Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction of Vaccination
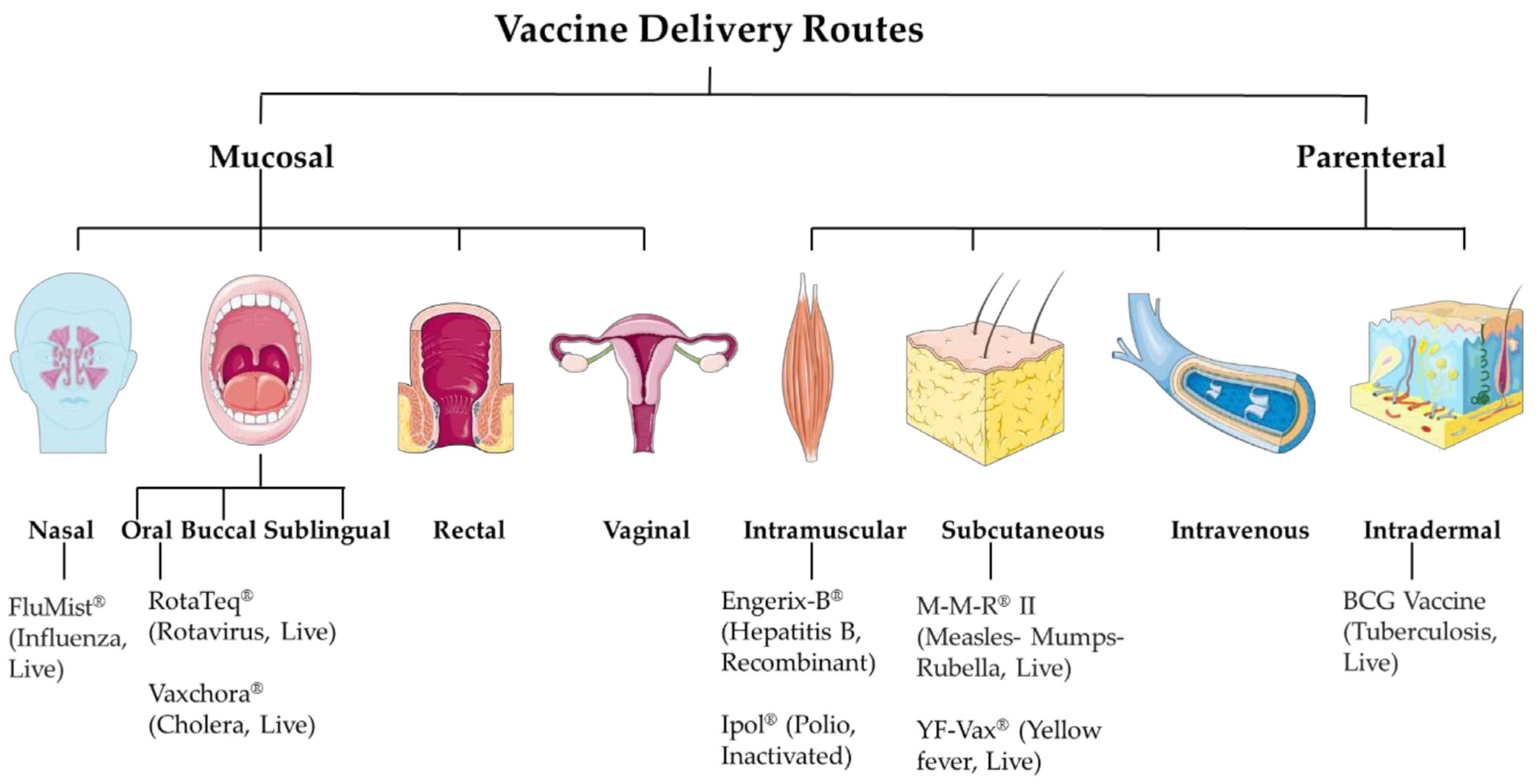
1.2. Route of Vaccine Delivery
1.3. Classification of Vaccines
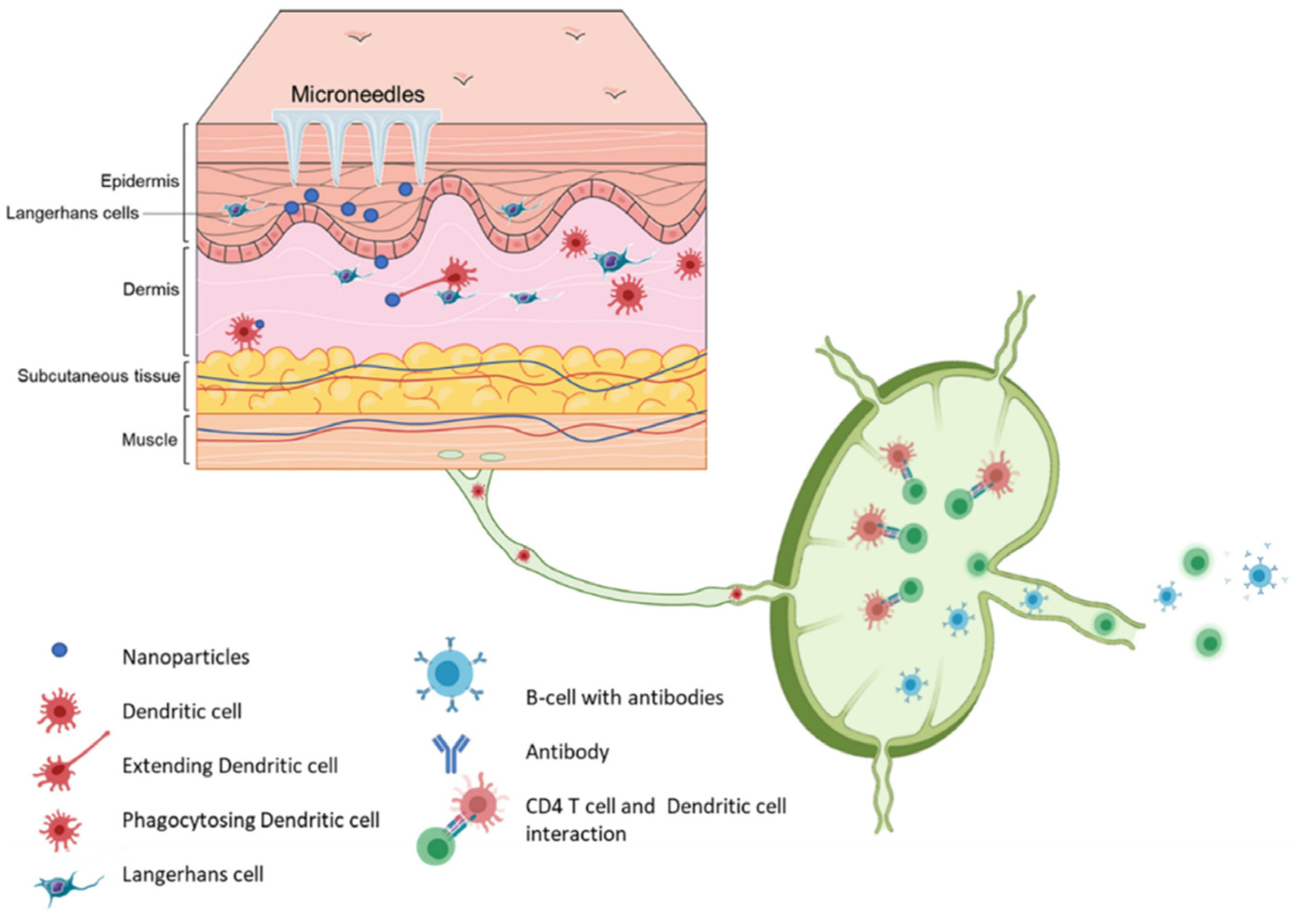
2. Roles of Skin in Vaccination
3. Skin Vaccination Strategies
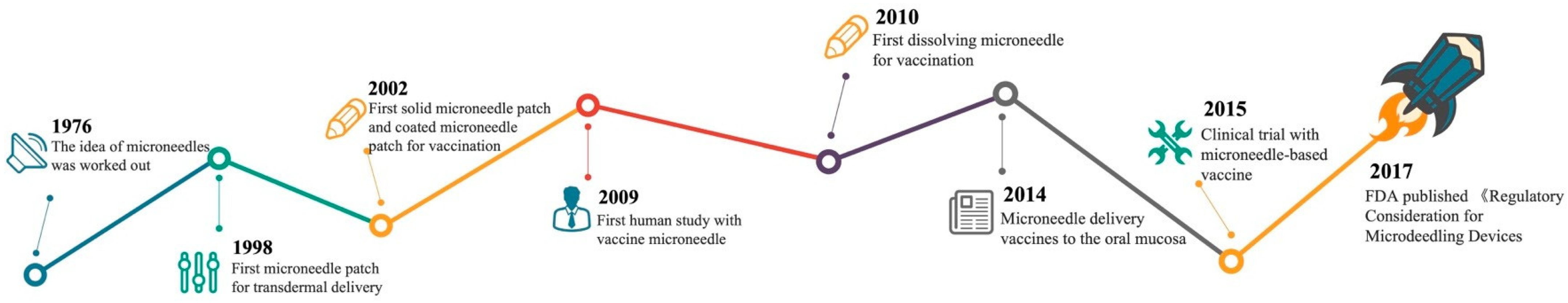
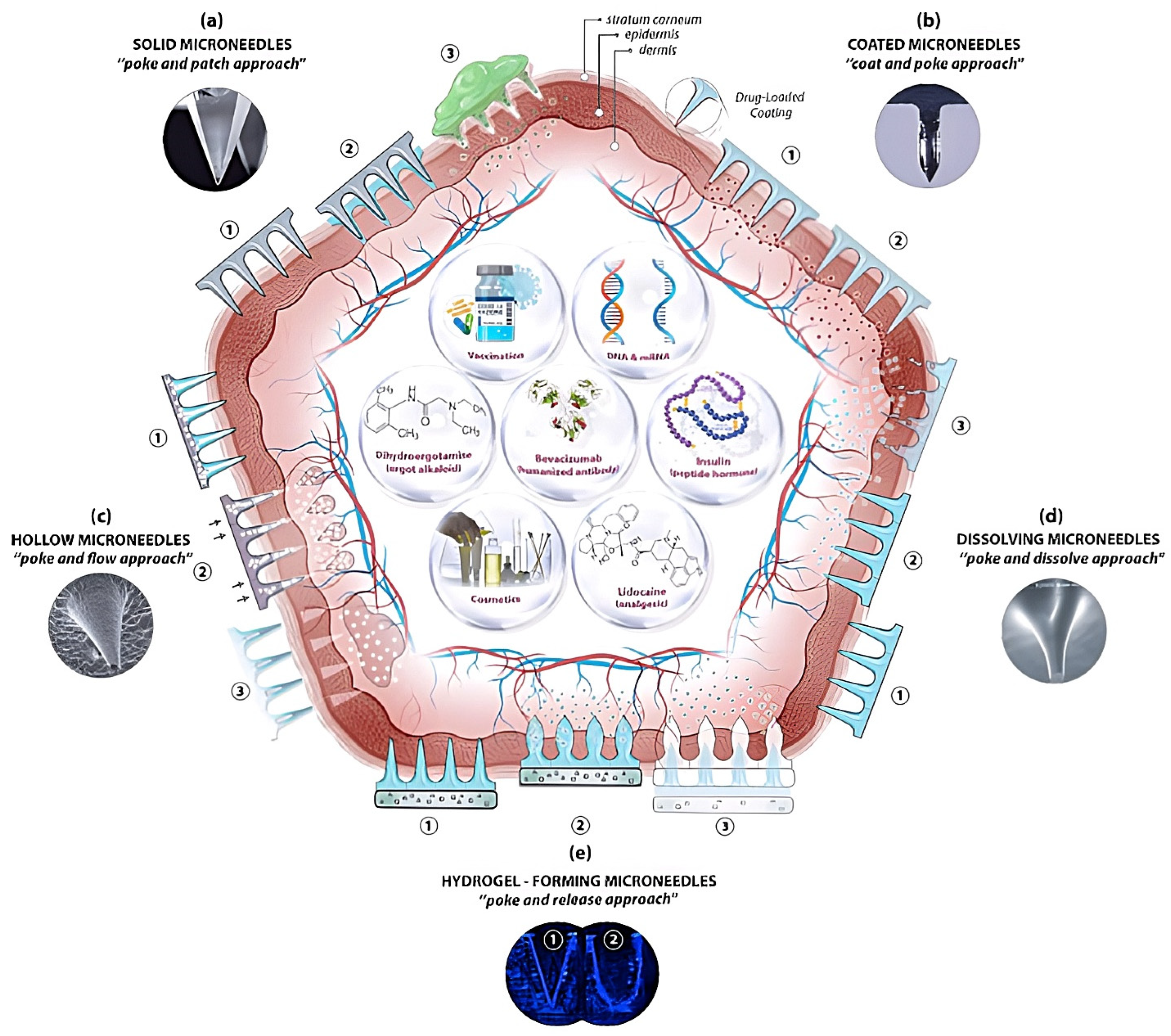
4. Microneedle-Mediated Vaccination Strategies
4.1. Solid Microneedles
4.2. Hollow Microneedles
4.3. Coated Microneedles
4.4. Dissolving Microneedles
4.5. Swelling Microneedles
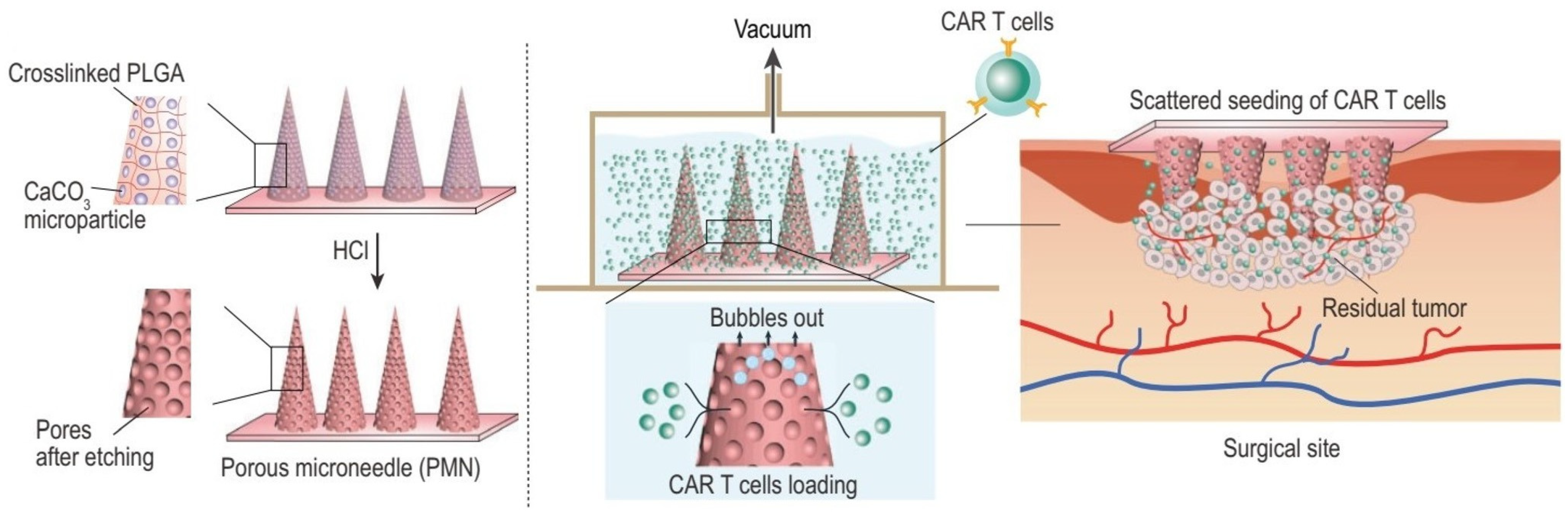
4.6. Porous Microneedles
4.7. Advantages of Microneedle-Based Vaccination
4.8. Barriers to Microneedle-Based Vaccination
5. Microneedle Applications for Different Types of Vaccines
6. Technical Considerations
6.1. Safety
6.2. Efficacy
6.3. Acceptability
6.4. Cost-Effectiveness
6.5. Applicators and Wear Times
6.6. Microneedle Dimensions
6.7. Microneedle Manufacturing
6.8. Regulation
6.9. Sustainability
7. Pre-Clinical Studies of Microneedle-Based Vaccination
8. Clinical Studies of Microneedle-Based Vaccination
9. Combination with Other Technologies
10. Conclusions
11. Future Perspectivesof Microneedle-Based Vaccination
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehreth, J. The Global Value of Vaccination. Vaccine 2003, 21, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finco, O.; Rappuoli, R. Designing Vaccines for the Twenty-First Century Society. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, P.; Eames, K.; Heymann, D.L. “Herd Immunity”: A Rough Guide. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnoy, A.; Ozawa, S.; Grewal, S.; Norman, B.A.; Rajgopal, J.; Gorham, K.M.; Haidari, L.A.; Brown, S.T.; Lee, B.Y. Costs of Vaccine Programs across 94 Low-and Middle-Income Countries. Vaccine 2015, 33, A99–A108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfattheicher, S.; Petersen, M.B.; Böhm, R. Information about Herd Immunity through Vaccination and Empathy Promote COVID-19 Vaccination Intentions. Health Psychol. 2022, 41, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappuoli, R. Vaccines: Science, Health, Longevity, and Wealth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Zimmermann, J.; Schülke, S. Novel Adjuvants in Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy: Where Do We Stand? Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1348305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P.; Elliott, S.; Krauer, K.; Davies, C.; Skinner, S.R.; Anderson, C.D.; Forster, A. Safety, Acceptability and Tolerability of Uncoated and Excipient-Coated High Density Silicon Micro-Projection Array Patches in Human Subjects. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6676–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Erdos, G.; Huang, S.; Kenniston, T.W.; Balmert, S.C.; Carey, C.D.; Raj, V.S.; Epperly, M.W.; Klimstra, W.B.; Haagmans, B.L. Microneedle Array Delivered Recombinant Coronavirus Vaccines: Immunogenicity and Rapid Translational Development. EBioMedicine 2020, 55, 102743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-Based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamee, M.; Wong, S.; Guy, O.; Sharma, S. Microneedle Technology for Potential SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, G.; Hirschberg, H. Needle-Free Vaccine Delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengistu, D.A.; Tolera, S.T.; Demmu, Y.M. Worldwide Prevalence of Occupational Exposure to Needle Stick Injury among Healthcare Workers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 9019534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, S.; Moore, A.C.; Sahm, L.J.; Fleming, A. Parent Attitudes about Childhood Vaccines: Point Prevalence Survey of Vaccine Hesitancy in an Irish Population. Pharm. J. Pharm. Educ. Pract. 2021, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddio, A.; Ipp, M.; Thivakaran, S.; Jamal, A.; Parikh, C.; Smart, S.; Sovran, J.; Stephens, D.; Katz, J. Survey of the Prevalence of Immunization Non-Compliance Due to Needle Fears in Children and Adults. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4807–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Oh, Y.; Kim, Y.; Shin, Y.; Baek, S.-K.; Park, J.-H. Progress in Microneedle Array Patch (MAP) for Vaccine Delivery. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.R. What’s Fueling the Biotech Engine—2012 to 2013. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamazo, C.; Pastor, Y.; Larrañeta, E.; Berzosa, M.; Irache, J.M.; Donnelly, R.F. Understanding the Basis of Transcutaneous Vaccine Delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Gomes, K.B.; Bajaj, L.; Gala, R.; Uddin, M.N.; D’souza, M.J.; Zughaier, S.M. Microneedles: A New Generation Vaccine Delivery System. Micromachines 2021, 12, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, E.L.; Campbell, J.D. Needle-Free Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.E.V.; Sharpe, L.A.; Peppas, N.A. Current State and Challenges in Developing Oral Vaccines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 114, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, E.; Caputo, V.; Diotti, R.A.; Sautto, G.A.; Kirchenbaum, G.A.; Clementi, N. Alternative Methods of Vaccine Delivery: An Overview of Edible and Intradermal Vaccines. J. Immunol. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhu, S.J.; Qiu, H.-J. Mucosal Vaccines: Strategies and Challenges. Immunol. Lett. 2020, 217, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabst, R. Mucosal Vaccination by the Intranasal Route. Nose-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (NALT)—Structure, Function and Species Differences. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4406–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miquel-Clopés, A.; Bentley, E.G.; Stewart, J.P.; Carding, S.R. Mucosal Vaccines and Technology. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraan, H.; Vrieling, H.; Czerkinsky, C.; Jiskoot, W.; Kersten, G.; Amorij, J.-P. Buccal and Sublingual Vaccine Delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Logtestijn, M.D.A.; Domínguez-Hüttinger, E.; Stamatas, G.N.; Tanaka, R.J. Resistance to Water Diffusion in the Stratum Corneum Is Depth-Dependent. