Acquired Hemophilia A: A Permanent Challenge for All Physicians
Abstract
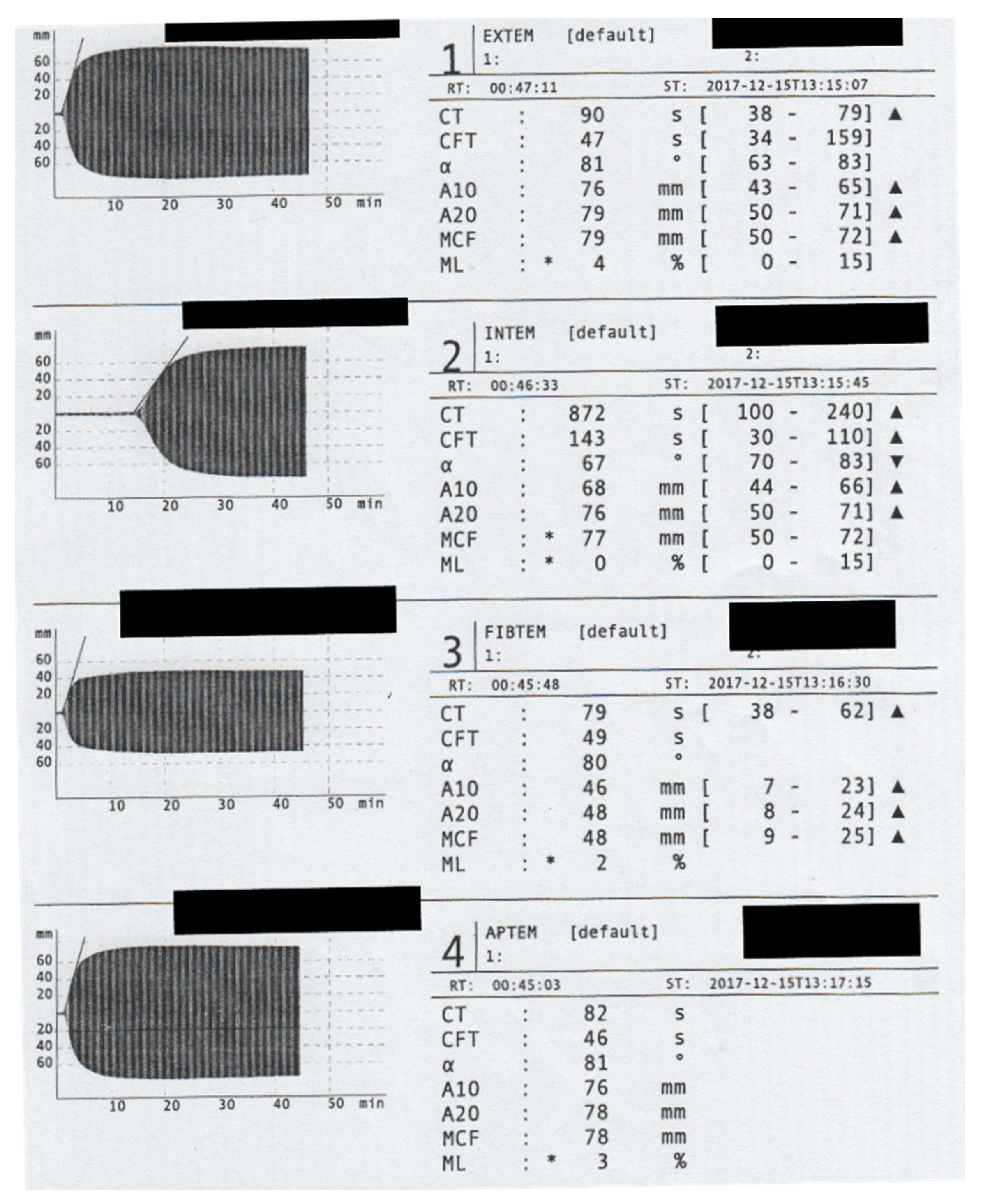
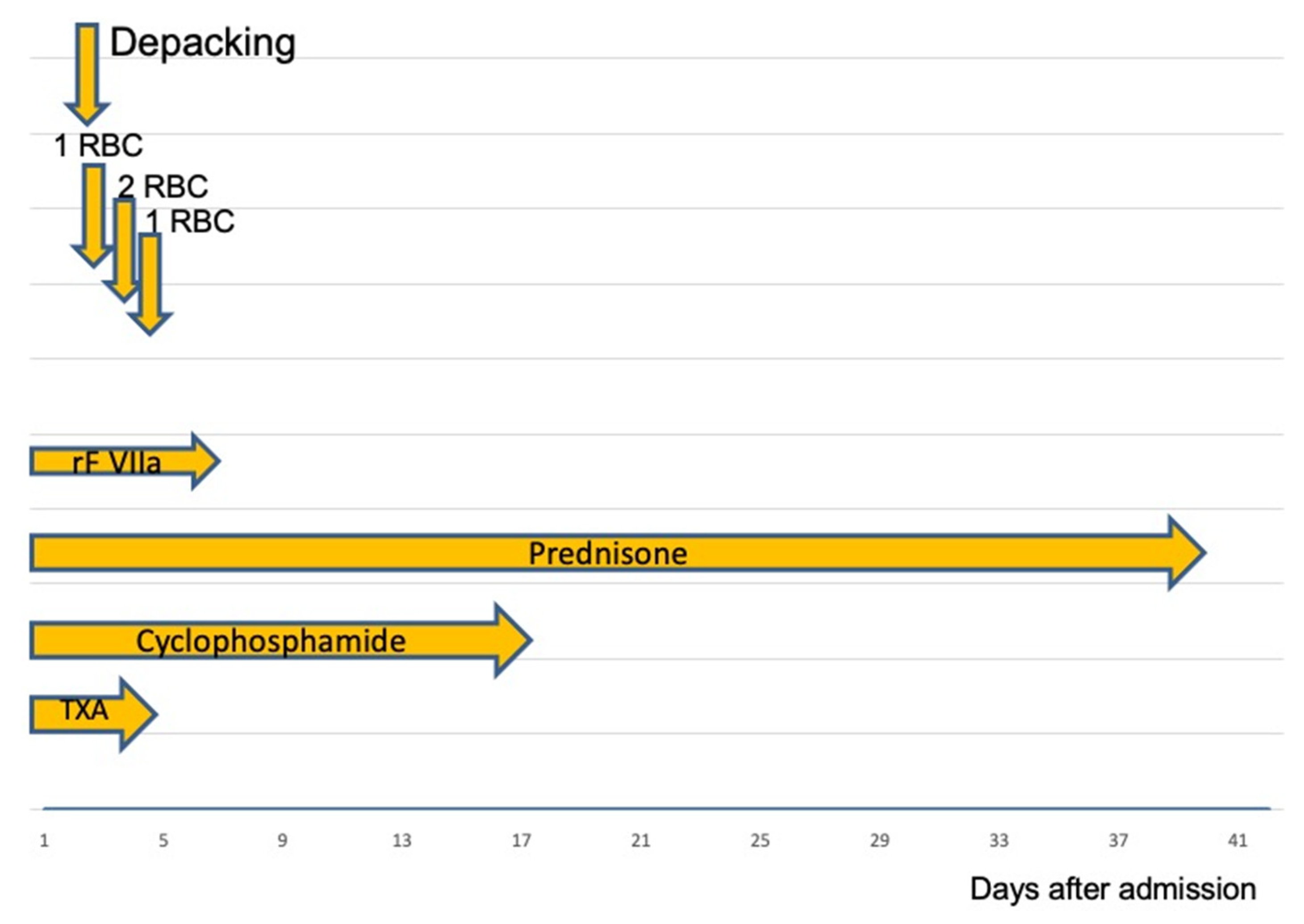
:1. Case Report
2. Discussion
2.1. Epidemiology
2.2. Diagnostic
2.3. Discussion of AHA Treatment
2.3.1. Factor VIII Replacement Treatment
2.3.2. Bypass-Treatment
2.4. Inhibitor Eradication
2.5. Do Patients with AHA and Bleeding Requires Thrombosis Prophylaxis?
3. Conclusion for Daily Practice
- An isolated prolonged PTT value or prolonged clotting time in INTEM assay, with normal values in standard laboratory parameters or ROTEM (beside CT in INTEM), is suspicious for AHA. FVIII activity and possible inhibitors should be determined in these cases.
- The standard of care is based on controlling the bleeding with mainly “bypass agents” and antibody eradication therapy.
