Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology Using an Integrated Water Quality Index
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
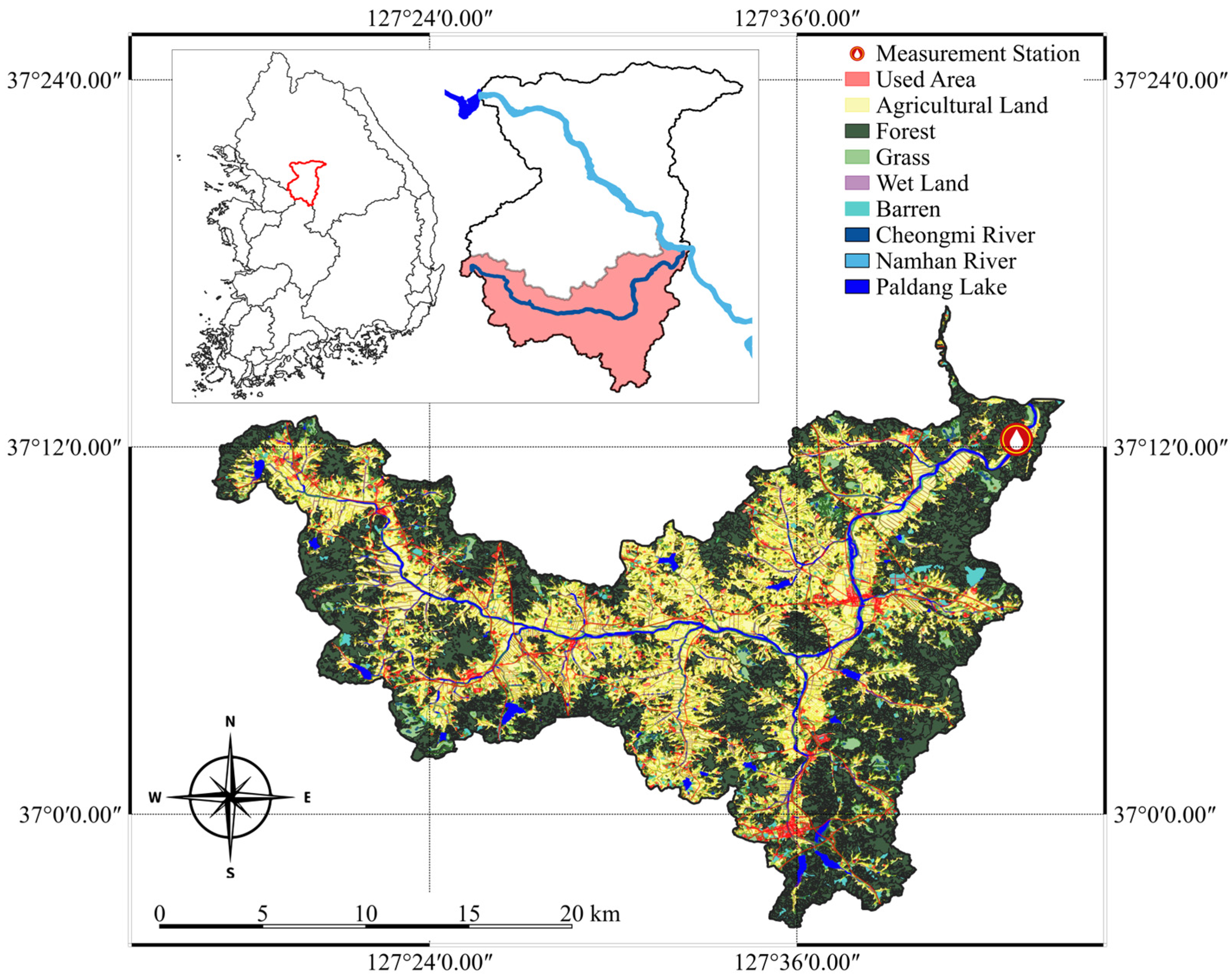
2.1. Study Watershed
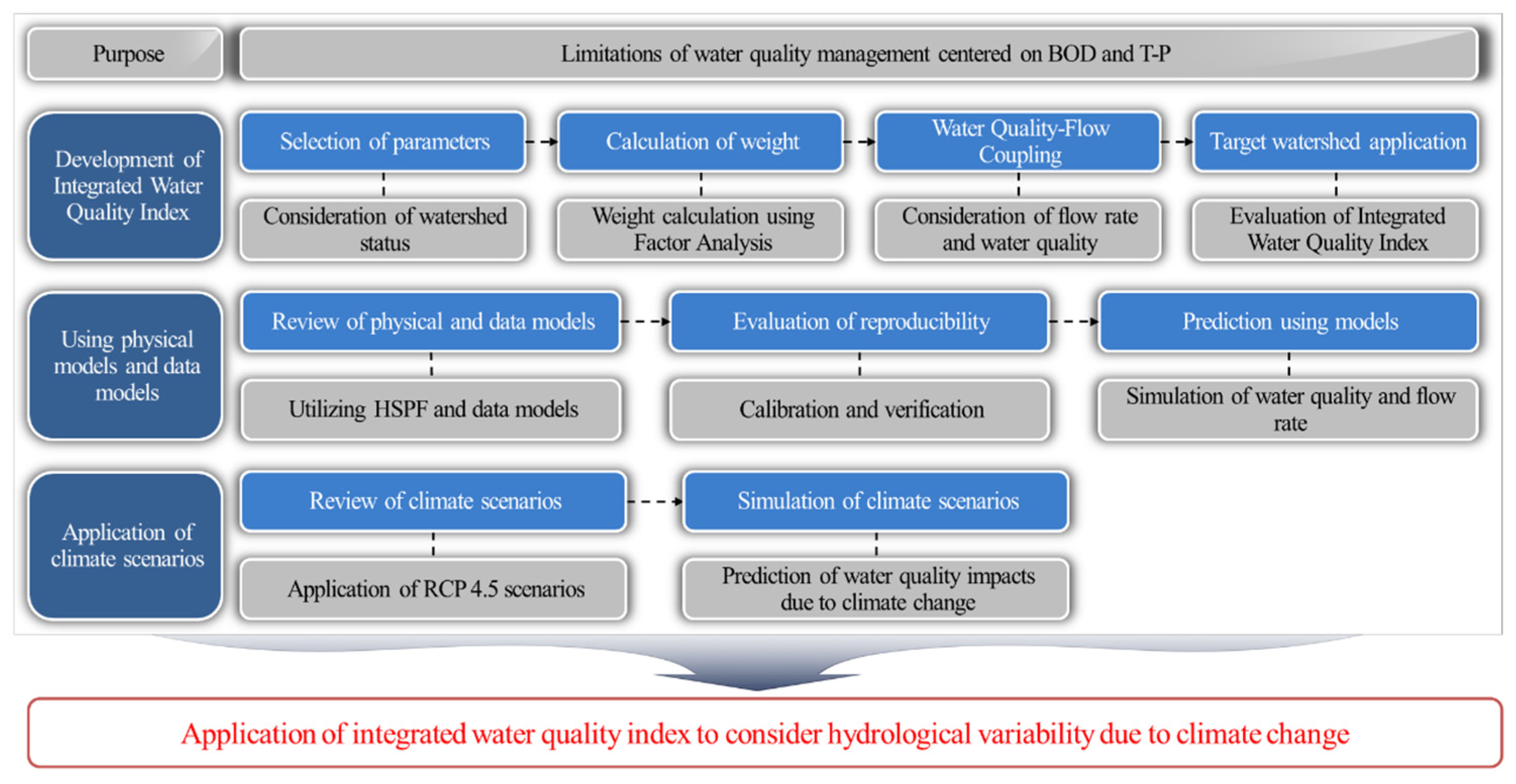
2.2. Integrated Water Quality Index (IWQI) Development
2.2.1. Integrated Water Quality Index (IWQI)
2.2.2. Factor Analysis (FA)
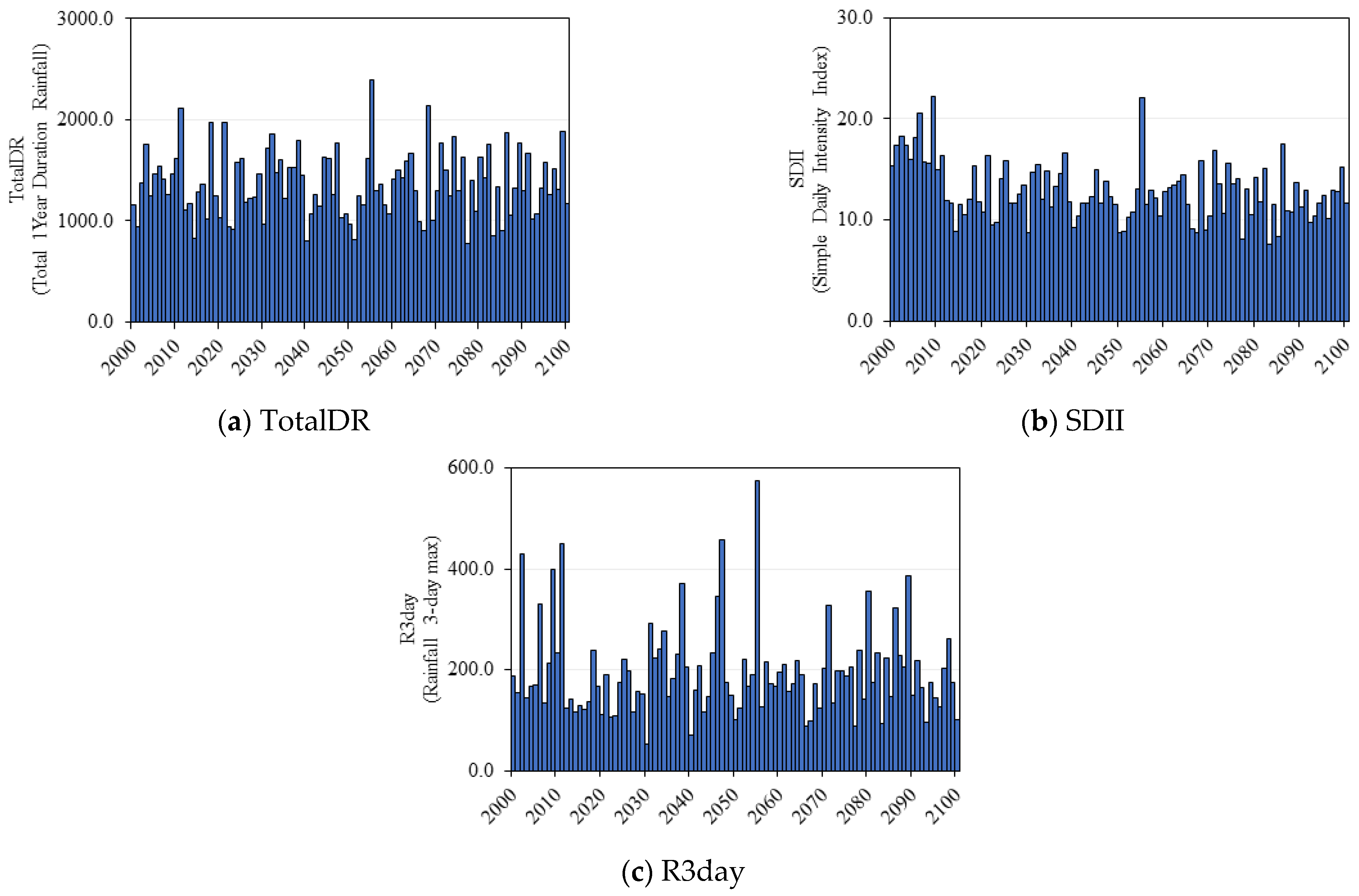
2.3. Climate Change Assessment Model
2.3.1. HSPF
2.3.2. Regression Models
3. Result and Discussion
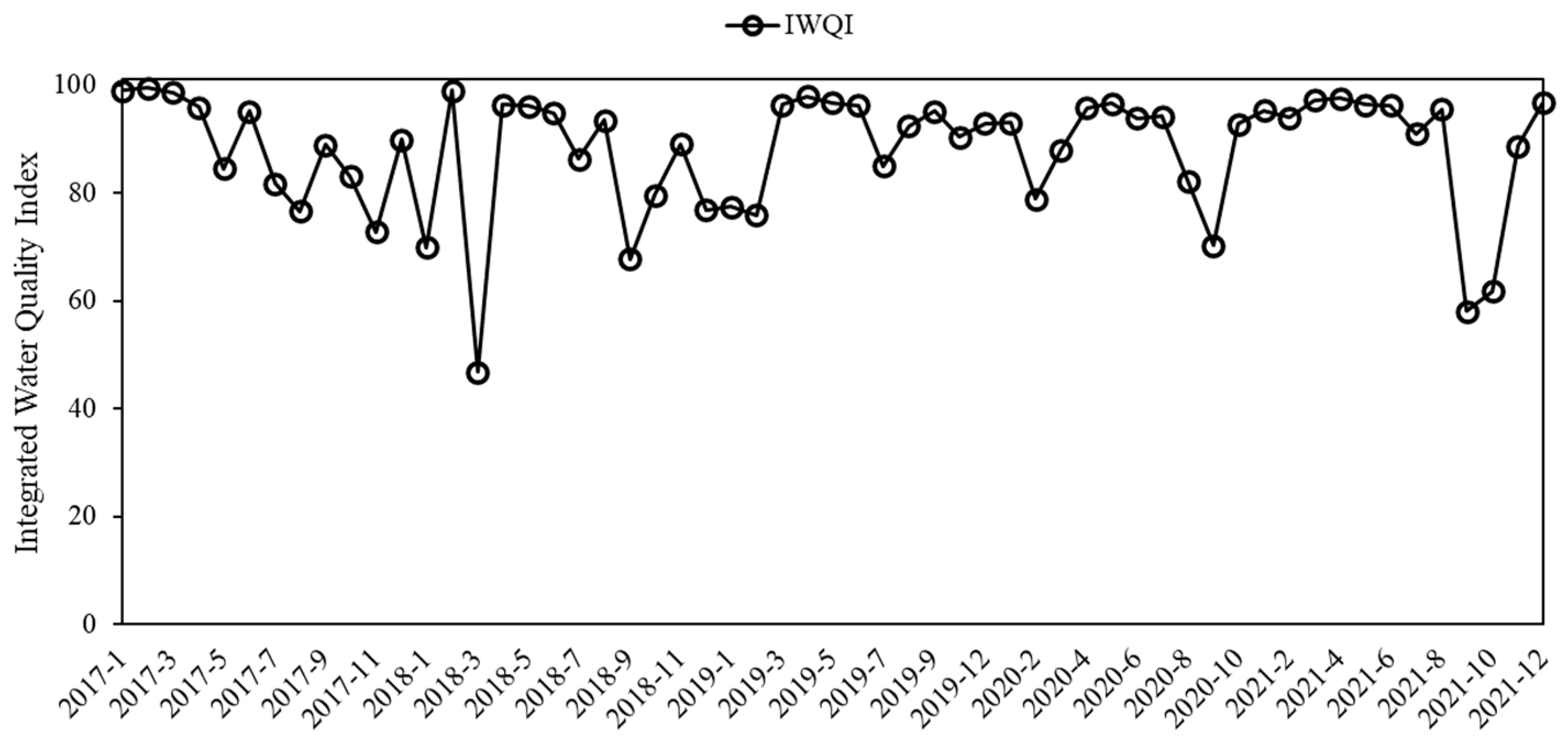
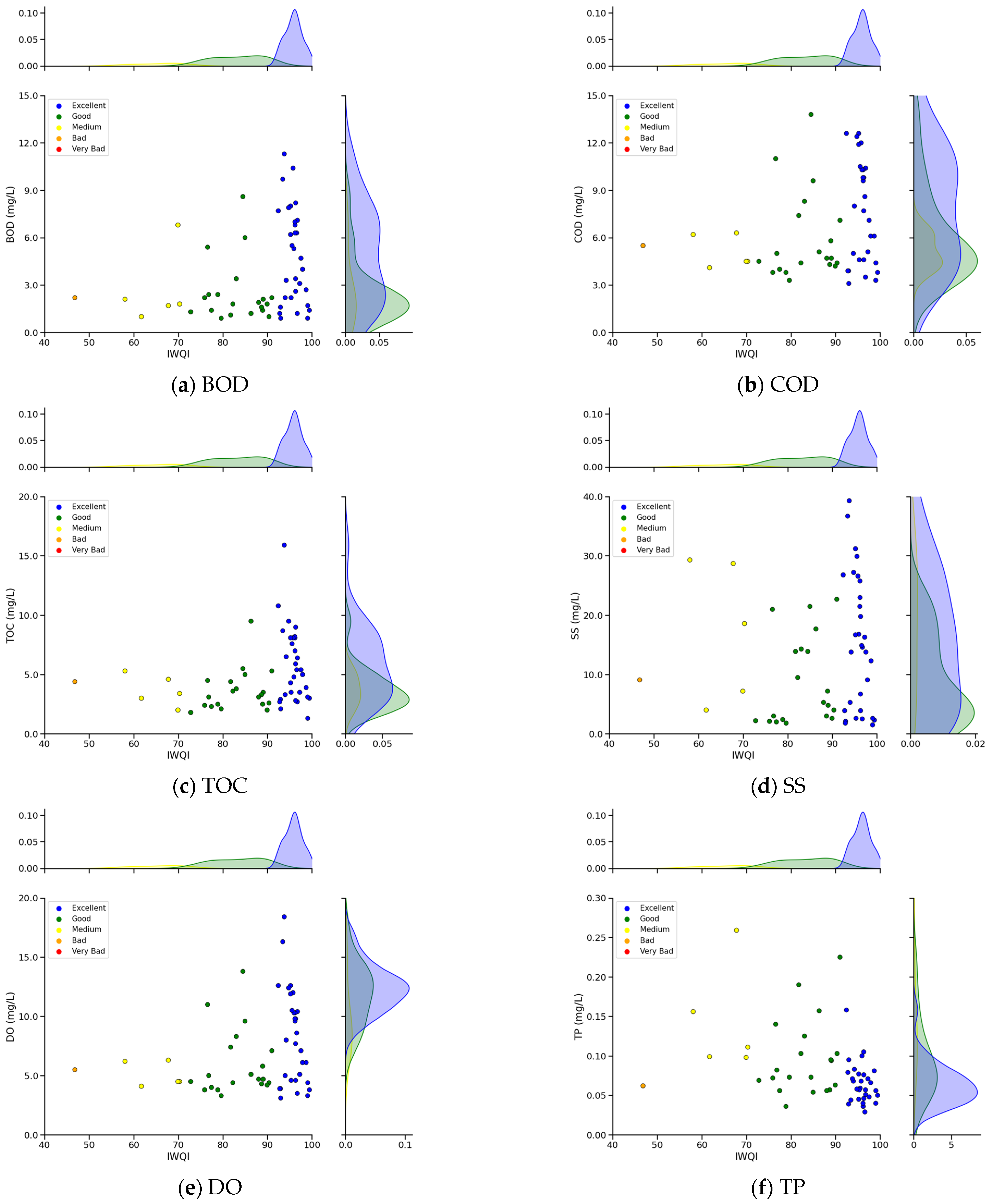
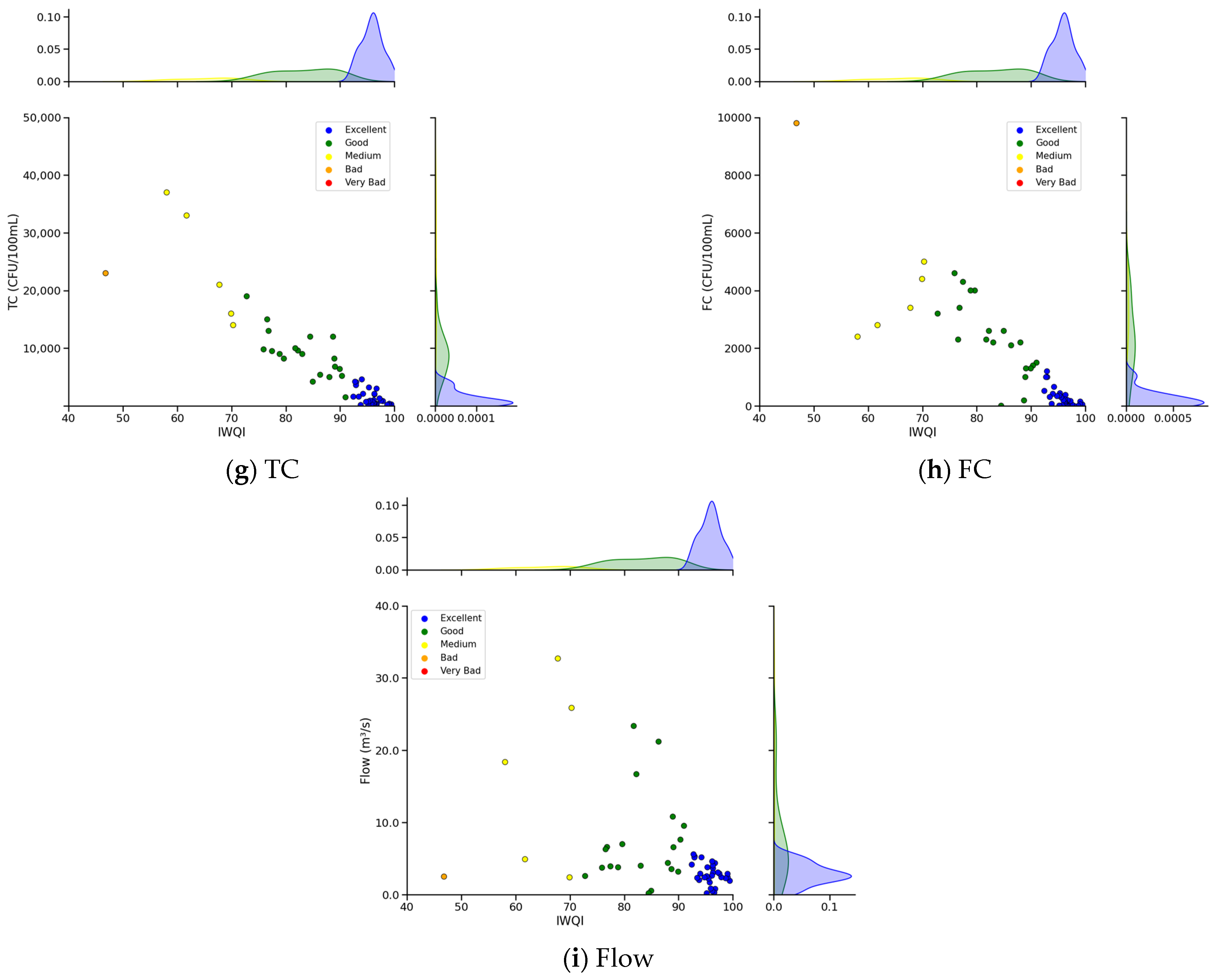
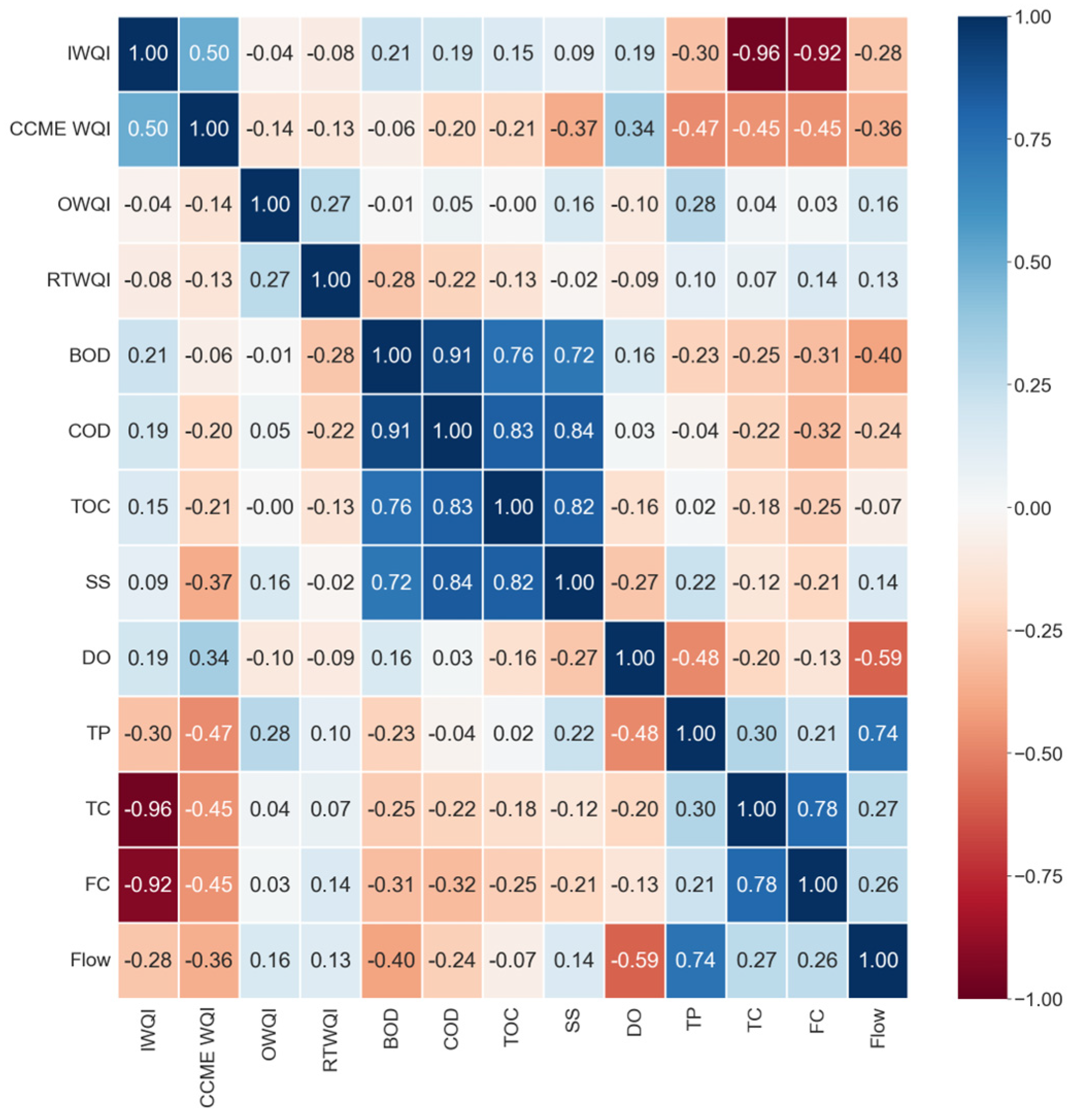
3.1. Comprehensive Evaluation of River Water Quality Using the IWQI
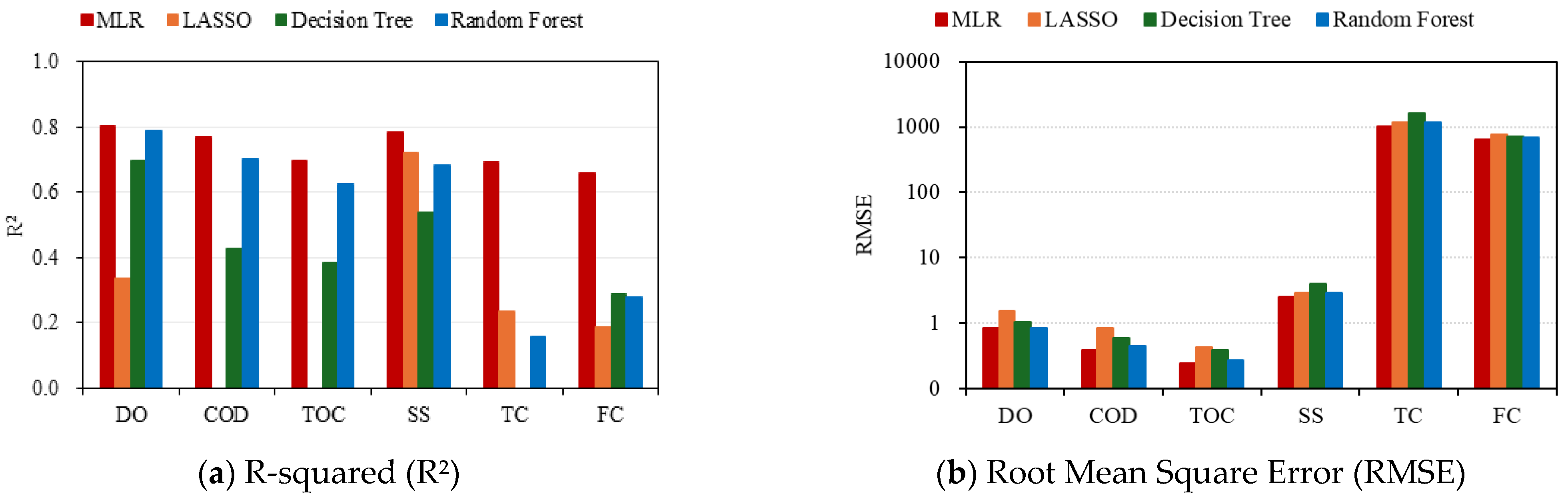
3.2. Evaluation of the Reproducibility of the Physics-Based and Data-Based Models
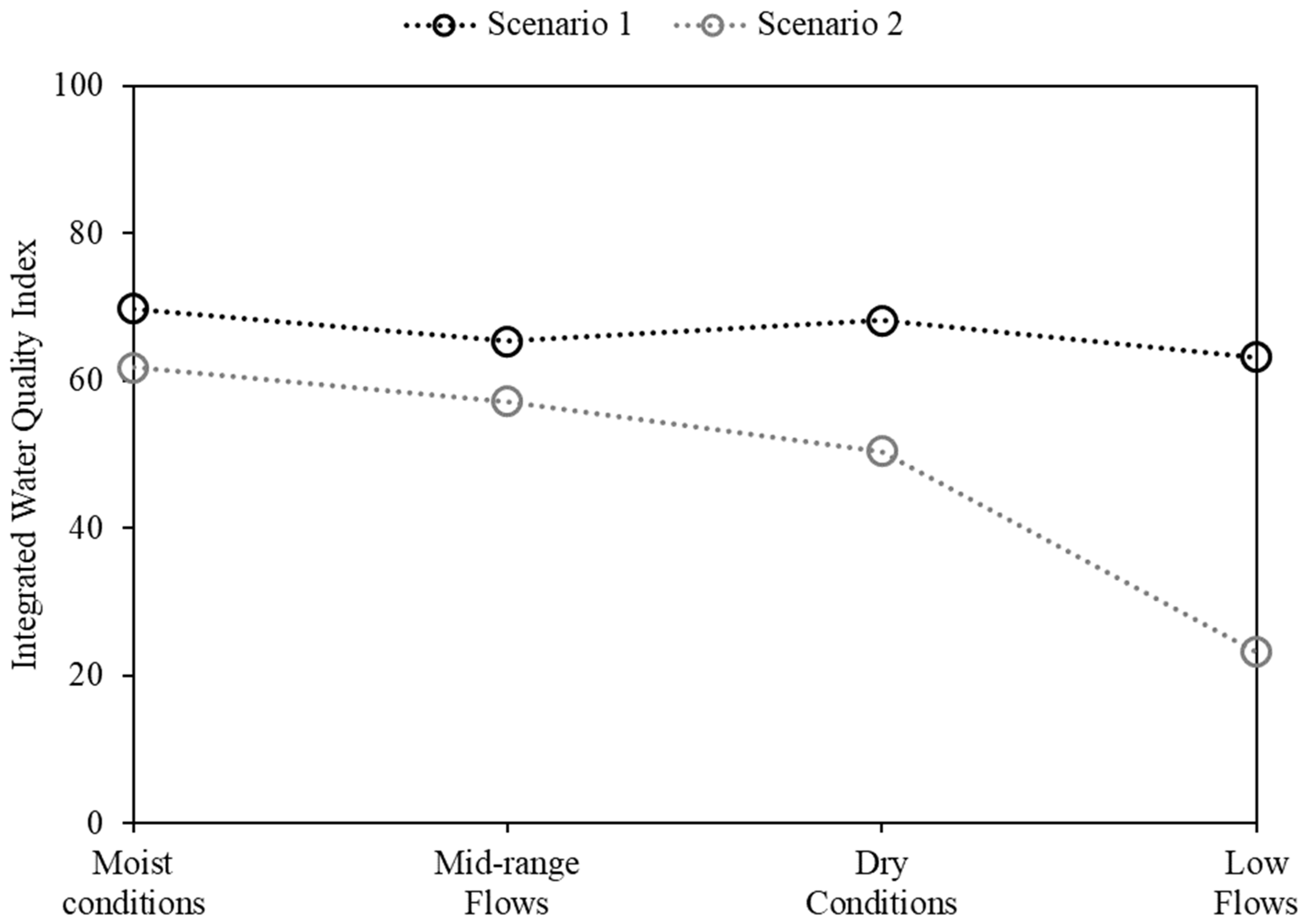
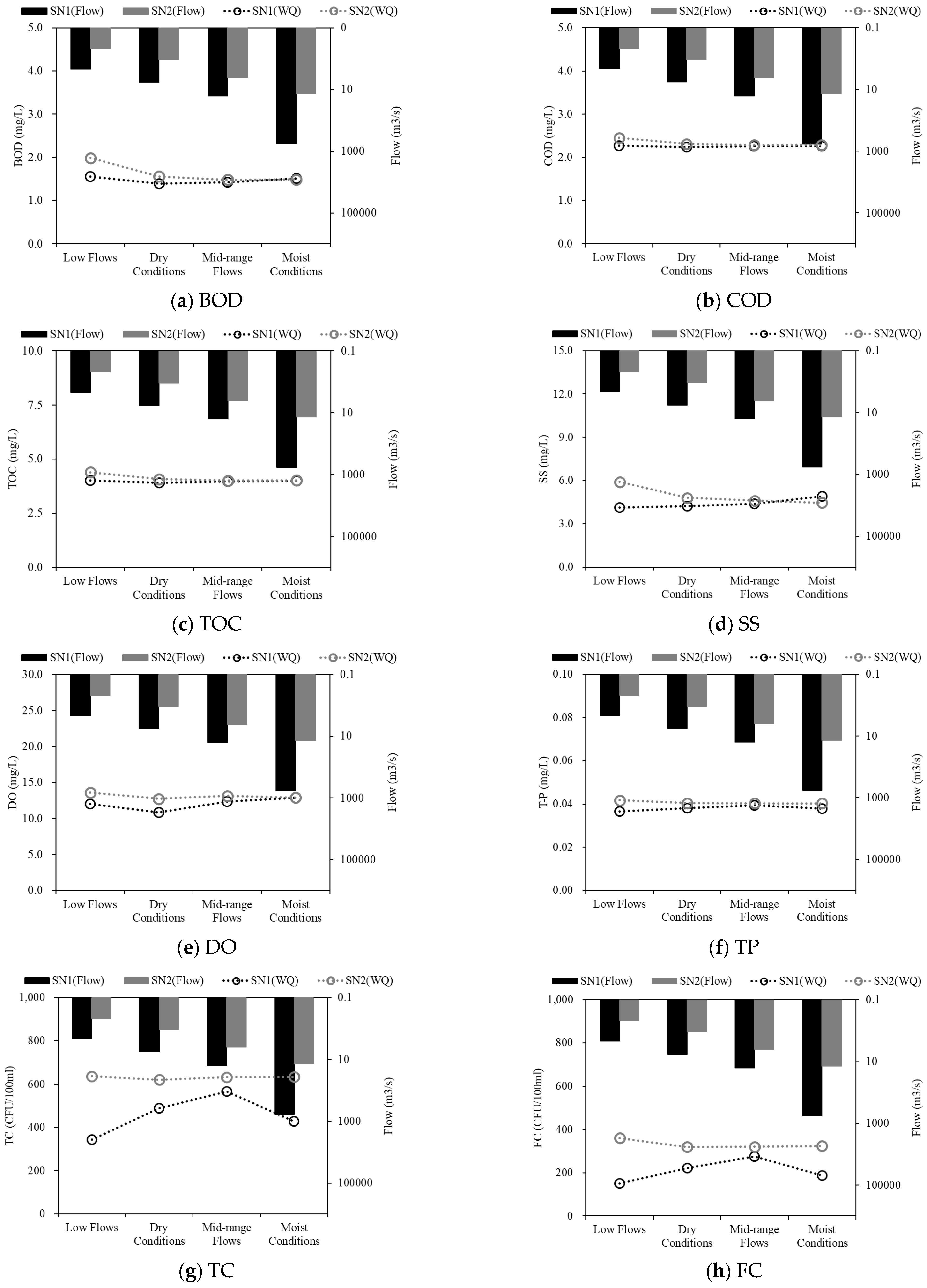
3.3. Evaluation of Climate Change Using the IWQI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mukate, S.; Wagh, V.; Panaskar, D.; Jacobs, J.A.; Sawant, A. Development of new integrated water quality index (IWQI) model to evaluate the drinking suitability of water. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ha, H.J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Cha, Y.K.; Koo, J.Y. Assessment of water quality of major tributaries in Seoul using water quality index and cluster analysis. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2020, 42, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apogba, J.N.; Anornu, G.K.; Koon, A.B.; Dekongmen, B.W.; Sunkari, E.D.; Fynn, O.F.; Kpiebaya, P. Application of machine learning techniques to predict groundwater quality in the Nabogo Basin. North. Ghana Heliyon 2024, 10, e28527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lap, B.Q.; Phan, T.; Du Nguyen, H.; Hang, P.T.; Phi, N.Q.; Hoang, V.T.; Linh, P.G.; Hang, B.T.T. Predicting Water Quality Index (WQI) by feature selection and machine learning: A case study of An Kim Hai irrigation system. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 74, 101991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azha, S.F.; Sidek, L.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Zhang, J.; Basri, H.; Zawawi, M.H.; Noh, N.M.; Ahmed, A.N. Enhancing river health monitoring: Developing a reliable predictive model and mitigation plan. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.D.; Kang, D.H.; So, Y.H.; Kim, I.K. Temporal-spatial variations of water quality level and water quality index on the living environmental standards in the west Nakdong River. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2019, 28, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, J.G.; Patil, L.G.; Patki, V.K. Development of water quality index for Godavari River (India) based on fuzzy inference system. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kal, B.; Kim, S. Long-term trend analysis of major tributaries of Nakdong River using water quality index. J. Wetl. Res. 2018, 20, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Gupta, S.K. A critical review on water quality index tool: Genesis, evolution and future directions. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, G.; Kootenaei, F.G.; Ramezani, M.; Lotfi, E.; Asgharnia, H. Comparative investigation of river water quality by OWQI, NSFWQI and Wilcox indexes (Case study: The Talar River—Iran). Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagbor, I.A.; Johnny, V.I.; Ogbolokot, I.E. Application of national sanitation foundation and weighted arithmetic water quality indices for the assessment of Kaani and Kpean Rivers in Nigeria. Am. J. Water Resour. 2019, 7, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zotou, I.; Tsihrintzis, V.A.; Gikas, G.D. Performance of seven water quality indices (WQIs) in a Mediterranean river. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.T.; Park, M.; Kwon, H.H. Spatio-temporal summer rainfall pattern in 2020 from a rainfall frequency perspective. J. Korean Soc. Disaster Secur. 2020, 13, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.E.; Kim, H.N.; Ryoo, K.S.; Lee, E.R. Evaluation of flexible criteria for river flow management with consideration of spatio-temporal flow variation. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 49, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.H.; Lee, J.K.; Jo, J.W. Evaluation of instream flow in the Imjingang River according to the operation of Hwanggang Dam in North Korea. Crisis Emerg. Manag. Theory Prax. 2020, 16, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.H.; Park, S.Y.; Na, J.M.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.H. Hydrological and ecological alteration of river dynamics due to multipurpose dams. J. Wetl. Res. 2019, 21, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jun, H.; Kim, S. Analysis of future hydrological cycle considering the impact of climate change and hydraulic structures in Geum River Basin. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2014, 14, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, I.S.; Jung, J.K.; Park, K.B. Analysis of correlation relationship for flow and water quality at up and down streams. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2010, 19, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.K. A study on the related characteristics of discharge-water quality in Nakdong river. J. Environ. Sci. Int. 2011, 20, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.C.; Park, M.; Shin, K.; Choi, H.M.; Kim, S.; Yu, S. A study on grade classification for improvement of water quality and water quality characteristics in the Han River watershed tributaries. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2019, 28, 215–230. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, S.J.; Jung, C.G. Assessment of changes on water quality and aquatic ecosystem health in Han River basin by additional dam release of stream maintenance flow. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2019, 52, 777–789. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, J.; Son, M. Effects of climate change and reduction method on water quality in Cheongmicheon watershed. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2018, 51, 585–597. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D.; Min, J.K.; Byeon, M.; Park, H.K.; Cheon, S.U. Temporal and spatial characteristics of water quality in a river-reservoir (Paldang). J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 470–486. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S. The analysis of water factors for management of lake eutrophication in Paldang lake. J. Korean Ecol. Eng. Soc. 2022, 9, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Kwak, J.; Kim, J.; Kang, M. Evaluation of estuary reservoir management based on robust decision making considering water use-flood control-water quality under Climate Change. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2023, 56, 419–429. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Im, J.; Lee, B. Effect of air temperature changes on water temperature and hysteresis phenomenon in lake Paldang. J. Environ. Impact Assess. 2020, 29, 323–337. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, D. Evaluating effect of density flow from upstream on vertical distribution of water quality at the Paldang Reservoir. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2019, 35, 557–566. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.K.; Lee, S.H.; Bang, H.H.; Hwang, S.O. Characteristics of algae occurrence in Lake Paldang. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2009, 31, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ryu, I.G.; Lee, B.M.; Cho, Y.C.; Choi, H.J.; Shin, D.S.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, S.J. Analyzing Flow Variation and Stratification of Paldang Reservoir Using High-frequency Water Temperature Data. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2020, 36, 392–404. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.J.; Kim, K.; Park, C.; Seo, W.; Choi, B.G.; Eum, H.S.; Park, M.H.; Noh, H.R.; Sim, Y.B.; Shin, J.K. Hydro-meteorological effects on water quality variability in Paldang reservoir, confluent area of the South-Han River-North-Han River-Gyeongan Stream, Korea. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 49, 354–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shin, J.Y.; Lee, G.; Sung, Y.; Kim, K.; Lim, K.J.; Kim, J. Analysis of Water Pollutant Load Characteristics and Its Contributions During Dry Season: Focusing on Major Streams Inflow into South-Han River of Chungju-dam Downstream. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2018, 40, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.C.; Choi, H.M.; Ryu, I.G.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, D.; Yu, S. Assessment of water quality in the lower reaches Namhan River by using statistical analysis and water quality index (WQI). J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2021, 37, 114–127. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, C.H. Tracing Water Pollution Source using FDC and Exceedance Rate in Cheongmicheon Watershed. J. Wetl. Res. 2018, 20, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Jung, W.; Hwang, H.; Kim, Y. Water Quality Improvement Plans of Daeho Reservoir based on the Analysis of Watershed Characteristics and Water Quality Modelling. J. Korean Soc. Environ. Eng. 2018, 40, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jo, B.; Kim, Y.D. Assessment of water quality index suitability of domestic watersheds. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2022, 55, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Yeon, I.S.; Ahn, S.J. A Development of Real Time Artificial Intelligence Warning System Linked Discharge and Water Quality (I) Application of Discharge-Water Quality Forecasting Model. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2005, 38, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banda, T.D.; Kumarasamy, M.V. Development of Water Quality Indices (WQIs): A Review. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Qiao, D.; Qian, B.; Ma, L.; Xing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Improvement of CCME WQI using grey relational method. J. Hydrol. 2016, 543, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnaiah, C.R.; Sadashivaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. J. Chem. 2009, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.C.; Kim, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Youn, H.K.; Lee, S.H. Analysis of fire risk assessment indicators of publicly-used establishments using Delphi/AHP. Fire Sci. Eng. 2019, 33, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, D.G.; Jun, H.D.; Jung, D.H.; Kim, J.H. Suggestion of Weighted Utopian Approach for Combining Weighting Methods and Utopian Approach. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2010, 10, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Xin, X.; Sun, L.; Li, W.; Jia, R. Assessing water quality of five typical reservoirs in lower reaches of Yellow River, China: Using a water quality index method. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 61, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahin, H.S.; Abuzaid, A.S.; Abdellatif, A.D. Using multivariate analysis to develop irrigation water quality index for surface water in Kafr El-Sheikh Governorate, Egypt. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutadian, A.D.; Muttil, N.; Yilmaz, A.G.; Perera, B.J.C. Development of river water quality indices—A review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Moon, M.; Lee, H.; Kim, K. A study on characteristics of water quality using multivariate analysis in Sumjin River basin. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2014, 30, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kal, B.; Kim, S. Application of multivariate statistical techniques to analyze the pollution characteristics of major tributaries of the Nakdong River. J. Wetl. Res. 2019, 21, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, P.S.; Park, M.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Cho, Y.C.; Noh, C.W.; Jung, W.S.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, S.J. Evaluation of water quality characteristics at Kyeongan stream using the flow-loading equation and factor analysis. Ecol. Resilient Infrastruct. 2017, 4, 226–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Park, S.W. Calibration and Validation of HSPF Mode1 to Estimate the Pollutant Loads from Rural Small Watershed. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 37, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Kim, S.M. Estimation of the Hapcheon dam inflow using HSPF model. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 61, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.M.; Shin, H.S.; Kwon, S. Evaluation of riparian buffer for the reduction efficiency of non-point sources using HSPF Model. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2019, 19, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.H.; Chung, G. Estimation of snow damages using multiple regression model-The case of gangwon province. KSCE J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. 2017, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.Y.J.; Lee, K.L.; Ingersoll, G.M. An introduction to logistic regression analysis and reporting. J. Educ. Res. 2002, 96, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.H. High-school baseball pitcher’s ERA (Earned Run Average) prediction using multi-variable linear regression analysis method. J. Knowl. Inf. Technol. Syst. 2020, 14, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.H.; Lee, J.; Chung, G. Snow damages estimation using artificial neural network and multiple regression analysis. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2017, 17, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, N.; Kim, H.; Kang, P. Evaluating variable selection techniques for multivariate linear regression. J. Korean Inst. Ind. Eng. 2016, 42, 314–326. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.Y.; Han, K.Y.; Kim, B.H. Comparison of different multiple linear regression models for real-time flood stage forecasting. KSCE J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. 2012, 32, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Huo, X. Accelerate the warm-up stage in the Lasso computation via a homotopic approach. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2023, 184, 107747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yao, Y. Variable selection method for fault isolation using least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 146, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozafari, Z.; Chamjangali, M.A.; Arashi, M. Combination of least absolute shrinkage and selection operator with Bayesian Regularization artificial neural network (LASSO-BR-ANN) for QSAR studies using functional group and molecular docking mixed descriptors. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 200, 103998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, Q.; Li, M.; Wei, Y. A new LASSO-BiLSTM-based ensemble learning approach for exchange rate forecasting. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagow, M.; Elbany, M.; Darwish, A.M. Identifying urban, transportation, and socioeconomic characteristics across US zip codes affecting CO2 emissions: A decision tree analysis. Energy Built Environ. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ramírez, J.; Estrada-García, J.A.; Figueroa-Sayago, J. Predicting transport mode choice preferences in a university district with decision tree-based models. City Environ. Interact. 2023, 20, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.L.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.; Wahab, M.A. An effective approach for VARANS-VOF modelling interactions of wave and perforated breakwater using gradient boosting decision tree algorithm. Ocean Eng. 2023, 268, 113398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Sun, W.; Chen, C.; Yang, G.; Meng, X.; Peng, J. Marine floating raft aquaculture extraction of hyperspectral remote sensing images based decision tree algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, P.; Yin, A.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Gao, C. Prediction of soil organic carbon in an intensively managed reclamation zone of eastern China: A comparison of multiple linear regressions and the random forest model. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddar, A.; Rangwani, N.; Palekar, S.; Kalambe, J. Glucose Monitoring System Using Machine Learning. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 73, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouabah, A.; Meiss, H.; Villerd, J.; Lasserre-Joulin, F.; Tosser, V.; Chabert, A.; Therond, O. Predicting the abundances of aphids and their natural enemies in cereal crops: Machine-learning versus linear models. Biol. Control 2022, 169, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Gitau, M.W.; Pai, N.; Daggupati, P. Hydrologic and water quality models: Performance measures and evaluation criteria. Trans. ASABE 2015, 58, 1763–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Toft, H.B.; Müller, K.; Hendrikx, J.; Jaedicke, C.; Bühler, Y. Can big data and random forests improve avalanche runout estimation compared to simple linear regression? Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2023, 211, 103844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounaridis, D.; Koukoulas, S. Urban land cover thematic disaggregation, employing datasets from multiple sources and RandomForests modeling. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuchi, W.; Gombojav, E.; Boldbaatar, B.; Galsuren, J.; Enkhmaa, S.; Beejin, B.; Naidan, G.; Ochir, C.; Legtseg, B.; Byambaa, T.; et al. Evaluation of random forest regression and multiple linear regression for predicting indoor fine particulate matter concentrations in a highly polluted city. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokde, J.R.; Thosar, A.G. Linear regression approach for performance evaluation of ES with load impedance variations of non-critical and critical load. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering. Electron. Energy 2023, 6, 100312. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Kang, M.S.; Song, I.; Hwang, S.H.; Song, J.H. Development of IDF curves based on RCP4. 5 scenario for 30-reservoirs in South Korea. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2013, 13, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jo, B.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, J.H. Analysis of effects of drought on water quality using HSPF and QUAL-MEV. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2023, 56, 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kang, J.; Park, H.; Kang, J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.P.; Kim, G. A study on the variation of water quality and the evaluation of target water quality using LDC in major tributaries of Nakdong river basin. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2020, 36, 521–534. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.J.; Kim, T.G.; Keum, H.J. Application of FDC and LDC using HSPF model to support total water load management system. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2018, 34, 33–45. [Google Scholar]
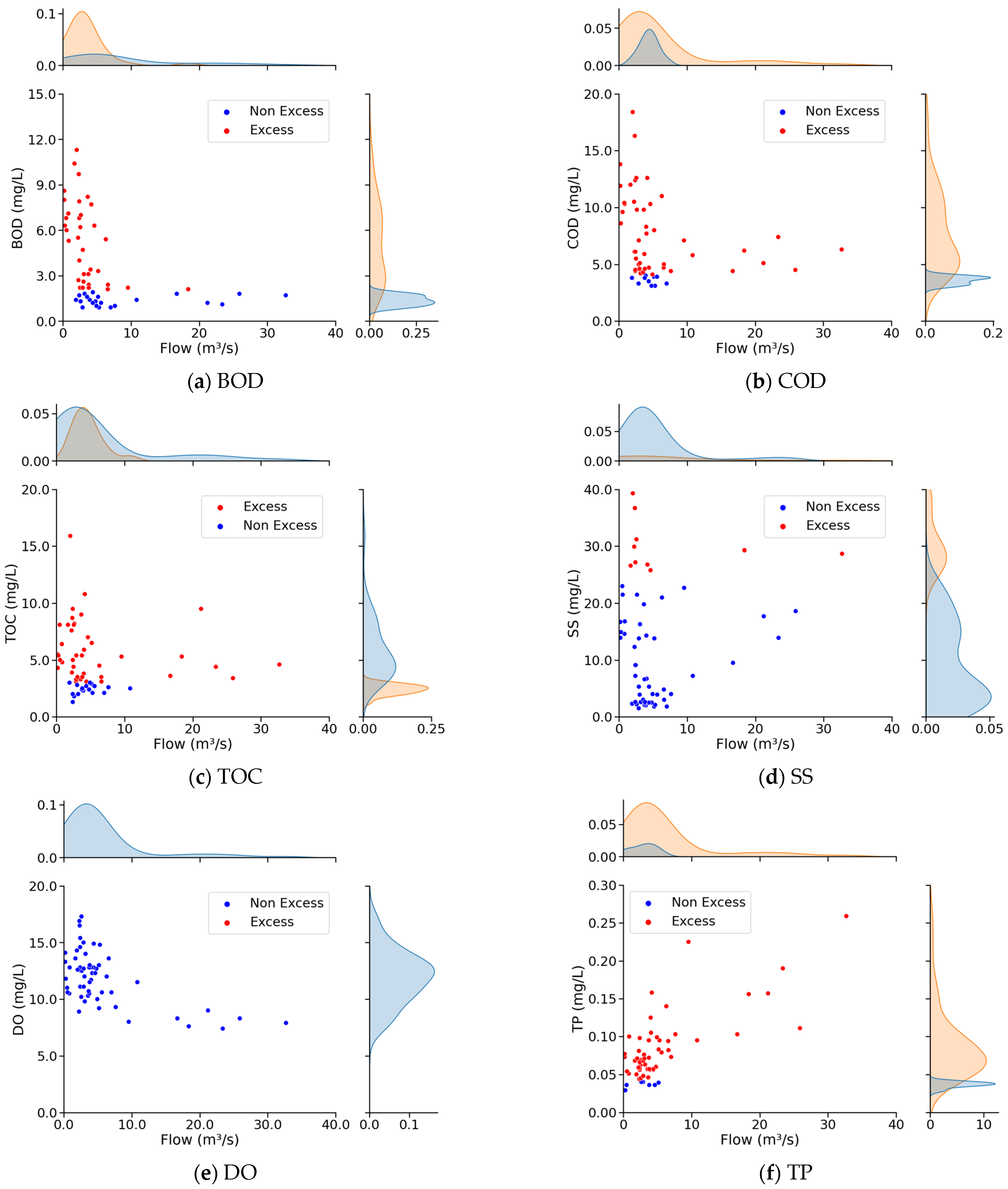
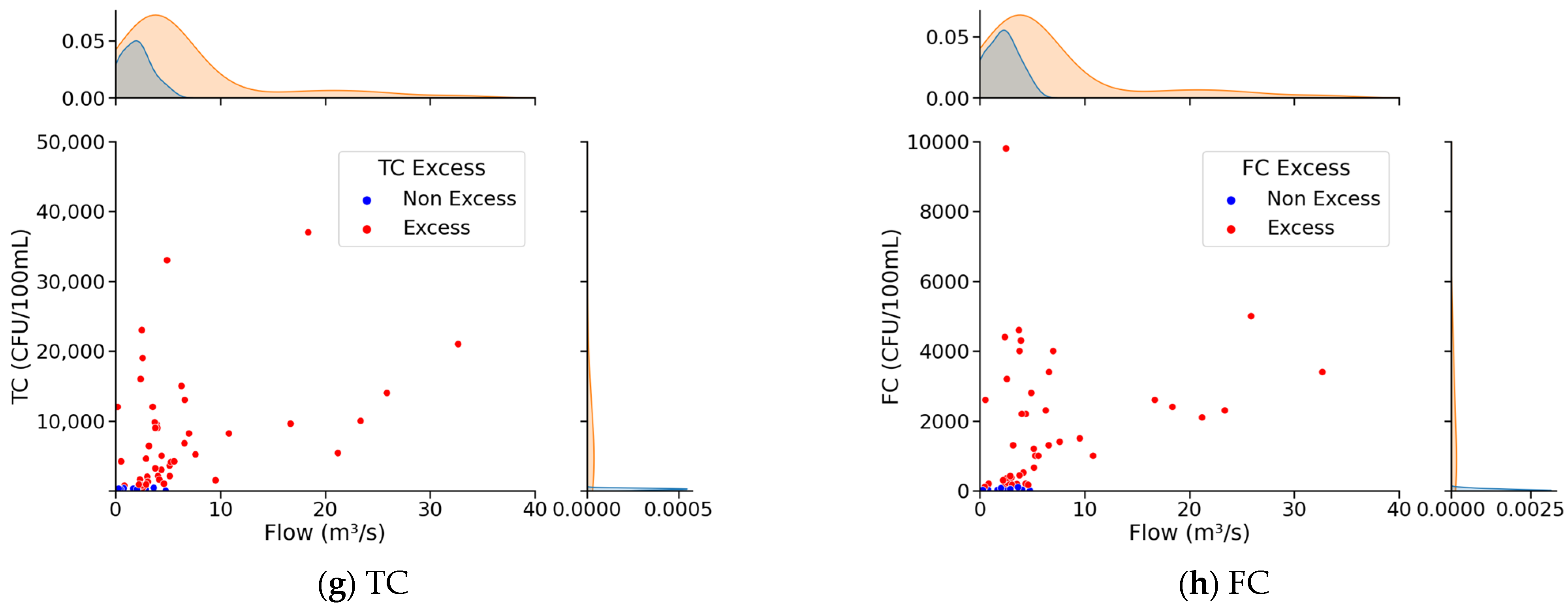

| Parameter | Standard |
|---|---|
| BOD | 2.0 mg/L |
| COD | 4.0 mg/L |
| TOC | 3.0 mg/L |
| SS | 25.0 mg/L |
| DO | 5.0 mg/L |
| TP | 0.04 mg/L |
