Brazil’s Daily Precipitation Concentration Index (CI) Using Alternative Fitting Equation and Ensemble Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
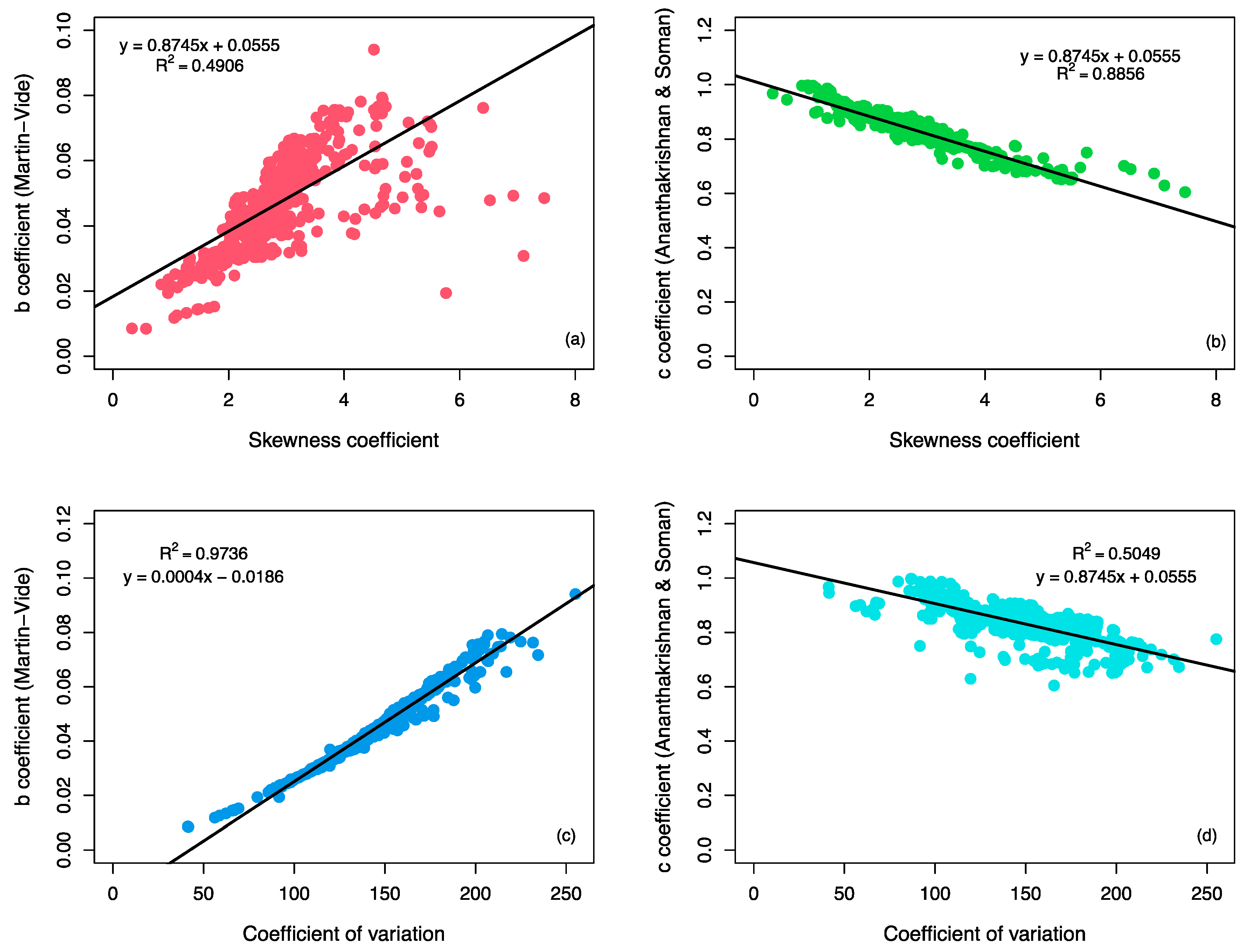
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashiq, A.; Kumar, V.; Prakash, O. A Spatiotemporal Assessment of the Precipitation Variability and Pattern and an Evaluation of the Predictive Reliability of Global Climate Models over Bihar. Hydrology 2024, 11, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, L.; Li, J. Radar-Based Precipitation Nowcasting Based on Improved U-Net Model. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-González, G. Analysis of the trends in precipitation and precipitation concentration in some climatological stations of Mexico from 1960 to 2010. Nat. Hazards 2020, 104, 1747–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratto, J.; De Bodas Terassi, P.M.; De Beserra De Lima, N.G.; Galvani, E. Precipitation Anomalies and Trends Estimated via Satellite Rainfall Products in the Cananeia–Iguape Coastal System, Southeast Region of Brazil. Climate 2024, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, Y.; Yavuz, V.; Temiz, C.; Lupo, A.R. Exploring Spatio-Temporal Precipitation Variations in Istanbul: Trends and Patterns from Five Stations across Two Continents. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Risi, R.; Jalayer, F.; De Paola, F.; Carozza, S.; Yonas, N.; Giugni, M.; Gasparini, P. From flood risk mapping toward reducing vulnerability: The case of Addis Ababa. Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byakatonda, J.; Parida, B.P.; Moalafhi, D.B.; Kenabatho, P.K.; Lesolle, D. Investigating relationship between drought severity in Botswana and ENSO. Nat. Hazards 2020, 100, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehl, H. Some Aspects of Hawaiian Rainfall. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1949, 30, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olascoaga, M.J. Some Aspects of Argentine Rainfall. Tellus Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 1950, 2, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Vide, J. Spatial distribution of a daily precipitation concentration index in peninsular Spain. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhamrouche, A.; Boucherf, D.; Hamadache, R.; Bendahmane, L.; Martin-Vide, J.; Teixeira Nery, J. Spatial distribution of the daily precipitation concentration index in Algeria. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yeşilırmak, E.; Atatanır, L. Spatiotemporal variability of precipitation concentration in western Turkey. Nat. Hazards 2016, 81, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Notivoli, R.; Martín-Vide, J.; Saz, M.A.; Longares, L.A.; Beguería, S.; Sarricolea, P.; Meseguer-Ruiz, O.; De Luis, M. Spatio-temporal variability of daily precipitation concentration in Spain based on a high-resolution gridded data set. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, e518–e530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubieta, R.; Saavedra, M.; Silva, Y.; Giráldez, L. Spatial analysis and temporal trends of daily precipitation concentration in the Mantaro River basin: Central Andes of Peru. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1305–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, M.P. Spatial distribution of the daily rainfall concentration index in Argentina: Comparison with other countries. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 133, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyshkvarkova, E.; Voskresenskaya, E.; Martin-Vide, J. Spatial distribution of the daily precipitation concentration index in Southern Russia. Atmospheric Res. 2018, 203, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, A.; Martin-Vide, J.; Royé, D.; Santaella, O. Spatial analysis of daily precipitation concentration in Puerto Rico. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2019, 136, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer-Ruiz, O.; Ponce-Philimon, P.I.; Guijarro, J.A.; Sarricolea, P. Spatial distribution and trends of different precipitation variability indices based on daily data in Northern Chile between 1966 and 2015. Int. J. Climatol. 2019, 39, 4595–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Ren, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Liu, R.; Wei, L. Spatial and Temporal Variability in Precipitation Concentration over Mainland China, 1961–2017. Water 2019, 11, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-L.; Li, F.-F.; Zhao, K.; Wang, H.-R.; Wang, G.-Q.; Qiu, J. Indices for exploring information in Lorentz curve of daily precipitation and their application in natural disaster risk assessment. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 126840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-González, G.; Velázquez-Pérez, D.; Pelayo-Cortés, F.J. Evaluation of an Alternative Functional Form to Fit the Lorenz Curve for the Concentration Index Calculation. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, R.; Soman, M.K. Statistical distribution of daily rainfall and its association with the coefficient of variation of rainfall series. Int. J. Climatol. 1989, 9, 485–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; De Moraes Gonçalves, J.L.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almagro, A.; Oliveira, P.T.S.; Meira Neto, A.A.; Roy, T.; Troch, P. CABra: A novel large-sample dataset for Brazilian catchments. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 3105–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, A.C.; King, C.W.; Scanlon, B.R. Daily gridded meteorological variables in Brazil (1980–2013). Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2644–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, J.T.; Carfan, A.C.; Martin-Vide, J. Analysis of Rain Variability Using the Daily and Monthly Concentration Indexes in Southeastern Brazil. Atmospheric Clim. Sci. 2017, 07, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, B.; Nery, J.T. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation concentration in northeastern Brazil. Investig. Geográficas 2021, 104, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Back, Á.J.; Souza, G.D.S.; Galatto, S.L. Sérgio Luciano Evaluation of the daily rainfall concentration index in Brazil: Avaliação do índice de concentração de precipitação diária no Brasil. Concilium 2024, 24, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; [En línea]; Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 March 2024).
