Abstract
Copper sulfide ores often contain significant amounts of silica and sulfur-bearing gangue minerals, complicating flotation efficiency. However, these challenges can be mitigated through collectorless flotation, which exploits the natural floatability of chalcopyrite and the hydrophilicity of silica minerals. Pyrite, the main sulfur gangue mineral, is also depressed under these conditions, improving concentrate quality by reducing the sulfur and iron content. Air exposure and pulp pre-aeration techniques can enhance chalcopyrite floatability, resulting in high recovery and grade. However, further processing of chalcopyrite concentrate using direct leaching remains challenging due to sulfur passivating layers. To overcome this, additive roasting is used as a pretreatment to improve the leachability of chalcopyrite. This study explored a combined collectorless flotation and additive roasting-leaching method using copper sulfide ore with chalcopyrite, quartz, and pyrite as the main minerals. Collectorless flotation achieved 94.5% recovery and a concentrate of 7.12% Cu from an initial 0.94%. Roasting this concentrate with additives like KCl and NaOH at 600 °C for 1 h, followed by leaching in 0.1 M H2SO4 at 25 °C with a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) addition, resulted in copper dissolutions of 97% and 96.5%, respectively, with low iron dissolution. The proposed process achieved an overall copper recovery of 92%, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining collectorless flotation with additive roasting and atmospheric leaching.
1. Introduction
As the demand for copper continues to rise annually, its production is confronted with several challenges. The most notable trend is the decline in ore grades [1,2], with an average reduction of approximately 25% per decade. At the same time, overall energy consumption is increasing at a faster rate than production [3]. Therefore, with metal demand ramping up rapidly and in the face of the energy transition to reach net zero, improving existing methods and investigating alternative routes for the recovery of metals is of paramount importance.
For more than a century, the minerals industry has extensively employed the flotation process to concentrate various types of ores [4]. Flotation is the most efficient beneficiation method that utilizes the differences in the physical and chemical properties of the mineral surface [5]. Through this process, valuable minerals and gangue can be separated by exploiting the differences in their hydrophobicity. The most abundant copper mineral, chalcopyrite, is usually concentrated using froth flotation. Chemical reagents, such as collectors, are used to impart hydrophobic properties by the oxidation of the surface of target minerals, thereby enhancing their floatability to the surface of the flotation cell. Xanthates are the most widely applied collectors in sulfide flotation, yet their lack of selectivity often leads to the co-flotation of pyrite, an iron-bearing gangue mineral [6]. As a result, achieving a clean copper concentrate requires collectors with stronger selectivity for chalcopyrite over pyrite. This challenge has stimulated research into new collectors that offer improved selectivity for chalcopyrite relative to iron-bearing phases. Xu et al. [7] investigated the adsorption mechanism of a thionocarbamate collector (Z-200) (Yantai Junbang Mineral Materials, Shandong Kejian Chemical, Qingdao Ruchang, Hunan Fortune Technology, China) on polymetallic ore that contained chalcopyrite, sphalerite, and magnetite. It was found that collector Z-200 showed a stronger tendency to adsorb onto the chalcopyrite surface. Analyses of bond lengths revealed that Z-200 was chemically adsorbed onto the chalcopyrite surface through both a normal covalent bond and a back donation covalent bond, with the normal covalent bond being the dominant interaction. Qiu et al. [8] studied the separation of chalcopyrite and pyrite using a novel collector O-n-butyl-N-isobutyl thionocarbamate (NBIB) during flotation. The experimental results from the adsorption capacity tests indicated that NBIB exhibited a strong collecting ability for chalcopyrite across the pH range of 6–11, while its adsorption onto pyrite was weak and decreased with increasing pH.
Nevertheless, conventional copper sulfide flotation, where collectors are applied, often faces challenges such as limited selectivity toward the target valuable minerals, frequently adsorbing onto sulfide gangue (e.g., pyrite) [9,10] and silica minerals [11], which are commonly abundant in copper ores. This non-selective adsorption may not only diminish reagent efficiency but also deteriorate concentrate purity, as both valuable and non-valuable particles rendered hydrophobic are more likely to attach to air bubbles and appear in the froth. Given the limitations of collectors, alternative approaches such as collectorless flotation have been widely investigated. Numerous studies have demonstrated that chalcopyrite can also float in the absence of added collectors [12,13,14,15,16]. Fairthorne et al. [9] showed that the floatability of chalcopyrite depends strongly on surface oxidation: sulfur-rich layers impart hydrophobicity, while coverage by hydrophilic metal hydroxides reduces recovery. These results, together with those of Gardner and Woods [14], emphasize that chalcopyrite natural floatability is controlled by pulp potential and anodic surface reactions. These findings are consistent with other reports that identified a positive pulp potential and suitable pH conditions as critical for this self-induced floatability [13,15,17].
For the further processing of chalcopyrite concentrate to extract metals, pyro- and hydrometallurgical methods are usually applied [18]. The pyrometallurgical method, which involves smelting and refining at high temperatures, is considered highly efficient; however, it has several disadvantages. In addition to this process requiring a high-grade concentrate, the major drawbacks include high energy consumption and substantial greenhouse gas and sulfur dioxide emissions [19,20]. The hydrometallurgical approach for treating copper sulfide ores is promising because, in addition to producing sulfuric acid and soluble sulfate salts, it prevents SO2 emissions, which are a huge ecological burden on the environment. However, the process of extracting copper from copper sulfide concentrate, specifically chalcopyrite, is extremely complex and requires a strong oxidizing reagent to rupture its robust crystal lattice [21], which is introduced during roasting processes. Numerous studies have been conducted to evaluate the efficiency of the direct leaching of chalcopyrite in different acidic and other media without prior thermal treatment [22,23,24,25,26]. Nevertheless, it was confirmed that the dissolution of copper from chalcopyrite by direct leaching is very low even at elevated temperatures and in concentrated acidic media [27] due to the stable coating of sulfur passivation layers.
Thus, the pretreatment of copper concentrate, such as roasting before leaching, is an effective technique that operates at much lower temperatures than smelting processes and hence has a less detrimental impact on the environment. Copper minerals are typically roasted in the presence or absence of additives. These types of additives include various compounds, such as oxides, sulfides, sulfates, and carbonates [28]. Roasting without the use of additives can be as effective as calcination with additives; however, unlike calcination, the sulfur released during roasting cannot be captured in the calcine. Therefore, additive roasting is of great importance because, in addition to the environmental benefits, it offers accelerated reaction kinetics and high metal recovery. Most of the research on chalcopyrite roasting with additives reported in the literature is related to salts, such as chlorides. Particularly, the roasting of sulfide minerals with chloride salts, such as KCl, demonstrates its effectiveness with subsequent atmospheric leaching, yielding high copper recovery (>90%) with minimum SO2 emissions under optimized conditions [21,29,30]. The roasting of copper sulfide concentrate using potassium chloride seems to be promising due to the production of soluble chlorides and sulfate salts. One of the benefits of roasting copper sulfide concentrates with KCl is the generation of intermediate ferric and copper chlorides along with gases that serve as effective chlorination agents [31]. Amongst other compounds utilized for oxidative roasting with chalcopyrite are oxides and carbonates. Ma et al. [32] investigated the chalcopyrite phase conversion mechanism during roasting with calcium oxide. Under optimal conditions, by pelletizing with CaO, chalcopyrite was transformed into an easily soluble oxide form, and copper recovery was over 98%, while sulfur was fixed in the formed calcium sulfate. Hua et al. [20] roasted copper sulfide concentrate in the presence of calcium carbonate using microwave heating before leaching in ammonium carbonate with an ammonia solution. It was found that the reaction kinetics were significantly accelerated by microwave heating, and the recovery of copper was over 90% compared with less than 80% by conventional heating. Despite the advantages of microwave heating, the ammonia leaching medium has several drawbacks, including respiratory and environmental issues [33], and its operational usage is limited.
Although the above-mentioned additives proved their effectiveness during roasting experiments, based on the literature review, there is still no data available on the roasting of chalcopyrite with other components such as alkalis. Although they may share chemical characteristics with some oxides, alkalis can facilitate faster reaction kinetics during roasting and have no adverse impact as chlorides. To evaluate the efficiency of metal dissolution after alkali roasting, NaOH, the most common alkali, was selected for the chalcopyrite-alkali calcination process.
In this study, collectorless flotation and additive roasting experiments were conducted to assess the efficiency of copper recovery. It was confirmed that collectorless flotation can be efficient in reducing reagent consumption and, most importantly, the effective separation of Cu-Fe under optimal conditions. During flotation without a collector, the natural hydrophobicity of chalcopyrite and the depression of pyrite, the main iron-bearing gangue mineral, enabled achieving a relatively high copper grade and recovery with minimal iron content in the concentrate. This helped achieve a significant advantage in subsequent roasting-leaching processes, where iron contamination can hinder effective copper recovery. Additives like KCl and NaOH were used in the roasting experiments, and the effects of key parameters, such as the concentrate-additive ratio, roasting temperature, and roasting time, were evaluated. Based on these experiments, the efficiency of each additive and its impact on the environment are considered. Moreover, the effect of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as an oxidizing reagent was also considered. Hydrogen peroxide addition enhanced copper dissolution during leaching experiments by preventing copper precipitation and facilitating the oxidation of copper compounds to the more soluble state. Thus, this research aims to propose the efficient recovery of copper from copper sulfide ore using collectorless flotation with greater Cu-Fe selectivity and additive roasting, followed by subsequent atmospheric leaching.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
A copper sulfide ore collected from the Kalmakyr mine, Uzbekistan, was used in this study. The chemical assay of the ore is presented in Table 1. The ore was crushed using a laboratory jaw crusher and ground using a grinding machine (<100 µm). The obtained sample was dissolved in aqua regia, and chemical analysis was performed using a microwave plasma atomic emission spectrometer (MP-AES) (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to determine the initial metal content. Other elemental components were determined using X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF, ZSX Primus II Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan). X-ray diffraction (XRD, Rigaku RINT 2200 V, Tokyo, Japan) analysis showed that the sample contained quartz (SiO2), muscovite KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2, chlorite ((Mg, Fe)6(Si, Al)4O10(OH)8), pyrite (FeS2), and chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) as the dominant phases, as shown in Figure 1.

Table 1.
The chemical composition of the copper sulfide ore (wt.%).
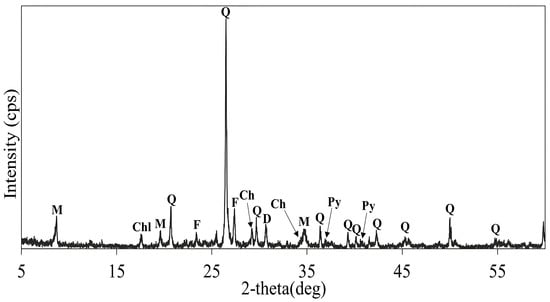
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of the copper sulfide ore sample. Q: Quartz (SiO2), Chl: Chlorite ((Mg,Fe)6(Si,Al)4O10(OH)8), M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), F: Feldspar (K[AlSi3O8]), D: Dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2), Ch: Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), Py: Pyrite (FeS2).
2.2. Experimental Procedure
2.2.1. Flotation
Flotation experiments were conducted using a laboratory flotation machine equipped with a 400 mL cell, a speed stirrer, and an air injection controller. Conventional reagents for copper sulfide ore flotation, such as collector potassium amyl xanthate (PAX, CH3(CH2)4OCS2K), frother methyl isobutyl carbinol (MIBC, C6H14O), and 1 M H2SO4 or 1 M NaOH solutions, were used for conditioning and to adjust pulp pH during the flotation experiments. Under continuous stirring (800 rpm), the ore sample (40–160 g) was introduced into a cell with 360 mL of distilled water to achieve different pulp densities. By adding NaOH or H2SO4 solutions into the pulp, the desired pulp pH (4–11) was adjusted. After conditioning for several minutes, 0.1% PAX solution (0–200 g/t) and MIBC (200 g/t) were added, and the conditioning proceeded. Thereafter, the air injection was turned on, and froth collection began. After the set flotation time, the flotation machine was turned off, and the obtained concentrates and tailings were filtered and dried overnight at 70 °C. Copper and iron concentrations were determined using MP-AES (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA), XRF and mineralogical analysis was performed by XRD. To calculate the recovery of each metal, the following Equation (1) was used:
where F and C are the weights of the feed and concentrate, and f and c are the grades of the feed and concentrate, respectively.
