Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
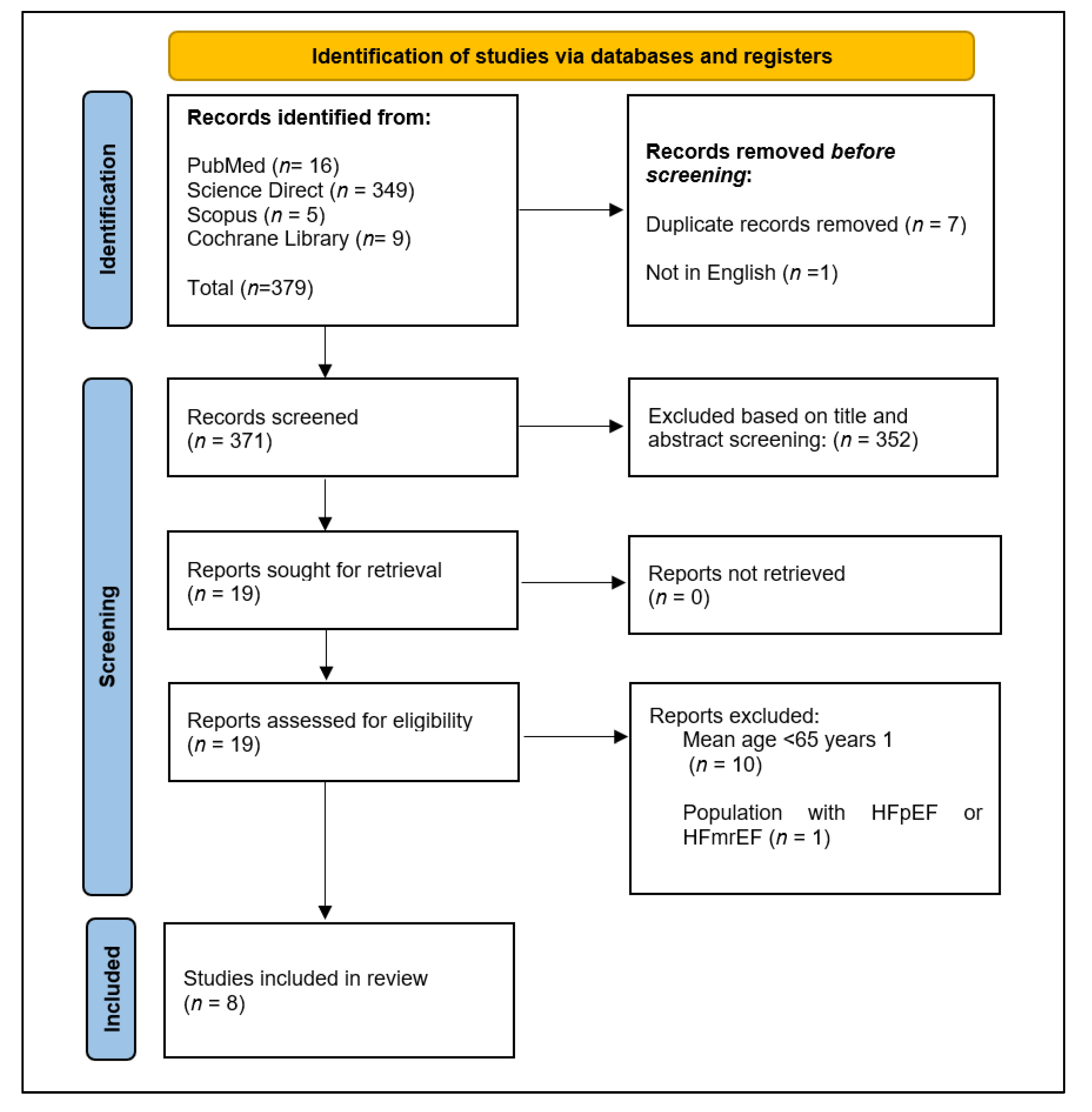
2.4. Study Selection and Documentation
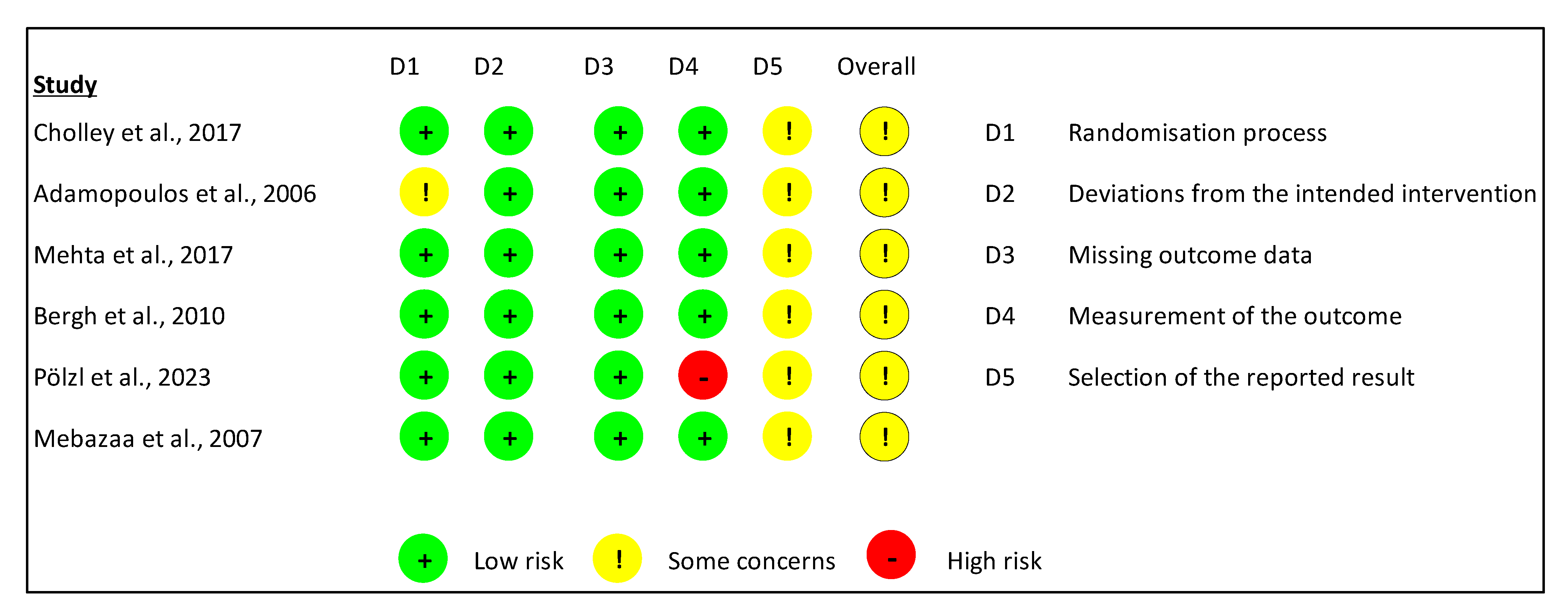
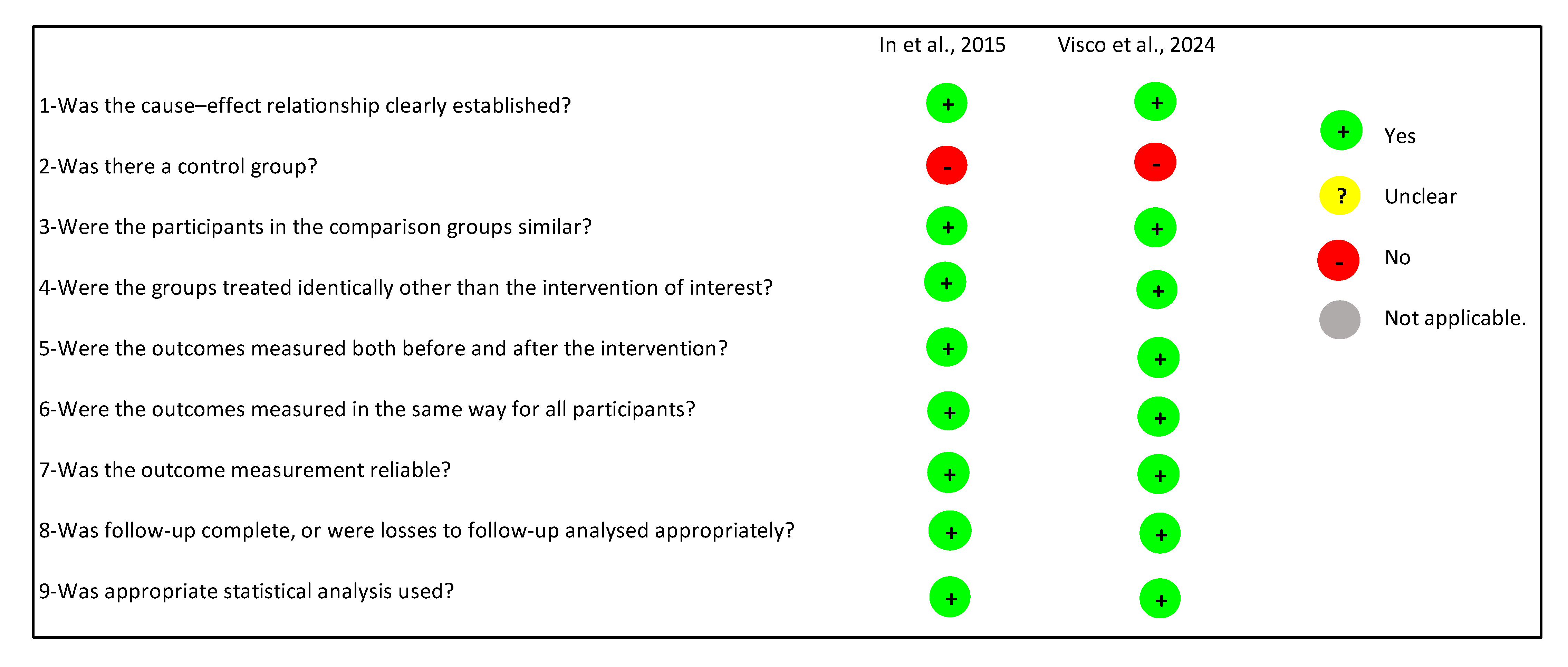
2.5. Risk of Bias
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Characteristics of the Included Studies
3.3. Primary Outcomes
3.3.1. Mortality and Hospitalization
3.3.2. Cardiac Function and Hemodynamics
3.4. Secondary Outcomes
3.4.1. Adverse Events (AE)
3.4.2. Treatment Discontinuations
3.5. Methodological Quality
3.5.1. Assessment Using the ROB-2 Tool
3.5.2. Evaluation Using the JBI Critical Appraisal Tool
3.6. Summary of Findings for the Prespecified Outcomes and Certainty of the Evidence (GRADE)
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness of Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure in Older Adults
4.1.1. Mortality and Hospitalizations
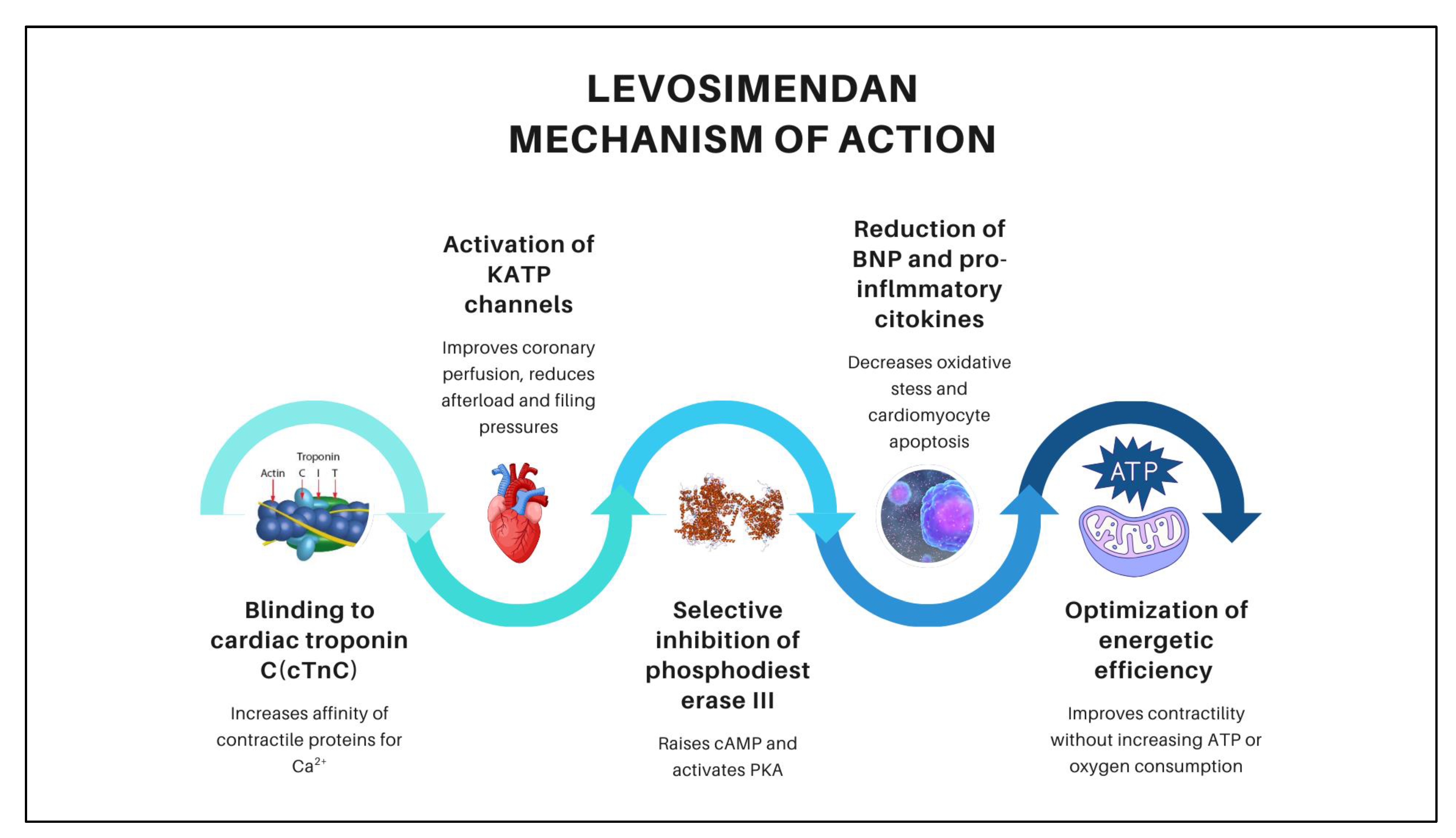
4.1.2. Hemodynamic Effects
4.2. Security of Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure in Older Adults
4.2.1. Tolerability and Adverse Effects of Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure in Older Adults
4.2.2. Considerations and Precautions for the Use of Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure in Older Adults
4.2.3. Practical Precautions and Titration Guidelines for Levosimendan in Geriatric Decompensated Heart Failure
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HFrEF | Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction |
| HFpEF | Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction |
| LVEF | Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction |
| PCWP | Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure |
| CI | Cardiac Index |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-B-type Natriuretic Peptide |
| SVI | Stroke Volume Index |
| RoB-2 | Risk of Bias 2 |
| JBI | Joanna Briggs Institute |
| LVAD | Left Ventricular Assist Device |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| PROSPERO | International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews |
| AE | Adverse Events |
| VT | Ventricular Tachycardia |
| AF | Atrial Fibrillation |
| SVT | Supraventricular Tachycardia |
| RRT | Renal Replacement Therapy |
| CABG | Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting |
| HF | Heart failure |
| cTnC | Cardiac troponin C |
| cAMP | Cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate |
| ATP | Adenosine Triphosphate |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
Appendix A