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liard, C.; Munier, S.; Joulin-Giet, A.; Bonduelle, O.; Hadam, S.; Duffy, D.; Vogt, A.; Verrier, B.; Combadière, B. Intradermal Immunization Triggers Epidermal Langerhans Cell Mobilization Required for CD8 T-Cell Immune Responses. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, A.B.; Pereira, E.R.; Magnago, C.; Silva, R.M.C.R.A.; Martins, A. de O. Nursing Process for a Patient with Needle Phobia: A Case Study. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2020, 73, e20190095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duttagupta, C.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Narayanan, P.; Pattanshetty, S.M. Vaccine Wastage at the Level of Service Delivery: A Cross-Sectional Study. Public Health 2017, 148, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, S.; Jasny, E.; Schmidt, K.E.; Petsch, B. New Vaccine Technologies to Combat Outbreak Situations. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khobragade, A.; Bhate, S.; Ramaiah, V.; Deshpande, S.; Giri, K.; Phophle, H.; Supe, P.; Godara, I.; Revanna, R.; Nagarkar, R.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Immunogenicity of the DNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine (ZyCoV-D): The Interim Efficacy Results of a Phase 3, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study in India. Lancet 2022, 399, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Roberts, C.C.; Song, J.Y.; Yoon, J.G.; Seong, H.; Hyun, H.-J.; Lee, H.; Gil, A.; Oh, Y.; Park, J.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the Bi-Cistronic GLS-5310 COVID-19 DNA Vaccine Delivered with the GeneDerm Suction Device. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 128, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elveborg, S.; Monteil, V.M.; Mirazimi, A. Methods of Inactivation of Highly Pathogenic Viruses for Molecular, Serology or Vaccine Development Purposes. Pathogens 2022, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Wirth, D.M.; Ortega-Rivera, O.A.; Steinmetz, N.F.; Pokorski, J.K. Dissolving Microneedle Delivery of a Prophylactic HPV Vaccine. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakovija, A.; Chtanova, T. Skin Immunity in Wound Healing and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1060258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Awady, A.R.; Elashiry, M.; Morandini, A.C.; Meghil, M.M.; Cutler, C.W. Dendritic Cells a Critical Link to Alveolar Bone Loss and Systemic Disease Risk in Periodontitis: Immunotherapeutic Implications. Periodontology 2000 2022, 89, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, T.; Luo, B.; Zhang, W.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z. Microneedle-Mediated Vaccination: Innovation and Translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 113919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.S.; Herman, E.I.; Lainez, B.; Licona-Limón, P.; Esplugues, E.; Flavell, R.; Craft, J. TFH Cells Progressively Differentiate to Regulate the Germinal Center Response. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Szalay, S.; Wertz, P.W. Protective Barriers Provided by the Epidermis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, J.J.Y.; McMillan, C.L.D.; Young, P.R.; Muller, D.A. Microarray Patches: Scratching the Surface of Vaccine Delivery. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2023, 22, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauri, A.M.; Armstrong, G.L.; Hutin, Y.J. The Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Contaminated Injections given in Health Care Settings. Int. J. STD AIDS 2004, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.H.; Laurent, P.E. Intradermal Vaccine Delivery: Will New Delivery Systems Transform Vaccine Administration? Vaccine 2008, 26, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, A.; Mistretta, F.; Bottigioli, D.; Dahel, K.; Goujon, C.; Nicolas, J.F.; Hennino, A.; Laurent, P.E. Echographic Measurement of Skin Thickness in Adults by High Frequency Ultrasound to Assess the Appropriate Microneedle Length for Intradermal Delivery of Vaccines. Vaccine 2007, 25, 6423–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, M. Engineering of Needle-Free Physical Methods to Target Epidermal Cells for DNA Vaccination. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4651–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchall, J.C. Microneedle Array Technology: The Time Is Right but Is the Science Ready? Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2006, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal Drug Delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhache, P.; Rodrigo, C.; Davie, S.; Ahuja, A.; Sudovar, B.; Crudup, T.; Rose, M. Health Care Providers’ and Parents’ Attitudes toward Administration of New Infant Vaccines—A Multinational Survey. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2013, 172, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Prausnitz, M.R. Enabling Skin Vaccination Using New Delivery Technologies. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2011, 1, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.J.; AlAwaidy, S.; Bawikar, S.; Kurup, P.J.; Elamir, E.; Shaban, M.M.; Sharif, S.M.; van der Avoort, H.G.; Pallansch, M.A.; Malankar, P. Fractional Doses of Inactivated Poliovirus Vaccine in Oman. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2351–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bins, A.D.; Jorritsma, A.; Wolkers, M.C.; Hung, C.-F.; Wu, T.C.; Schumacher, T.N.; Haanen, J.B. A Rapid and Potent DNA Vaccination Strategy Defined by in Vivo Monitoring of Antigen Expression. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, J.; Mitragotri, S. Needle-Free Liquid Jet Injections: Mechanisms and Applications. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2006, 3, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, M.