2.2.2. Collectorless Flotation
To evaluate copper and iron flotation without a collector, various sets of experiments were conducted with, without, and with staged collector addition. Additionally, methods such as sample air exposure and the pre-aeration of the pulp before flotation were employed to assess the effect of sample oxidation. Experiments were carried out under the following conditions: pulp density of 10%, pulp pH of 10, MIBC frother of 200 g/t, and PAX collector of 50 g/t when needed, and the rest of the conditions were kept the same as mentioned above.
2.2.3. Flotation Kinetics
Flotation kinetics plays a crucial role in assessing the flotation performance of minerals. Many kinetic models have been proposed, and in this study, the conventional first-order model was used to compare the flotation rate constants with and without a collector [34,35,36]. The flotation process can be regarded as a time-dependent recovery process as the cumulative mineral recovery to concentrate depends on the flotation time [37]. This is presented in Equation (2) as follows [38]:
where R is the cumulative copper recovery at time t (%), k is the flotation rate constant (min−1), and t is the flotation time (min).
ln(1 − R) = −kt
2.2.4. Roasting
To transform chalcopyrite into oxide form, roasting experiments were conducted by mixing the froth concentrate with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium chloride (KCl) at different mass ratios (1:0.05–1:0.5 for NaOH and 1:0.1–1:0.75 for KCl). The mixtures were placed in a crucible and roasted in an electric muffle furnace at various temperatures (500–650 °C) for 1–4 h at atmospheric pressure. After roasting was completed, the samples were cooled and stored in a desiccator before the structural analysis and leaching experiments. The mineralogical characteristics of calcines were analyzed by XRD and scanning electron microscope-energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
2.2.5. Atmospheric Acid Leaching
After roasting, the mixtures were dissolved in a continuously stirred sulfuric acid solution placed in a beaker. Slurry samples were prepared by mixing 2 g of the roasted mixture with 18 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid solution. Then, a slurry contained beaker was placed on a preheated mixer (25 °C), and leaching started at 500 rpm. To oxidize cuprous ions (Cu+) into cupric (Cu2+) ions and enhance copper dissolution during leaching, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 30% w/w) was introduced as an oxidizing reagent during leaching. The required volume of 30% H2O2 solution (2–7 mL/L) was added in stages (2 mL/L each time) immediately after leaching started, with intervals of 5 and 10 min. After a fixed reaction time (60 min), the slurry sample was cooled to ambient temperature and then filtered. The obtained PLS was analyzed for copper and iron concentrations using MP-AES (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The solid residues were dried overnight at 70 °C in an electric oven and analyzed by MP-AES and XRD.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flotation
3.1.1. Effect of Flotation Time
The effect of flotation time on copper recovery was studied by varying the flotation time between 5 and 15 min. Other conditions, namely pulp density, pulp pH, collector dosage (PAX), frother dosage (MIBC), and air injection rate, were kept constant at 10%, pH of 10, 100 g/t, 200 g/t, and 1.5 L/min, respectively. The results presented in Figure 2 show that the copper grade decreased from 5.6% to 2.87% as the flotation time increased, while the copper recovery increased from 91.25% to 96.83%. Iron demonstrated a similar trend, showing a gradual increase in recovery, reaching 80.9% and a grade of 8.54% after 15 min. As seen from Figure 2, after a rapid increase in copper recovery from 5 to 7 min, there was virtually no further increase at subsequent times. Therefore, a flotation time of 7 min was selected as an optimal and sufficient condition for further experiments.
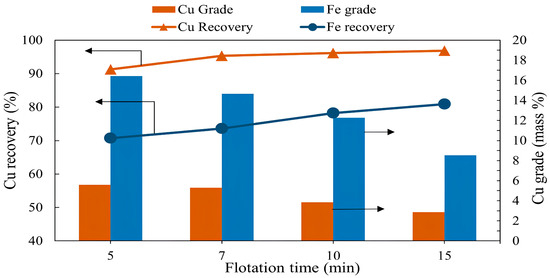
Figure 2.
The grade and recovery of copper and iron as a function of flotation time (flotation conditions: time 5–15 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector dosage (PAX) 100 g/t, frother dosage (MIBC) 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
3.1.2. Effect of Pulp pH
The flotation experiments were conducted at pH values ranging from 4 to 11. All other conditions were fixed: pulp density of 10%, collector (PAX) dosage of 100 g/t, flotation time of 7 min, frother dosage (MIBC) of 200 g/t, and air injection rate of 1.5 L/min. The effect of pulp pH is shown in Figure 3. The results show that copper grade and recovery generally increase when the pulp pH increases from 4 to 10. The highest copper grade of 5.46% was obtained at a pH of 10, while the copper recovery increased to 95.82%. A further increase in the pulp pH resulted in a reduced copper grade of 3.78%, while the copper recovery did not change significantly (96.58%). Figure 4 shows the Eh-pH diagram of chalcopyrite, which displays the self-induced floatability range (yellow background), characterized by broad upper and lower potential limits across nearly the entire pH range [17]. However, when conditions shift above or below this stability range, hydrophilic products such as thiosulfates and metal hydroxides form on the sulfur-rich surface, suppressing chalcopyrite flotation [9,15,36,39].
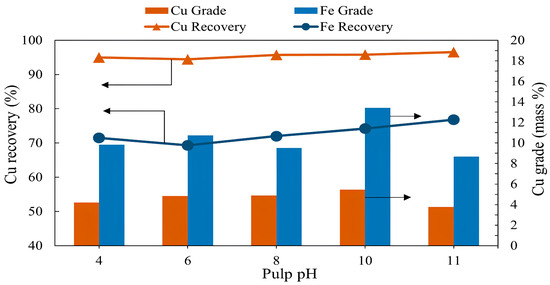
Figure 3.
The grade and recovery of copper and iron as a function of pulp pH (flotation conditions: pulp pH 4–11, flotation time 7 min, pulp density 10%, collector (PAX) dosage 100 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
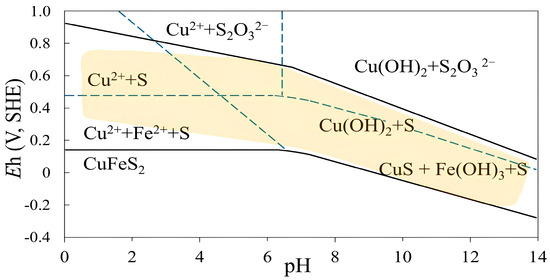
Figure 4.
Eh-pH diagram of chalcopyrite illustrating elemental sulfur (yellow background) as a metastable surface phase (reproduced from Hu et al. [17]).
The recovery of iron increased from 71.5% to 76.8% with increasing the pulp pH from 4 to 11. The maximum iron grade of 13.42% was obtained at pH 10, likely due to the increased recovery of chalcopyrite. Under acidic conditions, partial oxidation may produce sulfur-enriched surfaces, such as elemental sulfur or polysulfides, which can temporarily improve pyrite floatability; however, the range of stability for this behavior is limited, which is shown in the Eh-pH diagram of pyrite (Figure 5, blue area). At a pH of 11, iron grade decreased to 8.68%, indicating pyrite depression. Under strong alkaline and oxidizing conditions, pyrite readily forms Fe(III) hydroxides and sulfates on its surface (Figure 5, red area), which are both hydrophilic phases that lead to its depression [17,40,41]. These results demonstrate that copper recovery improves within the pH range of 7 to around 10, due to the low concentrations of metal hydroxides, which are pH-dependent. Overall, a moderate alkaline pH and positive pulp potential favor chalcopyrite recovery while simultaneously depressing pyrite, enabling their selective separation. In addition, as in the case of Cu and Fe ions, dissolved cations such as Ca2+ from other minerals like dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) form positively charged hydroxides and adsorb onto the chalcopyrite surface, which impedes chalcopyrite recovery at a higher pH > 10 [42].
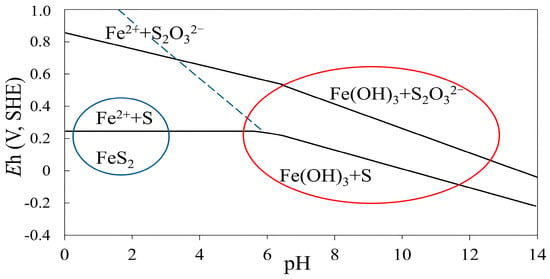
Figure 5.
Eh-pH diagram of pyrite in aqueous solutions, showing elemental sulfur as a metastable phase (blue area). The Eh-pH diagram of pyrite in aqueous solutions, showing the region where metal hydroxides and sulfates form (red area). The equilibrium boundaries represent dissolved species at concentrations of 10−4 mol/L (reproduced from Hu et al. [17]).
3.1.3. Effect of Collector Dosage
Flotation tests were carried out with the collector (PAX) dosage varied from 0 to 200 g/t with other fixed conditions: pulp density of 10%, pH of 10, flotation time of 7 min, frother dosage (MIBC) of 200 g/t, and air injection rate of 1.5 L/min. Figure 6 shows a copper grade of 4.89% and recovery of 93.9% with 0 g/t of a collector, which was almost comparable to that with 50 g/t of a collector with 4.95% copper grade and 95.2% recovery. As shown in the Eh-pH diagram in Figure 4, chalcopyrite displays natural floatability within the stability field of elemental sulfur and Cu-bearing surface species such as CuS [17,39]. In alkaline conditions, chalcopyrite with these hydrophobic species retains hydrophobicity and can float without added collectors. With an increase in the collector dosage to 200 g/t, the copper grade in the concentrate was 4.77%, and no significant increase in copper recovery was detected. Iron remained depressed without a collector, but after the addition of 50 g/t of PAX collector, its recovery increased significantly, reaching 82.8%. This proved that iron recovery depends strongly on collector addition [43]. A further increase in collector dosage did not show any significant change in both iron grade and recovery. It was reported that excessive dosage of the collector can also reduce copper recovery through the creation of a double layer on the mineral surface. After collector molecules cover the entire surface of a particle, excessive collector molecules are attached to the first layer by the hydrophobic side, thus exposing the polar-hydrophilic side to the solution [12,44,45].
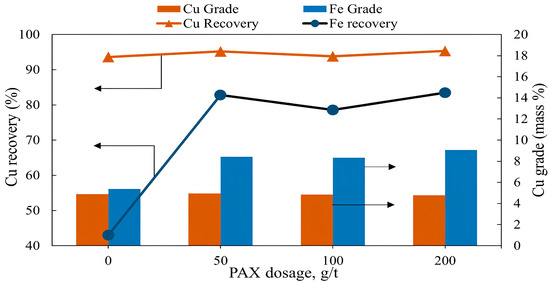
Figure 6.
The grade and recovery of copper and iron as a function of collector dosage (flotation conditions: collector dosage (PAX) 0–200 g/t, flotation time 7 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, frother dosage (MIBC) 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
3.1.4. Effect of Pulp Density
The flotation experiments were performed at pulp densities varying from 10 to 40% with other variables: flotation time of 7 min, frother dosage (MIBC) of 200 g/t, collector (PAX) dosage of 0 g/t, and pH of 10. The results of the experiments are shown in Figure 7. The copper grade and recovery increased from 5.54% to 7.12% and from 91.23% to 94.5% when the pulp density increased from 10% to 20%. A further increase in pulp density showed a gradual decrease in both copper grade and recovery, reaching 5.85% and 92.75% at a pulp density of 40%. Iron showed a similar pattern, with a gradual increase in recovery and grade with an increase in pulp density. As the pulp density increased to 20%, the recovery of iron significantly increased to 68.8% and the grade rose to 6.23%. The highest iron recovery and grade were observed at a pulp density of 30% with 70.4% and 6.96%, respectively. However, a further increase in pulp density did not result in any notable improvement in iron grade and recovery. Lynch et al. [46] reported that at a high pulp density, bubbles are too overloaded by increased particle density, and this can severely hinder the flotation of the particles. Another reason for decreased recovery at higher pulp densities may be the creation of very fine bubbles that are not capable of carrying pulp particles efficiently [47]. These circumstances overall directly affect the flotation kinetics. Therefore, the flotation kinetics is accelerated at lower pulp densities because of the high probability of bubble-particle collision and attachment [48].