| Date Base | Keywords | Search Strategy | Filters Applied in the Database | Number of Possible Items to Select |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PubMed/Medline | Levosimendan, Simdax, Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction, HFrEF, Older Adults, Elderly, Hemodynamics, Cardiac Output, Left Ventricular Function | (Levosimendan) AND (Heart Failure, Systolic [MeSH] OR Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction OR HFrEF) AND (Older Adults OR Elderly) AND (Randomized Controlled Trial [Publication Type] OR Clinical Trial OR Observational Study) AND (Hemodynamics [MeSH] OR Cardiac Output OR Left Ventricular Function) | Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses, Clinical Trials, and Observational Studies, published in the Last 20 Years. | 16 |
| ScienceDirect | Levosimendan AND Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction AND Older Adults | “Levosimendan AND Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction AND Older Adults” | Research Articles and Review Articles published in the Last 20 Years. | 349 |
| Scopus | Levosimendan, HFrEF, Elderly, Hemodynamics, Clinical Trials, Observational Studies | “Levosimendan” AND “Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction” AND (“Older Adults” OR “Elderly”) | Research Articles and Review Articles published in the Last 20 Years. | 5 |
| Cochrane Library | Levosimendan, Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction, Elderly, Systematic Reviews, Meta-Analysis | “Levosimendan” AND “Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction” | Clinical Trials, Observational Studies, Systematic Reviews, and Meta-analyses published in the Last 20 Years. | 9 |
References
- Uchmanowicz, I.; Nessler, J.; Gobbens, R.; Gackowski, A.; Kurpas, D.; Straburzynska-Migaj, E.; Kałuzna-Oleksy, M.; Jankowska, E.A. Coexisting Frailty with Heart Failure. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. The Anti-Inflammatory and Haemodynamic Effects of Levosimendan on Advanced Heart Failure Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Published Studies. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 3000605221148402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yao, Y.; Qian, J.; Huang, J. Levosimendan Improves Clinical Outcomes of Refractory Heart Failure in Elderly Chinese Patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2015, 21, 2439–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kirlidis, T.T.; Skoularigis, J.; Tsaknakis, K.T.; Karayiannis, G.; Tsaknakis, T.K.; Triposkiadis, F. The Influence of Beta-Blockade on the Hemodynamic Effects of Levosimendan in Elderly (>= 70 Years) Patients with Acutely Decompensated Systolic Heart Failure. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2009, 47, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamopoulos, S.; Parissis, J.T.; Iliodromitis, E.K.