- QGIS Development Team. QGIS Geographic Information System F; Open Source Geospatial Foundation: Beaverton, OR, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Monjo, R.; Martin-Vide, J. Daily precipitation concentration around the world according to several indices. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-González, G. Comparison of the behavior of the precipitation concentration index on global and local scale. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 139, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
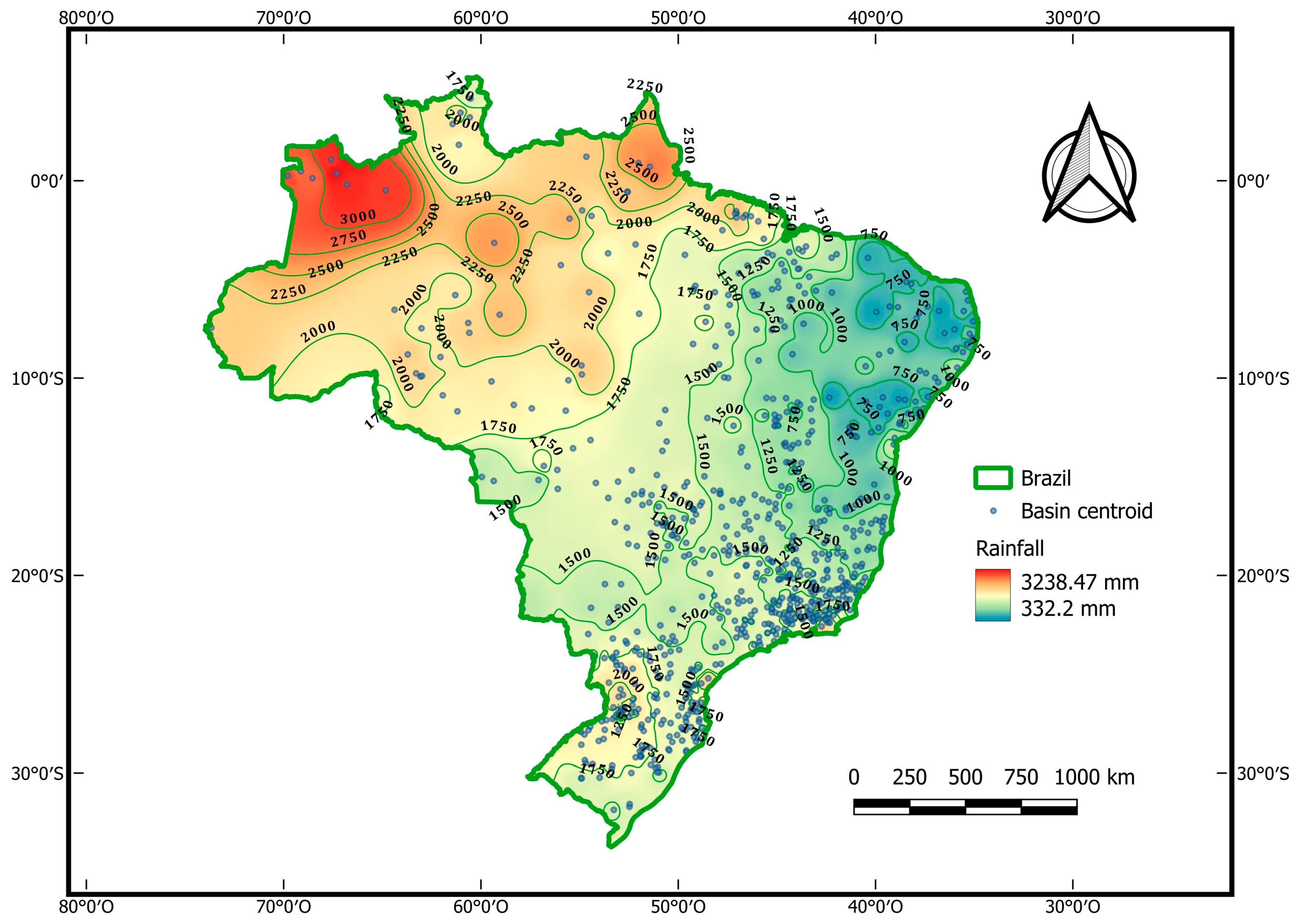
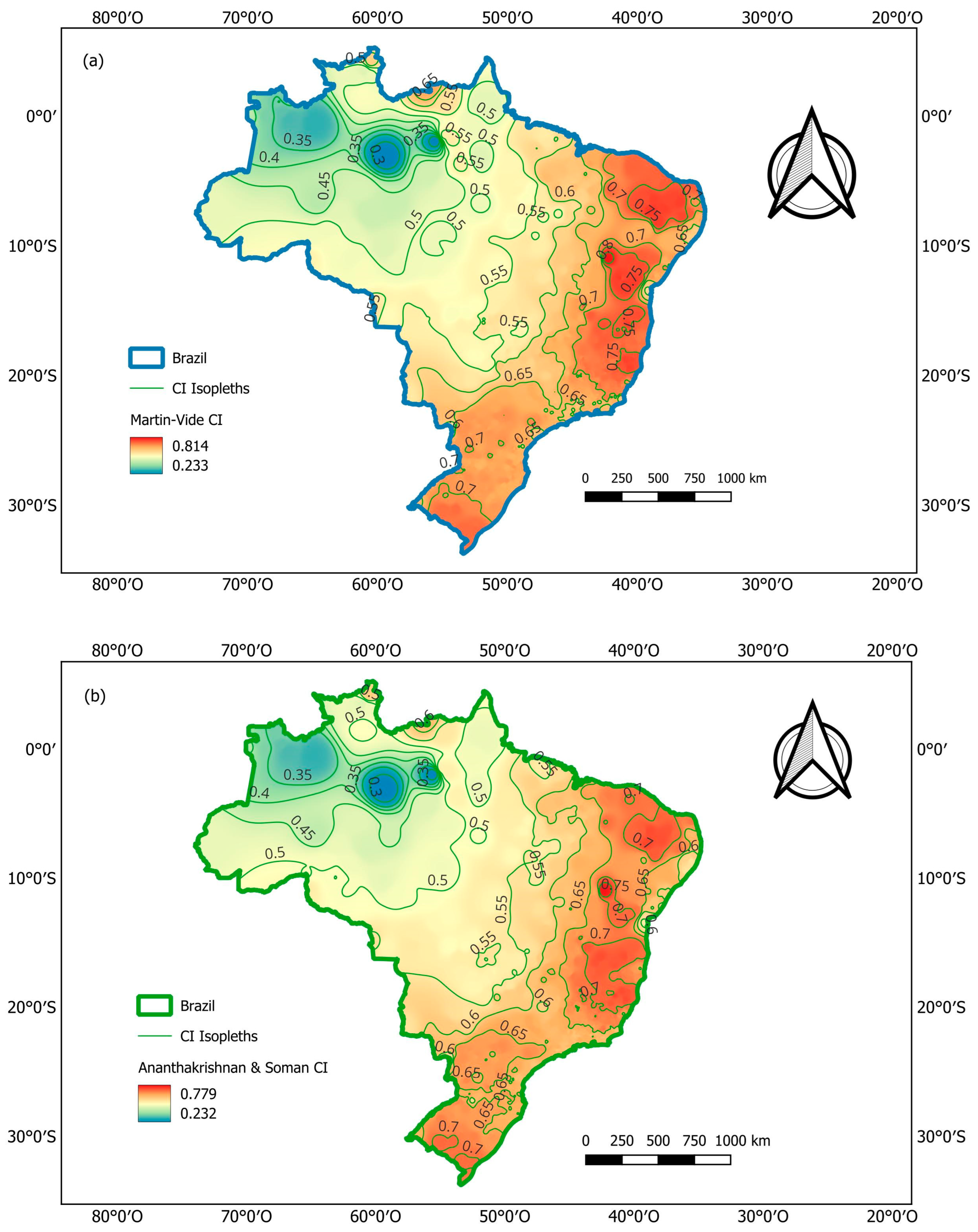
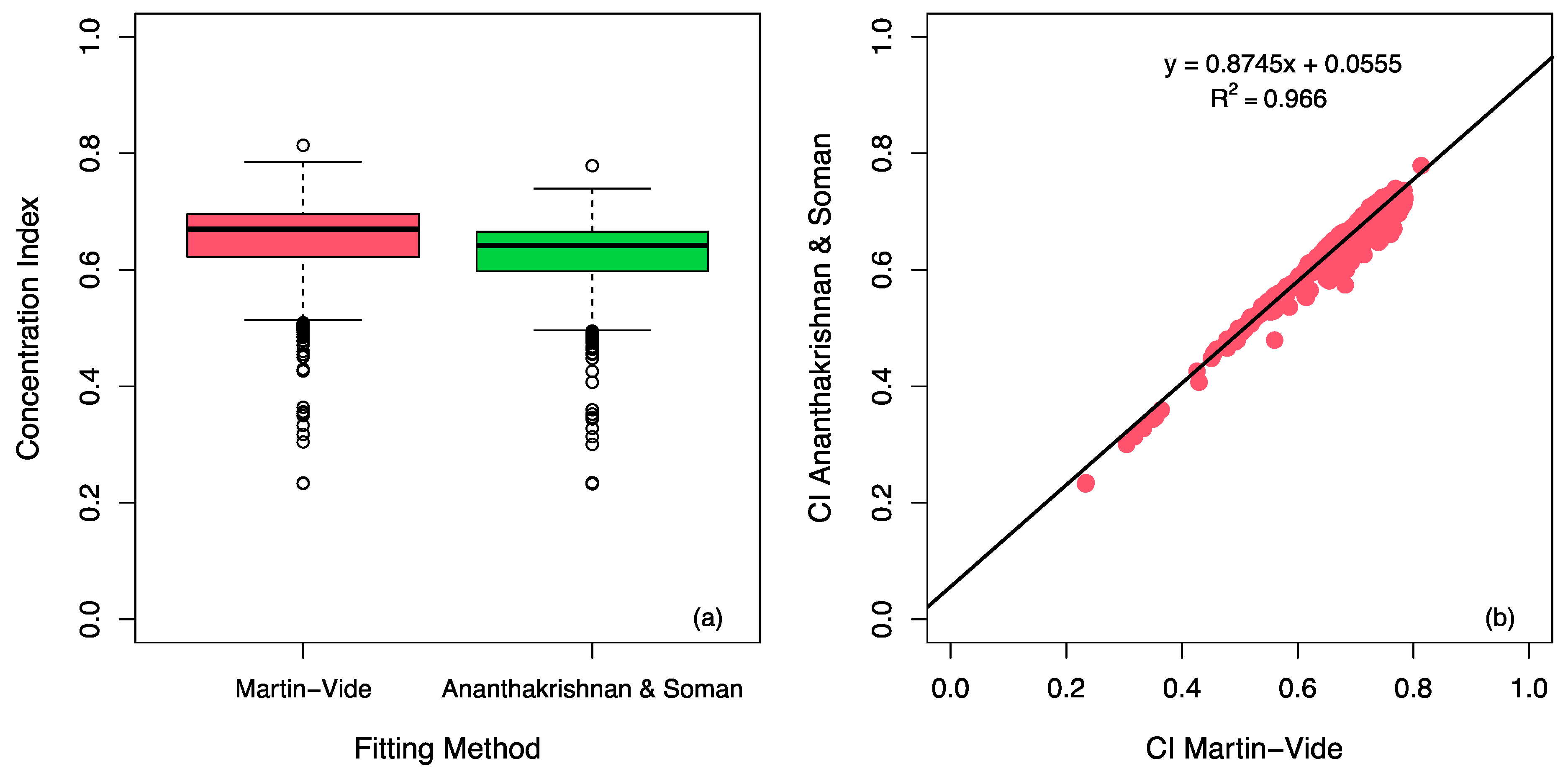
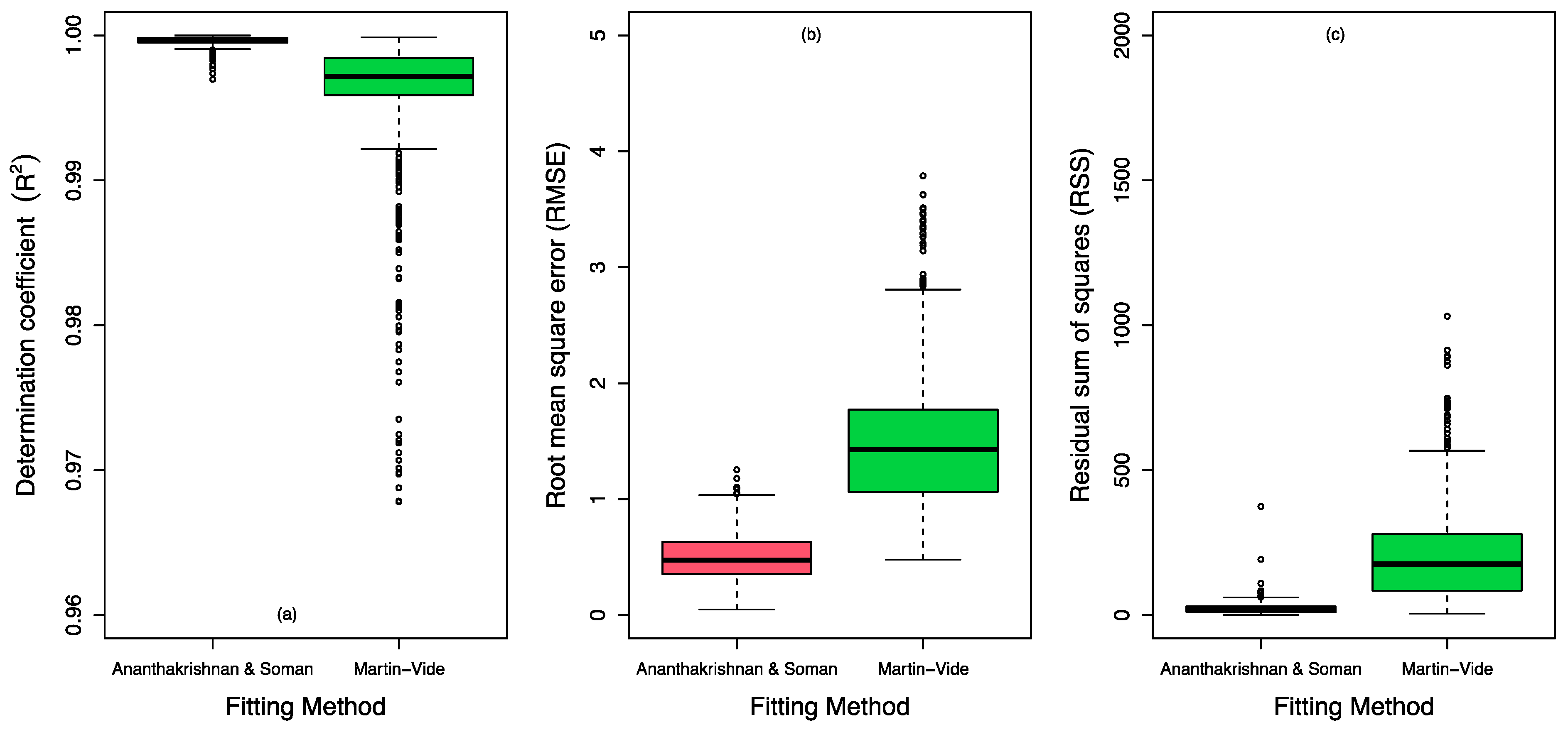

| Class | ni (Number) | ∑ ni (Number) | pi (mm) | ∑ pi (mm) | ∑ ni (%) | ∑ pi (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1–0.9 | 21 | 21 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 21.65 | 0.83 |