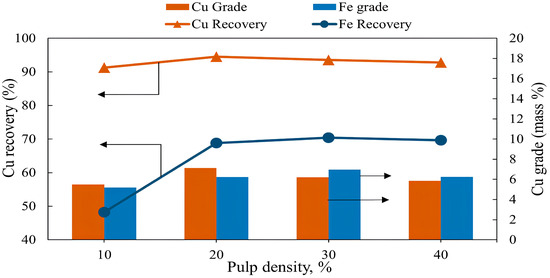
Figure 7.
The grade and recovery of copper and iron as a function of pulp density (flotation conditions: pulp density 10–40%, flotation time 7 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector dosage (PAX) 0 g/t, frother dosage (MIBC) 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
3.1.5. Copper Recovery with and Without a Collector
Another set of flotation tests were carried out to evaluate chalcopyrite floatability in the absence and presence of a collector. Three different types of experiments were conducted, test 1 without a collector, test 2 with 50 g/t of PAX collector, and test 3 with 50 g/t of PAX collector added after 2 min of collectorless flotation, to evaluate the floatability of the mildly oxidized sample used in this test. All other conditions with a pulp density of 10%, pH of 10, flotation time of 2–10 min, frother dosage (MIBC) of 200 g/t, and air injection rate of 1.5 L/min were kept constant for all the experiments, except that the sample for the third test was exposed to the air atmosphere at room temperature for 24 h for surface oxidation.
The flotation results with and without a collector, shown in Figure 8, illustrate copper grade curves. The copper grade in the first two minutes of flotation with and without a collector was 5.85% and 5.5%, while copper recovery was 89% and 64%, respectively (Figure 9). This difference in copper recovery is due to slower flotation kinetics during collectorless flotation, the result of which is the lower recovery of copper compared with that with a collector [43]. However, the copper recovery without a collector improved noticeably after 4 min and by the end of 10 min, it was 95.6% compared with 97.82% with a collector. This difference in final copper recovery can be attributed to chalcopyrite-pyrite compounds, which were additionally recovered by the addition of a collector.
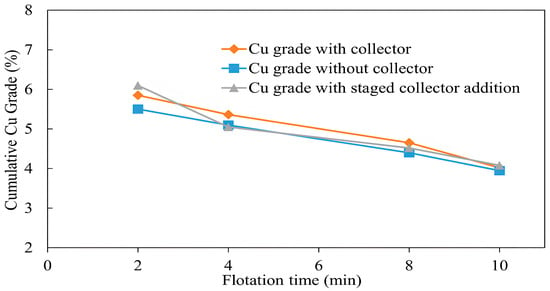
Figure 8.
Effect of collector addition on copper grade (flotation conditions: flotation time 2–10 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 0 g/t and 50 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
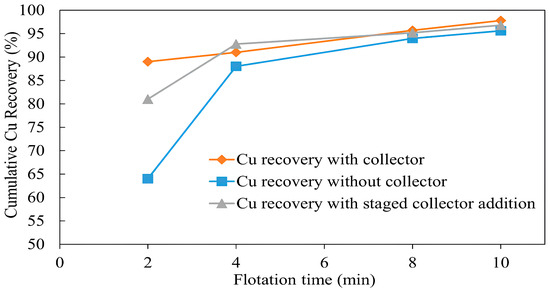
Figure 9.
Effect of collector addition on copper recovery (flotation conditions: flotation time 2–10 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 0 g/t and 50 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
During the third test, a notably higher copper grade of 6.1% was obtained without a collector in the first 2 min, which was higher than with the addition of a collector in the second test. Moreover, the recovery of copper in the third test was noticeably higher, at 81%, compared with the 64% obtained in the first test, during the first two minutes without a collector. As shown in Figure 9, there was actually no difference in final copper recovery after 10 min between test 2 and test 3. This implies that the mildly oxidized sample used in test 3 helped to improve the flotation kinetics of copper. It has been proposed that when a sulfide mineral like chalcopyrite oxidizes in air, layers of hydrated metal oxides and hydroxides develop on its surface, resulting in a metal-deficient chalcopyrite surface while sulfur atoms stay embedded within the lattice. Consequently, during flotation, these oxide and hydroxide layers are dissolved in an alkaline aqueous solution, leaving the metal-deficient layer that is hydrophobic [39,49,50,51,52].
It was revealed that the flotation of iron is significantly dependent on collector addition. Iron remained mostly depressed during collectorless flotation, but its recovery increased significantly after adding a collector, as shown in Figure 10a. The recovery of iron in the first 2 min was 67.1% and 18.6% with and without a collector, respectively. The iron grade with a collector reached 19.75% compared with 6.87% without a collector at the same time, as shown in Figure 10b. At the end of 10 min of flotation, the recovery of iron was 78.2% with a collector and 67.8% without a collector. In the third experiment, a sharp increase in iron recovery from 19.4% to 77.6% after collector addition was noted. As shown in Figure 10a, the final recovery of iron was higher in the third test than in the second test, although the collector was added with 2 min delay. Higher iron recovery in the third experiment was attributed to the oxidation of iron sulfide mineral, i.e., pyrite. With pyrite being a sulfide mineral, the same oxidation processes as in the case of copper could be responsible for the improved recovery of iron. Overall, this suggests that, besides the addition of a collector, air oxidation provided additional hydrophobicity to the sample, resulting in higher recovery [53].
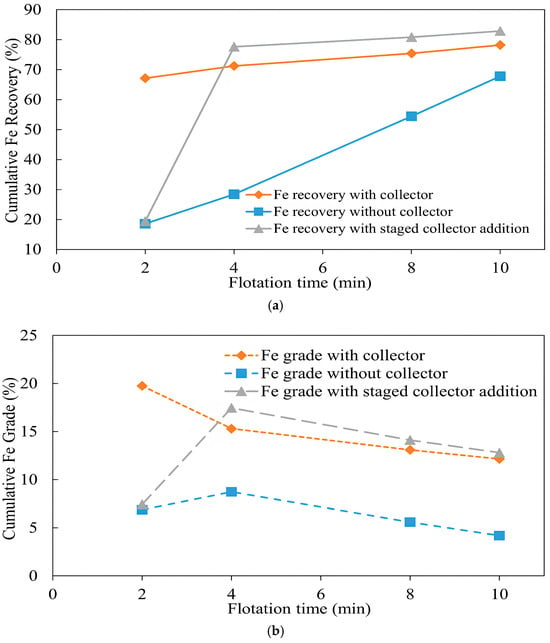
Figure 10.
Effect of collector addition on iron (a) recovery and (b) grade (flotation conditions: flotation time 2–10 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 0 g/t and 50 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
3.1.6. Effect of Aeration on Collectorless Flotation
Two sets of experiments were performed: with and without pulp aeration before flotation. All conditions were the same for both tests, including a pulp density of 10%, frother of 200 g/t, and pH of 10, except in the second test, the pulp was pre-aerated for 40 min before the flotation experiment with an air injection rate of 1.5 L/min. No collector was added in the first 6 min of flotation, after which 50 g/t of PAX collector was introduced into the cell, and the flotation continued for an additional 4 min.
The results plotted in Figure 11 show that pulp pre-aeration had a positive impact on both Cu grade and recovery. As can be seen from Figure 11, there is a clear separation of recovery and grade curves with and without pulp pre-aeration. As a result of pulp pre-aeration, the recovery of copper was higher than that without pre-aeration, showing 67% and 64% after 2 min of flotation, respectively. The copper grade was also higher when the pulp was pre-aerated, reaching 6.46% compared with 5.9% without pre-aeration at the same time. However, this trend started diminishing after collector addition at 6 min, and by the end of 10 min of flotation, there was almost no difference in copper grade and recovery, both with and without pre-aeration. It was proved that copper recovery can be increased by increasing pulp potential if pre-aerated moderately [54]. Moreover, pre-aeration enhances copper selectivity over iron by promoting pyrite depression and reducing its recovery [54,55].
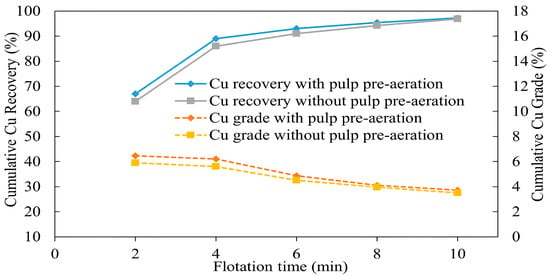
Figure 11.
Effect of pulp aeration on the recovery and grade of copper (flotation conditions: pulp pre-aeration 40 min, flotation time 2–10 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 0 g/t and 50 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
The pulp pre-aeration impact on iron grade and recovery was different compared with copper. The results in Figure 12 show that pulp pre-aeration resulted in a decreased iron recovery of 16.7%, while it was 19.35% without pre-aeration. A serious increase was observed following collector addition at 6 min, and after 10 min of flotation, the final iron recovery was 81.8% and 84.5% with and without pre-aeration, respectively. It is noteworthy that the difference in iron recovery remained until the end of flotation, and its effect was not weakened or almost disappeared as in the case of copper.
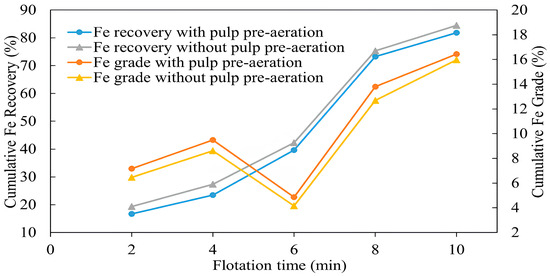
Figure 12.
Effect of pulp aeration on the recovery and grade of iron (flotation conditions: pulp pre-aeration 40 min, flotation time 2–10 min, pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 0 g/t and 50 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
When pre-aerated, the iron grade, on the contrary, showed a higher grade of 7.16% compared with 6.45% without pre-aeration. Then, after a gradual increase, iron grade started to decline until collector addition after 6 min, after which a sharp increase was observed, reaching 16.44% with and 15.97% without pre-aeration at the end of flotation [56]. The depression of pyrite is primarily related to its coverage by hydrophilic iron oxide/hydroxides created by aeration [57]. A high oxygen concentration during the pulp pre-aeration facilitates the formation of metal oxide/hydroxides on the pyrite surface, making it hydrophilic and reducing its floatability [58,59]. It was also found that the depression degree depends on grind size, i.e., the greater the mineral liberation degree, the higher the depression. It was related to an increased oxygen consumption rate at a very fine size (<10 μm) when a greater reactive area is available for interaction with oxygen. However, the low probability of bubble-particle collision also had an impact on pyrite depression [60]. The difference in grades with and without pre-aeration is likely attributed to the recovery of iron associated with chalcopyrite and the depression of pyrite, which explains the higher iron grade produced with pre-aeration. The high sulfide content also enhances galvanic interactions, where pyrite (acting as a cathode) is preferentially oxidized in contact with chalcopyrite (anode), further improving selectivity. These mechanisms are consistent with previous studies highlighting the electrochemical and surface chemistry basis of collectorless flotation in sulfide systems [61,62].
3.1.7. The Beneficiation of Copper from Copper Sulfide Ore Under Optimum Flotation Conditions
The flotation experiments described in Section 3.1.1, Section 3.1.2, Section 3.1.3 and Section 3.1.4 were conducted to evaluate the flotation performance of copper sulfide ore with high silica and sulfur content under different conditions and the results are summarized in Table 2. The chemical compositions of the copper sulfide ore and its concentrate under the established flotation conditions yielding maximum copper recovery are presented in Table 3. A copper concentrate with 7.12% Cu was obtained, achieving copper recovery of 94.5%. The XRD patterns of the copper sulfide ore and its concentrate are shown in Figure 13, revealing chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) and pyrite (FeS2) as major constituents in the concentrate, along with quartz (SiO2) and muscovite KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2. The resulting concentrate containing 7.12% Cu and 6.23% Fe was subjected to additive roasting and subsequent acid leaching to evaluate metal dissolution efficiencies.