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Tsiapras, D.; Farmakis, D.; Karatzas, D.; Gheorghiade, M.; Filippatos, G.S.; Kremastinos, D.T. Effects of Levosimendan versus Dobutamine on Inflammatory and Apoptotic Pathways in Acutely Decompensated Chronic Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2006, 98, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mebazaa, A.; Nieminen, M.S.; Packer, M.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Kleber, F.X.; Pocock, S.J.; Thakkar, R.; Padley, R.J.; Põder, P.; Kivikko, M.; et al. Levosimendan vs Dobutamine for Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: The SURVIVE Randomized Trial. JAMA 2007, 297, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, C.-H.; Andersson, B.; Dahlström, U.; Forfang, K.; Kivikko, M.; Sarapohja, T.; Ullman, B.; Wikström, G. Intravenous Levosimendan vs. Dobutamine in Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Patients on Beta-Blockers. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-González, M.J.; Jorge-Pérez, P.; Jiménez-Sosa, A.; Acea, A.B.; Lacalzada Almeida, J.B.; Ferrer Hita, J.J. Levosimendan Improves Hemodynamic Status in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Aortic Stenosis and Left Ventricular Dysfunction: An Interventional Study. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2015, 33, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholley, B.; Caruba, T.; Grosjean, S.; Amour, J.; Ouattara, A.; Villacorta, J.; Miguet, B.; Guinet, P.; Lévy, F.; Squara, P.; et al. Effect of Levosimendan on Low Cardiac Output Syndrome in Patients with Low Ejection Fraction Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting with Cardiopulmonary Bypass: The LICORN Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 548–556. Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2647870 (accessed on 11 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.H.; Leimberger, J.D.; van Diepen, S.; Meza, J.; Wang, A.; Jankowich, R.; Harrison, R.W.; Hay, D.; Fremes, S.; Duncan, A.; et al. Levosimendan in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2032–2042. Available online: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1616218 (accessed on 11 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Pölzl, G.; Altenberger, J.; Comín-Colet, J.; Delgado, J.F.; Fedele, F.; García-González, M.J.; Gustafsson, F.; Masip, J.; Papp, Z.; Störk, S.; et al. Repetitive Levosimendan Infusions for Patients with Advanced Chronic Heart Failure in the Vulnerable Post-Discharge Period: The Multinational Randomized LeoDOR Trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visco, V.; Esposito, C.; Rispoli, A.; Di Pietro, P.; Izzo, C.; Loria, F.; Di Napoli, D.; Virtuoso, N.; Bramanti, A.; Manzo, M.; et al. The Favourable Alliance between CardioMEMS and Levosimendan in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 2835–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.-C.; Lee, K.-T.; Ho, W.