| 1.0–1.9 | 6 | 27 | 9 | 19.5 | 27.84 | 1.54 |
| 2.0–2.9 | 7 | 34 | 17.5 | 37 | 35.05 | 2.93 |
| . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| . | . | . | . | . | . | . |
| 84.0–84.9 | 0 | 96 | 0 | 1178 | 98.87 | 93.23 |
| 85.0–85.9 | 1 | 97 | 85.5 | 1263.5 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| State | Basins by State | Martin-Vide | Ananthakrishnan and Soman | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Mean | Max | SD | Min | Mean | Max | SD | ||
| Acre | 1 | 0.493 | 0.476 | ||||||
| Alagoas | 6 | 0.613 | 0.651 | 0.661 | 0.019 | 0.554 | 0.616 | 0.642 | 0.038 |
| Amapá | 4 | 0.486 | 0.494 | 0.504 | 0.009 | 0.479 | 0.486 | 0.493 | 0.007 |
| Amazonas | 15 | 0.233 | 0.385 | 0.484 | 0.073 | 0.232 | 0.381 | 0.48 | 0.073 |
| Bahia | 64 | 0.586 | 0.691 | 0.814 | 0.056 | 0.536 | 0.647 | 0.779 | 0.042 |
| Ceará | 7 | 0.738 | 0.758 | 0.784 | 0.017 | 0.689 | 0.713 | 0.736 | 0.017 |
| Distrito Federal | 4 | 0.562 | 0.57 | 0.583 | 0.009 | 0.549 | 0.558 | 0.569 | 0.008 |
| Espírito Santo | 27 | 0.686 | 0.734 | 0.774 | 0.025 | 0.647 | 0.694 | 0.731 | 0.023 |
| Goiás | 48 | 0.527 | 0.56 | 0.619 | 0.024 | 0.519 | 0.546 | 0.611 | 0.021 |
| Maranhão | 32 | 0.548 | 0.625 | 0.68 | 0.027 | 0.541 | 0.603 | 0.659 | 0.026 |
| Mato Grosso | 21 | 0.477 | 0.525 | 0.569 | 0.023 | 0.474 | 0.518 | 0.557 | 0.02 |
| Mato Grosso do Sul | 7 | 0.543 | 0.598 | 0.644 | 0.038 | 0.537 | 0.579 | 0.618 | 0.03 |
| Minas Gerais | 185 | 0.56 | 0.685 | 0.775 | 0.042 | 0.479 | 0.661 | 0.74 | 0.039 |
| Pará | 22 | 0.234 | 0.53 | 0.675 | 0.08 | 0.235 | 0.516 | 0.614 | 0.071 |
| Paraíba | 6 | 0.694 | 0.744 | 0.775 | 0.034 | 0.623 | 0.679 | 0.729 | 0.045 |
| Paraná | 57 | 0.548 | 0.683 | 0.715 | 0.023 | 0.545 | 0.653 | 0.679 | 0.02 |