Table 2.
The identified optimal conditions for the recovery of copper from copper sulfide ore.

Table 3.
Chemical composition of copper sulfide ore and its concentrate.
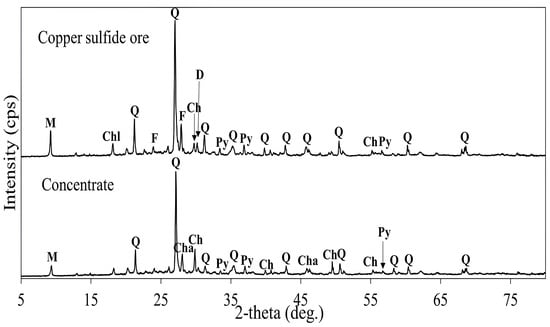
Figure 13.
XRD patterns of copper sulfide ore and its concentrate. M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), Chl: Chlorite ((Mg,Fe)6(Si,Al)4O10(OH)8), Q: Quartz (SiO2), F: Feldspar (K[AlSi3O8]), Ch: Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), D: Dolomite (Ca,Mg(CO3)2), Py: Pyrite (FeS2), Cha: Chalcocite (Cu2S).
Techniques such as exposing the ore sample to air and pre-aerating the flotation pulp in Section 3.1.5 and Section 3.1.6 were shown to increase copper recovery and concentrate grade during collectorless flotation. These methods promote mild surface oxidation of chalcopyrite, which favors the formation of hydrophobic species during flotation while simultaneously passivating pyrite surface, thereby improving the selectivity of copper over iron. As a result, these approaches can enhance the selectivity of copper over iron under collectorless flotation conditions.
3.2. Flotation Kinetics
The flotation kinetics experiments were conducted with and without a collector at a pulp density of 10%, a pulp pH of 10, a frother dosage (MIBC) of 200 g/t, an air injection rate of 1.5 L/min, and a collector dosage (PAX) of 100 g/t. The flotation rate constant k was calculated to obtain the slope by substituting experimental data into Equation (2). The fitted rate constants were kwith PAX = 0.4314 min−1 (R2 = 0.9111) with a collector and kw/o PAX = 0.3896 min−1 (R2 = 0.8974) without a collector. The difference in rate constants (Δk = 0.041 min−1) corresponds to an approximate 10% relative increase with PAX addition and it can be assumed to be not statistically significant. This indicates that flotation proceeded at comparable overall rates in both cases, confirming the effectiveness of collectorless flotation for this ore under the tested conditions. However, the flotation rate constant obtained without a collector was lower than that measured with the addition of a collector, indicating that the presence of a collector accelerates flotation kinetics by enhancing the hydrophobicity of chalcopyrite. This observation is consistent with the cumulative copper recoveries, where Rwith PAX > Rw/o PAX, (Figure 14), confirming that copper recovery without a collector progresses more slowly compared with flotation with a collector.
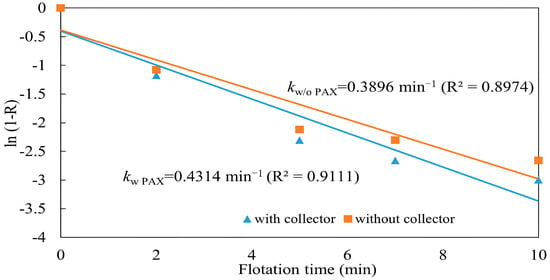
Figure 14.
Comparison of flotation rate constants with and without collector (PAX) (flotation conditions: pulp density 10%, pulp pH 10, collector (PAX) dosage 100 g/t, frother (MIBC) dosage 200 g/t, air injection rate 1.5 L/min).
3.3. Roasting and Leaching
3.3.1. Effect of Concentrate:KCl Mass Ratio
Experiments were performed to assess the effect of the concentrate:KCl ratio on copper and iron dissolution by varying the concentrate and additive mass ratio from 1:0.1 to 1:0.75. The other parameters remained constant at a roasting temperature of 500 °C and roasting time of 3 h. The results in Figure 15 indicate that the dissolution of copper generally increased with increasing the additive ratio, showing that the highest copper dissolution of 91.89% was achieved at a concentrate:KCl mass ratio of 1:0.5, but remained over 90% across all ratios. As seen in Figure 15, the copper concentrate was also roasted without an additive for comparison. While copper recovery was almost as high as roasting with an additive, there was a notable difference in iron recovery. An increase in the additive mass ratio leads to a continuous decrease in iron dissolution from 6.82% at a concentrate to additive ratio of 1:0 to 1.67% at a 1:0.75 mass ratio and remaining under 5% across all ratios tested with KCl. Considering that copper dissolution remains relatively high and iron dissolution is low, and to avoid overconsumption of the additive, it can be concluded that the optimal copper recovery can be achieved with a concentrate:KCl ratio of approximately 1:0.1, while maintaining minimal iron dissolution.
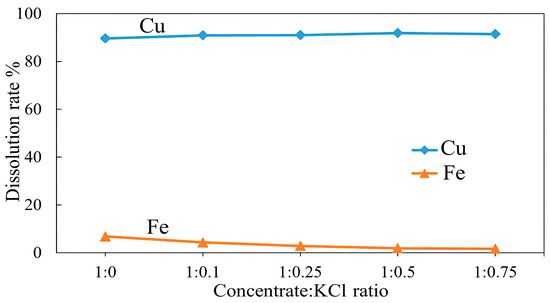
Figure 15.
Effect of concentrate:KCl mass ratios on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: temperature 500 °C, time 3 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
Figure 16 shows the XRD patterns of the copper concentrate and the roasted concentrate with KCl at 500 °C for 3 h. At this temperature, copper sulfide as chalcocite was observed, which was the product of chalcopyrite decomposition via Equation (5). Further oxidation of chalcocite resulted in the formation of copper (I) oxide and copper sulfate, described in Equations (7) and (8). The formed chalcocite, without further oxidation, can hinder copper dissolution due to a sulfur passivation layer, which is stable in the sulfuric acid solution [27]. Pyrite was oxidized into iron chloride (II) and magnetite as the main iron phases at this temperature as shown in Equations (14)–(16); however, unreacted pyrite peaks were also observed.
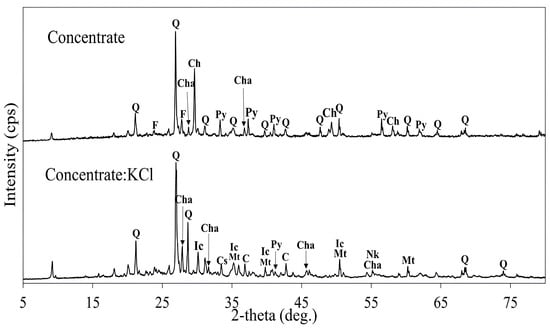
Figure 16.
XRD patterns of the concentrate and the roasted concentrate with KCl (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.5, temperature 500 °C, time 3 h). Q: Quartz (SiO2), F: Feldspar (K[AlSi3O8]), Ch: Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), Py: Pyrite (FeS2), Cha: Chalcocite (Cu2S), Nk: Nantokite/Copper (I) Chloride (CuCl), Cs: Copper Sulfate (CuSO4), Ic: Iron chloride (II) (FeCl2), Py: Pyrite FeS2, Mt: Magnetite (Fe3O4), C: Cuprite/Copper (I) Oxide (Cu2O).
3.3.2. Effect of Roasting Temperature Using KCl Additive
The roasting temperature significantly affects the subsequent leaching procedure. The effect of roasting temperature was investigated at different temperatures (400–650 °C) to evaluate the copper and iron dissolution after roasting with KCl; the results are plotted in Figure 17. The results showed that with increasing temperature, copper dissolution also increased significantly, reaching 95.25% at 500 °C from 22.6% at 400 °C. The sharp increase in copper dissolution at 500 °C was caused by the transformation of sulfide minerals into sulfates, resulting in a higher leaching efficiency [63,64,65]. However, a further increase in the temperature to 650 °C did not result in a major change in copper dissolution. Additionally, a slight decrease in copper dissolution of 89.28% was detected at 650 °C. This implies that the roasting of chalcopyrite at the early stages (starting from 500 °C) is a highly temperature-dependent process, and from around this point, soluble sulfate and oxide forms are generated.
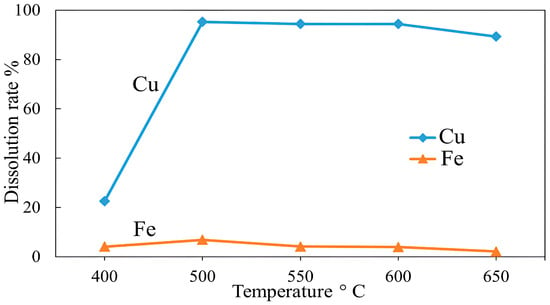
Figure 17.
Effect of roasting temperature on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, time 1 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
The XRD analysis was conducted on the roasted concentrate with KCl samples after roasting tests at different temperatures (Figure 18). The intensity of the quartz and muscovite peaks remained unchanged across all the roasted samples, indicating their thermal stability. At 400 °C, both copper and iron sulfide phases (chalcopyrite, pyrite, and chalcocite) remain prominent, suggesting limited decomposition at this stage. The peaks of chalcocyanite (CuSO4) and nantokite (CuCl) were observed across a temperature range of 400–500 °C. Nantokite is the product of copper (II) chloride decomposition (Equation (4)), which forms as the primary copper phase following the reaction of chalcopyrite with KCl, as described by Equation (3). Chalcocyanite or copper sulfate is usually formed through chalcocite oxidation via Equation (8). At 500 °C, iron-bearing phases such as magnetite, hematite, and troilite were identified, with troilite forming due to the partial oxidation of pyrite. From 500 °C, the peaks of cuprite (Cu2O) and tenorite (CuO) began to appear, becoming the dominant copper phases at 600 °C. Equations (7) and (10) show the formation of these copper oxides through the oxidation processes of chalcocite. Among the iron compounds, hematite was the dominant phase at 600 °C, indicating the completion of hematite formation via the reactions described in Equations (17)–(20).
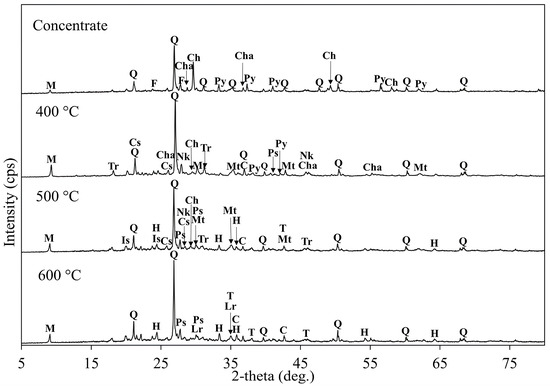
Figure 18.
The XRD patterns of the copper concentrate and roasted concentrates with KCl at different temperatures (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, temperature 400–600 °C, time 1 h). M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), Q: Quartz (SiO2), F: Feldspar, Cha: Chalcocite (Cu2S), Ch: Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), Py: Pyrite (FeS2), Tr: Troilite (FeS), Cs: Copper Sulfate (CuSO4), Nk: Nantokite/Copper (I) Chloride (CuCl), Mt: Magnetite (Fe3O4), C: Cuprite/Copper (I) Oxide (Cu2O), Ps: Potassium Sulfate (K2SO4), Is: Iron Sulfate (FeSO4), H: Hematite (Fe2O3), T: Tenorite/Copper (II) Oxide (CuO), Lr: Lawrencite (FeCl2).