-J.; Chan, Y.-H.; Chu, P.-H. Levosimendan Use in Patients with Acute Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction with or without Severe Renal Dysfunction in Critical Cardiac Care Units: A Multi-Institution Database Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2021, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Tang, L.; Chen, P.; Huang, J.; Peng, X.; Hu, X. Levosimendan in Patients with Left Ventricular Dysfunction Undergoing Cardiac Surgery: A Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Trials. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landoni, G.; Biondi-Zoccai, G.; Greco, M.; Greco, T.; Bignami, E.; Morelli, A.; Guarracino, F.; Zangrillo, A. Effects of Levosimendan on Mortality and Hospitalization. A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 40, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.-X.; Cui, D.-Y.; Kuang, X.; Hu, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.-Z. Effect of Levosimendan on Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Functions in Heart Failure Patients: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terbeck, S.; Heinisch, P.P.; Lenz, A.; Friess, J.-O.; Guensch, D.; Carrel, T.; Eberle, B.; Erdoes, G. Levosimendan and Systemic Vascular Resistance in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, D.; Kittleson, M.M.; Pollesello, P.; Marini, M.; Iacoviello, M.; Oliva, F.; Caiazzo, A.; Petraio, A.; Pacileo, G. Use of Levosimendan in Patients with Advanced Heart Failure: An Update. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześk, G.; Wołowiec, Ł.; Rogowicz, D.; Gilewski, W.; Kowalkowska, M.; Banach, J.; Hertmanowski, W.; Dobosiewicz, M. The Importance of Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamic and Repetitive Use of Levosimendan. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørstavik, Ø.; Ata, S.H.; Riise, J.; Dahl, C.P.; Andersen, G.Ø.; Levy, F.O.; Skomedal, T.; Osnes, J.-B.; Qvigstad, E. Inhibition of Phosphodiesterase-3 by Levosimendan Is Sufficient to Account for Its Inotropic Effect in Failing Human Heart. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 5169–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Jia, L.; Hao, Y.; Huang, S.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, M.; Mao, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Levosimendan in Patients with Acute Right Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. Life Sci. 2017, 184, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, M.; Colucci, W.; Fisher, L.; Massie, B.M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Young, J.; Padley, R.J.; Thakkar, R.; Delgado-Herrera, L.; Salon, J.; et al. Effect of Levosimendan on the Short-Term Clinical Course of Patients with Acutely Decompensated Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2013, 1, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholley, B.; Bojan, M.; Guillon, B.; Besnier, E.; Mattei, M.; Levy, B.; Ouattara, A.; Tafer, N.; Delmas, C.; Tonon, D.; et al. Overview of the Current Use of Levosimendan in France: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2023, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, B.; Li, Z.; Yat Wong, P.C. Levosimendan Treatment for Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2015, 29, 1415–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieminen, M.S.; Akkila, J.; Hasenfuss, G.; Kleber, F.X.; Lehtonen, L.A.; Mitrovic, V.; Nyquist, O.; Remme, W.J. Hemodynamic and Neurohumoral Effects of Continuous Infusion of Levosimendan in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Ma, Z.; Ning, B. Serum Potassium Is a Critical Risk Factor for Cardiac Arrhythmias in Acute Heart Failure Patients Treated with Levosimendan: A Retrospective Study in a Cohort of 250 Patients. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 63, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landoni, G.; Lomivorotov, V.V.; Alvaro, G.; Lobreglio, R.; Pisano, A.; Guarracino, F.; Calabrò, M.G.; Grigoryev, E.V.; Likhvantsev, V.V.; Salgado-Filho, M.F.; et al. Levosimendan for Hemodynamic Support after Cardiac Surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2021–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Study Type | Study Population | Average Age | Study Focus | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adamopoulos et al., 2006 [6]. | Randomized controlled trial | 69 patients with chronic decompensated heart failure, NYHA class III or IV, left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≤30% | Mean age: 67 years in the dobutamine group, 71 years in the levosimendan group, and 71 years in the placebo group. | Cardiac function parameters, inflammatory markers, event-free survival | Levosimendan improved hemodynamic parameters and reduced inflammatory and pro-apoptotic markers. It showed greater event-free survival compared to dobutamine and placebo |
| Mebazaa et al., 2007 [7]. | Randomized, double-blind, multicenter trial | 1327 patients with acute decompensated heart failure | Mean age: 67 years in the levosimendan group, 66 years in the dobutamine group | All-cause mortality at 180 days | The SURVIVE trial found no difference in survival between levosimendan and dobutamine, although levosimendan more effectively reduced BNP level |
| Bergh et al., 2010 [8]. | Phase IV, randomized, double-blind study | 60 patients with acute decompensated heart failure, NYHA class III-IV, LVEF < 35% | Mean age: 70 years in the levosimendan group, 71 years in the dobutamine group | Changes in cardiac index and pulmonary capillary wedge pressure | Levosimendan showed hemodynamic and neurohormonal improvement comparable to dobutamine at 24 h and superior at 48 h in decompensated HF patients receiving beta-blockers. |
