Analgesic Effect of Combined Therapy with the Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” and Electroacupuncture in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
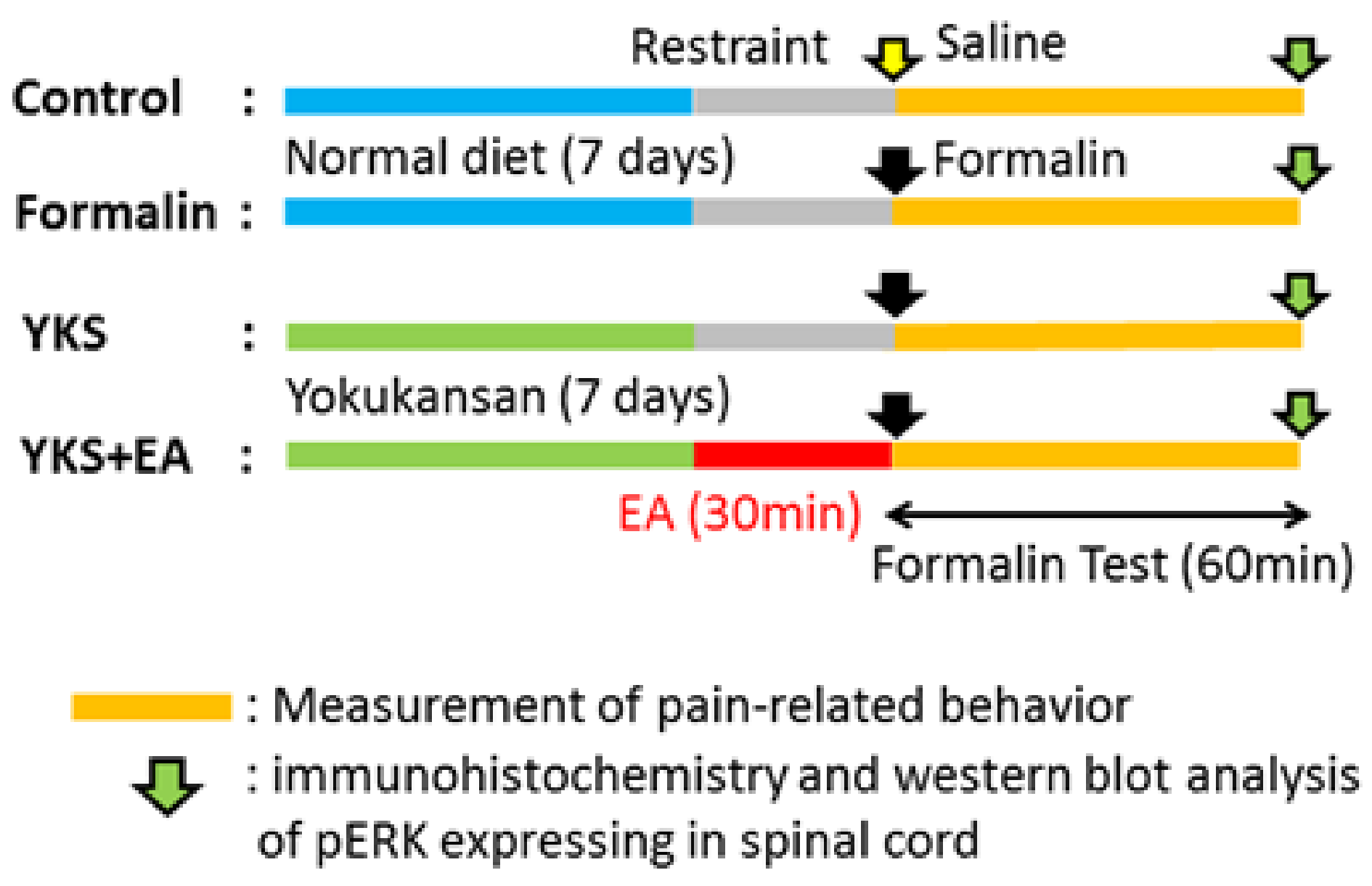
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. YKS Treatment
2.3. Electroacupuncture
2.4. Formalin Test
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
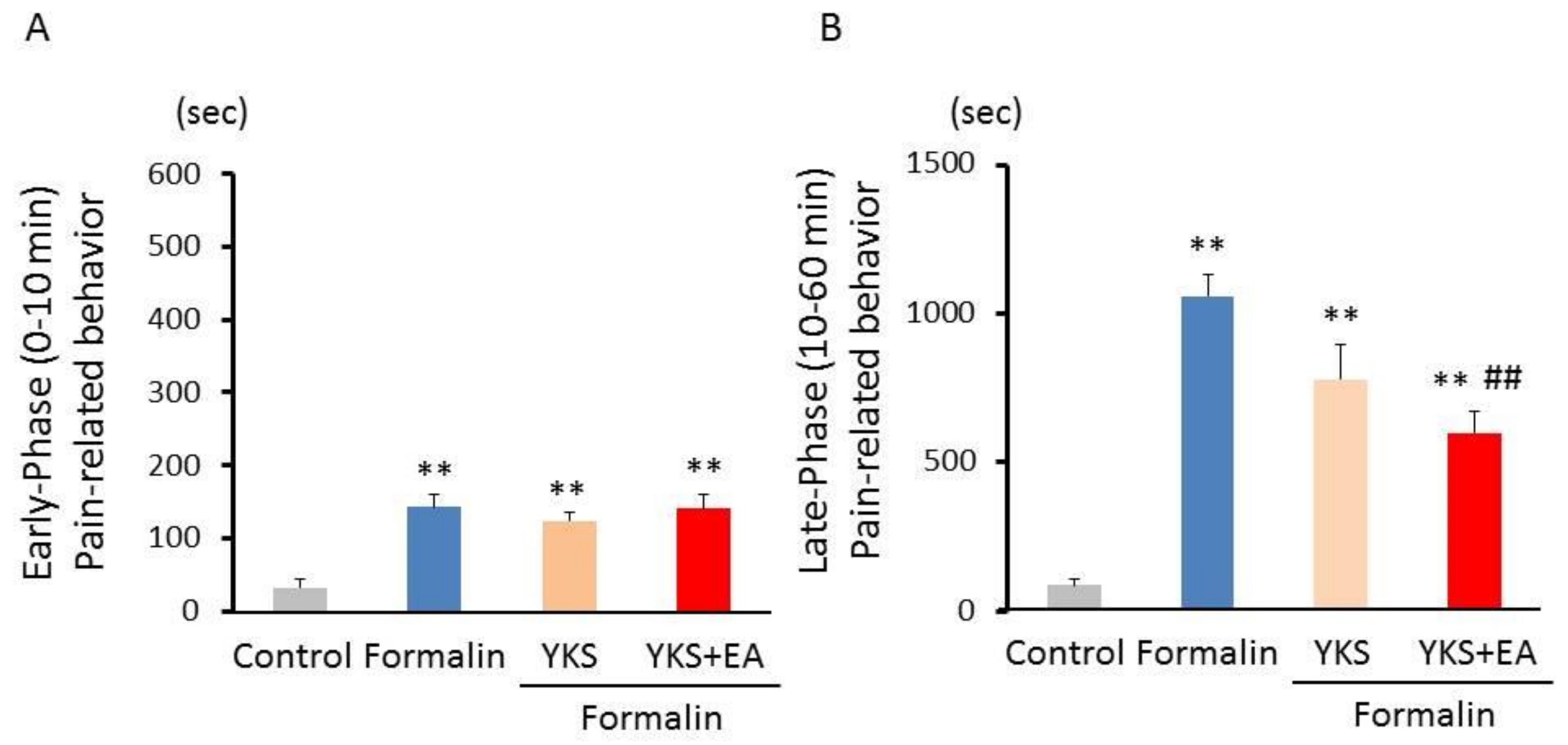
3.1. Formalin Test
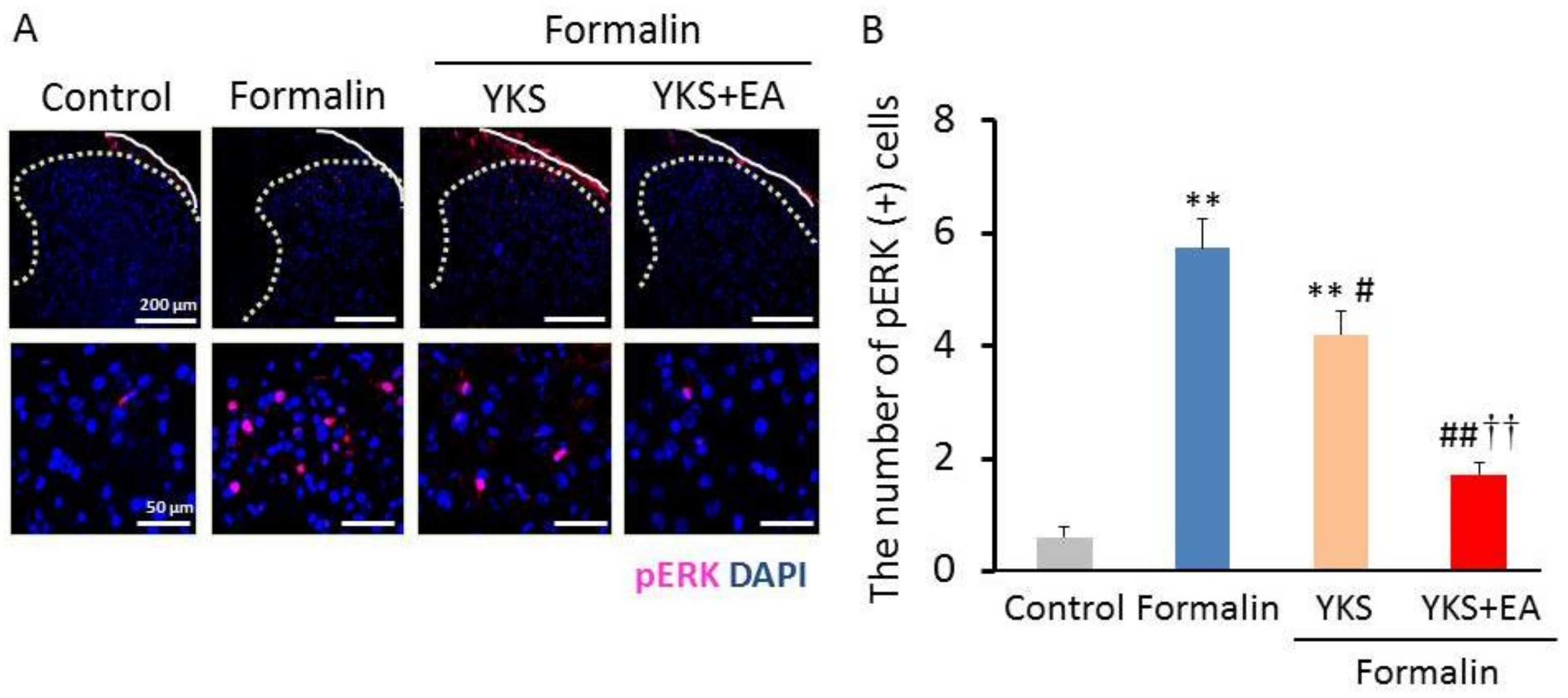
3.2. Immunostaining of pERK1/2-Positive Cells
3.3. Western Blot Analysis of the pERK1/2 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, R.R.; Kohno, T.; Moore, K.A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization and LTP: Do pain and memory share similar mechanisms? Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 696–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.J. Economic burden of chronic pain. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2006, 6, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.R.; Vierck, C.J. The transition of acute postoperative pain to chronic pain: An integrative overview of research on mechanisms. J. Pain 2017, 18, 359.e1–359.e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, M.; Nakada, Y.; Izumi, S.I. The education of traditional Japanese (Kampo) medicine: Surveys of training hospitals and residents. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulett, G.A.; Han, S.; Han, J.S. Electroacupuncture: Mechanisms and clinical application. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 44, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Wilt, T.J.; McLean, R.M.; Forciea, M.A. Noninvasive Treatments for Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Low Back Pain: Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 166, 514–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Oltean, H.; van Tulder, M.W.; Berman, B.M.; Bombardier, C.; Robbins, C.B. Herbal medicine for low back pain: A Cochrane review. Spine 2016, 41, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawata, M.; Kurihara, A.; Nitta, K.; Iwase, E.; Gan, N.; Onaya, T. The effects of goshajinkigan, a herbal medicine, on subjective symptoms and vibratory threshold in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 1994, 26, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanada, Y.; Katayama, A.; Ikemoto, H.; Takahashi, K.; Tsukada, M.; Nakamura, A.; Ishino, S.; Hisamitsu, T.; Sunagawa, M. Inhibitory effect of the Kampo medicinal formula Yokukansan on acute stress-induced defecation in rats. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukami, K.; Asada, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Tanaka, K.; Sonohara, K.; Nakai, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Hanyu, H.; Kanaya, K.; Takao, T.; et al. A randomized cross-over study of a traditional Japanese medicine (kampo), yokukansan, in the treatment of the behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Yokoyama, E.; Yamazaki, T.; Takano, D.; Maeda, T.; Takahashi, S.; Terayama, Y. Effects of yokukansan on behavioral and psychological symptoms of vascular dementia: Anopen-label trial. Phytomedicine 2012, 19, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, M.; Takeuchi, T.; Miyagawa, K.; Ishii, D.; Imai, T.; Takeda, K.; Kitajima, M.; Takeda, H. Yokukansan, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, alleviates the emotional abnormality induced by maladaptation to stress in mice. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, M.; Hasegawa, T.; Ninoyu, Y.; Hirano, S. Efficacy of Yokukansan, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, in patients with dizziness and irritability. Auris Nasus Larynx 2021, 29, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Jung, K.; Kim, J.S.; Jung, I.; Yoo, H.; Moon, C. Potential application of Yokukansan as a remedy for Parkinson’s Disease. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1875928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaoka, T.; Furuya, M.; Yasuda, H.; Hayashida, M.; Nishida, A.; Inagaki, T.; Horiguchi, J. Yi-gan san for the treatment of neuroleptic-induced tardive dyskinesia: An open-label study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 761–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, H.; Hasegawa, Y. Effectiveness of the traditional Japanese Kampo medicine Yokukansan for chronic migraine: A case report. Medicine 2019, 98, e17000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, K.; Satoh-Nakagawa, T.; Maruyama, M.; Monma, Y.; Nemoto, M.; Tomita, N.; Tanji, H.; Fujiwara, H.; Seki, T.; Fujii, M.; et al. A randomized, observer-blind, controlled trial of the traditional Chinese medicine Yi-Gan San for improvement of behavioral and psychological symptoms and activities of daily living in dementia patients. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2005, 66, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, Y.; Kishi, T.; Shibayama, H.; Iwata, N. Yokukansan in the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hum. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 28, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Tajima, K.; Kawagoe, I.; Kanai, M.; Mitsuhata, H. Efficacy of traditional herbal medicine Yokukansan on patients with neuropathic pain. Masui Jpn. J. Anesthesiol. 2009, 58, 1248–1255, (In Japanese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Mitsuhata, H.; Yuzurihara, M.; Kase, Y. Antiallodynic effect of herbal medicine yokukansan on peripheral neuropathy in rats with chronic constriction injury. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 953459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, K.; Fujiwara, A.; Komasawa, N.; Jin, D.; Kitano, M.; Matsunami, S.; Takai, S.; Ito, S.; Minami, T. Yokukansan Alleviates Cancer Pain by Suppressing Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 in a Mouse Bone Metastasis Model. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2956920. [Google Scholar]