Depending on the roasting temperature, the main copper-bearing phases are chalcocite, copper sulfate, and copper oxides. Roasting the chalcopyrite concentrate with KCl within the specified temperature range can be described by the following Equations (3)–(6) [22,56,60]:
CuFeS2 + 4KCl + 4O2 → 2K2SO4 + FeCl2 + CuCl2
2CuCl2 → 2CuCl + Cl2
2CuFeS2 + O2 → Cu2S + 2FeS + SO2
Cu2S +2KCl + 2O2 → 2CuCl + K2SO4
Incomplete copper dissolution is attributed to the presence of insoluble sulfide phases such as Cu2S and CuS, as well as poorly soluble oxide compounds like Cu2O. The oxidation of chalcocite proceeds at temperatures 490–590 °C to form copper oxides, CuSO4 and dolerophanite CuO·CuSO4 (Equations (7)–(10)). As Dunn et al. [66] reported, copper sulfate and copper (I) oxide may start forming at relatively lower temperatures, beginning around 430 °C. From 590 °C, the oxidation of copper (I) oxide to copper (II) oxide occurs through the reaction in Equation (10) [67].
2Cu2S + 3O2 → 2Cu2O + 2SO2
Cu2S + SO2 + 3O2 → 2CuSO4
Cu2S + 2.5O2 → CuO∙CuSO4
Cu2O + 0.5O2 → 2CuO
Copper oxides are dissolved in sulfuric acid according to the reactions described in Equations (11) and (12):
CuO + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + H2O
Cu2O + H2SO4 → Cu↓ + CuSO4 + H2O
In the case of pyrite, the following reactions take place during roasting with the KCl additive, as shown in Equations (13)–(20) [29,64]:
FeS2 + 4KCl + 4O2 → FeCl3 + 2K2SO4 + Cl
2FeCl3 → 2FeCl2 + Cl2
FeS2 + O2 → FeS + SO2
3FeS + 5O2 → Fe3O4 + 3SO2
FeS + 2O2 → FeSO4
2FeSO4 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
2FeS + 4O2 → Fe2O3 + SO2 + SO3
4Fe3O4 + O2 → 6Fe2O3
Similarly, iron dissolution after an increase at 500 °C decreased steadily from 6.85% at 500 °C to 3.94% at 600 °C. As in the case of chalcopyrite, iron sulfides start converting into soluble sulfate forms at around 500 °C, and with a further increase in temperature, iron dissolution decreases due to the formation of stable, unreactive oxide phases such as hematite (Fe2O3) [63,68,69] or other refractory phases, which are resistant to leaching in a weak sulfuric medium. Moreover, with an increase in temperature, the agglomeration and sintering of particles occur, resulting in a reduction in the surface area available for leaching, which in turn reduces metal dissolution. The described transformation reactions have been reported in similar systems and experimental conditions, and it is reasonable to assume that such reactions could also occur under the roasting conditions investigated in this study.
3.3.3. Effect of Roasting Time Using KCl Additive
Roasting experiments were conducted to investigate the effect of roasting time on the dissolution of copper and iron after roasting with KCl. A mixture of copper concentrate and additive (1:0.1) was roasted for 1–4 h at 600 °C. The results shown in Figure 19 indicate that copper and iron dissolution decreased gradually over time. The highest copper and iron dissolutions of 94.4% and 4.19% were obtained after 1 h, respectively. With a further increase in roasting time, the dissolution of copper and iron gradually decreased, reaching 89.3% and 1.12% after 4 h, respectively. These results indicate that roasting for a longer time often results in the agglomeration and sintering of particles, phenomena that cause particles to stick together and promote the densification of these agglomerates and filling in pores and grain boundaries, which leads to a more compact structure. The SEM results in Figure 20b, compared with the unroasted concentrate in Figure 20a, clearly show that 3 h of roasting led to particle sintering and agglomeration, resulting in the formation of compact agglomerates. These agglomerates reduce the surface area available for leaching and thus impede metal dissolution. Similarly, Zhang et al. [68] reported that during pyrite roasting, elevated temperatures destabilize iron sulfates and induce particle sintering, which traps valuable gold inside.
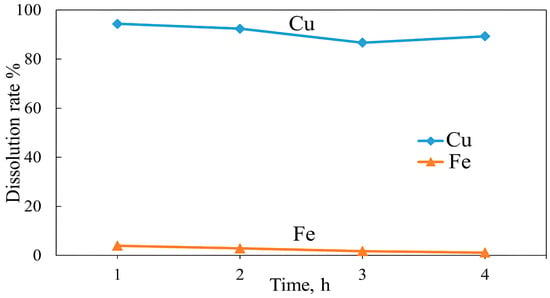
Figure 19.
Effect of roasting time on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, temperature 600 °C; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
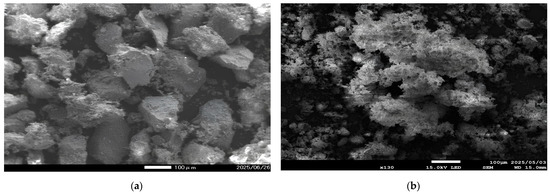
Figure 20.
SEM-EDS images of (a) copper concentrate (SE mode); (b) the roasted concentrate with KCl (BSE mode) (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, temperature 600 °C, time 3 h).
3.3.4. Effect of Concentrate:NaOH Mass Ratio
To investigate the effect of copper concentrate-alkali mass ratio on copper and iron dissolution, roasting experiments were conducted with a concentrate-NaOH ratio from 1:0.05 to 1:0.5 at 500 °C for 3 h. The results in Figure 21 show a substantial decline in copper dissolution when the alkali mass ratio was increased, while iron dissolution in contrast, remained low across all ratios. The highest copper and iron dissolutions of 93.5% and 2.7% were achieved at a concentrate to NaOH ratio of 1:0.05. In the subsequent ratios, an elevated NaOH mass ratio resulted in a drastic reduction in both copper and iron dissolution, which was less than 2% and 1% at a 1:0.5 mass ratio, respectively.
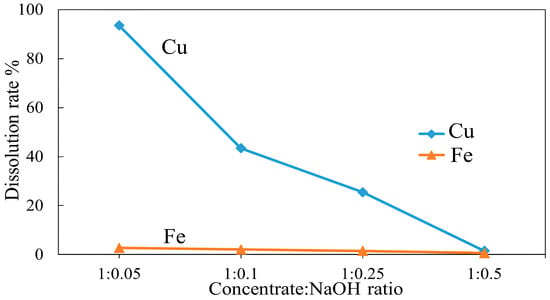
Figure 21.
Effect of concentrate:NaOH mass ratio on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: temperature 500 °C, time 3 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
As shown in Figure 21, a high NaOH mass ratio negatively influences metal dissolution, which may be due to the formation of compounds that can passivate the mineral surface and inhibit further copper leaching. To determine the reason for reduced metal dissolution, SEM-EDS analysis (Figure 22) was performed, revealing a thick sintered coating of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), which may have formed through the reactions outlined in Equations (27)–(29). A high NaOH mass ratio leads to the formation of excessive Na2SO4, which can form viscous melt layers around particles during roasting. When cooling, this layer solidifies, creating a firm crystalline barrier that covers the particle surface. Subsequently, such a barrier remains physically and chemically resistant to sulfuric acid leaching, preventing efficient copper and iron dissolution. Figure 23 shows the XRD pattern of the roasted concentrate with NaOH at 500 °C for 3 h at a 1:0.25 mass ratio. The strong peaks of sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and their intensity confirmed the SEM-EDS results.
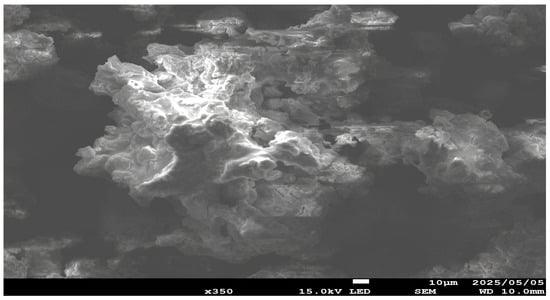
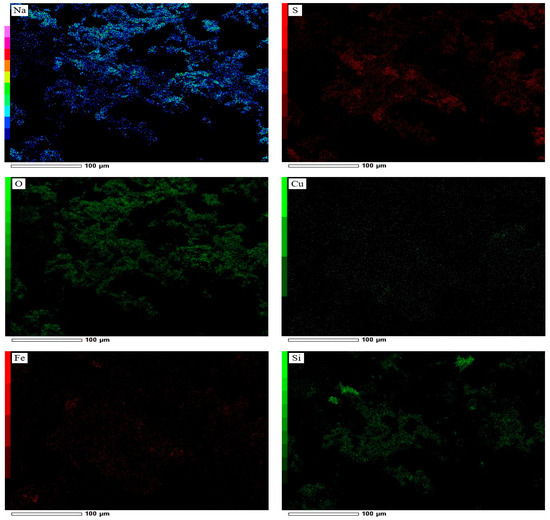
Figure 22.
SEM-EDS (SE mode) image and elemental map of the elements of the roasted concentrate with NaOH (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.25, temperature 500 °C, time 3 h).
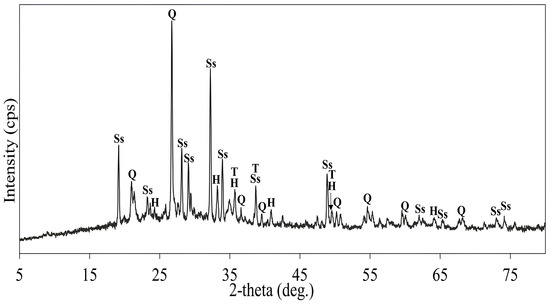
Figure 23.
The XRD pattern of the roasted concentrate with NaOH (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.25, temperature 500 °C, time 3 h). Q: Quartz, Ss: Sodium Sulfate (Na2SO4), H: Hematite, T: Tenorite/Copper (II) Oxide.
Thus, a low mass ratio of NaOH when roasting with copper concentrate is found to be crucial as it allows optimal chalcopyrite oxidation without forming unreactive sodium compounds. As a result, at a concentrate to NaOH mass ratio of 1:0.05, a high recovery of copper was achieved, while iron dissolution remained low.
3.3.5. Effect of Roasting Temperature Using NaOH Additive
To examine the effect of roasting temperature on copper and iron dissolution after roasting with NaOH, roasting tests were conducted at different temperatures (400–650 °C), and the results are shown in Figure 24. An increase in roasting temperature significantly improved copper dissolution, from 44.74% at 400 °C to a maximum of 92% at 600 °C. Iron dissolution after a moderate growth to 6.62% at 500 °C showed a steady decrease, falling below 1% at 650 °C. As in the case of KCl roasting tests, similar reactions are responsible for the increased copper dissolution, i.e., at higher temperatures, sulfides are transformed into copper sulfates and oxides, favoring high copper recovery. The possible reactions that take place when chalcopyrite concentrate is roasted with NaOH are presented in Equations (21)–(23):
2CuFeS2 + 8NaOH + 8O2 → Cu2O + Fe2O3 + 4Na2SO4 + 4H2O
2CuFeS2 + 8NaOH + 8.5O2 → 2CuO + Fe2O3 + 4Na2SO4 + 4H2O
Cu2S + 2NaOH + 2O2 → Cu2O + Na2SO4 + H2O
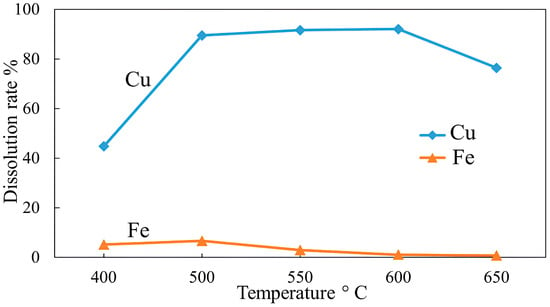
Figure 24.