| In et al., 2015 [9] | Single-arm interventional study | 9 patients with severe aortic stenosis and reduced LVEF (≤40%) | Mean age 76 for levosimendan | Change in cardiac index | Levosimendan improved hemodynamic parameters in patients with severe aortic stenosis and reduced LVEF, serving as an effective bridge to valve replacement or vasodilator therapy |
| Cholley et al., 2017 [10]. | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 336 patients with LVEF ≤ 40% undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) with cardiopulmonary bypass | Mean age 69 for group of levosimendan vs. 67 placebo | Need for prolonged catecholamines, left ventricular assist device, or renal replacement therapy | Preoperative levosimendan did not significantly reduce postoperative low cardiac output syndrome in patients with low LVEF undergoing CABG. |
| Mehta et al., 2017 [11]. | Randomized, placebo-controlled trial | 849 patients with LVEF ≤ 35% undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass | Mean age 65 for group of levosimendan and placebo | Composite outcome of death, renal replacement therapy, perioperative myocardial infarction, or use of mechanical circulatory support | Prophylactic levosimendan did not reduce the rate of the composite outcome of death, renal replacement therapy (RRT), perioperative infarction, or mechanical support use in patients with reduced LVEF undergoing cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. |
| Pölzl et al., 2023 [12]. | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 148 patients with advanced chronic heart failure | Mean age 69.3 for group of levosimendan vs. 67.8 placebo | Global assessment including death, urgent heart transplant/VAD use, and change in NT-proBNP | The LeoDOR trial did not demonstrate improvement in clinical stability with intermittent levosimendan post-discharge in advanced HF due to increased cardiovascular events and low statistical power. |
| Visco et al., 2024 [13]. | Observational study | 7 patients with advanced heart failure who received a CardioMEMS implant (a pulmonary artery pressure monitoring system) | Mean age 69 for levosimendan | Hospitalizations, quality of life, echocardiographic parameters | Real-world study showed that CardioMEMS reduced hospitalizations and improved quality of life in HF patients by optimizing levosimendan use and generating economic benefits. |
| Study | Cardiac Function/Hemodynamics | Mortality/Hospitalizations | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adamopoulos et al., 2006 [6]. | Decrease in PCWP, improvement in CI and LVEF | Greater event-free survival with levosimendan | p < 0.05 for all hemodynamic parameters |