-E.; Kikuta, A.; Taddio, A. A Systematic Review of Measures for Reducing Injection Pain during Adult Immunization. Vaccine 2010, 28, 1514–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for Drug and Vaccine Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 1547–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarkar, R.; Singh, M.; Nguyen, H.X.; Jonnalagadda, S. A Review of Recent Advances in Microneedle Technology for Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Arrays for Vaccine Delivery: The Possibilities, Challenges and Use of Nanoparticles as a Combinatorial Approach for Enhanced Vaccine Immunogenicity. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 851–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.-X.; Hu, H.; Wong, Y.-Y.; Yao, X.; He, M.-L. Microneedles: An Emerging Vaccine Delivery Tool and a Prospective Solution to the Challenges of SARS-CoV-2 Mass Vaccination. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikszta, J.A.; Alarcon, J.B.; Brittingham, J.M.; Sutter, D.E.; Pettis, R.J.; Harvey, N.G. Improved Genetic Immunization via Micromechanical Disruption of Skin-Barrier Function and Targeted Epidermal Delivery. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcil, M.; Çelik, A. Microneedles in Drug Delivery: Progress and Challenges. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, D.; Gadade, D.; Chapaitkar, N.; Shelke, S.; Pekamwar, S.; Aher, R.; Ahire, A.; Avhale, M.; Badgule, R.; Bansode, R.; et al. Polymeric Microneedles: An Emerging Paradigm for Advanced Biomedical Applications. Sci. Pharm. 2023, 91, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X. Microneedles: The Future of Drug Delivery; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Nguyen, C.N. Microneedle-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.X.; Kipping, T.; Banga, A.K. Polymeric Microneedles Enhance Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeqi, A.; Kiaee, G.; Zeng, W.; Rezaei Nejad, H.; Sonkusale, S. Hard Polymeric Porous Microneedles on Stretchable Substrate for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, G.J.; Hickling, J.; Flores, C.M.J.; Griffin, P.; Anderson, C.D.; Skinner, S.R.; Davies, C.; Witham, K.; Pryor, M.; Bodle, J. Safety, Tolerability, Acceptability and Immunogenicity of an Influenza Vaccine Delivered to Human Skin by a Novel High-Density Microprojection Array Patch (NanopatchTM). Vaccine 2018, 36, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Jin, S.G. Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery: Current Trends and Fabrication. J. Pharm. Investig. 2021, 51, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, I.; Eassa, H.A.; Mohammed, K.H.A.; Abd El-Fattah, M.A.; Abdo, M.H.; Rashad, E.; Eassa, H.A.; Saleh, A.; Amin, O.M.; Nounou, M.I.; et al. Microneedle-Based Vaccine Delivery: Review of an Emerging Technology. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kasasbeh, R.; Brady, A.J.; Courtenay, A.J.; Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; O’Kane, D.; Liggett, S.; Donnelly, R.F. Evaluation of the Clinical Impact of Repeat Application of Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Array Patches. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 690–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed Saeed Al-Japairai, K.; Mahmood, S.; Hamed Almurisi, S.; Reddy Venugopal, J.; Rebhi Hilles, A.; Azmana, M.; Raman, S. Current Trends in Polymer Microneedle for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 587, 119673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, T.; Feng, N. Recent Progress of Microneedles in Transdermal Immunotherapy: A Review. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 662, 124481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Arrays as Transdermal and Intradermal Drug Delivery Systems: Materials Science, Manufacture and Commercial Development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2016, 104, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A Smart Approach and Increasing Potential for Transdermal Drug Delivery System. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, S.A.; Ng, C.-Y.; Simmers, R.; Moeckly, C.; Brandwein, D.; Gilbert, T.; Johnson, N.; Brown, K.; Alston, T.; Prochnow, G.; et al. Rapid Intradermal Delivery of Liquid Formulations Using a Hollow Microstructured Array. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, C.J.W.; Howells, O.; Blayney, G.J.; Eng, P.F.; Birchall, J.C.; Gualeni, B.; Roberts, K.; Ashraf, H.; Guy, O.J. Hollow Silicon Microneedle Fabrication Using Advanced Plasma Etch Technologies for Applications in Transdermal Drug Delivery. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 2788–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.M.; Cornwell, M.; Hill, J.; Prausnitz, M.R. Precise Microinjection into Skin Using Hollow Microneedles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Maaden, K.; Jiskoot, W.; Bouwstra, J. Microneedle Technologies for (Trans)Dermal Drug and Vaccine Delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogai, N.; Nonaka, I.; Toda, Y.; Ono, T.; Minegishi, S.; Inou, A.; Hachiya, M.; Fukamizu, H. Enhanced Immunity in Intradermal Vaccination by Novel Hollow Microneedles. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, W.; Li, J.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gu, Q.; Wang, X.; Cai, L.; Shi, L.; Sun, M. Dose-Sparing Intradermal DTaP-sIPV Immunization with a Hollow Microneedle Leads to Superior Immune Responses. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 757375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, M.; Romeijn, S.; Du, G.; Le Dévédec, S.E.; Vrieling, H.; O’Mahony, C.; Bouwstra, J.A.; Kersten, G. Diphtheria Toxoid Dissolving Microneedle Vaccination: Adjuvant Screening and Effect of Repeated-Fractional Dose Administration. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Chu, L.Y.; Burton, S.A.; Hansen, K.J.; Panyam, J. Intradermal Delivery of Vaccine Nanoparticles Using Hollow Microneedle Array Generates Enhanced and Balanced Immune Response. J. Control. Release 2019, 294, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, A.; Sirbubalo, M.; Hindija, L.; Rahić, O.; Hadžiabdić, J.; Muhamedagić, K.; Čekić, A.; Vranić, E. Microneedles: Characteristics, Materials, Production Methods and Commercial Development. Micromachines 2020, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, J.J.Y.; Vet, L.J.; McMillan, C.L.D.; Harrison, J.J.; Scott, C.A.P.; Depelsenaire, A.C.I.; Fernando, G.J.P.; Watterson, D.; Hall, R.A.; Young, P.R.; et al. A Chimeric Dengue Virus Vaccine Candidate Delivered by High Density Microarray Patches Protects against Infection in Mice. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- vander Straeten, A.; Sarmadi, M.; Daristotle, J.L.; Kanelli, M.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Collins, J.; Pardeshi, A.; Han, J.; Varshney, D.; Eshaghi, B.; et al. A Microneedle Vaccine Printer for Thermostable COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, C.L.D.; Choo, J.J.Y.; Idris, A.; Supramaniam, A.; Modhiran, N.; Amarilla, A.A.; Isaacs, A.; Cheung, S.T.M.; Liang, B.; Bielefeldt-Ohmann, H.; et al. Complete Protection by a Single-Dose Skin Patch–Delivered SARS-CoV-2 Spike Vaccine. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabj8065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Gupta, V.; Bird, C.; Pullagurla, S.R.; Fahey, P.; Forster, A.; Volkin, D.B.; Joshi, S.B. Formulation Development and Improved Stability of a Combination Measles and Rubella Live-Viral Vaccine Dried for Use in the NanopatchTM Microneedle Delivery System. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 2501–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, A.H.; Witham, K.; Depelsenaire, A.C.I.; Veitch, M.; Wells, J.W.; Wheatley, A.; Pryor, M.; Lickliter, J.D.; Francis, B.; Rockman, S.; et al. Safety, Tolerability, and Immunogenicity of Influenza Vaccination with a High-Density Microarray Patch: Results from a Randomized, Controlled Phase I Clinical Trial. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, E.; Balmert, S.C.; Sumpter, T.L.; Carey, C.D.; Erdos, G.; Falo, L.D. Microarray Patches Enable the Development of Skin-Targeted Vaccines against COVID-19. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 171, 164–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zeng, M.; Shan, H.; Tong, C. Microneedle Patches as Drug and Vaccine Delivery Platform. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2413–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.T.T.; Yin, Y.; Thambi, T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Giang Phan, V.H.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, D.S. Smart Vaccine Delivery Based on Microneedle Arrays Decorated with Ultra-pH-Responsive Copolymers for Cancer Immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 185, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hong, C.; Li, J.; Howard, M.T.; Li, Y.; Turvey, M.E.; Uppu, D.S.S.M.; Martin, J.R.; Zhang, K.; Irvine, D.J.; et al. Synthetic Charge-Invertible Polymer for Rapid and Complete Implantation of Layer-by-Layer Microneedle Drug Films for Enhanced Transdermal Vaccination. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10272–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Quan, F.-S.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.-M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Formulation and Coating of Microneedles with Inactivated Influenza Virus to Improve Vaccine Stability and Immunogenicity. J. Control. Release 2010, 142, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wendorf, J.R.; Ghartey-Tagoe, E.B.; Williams, S.C.; Enioutina, E.; Singh, P.; Cleary, G.W. Transdermal Delivery of Macromolecules Using Solid-State Biodegradable Microstructures. Pharm. Res. 2010, 28, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, Y. Recent Advances of Microneedles for Biomedical Applications: Drug Delivery and Beyond. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xia, D.; Prausnitz, M.R. Efficient Drug Delivery into Skin Using a Biphasic Dissolvable Microneedle Patch with Water-Insoluble Backing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Xiang, L. Microneedle-Mediated Transcutaneous Immunization: Potential in Nucleic Acid Vaccination. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2300339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Namjoshi, S.; Benson, H.A.; Mohammed, Y.; Kumeria, T. Dissolvable Polymer Microneedles for Drug Delivery and Diagnostics. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 561–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q. Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Optimized Needle Geometry for Transcutaneous Immunization. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 151, 105361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makvandi, P.; Kirkby, M.; Hutton, A.R.; Shabani, M.; Yiu, C.K.; Baghbantaraghdari, Z.; Jamaledin, R.; Carlotti, M.; Mazzolai, B.; Mattoli, V. Engineering Microneedle Patches for Improved Penetration: Analysis, Skin Models and Factors Affecting Needle Insertion. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, O.; Dillane, K.; Lanza, J.S.; Marshall, J.M.; Jin, J.; Silk, S.E.; Draper, S.J.; Moore, A.C. Low Adenovirus Vaccine Doses Administered to Skin Using Microneedle Patches Induce Better Functional Antibody Immunogenicity as Compared to Systemic Injection. Vaccines 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistilis, M.J.; Joyce, J.C.; Esser, E.S.; Skountzou, I.; Compans, R.W.; Bommarius, A.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Long-Term Stability of Influenza Vaccine in a Dissolving Microneedle Patch. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2017, 7, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.Y.; Prausnitz, M.R. Separable Arrowhead Microneedles. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Min, H.S.; Shin, J.; Nam, J.; Kang, G.; Sim, J.; Yang, H.; Jung, H. Film-Trigger Applicator (FTA) for Improved Skin Penetration of Microneedle Using Punching Force of Carboxymethyl Cellulose Film Acting as a Microneedle Applicator. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; White, L.R.; Estrela, P.; Leese, H.S. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedles: Current Advancements and Future Trends. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, P.