- Surgical therapy should only be considered for avoiding nerve compression, circulatory disorders, or other such emergency indications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forces, A.D.T.; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- Yee, T.T.; Griffioen, A.; A Sabin, C.; Dusheiko, G.; A Lee, C. The natural history of HCV in a cohort of haemophilic patients infected between 1961 and 1985. Gut 2000, 47, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knoebl, P.; Marco, P.; Baudo, F.; Collins, P.; Huth-Kühne, A.; Nemes, L.; Pellegrini, F.; Tengborn, L.; Lévesque, H. Demographic and clinical data in acquired hemophilia A: Results from the European Acquired Haemophilia Registry (EACH2). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiede, A.; Hofbauer, C.J.; Werwitzke, S.; Knobl, P.; Gottstein, S.; Scharf, R.E.; Heinz, J.; Gross, J.; Holstein, K.; Dobbelstein, C.; et al. Anti-factor VIII IgA as a potential marker of poor prognosis in acquired hemophilia A: Results from the GTH-AH 01/2010 study. Blood 2016, 127, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiede, A.; Klamroth, R.; Scharf, R.E.; Trappe, R.U.; Holstein, K.; Huth-Kuhne, A.; Gottstein, S.; Geisen, U.; Schenk, J.; Scholz, U.; et al. Prognostic factors for remission of and survival in acquired hemophilia A (AHA): Results from the GTH-AH 01/2010 study. Blood 2015, 125, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werwitzke, S.; Geisen, U.; Nowak-Gottl, U.; Eichler, H.; Stephan, B.; Scholz, U.; Holstein, K.; Klamroth, R.; Knobl, P.; Huth-Kuhne, A.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of factor VIII binding antibodies in acquired hemophilia A: Data from the GTH-AH 01/2010 study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstein, K.; Liu, X.; Smith, A.; Knobl, P.; Klamroth, R.; Geisen, U.; Eichler, H.; Miesbach, W.; Tiede, A. Bleeding and response to hemostatic therapy in acquired hemophilia A: Results from the GTH-AH 01/2010 study. Blood 2020, 136, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse-Jarres, R.; Kempton, C.L.; Baudo, F.; Collins, P.W.; Knoebl, P.; Leissinger, C.A.; Tiede, A.; Kessler, C.M. Acquired hemophilia A: Updated review of evidence and treatment guidance. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 695–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudo, F.; Collins, P.; Huth-Kühne, A.; Lévesque, H.; Marco, P.; Nemes, L.; Pellegrini, F.; Tengborn, L.; Knoebl, P. Management of bleeding in acquired hemophilia A: Results from the European Acquired Haemophilia (EACH2) Registry. Blood 2012, 120, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.W.M.; De Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M.; Cohen, H.; Machin, S.J.; Mackie, I. Guidelines on The Investigation and Management of The Antiphospholipid Syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2000, 109, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nemes, L.; Pitlik, E. New protocol for immune tolerance induction in acquired hemophilia. Haematologica 2000, 85, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kruse-Jarres, R.; St-Louis, J.; Greist, A.; Shapiro, A.; Smith, H.; Chowdary, P.; Drebes, A.; Gomperts, E.; Bourgeois, C.; Mo, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of OBI-1, an antihaemophilic factor VIII (recombinant), porcine sequence, in subjects with acquired haemophilia A. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, P.M. Hemophilia therapy: The future has begun. Haematologica 2020, 105, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, T.; Igawa, T.; Sampei, Z.; Muto, A.; Kojima, T.; Soeda, T.; Yoshihashi, K.; Okuyama-Nishida, Y.; Saito, H.; Tsunoda, H.; et al. A bispecific antibody to factors IXa and X restores factor VIII hemostatic activity in a hemophilia A model. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1570–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shima, M.; Hanabusa, H.; Taki, M.; Matsushita, T.; Sato, T.; Fukutake, K.; Fukazawa, N.; Yoneyama, K.; Yoshida, H.; Nogami, K. Factor VIII–Mimetic Function of Humanized Bispecific Antibody in Hemophilia A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, N.; Sambe, T.; Yoneyama, K.; Fukazawa, N.; Kawanishi, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Shima, M. A first-in-human phase 1 study of ACE910, a novel factor VIII–mimetic bispecific antibody, in healthy subjects. Blood 2016, 127, 1633–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, V.M.; Abou-Ismail, M.Y.; Lim, M.Y. Off-label use of emicizumab in persons with acquired haemophilia A and von Willebrand disease: A scoping review of the literature. Haemophilia 2021, 28, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvas, A.