| Mebazaa et al., 2007 [7]. | N/R | No significant difference in 180-day mortality vs. dobutamine | p = 0.40 |
| Bergh et al., 2010 [8]. | Decrease in PCWP, improvement in CI at 48 h | N/R | CI p = 0.037, PCWP p = 0.015, BNP p = 0.03 |
| In et al., 2015 [9]. | Improvement in CI and decrease in PCWP at 24 h. Decrease in SVI | 75% 30-day survival observed | p < 0.05 for all hemodynamic parameters |
| Cholley et al., 2017 [10]. | N/R | No significant difference in 180-day mortality | p = 0.15 |
| Mehta et al., 2017 [11]. | N/R | No significant difference in 90-day mortality | p = 0.98 |
| Pölzl et al., 2023 [12]. | N/R | No significant difference in mortality at 14 weeks | p = 0.064 |
| Visco et al., 2024 [13]. | N/R | 68.7% reduction in hospitalization days and 50% reduction in total hospitalizations | N/R |
| Study | Hypotension | Arrhythmias | Other Adverse Events | Drug Discontinuation | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mebazaa et al., 2007 [7]. | No significant difference | AF: 9.1% vs. 6.1% (dobutamine) | Hypokalemia: 9.4% vs. 5.9% (dobutamine), Headache: 8.3% vs. 4.7% (dobutamine) | N/R | p < 0.05 for all AEs |
| Bergh et al., 2010 [8]. | 35% vs. 7% (dobutamine) | No increase in AF or ventricular tachycardia (VT) | Nausea is more frequent with levosimendan | N/R | p < 0.05 for all AEs |
| Cholley et al., 2017 [10]. | 57% vs. 48% (placebo) | AF: 50% vs. 40% (placebo) | Third-degree AV block: 4% vs. 9% (placebo) | 8% vs. 3% (placebo) | There is no significant difference in any AE |
| Mehta et al., 2017 [11]. | 36.2% vs. 32.8% (placebo) | AF: 38.1% vs. 33.0% (placebo), VT/VF: 10.7% vs. 9.7% (placebo) | Stroke: 3.5% vs. 2.4% (placebo) | Temporary interruption: 5.8% vs. 3.8% (placebo) | There is no significant difference in any AE |
| Pölzl et al., 2023 [12]. | 9.7% vs. 11.1% (placebo) | Trend toward more frequent arrhythmias (2.7% vs. 0.8% placebo) | N/R | N/R | There is no significant difference in any AE |
| Outcome and Follow-Up | Nº Participants (Nº Studies and Type) | Effect (95% CI) | Absolute Effects | Certainty of Evidence (Quality of Evidence) | Plain Language Summary | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Care Without Inotropes or with Alternative Inotropes (Dobutamine, Milrinone | Levosimendan | Difference | |||||
| Mortality | 2656 (4 RCTs) | RR = 0.92 (0.73 to 1.18) | 95 per 1000 | 87 per 1000 | 8 fewer per 1000 (26 fewer to 17 more) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low ab | Low-certainty evidence suggests levosimendan probably results in little or no difference in mortality compared to standard care without inotropes or with alternative inotropes. |