- Tjølsen, A.; Berge, O.G.; Hunskaar, S.; Rosland, J.H.; Hole, K. The formalin test: An evaluation of the method. Pain 1992, 51, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler-Aceto, H.; Porreca, F.; Cowan, A. The rat paw formalin test: Comparison of noxious agents. Pain 1990, 40, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The formalin test: A quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.Y.; Light, A.R.; Matsushima, G.K.; Maixner, W. Microglial reactions after subcutaneous formalin injection into the rat hind paw. Brain Res. 1999, 825, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahara-Yamauchi, R.; Ikemoto, H.; Okumo, T.; Sakhri, F.Z.; Horikawa, H.; Nakamura, A.; Sakaue, S.; Kato, M.; Adachi, N.; Sunagawa, M. Analgesic effect of voluntary exercise in a rat model of persistent pain via suppression of microglial activation in the spinal cord. Biomed. Res. 2021, 42, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.K.; Choi, E.J. Pathological roles of MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolch, W. Meaningful relationships: The regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem. J. 2000, 351, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.S.; Cao, J.L.; Xu, Y.B.; He, J.H.; Zhang, L.C.; Zeng, Y.M. Activation of ERK/CREB pathway in spinal cord contributes to chronic constrictive injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nan, G. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway in neurological diseases: A potential therapeutic target (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impey, S.; Obrietan, K.; Storm, D.R. Making new connections: Role of ERK/MAP kinase signaling in neuronal plasticity. Neuron 1999, 23, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.R.; Befort, K.; Brenner, G.J.; Woolf, C.J. ERK MAP Kinase Activation in Superficial Spinal Cord Neurons Induces Prodynorphin and NK-1 Upregulation and Contributes to Persistent Inflammatory Pain Hypersensitivity. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.R.; Baba, H.; Brenner, G.J.; Woolf, C.J. Nociceptive-specific activation of ERK in spinal neurons contributes to pain hypersensitivity. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanuma, Y.; Kato, M.; Takayama, Y.; Ikemoto, H.; Adachi, N.; Ohashi, Y.; Yogi, W.; Okumo, T.; Tsukada, M.; Sunagawa, M. Analgesic Efficacy of a Combination of Fentanyl and a Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain. Medicines 2020, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suga, H.; Sunagawa, M.; Ikemoto, H.; Nakanishi-Ueda, T.; Fujiwara, A.; Okada, M.; Mera, H.; Ishino, S.; Hisamitsu, T. The Analgesic and anti-stress effects of a Kampo medicine (Yokukansan) in rats with chronic constriction injury—A comparative study with Kamishoyosan. J. Integr. Med. Ther. 2015, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Honda, Y.; Sunagawa, M.; Yoneyama, S.; Ikemoto, H.; Nakanishi-Ueda, T.; Iwanami, H.; Suga, H.; Ishikawa, S.; Ishino, S.; Hisamitsu, T. Analgesic and anti-stress effects of yokukansan in rats with adjuvant arthritis. Kampo Med. 2012, 64, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, A.; Yin, N.