-M.; Sørensen, H.T.; Norengaard, L.; Christiansen, K.; Ingerslev, J.; Sørensen, B. Tranexamic acid combined with recombinant factor VIII increases clot resistance to accelerated fibrinolysis in severe hemophilia A. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2408–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Sørensen, B.; Rea, C.J.; Bjørnsen, S.; Ueland, T.; Pripp, A.H.; Tjønnfjord, G.E.; Holme, P.A. Tranexamic acid as adjunct therapy to bypassing agents in haemophilia A patients with inhibitors. Haemophilia 2013, 20, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, M.J.; Geldziler, B.D.; Pedersen, M.; Seremetis, S. Treatment of acquired haemophilia with recombinant activated FVII: A critical appraisal. Haemophilia 2007, 13, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingerslev, J.; Sørensen, B. Parallel use of by-passing agents in haemophilia with inhibitors: A critical review. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 155, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, K.; Seita, I.; Higasa, S.; Sawada, A.; Kuwahara, M.; Shima, M. Treatment of acute bleeding in acquired haemophilia A with recombinant activated factor VII: Analysis of 10-year Japanese postmarketing surveillance data. Haemophilia 2016, 23, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.; Lechner, K. A survey of 215 non-hemophilic patients with inhibitors to Factor VIII. Thromb. Haemost. 1981, 45, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.; Baudo, F.; Knoebl, P.; Lévesque, H.; Nemes, L.; Pellegrini, F.; Marco, P.; Tengborn, L.; Huth-Kühne, A. Immunosuppression for acquired hemophilia A: Results from the European Acquired Haemophilia Registry (EACH2). Blood 2012, 120, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado, J.; Jiménez-Yuste, V.; Hernandez-Navarro, F.; Villar, A. Acquired Haemophilia: Review and Meta-Analysis Focused on Therapy and Prognostic Factors. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impfkommission, S. Wissenschaftliche Begrundung fur die Aktualisierung der Empfehlungen zur Indikationsimpfung gegen Pneumokokken fur Risikogruppen. Epidemiol. Bull. 2016, 37, 385–406. [Google Scholar]
- Monach, P.A.; Arnold, L.M.; Merkel, P.A. Incidence and prevention of bladder toxicity from cyclophosphamide in the treatment of rheumatic diseases: A data-driven review. Arthritis Care Res. 2010, 62, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Agent | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| rpFVIII (50–100 IU/kg); FVIII activity assessment every 3 h. Assessment of Ab against rpFVIII => If evident, increase the dose up to 200 IU/kg | Serum levels of FVIII could be monitored | Possible cross-reaction with FVIII-inhibitors => less effectivity |
| aPCC 50–100 IU/kg every 8–12 h | Always effective even at high levels of AHA inhibitors >10 BE | No possible monitoring, thromboembolic events are possible |
| rFVIIa 70–90 µg/kg every 3 h until bleeding is stopped; then maintain the dose and extend the intervals | Always effective even at high levels of AHA inhibitors >10 BE | No possible monitoring, thromboembolic events are possible short half-life: 2–3 h |
| Recommended Treatment | Dose | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Prednisone | 1 mg/kg p.o. 4 weeks | Ineffective for patients with FVIII <1% and inhibitor titer >20 BE Side effects: hyperglycemia, infections, steroid psychosis |
| Prednisone + Cyclophosphamide | Prednisone 1 mg/kg Cyclophosphamide: 1–2 mg/kg po daily or 5 mg/kg iv for 4 weeks | May shorten the course of the disease More side effects Highest cure rate Bone marrow toxic (leukopenia/thrombopenia) |
| Prednisone + Rituximab | Prednisone 1 mg/kg Rituximab 375 mg/m2 iv/week for 4 weeks | Rituximab is only recommended if the above regimes have failed; Pneumococcal vaccination recommended |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowak, K.M.; Carpinteiro, A.; Szalai, C.; Saner, F.H. Acquired Hemophilia A: A Permanent Challenge for All Physicians. Medicines 2022, 9, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9030021
Nowak KM, Carpinteiro A, Szalai C, Saner FH. Acquired Hemophilia A: A Permanent Challenge for All Physicians. Medicines. 2022; 9(3):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9030021
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowak, Knut M., Alexander Carpinteiro, Cynthia Szalai, and Fuat H. Saner. 2022. "Acquired Hemophilia A: A Permanent Challenge for All Physicians" Medicines 9, no. 3: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9030021
APA StyleNowak, K. M., Carpinteiro, A., Szalai, C., & Saner, F. H. (2022). Acquired Hemophilia A: A Permanent Challenge for All Physicians. Medicines, 9(3), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines9030021