Effect of roasting temperature on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05, time 1 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
Pyrite’s reaction with NaOH is described by the following reaction shown in Equation (24):
2FeS2 + 8NaOH + 7.5O2 → Fe2O3 + 4Na2SO4 + 4H2O
An increase in temperature to 650 °C resulted in a rapid decline in copper dissolution. As explained earlier, agglomerated and sintered particles at higher temperatures decrease the surface area, limiting metal dissolution. These results suggest that high temperatures can promote high copper recovery while reducing iron dissolution; however, sintering occurs when a defined temperature threshold is exceeded (Figure 25).
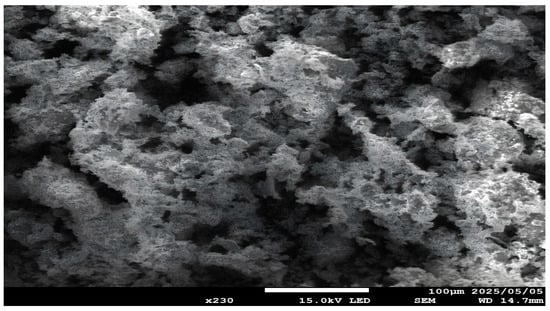
Figure 25.
SEM-EDS results of the roasted concentrate with NaOH (BSE mode) (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05, temperature 650 °C, time 1 h).
The XRD analysis of the roasted concentrates with NaOH at different temperatures is shown in Figure 26. Peaks corresponding to quartz, muscovite, and sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) were observed across all roasted samples. At 400 °C, residual chalcopyrite and pyrite peaks were still detectable, while the appearance of chalcocite peaks at 500 °C indicated the partial oxidation of chalcopyrite. At 600 °C, more peaks of tenorite (CuO) and dolerophanite (CuO(CuSO4)) were observed in the roasted concentrate sample. The formation of dolerophanite and copper (II) oxide through chalcocite oxidation is favorable (Equations (9) and (10)) because it enhances copper dissolution during leaching. Additionally, new peaks of sodium monocuprate (NaCuO) and sodium ferrite (NaFeO2) appeared at this temperature, likely formed through the sintering of copper and iron oxides with sodium hydroxide.
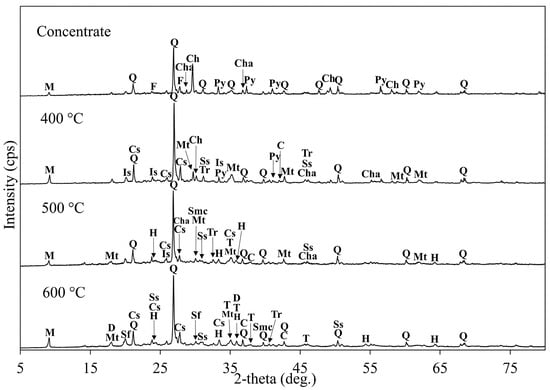
Figure 26.
XRD patterns of the copper concentrate and roasted concentrates with NaOH at different temperatures (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05, temperature 400–600 °C, time 1 h). M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), Q: Quartz (SiO2), F: Feldspar (K[AlSi3O8]), Cha: Chalcocite (Cu2S), Ch: Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), Py: Pyrite (FeS2), Tr: Troilite (FeS), Cs: Copper Sulfate (CuSO4), Mt: Magnetite (Fe3O4), Ss: Sodium Sulfate (Na2SO4), C: Cuprite/Copper (I) Oxide (Cu2O), Is: Iron Sulfate (FeSO4), H: Hematite (Fe2O3), T: Tenorite/Copper (II) Oxide (CuO), D: Dolerophanite (CuO(CuSO4)), Sf: Sodium ferrite (NaFeO2), Smc: Sodium Monocuprate (NaCuO).
3.3.6. Effect of Roasting Time Using NaOH Additive
The effect of roasting time on the dissolution of copper and iron was evaluated over varying roasting times (1–4 h), while other parameters such as the concentrate-additive ratio and roasting temperature were fixed at 1:0.05 and 600 °C. The results in Figure 27 show that copper and iron dissolutions exhibited a moderate decrease with an increase in roasting time. The highest copper and iron dissolutions of 93.2% and 0.96% were achieved after a roasting time of 1 h. The dissolutions of both copper and iron declined gradually after subsequent roasting times (2–4 h) and reached 84.15% and 0.83% after 4 h, respectively. These findings suggest that the formation of dense agglomerates is responsible for decreased copper and iron dissolution. In addition, the decline in iron dissolution is linked to the rapid decrease in formed iron sulfates that are stable up to 600 °C, which are then converted to less soluble Fe2O3 [64]. Moreover, during alkali roasting of the copper concentrate, NaOH could accelerate reaction kinetics by forming mostly iron oxides, since iron dissolution was low already after 1 h of roasting. As a result, a high Cu selectivity over Fe was achieved within this time range.
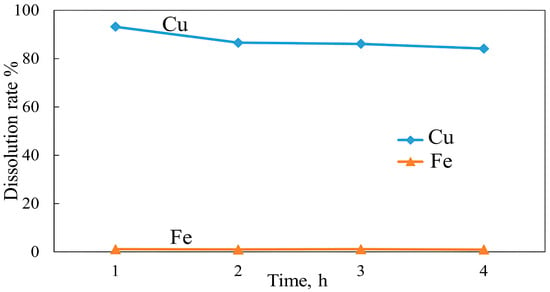
Figure 27.
Effect of roasting time on Cu and Fe dissolution (roasting conditions: temperature 600 °C, concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
3.4. Effect of an Oxidizing Reagent on Copper Recovery
The effect of hydrogen peroxide addition on copper recovery was examined to prevent the formation of metallic copper and its precipitation during leaching (Equation (12)) by varying the volumes of 30% H2O2 solution added to the leach slurry (2–7 mL/L). The results in Figure 28 show that the dissolution of copper generally increases with increasing H2O2 amount. The highest copper dissolutions were achieved after adding 5 mL/L of hydrogen peroxide solution, reaching 97% for the concentrate roasted with KCl and 96.5% for the concentrate roasted with NaOH. With an increase in H2O2 solution amount to 7 mL/L, the dissolution of copper was reduced during the leaching of both calcines, showing 96% and 95.7% for the concentrates roasted with KCl and NaOH, respectively. The copper concentration in the pregnant leach solution reached 1.1 g/L for the KCl roasted and 1.2 g/L for the NaOH roasted concentrates. These results suggest that increasing the amount of hydrogen peroxide in the leach slurry leads to its rapid decomposition into water and oxygen [70], reducing the oxidative potential available for copper species (Equation (25)). Xiao et al. [71] found that a high concentration of H2O2 can lead to the increased dissolution of other metals contained in the feed sample. This accelerates the decomposition of H2O2, resulting in the formation of excessive oxygen bubbles. These bubbles act as a barrier between the copper species and the leaching solution, hindering the leaching efficiency [72,73].
2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2↑
Cu2O + H2O2 + 2H2SO4 → 2CuSO4 + 3H2O
CuCl + H2O2 + H2SO4 → CuSO4 + 2H2O + Cl
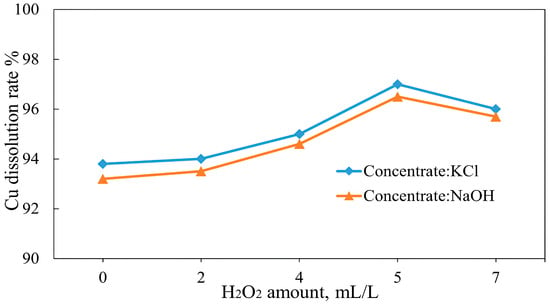
Figure 28.
Effect of an oxidizing reagent on copper dissolution (roasting conditions: temperature 600 °C, concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min).
An increase in copper dissolution is attributed to the oxidative action of H2O2 on Cu(I) species such as Cu2O and CuCl, which are poorly soluble in dilute sulfuric acid. Hydrogen peroxide, having a high redox potential (E° = +1.78 V), promotes the conversion of Cu+ to the more soluble Cu2+ form via the reactions shown in Equations (26) and (27), thereby enhancing the leachability of poorly soluble copper compounds. Moreover, adding H2O2 early in the leaching process helps prevent the disproportionation of Cu(I), which can otherwise produce insoluble metallic copper (Cu0). Once Cu0 forms, it becomes challenging to re-oxidize under mild conditions, which can reduce overall copper recovery.
The observed recovery trend suggests that additions below 5 mL/L may cause incomplete oxidation, while larger additions could lead to rapid H2O2 decomposition and foaming, without further improvement in dissolution efficiency. These findings demonstrate that small, stoichiometrically controlled additions of H2O2 can enhance copper leaching after roasting by both promoting Cu(I) oxidation and preventing Cu0 precipitation.
The solid residues of roasted samples with KCL and NaOH obtained after leaching with H2O2 addition were characterized by XRD analysis and the results are shown in Figure 29a,b. The XRD patterns revealed a predominance of refractory iron phases that were resistant to leaching under the applied conditions. Major iron components, which remained unaffected in both samples, included oxides like hematite and magnetite.
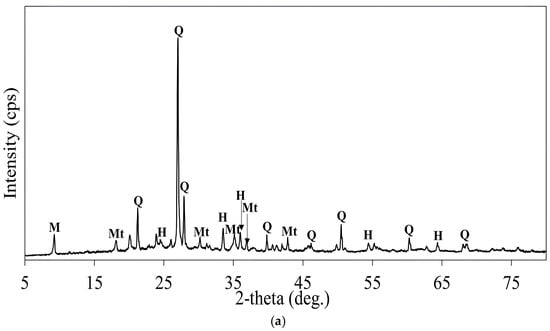
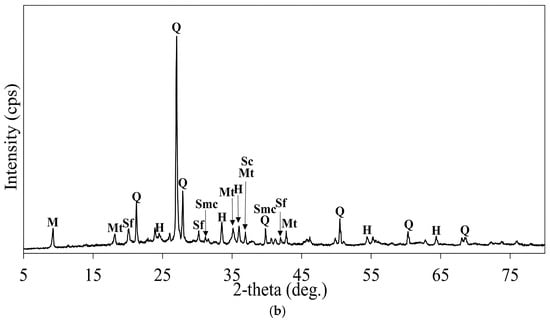
Figure 29.
(a) XRD pattern of the solid residue of the roasted concentrate with KCl after leaching (roasting conditions: concentrate:KCl ratio 1:0.1, roasting temperature 600 °C, roasting time 1 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min, H2O2 amount: 5 mL/L). M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), Q: Quartz (SiO2), Mt: Magnetite (Fe3O4), H: Hematite (Fe2O3). (b) XRD pattern of the solid residue of the roasted concentrate with NaOH after leaching (roasting conditions: concentrate:NaOH ratio 1:0.05, roasting temperature 600 °C, roasting time 1 h; leaching conditions: 0.1 M H2SO4, 25 °C, 60 min, H2O2 amount: 5mL/L). M: Muscovite (KAl2(AlSi3O10)(OH)2), Q: Quartz (SiO2), Mt: Magnetite (Fe3O4), Sodium ferrite (NaFeO2), H: Hematite (Fe2O3), Smc: Sodium Monocuprate (NaCuO), Sc: Sodium Cuprate (NaCuO2).
In the solid residue of the calcine roasted with NaOH, the presence of Na-bearing copper phases, such as sodium monocuprate (NaCuO) and sodium cuprate (NaCuO2), was observed (Equations (28)–(30), suggesting mineral formation as a result of the interaction between copper oxides and sodium hydroxide and the resistance of these minerals in acidic solution, as shown in Figure 29b. The peaks of sodium-iron compounds such as sodium ferrite (NaFeO2) were detected in the roasted sample with NaOH after leaching, indicating that this mineral remained chemically stable in a weak sulfuric acid solution. Equation (31) shows the formation of sodium ferrite through the reaction of hematite with sodium hydroxide.
CuO + NaOH → NaCuO + 0.5H2O + 0.25O2
2CuO + 2NaOH + 0.5O2→ 2NaCuO2 + H2O
Cu2O + 2NaOH + O2→ 2NaCuO2 + H2O
Fe2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaFeO2 + H2O
Notably, copper oxide phases were absent or significantly diminished in both XRD patterns, suggesting the effective leaching of copper-bearing minerals. Weak signals associated with basic iron sulfates (Fe(OH)SO4) were occasionally detected, which likely remained unaffected during the leaching process.
