Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Impact Factors in the Mainstream Basin of the Tarim River from 1980 to 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
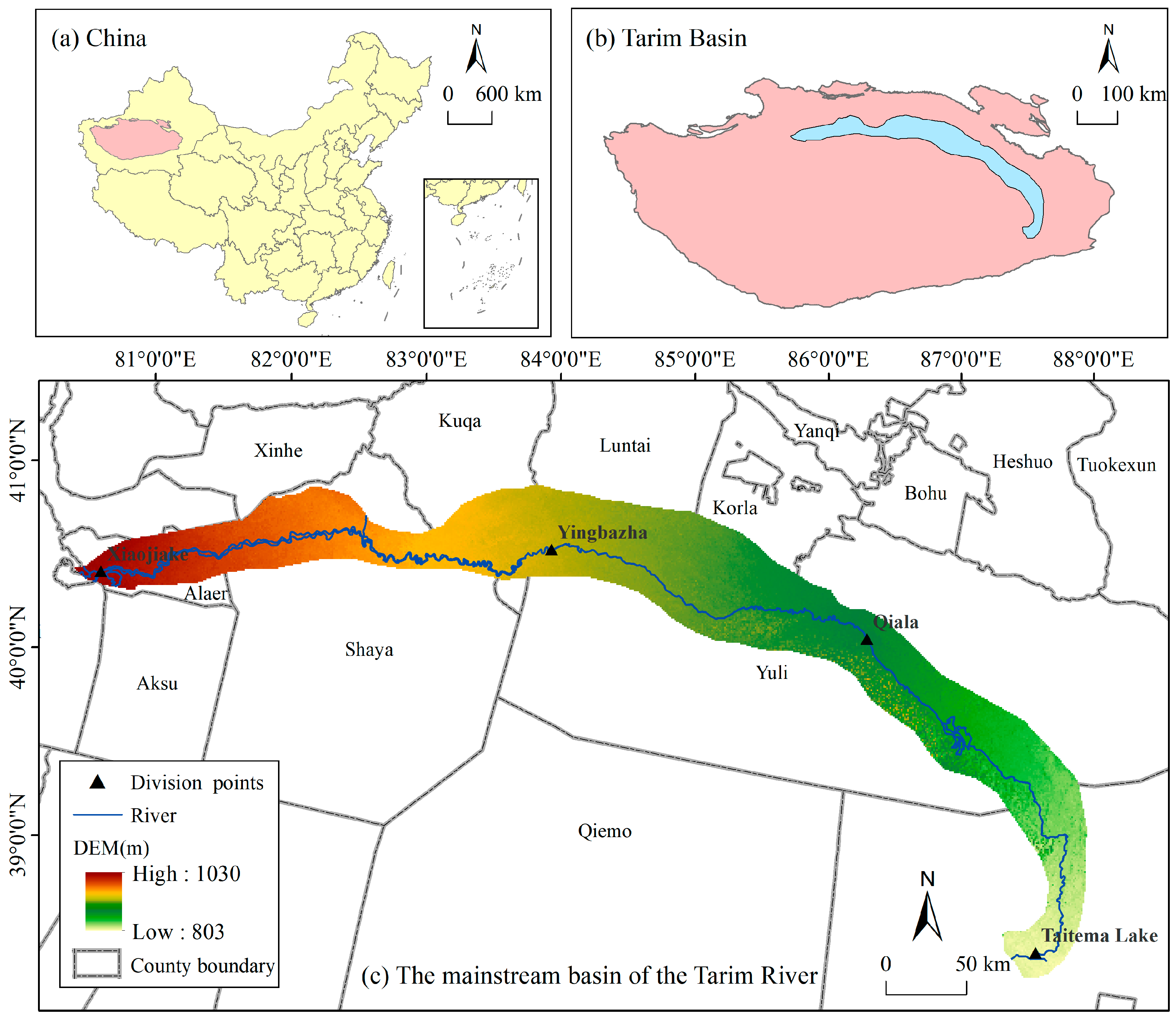
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Landscape Classification
2.3. Data Source
2.4. Research Methodology
2.4.1. Landscape Pattern Indices
2.4.2. Canonical Correspondence Analysis
2.4.3. Bivariate Local Spatial Autocorrelation
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Landscape Evolution Analysis
3.1.1. Characteristics of Landscape’s Spatiotemporal Evolution
3.1.2. Characteristics of Landscape Transfer
3.2. Landscape Pattern Analysis
3.2.1. Landscape Pattern Analysis at Class Level
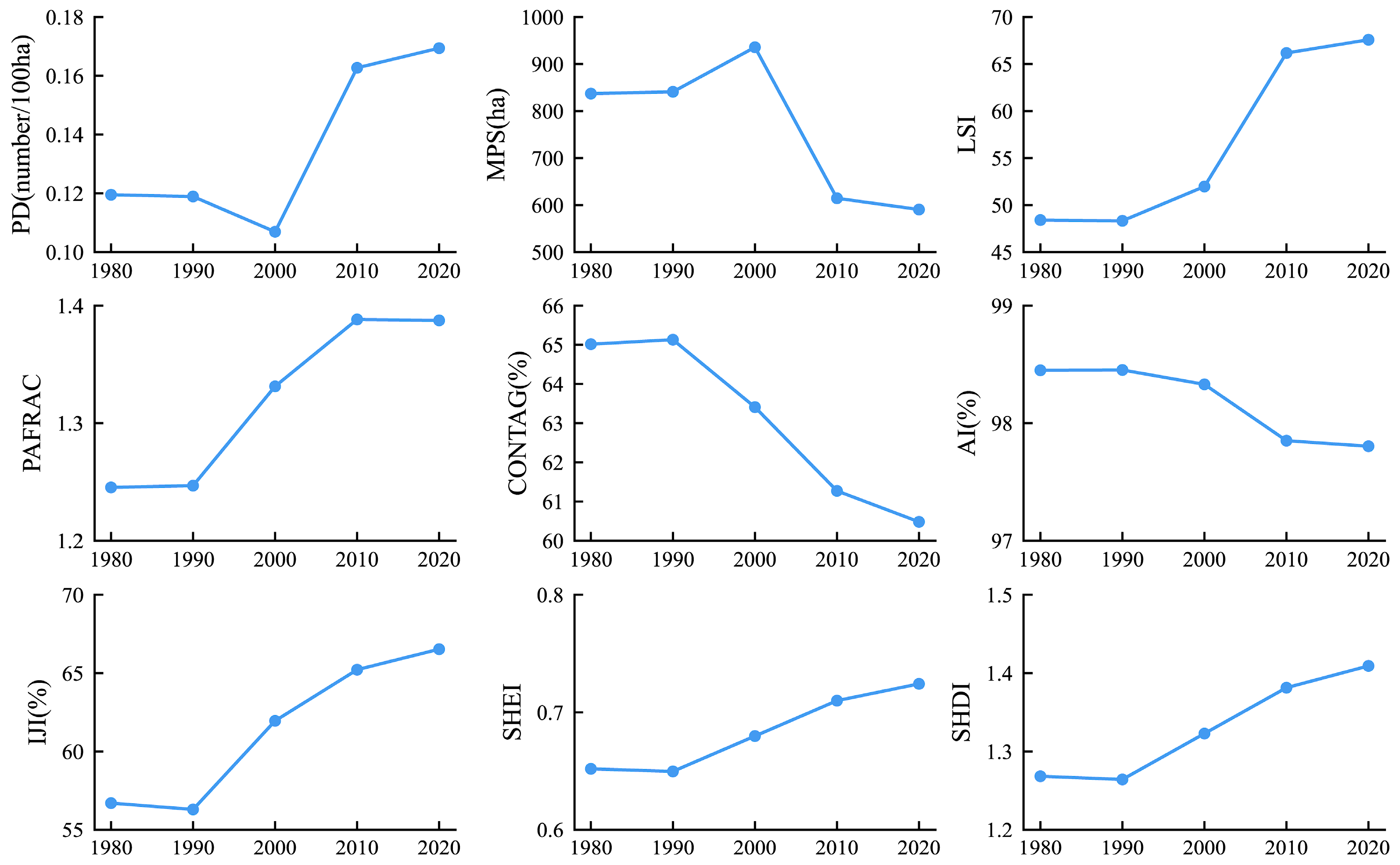
3.2.2. Landscape Pattern Analysis at Landscape Level
3.3. Analysis of Factors Influencing Landscape Pattern
3.3.1. Feasibility Analysis of CCA
3.3.2. CCA of the Landscape Area Shares and Impact Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Driving Factors of Landscape Pattern
4.2. Impact of Policies on Landscape Pattern
4.3. Suggestions to Improve Ecological Conditions of MBTR
4.4. Limitations and Prospects
4.4.1. Determination of Optimal Landscape Scale
4.4.2. Selection and Expansion of Impact Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schaubroeck, T.; Deckmyn, G.; Giot, O.; Campioli, M.; Vanpoucke, C.; Verheyen, K.; Rugani, B.; Achten, W.; Verbeeck, H.; Dewulf, J.; et al. Environmental impact assessment and monetary ecosystem service valuation of an ecosystem under different future environmental change and management scenarios; a case study of a Scots pine forest. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Chakraborti, S.; Joshi, P.K.; Keesstra, S.; Sen, S.; Paul, S.K.; Kreuter, U.; Sutton, P.C.; Jha, S.; Dang, K.B. Ecosystem service value assessment of a natural reserve region for strengthening protection and conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Jing, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y. Intermediate human activities maximize dryland ecosystem services in the long-term land-use change: Evidence from the Sangong River watershed, northwest China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziter, C.D.; Pedersen, E.J.; Kucharik, C.J.; Turner, M.G. Scale-dependent interactions between tree canopy cover and impervious surfaces reduce daytime urban heat during summer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 7575–7580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Cao, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, B. The impacts of landscape patterns spatio-temporal changes on land surface temperature from a multi-scale perspective: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 821, 153381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Mondal, P.; Sutradhar, S.; Ghosh, R. Assessment of variation of land use/land cover and its impact on land surface temperature of Asansol subdivision. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2021, 24, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Tian, P.; Mu, X.; Tian, X. Linkages between soil erosion and long-term changes of landscape pattern in a small watershed on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Catena 2023, 220, 106659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yu, D.; Li, X. Impacts of changes in climate and landscape pattern on soil conservation services in a dryland landscape. CATENA 2023, 222, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Z. The grassland farming system and sustainable agricultural development in China. Grassl. Sci. 2005, 51, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; He, G.; Wang, G. Spatial-temporal analysis of the changes in Populus euphratica distribution in the Tarim National Nature Reserve over the past 60 years. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 113, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, G.