| TC | 500 CFU/100 mL |
| FC | 100 CFU/100 mL |
| Flow | 0.96 m3/s |
| Parameter | Mean | Median | Max | Min | Std | 25th | 75th | Exceedance Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | 3.3 | 2.0 | 11.6 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 5.1 | 48.7 |
| COD | 7.8 | 6.7 | 21.7 | 3.0 | 3.7 | 4.5 | 10.5 | 86.6 |
| TOC | 3.9 | 3.8 | 8.3 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 2.7 | 4.9 | 63.6 |
| SS | 18.5 | 12.9 | 21.0 | 0.8 | 23.3 | 3.5 | 27.4 | 28.9 |
| DO | 11.5 | 11.9 | 18.3 | 6.3 | 2.4 | 9.7 | 13.3 | 0.0 |
| TP | 0.149 | 0.125 | 1.005 | 0.0025 | 0.117 | 0.080 | 0.180 | 94.7 |
| TC | 3741.3 | 1500.0 | 49,000.0 | 20.0 | 7548.2 | 435.0 | 3900.0 | 98.3 |
| FC | 1590.9 | 470.0 | 26,000.0 | 5.0 | 3662.5 | 125.0 | 1050.0 | 74.6 |
| Flow | 8.6 | 4.2 | 137.4 | 0.1 | 15.3 | 2.6 | 7.5 | 8.6 |
| Parameter | Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BOD | 0.87 | −0.31 | −0.05 |
| COD | 0.94 | 0.05 | −0.07 |
| TOC | 0.79 | 0.19 | −0.04 |
| SS | 0.78 | 0.52 | −0.02 |
| DO | −0.24 | −0.69 | −0.15 |
| TP | 0.01 | 0.82 | 0.15 |
| TC | −0.01 | 0.18 | 0.98 |
| FC | −0.10 | 0.11 | 0.77 |
| Flow | −0.07 | 0.93 | 0.09 |
| Parameter | Fa Loadings | Weight |
|---|---|---|
| BOD | 0.87 | 0.12 |
| COD | 0.94 | 0.13 |
| TOC | 0.79 | 0.10 |
| SS | 0.78 | 0.10 |
| DO | −0.69 | 0.09 |
| TP | 0.82 | 0.11 |
| TC | −0.98 | 0.13 |
| FC | 0.77 | 0.10 |
| Flow | 0.93 | 0.12 |
| Parameter | CCME WQI | OWQI | RTWQI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excellent | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Good | Fair | Excellent | Excellent |
| Medium | Marginal | Good | Good |
| Bad | Marginal | Fair | Fair |
| Very Bad | Poor | Very Poor | Very Poor |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Jo, B.G.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.D. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology Using an Integrated Water Quality Index. Hydrology 2024, 11, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11110178
Lee S, Jo BG, Lim J, Lee JM, Kim YD. Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology Using an Integrated Water Quality Index. Hydrology. 2024; 11(11):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11110178
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Sangung, Bu Geon Jo, Jaeyeon Lim, Jong Mun Lee, and Young Do Kim. 2024. "Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology Using an Integrated Water Quality Index" Hydrology 11, no. 11: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11110178
APA StyleLee, S., Jo, B. G., Lim, J., Lee, J. M., & Kim, Y. D. (2024). Assessment of Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology Using an Integrated Water Quality Index. Hydrology, 11(11), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology11110178







