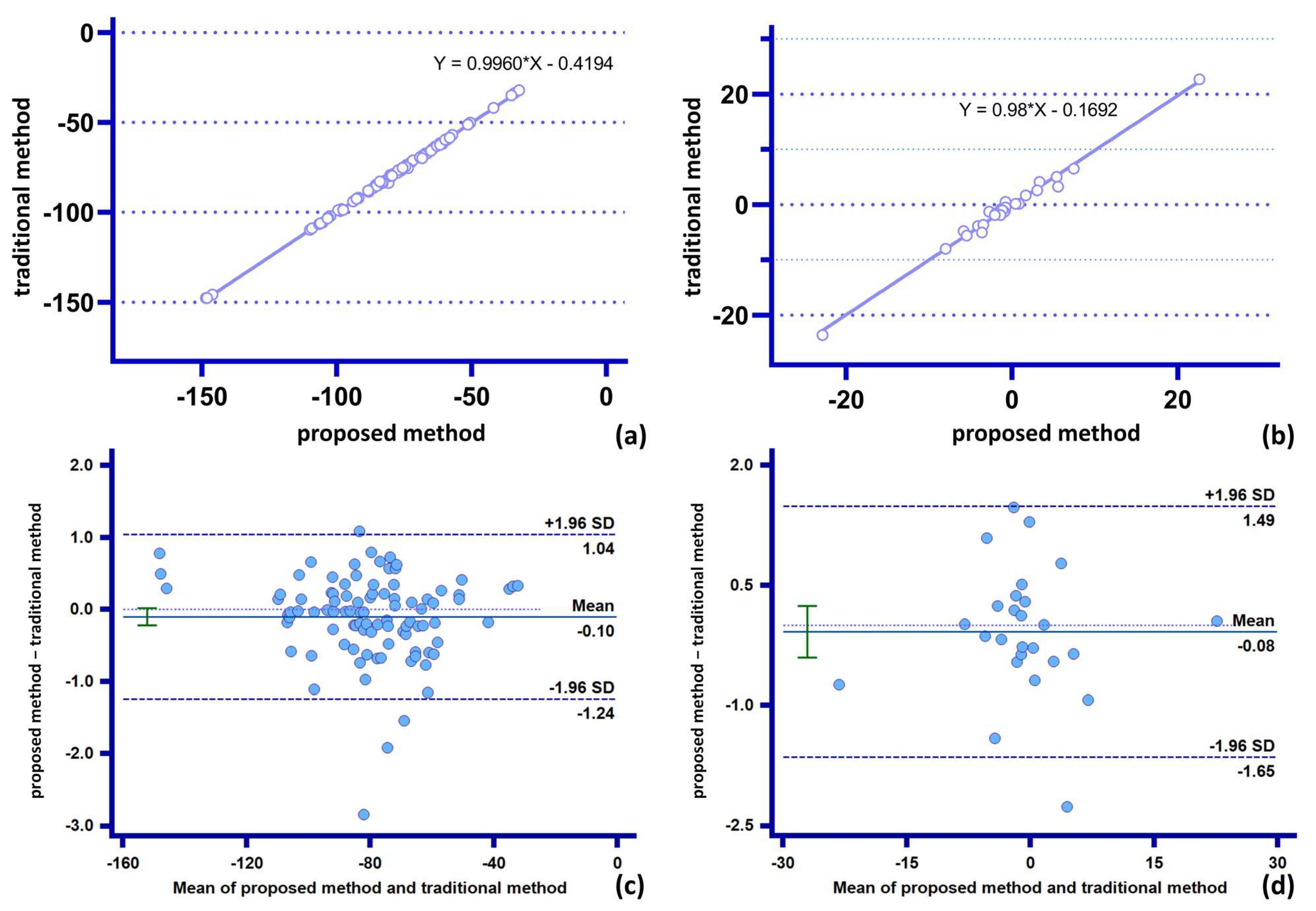
- The proposed method can accomplish accurate statistics for low-complexity parameters within a shorter time. The stent slip space vector obtained by the proposed method (with the lowest number of participation points n = 2 and the lowest measurement complexity) is in excellent agreement with the traditional method. This verifies the accuracy and stability of the “combined” measurement method on parameters with low combined complexity. Further, the proposed method eliminates the need to repeat the statistics for basic parameters (spatial basis points), thus significantly reducing the statistical time needed for the parameters;
- (2)
- The proposed method can effectively correct “manual measurement errors” in parameters of medium complexity. For example, the radial characteristic diameter of the stent involves a comparative analysis of the length of multiple points on the stent ring. The increase in the amount of data involved in the operation (the number of participating points n = 16, which has medium measurement complexity) causes an increase in data complexity and the gradual appearance of accumulation of manual measurement errors at each observation point, which causes the differences between the traditional measurement and the proposed method (Appendix A Figure A4). Furthermore, the proposed method not only avoids the risk of statistical errors by using the basic data points for the “combination operation,” but can also be programmed to incorporate more “combination functions” into the operating system, thus exhibiting higher data accuracy and measurement speed. This minimizes the cost of human statistical analysis;
- (3)
- The proposed method allows fast and accurate measurement of morphological parameters of high complexity, for which it is difficult to make statistics by traditional methods. For example, we define the stent circumferential deflection angle (with high combinatorial complexity and n = 26 points involved in the combination). Therefore, the complexity of the calculation method of the stent torsional deflection angle composition by far exceeds the reasonable measurement statistics acceptable by the traditional method, and the statistical analysis of the composition of this quantity one by one is extremely time-consuming. The proposed method, however, does not need to expand the base data set owing to its “combinatorial” nature, and only expands the set of generalized combinatorial functions to rapidly perform combinatorial analysis and visualization of the quantity using the computer. This demonstrates the good scalability and speed advantages of the proposed method for the calculation of parameters with high combinatorial complexity.
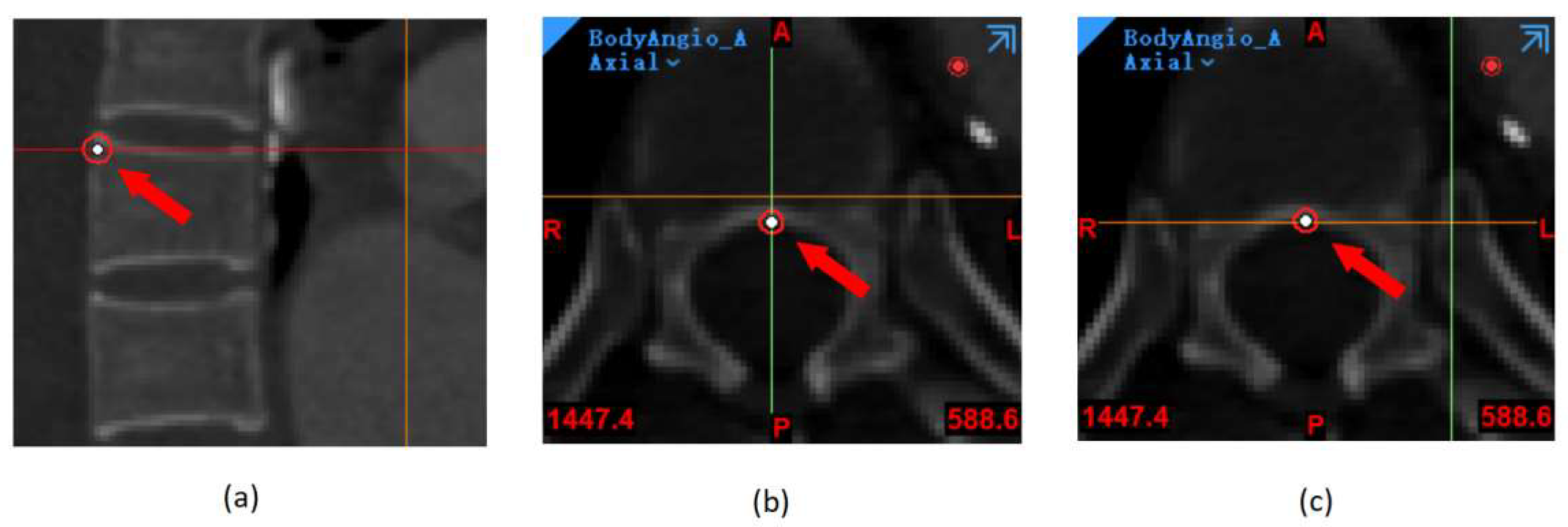
4.1. Improved Image Registration at Different Follow-Up Periods
4.2. Method Efficiency Is Influenced by Sample Size
4.3. Integrity of the Original Information
4.4. Clinical Outcome and Prognostic
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Statistical Information | Data |
|---|---|
| Total number | 26 |
| Male | 24 |
| Female | 2 |
| Age 40–50 | 4 |
| Age 50–60 | 14 |
| Age 60–70 | 3 |
| Age 70–80 | 5 |
References
- Nakatamari, H.; Ueda, T.; Ishioka, F.; Raman, B.; Kurihara, K.; Rubin, G.D.; Ito, H.; Sze, D.Y. Discriminant analysis of native thoracic aortic curvature: Risk prediction for endoleak formation after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 974–979.e972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerny, M.; Schmidli, J.; Adler, S.; van den Berg, J.C.; Bertoglio, L.; Carrel, T.; Chiesa, R.; Clough, R.E.; Eberle, B.; Etz, C.; et al. Editor’s Choice—Current Options and Recommendations for the Treatment of Thoracic Aortic Pathologies Involving the Aortic Arch: An Expert Consensus Document of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) & the European Society for Vascular Surgery (ESVS). Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2019, 57, 165–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, M.F.; Crawford, R.S.; Kwolek, C.J.; Brewster, D.C.; Brady, T.J.; Cambria, R.P. Aortic remodeling after endovascular repair of acute complicated type B aortic dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 50, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.A.; Olsen, D.M.; Lucas, L.; Wheatley, G.; Ramaiah, V.; Diethrich, E.B. Aortic remodeling after endografting of thoracoabdominal aortic dissection. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 47, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Hirano, T.; Shimono, T.; Ishida, M.; Takano, K.; Nishide, Y.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yada, I.; Takeda, K. Treatment of Chronic Aortic Dissection by Transluminal Endovascular Stent-Graft Placement: Preliminary Results. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.S.; Dake, M.D.; Semba, C.P.; Fogarty, T.J.; Zarins, C.K.; Liddell, R.P.; Miller, D.C. Endovascular stent–graft repair of thoracic aortic aneurysms. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 1996, 111, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dake, M.D.; Miller, D.C.; Semba, C.P.; Mitchell, R.S.; Walker, P.J.; Liddell, R.P. Transluminal placement of endovascular stent-grafts for the treatment of descending thoracic aortic aneurysms. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janosi, R.A.; Tsagakis, K.; Bettin, M.; Kahlert, P.; Horacek, M.; Al-Rashid, F.; Schlosser, T.; Jakob, H.; Eggebrecht, H.; Erbel, R. Thoracic aortic aneurysm expansion due to late distal stent graft-induced new entry. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 85, E43–E53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabenwoger, M.; Alfonso, F.; Bachet, J.; Bonser, R.; Czerny, M.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Fattori, R.; Jakob, H.; Lonn, L.; et al. Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR) for the treatment of aortic diseases: A position statement from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), in collaboration with the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, T.; Webster, M.W.I.; Ormiston, J.A.; Ruygrok, P.N.; Stewart, J.T. Long and short of optimal stent design. Open Heart 2017, 4, e000680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.; Xiao, N.; Gong, X.Y.; Zarins, C.K.; Figueroa, C.A. A computational framework for investigating the positional stability of aortic endografts. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2013, 12, 869–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.W.; Ho, P.; Leo, H.L. Effects of Microporous Stent Graft on the Descending Aortic Aneurysm: A Patient-Specific Computational Fluid Dynamics Study. Artif. Organs 2016, 40, E230–E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.W.; Elkins, C.; Sakai, T.; Kato, N.; Vestring, T.; Semba, C.P.; Slonim, S.M.; Dake, M.D. True-lumen collapse in aortic dissection: Part II. Evaluation of treatment methods in phantoms with pulsatile flow. Radiology 2000, 214, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Kan, X.; Xu, X.Y.; Nienaber, C.A. Finite element modeling to predict procedural success of thoracic endovascular aortic repair in type A aortic dissection. JTCVS Tech. 2020, 4, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhu, T.; Fan, J.; Luo, K. Biomechanical implications of the fenestration structure after thoracic endovascular aortic repair. J. Biomech. 2020, 99, 109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, S.; Scardulla, F.; Rinaudo, A.; Raffa, G.M.; D’Ancona, G.; Pilato, M.; Scardulla, C. An In Vitro Phantom Study on the Role of the Bird-Beak Configuration in Endograft Infolding in the Aortic Arch. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2016, 23, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, F.; Biffi, B.; Milano, E.G.; Bruse, J.; Caputo, M.; Rajakaruna, C.; Schievano, S.; Emanueli, C.; Bucciarelli-Ducci, C.; Biglino, G. Aortic morphological variability in patients with bicuspid aortic valve and aortic coarctation. Eur. J.Cardiothorac. Surg. 2019, 55, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xu, H.; Xiong, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, G.; Shu, H.; Chen, D. 3D Morphologic Findings Before and After Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair for Type B Aortic Dissection. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, T. Predictor of false lumen thrombosis after thoracic endovascular aortic repair for type B dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 160, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, T. Effect of Geometric Accuracy at the Proximal Landing Zone on Simulation Results for Thoracic Endovascular Repair Patients. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rychla, M.; Dueppers, P.; Meuli, L.; Rancic, Z.; Menges, A.L.; Kopp, R.; Zimmermann, A.; Reutersberg, B. Influence of measurement and sizing techniques in thoracic endovascular aortic repair on outcome in acute complicated type B aortic dissections. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2022, 34, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Li, M.; He, H.; Wang, T.; Li, J.; Shu, C. Morphological Features of Aortic Arch Predicting the Risk for Acute Type B Aortic Dissection. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 3458–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zheng, T.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yuan, D.; Fan, Y. Influence of Distal Re-entry Tears on False Lumen Thrombosis After Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair in Type B Aortic Dissection Patients: A Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulation. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 2021, 12, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebersberger, U.; Tricarico, F.; Schoepf, U.J.; Blanke, P.; Spears, J.R.; Rowe, G.W.; Halligan, W.T.; Henzler, T.; Bamberg, F.; Leber, A.W.; et al. CT evaluation of coronary artery stents with iterative image reconstruction: Improvements in image quality and potential for radiation dose reduction. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maintz, D.; Juergens, K.U.; Wichter, T.; Grude, M.; Heindel, W.; Fischbach, R. Imaging of coronary artery stents using multislice computed tomography: In vitro evaluation. Eur. Radiol. 2003, 13, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, S.; Cao, S. Research on Python Data Visualization Technology. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1757, 012122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-Net: Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.04797. [Google Scholar]
- de Vos, B.D.; Berendsen, F.F.; Viergever, M.A.; Sokooti, H.; Staring, M.; Isgum, I. A deep learning framework for unsupervised affine and deformable image registration. Med. Image Anal. 2019, 52, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, M.; Liu, X.; Jomier, J.; Marion, C.; Ibanez, L. ITK: Enabling reproducible research and open science. Front. Neuroinform. 2014, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, T.S.; Ackerman, M.J.; Lorensen, W.E.; Schroeder, W.; Chalana, V.; Aylward, S.; Metaxas, D.; Whitaker, R. Engineering and algorithm design for an image processing API: A technical report on ITK—The insight toolkit. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual Medicine Meets Virtual Reality Conference, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 23 January 2002; pp. 586–592. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, H.; Fujimoto, E.; Arase, H.; Kurobe, H.; Chikugo, F.; Sogabe, H.; Kitaichi, T.; Kitagawa, T. Efficacy and Optimal Timing of Endovascular Treatment for Type B Aortic Dissection. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2015, 8, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Sadahiro, M. Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair for Acute Aortic Dissection. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2018, 11, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, H. Treatment of uncomplicated type B aortic dissection. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedi, V.S.; Swain, P.; Yadav, A. Medical therapy versus TEVAR for uncomplicated type B aortic dissection. Indian J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 35, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nienaber, C.A.; Rousseau, H.; Eggebrecht, H.; Kische, S.; Fattori, R.; Rehders, T.C.; Kundt, G.; Scheinert, D.; Czerny, M.; Kleinfeldt, T.; et al. Randomized comparison of strategies for type B aortic dissection: The INvestigation of STEnt Grafts in Aortic Dissection (INSTEAD) trial. Circulation 2009, 120, 2519–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, D.; Martin, J.; Shennib, H.; Dunning, J.; Muneretto, C.; Schueler, S.; Von Segesser, L.; Sergeant, P.; Turina, M. Endovascular aortic repair versus open surgical repair for descending thoracic aortic disease a systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienaber, C.A.; Fattori, R.; Lund, G.; Dieckmann, C.; Wolf, W.; von Kodolitsch, Y.; Nicolas, V.; Pierangeli, A. Nonsurgical reconstruction of thoracic aortic dissection by stent-graft placement. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nienaber, C.A.; Kische, S.; Rousseau, H.; Eggebrecht, H.; Rehders, T.C.; Kundt, G.; Glass, A.; Scheinert, D.; Czerny, M.; Kleinfeldt, T.; et al. Endovascular repair of type B aortic dissection: Long-term results of the randomized investigation of stent grafts in aortic dissection trial. Circ. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 6, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fejzic, Z.; van Oort, A. Fatal dissection of the descending aorta after implantation of a stent in a 19-year-old female with Turner’s syndrome. Cardiol. Young 2005, 15, 529–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teraa, M.; Hazenberg, C.E.; Houben, I.B.; Trimarchi, S.; van Herwaarden, J.A. Important issues regarding planning and sizing for emergent TEVAR. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 61, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, F.H.; Verhagen, H.J.; Mojibian, H.; Davis, K.A.; Moll, F.L.; Muhs, B.E. Aortic endograft sizing in trauma patients with hemodynamic instability. J. Vasc. Surg. 2010, 52, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasta, S.; Gentile, G.; Raffa, G.M.; Scardulla, F.; Bellavia, D.; Luca, A.; Pilato, M.; Scardulla, C. Three-dimensional parametric modeling of bicuspid aortopathy and comparison with computational flow predictions. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, E92–E102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhs, B.E.; Vincken, K.L.; van Prehn, J.; Stone, M.K.; Bartels, L.W.; Prokop, M.; Moll, F.L.; Verhagen, H.J. Dynamic cine-CT angiography for the evaluation of the thoracic aorta; insight in dynamic changes with implications for thoracic endograft treatment. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2006, 32, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Q.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xu, B. Impact of Oversizing on the Risk of Retrograde Dissection After TEVAR for Acute and Chronic Type B Dissection. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2016, 23, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cruz, R., T.; Syn, N.; Wee, I.; Choong, A.; Singapore Vascular Surgical, C. Risk factors for distal stent graft-induced new entry in type B aortic dissections: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 70, 1682–1693.e1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guangqi, C.; Xiaoxi, L.; Wei, C.; Songqi, L.; Chen, Y.; Zilun, L.; Shenming, W. Endovascular repair of Stanford type B aortic dissection: Early and mid-term outcomes of 121 cases. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2009, 38, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylski, B.; Munoz, C.; Beyersdorf, F.; Siepe, M.; Reser, D.; Carrel, T.; Schoenhoff, F.; Schlensak, C.; Lescan, M.; Eckstein, H.H.; et al. How does descending aorta geometry change when it dissects? Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2018, 53, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, R.; Aboyans, V.; Boileau, C.; Bossone, E.; Bartolomeo, R.D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Falk, V.; Frank, H.; Gaemperli, O.; et al. 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2873–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Tuzcu, E.M.; Kapadia, S.R.; Svensson, L.G.; Greenberg, R.K.; Roselli, E.E.; Halliburton, S.; Kurra, V.; Schoenhagen, P.; Sola, S. Aortic root morphology in patients undergoing percutaneous aortic valve replacement: Evidence of aortic root remodeling. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2009, 137, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, R.R.; Ivens, E.; Pasupati, S.; Humphries, K.; Thompson, C.R.; Munt, B.; Sinhal, A.; Webb, J.G. Role of echocardiography in percutaneous aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2008, 1, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurvitch, R.; Webb, J.G.; Yuan, R.; Johnson, M.; Hague, C.; Willson, A.B.; Toggweiler, S.; Wood, D.A.; Ye, J.; Moss, R.; et al. Aortic annulus diameter determination by multidetector computed tomography: Reproducibility, applicability, and implications for transcatheter aortic valve implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2011, 4, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, A.H.; Hinchliffe, R.J.; Yates, M.; Holt, P.J.; Loftus, I.M.; Thompson, M.M. Morphology of aortic arch pathology: Implications for endovascular repair. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2010, 17, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlay, A.; Johnson, M.; Forbes, T.L. Surgically relevant aortic arch mapping using computed tomography. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 26, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markelj, P.; Tomazevic, D.; Likar, B.; Pernus, F. A review of 3D/2D registration methods for image-guided interventions. Med. Image Anal. 2012, 16, 642–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.L.; Batchelor, P.G.; Holden, M.; Hawkes, D.J. Medical image registration. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 46, R1-45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, H.; Rangarajan, A. A new point matching algorithm for non-rigid registration. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2003, 89, 114–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xin, J. Breast Cancer Detection Using Extreme Learning Machine Based on Feature Fusion With CNN Deep Features. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 105146–105158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesamian, M.H.; Jia, W.; He, X.; Kennedy, P. Deep Learning Techniques for Medical Image Segmentation: Achievements and Challenges. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 582–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fu, H.; Zhou, K.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gao, S.; Liu, J. CE-Net: Context Encoder Network for 2D Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 2281–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A Comprehensive Survey on Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural. Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, N.A.; Sarker, Y.