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Raven, P.H. Vertebrates on the brink as indicators of biological annihilation and the sixth mass extinction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13596–13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Yuan, Z.; Ye, B.; Zhu, F.; Chu, Z.; Liu, X. Impacts of landscape pattern on plants diversity and richness of 20 restored wetlands in Chaohu Lakeside of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Ran, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment for the Tarim River Basin on the Basis of Land-Use Change. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Baldi, G.; Hirota, M.; Syktus, J.; McAlpine, C. Land use and land cover change impacts on the regional climate of non-Amazonian South America: A review. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2015, 128, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, D.; Chen, K. Evolution and Prediction of Landscape Patterns in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Land 2021, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitiyiming, M.; Ghulam, A.; Tiyip, T.; Pla, F.; Latorre-Carmona, P.; Halik, Ü.; Sawut, M.; Caetano, M. Effects of green space spatial pattern on land surface temperature: Implications for sustainable urban planning and climate change adaptation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 89, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; You, Z. Scientific connotation and practical paths about the principle of ‘taking mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes, and grasslands as a life community’. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2019, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Zhong, X.; Deng, S.; Nie, S. Impact of LUCC on landscape pattern in the Yangtze River Basin during 2001–2019. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 69, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wan, W.; Fan, H.; Dong, X.; Lv, T. Evaluating temporal and spatial responses of landscape patterns to habitat quality changes in the Poyang Lake region, China. J. Nat. Conserv. 2023, 77, 126546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Gu, Y.; Yan, J.; Yuan, R.; Shi, Y. Spatial-temporal changes of land use/cover change and habitat quality in Sanjiang plain from 1985 to 2017. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1032584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Gao, L.; Hu, J. Spatiotemporal evolution and impact mechanism of ecological vulnerability in the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 157, 111214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Z.; Zou, X.; Zuo, P.; Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Impact of landscape patterns on ecological vulnerability and ecosystem service values: An empirical analysis of Yancheng Nature Reserve in China. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 72, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, H.; Chuai, X.; Dai, C.; Lai, L.; Zhang, M. The impact of land use change on the temporospatial variations of ecosystems services value in China and an optimized land use solution. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 44, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.G.E.; Suarez-Castro, A.F.; Martinez-Harms, M.; Maron, M.; McAlpine, C.; Gaston, K.J.; Johansen, K.; Rhodes, J.R. Reframing landscape fragmentation’s effects on ecosystem services. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Kang, J.; Wang, Y. Distinguishing the relative contributions of landscape composition and configuration change on ecosystem health from a geospatial perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 165002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansori, M.; Badehian, Z.; Ghobadi, M.; Maleknia, R. Assessing the environmental destruction in forest ecosystems using landscape metrics and spatial analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.; Li, B. Study on soil erosion and its driving factors from the perspective of landscape in Xiushui watershed, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Li, C.; Du, J.; He, P.; Zhong, S.; Wu, P.; Lu, H.; Fang, S. Quantifying the dynamics and driving forces of the coastal wetland landscape of the Yangtze River Estuary since the 1960s. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 32, 100854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lausch, A.; Blaschke, T.; Haase, D.; Herzog, F.; Syrbe, R.-U.; Tischendorf, L.; Walz, U. Understanding and quantifying landscape structure—A review on relevant process characteristics, data models and landscape metrics. Ecol. Model. 2015, 295, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-C. Spatiotemporal changes of landscape pattern in response to urbanization. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 81, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, H.; Eddine Lakraychi, A.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zheng, H.; Han, X.; Shan, X.; He, C.; Yao, Y. Electrochemical swelling induced high material utilization of porous polymers in magnesium electrolytes. Mater. Today 2022, 55, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Dong, C.; Kang, X.; Qian, X.; Gu, L. Spatiotemporal evolution of land cover changes and landscape ecological risk assessment in the Yellow River Basin, 2015–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, L.; Liang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Gou, Y.; et al. Dynamic landscapes and the influence of human activities in the Yellow River Delta wetland region. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 166239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, F.; Kung, H.-t.; Johnson, V.C.; Bane, C.S.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of land cover and landscape change patterns in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, China from 1972 to 2013. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 25, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plexida, S.G.; Sfougaris, A.I.; Ispikoudis, I.P.; Papanastasis, V.P. Selecting landscape metrics as indicators of spatial heterogeneity—A comparison among Greek landscapes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Lin, Q.; Hao, J.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lou, P.; Liu, Y. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment and Analysis of Influencing Factors in Selenga River Basin. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berihun, M.L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Masunaga, T.; Fenta, A.A.; Sultan, D.; Yibeltal, M. Exploring land use/land cover changes, drivers and their implications in contrasting agro-ecological environments of Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasser, E.; Leitinger, G.; Tappeiner, U. Climate change versus land-use change—What affects the mountain landscapes more? Land Use Policy 2017, 60, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Tan, Z. Dynamic landscapes and the driving forces in the Yellow River Delta wetland region in the past four decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Carl Johnson, V.; Duan, P.; Kung, H.-t. Spatio-temporal variation of oasis landscape pattern in arid area: Human or natural driving? Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Qiao, J. Underlying the influencing factors behind the heterogeneous change of urban landscape patterns since 1990: A multiple dimension analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 108967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Liu, J. Integrated geographical environment factors explaining forest landscape changes in Luoning County in the middle reaches of the Yiluo River watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes, N.B.P.; Sendra, J.B.; Delgado, M.G.; Plata, R.F. Exploring the driving forces behind deforestation in the state of Mexico (Mexico) using geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2010, 30, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Liang, H.; Liang, W.; Zhang, C. Cultivated land fragmentation and affecting factors of Lulong County based on landscape pattern. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 265–269+276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Niu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Evolution of farmland landscape fragmentation and its driving factors in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, A.; Wang, J. Quantitative study on spatio-temporal evolution and mechanisms of wetland landscape patterns in Shanghai. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2622–2631. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Wei, F.; Xia, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Mu, X.; XU, D. Landscape pattern evolution and driving forces of land use in Kuye River Basin from 1980 to 2020. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 30, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, D.; Cao, A. Analysis of the heterogeneity of landscape risk evolution and driving factors based on a combined GeoDa and Geodetector model. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, O.P.; Sharma, C.M.; Rana, Y.S.; Krishan, R. Disturbance, diversity, regeneration and composition in temperate forests of Western Himalaya, India. J. For. Environ. Sci. 2019, 35, 6–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, C.-F.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.-S.; Shao, H.-B.; Wu, S.-F. Spatial distribution of biological soil crusts on the slope of the Chinese Loess Plateau based on canonical correspondence analysis. Catena 2016, 137, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Mi, K.; Qing, F.; Xue, D. Identification of the main factors determining landscape metrics in semi-arid agro-pastoral ecotone. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 124, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhanf, B.; Jin, X.; Weng, B.; Yan, D.; Bao, S. Spatial gradients pattern of landscapes and their relations with environmental factors in Haihe River basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 1925–1935. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hao, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z. Study on water system connectivity and ecological protection countermeasures of Tarim River Basin in Xinjiang. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2019, 34, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Jiao, A.; Wang, W.; Chen, C.; Ling, H.; Yan, J.; Chen, F. Change and Driving Factor Analysis of Eco-Environment of Typical Lakes in Arid Areas. Water 2023, 15, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, J.; Ling, H.; Han, F.; Kong, Z.; Wang, W. Function zoning based on spatial and temporal changes in quantity and quality of ecosystem services under enhanced management of water resources in arid basins. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Ma, X.; Yan, W.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Luo, C.; Yu, W.; Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Trade-offs and synergies among ecosystem services in Inland River Basins under the influence of ecological water transfer project: A case study on the Tarim River basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, Y.; Fu, A. Climate change may accelerate the decline of desert riparian forest in the lower Tarim River, Northwestern China: Evidence from tree-rings of Populus euphratica. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 105997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, C.; Hao, X.