Ammonia Removal Using Biotrickling Filters: Part A: Determination of the Ionic Nitrogen Concentration of Water Using Electrical Conductivity Measurement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Rationale
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Water Samples
3.2. Analytical
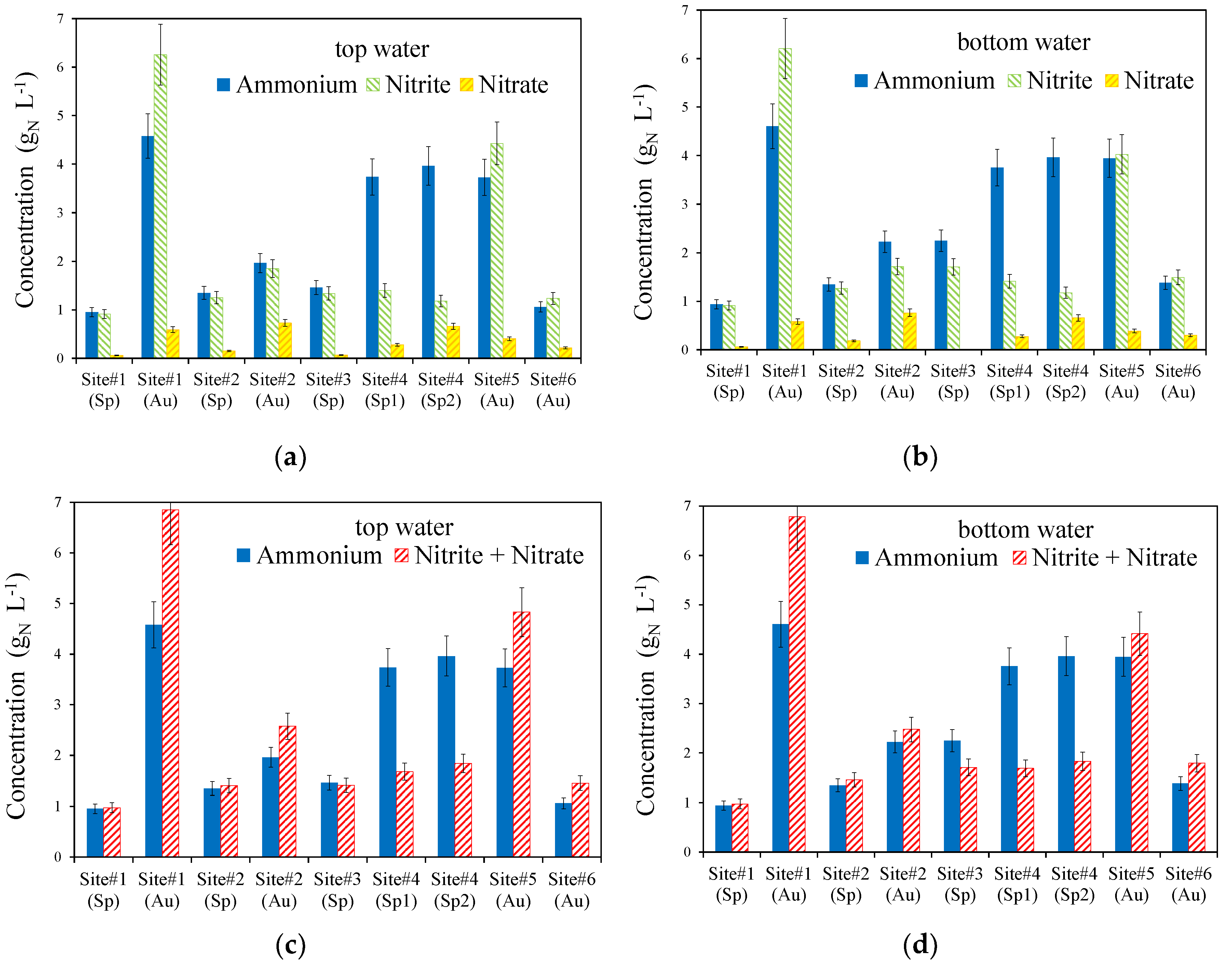
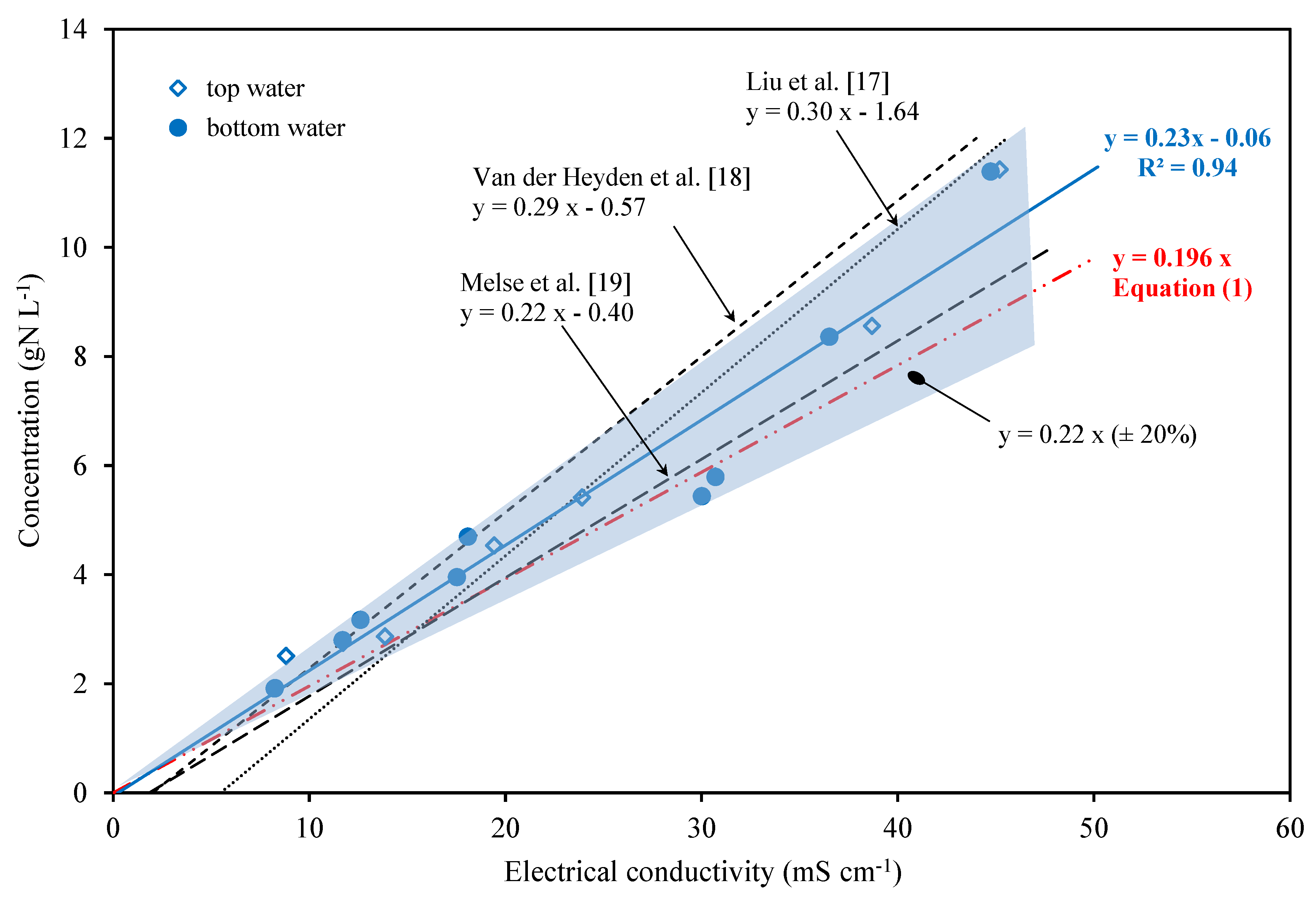
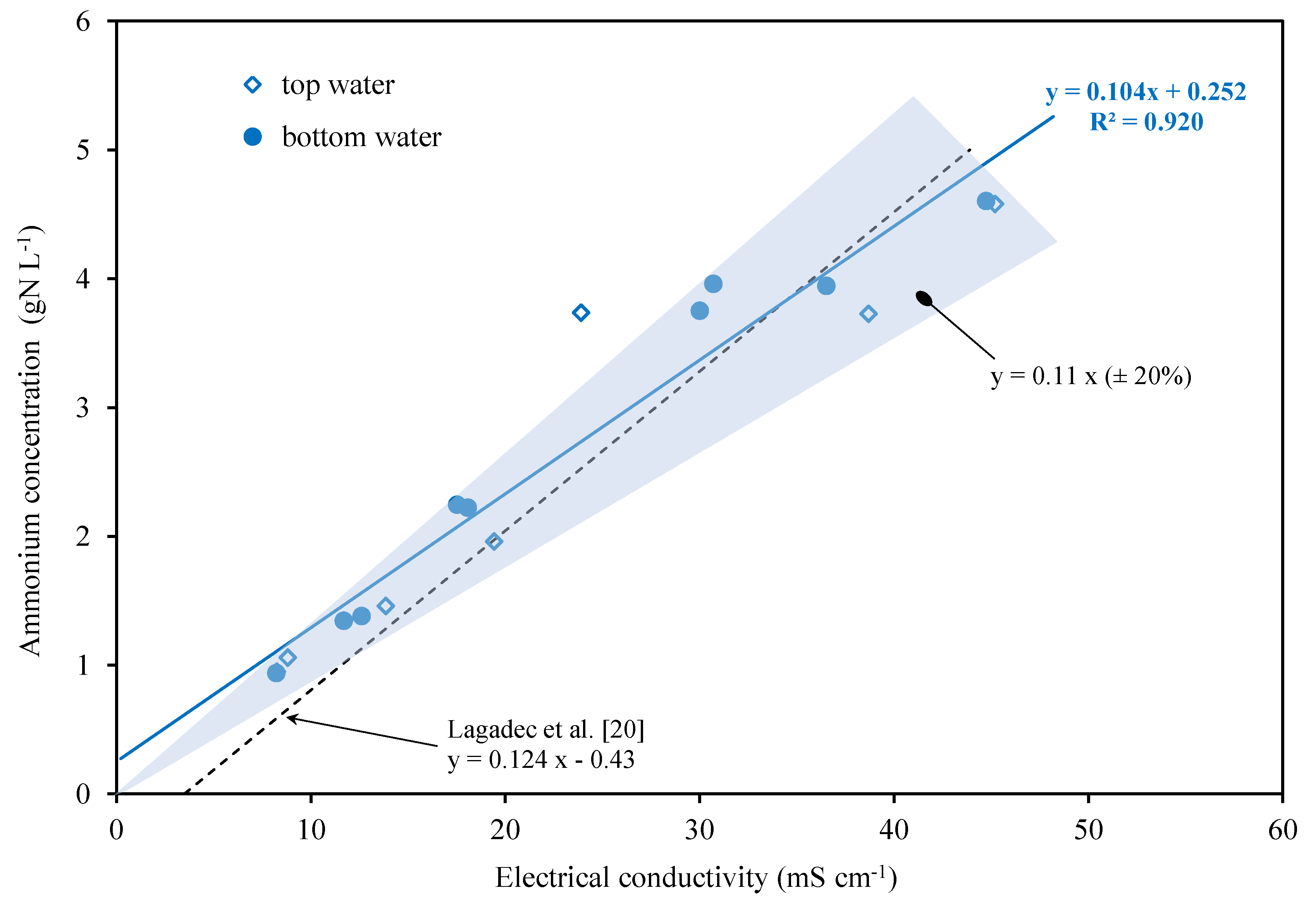
4. Results
4.1. Balance between [NH4+] and Σ ([NO2−] + [NO3−])
4.2. Electrical Conductivity vs. Ion Concentration
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hamon, L.; Andrès, Y.; Dumont, E. Aerial Pollutants in Swine Buildings: A Review of Their Characterization and Methods to Reduce Them. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12287–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J.W.; Melse, R.W. Comparing environmental impact of air scrubbers for ammonia abatement at pig houses: A life cycle assessment. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 161, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, F.-X.; Nicks, B. Review on greenhouse gas emissions from pig houses: Production of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide by animals and manure. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 199, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippe, F.-X.; Cabaraux, J.-F.; Nicks, B. Ammonia emissions from pig houses: Influencing factors and mitigation techniques. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE). Framework Code for Good Agricultural Practice for Reducing Ammonia Emissions; Geneva: UN: Genève, Switzerland, 2015.
