TGF-β and SHH Regulate Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation into Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Generating an In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Medium Composition
2.2. Differentiation and Isolation of hPSC-Derived BME-like Cells
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR Analysis
2.6. RNA-Sequence Analysis
2.7. Immunocytochemistry and Fluorescence Microscopy
2.8. Acetylated LDL Uptake Assay and Vascular Tube-like Structure Formation Assay
2.9. Cell Proliferation Analysis
2.10. Monocyte Adhesion Assay
2.11. Efflux Transport Assay
2.12. Measurement of TEER and Permeability Assay
2.13. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
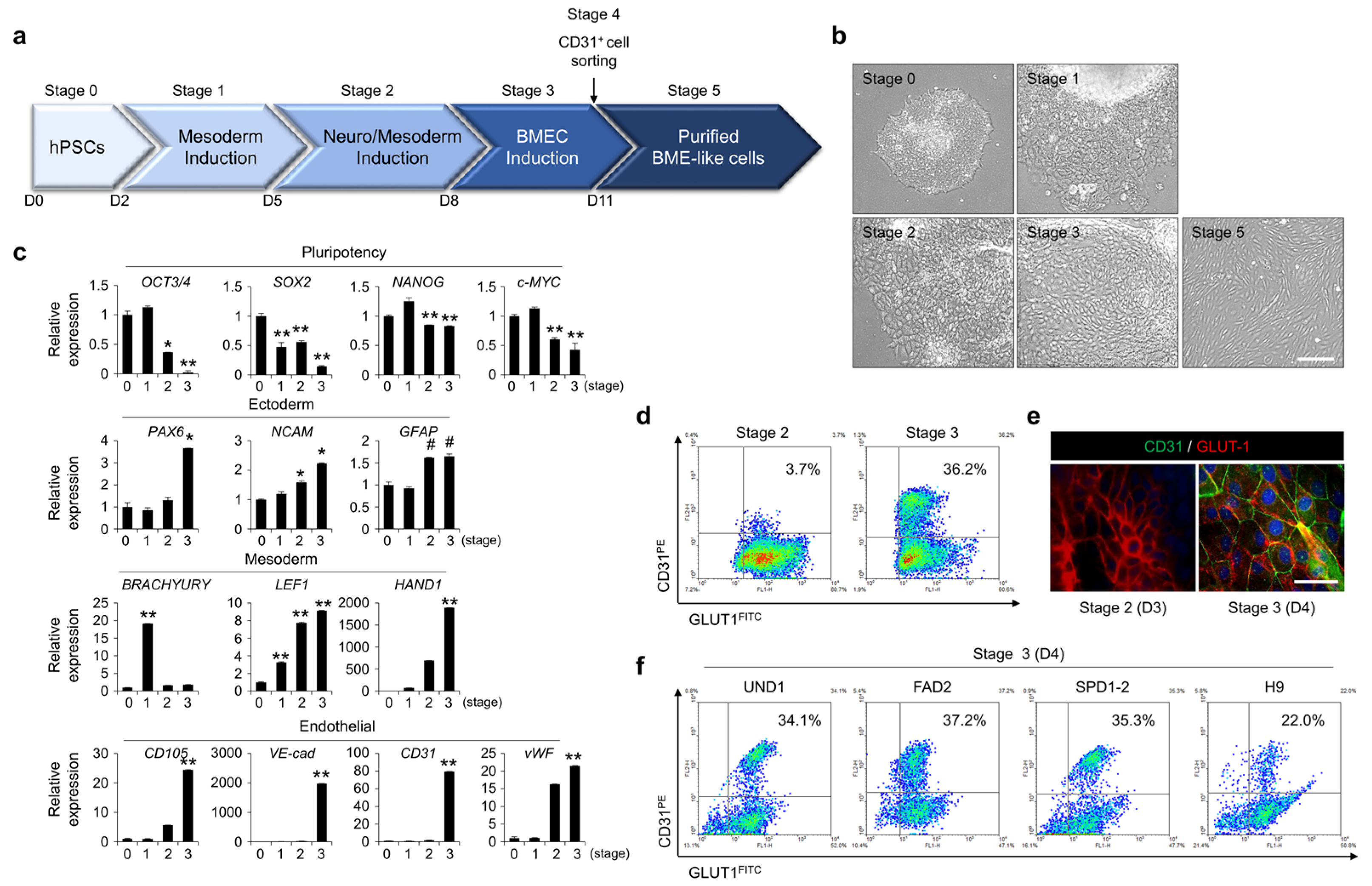
3.1. Differentiation of hPSCs into BME-like Cells
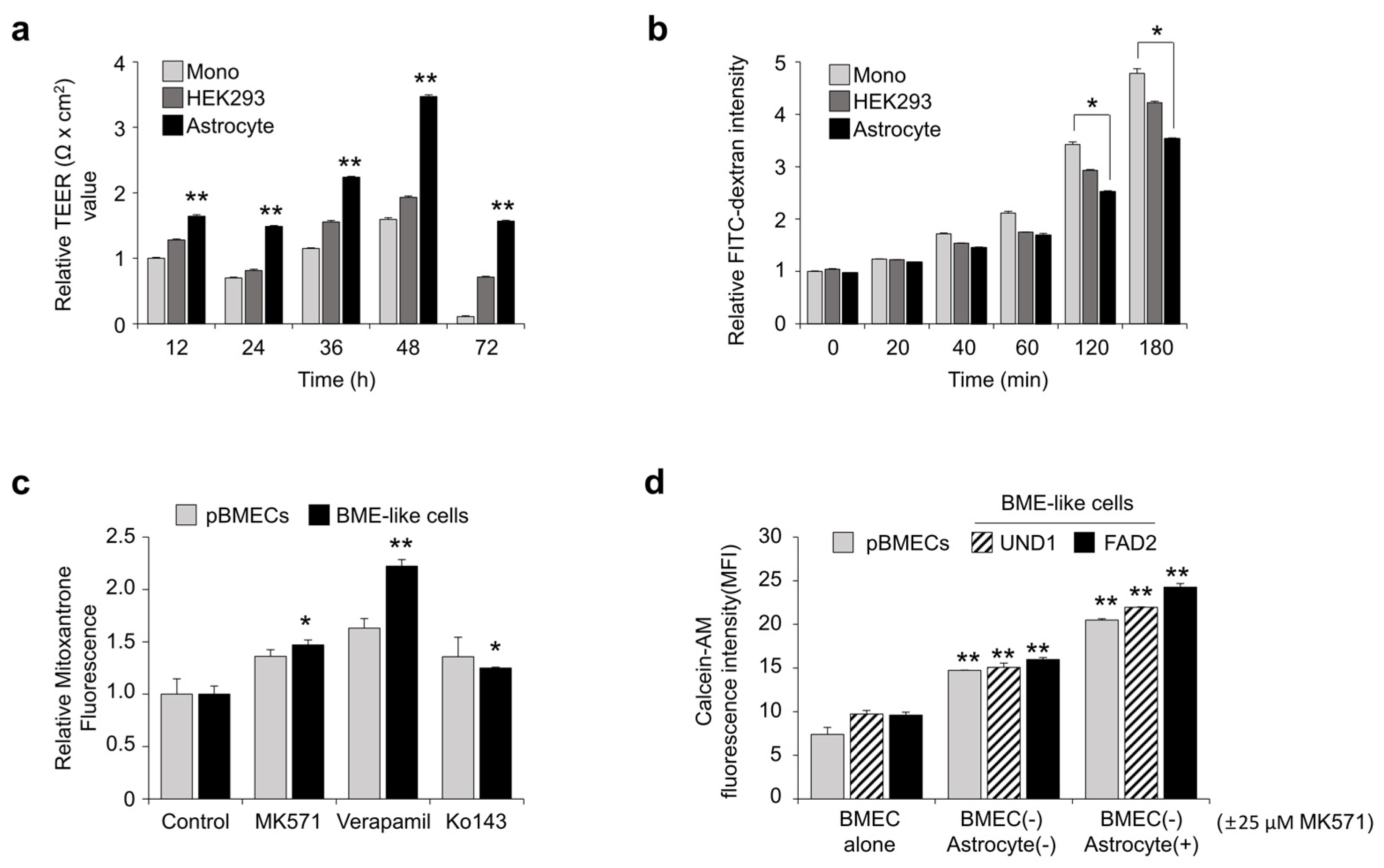
3.2. Similarity of BME-like Cells Derived from hPSCs with Primary BMECs
3.3. Assessment of BBB Properties of BME-like Cells Derived from hPSCs
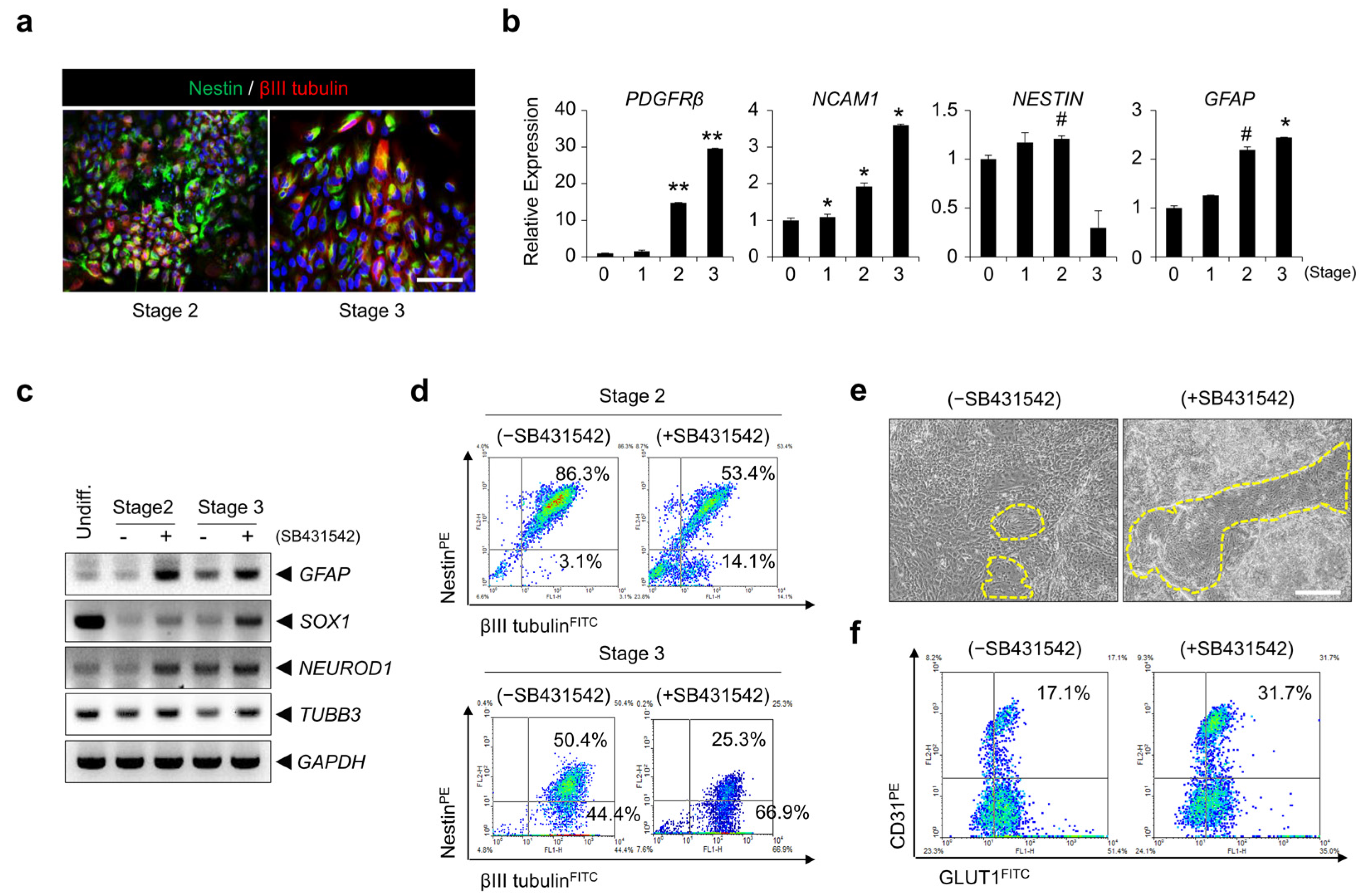
3.4. Inhibition of TGF-β Signaling Is Involved in BBB Specification during BMEC Differentiation
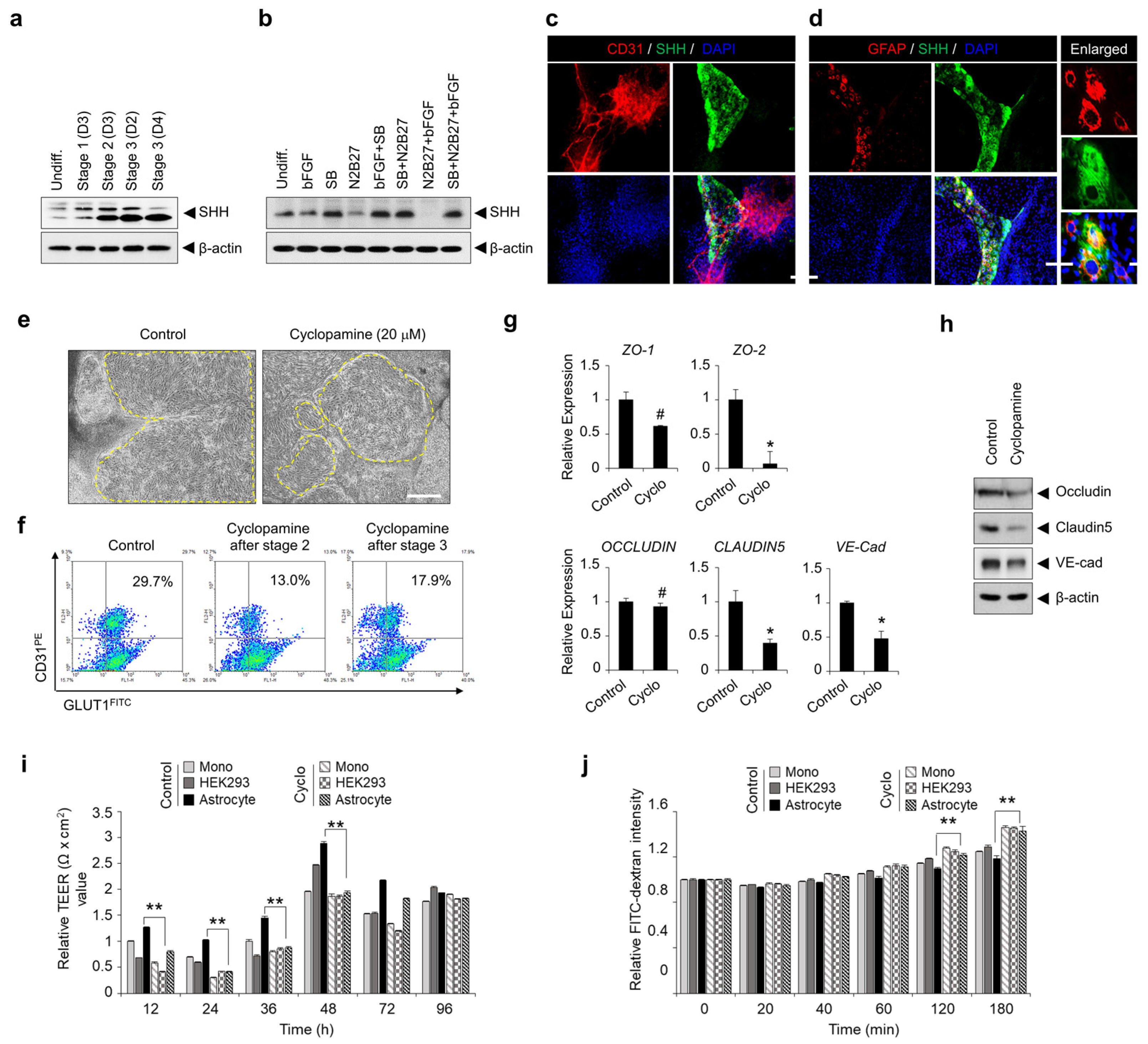
3.5. TGF-β Signaling-Mediated SHH Expression Is Important for hPSC Differentiation into BME-like Cells and the Acquisition of BBB Properties
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, N.J.; Ronnback, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Nelson, A.R.; Betsholtz, C.; Zlokovic, B.V. Establishment and Dysfunction of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Cell 2015, 163, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeken, J.F.; Loscher, W. The blood-brain barrier and cancer: Transporters, treatment, and Trojan horses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1663–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, B.W.; Gu, C. The molecular constituents of the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Azarin, S.M.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. A retinoic acid-enhanced, multicellular human blood-brain barrier model derived from stem cell sources. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K. Drug delivery systems, CNS protection, and the blood brain barrier. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 869269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagchi, S.; Chhibber, T.; Lahooti, B.; Verma, A.; Borse, V.; Jayant, R.D. In-vitro blood-brain barrier models for drug screening and permeation studies: An overview. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3591–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, I.; Krizbai, I.A. In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier for the study of drug delivery to the brain. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1949–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, M.S.; Zerangue, N.; Woodford, K.; Roberts, L.M.; Tate, E.H.; Feng, B.; Li, C.; Feuerstein, T.J.; Gibbs, J.; Smith, B.; et al. Comparative gene expression profiles of ABC transporters in brain microvessel endothelial cells and brain in five species including human. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 59, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, H.C.; Abbott, N.J.; Burek, M.; Cecchelli, R.; Couraud, P.O.; Deli, M.A.; Forster, C.; Galla, H.J.; Romero, I.A.; Shusta, E.V.; et al. In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: An overview of commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines for their use. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Marco, A.; Vignone, D.; Gonzalez Paz, O.; Fini, I.; Battista, M.R.; Cellucci, A.; Bracacel, E.; Auciello, G.; Veneziano, M.; Khetarpal, V.; et al. Establishment of an in Vitro Human Blood-Brain Barrier Model Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Comparison to a Porcine Cell-Based System. Cells 2020, 9, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchelli, R.; Berezowski, V.; Lundquist, S.; Culot, M.; Renftel, M.; Dehouck, M.P.; Fenart, L. Modelling of the blood-brain barrier in drug discovery and development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, T.; Maguire, S.E.; Canfield, S.G.; Bao, X.; Olson, W.R.; Shusta, E.V.; Palecek, S.P. Directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to blood-brain barrier endothelial cells. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Azarin, S.M.; Kay, J.E.; Nessler, R.A.; Wilson, H.K.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Derivation of blood-brain barrier endothelial cells from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aday, S.; Cecchelli, R.; Hallier-Vanuxeem, D.; Dehouck, M.P.; Ferreira, L. Stem Cell-Based Human Blood-Brain Barrier Models for Drug Discovery and Delivery. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Modeling the blood-brain barrier using stem cell sources. Fluids Barriers CNS 2013, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauschke, K.; Frederiksen, L.; Hall, V.J. Paving the Way Toward Complex Blood-Brain Barrier Models Using Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 857–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichmann, A.; Thomas, J.L. Molecular parallels between neural and vascular development. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a006551. [Google Scholar]
- Paredes, I.; Himmels, P.; Ruiz de Almodovar, C. Neurovascular Communication during CNS Development. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S. Tgf-Beta family signaling in embryonic stem cells. Int. J. Stem Cells 2011, 4, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.R.; Vallier, L.; Lupo, G.; Alexander, M.; Harris, W.A.; Pedersen, R.A. Inhibition of Activin/Nodal signaling promotes specification of human embryonic stem cells into neuroectoderm. Dev. Biol. 2008, 313, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, S.M.; Fasano, C.A.; Papapetrou, E.P.; Tomishima, M.; Sadelain, M.; Studer, L. Highly efficient neural conversion of human ES and iPS cells by dual inhibition of SMAD signaling. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Laco, F.; Liao, M.C.; Woo, T.L.; Oh, S.K.W.; Chai, C.L.L. Influencing the Fate of Cardiac and Neural Stem Cell Differentiation Using Small Molecule Inhibitors of ALK5. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.I.; Dodelet-Devillers, A.; Kebir, H.; Ifergan, I.; Fabre, P.J.; Terouz, S.; Sabbagh, M.; Wosik, K.; Bourbonniere, L.; Bernard, M.; et al. The Hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science 2011, 334, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.H.; Jeung, I.C.; Jeong, J.; Yoon, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.; Kang, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Park, Y.J.; Lee, H.G.; et al. Graphene oxide induces apoptotic cell death in endothelial cells by activating autophagy via calcium-dependent phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinases. Acta Biomater. 2016, 46, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, J.; Dunstan, H.; Chambers, I.; Smith, A. Functional gene screening in embryonic stem cells implicates Wnt antagonism in neural differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebner, S.; Corada, M.; Bangsow, T.; Babbage, J.; Taddei, A.; Czupalla, C.J.; Reis, M.; Felici, A.; Wolburg, H.; Fruttiger, M.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling controls development of the blood-brain barrier. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 183, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, J.M.; Rajagopal, J.; Carroll, T.J.; Ishibashi, M.; McMahon, J.; McMahon, A.P. Canonical Wnt signaling regulates organ-specific assembly and differentiation of CNS vasculature. Science 2008, 322, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, K.C.; Adams, A.M.; Goodson, J.M.; McDonald, C.E.; Potter, J.C.; Berndt, J.D.; Biechele, T.L.; Taylor, R.J.; Moon, R.T. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes differentiation, not self-renewal, of human embryonic stem cells and is repressed by Oct4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4485–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Bao, X.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Dong, W.; Dunn, K.K.; Shusta, E.V.; Palecek, S.P. Efficient differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to endothelial progenitors via small-molecule activation of WNT signaling. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul Muneer, P.M.; Alikunju, S.; Szlachetka, A.M.; Murrin, L.C.; Haorah, J. Impairment of brain endothelial glucose transporter by methamphetamine causes blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stebbins, M.J.; Wilson, H.K.; Canfield, S.G.; Qian, T.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Differentiation and characterization of human pluripotent stem cell-derived brain microvascular endothelial cells. Methods 2016, 101, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippmann, E.S.; Weidenfeller, C.; Svendsen, C.N.; Shusta, E.V. Blood-brain barrier modeling with co-cultured neural progenitor cell-derived astrocytes and neurons. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marco, A.; Gonzalez Paz, O.; Fini, I.; Vignone, D.; Cellucci, A.; Battista, M.R.; Auciello, G.; Orsatti, L.; Zini, M.; Monteagudo, E.; et al. Application of an in Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model in the Selection of Experimental Drug Candidates for the Treatment of Huntington’s Disease. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2069–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvanen, S.; Lindhe, O.; Palner, M.; Kornum, B.R.; Rahman, O.; Langstrom, B.; Knudsen, G.M.; Hammarlund-Udenaes, M. Species differences in blood-brain barrier transport of three positron emission tomography radioligands with emphasis on P-glycoprotein transport. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weksler, B.B.; Subileau, E.A.; Perriere, N.; Charneau, P.; Holloway, K.; Leveque, M.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Nicotra, A.; Bourdoulous, S.; Turowski, P.; et al. Blood-brain barrier-specific properties of a human adult brain endothelial cell line. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1872–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Deli, M.A.; Kawaguchi, H.; Shimizudani, T.; Shimono, T.; Kittel, A.; Tanaka, K.; Niwa, M. A new blood-brain barrier model using primary rat brain endothelial cells, pericytes and astrocytes. Neurochem. Int. 2009, 54, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamizu, K.; Iwasaki, M.; Takakubo, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Ikuno, T.; Miyoshi, M.; Kondo, T.; Nakao, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; Inoue, H.; et al. In Vitro Modeling of Blood-Brain Barrier with Human iPSC-Derived Endothelial Cells, Pericytes, Neurons, and Astrocytes via Notch Signaling. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronaldson, P.T.; Davis, T.P. Blood-brain barrier integrity and glial support: Mechanisms that can be targeted for novel therapeutic approaches in stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 3624–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermeier, B.; Daneman, R.; Ransohoff, R.M. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchette, M.; Daneman, R. Formation and maintenance of the BBB. Mech. Dev. 2015, 138 Pt 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geranmayeh, M.H.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Farhoudi, M. Targeting pericytes for neurovascular regeneration. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Agalliu, D.; Zhou, L.; Kuhnert, F.; Kuo, C.J.; Barres, B.A. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is required for CNS, but not non-CNS, angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, E.A.; Bell, R.D.; Zlokovic, B.V. Central nervous system pericytes in health and disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Meng, F.; Han, H.; Meng, A.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Endothelial Smad4 maintains cerebrovascular integrity by activating N-cadherin through cooperation with Notch. Dev. Cell 2011, 20, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneman, R.; Zhou, L.; Kebede, A.A.; Barres, B.A. Pericytes are required for blood-brain barrier integrity during embryogenesis. Nature 2010, 468, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.; Nam, H.S.; Seandel, M.; Nolan, D.; Janovitz, T.; Tomishima, M.; Studer, L.; Lee, G.; Lyden, D.; Benezra, R.; et al. Expansion and maintenance of human embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells by TGFbeta inhibition is Id1 dependent. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuccillo, M.; Joyner, A.L.; Fishell, G. Morphogen to mitogen: The multiple roles of hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, N.G.; Lim, M.-H.; Park, J.; Jeung, I.C.; Hwang, B.; Lee, J.; Park, J.-G.; Son, M.-Y.; Han, B.S.; Yoon, S.-J.; et al. TGF-β and SHH Regulate Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation into Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Generating an In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101132
Lee NG, Lim M-H, Park J, Jeung IC, Hwang B, Lee J, Park J-G, Son M-Y, Han BS, Yoon S-J, et al. TGF-β and SHH Regulate Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation into Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Generating an In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(10):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101132
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Na Geum, Mi-Hee Lim, Jongjin Park, In Cheul Jeung, Byungtae Hwang, Jangwook Lee, Jong-Gil Park, Mi-Young Son, Baek Soo Han, Sung-Jin Yoon, and et al. 2023. "TGF-β and SHH Regulate Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation into Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Generating an In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model" Bioengineering 10, no. 10: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101132
APA StyleLee, N. G., Lim, M.-H., Park, J., Jeung, I. C., Hwang, B., Lee, J., Park, J.-G., Son, M.-Y., Han, B. S., Yoon, S.-J., Lee, S.-J., Park, Y.-J., Kim, J. H., Lee, N.-K., Lee, S. C., & Min, J.-K. (2023). TGF-β and SHH Regulate Pluripotent Stem Cell Differentiation into Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells in Generating an In Vitro Blood–Brain Barrier Model. Bioengineering, 10(10), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10101132