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, C. Fifty-year climate change and its effect on annual runoff in the Tarim River Basin, China. Quat. Int. 2009, 208, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Chen, L.; Sun, H.; Liao, W.; Chen, H.; Wei, G.; Zhang, W.; Tuo, Y. Allocation of ecological water rights considering ecological networks in arid watersheds: A framework and case study of Tarim River basin. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 267, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Beeton, R.J.S.; Carter, R.W.; Dong, X.G.; Li, X. Response to environmental flows in the lower Tarim River, Xinjiang, China: Ground water. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 83, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, Q. Expressing the spatio-temporal pattern of farmland change in arid lands using landscape metrics. J. Arid Environ. 2016, 124, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, D.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, K. Changes of wetland landscape pattern in the middle and lower reaches of the Tarim River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2006, 26, 3470–3478. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, Y.; Xia, Z. Assessment of the irrigation water requirement and water supply risk in the Tarim River Basin, Northwest China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Effects of land use/cover change on soil organic carbon storage in the main stream of Tarim River. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2784–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, H.; Guo, B.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Deng, X. Evaluation of the ecological protective effect of the “large basin” comprehensive management system in the Tarim River basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 1696–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhao, C.; Ma, X.; Shi, F.; Wu, S.; Zhu, J. Optimization of land use structure based on ecosystem service value in the mainstream of Tarim river. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shen, Y.; Pei, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y. Revegetation projects significantly improved ecosystem service values in the agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China in recent 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Kung, H.-T.; Johnson, V.C. Assessment of Land-Cover/Land-Use Change and Landscape Patterns in the Two National Nature Reserves of Ebinur Lake Watershed, Xinjiang, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Niu, C.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Cui, Y. Spatiotemporal patterns and modifiable areal unit problems of the landscape ecological risk in coastal areas: A case study of the Shandong Peninsula, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Hua, S.; Zeng, G.; Yuan, Y.; Lai, X.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Yu, X. Application of weight method based on canonical correspondence analysis for assessment of Anatidae habitat suitability: A case study in East Dongting Lake, Middle China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 77, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995–2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaither, C.J.; Poudyal, N.C.; Goodrick, S.; Bowker, J.M.; Malone, S.; Gan, J. Wildland fire risk and social vulnerability in the Southeastern United States: An exploratory spatial data analysis approach. For. Policy Econ. 2011, 13, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L. The Moran Scatterplot as an ESDA Tool to Assess Local Instability in Spatial Association. Regional Research Institute, West Virginia University: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1993; pp. 