Hydrological Modeling and Runoff Mitigation in an Ungauged Basin of Central Vietnam Using SWAT Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Model Configuration
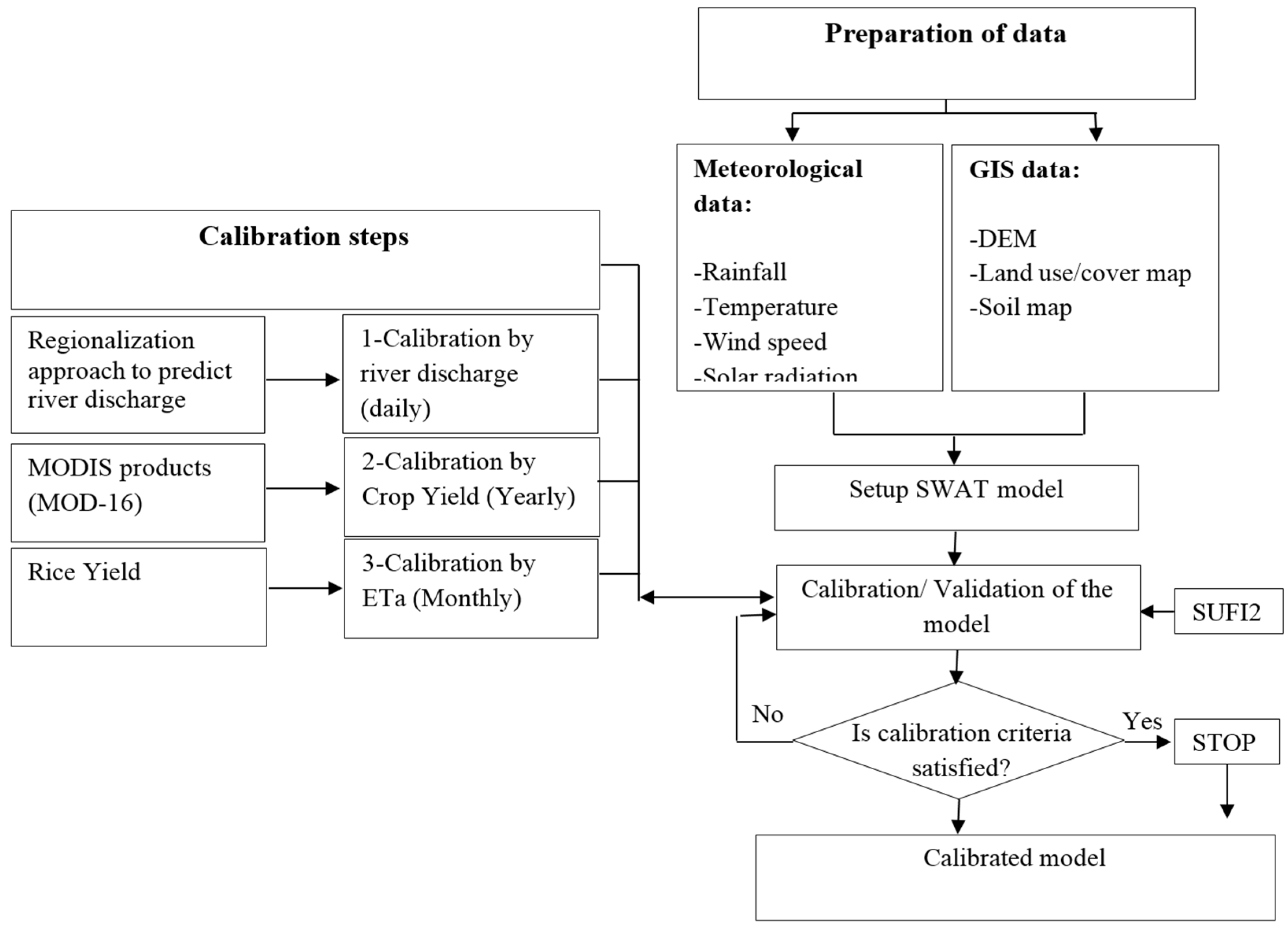
2.4. Calibration, Validation and Uncertainty Analysis
2.4.1. Regionalization Approach
2.4.2. Calibration Based on Crop Yield
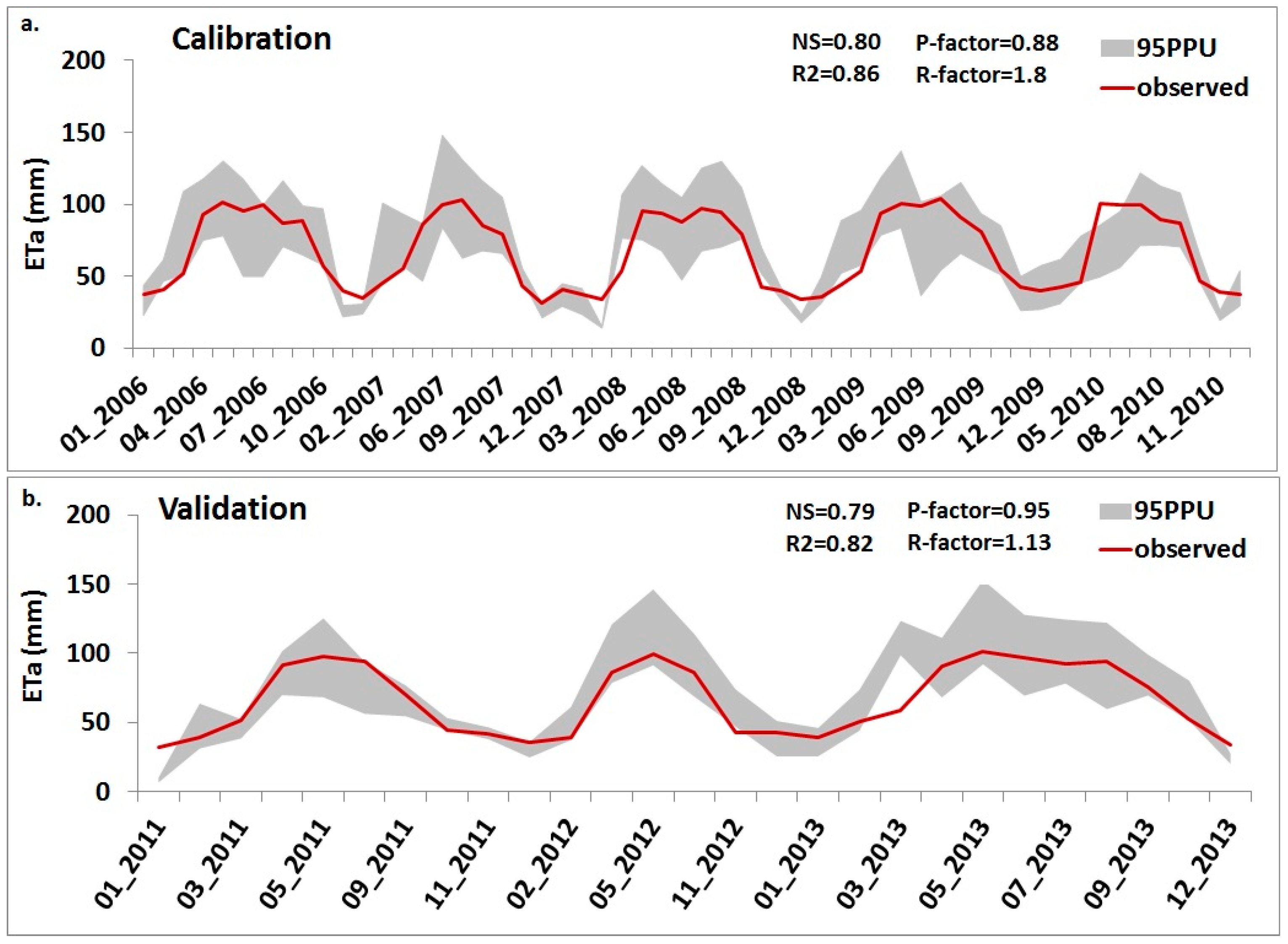
2.4.3. Calibration Based on ETa Using MODIS Products
3. Results and Discussion
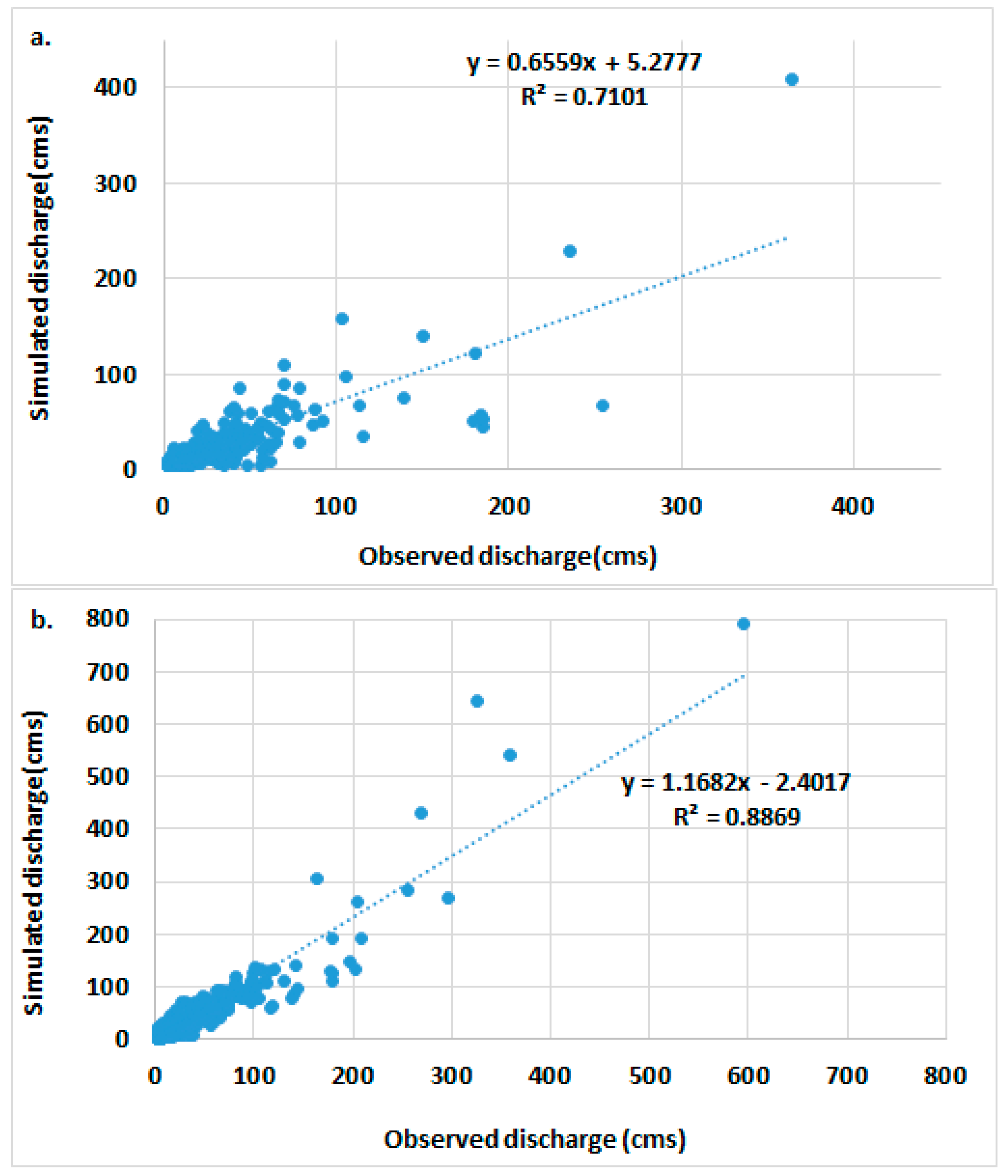
3.1. Regionalization Outcome
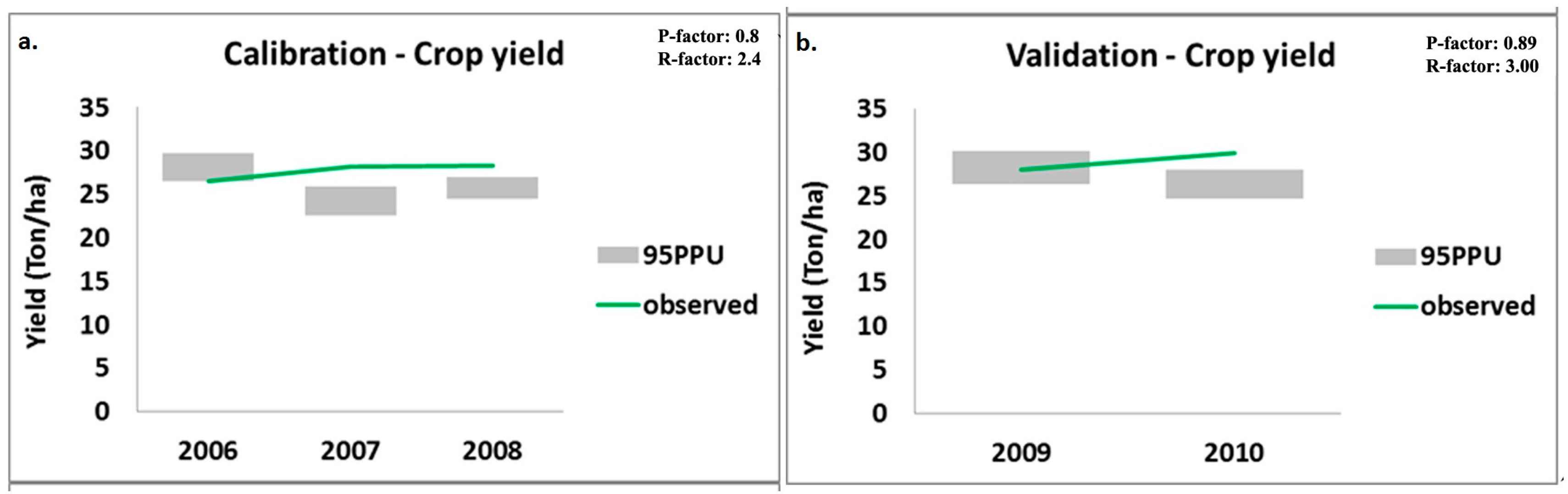
3.2. Parameterization for Crop Yield
3.3. Parameterization for ETa Based on MODIS ET Time Series
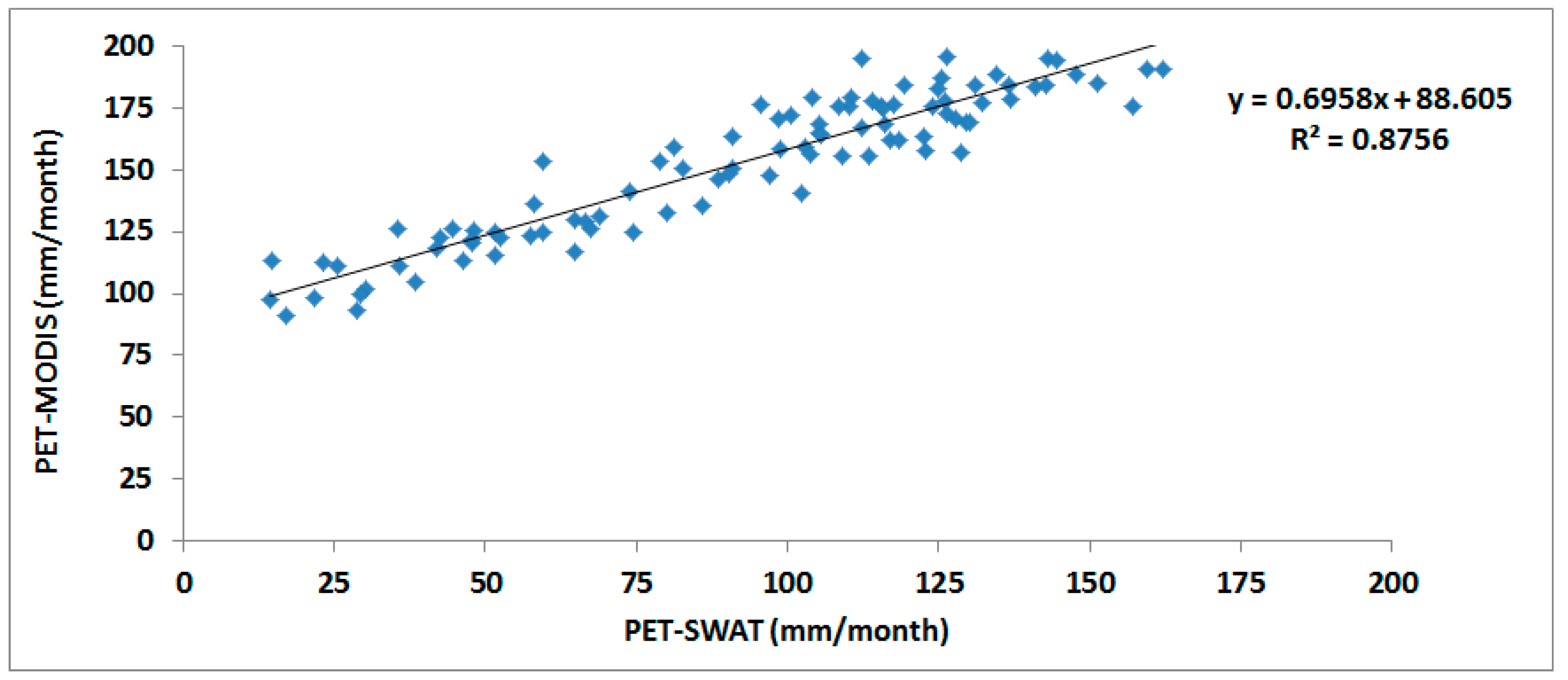
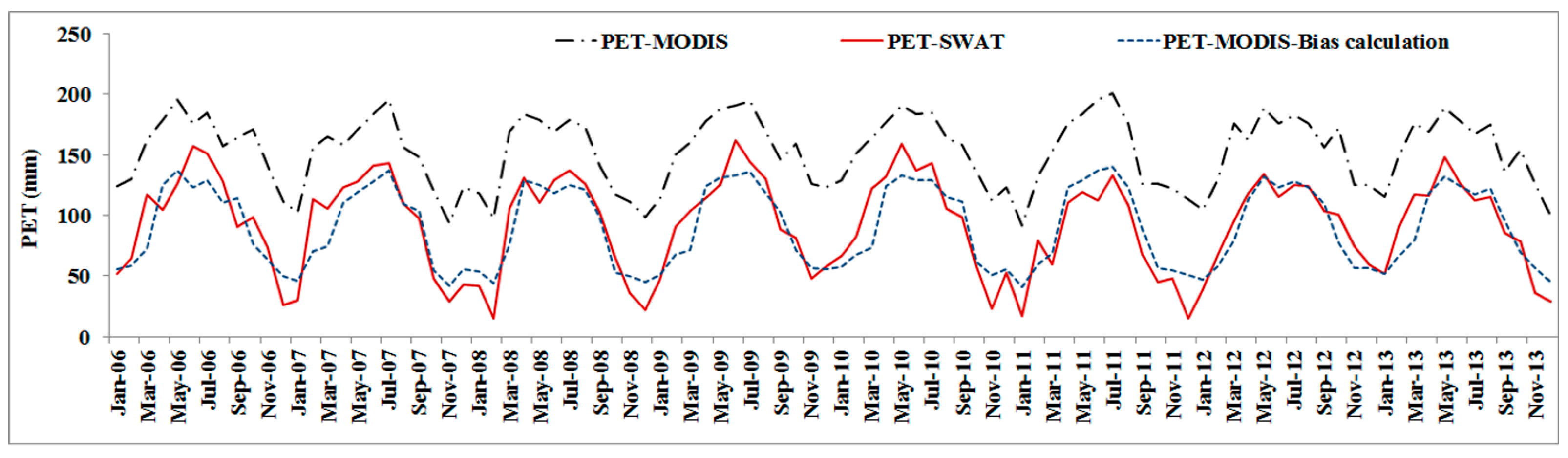
3.3.1. Reliability of MODIS Data
3.3.2. Procedure of Model Calibration Using ET-MODIS
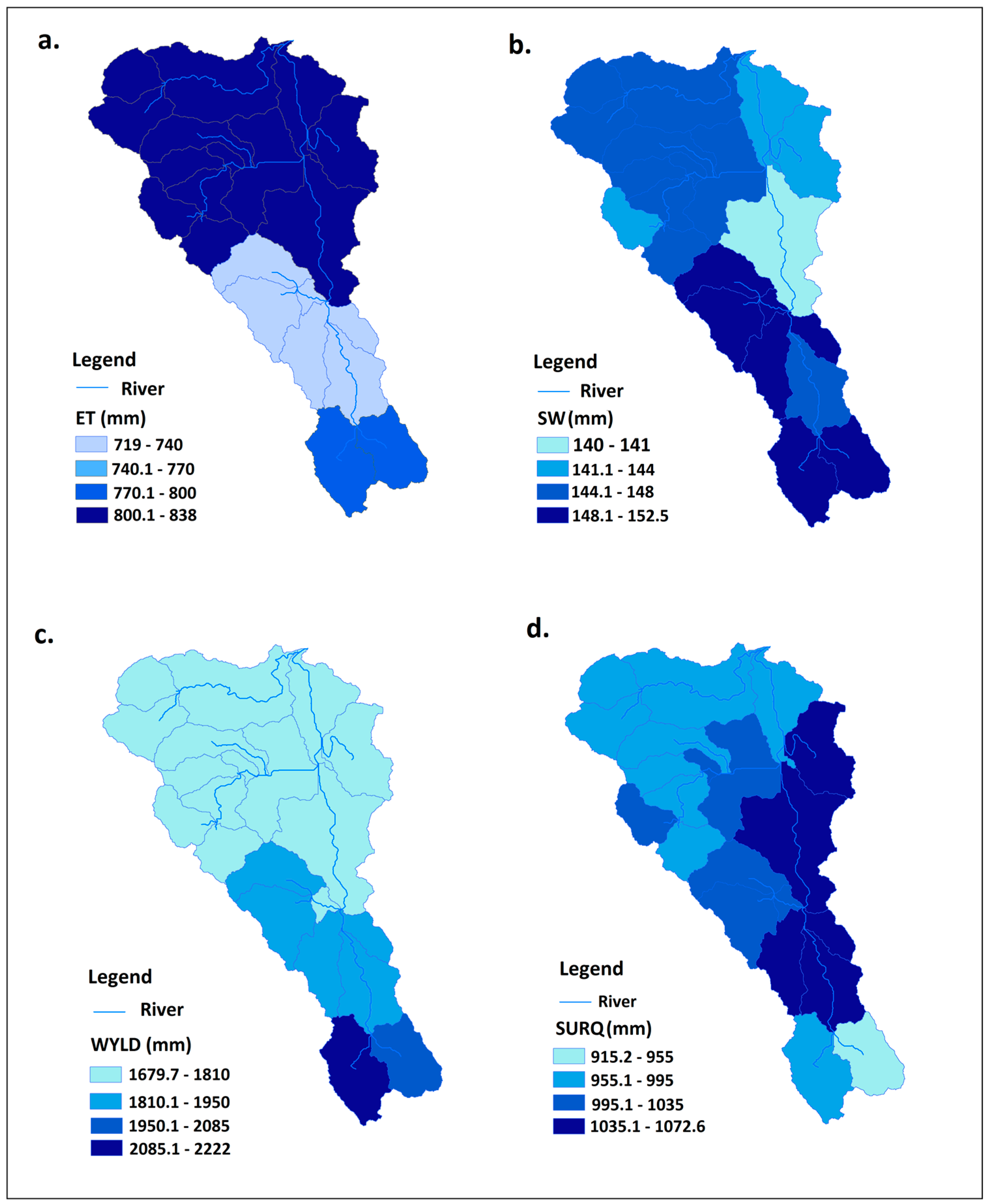
3.4. Quantification of Water Components
3.5. Surface Runoff
3.6. Best Management Practices (BMPs)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment—Part 1, model development. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei Emam, A.; Kappas, M.; Abbaspour, K.C. Simulation of water balance components in a watershed located in central drainage basin of Iran. In Remote Sensing of the Terrestrial Water Cycle, Geophysical Monograph 206; Lakshmi, V., Ed.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA; Wiley & Sons Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 463–478. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Kappas, M. Modeling Surface Runoff and Evapotranspiration using SWAT and BEACH for a Tropical Watershed in North Vietnam, Compared to MODIS Products. Int. J. Adv. Remote Sens. GIS 2015, 4, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Schuol, J.; Abbaspour, K.C.; Yang, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Zehnder, A.J.B. Modeling blue and green water availability in Africa. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, T.T.; Thong, C.V.T.; Ngoc, N.B.; Chuong, H.V. Modeling Soil Erosion within Small Moutainous Watershed in Central Vietnam Using GIS and SWAT. Resour. Environ. 2014, 4, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, L.; Herrmann, R.B.; Pan, Z. Parameter Uncertainty Reduction for SWAT Using Grace, Streamflow, and Groundwater Table Data for Lower Missouri River Basin. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrière, N.; Locatelli, B.; Laumonier, Y.; Freycon, V.; Bernoux, M. Soil erosion in the humid tropics: A systematic quantitative review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 203, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Effect of climate on surface flow along a climatological gradient. A field rainfall simulation approach. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 38, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Yang, H.B.; Yang, D.W.; Ma, H. Assessing the impact of climate variability and human activities on annual runoff in the Luan River basin, China. Hydrol. Res. 2013, 44, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.H. Comprehensively Studying Geographical Arising and Land Degradation Aiming the Purpose of Reasonably Using Land Resource and Preventing Disaster in Binh-Tri-Thien Region. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Mining and Geology, Hanoi, Vietnam, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Phuong, T.T.; Chuong, H.V. Simulating effects of land use change on soil erosion in Bo River basin in the Central of Vietnam. J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2013, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 12th ed.USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The Digital Soil Map of the World and Derived Soil Properties; Version 3.6; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Master Plan of Aluoi 2015, District, Development, and Investment Plan (DDIP); Aluoi district Authority: Aluoi, Vietnam.