| Hospitalizations | 18 (1 observational) | In a small observational study, CardioMEMS monitoring combined with repeated levosimendan infusions was linked to fewer heart failure hospitalizations and hospitalization days, though the effect cannot be attributed solely to levosimendan due to co-intervention and the non-randomized design. | ⊕◯◯◯ Very Low ac | Very uncertain about the effect of levosimendan on hospitalizations; only one study at high risk of bias and possible confounding from CardioMEMS device. | |||
| Hemodynamics—Cardiac Index (48 h) | 106 (2 RCTs) | ---------- | 2.02 L/min/m2 | 2.20 L/min/m2 | 0.15 L/min/m2 | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate a | Levosimendan is likely to result in a small to no difference in hemodynamics (CI). |
| Hemodynamics (PCWP) | 106 (2 RCTs) | ----------- | 20.9 mmHg | 16.64 mmHg | −4.26 (−6.46 to −2.06) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate a | Levosimendan probably reduces pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) compared to standard care. |
| Hypotension | 1361 (4 RCTs) | RR = 1.13 (0.96 to 1.33) | 401 per 1000 | 453 per 1000 (385 to 533) | 52 more per 1000 (from 16 fewer to 132 more) | ⊕⊕⊕◯ Moderate ab | Levosimendan is likely to result in a slight increase in hypotension. |
| Arrhythmias | 1359 (4 RCTs) | RR = 1.14 (0.98 to 1.32) | 314 per 1000 | 358 per 1000 (308 to 415) | 44 more per 1000 (from 6 fewer to 100 more) | ⊕⊕◯◯ Low ab | Levosimendan may result in a small to no difference in arrhythmias. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zavaleta-Monestel, E.; Mora-Jiménez, J.; Cruz-Mora, K.; Martinez-Vargas, E.; Díaz-Madriz, J.P.; Arguedas-Chacón, S.; Fallas-Mora, A.; Wu-Chin, C.; Chaverrí-Fernandez, J.M. Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy. Medicines 2025, 12, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12040023
Zavaleta-Monestel E, Mora-Jiménez J, Cruz-Mora K, Martinez-Vargas E, Díaz-Madriz JP, Arguedas-Chacón S, Fallas-Mora A, Wu-Chin C, Chaverrí-Fernandez JM. Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy. Medicines. 2025; 12(4):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12040023
Chicago/Turabian StyleZavaleta-Monestel, Esteban, Jeaustin Mora-Jiménez, Kevin Cruz-Mora, Ernesto Martinez-Vargas, José Pablo Díaz-Madriz, Sebastián Arguedas-Chacón, Abigail Fallas-Mora, Carlos Wu-Chin, and Jose Miguel Chaverrí-Fernandez. 2025. "Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy" Medicines 12, no. 4: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12040023
APA StyleZavaleta-Monestel, E., Mora-Jiménez, J., Cruz-Mora, K., Martinez-Vargas, E., Díaz-Madriz, J. P., Arguedas-Chacón, S., Fallas-Mora, A., Wu-Chin, C., & Chaverrí-Fernandez, J. M. (2025). Levosimendan in Decompensated Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Safety and Efficacy. Medicines, 12(4), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12040023