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; Yi, L.; Liu, F. Multitemporal analysis of cropland transition in a climate-sensitive area: A case study of the arid and semiarid region of northwest China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Wang, X.; Shi, M. Human Driving Forces of Oasis Expansion in Northwestern China During the Last Decade-A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin: Human Driving Forces of Oasis Expansion in Northwestern China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Hai, W.; Tang, M.; Song, J.; Quan, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y. Spatiotemporal evolution law and driving mechanism of production–living–ecological space from 2000 to 2020 in Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W. Groundwater recharge in the oasis-desert areas of northern Tarim Basin, Northwest China. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Chi, C.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S. Analysis of change characteristics and mutation on climate in the main stream of tarim river. J. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 36, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Yimit, H.; Li, X. Analysis on the change of cultivated land in the Hetian district. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 12, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Halik, W.; Ma, Y. The study on population driving forces to cultivated land change in Hotan oases. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 2, 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Feng, Q.; Si, J.; Wei, Y.; Bao, T.; Xi, H.; Li, Z. Identifying the origin of groundwater for water resources sustainable management in an arid oasis, China. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1253–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, Y.; Wan, J. Groundwater fluctuations induced by ecological water conveyance in the lower Tarim River, Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chang, N.-B.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T. Evaluation of ecological restoration through vegetation patterns in the lower Tarim River, China with MODIS NDVI data. Ecol. Inform. 2011, 6, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Gu, X.; Chang, L.; Dong, J.; Long, R.; Wang, Q.; Yang, B. Spatio-temporal evolution of land use and human activity intensity in the Tarim River Basin, Xinjiang. Geol. China 2023, 51, 203–220. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, C.; Shi, F.; Peng, D.; Wu, S. Analysis on land use change in the mainstream area of the Tarim River in recent 20 years. Arid Zone Research 2013, 30, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, F. Ecological impacts of land use change in the arid Tarim River Basin of China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Chang, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xing, G.; Lu, R.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z. Landscape pattern evolution and ecological risk assessment of the Yellow River Basin based on optimal scale. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhan, Y.; Cui, W.; Yuan, Y. Using landscape indicators and Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to determine the optimum spatial scale of urban land use patterns in Wuhan, China. Earth Sci. Inform. 2018, 11, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Type | Concept |
|---|---|
| Desert Landscape (DTL) | Refers to land with less than 5% vegetation cover, including sandy land, gobi, saline land, and bare rocky substrates. |
| Grassland Landscape (GDL) | Refers to land covered by herbaceous plants, including high-cover grassland, medium-cover grassland, and low-cover grassland. |
| Forest Landscape (FTL) | Refers to land on which trees, shrubs, and bamboos grow, including forest land, open forests, shrubland, and other forest land. |
| Farmland Landscape (FDL) | Refers to land used for the cultivation of crops, including dryland and paddy land. |
| Water Landscape (WRL) | Refers to all types of natural or artificial water bodies, including reservoirs and ponds, rivers and canals, lakes, marshes, and beach land. |
| Settlement Landscape (STL) | Refers to land covered by structures or buildings, including urban land, rural settlements, and other construction land. |