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Mechanisms of Sampling Interstitial Fluid from Skin Using a Microneedle Patch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4583–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtenay, A.J.; McAlister, E.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Vora, L.; Steiner, L.; Levin, G.; Levy-Nissenbaum, E.; Shterman, N.; Kearney, M.-C.; McCarthy, H.O.; et al. Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Arrays as a Therapeutic Option for Transdermal Esketamine Delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 322, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárcamo-Martínez, Á.; Domínguez-Robles, J.; Mallon, B.; Raman, M.T.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Bell, S.E.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. Potential of Polymeric Films Loaded with Gold Nanorods for Local Hyperthermia Applications. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, L.; Samandari, M.; Schmidt, T.A.; Tamayol, A. Microneedle Arrays for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Wang, Z.; Chang, H.; Wang, L.; Chew, S.W.T.; Lio, D.C.S.; Cui, M.; Liu, L.; Tee, B.C.K.; Xu, C. Osmosis-Powered Hydrogel Microneedles for Microliters of Skin Interstitial Fluid Extraction within Minutes. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e1901683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himawan, A.; Vora, L.K.; Permana, A.D.; Sudir, S.; Nurdin, A.R.; Nislawati, R.; Hasyim, R.; Scott, C.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Where Microneedle Meets Biomarkers: Futuristic Application for Diagnosing and Monitoring Localized External Organ Diseases. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtenay, A.J.; Rodgers, A.M.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; McCarthy, H.O.; Donnelly, R.F. Novel Hydrogel-Forming Microneedle Array for Intradermal Vaccination in Mice Using Ovalbumin as a Model Protein Antigen. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Park, J.; Bonfante, G.; Kim, B. Recent Advances in Porous Microneedles: Materials, Fabrication, and Transdermal Applications. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, M.; Bystrova, S.; Winnubst, L.; Qureshi, H.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Scheper, R.J.; Luttge, R. Applying Ceramic Nanoporous Microneedle Arrays as a Transport Interface in Egg Plants and an Ex-Vivo Human Skin Model. Microelectron. Eng. 2012, 98, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Bonfante, G.; Sasaki, Y.; Takama, N.; Minami, T.; Kim, B. Porous Microneedles on a Paper for Screening Test of Prediabetes. Med. Devices Sens. 2020, 3, e10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Du, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Mao, J.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Zhu, J. Polymer Microneedles with Interconnected Porous Structures via a Phase Inversion Route for Transdermal Medical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Albakr, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, A.; Chen, W.; Shao, T.; Zhu, L.; Yuan, H.; Yang, G.; et al. Microneedle-Enabled Therapeutics Delivery and Biosensing in Clinical Trials. J. Control. Release 2023, 360, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Ogunnaike, E.A.; Wu, Q.; Chen, G.; Hu, Q.; Ci, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Wen, D.; et al. Scattered Seeding of CAR T Cells in Solid Tumors Augments Anticancer Efficacy. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2022, 9, nwab172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, H.; Kimura, N.; Segawa, R.; Kusama, S.; Abe, H.; Terutsuki, D.; Yamasaki, K.; Nishizawa, M. Intradermal Vaccination via Electroosmotic Injection from a Porous Microneedle Patch. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.M.; McCrudden, M.T.; Vincente-Perez, E.; Dubois, A.V.; Ingram, R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Kissenpfennig, A.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and Characterisation of a Dissolving Microneedle Patch for Intradermal Vaccination with Heat-Inactivated Bacteria: A Proof of Concept Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 549, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Excler, J.-L.; Privor-Dumm, L.; Kim, J.H. Supply and Delivery of Vaccines for Global Health. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 71, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privor-Dumm, L.; Excler, J.-L.; Gilbert, S.; Karim, S.S.A.; Hotez, P.J.; Thompson, D.; Kim, J.H. Vaccine Access, Equity and Justice: COVID-19 Vaccines and Vaccination. BMJ Glob. Health 2023, 8, e011881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommareddy, S.; Baudner, B.C.; Oh, S.; Kwon, S.; Singh, M.; O’Hagan, D.T. Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for the Delivery of Cell-Culture-Derived Influenza Vaccine Antigens. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Koutsonanos, D.G.; Del Pilar Martin, M.; Lee, J.W.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Choi, S.-O.; Murthy, N.; Compans, R.W.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving Polymer Microneedle Patches for Influenza Vaccination. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnou, R.; Eavis, P.; De Juanes Pardo, J.-R.; Ambrozaitis, A.; Kazek, M.-P.; Weber, F. Immunogenicity, Large Scale Safety and Lot Consistency of an Intradermal Influenza Vaccine in Adults Aged 18–60 Years: Randomized, Controlled, Phase III Trial. Hum. Vaccin. 2010, 6, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, P.; Oosterhuis-Kafeja, F.; Van der Wielen, M.; Almagor, Y.; Sharon, O.; Levin, Y. Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Microneedle Device for Dose Sparing Intradermal Influenza Vaccination in Healthy Adults. Vaccine 2009, 27, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, M.; Priester, M.I.; Romeijn, S.; Nejadnik, M.R.; Mönkäre, J.; O’Mahony, C.; Jiskoot, W.; Kersten, G.; Bouwstra, J.A. Hyaluronan-Based Dissolving Microneedles with High Antigen Content for Intradermal Vaccination: Formulation, Physicochemical Characterization and Immunogenicity Assessment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 134, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudill, C.; Perry, J.L.; Iliadis, K.; Tessema, A.T.; Lee, B.J.; Mecham, B.S.; Tian, S.; DeSimone, J.M. Transdermal Vaccination via 3D-Printed Microneedles Induces Potent Humoral and Cellular Immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102595118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Rouphael, N. Dissolvable Microneedle Patches to Enable Increased Access to Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and Future Pandemic Outbreaks. Vaccines 2021, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkby, M.; Hutton, A.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Protein, Peptide and Antibody Based Therapeutics: Current Status and Future Considerations. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, E.; Balmert, S.C.; Carey, C.D.; Erdos, G.; Louis D Falo, J. Emerging Skin-Targeted Drug Delivery Strategies to Engineer Immunity: A Focus on Infectious Diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 18, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwentrai, C.; Yu, J.; Rong, L.; Zhang, B.-Z.; Hu, Y.-F.; Gong, H.-R.; Dou, Y.; Deng, J.; Huang, J.-D.; Xu, C. Intradermal Delivery of Receptor-Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein with Dissolvable Microneedles to Induce Humoral and Cellular Responses in Mice. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, e10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Shayan, F.L.; Kim, S.; Huh, I.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Jung, H. Physicochemical Study of Ascorbic Acid 2-Glucoside Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Dissolving Microneedles Irradiated by Electron Beam and Gamma Ray. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.D.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, B.L.; Hao, Y.Y.; Guo, X.D. Safety Assessment of Microneedle Technology for Transdermal Drug Delivery: A Review. Adv. Ther. 2020, 3, 2000033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, W.C.; Martin, M.P.; Zarnitsyn, V.; Wang, B.; Koutsonanos, D.; Skountzou, I.; Prausnitz, M.R.; Compans, R.W. Microneedle Vaccination with Stabilized Recombinant Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin Induces Improved Protective Immunity. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. CVI 2011, 18, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathuria, H.; Kang, K.; Cai, J.; Kang, L. Rapid Microneedle Fabrication by Heating and Photolithography. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Cheng, H.-F.; Yeh, M.-K. Development of Yersinia Pestis F1 Antigen-Loaded Liposome Vaccine against Plague Using Microneedles as a Delivery System. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumel, A.B.; Iboi, E.A.; Ngonghala, C.N.; Ngwa, G.A. Toward Achieving a Vaccine-Derived Herd Immunity Threshold for COVID-19 in the US. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 709369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.-J.; Cha, H.-R.; Hwang, S.J.; Baek, S.-K.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, S.-O. Live Vaccinia Virus-Coated Microneedle Array Patches for Smallpox Vaccination and Stockpiling. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, J.M.; Dewitt, K.; Scott-Garrard, M.; Chiang, Y.-W.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rabies Vaccination in Dogs Using a Dissolving Microneedle Patch. J. Control. Release 2016, 239, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, L.J.J.; Daoussi, R.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.-P.; De Beer, T.R.M. Freeze-Drying of Live Virus Vaccines: A Review. Vaccine 2015, 33, 5507–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, C.; Collins, M.L.; Goodson, J.L.; Rota, P.A.; Prausnitz, M.R. A Microneedle Patch Containing Measles Vaccine Is Immunogenic in Non-Human Primates. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4712–4718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawar, S.D.; Murtadak, V.B.; Kale, S.D.; Shinde, P.V.; Parkhi, S.S. Evaluation of Different Inactivation Methods for High and Low Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses in Egg-Fluids for Antigen Preparation. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 222, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, H.J.H.B.; van de Wijdeven, G.G.P.; Kraan, H.; Amorij, J.-P.; Kersten, G.F.A. Bioneedles as Alternative Delivery System for Hepatitis B Vaccine. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzler, M.A.; Weiner, D.B. DNA Vaccines: Ready for Prime Time? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, K.J.; Sagar, S.; Murphy, J.; Chartrain, M. Industrial Scale Production of Plasmid DNA for Vaccine and Gene Therapy: Plasmid Design, Production, and Purification. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 33, 865–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Sun, X.; Aikins, M.E.; Moon, J.J. Non-Viral COVID-19 Vaccine Delivery Systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 169, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Dewitte, H. Three Decades of Messenger RNA Vaccine Development. Nano Today 2019, 28, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; Quan, F.-S.; Compans, R.W.; Kang, S.-M.; Prausnitz, M.R. Formulation of Microneedles Coated with Influenza Virus-like Particle Vaccine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edens, C.; Collins, M.L.; Ayers, J.; Rota, P.A.; Prausnitz, M.R. Measles Vaccination Using a Microneedle Patch. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3403–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edens, C.; Dybdahl-Sissoko, N.C.; Weldon, W.C.; Oberste, M.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Inactivated Polio Vaccination Using a Microneedle Patch Is Immunogenic in the Rhesus Macaque. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4683–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Shan, W.; Cheng, Z.; Dai, X.; Xue, Y.; Chen, F. Enhancement of Ag85B DNA Vaccine Immunogenicity against Tuberculosis by Dissolving Microneedles in Mice. Vaccine 2018, 36, 4471–4476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, A.V.; Mandal, A.; Kulp, D.W.; Menis, S.; Bennett, N.R.; Watkins, H.C.; Wang, W.; Martin, J.T.; Thai, N.T.; He, Y.; et al. Enhancing Humoral Immunity via Sustained-Release Implantable Microneedle Patch Vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 16473–16478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcon, J.B.; Hartley, A.W.; Harvey, N.G.; Mikszta, J.A. Preclinical Evaluation of Microneedle Technology for Intradermal Delivery of Influenza Vaccines. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, A.M.; Cordeiro, A.S.; Donnelly, R.F. Technology Update: Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for Vaccine Delivery. Med. Devices 2019, 12, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrole, R.S.; Azizoglu, E.; Dul, M.; Birchall, J.C.; Gill, H.S.; Prausnitz, M.R. Trends of Microneedle Technology in the Scientific Literature, Patents, Clinical Trials and Internet Activity. Biomaterials 2021, 267, 120491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iredahl, F.; Muller, D.A.; Togö, T.; Jonasson, H.; Baker, B.; Anderson, C.D.; Henricson, J. Local Response and Barrier Recovery in Elderly Skin Following the Application of High-Density Microarray Patches. Vaccines 2022, 10, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, T.M.T.; Moniz, T.; Nunes, C.; Zaharieva, M.M.; Kaleva, M.; Yoncheva, K.; Najdenski, H.; Costa Lima, S.A.; Reis, S. Polymeric Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Rivastigmine: Design and Application in Skin Mimetic Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Jeong, S.S.; Roh, D.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Choi, H.-K.; Lee, E.H. A Practical Guide to the Development of Microneedle Systems—In Clinical Trials or on the Market. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Mumper, R.J. Topical Immunization Using Nanoengineered Genetic Vaccines. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Wonganan, P.; Sandoval, M.A.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Cui, Z. Microneedle-Mediated Transcutaneous Immunization with Plasmid DNA Coated on Cationic PLGA Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Petrovsky, N. Molecular Mechanisms for Enhanced DNA Vaccine Immunogenicity. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depelsenaire, A.C.I.; Meliga, S.C.; McNeilly, C.L.; Pearson, F.E.; Coffey, J.W.; Haigh, O.L.; Flaim, C.J.; Frazer, I.H.; Kendall, M.A.F. Colocalization of Cell Death with Antigen Deposition in Skin Enhances Vaccine Immunogenicity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, Y.; Kochba, E.; Kenney, R. Clinical Evaluation of a Novel Microneedle Device for Intradermal Delivery of an Influenza Vaccine: Are All Delivery Methods the Same? Vaccine 2014, 32, 4249–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, H.; Kakita, K.; Imafuku, K.; Takashima, S.; Haga, N.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Oyamada, T. Safety and Dose-Sparing Effect of Japanese Encephalitis Vaccine Administered by Microneedle Patch in Uninfected, Healthy Adults (MNA-J): A Randomised, Partly Blinded, Active-Controlled, Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Microbe 2022, 3, e96–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouphael, N.G.; Paine, M.; Mosley, R.; Henry, S.; McAllister, D.V.; Kalluri, H.; Pewin, W.; Frew, P.M.; Yu, T.; Thornburg, N.J. The Safety, Immunogenicity, and Acceptability of Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Delivered by Microneedle Patch (TIV-MNP 2015): A Randomised, Partly Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 1 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franck, C.O.; Fanslau, L.; Bistrovic Popov, A.; Tyagi, P.; Fruk, L. Biopolymer-based Carriers for DNA Vaccine Design. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13225–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruggi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Ulmer, J.B.; Yu, D. mRNA as a Transformative Technology for Vaccine Development to Control Infectious Diseases. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Weissman, D. Recent Advances in mRNA Vaccine Technology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 65, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.B.; Goodson, J.L.; Chu, S.Y.; Rota, P.A.; Meltzer, M.I. Assessing the Potential Cost-Effectiveness of Microneedle Patches in Childhood Measles Vaccination Programs: The Case for Further Research and Development. Drugs RD 2016, 16, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter-Johnson, J.; Kumar, P.; Choonara, Y.E.; du Toit, L.C.; Pillay, V. Therapeutic Applications and Pharmacoeconomics of Microneedle Technology. Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2018, 18, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, M.-K.; You, J.H. Cost-Effectiveness of an Influenza Vaccination Program Offering Intramuscular and Intradermal Vaccines versus Intramuscular Vaccine Alone for Elderly. Vaccine 2016, 34, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Jiang, M.; You, J.H. Potential Cost-Effectiveness of an Influenza Vaccination Program Offering Microneedle Patch for Vaccine Delivery in Children. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0169030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.Y.; Bartsch, S.M.; Mvundura, M.; Jarrahian, C.; Zapf, K.M.; Marinan, K.; Wateska, A.R.; Snyder, B.; Swaminathan, S.; Jacoby, E. An Economic Model Assessing the Value of Microneedle Patch Delivery of the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4727–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez-Graña, C.; Bryan, K.; Vucen, S.; O’Sullivan, C. Development of a Novel Single-Use Microneedle Design Platform for Increased Patient Compliance. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 13, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.G.; Ma, Y.; Huh, I.; Lahiji, S.F.; Lee, S.