- Rafiei Emam, A.; Kappas, M.; Akhavan, S.; Hosseini, S.Z.; Abbaspour, K.C. Estimation of groundwater recharge and its relation to land degradation: Case study of a semi-arid river basin in Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. J. 2015, 74, 6791–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA: United States Department of Agriculture. Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds, Technical Release 55 (TR-55), 2nd ed.Natural Resources Conservation Service, Conservation Engineering Division: Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
- Ritchie, J.T. A model for predicting evaporation from a row crop with incomplete cover. Water Resour. Res. 1972, 8, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.R. Sediment Yield Prediction with Universal Equation Using Runoff Energy Factor; Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1975; Volume ARS-S-40.
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains. Agriculture Handbook; U.S. Department Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965; p. 282.
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M. Automated methods for estimating base flow and ground water recharge from streamflow records. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Cimino, J.; Ross, M. Calibration of Base Flow Separation Methods with Streamflow Conductivity. Ground Water 2007, 45, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaurio, M.; Zabaleta, A.; Uriarte, J.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Antigüedad, I. Evaluation of SWAT models performance to simulate streamflow spatial origin. The case of a small forested watershed. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Allen, P.M. Estimating hydrologic budgets for three Illinois watersheds. J. Hydrol. 1996, 176, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewiele, G.L.; Atlabachew, E. Monthly water balance of ungauged catchments obtained by geographical regionalization. J. Hydrol. 1995, 170, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A. Calibration of hydrological model parameters for ungauged catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego, L.; Bárdossy, A. Robust parametric models of runoff characteristics at the mesoscale. J. Hydrol. 2005, 303, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastola, S.; Ishidaira, H.; Takeuchi, K. Regionalization of hydrological model parameters under parameter uncertainty: A case study involving TOPMODEL and basins across the globe. J. Hydrol. 2008, 357, 188–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, R.; Blöschla, G. Regionalisation of catchment model parameters. J. Hydrol. 2004, 287, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, N.; Lee, H.; Wheater, H.; Young, A.; Wagener, T. Ensemble predictions of runoff in ungauged catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W12434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Merz, R.; Bloschl, G. A comparison of regionalization methods for catchment model parameters. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.C.; Ishidaira, H.; Bastola, S. Calibration of hydrological models in ungauged basins based on satellite radar altimetry observations of river water level. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 26, 3524–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.C.; Ishidaira, H.; Bastola, S. Towards improving river discharge estimation in ungauged basins: calibration of rainfall-runoff models based on satellite observations of river flow width at basin outlet. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, K.C. SWAT-CUP: SWAT Calibration and Uncertainty Programs—A User Manual; Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology: Dubendorf, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiei Emam, A.; Kappas, M.; Hosseini, S.Z. Assessing the impact of climate change on water resources, crop production and land degradation in a semi-arid river basin. Hydrol. Res. 2015, 46, 854–870. [Google Scholar]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Droogers, P. Calibration of a distributed hydrological model based on satellite evapotranspiration. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, M.J.M.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Bastiaanssen, W. Spatial quantification of groundwater abstraction in the irrigated Indus basin. Groundwater 2014, 52, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS Global Terrestrial Evapotranspiration Algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei Emam, A.; Mishra, B.; Kumar, P.; Masago, Y.; Fukushi, K. Impact Assessment of Climate and Land-Use Changes on Flooding Behaviour in the Upper Ciliwung River, Jakarta, Indonesia. Water 2016, 8, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Arnold, J.; Allen, P.; Chen, X. Base flow simulation using SWAT model in an inland river basin in Tianshan Mountains, Northwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, S.; Abedi-Koupai, J.; Mousavi, S.F.; Afyuni, M.; Eslamian, S.S.; Abbaspour, K.C. Application of SWAT model to investigate nitrate leaching in Hamadan–Bahar Watershed, Iran. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. J. 2010, 139, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Srinivasan, R.; Williams, J.R.; Naney, E.B.; Neitsch, S.L. Soil and Water Assessment Tool. Input/Output Documentation, Version 2012, TWRI TR-439; Texas Water Resources Institute, College Station: Texas, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bringer, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model evaluation guidelines for systematic quantification of accuracy in watershed simulations. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Dugas, W.A.; Srinivasan, R.; Hauck, L.M. Validation of the SWAT model on a large river basin with point and nonpoint sources. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2001, 37, 1169–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petković, D.; Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S.; Shamshirband, S.; Motamedi, S.; Hashim, R.; Bonakdari, H. Determination of the Most Influential Weather Parameters on Reference Evapotranspiration by Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Methodology. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 114, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kateb, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Mosandl, R. Soil erosion and surface runoff on different vegetation covers and slope gradients: A field experiment in Southern Shaanxi Province, China. CATENA 2013, 105, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheshukov, A.Y.; Douglas-Mankin, K.R.; Sinnathamby, S.; Daggupati, P. Pasture BMP effectiveness using an HRU-based subarea approach in SWAT. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.M.; Nejadhashemi, A.P.; Leatherman, J.C. Using a BMP Auction as a Tool for the Implementation of Conservation Practices. J. Extens. 2009, 47, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Arabi, M.; Govindaraju, R.S.; Hantush, M.M.; Engel, B.A. Role of watershed subdivision on modeling the effectiveness of best management practice with SWAT. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2006, 42, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

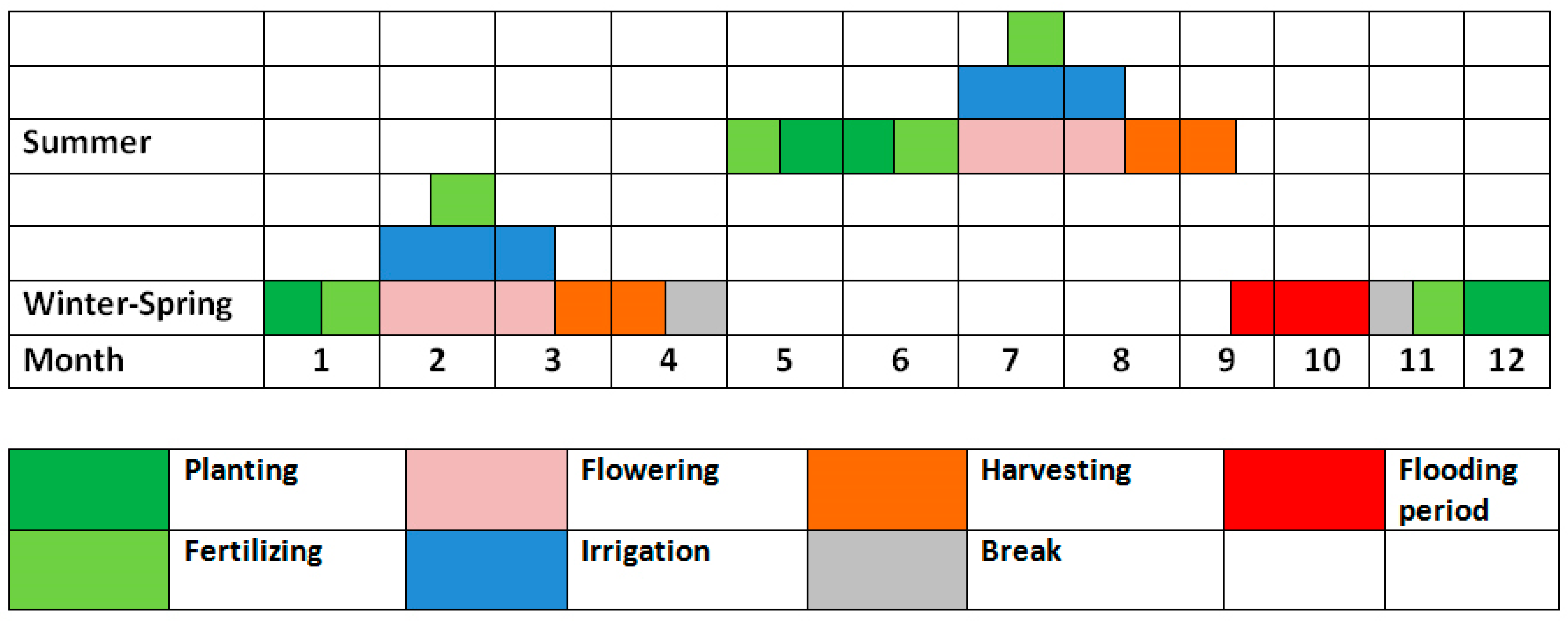

| Catchment | Climate Station | River | Rain Gauge Station | Rainfall (Annual) mm | Area Km2 | Slope (Mean) % | Elevation (Mean) m | Land- Use * | Soil * | L/W ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-Luoi | Aluoi | Song Sia River | Aluoi | 3900 | 408 | 38 | 495 | Forest | Orthic Acrisols | 1.90 |