| Other Landscape (ORL) | Refers to bare land. |
| Data | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use | 30 m | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| Mean Annual Temperature | 1 km | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| Mean Annual Precipitation | 1 km | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| Mean Annual Relative Humidity | 1 km | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| Elevation | 1 km | Yearly, 2020 | RESDC |
| Soil Organic Matter Content | Yearly, 2010 | TPDC | |
| Soil Thickness | 1 km | Yearly, 2010 | NESSDC |
| Annual Actual Evapotranspiration | 1 km | Monthly, 1980–2020 | Harvard Dataverse |
| Natural Water | - | Yearly, 2002 | NCDC |
| Artificial Water | - | Yearly, 2002 | NCDC |
| Population Density | 1 km | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| GDP Density | 1 km | Yearly, 1980–2020 | RESDC |
| Road | - | Yearly, 2010 | NCDC |
| Index | Level | Dimension |
|---|---|---|
| Patch density (PD) | class/landscape | fragmentation |
| Mean patch size (MPS) | class/landscape | fragmentation |
| Percentage of landscape (PLAND) | class | dominance |
| Largest patch index (LPI) | class | dominance |
| Landscape shape index (LSI) | class/landscape | shape complexity |
| Perimeter-area fractal dimension (PAFRAC) | class/landscape | shape complexity |
| Aggregation index (AI) | class/landscape | aggregation |
| Interspersion juxtaposition index (IJI) | class/landscape | aggregation |
| Contagion (CONTAG) | landscape | aggregation |
| Shannon’s diversity index (SHDI) | landscape | diversity |
| Shannon’s evenness index (SHEI) | landscape | diversity |
| Type | Factor | Description | Landscape Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural Factors | Climate | MAT | Mean Annual Temperature | The temperature affects the suitability of the ecological environment, thereby influencing the spatial distribution and evolution of the landscape. |
| MAP | Mean Annual Precipitation | The precipitation can reflect the humidity level of a region, which may affect the vegetation coverage and the distribution of water bodies. | ||
| MAH | Mean Annual Relative Humidity | The relative humidity can reflect the humidity level of the climate, which may affect plant growth, water evaporation, and soil moisture. | ||
| Terrain | ELE | Elevation | The elevation influences the oxygen content and temperature of the atmosphere, which can reflect the suitability of the landscape distribution in the vertical direction. | |
| SLP | Slope | The slope can indicate the undulating morphology of the terrain, and gentle slopes typically have richer vegetation coverage. | ||
| Soil | SOM | Soil Organic Matter Content | The soil organic matter can reflect the soil fertility, and higher organic content often can support more diverse landscape distributions. | |
| SOT | Soil Thickness | The soil thickness can directly affect the growth and nutrient uptake of plant roots. Different soil thicknesses have varying potential for land use. | ||
| Hydrology | AAE | Annual Actual Evapotranspiration | Regions with higher actual evapotranspiration tend to have relatively abundant water resources and better ecological environments. | |
| DNW | Distance to Natural Water | The distance to natural water reveals the proximity to water sources. Areas closer to natural water tend to have more vegetation coverage. | ||
| DAW | Distance to Artificial Water | The distance to artificial water reveals the proximity to water sources. Areas closer to artificial water typically have a higher distribution of water-demanding landscapes. | ||
| Human Factors | Population | POD | Population Density | The population distribution and human activities can affect the types of landscape formation and the rate of landscape evolution. |