The phases in the residue after leaching, such as hematite and magnetite, are chemically stable, non-leachable under neutral pH conditions, and can be reused as a pigment [74,75] as sorbents in wastewater treatment [76] and in coal washing operations to separate coal from impurities [77]. Potassium sulfate is soluble in water with low acute toxicity and widely used in the fertilizer industry [78]. The chloride in residues after the leaching of KCl-assisted calcines can cause effluent salinity issues and accelerate equipment corrosion. Mitigation options include multi-stage washing to remove over 90% of chlorides [79], evaporation-crystallization to recover salts such as NaCl [80], and thermal treatment at 500–800 °C to remove chlorides that existed in fly ash [81]. The dechlorination of acid wastewater with sulfuric acid and alkaline washing can significantly decrease chloride content [82], reduce environmental risks, and assist the recovery of potential resources.
Heponiemi et al. [83] showed that industrial waste Na2SO4 can be utilized to manufacture alkali-activated materials (geopolymers), achieving a high mechanical strength (≥13 MPa), thereby adding value to what would otherwise be a low-value by-product. Ogedengbe et al. [84] examined an optimized two-stage Glaserite process to convert Na2SO4 into high-value K2SO4 fertilizer. Moreover, industrial projects have already implemented the conversion of sodium sulfate, a by-product from battery production, into potassium sulfate fertilizer. The process is more environmentally friendly and cost-effective than conventional high-temperature routes [85]. Sodium ferrite (NaFeO2) is notable because it can be reused in many different practical ways. Takasu et al. [86] showed that NaFeO2 undergoes reversible carbonation/decarbonation at high temperatures (>700 °C), making it a promising material for thermochemical CO2 capture and energy storage systems. Jabeen et al. [87] demonstrated that β-NaFeO2 nanoparticles exhibit strong photocatalytic (>90% efficiency), antibacterial, and antioxidant activities. Furthermore, NaFeO2 has been examined as a cathode material for sodium-ion batteries in layered solid-solution systems [88], highlighting its potential in energy storage applications.
3.5. A Flowchart for Copper Recovery from Copper Sulfide Ore Using Collectorless Flotation and Additive Roasting
A flowchart illustrating the copper recovery process from copper sulfide ore using collectorless flotation and additive roasting, based on experimental results, is shown in Figure 30. The copper grade of 7.12% from an initial 0.94% was obtained at a pulp density of 20%, while copper recovery was 94.5% without adding a collector. In addition, sample air exposure and the pre-aeration of the pulp before flotation enhanced the floatability of chalcopyrite without a collector by mild surface oxidation as well as pyrite depression, which improved copper-iron selectivity. The obtained concentrate was roasted with KCl and NaOH additives and leached in a weak sulfuric acid solution with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) addition at room temperature. The addition of hydrogen peroxide solution increased copper dissolution by an additional 2.5–3.5% by enhancing the leachability of copper species such as Cu2O and CuCl and preventing the precipitation of metallic copper. Under optimized roasting and leaching conditions, copper recovery reached 97% with KCl roasted and 96.5% with NaOH roasted concentrates, with a copper concentration of 1.1 g/L (KCl) and 1.2 g/L (NaOH) in the PLS. Copper concentrate roasting with NaOH demonstrates significant advantages over roasting with KCl, particularly in terms of reagent efficiency and process selectivity. The mass of NaOH required is approximately half that of KCl to achieve comparable outcomes, providing notable economic benefits through reduced raw material consumption. NaOH also showed better selectivity in immobilizing iron, resulting in minimal iron dissolution, with less than 1% dissolution (0.009 g/L in the PLS), compared to around 4% with KCl (0.049 g/L in the PLS). This improves the purity of the resulting PLS and makes downstream separation easier. Additionally, the absence of chloride-containing products after roasting reduces the environmental impact and facilitates more straightforward waste management. These factors collectively establish NaOH as the more effective and environmentally sustainable option for alkali roasting processes.
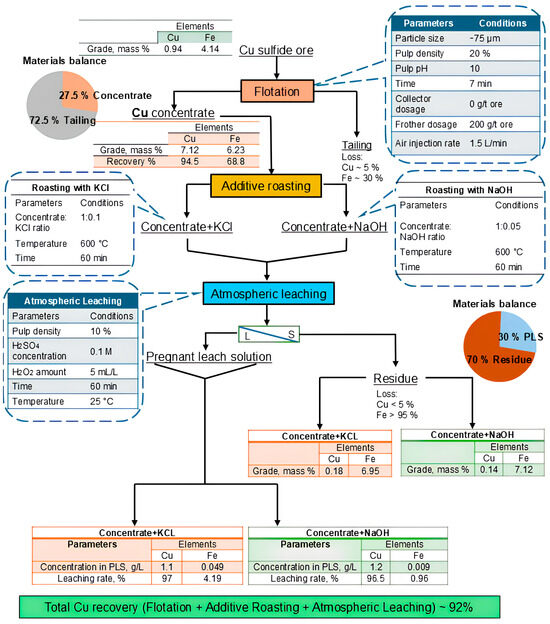
Figure 30.
A flowsheet of the recovery of copper from copper sulfide ore.
4. Conclusions
In this study, the selective recovery of copper and iron using a combination of collectorless flotation, additive roasting, and atmospheric leaching from a copper sulfide ore was investigated. The main conclusions of this study are as follows:
Flotation: Collectorless flotation shows potential as a selective method for copper recovery. Although flotation kinetics is slower without a collector, extending flotation time can offset this limitation. Ultimately, copper recovery comparable to that achieved with collector-assisted flotation can be achieved.
A key advantage is the effective depression of pyrite. Without a collector, pyrite floats slowly, resulting in an iron grade of about 6% and a recovery of around 60%. In contrast, with a collector, iron recovery can reach 80% with a grade up to 19%, leading to decreased selectivity.
Surface oxidation methods, such as air exposure and pulp pre-aeration, improved both copper and iron grades and recoveries. Notably, pre-aeration enhanced iron grade but reduced its recovery, likely due to the surface passivation of pyrite that limits its floatability.
Additive roasting with KCl and NaOH: It was revealed that good selectivity of Cu/Fe was achieved at a lower concentrate to additive mass ratio of 1:0.1 for KCl and 1:0.05 for NaOH. An increase in temperature to 600 °C, which was one of the main parameters during roasting, resulted in the higher recovery of copper, while iron dissolution tended to decrease. Roasting time experiments revealed that with increasing roasting time, the dissolution of Cu and Fe declined gradually, which was attributed to particle agglomeration and sintering.
Roasting chalcopyrite concentrates with additives such as KCl and NaOH has confirmed the efficiency for enhancing copper recovery through oxidative decomposition. KCl roasting is known to facilitate chloride-assisted oxidation and metal activation, often improving copper leachability. However, roasting copper concentrate with NaOH presents a more environmentally sustainable alternative, as it does not produce hazardous and corrosive by-products. Under optimized roasting and leaching conditions, 97% (KCl) and 96.5% (NaOH) of copper recovery was achieved while copper concentration in the PLS reached 1.1 g/L (KCl) and 1.2 g/L (NaOH). Furthermore, iron dissolution was significantly lower with NaOH (<1%) compared to KCl (>4%), which suggests that NaOH can promote faster kinetics, leading to the improved selectivity and reduced contamination of the leach solution. Given these advantages, NaOH emerges as a more suitable reagent for the selective and eco-friendly processing of copper concentrate.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov) and A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama); methodology, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov) and A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama); validation, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov), B.G. (Bobur Gayratov), A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama), and L.L.G.; formal analysis, B.G. (Bobur Gayratov), L.L.G., S.J., A.S. (Abduqahhor Saynazarov), and S.M.; investigation, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov); resources, A.S. (Abduqahhor Saynazarov) and S.M.; data curation, L.L.G.; writing—original draft preparation, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov); writing—review and editing, L.L.G.; visualization, B.G. (Bekhzod Gayratov) and B.G. (Bobur Gayratov); supervision, A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama); project administration, A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama) and L.L.G.; funding acquisition, A.S. (Atsushi Shibayama); All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Additional data will be provided if requested.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the KIZUNA program, Human Resources Development in the Mining Sector, Japan International Cooperation Agency. The experimental work was supported by Akita University. We also greatly appreciate Almalyk Mining and Metallurgical Complex for providing the copper sulfide ore samples.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Abduqahhor Saynazarov was employed by the Almalyk Mining and Metallurgical Complex. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ndoro, T.O.; Witika, L.K. A review of the flotation of copper minerals. Int. J. Sci. Basic Appl. Res. 2017, 34, 145–165. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Bhambhani, T. Preface to the MME special focus issue on managing gangue minerals. Min. Metall. Explor. 2021, 38, 669–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, G.; Mudd, G.; Valero, A.; Valero, A. Decreasing ore grades in global metallic mining: A Theoretical Issue or a Global Reality? Resources 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, B.A.; Finch, J.A. Wills’ Mineral Processing Technology: An Introduction to the Practical Aspects of Ore Treatment and Mineral Recovery, 8th ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2015; p. 265. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Xie, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C. Flotation behavior and mechanism of styrene phosphonic acid as collector on the flotation separation of fluorite from calcite. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 326, 115261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S.J.; Pearse, M.J. The Influences of Collector Chemistry on Kinetics and Selectivity in Base-Metal Sulphide Flotation. Miner. Eng. 1992, 5, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhong, S.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jiang, T. A comprehensive recovery process for selective separation and enrichment of copper, zinc and iron minerals from a polymetallic ore and the adsorption mechanism of collector Z–200. Minerals 2022, 12, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Huang, Z.; Cao, F.; Sun, D.; Wang, P.; Chen, C. Flotation separation of chalcopyrite from pyrite using a novel O-n-butyl-N-isobutyl thionocarbamate as the selective collector. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 661, 130890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairthorne, G.; Fornasiero, D.; Ralston, J. Effect of oxidation on the collectorless flotation of chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 49, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoso, S.A.; Hu, Y.; Liu, R.; Tian, M.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y.; Han, H.; Gao, Z. Selective depression of pyrite with a novel functionally modified biopolymer in a Cu–Fe flotation system. Miner. Eng. 2019, 135, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulatovic, S.M. Handbook of Flotation Reagents: Chemistry, Theory and Practice: Volume 1: Flotation of Sulfide Ores; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 0080471374. [Google Scholar]
- Castellón, C.I.; Toro, N.; Gálvez, E.; Robles, P.; Leiva, W.H.; Jeldres, R.I. Froth Flotation of Chalcopyrite/Pyrite Ore: A Critical Review. Materials 2022, 15, 6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, G.W.; Trahar, W.J. The natural flotability of chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1977, 4, 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.R.; Woods, R. An electrochemical investigation of the natural floatability of chalcopyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1979, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrell, G.H.; Yoon, R.H. Surface studies of the collectorless flotation of chalcopyrite. Colloids Surf. 1984, 12, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, R.S.C.; Amarantidis, J.; Skinner, W.; Prestidge, C.A.; LaVanier, L.; Grando, S. Surface analytical studies of oxidation and collector adsorption in sulphide mineral flotation. Scanning Microsc. 1998, 12, 553–583. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, D. Natural Floatability and Collectorless Flotation of Sulphide Minerals. In Electrochemistry of Flotation of Sulphide Minerals; Hu, Y., Sun, W., Wang, D., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 20–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chakravortty, M.; Srikanth, S. Kinetics of salt roasting of chalcopyrite using KCl. Thermochim. Acta 2000, 362, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Pandey, B.D. Alternative processes for treatment of chalcopyrite—A review. Miner. Eng. 1998, 11, 763–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Cai, C.; Cui, Y. Microwave-enhanced roasting of copper sulfide concentrate in the presence of CaCO3. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 50, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumen-Ulzii, N.; Garnaad, A.; Silam, A.; Tumendelger, A.; Gunchin, B.; Shirchinnamjil, N.; Haga, K.; Shibayama, A.; Batnasan, A. Copper recovery from chalcopyrite concentrate by oxidative roasting and acid leaching. Int. J. Soc. Mater. Eng. Resour. 2022, 25, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prater, J.D.; Queneau, P.B.; Hudson, T.J. The sulphation of copper-iron sulphides with concentrated sulphuric acid. J. Met. 1970, 22, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dutrizac, J.E.; MacDonald, J.C. Ferric ion as a leaching medium. Min. Sci. Eng. 1974, 6, 59–100. [Google Scholar]
