Assessing Impacts of Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Case Study over Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
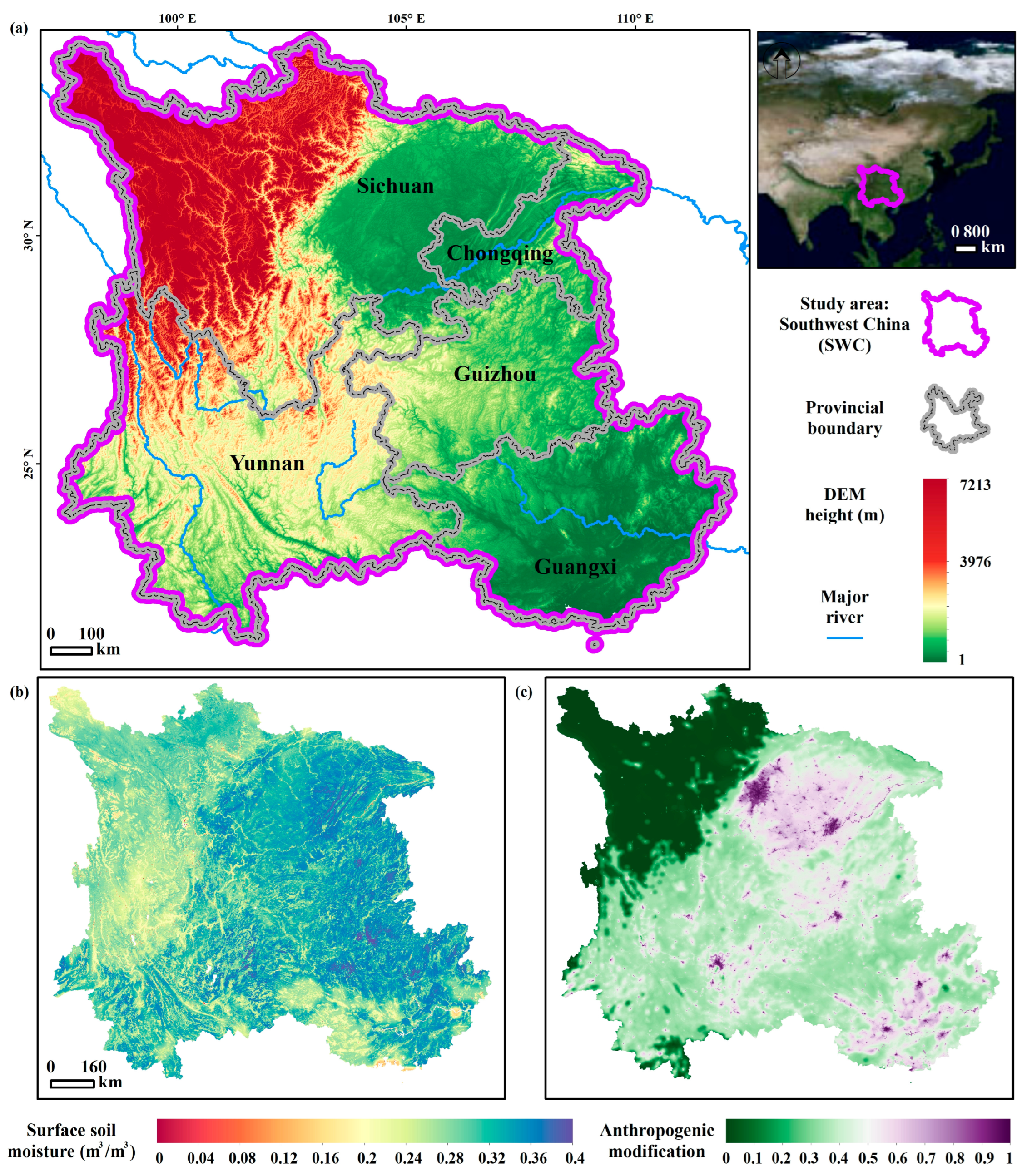
2.1. Study Area
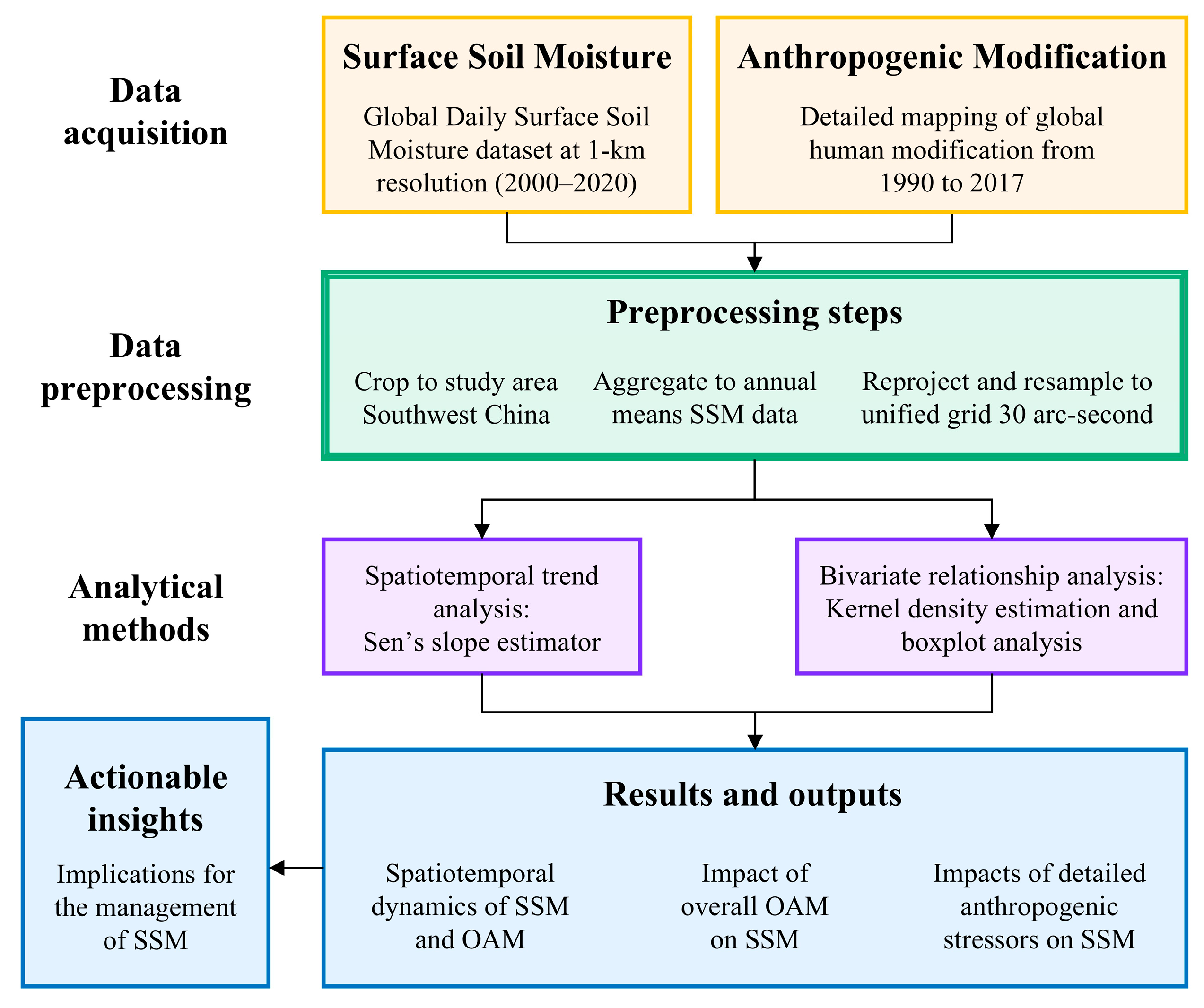
2.2. Data and Preprocessing Process
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Sen’s Slope
2.3.2. Bivariate Kernel Density and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
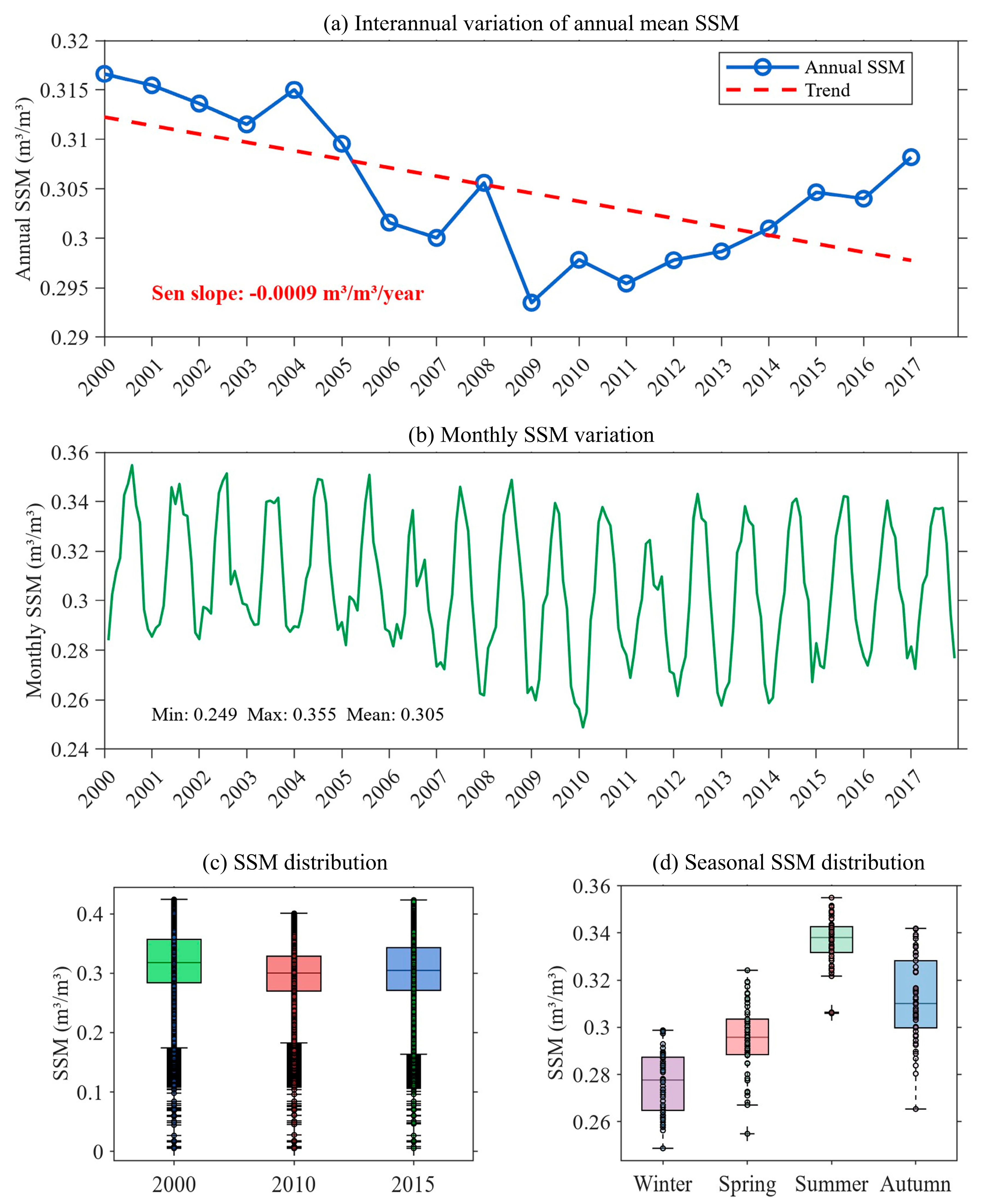
3.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Surface Soil Moisture
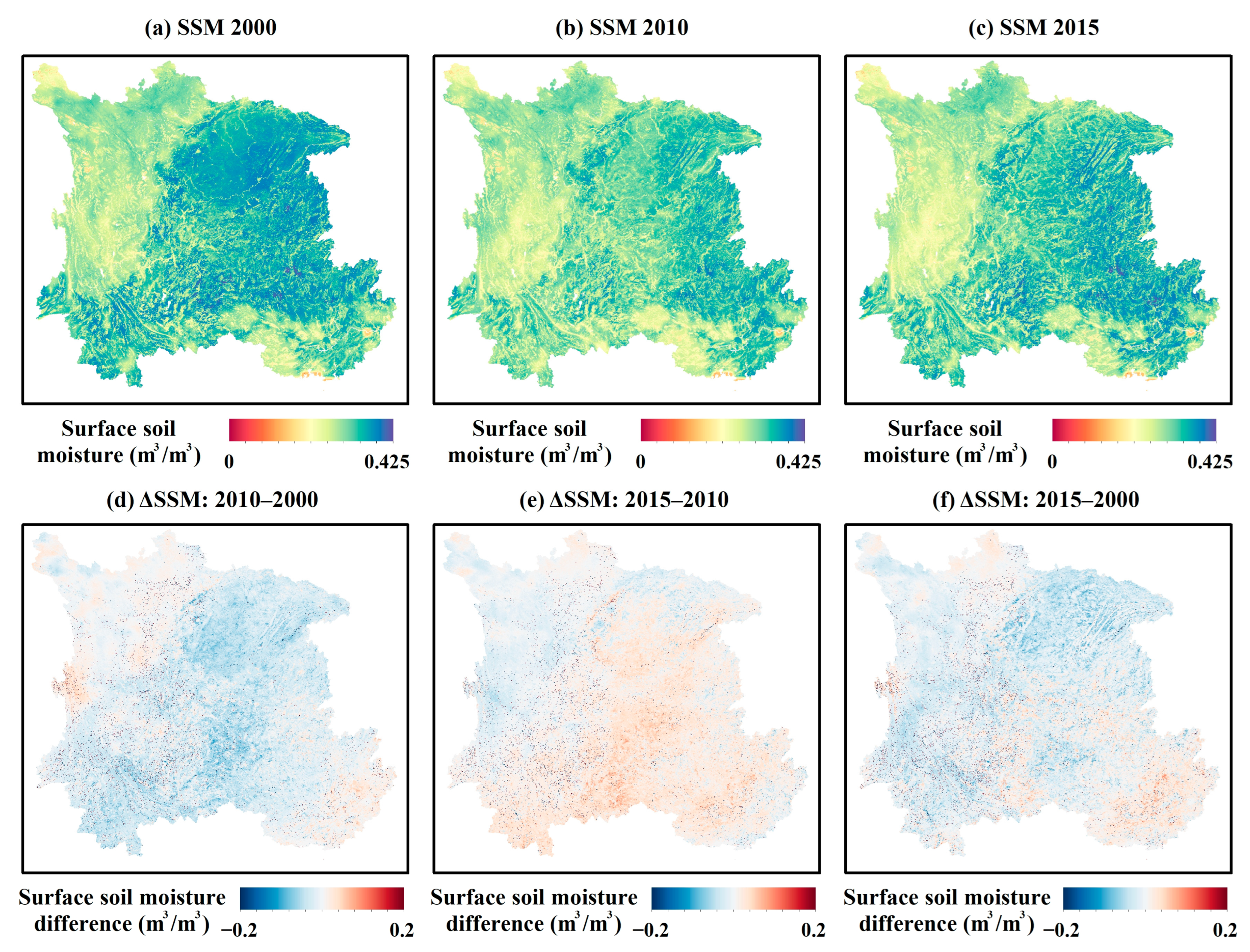
3.1.1. Characteristics of Spatial Distribution
3.1.2. Temporal Patterns Dynamics
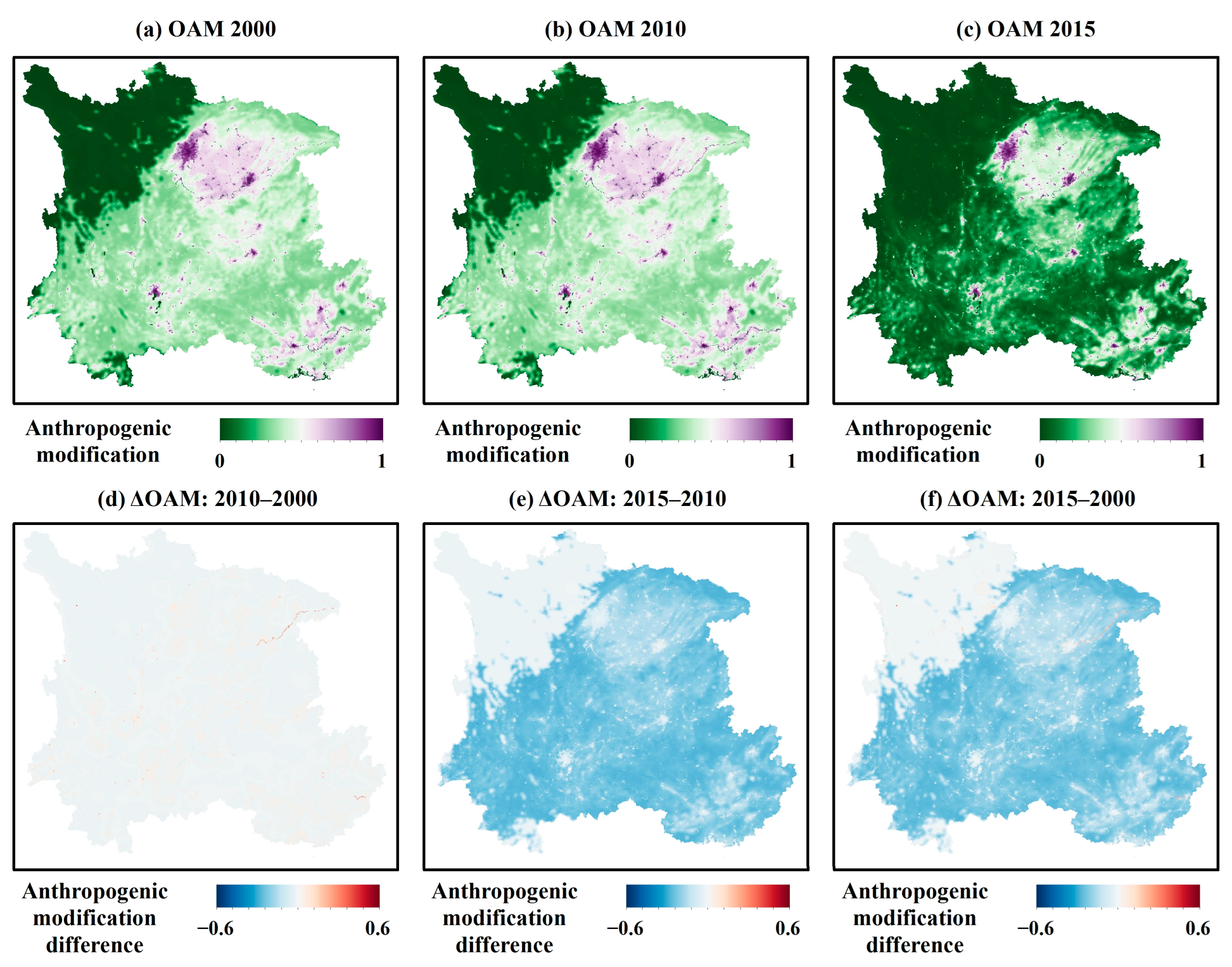
3.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Anthropogenic Modification
3.2.1. Characteristics of Spatial Distribution
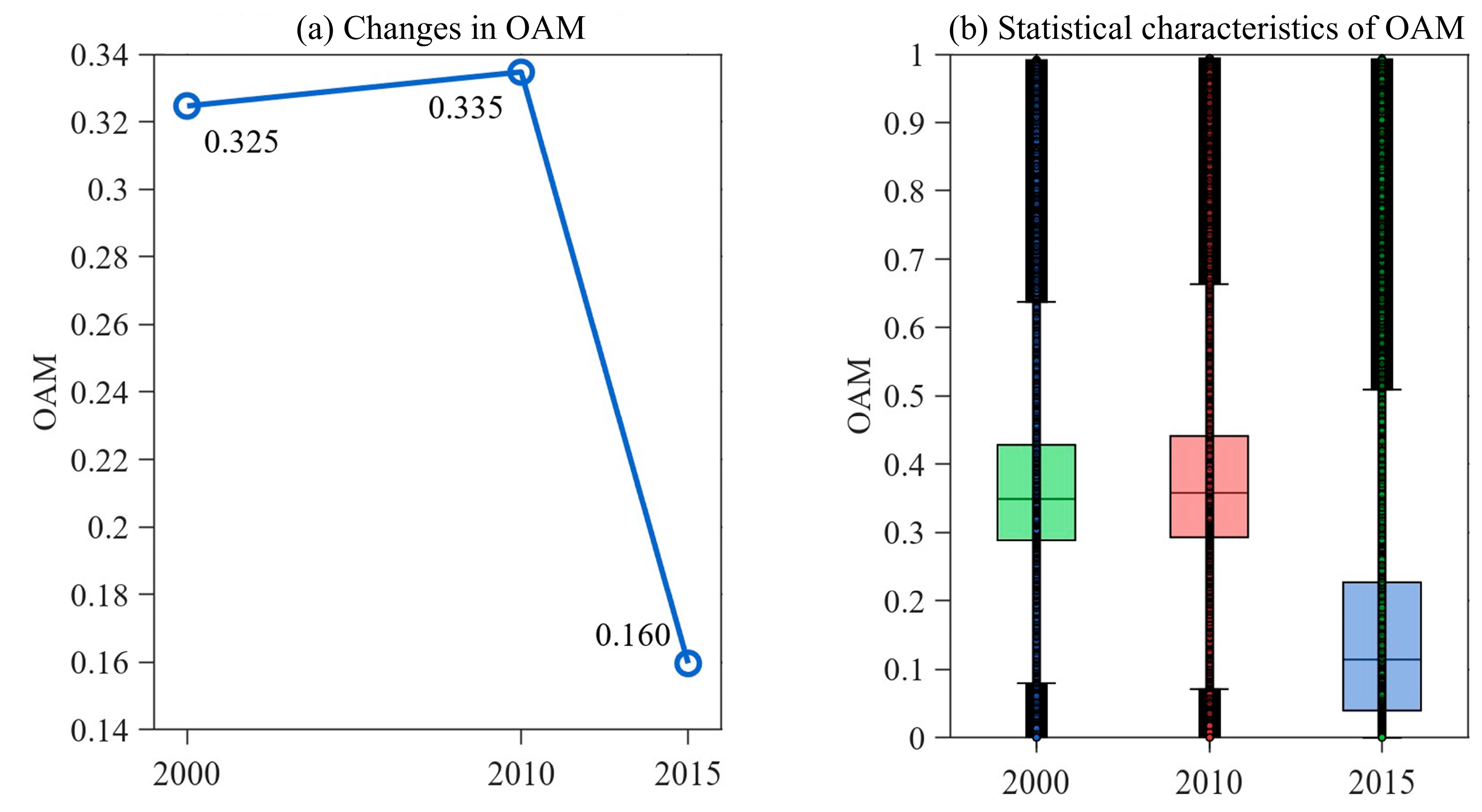
3.2.2. Temporal Patterns Dynamics
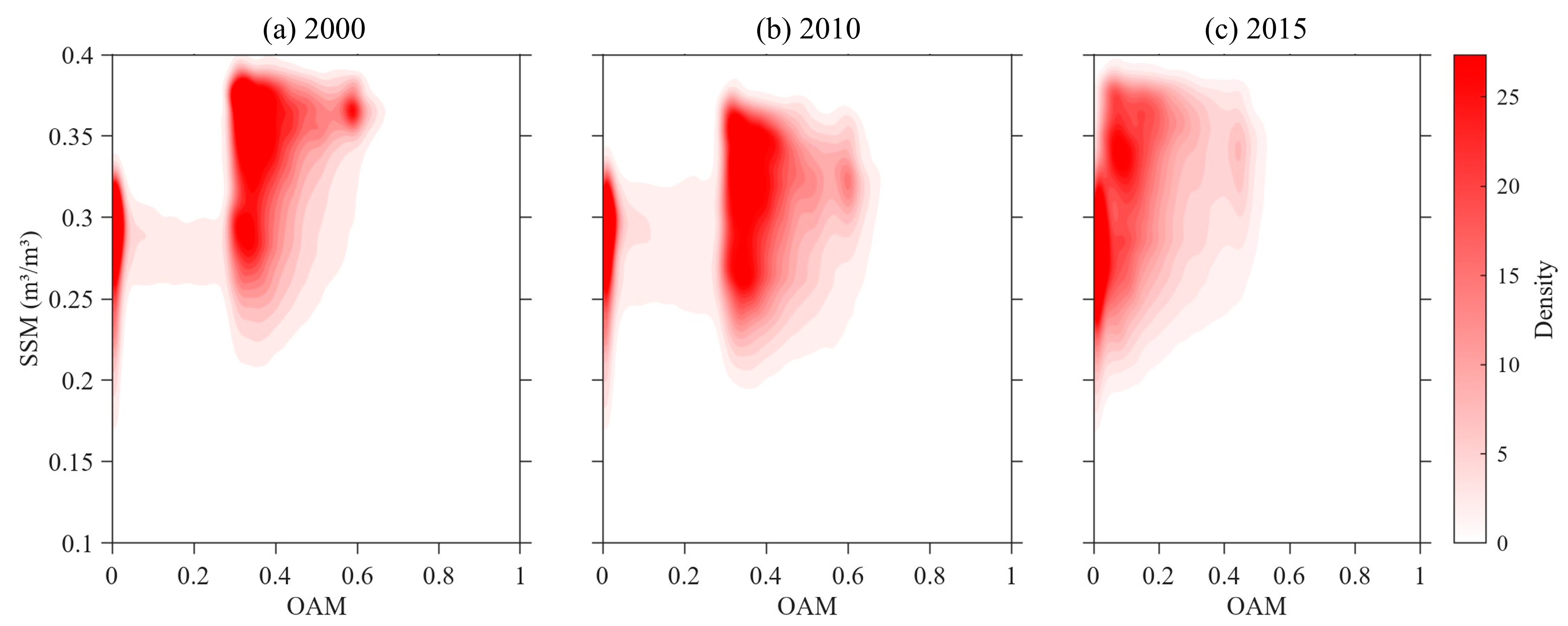
3.3. Impacts of Overall Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture
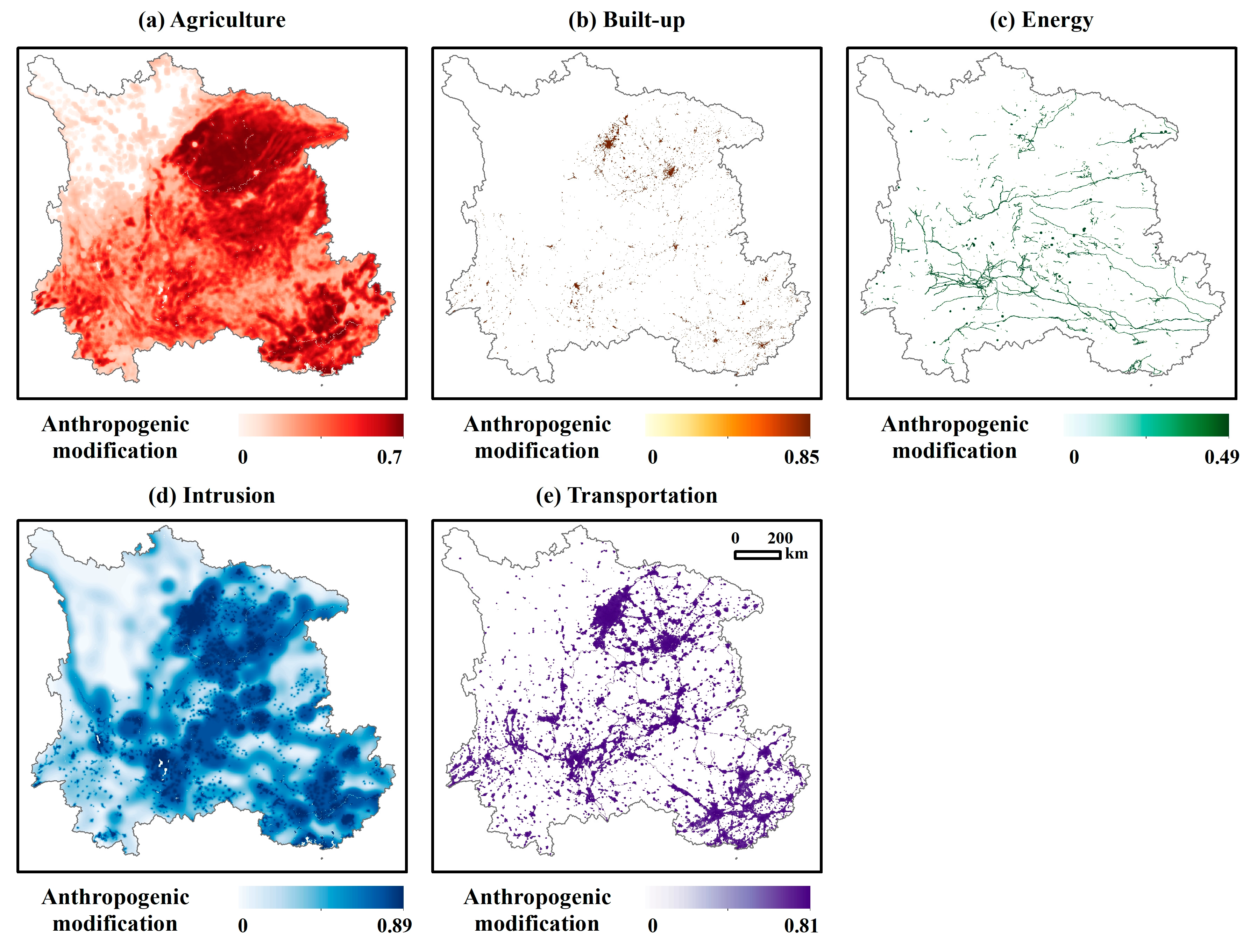
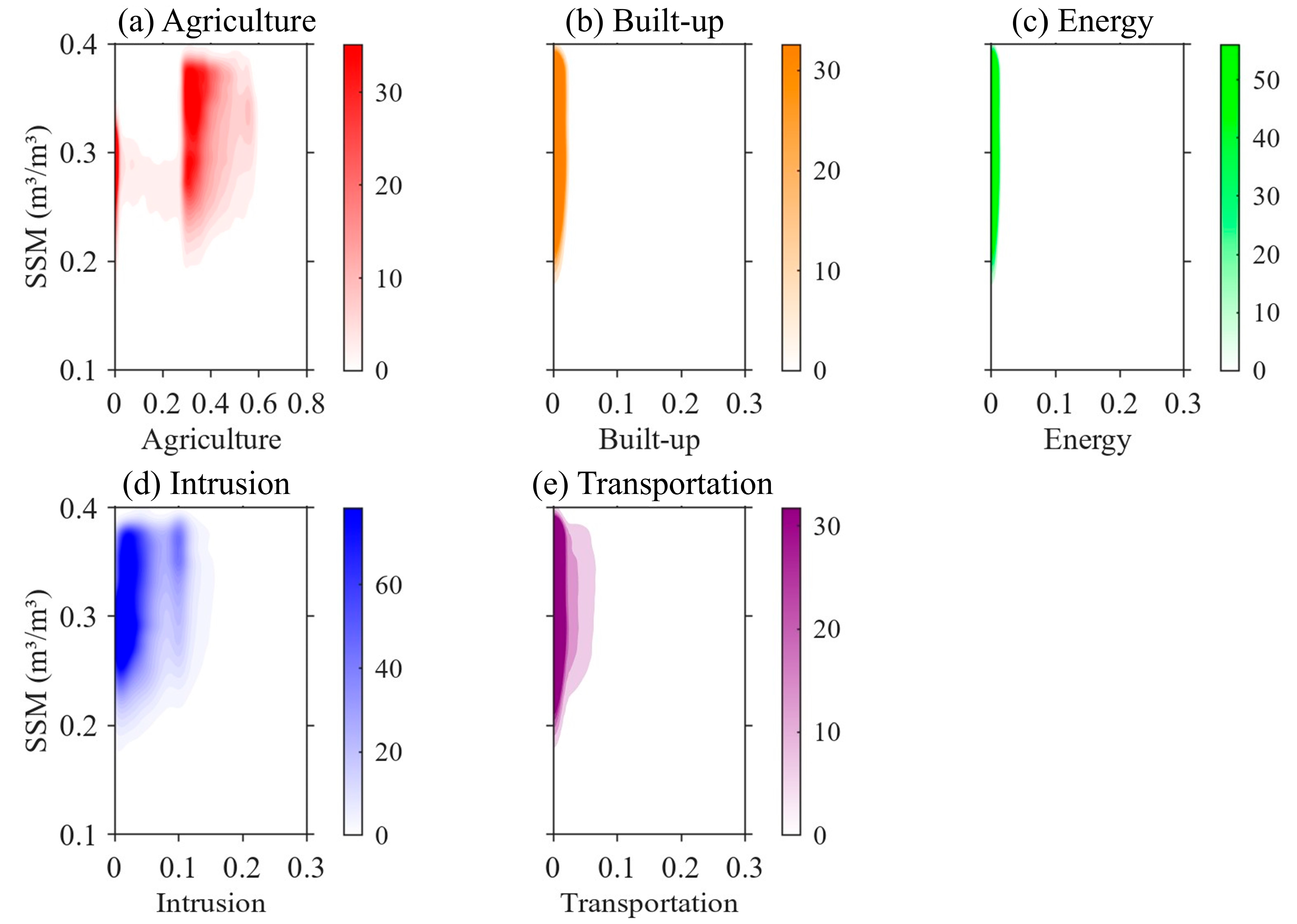
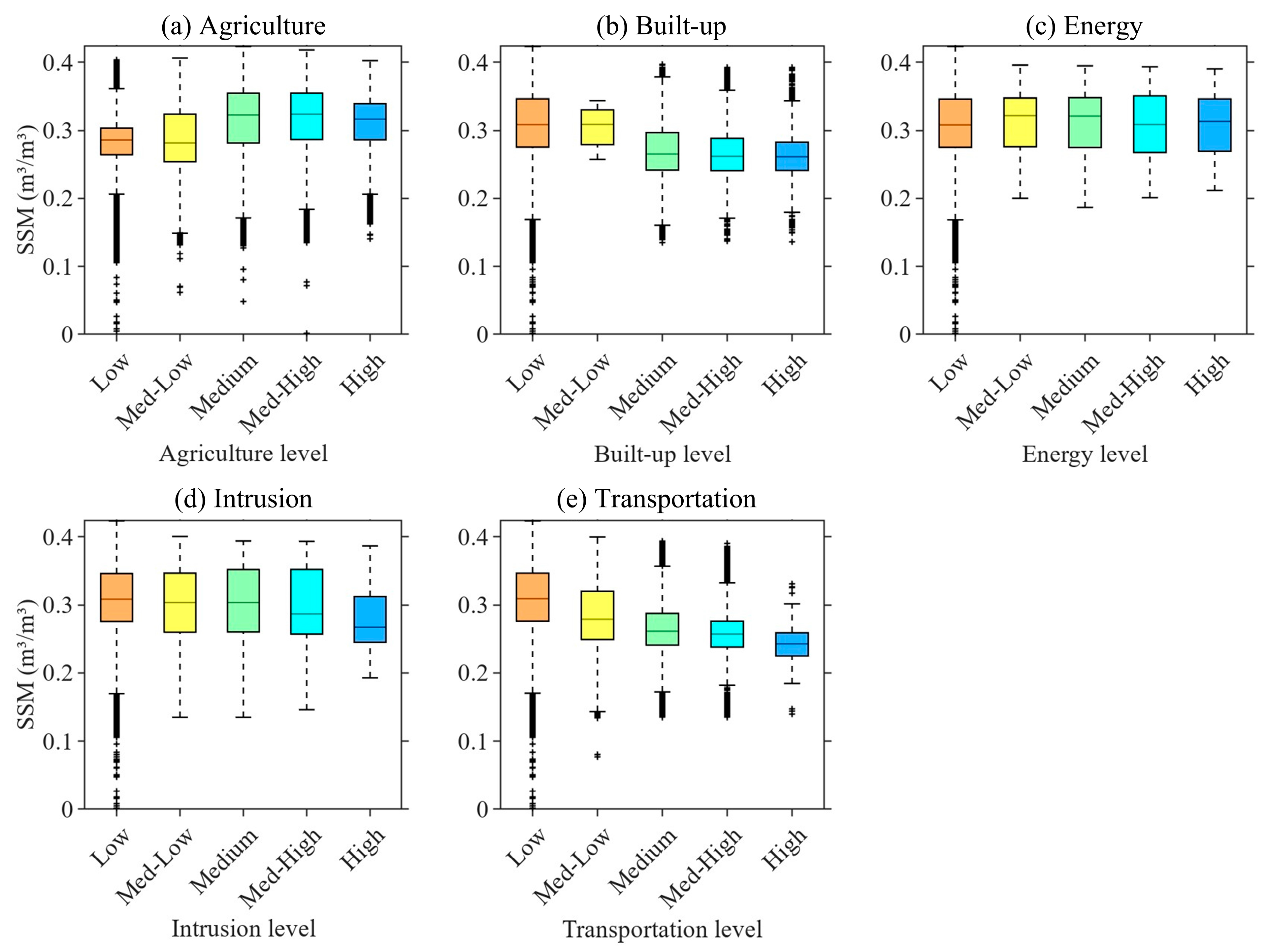
3.4. Impacts of Detailed Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Implications for the Management of Surface Soil Moisture
5. Conclusions
- Our analysis revealed distinct spatiotemporal patterns for both variables. The SSM exhibited persistent spatial heterogeneity, with wetter conditions in the north and northwest and drier conditions in the southeast. Temporally, a slight long-term declining trend (Sen’s slope = −0.0009 m3/m3/year) was observed, characterized by a decrease until ~2011 followed by a gradual recovery. Concurrently, OAM showed a complex non-monotonic trend, intensifying and expanding until 2010 before undergoing a significant decline by 2015. This inverse trajectory post-2010 suggests that large-scale environmental policies, such as the environmental protection projects and Grain-for-Green Program, may have effectively mitigated human pressure, subsequently facilitating a recovery in regional soil moisture conditions.
- More importantly, beyond mere co-variation, our findings uncover a systematic homogenizing effect whereby higher anthropogenic modification intensity corresponds to both elevated median SSM and a reduction in spatial moisture variability. Based on these correlations, we hypothesize that human modification may act as a structural forcing factor that reorganizes soil moisture distribution at the regional scale, though further research is needed to confirm this mechanistic link.
- The differentiated response patterns across stressor types demonstrate that aggregated human footprint indices are insufficient to interpret hydrological impacts. Agricultural modification enhances SSM, while transportation and energy-related disturbances suppress soil moisture, and built-up land reduces spatial variance without a linear effect on median moisture levels.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Niel, T.G.; McVicar, T.R.; Callow, J.N.; Moore, C.E.; Beringer, J.; Cai, D. Water or Energy Supply Driven Change in Moisture Availability Switches the Slope Direction between Shallow Soil Moisture and Actual Evapotranspiration: Interpretation within the Context of the Complementary Relationship. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR039632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Akbar, R.; Konings, A.G.; Yueh, S.; Entekhabi, D. The Global Distribution and Dynamics of Surface Soil Moisture. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Ciais, P.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Gentine, P.; Feldman, A.F.; Makowski, D.; Viovy, N.; Kemanian, A.R.; Goll, D.S.; Stoy, P.C.; et al. Global Critical Soil Moisture Thresholds of Plant Water Stress. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wang, C. The Potential of Urban Irrigation for Counteracting Carbon-Climate Feedback. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, H.; Amelung, W.; Bauke, S.L.; Bogena, H.; Brüggemann, N.; Montzka, C.; Vanderborght, J.; Bechtold, M.; Blöschl, G.; Carminati, A.; et al. Soil Hydrology in the Earth System. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataki, A.; Bertalan, L.; Pásztor, L.; Nagy, L.A.; Abriha, D.; Liang, S.; Singh, S.K.; Szabó, S. Soil Moisture Satellite Data under Scrutiny: Assessing Accuracy through Environmental Proxies and Extended Triple Collocation Analysis. Earth Syst. Environ. 2025, 9, 801–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.W.; Bishop, K.; Zarnetske, J.P.; Minaudo, C.; Chapin, F.S.; Krause, S.; Hannah, D.M.; Conner, L.; Ellison, D.; Godsey, S.E.; et al. Human Domination of the Global Water Cycle Absent from Depictions and Perceptions. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, Q.; Woolway, R.I.; Merder, J.; Rosa, L.; Michalak, A.M. Decoupling of Surface Water Storage from Precipitation in Global Drylands Due to Anthropogenic Activity. Nat. Water 2025, 3, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.F.; Chen, D.; Wang, B.; Ou, T.; Lu, M. Human-Induced Warming Accelerates Local Evapotranspiration and Precipitation Recycling over the Tibetan Plateau. Commun. Earth Environ. 2024, 5, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, Y.; Ma, X. A Review of Soil Moisture Data in China: Definitions, Sources, and Applications in Hydrometeorology Research. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2025, 106, E1108–E1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, F.; Ma, C.; Hou, J.; Zheng, D.; Ma, H.; Bai, Y.; Han, X.; Vereecken, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Land Data Assimilation: Harmonizing Theory and Data in Land Surface Process Studies. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2022RG000801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galelli, S.; Turner, S.W.D.; Pokhrel, Y.; Ng, J.Y.; Castelletti, A.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Pianosi, F.; Biemans, H. Advancing the Representation of Human Actions in Large-Scale Hydrological Models: Challenges and Future Research Directions. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR039486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Mao, H.; Wang, C.; Hu, J.; Ninsawat, S.; Song, X.; Jing, G.; Li, R.; Wang, M.; Duan, Z. Advancing Hydrological Modeling through Multivariate Calibration of Multi-Layer Soil Moisture Dynamics. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckage, B.; Moore, F.C.; Lacasse, K. Incorporating Human Behaviour into Earth System Modelling. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2022, 6, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Gulakhmadov, A.; Niyogi, D.; Chen, N. Global Anthropogenic Effects on Meteorological—Hydrological—Soil Moisture Drought Propagation: Historical Analysis and Future Projection. J. Hydrol. 2025, 653, 132755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.; Shah, H.L.; Dave, H.M.; Mishra, V. Contrasting Influence of Human Activities on Agricultural and Hydrological Droughts in India. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 144959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; He, Y.; Peng, S.; Yang, X. Comprehensive Evaluation of Multisource Soil Moisture Products in a Managed Agricultural Region: An Integrated Hydrologic Modeling Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, V.; Mohanty, B.P.; Reichle, R.H. Rootzone Soil Moisture Dynamics Using Terrestrial Water–energy Coupling. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL110342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Song, J. Variations in Global Soil Moisture during the Past Decades: Climate or Human Causes? Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, e2023WR034915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Liu, Y.; Pan, T.; Tan, Q.; Ma, Z. Evaluating the Effects of Climate Change and Human Activities on the Seasonal Trends and Spatial Heterogeneity of Soil Moisture. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Singh, V.P.; Liu, J.; Sun, P.; Cheng, C. Attribution of Global Soil Moisture Drying to Human Activities: A Quantitative Viewpoint. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, G. Estimation of Global Irrigation Water Use by the Integration of Multiple Satellite Observations. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, J.; Danesh-Yazdi, M. Quantifying the Impacts of Agricultural Alteration and Climate Change on the Water Cycle Dynamics in a Headwater Catchment of Lake Urmia Basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 270, 107749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Luo, H.; Gao, H. Groundwater Infiltration Inverse Estimation in Urban Sewers Network: A Two-Stage Simulation-Optimization Model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 121, 106205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeydalinejad, N.; Javadi, A.A.; Baldock, D.; Webber, J.L. An Integrated Hydrological-Hydrogeological Model for Analysing Spatio-Temporal Probability of Groundwater Infiltration in Urban Infrastructure. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 116, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Choudhury, R.; Nath, B. Quantification of Urban Groundwater Recharge: A Case Study of Rapidly Urbanizing Guwahati City, India. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaBianca, A.; Mortensen, M.H.; Sandersen, P.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Jensen, K.H.; Kidmose, J. Impact of Urban Geology on Model Simulations of Shallow Groundwater Levels and Flow Paths. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Niu, L.; Jia, X.; Yang, T.; Hu, W.; Wu, C.; Chu, J.; Biswas, A.; Shao, M. Disentangling Ecological Restoration’s Impact on Terrestrial Water Storage. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2024GL111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, S.; Wu, X.; Wei, F.; Chen, P.; Grünzweig, J.M. Locating Hydrologically Unsustainable Areas for Supporting Ecological Restoration in China’s Drylands. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Metternicht, G.; Zou, Z.; et al. Ecological Restoration Exacerbates the Agriculture-Induced Water Crisis in North China Region. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 331, 109341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzegari, N.; Bolboli Zadeh, M.; Jimenez Arellano, C.; Afzali Gorooh, V.; Nguyen, P.; Meng, H.; Ferraro, R.R.; Kalluri, S.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K. Passive Microwave Imagers, Their Applications, and Benefits: A Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.M.; Oakleaf, J.R.; Theobald, D.M.; Baruch-Mordo, S.; Kiesecker, J. Managing the Middle: A Shift in Conservation Priorities Based on the Global Human Modification Gradient. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Wen, Y.; Huang, J.; Du, P.; Su, W.; Miao, S.; Geng, M. A Global Record of Annual Terrestrial Human Footprint Dataset from 2000 to 2018. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Jin, Y.; Gu, X.; Yin, W. Climate Change Regionalization in China (1961–2010). Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2676–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.-Q.; Chen, W.-X.; Yang, S.-Q. Observed Climate Changes in Southwest China during 1961–2010. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2013, 4, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Tao, L.; Yang, X.-Q.; Sang, X.; Fang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Yan, H. A Climate Perspective of the Quasi-Stationary Front in Southwestern China: Structure, Variation and Impact. Clim. Dyn. 2022, 59, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-F.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.-Q. Climate Change in Southwest China during 1961–2010: Impacts and Adaptation. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2013, 4, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z.; Xu, X. Spatial Heterogeneity of the Relationship between Vegetation Dynamics and Climate Change and Their Driving Forces at Multiple Time Scales in Southwest China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256–257, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, W.; Piao, J.; Cai, Q.; Chen, S.; Xue, X.; Ma, T. Synergistic Effects of High Atmospheric and Soil Dryness on Record-Breaking Decreases in Vegetation Productivity over Southwest China in 2023. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, X.; Long, X. Trends in Groundwater Changes Driven by Precipitation and Anthropogenic Activities on the Southeast Side of the Hu Line. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 94032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chai, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jin, R.; Xu, Z. Estimating Time Series Soil Moisture by Applying Recurrent Nonlinear Autoregressive Neural Networks to Passive Microwave Data over the Heihe River Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munguía, M.; Trejo, I.; González-Salazar, C.; Pérez-Maqueo, O. Human Impact Gradient on Mammalian Biodiversity. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 6, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukiainen, H.; Alahuhta, J.; Field, R.; Ala-Hulkko, T.; Lampinen, R.; Hjort, J. Spatial Relationship between Biodiversity and Geodiversity across a Gradient of Land-Use Intensity in High-Latitude Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, G.; Xiang, A.; Xiao, S.; Lin, D.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y. Terrain Gradient Response of Landscape Ecological Environment to Land Use and Land Cover Change in the Hilly Watershed in South China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Feng, H.; Yao, L.; Li, X.; Du, H.; Liu, Y. Landscape Ecological Risk and Drivers of Land-Use Transition under the Perspective of Differences in Topographic Gradient. Land 2024, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Jia, L.; Zhao, T. A 21-Year Dataset (2000–2020) of Gap-Free Global Daily Surface Soil Moisture at 1-Km Grid Resolution. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theobald, D.M.; Kennedy, C.; Chen, B.; Oakleaf, J.; Baruch-Mordo, S.; Kiesecker, J. Earth Transformed: Detailed Mapping of Global Human Modification from 1990 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 1953–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the Regression Coefficient Based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akritas, M.G.; Murphy, S.A.; Lavalley, M.P. The Theil-Sen Estimator with Doubly Censored Data and Applications to Astronomy. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Leblanc, S.G. Parametric (Modified Least Squares) and Non-Parametric (Theil–Sen) Linear Regressions for Predicting Biophysical Parameters in the Presence of Measurement Errors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhao, T.; Lü, H.; Shi, J.; Cosh, M.H.; Ji, D.; Jiang, L.; Cui, Q.; Lu, H.; Yang, K.; et al. Assessment of 24 Soil Moisture Datasets Using a New in Situ Network in the Shandian River Basin of China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Chai, L.; Crow, W.T.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Qu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, Z. Applying a Wavelet Transform Technique to Optimize General Fitting Models for SM Analysis: A Case Study in Downscaling over the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavagnini, I.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Magno, F. Theil–Sen Nonparametric Regression Technique on Univariate Calibration, Inverse Regression and Detection Limits. Talanta 2011, 87, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehboob, M.S.; Kim, Y. Impact of Climate Change on the Hydrological Projections over a Western Himalayan River Basin and the Associated Uncertainties. J. Hydrol. 2024, 628, 130460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Chai, L.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, T. Reconstruction of Time-Series Soil Moisture from AMSR2 and SMOS Data by Using Recurrent Nonlinear Autoregressive Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 980–983. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Ma, J.; Yan, P.; Tian, F.; Peñuelas, J.; Rao, M.P.; Fu, Y.; Hu, Z. Planted Forests in China Have Higher Drought Risk than Natural Forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Peng, S.; Wu, T.; Lei, J.; Wei, J.; Yang, X. Effects of Irrigation and Canal Networks on Groundwater–Land Surface Interactions in the Middle Heihe River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 60, 102532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, I.M.; Maxwell, R.M. Hydrologic and Land–Energy Feedbacks of Agricultural Water Management Practices. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 014006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, I.M.; Maxwell, R.M. Human Impacts on Terrestrial Hydrology: Climate Change versus Pumping and Irrigation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 044022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, L.E.; Maxwell, R.M. Groundwater-Fed Irrigation Impacts Spatially Distributed Temporal Scaling Behavior of the Natural System: A Spatio-Temporal Framework for Understanding Water Management Impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.M.; Condon, L.E. Connections between Groundwater Flow and Transpiration Partitioning. Science 2016, 353, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.M.F.; Tijerina, D.T.; Condon, L.E.; Maxwell, R.M. Assessment of the ParFlow–CLM CONUS 1.0 Integrated Hydrologic Model: Evaluation of Hyper-Resolution Water Balance Components across the Contiguous United States. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 7223–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, N.; Guo, S.; Yue, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhu, B.; Yu, X. Irrigation Strategy Optimization in Irrigation Districts with Seasonal Agricultural Drought in Southwest China: A Copula-Based Stochastic Multiobjective Approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 282, 108293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Xu, L.; Yang, M.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Migration of Microplastics in Surface Water, Groundwater and Sediment in Karst Areas: The Case of Yulong River in Guilin, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Liu, J.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, C.; Liu, Y. Understanding Urban Expansion Combining Macro Patterns and Micro Dynamics in Three Southeast Asian Megacities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Su, X.; Fan, C.; Han, H. Quantifying Residential Cooling Poverty and Its Drivers in China (2001–2020): Insights from Multiple Restrictive Behaviors of Accessing Air Conditioning. Cities 2025, 166, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Qiao, R.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wan, W.; Sun, X. Heterogeneous Residential Location Effects: Variations in How Suburban Communities Shape Older Adults’ Active Travel—A Case Study from Xiamen. Cities 2025, 160, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, C.A.; Lenton, T.M.; Boers, N. Reply to: Little Evidence That Amazonian Rainforests Are Approaching a Tipping Point. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 13, 1321–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Wang, T.; Yang, D.; Tang, L.; Yang, Y. Substantial Increases in Compound Climate Extremes and Associated Socio-Economic Exposure across China under Future Climate Change. npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2025, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ord, J.K.; Getis, A. Local Spatial Autocorrelation Statistics: Distributional Issues and an Application. Geogr. Anal. 1995, 27, 286–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, S.; Hamidi, S.A.; Ghanbari, R.N. Climate Variability and Anthropogenic Effects on Lake Urmia Water Level Fluctuations, Northwestern Iran. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, L.L.; Nian, D.; Bathiany, S.; Ben-Yami, M.; Smith, T.; Boulton, C.A.; Boers, N. Spatial Correlation Increase in Single–sensor Satellite Data Reveals Loss of Amazon Rainforest Resilience. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2023EF004040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Tong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y. What Is the Quality of Urban Expansion under Different Expansion Patterns? A Study of Chinese Cities. Cities 2026, 168, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Huffman, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, J. Influence of Topography and Land Management on Soil Nutrients Variability in Northeast China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 89, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Rong, L.; Zhang, G.; Hu, J.; Fang, H. Soil Productivity in the Yunnan Province: Spatial Distribution and Sustainable Utilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 147, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, K. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Soil Properties along an Elevation Gradient in the Karst Region of Southwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 320, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhou, L.; He, X.; Wei, P.; Lin, D.; Qian, S.; Zhao, L.; Luo, M.; Yin, X.; Zeng, L.; et al. Effects of Elevation Gradient on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen in a Typical Karst Region of Chongqing, Southwest China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2021JG006742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Lin, J.; Wu, T.; Yuan, Z.; Cao, W. Assessing Flood and Waterlogging Vulnerability and Community Governance in Urban Villages in the Context of Climate Change: A Case Study of 89 Urban Villages in Shanghai. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 126, 106377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Sehgal, V.; Alvarez, L.V.; Brocca, L.; Cai, S.; Cheng, R.; Cheng, X.; Du, J.; El Masri, B.; Endsley, K.A.; et al. Remotely Sensed High–resolution Soil Moisture and Evapotranspiration: Bridging the Gap between Science and Society. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR037929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yang, X. Effects of Microtopography on Patterns and Dynamics of Groundwater–Surface Water Interactions. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 188, 104704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, C.; Horton, D.E.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Niyogi, D.; Xia, J.; Chen, N. Widespread Global Exacerbation of Extreme Drought Induced by Urbanization. Nat. Cities 2024, 1, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, K.A.; Kumar, M. Imprint of Urbanization on Snow Precipitation over the Continental USA. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, D.; Meng, S.; Kou, X.; Jiao, L. Exploration of Spatiotemporal Covariation in Vegetation–Groundwater Relationships: A Case Study in an Endorheic Inland River Basin. Land 2025, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Shen, C.; Zhan, C.; Tang, H.; Luo, C.; Meng, S.; An, Y.; Wang, H.; Kou, X. Quantifying Multifactorial Drivers of Groundwater–Climate Interactions in an Arid Basin Based on Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, P.; Tian, S.; Duvert, C.; Wurm, P.; Riwu Kaho, N.; Edwards, A. Detecting Groundwater Dependence and Woody Vegetation Restoration with NDVI and Moisture Trend Analyses in an Indonesian Karst Savanna. Front. Remote Sens. 2024, 5, 1280712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wei, J.; Yang, X. Effects of Hydraulic Conductivity on Simulating Groundwater–Land Surface Interactions over a Typical Endorheic River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Wu, T.; Lei, J.; Yang, X. Assessing a High-Resolution Integrated Hydrologic Model (ParFlow-CLM-HRB) in an Endorheic Basin of China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Original Spatial Coverage | Original Spatial Resolution | Original Temporal Coverage | Original Temporal Resolution | Literature | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface soil moisture | Global | 30 arc-second | 2000–2020 | Daily/monthly | [46] |
| Anthropogenic modification | Global | 300 m | 1990, 2000, 2010, 2015, 2017 | - | [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, C.; Qin, C.; Lu, Z.; Ning, D.; Zang, Z.; Tang, H.; Pan, F.; Cheng, G.; Hu, J.; Meng, S. Assessing Impacts of Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Case Study over Southwest China. Hydrology 2025, 12, 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12110275
Shen C, Qin C, Lu Z, Ning D, Zang Z, Tang H, Pan F, Cheng G, Hu J, Meng S. Assessing Impacts of Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Case Study over Southwest China. Hydrology. 2025; 12(11):275. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12110275
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Chunying, Changrui Qin, Zheng Lu, Dehui Ning, Zhenxiang Zang, Honglei Tang, Feng Pan, Guaimei Cheng, Jimin Hu, and Shasha Meng. 2025. "Assessing Impacts of Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Case Study over Southwest China" Hydrology 12, no. 11: 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12110275
APA StyleShen, C., Qin, C., Lu, Z., Ning, D., Zang, Z., Tang, H., Pan, F., Cheng, G., Hu, J., & Meng, S. (2025). Assessing Impacts of Anthropogenic Modification on Surface Soil Moisture Dynamics: A Case Study over Southwest China. Hydrology, 12(11), 275. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12110275