| Economy | GDP | GDP Density | The GDP density can reflect the intensity and types of economic activities in a region, which may promote or restrict the development of specific landscape types. | |
| ROD | Road Density | Roads can disrupt the landscape connectivity and enhance fragmentation, but can also serve as ecological corridors, exerting multiple influences on the landscape pattern. |
| Type | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area /km2 | Proportion /% | Area /km2 | Proportion /% | Area /km2 | Proportion /% | Area /km2 | Proportion /% | Area /km2 | Proportion /% | |
| DTL | 9935 | 31.43 | 9947 | 31.47 | 10,559 | 33.41 | 11,696 | 37.00 | 11,532 | 36.49 |
| GDL | 14,827 | 46.91 | 14,876 | 47.06 | 13,359 | 42.26 | 10,716 | 33.90 | 10,309 | 32.61 |
| FTL | 4203 | 13.30 | 4190 | 13.26 | 4482 | 14.18 | 4799 | 15.18 | 4726 | 14.95 |
| FDL | 1349 | 4.27 | 1349 | 4.27 | 1768 | 5.60 | 3365 | 10.65 | 3930 | 12.44 |
| WRL | 1164 | 3.68 | 1118 | 3.53 | 1340 | 4.24 | 944 | 2.99 | 980 | 3.10 |
| STL | 56 | 0.18 | 56 | 0.18 | 53 | 0.17 | 74 | 0.23 | 92 | 0.29 |
| ORL | 73 | 0.23 | 73 | 0.23 | 46 | 0.15 | 12 | 0.04 | 36 | 0.11 |
| Type | 1980–1990 | 1990–2000 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DTL | 0.12 | 6.15 | 10.77 | −1.39 |
| GDL | 0.33 | −10.20 | −19.78 | −3.81 |
| FTL | −0.33 | 6.95 | 7.10 | −1.54 |
| FDL | 0.00 | 31.13 | 90.22 | 16.82 |
| WRL | −3.96 | 19.96 | −29.55 | 3.81 |
| STL | 0.00 | −5.36 | 39.62 | 25.68 |
| ORL | 0.00 | −35.62 | −72.34 | 176.92 |
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | |
| Eigenvalue | 0.38 | 0.21 | 0.42 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.19 |
| Correlation coefficient between landscape area shares and impact factors | 0.81 | 0.67 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 0.95 | 0.71 |
| Amount of landscape area shares explained by impact factors | 56.82 | 88.76 | 57.36 | 88.83 | 60.06 | 82.30 |
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | All Axes | Axis 1 | All Axes | Axis 1 | All Axes | |
| F-value | 287.25 | 38.44 | 323.85 | 42.94 | 540.16 | 68.40 |
| p-value | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 1980 | 2000 | 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | Axis 1 | Axis 2 | |
| MAT | 0.13 | −0.61 | −0.13 | −0.56 | 0.25 | −0.35 |
| MAP | 0.13 | −0.09 | −0.06 | 0.01 | −0.11 | −0.28 |
| MAH | 0.28 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.46 | 0.54 | −0.22 |
| ELE | 0.51 | 0.04 | 0.53 | −0.06 | 0.61 | −0.08 |
| SLP | −0.53 | 0.30 | −0.42 | 0.41 | −0.41 | 0.40 |
| SOM | 0.56 | −0.32 | 0.45 | −0.45 | 0.42 | −0.38 |
| SOT | 0.87 | −0.00 | 0.85 | −0.21 | 0.92 | −0.19 |
| AAE | 0.59 | −0.10 | 0.61 | −0.16 | 0.86 | 0.17 |
| DNW | −0.57 | 0.35 | −0.43 | 0.47 | −0.38 | 0.50 |
| DAW | −0.41 | −0.16 | −0.44 | 0.02 | −0.48 | 0.08 |
| POD | 0.55 | 0.46 | 0.65 | 0.35 | 0.69 | 0.26 |
| GDP | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.53 | 0.18 |
| ROD | 0.68 | 0.04 | 0.63 | −0.11 | 0.65 | −0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, L.; Li, Y. Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Impact Factors in the Mainstream Basin of the Tarim River from 1980 to 2020. Hydrology 2024, 11, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11070093
Jiang L, Li Y. Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Impact Factors in the Mainstream Basin of the Tarim River from 1980 to 2020. Hydrology. 2024; 11(7):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11070093
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Lili, and Yating Li. 2024. "Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Impact Factors in the Mainstream Basin of the Tarim River from 1980 to 2020" Hydrology 11, no. 7: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11070093
APA StyleJiang, L., & Li, Y. (2024). Analysis of Landscape Pattern Evolution and Impact Factors in the Mainstream Basin of the Tarim River from 1980 to 2020. Hydrology, 11(7), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11070093