- Haver, F.P.; Wang, M.M. Recovery of Cu, Fe and S from chalcopyrite concentrate using a ferric chloride leach. J. Met. 1971, 23, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, R.J.; Benner, B.R. The dissolution of copper concentrates. Miner. Sci. Eng. 1973, 5, 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bjorling, G.; Faldt, I.; Lindgren, E.; Toromanov, I. A nitric acid route in combination with solvent extraction for hydrometallurgical treatment of chalcopyrite. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Copper Extraction and Refining, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–26 February 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Han, B.; Batnasan, A.; Haga, K.; Takasaki, Y.; Shibayama, A. Copper recovery from silicate-containing low-grade copper ore using flotation followed by high-pressure oxidative leaching. Resour. Process. 2017, 64, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuson, S.W. Roasting of copper concentrate in presence of additives. Miner. Sci. Eng. 1980, 12, 21–36. [Google Scholar]
- Medvedev, A.S.; So, T.; Ptitsyn, A.M. Combined processing technology of the Udokan sulfide copper concentrate. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2012, 53, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedev, A.S.; Tu, S. Characteristics of electrochemical reactions accompanying chlorinating annealing of copper sulfide concentrates. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2013, 54, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zou, X.; Cheng, H.; Geng, S.; Xiong, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, X. A novel ammonium chloride roasting approach for the high-efficiency co-sulfation of nickel, cobalt, and copper in polymetallic sulfide minerals. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. 2020, 51, 2769–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.F.; Liao, Y.L.; Wu, M.; Jia, X.B.; Yang, S.Y. Phase transformation mechanism of oxidation roasting of low-grade polymetallic chalcopyrite ore in the presence of CaO. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metall. 2023, 59, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eksteen, J.J.; Oraby, E.A.; Tanda, B.C. A conceptual process for copper extraction from chalcopyrite in alkaline glycinate solutions. Miner. Eng. 2017, 108, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, S.; Wang, P.; Galvin, K.P. Investigating the system flotation kinetics of fine chalcopyrite in a REFLUX™ flotation cell using a standardised flotation cell reference method. Miner. Eng. 2022, 178, 107411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yin, W.; Yang, B.; Wang, D.; Yao, J.; Zhu, Z. Adsorption behavior of sodium oleate on iron minerals and its effect on flotation kinetics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 647, 129108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Godirilwe, L.L.; Haga, K.; Yamada, M.; Shibayama, A. Flotation behavior and surface analytical study of synthesized (octylthio) aniline and bis(octylthio)benzene as novel collectors on sulfide minerals. Miner. Eng. 2023, 204, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Xie, G.; Peng, Y.; Ge, L.; Ni, C. Kinetics of flotation. Order of process, rate constant distribution and ultimate recovery. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2017, 53, 342–365. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, M.; Patino, F.; Escudero, R.; P’erez, M.; Flores, M.U.; Reyes, I.A. Kinetics and hydrodynamics of silver ion flotation. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2012, 56, 408–416. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, A.N.; Woods, R. An x-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of the oxidation of chalcopyrite. Aust. J. Chem. 1984, 37, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, D. Corrosive Electrochemistry of Oxidation-Reduction of Sulphide Minerals. In Electrochemistry of Flotation of Sulphide Minerals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 167–200. [Google Scholar]
- Leppinen, J.O. FTIR and Flotation Investigation of the Adsorption of Ethyl Xanthate on Activated and Non-Activated Sulfide Minerals. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1990, 30, 245–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhao, G.; Fang, X.; Yan, H.; Qiu, X.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, T. Investigation the effect of filling materials on chalcopyrite flotation. Powder Technol. 2024, 431, 119049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Manton, P. A potential application of collectorless flotation in a copper/gold operation. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paria, S.; Khilar, K.C. A Review on Experimental Studies of Surfactant Adsorption at the Hydrophilic Solid–Water Interface. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2004, 110, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Abu-Khamsin, S.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Patil, S. Surfactant Adsorption Isotherms: A Review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32342–32348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, A.J.; Johnson, N.W.; Manlapig, E.V.; Thorne, C.G. Mineral and Coal Flotation Circuits; Their Simulation and Control; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 21–56. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, H. On the optimization of hydrodynamics in flotation process. In Proceedings of the 13th International Mineral Processing Congress, Warsaw, Poland, 4–9 June 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Runge, K.; Tabosa, E.; Crosbie, R.; McMaster, J. Effect of flotation feed density on the operation of a flotation cell. In Proceedings of the 11th AusIMM Mill Operators’ Conference, Hobart, TAS, Australia, 29–31 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, A.N.; Woods, R. An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of the oxidation of galena. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1984, 17, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarski, J.A.; Cases, J.M.; Alnot, M.; Ehrhardt, J.J. XPS characterization of chalcopyrite, tetrahedrite, and tennantite surface products after different conditioning. 1. Aqueous solution at pH 10. Langmuir 1996, 12, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S. Electrochemistry of sulfide flotation: Growth characteristics of surface coatings and their properties, with special reference to chalcopyrite and pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1991, 33, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.N.; Hamilton, I.C.; Woods, R. Investigation of the surface oxidation of bornite by linear potential sweep voltammetry and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1984, 14, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, A.N.; Woods, R. The surface oxidation of pyrite. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1987, 27, 347–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goktepe, F.; Williams, K.P. Electrochemical effects in flotation of a Turkish complex sulfide ore. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Finch, J.A.; Rao, S.R.; Lin, D. Reverse flotation of pyrite from a zinc concentrate using nitrogen. Miner. Eng. 1995, 8, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forson, P.; Zanin, M.; Skinner, W.; Asamoah, R. Differential flotation of pyrite and Arsenopyrite: Effect of pulp aeration and the critical importance of collector concentration. Miner. Eng. 2022, 178, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Lauten, R.A. The depression of pyrite in selective flotation by different reagent systems—A Literature review. Miner. Eng. 2016, 96-97, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuopanportti, H.; Suorsa, T.; Dahl, O.; Niinimaki, J. A model of conditioning in the flotation of a mixture of pyrite and chalcopyrite ores. Int. J.Miner. Process. 2000, 59, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, C.; Fornasiero, D.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Zanin, M. Influence of pulp aeration on the flotation of chalcopyrite with xanthate in chalcopyrite/pyrite mixtures. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 134, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorhom, E.A.; Skinner, W.; Zanin, M. Post-regrind selective depression of pyrite in pyritic copper–gold flotation using aeration and diethylenetriamine. Miner. Eng. 2015, 72, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekmekçi, Z.; Demirel, H. Effects of Galvanic Interaction on Collectorless Flotation Behaviour of Chalcopyrite and Pyrite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 52, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.Q.; Heping, L.; Li, Z. Study of Galvanic Interactions between Pyrite and Chalcopyrite in a Flowing System: Implications for the Environment. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sokić, M.; Ilić, I.; Živković, D.; Vučković, N. Investigation of mechanism and kinetics of chalcopyrite concentrate oxidation process. Metalurgija 2008, 47, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mitovski, A.; Štrbac, N.; Manasijević, D.; Sokić, M. Thermal analysis and kinetics of the chalcopyrite-pyrite concentrate oxidation process. Metalurgija 2015, 54, 311–314. [Google Scholar]
- Atesoglu, G.; Atilgan, İ. Effect of roasting temperature on the leaching of chalcopyrite concentrate in sulphuric acid. Min. Metall. Explor. 2022, 39, 2199–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.; Ginting, A.; O’Connor, B. A thermoanalytical study of the oxidation of chalcocite. J. Therm. Anal. 1994, 41, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.G.; Muzenda, C. Thermal oxidation of covellite (CuS). Thermochim. Acta 2001, 369, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Xu, B.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, T.A. Thermodynamic analysis on the roasting of pyrite. Minerals 2019, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadabad, F.K.; Hejazi, S.; Khaki, J.V.; Babakhani, A. Mechanochemical leaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by sulfuric acid. Int. J. Miner. 2016, 23, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, S.J.; Bogdanović, G.D.; Antonijević, M.M.; Vukčević, M.; Kovačević, R. The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite concentrate with hydrogen peroxide in sulfuric acid solution. Metals 2023, 13, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, Y.; van den Berg, J.; Sietsma, J.; Agterhuis, H.; Visser, G.; Bol, D. Hydrometallurgical recovery of copper from complex mixtures of end-of-life shredded ICT products. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 140, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonijević, M.M.; Dimitrijević, M.; Janković, Z. Leaching of pyrite with hydrogen peroxide in sulphuric acid. Hydrometallurgy 1997, 46, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, V.; Misra, M.; Zhong, K.; Fuerstenau, M.C. Enhanced leaching of copper from chalcopyrite in hydrogen peroxide–glycol system. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, O.C.; Bernardin, A.M. Ceramic colorant from untreated iron ore residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prim, S.R.; Folgueras, M.V.; de Lima, M.A.; Hotza, D. Synthesis and characterization of hematite pigment obtained from a steel waste industry. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena; Gumber, K. Magnetic nanoparticles as emerging sorbents for efficient wastewater treatment. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, I.; Rasyid, M.A.; Fadhilah, R.; Gusti, H.I.K. Beneficiation processing of magnetite ore from Lampung as dense media for dense medium separator in coal washing plant. In Proceedings of the IPMC 2023, Bandung, Indonesia, 12–13 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ersoy, L.; Akhoundnejad, Y.; Daşgan, H.Y.; Temur, B. The effect of potassium sulphate applications on plant growth and nutrient content of pepper plants grown under high temperature stress. Dergipark Akad. 2024, 13, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, J.; Lin, X.; Mao, T.; Zhu, Z.; Lv, J.; Fu, C.; Chen, S.; Wu, A.; Li, X.; et al. Study on three-stage counter-current water washing desalination characteristics and mechanism of high chlorine waste incineration fly ash. Processes 2022, 10, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Song, K.; Xin, Y.; Lv, X. Novel process for deep removal of chlorine and recycling of chlorinated tailings from titanium-bearing blast-furnace slag. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 842–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, D.; Feng, Y. Chlorine removal from MSWI fly ash by thermal treatment: Effects of iron/aluminum additives. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 88, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, L. Green and circular method for chloride separation from acid wastewater: Application in zinc smelter. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heponiemi, A.; Pesonen, J.; Tynjälä, P.; Lassi, U. Use of waste sodium sulfate from battery chemical production in the preparation of alkali-activated materials. ACS Sustain. Res. Man. 2024, 1, 1400–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogedengbe, A.; Achiobu, K.; Scoccimarro, S.; Brunet, S.; Gagnon, G.; Fabrik, M.; Ibrahim, H. Valorization of sodium sulfate waste to potassium sulfate fertilizer: Experimental studies, process modeling, and optimization. Int. J. Green Ener. 2020, 17, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical & Engineering News. Available online: https://cen.acs.org/energy/battery-industrys-sodium-sulfate-waste/102/i21 (accessed on 9 July 2024).
- Takasu, H.; Hoshino, H.; Tamura, Y.; Kim, S.T.; Kato, Y. Sodium ferrite/carbon dioxide reactivity for high temperature thermochemical energy storage. ISIJ Inter. 2019, 59, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, T.; Khan, M.S.; Javaid, S.; Azeem, W.; Ayoub, R.; Motola, M. Synergistic effects of β-NaFeO2 ferrite nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation, antibacterial, and antioxidant applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 12513–12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, K.; Asari, T.; Yoshida, H.; Yaabuuchi, N.; Shiiba, H.; Nakayama, M.; Komaba, S. Understanding the structural evolution and redox mechanism of a NaFeO2–NaCoO2 solid solution for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 6047–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).