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z. Enhancement of immune cytokines and splenic CD4+ T cells by electroacupuncture at ST36 acupoint of SD rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, M.; Ohkubo, T.; Takahashi, H.; Inoki, R. Modified formalin test: Characteristic biphasic pain response. Pain 1989, 38, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latremoliere, A.; Woolf, C.J. Central sensitization: A generator of pain hypersensitivity by central neural plasticity. J. Pain 2009, 10, 895–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yashpal, K.; Coderre, T.J. Influence of formalin concentration on the antinociceptive effects of anti-inflammatory drugs in the formalin test in rats: Separate mechanisms underlying the nociceptive effects of low- and high-concentration formalin. Eur. J. Pain 1998, 2, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teather, L.A.; Magnusson, J.E.; Wurtman, R.J. Platelet-activating factor antagonists decrease the inflammatory nociceptive response in rats. Psychopharmacology 2002, 163, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, R.; Sand, C.A.; Pezet, S.; Leiper, J.M.; Gaurilcikaite, E.; McMahon, S.B.; Dickenson, A.H.; Nandi, M. Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 1 is involved in spinal nociceptive plasticity. Pain 2015, 156, 2052–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, T.J.; Katz, J.; Vaccarino, A.L.; Melzack, R. Contribution of central neuroplasticity to pathological pain: Review of clinical and experimental evidence. Pain 1993, 52, 259–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Jang, M.; Jung, H.S.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, I.H. Ethyl pyruvate attenuates formalin-induced inflammatory nociception by inhibiting neuronal ERK phosphorylation. Mol. Pain 2012, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Shao, H.; Xue, Q.; Yu, B. ERK MAP kinase activation in spinal cord regulates phosphorylation of Cdk5 at serine 159 and contributes to peripheral inflammation induced pain/hypersensitivity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.C.; Yasui, H.; Isai, H.; Kawai, T.; Nishihara, M.; Sato, J.; Ikemoto, T.; Inoue, S.; Ushida, T. The review of innovative integration of Kampo medicine and Western medicine as personalized medicine at the first multidisciplinary pain center in Japan. EPMA J. 2014, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebisawa, S.; Andoh, T.; Shimada, Y.; Kuraishi, Y. Yokukansan improves mechanical allodynia through the regulation of interleukin-6 expression in the spinal cord in mice with neuropathic pain. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 870687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolf, C.J.; Thompson, S.W.N. The induction and maintenance of central sensitization is dependent on N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor activation; implications for the treatment of post-injury pain hypersensitivity states. Pain 1991, 44, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Z.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Isoliquiritigenin is a novel NMDA receptor antagonist in kampo medicine yokukansan. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, Z.; Kanno, H.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y. Yokukansan, a kampo medicine, protects against glutamate cytotoxicity due to oxidative stress in PC12 cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 134, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, A.S.; Pannunzio, P.; Rama Rao, K.V.; Pow, D.V.; Rambaldi, A. Thiamine deficiency results in downregulation of the GLAST glutamate transporter in cultured astrocytes. Glia 2003, 43, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lever, I.J.; Pezet, S.; McMahon, S.B.; Malcangio, M. The signaling components of sensory fiber transmission involved in the activation of ERK MAP kinase in the mouse dorsal horn. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2003, 24, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Vadakkan, K.I.; Toyoda, H.; Wu, L.J.; Zhao, M.G.; Xu, H.; Shum, F.W.; Jia, Y.H.; Zhuo, M. Calcium calmodulin-stimulated adenylyl cyclases contribute to activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase in spinal dorsal horn neurons in adult rats and mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Wang, Y.; Xin, J.; Lao, L.; Ren, K.; Berman, B.M.; Zhang, R.X. Electroacupuncture suppresses hyperalgesia and spinal Fos expression by activating the descending inhibitory system. Brain Res. 2007, 1186, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.S.; Seo, B.K.; Baek, Y.H. Analgesic effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory pain in collagen-induced arthritis rats: Mediation by α2- and β-adrenoceptors. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 33, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.S. Acupuncture and endorphins. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 361, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Induction of Inflammatory Pain by Regulating Opioid and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Kohno, T.; Ji, R.R. Different effects of opioid and cannabinoid receptor agonists on C-fiber-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation in dorsal horn neurons in normal and spinal nerve-ligated rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Price, D.D.; Mayer, D.J. Experimental mononeuropathy reduces the antinociceptive effects of morphine: Implications for common intracellular mechanisms involved in morphine tolerance and neuropathic pain. Pain 1995, 61, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, D.; Ossipov, M.H.; Ibrahim, M.; Raffa, R.B.; Tallarida, R.J.; Malan, T.P., Jr.