| Pernambuco | 9 | 0.615 | 0.674 | 0.778 | 0.043 | 0.553 | 0.622 | 0.719 | 0.051 |
| Piauí | 8 | 0.59 | 0.662 | 0.735 | 0.051 | 0.576 | 0.641 | 0.7 | 0.045 |
| Rio de Janeiro | 37 | 0.623 | 0.661 | 0.725 | 0.029 | 0.603 | 0.636 | 0.695 | 0.026 |
| Rio Grande do Norte | 4 | 0.728 | 0.755 | 0.775 | 0.021 | 0.661 | 0.697 | 0.725 | 0.027 |
| Rio Grande do Sul | 47 | 0.665 | 0.695 | 0.736 | 0.018 | 0.634 | 0.668 | 0.707 | 0.018 |
| Rondônia | 9 | 0.49 | 0.512 | 0.547 | 0.015 | 0.487 | 0.504 | 0.537 | 0.014 |
| Roraima | 5 | 0.478 | 0.52 | 0.61 | 0.053 | 0.465 | 0.505 | 0.59 | 0.05 |
| Santa Catarina | 48 | 0.654 | 0.675 | 0.695 | 0.01 | 0.574 | 0.643 | 0.662 | 0.014 |
| São Paulo | 32 | 0.627 | 0.66 | 0.704 | 0.017 | 0.602 | 0.636 | 0.675 | 0.018 |
| Sergipe | 1 | 0.684 | 0.6 | ||||||
| Tocantins | 13 | 0.516 | 0.556 | 0.579 | 0.015 | 0.514 | 0.548 | 0.568 | 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Núñez-González, G. Brazil’s Daily Precipitation Concentration Index (CI) Using Alternative Fitting Equation and Ensemble Data. Hydrology 2024, 11, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11120214
Núñez-González G. Brazil’s Daily Precipitation Concentration Index (CI) Using Alternative Fitting Equation and Ensemble Data. Hydrology. 2024; 11(12):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11120214
Chicago/Turabian StyleNúñez-González, Gerardo. 2024. "Brazil’s Daily Precipitation Concentration Index (CI) Using Alternative Fitting Equation and Ensemble Data" Hydrology 11, no. 12: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11120214
APA StyleNúñez-González, G. (2024). Brazil’s Daily Precipitation Concentration Index (CI) Using Alternative Fitting Equation and Ensemble Data. Hydrology, 11(12), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11120214