| Thuong Nhat | Nam Dong | Ta Trach River | Nam Dong | 3800 | 125 | 42 | 490 | Forest | Orthic Acrisols | 1.05 |
| ID | Parameters * | Description | Initial Range | Final Range | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | r__CN2.mgt | Curve number | −0.5 to 0.5 | −0.150 to 0.25 | Parameters of river discharge |
| 2 | r__SOL_BD().sol | Soil bulk density | −0.5 to 0.5 | −0.11 to 0.72 | |
| 3 | r__SOL_K().sol | Soil conductivity (mm/h) | −0.5 to 0.5 | −0.68 to 0.99 | |
| 4 | r__SOL_AWC().sol | Soil available water storage capacity (mm H2O/mm soil) | −0.5 to 0.5 | 0.07 to 0.50 | |
| 5 | v__CH_K2.rte | Effective hydraulic conductivity in main channel | 50 to 400 | 302 to 394 | |
| 6 | v__ALPHA_BNK.rte | Base flow alpha factor for bank storage | 0 to 1 | 0.1 to 0.7 | |
| 7 | r__CH_N2.rte | Manning value for main channel | −0.5 to 0.5 | −0.39 to 0.20 | |
| 8 | r__OV_N.hru | Manning value for overland channel | −0.5 to 0.5 | −0.15 to 0.42 | |
| 9 | r__SLSUBBSN.hru | Average slope length (m) | 0.5 to 0.5 | 0.46 to 0.90 | |
| 10 | v__GWQMN.gw | Threshold water level in shallow aquifer for base flow | 100 to 5000 | 1250 to 3600 | |
| 11 | v__GW_DELAY.gw | Ground water delay time (days) | 10 to 500 | 227 to 400 | |
| 12 | v__ALPHA_BF.gw | Base flow alpha factor (days) | 0.04 to 0.07 | 0.040 to 0.075 | |
| 13 | v__GW_REVAP.gw | Revap coefficient | 0.02 to 0.2 | 0.0.03 to 0.15 | |
| 14 | v__REVAPMN.gw | Threshold water level in shallow aquifer | 0 to 500 | 100 to 250 | |
| 15 | v__ESCO.hru | Soil evaporation compensation factor | 0.1 to 1.0 | 0.40 to 0.65 | |
| 16 | v__WAVP{8}.plant.dat | Rate of decline in radiation use efficiency per unit increase in vapor pressure deficit. | 1 to 50 | 43 to 46 | Parameters of ETa |