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F. Loss of antiallodynic and antinociceptive spinal/supraspinal morphine synergy in nerve-injured rats: Restoration by MK-801 or dynorphin antiserum. Brain Res. 1999, 831, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Navarro, M.; Maldonado, R.; Baños, J.E. Why mu-opioid agonists have less analgesic efficacy in neuropathic pain? Eur. J. Pain 2019, 23, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemoto, M.; Sunagawa, M.; Okada, M.; Ikemoto, H.; Suga, H.; Katayama, A.; Otake, H.; Hisamitsu, T. Yokukansan, a Kampo medicine, prevents the development of morphine tolerance through the inhibition of spinal glial cell activation in rats. Integr. Med. Res. 2016, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, T.; Nagayasu, K.; Nishitani, N.; Shirakawa, H.; Sekiguchi, K.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kase, Y.; Kaneko, S. Yokukansan inhibits morphine tolerance and physical dependence in mice: The role of α2A-adrenoceptor. Neuroscience 2012, 227, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto-Miyazaki, J.; Ushikoshi, H.; Miyata, S.; Miyazaki, N.; Nawa, T.; Okada, H.; Ojio, S.; Ogura, S.; Minatoguchi, S. Acupuncture and Traditional Herbal Medicine Therapy Prevent Deliriumin Patients with Cardiovascular Disease in Intensive Care Units. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2017, 45, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebihara, N.; Ikemoto, H.; Adachi, N.; Okumo, T.; Kimura, T.; Yusa, K.; Hattori, S.; Manabe, A.; Hisamitsu, T.; Sunagawa, M. Analgesic Effect of Combined Therapy with the Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” and Electroacupuncture in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain. Medicines 2021, 8, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060031
Ebihara N, Ikemoto H, Adachi N, Okumo T, Kimura T, Yusa K, Hattori S, Manabe A, Hisamitsu T, Sunagawa M. Analgesic Effect of Combined Therapy with the Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” and Electroacupuncture in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain. Medicines. 2021; 8(6):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060031
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbihara, Nachi, Hideshi Ikemoto, Naoki Adachi, Takayuki Okumo, Taro Kimura, Kanako Yusa, Satoshi Hattori, Atsufumi Manabe, Tadashi Hisamitsu, and Masataka Sunagawa. 2021. "Analgesic Effect of Combined Therapy with the Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” and Electroacupuncture in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain" Medicines 8, no. 6: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060031
APA StyleEbihara, N., Ikemoto, H., Adachi, N., Okumo, T., Kimura, T., Yusa, K., Hattori, S., Manabe, A., Hisamitsu, T., & Sunagawa, M. (2021). Analgesic Effect of Combined Therapy with the Japanese Herbal Medicine “Yokukansan” and Electroacupuncture in Rats with Acute Inflammatory Pain. Medicines, 8(6), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines8060031