- Van der Heyden, C.; Demeyer, P.; Volcke, E.I.P. Mitigating emissions from pig and poultry housing facilities through air scrubbers and biofilters: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 134, 74–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of Nitrification by Ammonia and Nitrous Acid. J. Water Pollut. Control. Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- Ottosen, L.D.M.; Juhler, S.; Guldberg, L.B.; Feilberg, A.; Revsbech, N.P.; Nielsen, L.P. Regulation of ammonia oxidation in biotrickling airfilters with high ammonium load. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 167, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juhler, S.; Revsbech, N.P.; Schramm, A.; Herrmann, M.; Ottosen, L.D.M.; Nielsen, L.P. Distribution and Rate of Microbial Processes in an Ammonia-Loaded Air Filter Biofilm. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 3705–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vadivelu, V.M.; Keller, J.; Yuan, Z. Free ammonia and free nitrous acid inhibition on the anabolic and catabolic processes of Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. Water Sci. Technol. 2007, 56, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buday, J.; Drtil, M.; Hutnan, M.; Derco, J. Substrate and product inhibition of nitrification. Chem. Pap. 1999, 53, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, F.X.; Laitat, M.; Nicks, B.; Cabaraux, J.F. Ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions during the fattening of pigs kept on two types of straw floor. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 150, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassouna, M.; Robin, P.; Charpiot, A.; Edouard, N.; Méda, B. Infrared photoacoustic spectroscopy in animal houses: Effect of non-compensated interferences on ammonia, nitrous oxide and methane air concentrations. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabie, N.M.; Jeppsson, K.H.; Nimmermark, S.; Swensson, C.; Gustafsson, G. Multi-location measurements of greenhouse gases and emission rates of methane and ammonia from a naturally-ventilated barn for dairy cows. Biosyst. Eng. 2009, 103, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melse, R.W.; Ogink, N.W.M. Air scrubbing techniques for ammonia and odor reduction at livestock operations: Review of on-farm research in the Netherlands. Trans. ASAE 2005, 48, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Fiencke, C.; Guo, J.; Rieth, R.; Dong, R.; Pfeiffer, E.-M. Performance evaluation and optimization of field-scale bioscrubbers for intensive pig house exhaust air treatment in northern Germany. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Fiencke, C.; Guo, J.; Rieth, R.; Cuhls, C.; Dong, R.; Pfeiffer, E.-M. Bioscrubber treatment of exhaust air from intensive pig production: Case study in northern Germany at mild climate condition. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heyden, C.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Brusselman, E.; Demeyer, P. Comparative 1-year performance study of two full-scale biotrickling filters for ammonia removal including nitrous oxide emission monitoring. Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 188, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melse, R.W.; Ploegaert, J.P.M.; Ogink, N.W.M. Biotrickling filter for the treatment of exhaust air from a pig rearing building: Ammonia removal performance and its fluctuations. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 113, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagadec, S.; Bellec, F.; Masson, L.; Dappelo, C.; Landrain, P.; Guingand, N. Enquête sur 31 laveurs d’air de porcherie en Bretagne, clés d’amélioration de l’efficacité sur l’abattement de l’ammoniac. Journées Rech. Porc. 2015, 47, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Lide, D.R. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 80th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 5–95. [Google Scholar]
- Atekwana, E.A.; Atekwana, E.A.; Rowe, R.S.; Werkema, D.D.; Legall, F.D. The relationship of total dissolved solids measurements to bulk electrical conductivity in an aquifer contaminated with hydrocarbon. J. Appl. Geophys. 2004, 56, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutmez, B.; Hatipoglu, Z.; Kaymak, U. Modelling electrical conductivity of groundwater using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Comput. Geosci. 2006, 32, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heyden, C.; De Mulder, T.; Volcke, E.I.P.; Demeyer, P.; Heyndrickx, M.; Rasschaert, G. Long-term microbial community dynamics at two full-scale biotrickling filters treating pig house exhaust air. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dumont, É.; Lagadec, S.; Guingand, N.; Loyon, L.; Amrane, A.; Couroussé, V.; Couvert, A. Ammonia Removal Using Biotrickling Filters: Part A: Determination of the Ionic Nitrogen Concentration of Water Using Electrical Conductivity Measurement. ChemEngineering 2020, 4, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030049
Dumont É, Lagadec S, Guingand N, Loyon L, Amrane A, Couroussé V, Couvert A. Ammonia Removal Using Biotrickling Filters: Part A: Determination of the Ionic Nitrogen Concentration of Water Using Electrical Conductivity Measurement. ChemEngineering. 2020; 4(3):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleDumont, Éric, Solène Lagadec, Nadine Guingand, Laurence Loyon, Abdeltif Amrane, Valérie Couroussé, and Annabelle Couvert. 2020. "Ammonia Removal Using Biotrickling Filters: Part A: Determination of the Ionic Nitrogen Concentration of Water Using Electrical Conductivity Measurement" ChemEngineering 4, no. 3: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030049
APA StyleDumont, É., Lagadec, S., Guingand, N., Loyon, L., Amrane, A., Couroussé, V., & Couvert, A. (2020). Ammonia Removal Using Biotrickling Filters: Part A: Determination of the Ionic Nitrogen Concentration of Water Using Electrical Conductivity Measurement. ChemEngineering, 4(3), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemengineering4030049