| 17 | V__DLAI{8}.plant.dat_____FRST | Fraction of growing season when leaf area begins to decline in forest area | 0.15 to 1 | 0.95 to 0.99 | |
| 18 | V__BLAI{8}.plant.dat_____FRST | Maximum potential leaf area index of forest areas | 2 to 10 | 2.7 to 5.7 | |
| 19 | v__HEAT_UNITS{[],1}.mgt____FRST | Total heat units for plant to reach maturity in forest areas | 1000 to 4500 | 2900 to 3350 | |
| 20 | v__HEAT_UNITS{[],1}.mgt____RICE | Total heat units for plant to reach maturity in paddy areas | 1000 to 4500 | 4000 to 4600 | Parameters of crop |
| 21 | v__HI{[],1}.mgt | harvest index | 0.6 to 0.99 | 0.9 to 0.99 | |
| 22 | v__BIO-TARG.mgt | bio target | 10 to 50 | 35 to 50 |
| BMP | Surface Runoff (mm) | Percolation (mm) | Soil Water Content (mm) | ETa (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No application | 150 | 1.5 | 11 | 28 |
| Terracing | 100.5 | 24 | 26 | 38 |
| Contouring | 75 | 41 | 37 | 44 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafiei Emam, A.; Kappas, M.; Linh, N.H.K.; Renchin, T. Hydrological Modeling and Runoff Mitigation in an Ungauged Basin of Central Vietnam Using SWAT Model. Hydrology 2017, 4, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010016
Rafiei Emam A, Kappas M, Linh NHK, Renchin T. Hydrological Modeling and Runoff Mitigation in an Ungauged Basin of Central Vietnam Using SWAT Model. Hydrology. 2017; 4(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafiei Emam, Ammar, Martin Kappas, Nguyen Hoang Khanh Linh, and Tsolmon Renchin. 2017. "Hydrological Modeling and Runoff Mitigation in an Ungauged Basin of Central Vietnam Using SWAT Model" Hydrology 4, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010016
APA StyleRafiei Emam, A., Kappas, M., Linh, N. H. K., & Renchin, T. (2017). Hydrological Modeling and Runoff Mitigation in an Ungauged Basin of Central Vietnam Using SWAT Model. Hydrology, 4(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology4010016