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M.J.; Ahamed, M.H.; Saha, D.K.; Badal, F.R.; Das, S.K.; Ali, M.F.; Moyeen, S.I.; et al. Graph Neural Network: A Comprehensive Review on Non-Euclidean Space. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 60588–60606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, L.R.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zaiem, F.; Almasri, J.; Prokop, L.J.; Heimbach, J.K.; Murad, M.H.; Mohammed, K. Imaging for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Qin, C.; Qiu, H.; Tarroni, G.; Duan, J.; Bai, W.; Rueckert, D. Deep Learning for Cardiac Image Segmentation: A Review. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmund, J.M.; Nyholm, T. A review of substitute CT generation for MRI-only radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, C.; Lenz, A.; Fischer, L.; Li, J.; Piecha, F.; Kluwe, J.; Adam, G.; Bannas, P. Abdominal Applications of 4D Flow MRI. Rofo 2021, 193, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Shimamura, K.; Yoshida, T.; Daimon, T.; Shirakawa, Y.; Torikai, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Shijo, T.; Toda, K.; Kuratani, T.; et al. Aortic remodeling as a prognostic factor for late aortic events after thoracic endovascular aortic repair in type B aortic dissection with patent false lumen. J. Endovasc. Ther. 2014, 21, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, C.; Sakaguchi, G.; Shimamoto, T.; Komiya, T. Prognostic factors in patients with uncomplicated acute type B aortic dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 767–773, discussion 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolliffe, I.T.; Cadima, J. Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philos. Trans. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.C.; Chen, S.L.; Jin, G.Z.; Shao, M.X.; Kan, J.; Lu, C.Y.; Xu, H. Acute renal injury after thoracic endovascular aortic repair of Stanford type B aortic dissection: Incidence, risk factors, and prognosis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.; Treichel, T.; Ritter, N.; Triebel, G.; Drossel, W.G.; Burgert, O. Surgical stent planning: Simulation parameter study for models based on DICOM standards. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2011, 6, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Number of Checkpoints | Missing Extraction | D_Mean (mm) | D_Max (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 408 | 9 (2.2%) | 0.73 | 3.55 |
| Variable | Difference Mean (mm) | Difference SD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spatial position of stent end | 0.1576 | 0.58 | 0.9992 |
| Vascular stent end-slip volume | 0.0997 | 0.81 | 0.98849 |
| Variable | Mean (mm) | SD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal support ring feature diameter | 0.337 | 1.35 | 0.9022 |
| Distal support ring feature diameter | 0.613 | 1.30 | 0.9204 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, M.; Li, D.; Xu, K.; Ouyang, S.; Yuan, D.; Zheng, T. Rapid Morphological Measurement Method of Aortic Dissection Stent Based on Spatial Observation Point Set. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020139
Bai M, Li D, Xu K, Ouyang S, Yuan D, Zheng T. Rapid Morphological Measurement Method of Aortic Dissection Stent Based on Spatial Observation Point Set. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Mateng, Da Li, Kaiyao Xu, Shuyu Ouyang, Ding Yuan, and Tinghui Zheng. 2023. "Rapid Morphological Measurement Method of Aortic Dissection Stent Based on Spatial Observation Point Set" Bioengineering 10, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020139
APA StyleBai, M., Li, D., Xu, K., Ouyang, S., Yuan, D., & Zheng, T. (2023). Rapid Morphological Measurement Method of Aortic Dissection Stent Based on Spatial Observation Point Set. Bioengineering, 10(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10020139