-G.; Jung, H. A Novel Ultrafine Needle (UN) for Innocuous and Efficient Subcutaneous Insulin Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1603228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detamornrat, U.; McAlister, E.; Hutton, A.R.J.; Larrañeta, E.; Donnelly, R.F. The Role of 3D Printing Technology in Microengineering of Microneedles. Small 2022, 18, 2106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Engineering Microneedle Patches for Vaccination and Drug Delivery to Skin. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2017, 8, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayarri, L. Drug-Device Combination Products: Regulatory Landscape and Market Growth. Drugs Today 2015, 51, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, J.J.; Arya, J.M.; McClain, M.A.; Frew, P.M.; Meltzer, M.I.; Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedle Patches: Usability and Acceptability for Self-Vaccination against Influenza. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, W.; Chen, C.-H.; Luo, Y.-C. Revisiting the Water-Use Efficiency Performance for Microelectronics Manufacturing Facilities: Using Taiwan’s Science Parks as a Case Study. Water-Energy Nexus 2018, 1, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.-J.; Cha, H.-R.; Kwon, D.; Kang, A.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.; Choi, J.-E.; Chung, H.W.; Park, S.; Shim, D.H.; et al. Development and Evaluation of Five-in-One Vaccine Microneedle Array Patch for Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, and Haemophilus Influenzae Type b: Immunological Efficacy and Long-Term Stability. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Neustrup, M.A.; Slütter, B.; O’Mahony, C.; Bouwstra, J.A.; van der Maaden, K. Intradermal Vaccination with PLGA Nanoparticles via Dissolving Microneedles and Classical Injection Needles. Pharm. Res. 2024, 41, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Yang, H.; Seong, B.-L.; Jung, H. Egg Microneedles for Transdermal Vaccination of Inactivated Influenza Virus. Biomater. Sci. 2024, 12, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, L.; He, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Xiang, M.; Yuan, X.; Gou, M. Intradermal Delivery of Cell Vaccine via Ice Microneedles for Cancer Treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, 2400678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wen, X.; Lu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, P.; Mu, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Qu, F.; Chang, H. Ice-Pop Making Inspired Photothermal Ultra-Swelling Microneedles to Facilitate Loading and Intradermal Vaccination of Tumor Antigen. J. Control. Release 2025, 379, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, C.; Fusciello, M.; Hamdan, F.; D’Alessio, F.; Bottega, P.; Saklauskaite, M.; Russo, S.; Cerioni, J.; Elbadri, K.; Kemell, M.; et al. Transdermal Delivery of PeptiCRAd Cancer Vaccine Using Microneedle Patches. Bioact. Mater. 2025, 45, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, P.; Lin, Z.; Hu, Z.; Lu, W. Liposome-Loaded Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for More Efficient Intradermal Antigen Delivery of Hepatitis B Vaccine. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 669, 125023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, Y.; Xu, N.; Ling, G.; Zhang, P. Multifunctional Nanomedicines for Synergistic Photodynamic Immunotherapy Based on Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 173, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, L.; Zhang, Z. Advances in Biological Application of and Research on Low-Frequency Ultrasound. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 2839–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Peng, H.; Chen, Z. 3D-Printed Integrated Ultrasonic Microneedle Array for Rapid Transdermal Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3314–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Banga, A. Electrically and Ultrasonically Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of Methotrexate. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.C.; Shukla, S.; Skoog, S.A.; Boehm, R.D.; Narayan, R.J. Current Advancements in Transdermal Biosensing and Targeted Drug Delivery. Sensors 2019, 19, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.; Jiang, X.; Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Yin, D.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Multimicrochannel Microneedle Microporation Platform for Enhanced Intracellular Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Company | Type of Microneedle | Vaccine |
|---|---|---|
| 3 M (Kindeva) | Coated microneedle | Influenza |
| Hollow microneedle | Cancer vaccines | |
| JUVIC | Dissolving microneedle | Scrub typhus |
| Micron Biomedical | Dissolving microneedle | Inactivated poliovirus vaccine and inactivated rotavirus vaccine Measles |
| Vaxxas (NanopatchTM) | Coated microneedle array patch | Influenza, COVID-19 |
| Quadmedicine | Dissolving microneedles Coated microneedles | Influenza, Hepatitis B, canine influenza |
| Vaxess | Dissolving microneedles | Influenza, COVID-19, skin cancer |
| Raphas | Dissolving microneedles | HPV, polio, Tdap, HBV, IPV, and Hepatitis B |
| BD Technologies (BS Soluvia) | Stainless steel microneedle | Influenza |
| Flugen | Metal microneedle | Influenza |
| Debiotech | Hollow microneedle | COVID-19 |
| Verndari (Vaxipatch) | Stainless steel microneedle | Influenza, COVID-19 |
| Nanopass (MicroJetTM) | Silicon microneedle | Influenza, polio, Varicella Zoster, cancers, Hepatitis B, COVID-19 |
| BioSerenTach Inc. | Dissolving microneedle | Vaccine |
| Sorrento therapeutics (Sofusa®) | Nanotopographical imprinted microneedle (Coated microneedles) | Immuno-oncology |
| NCT Number | Phase | Study Title | Interventions | Microneedle System | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02995057 | NA | Safety Demonstration of Microneedle Insertion | Gold- or silver-coated, or uncoated nickel microneedles | Metal microneedles | Allergic Reaction to Nickel | University of British Columbia |
| NCT06125717 | 1 | Phase 1 Evaluation of H1 Influenza Vaccine Delivered by MIMIX MAP | Biological: H1 influenza antigen | A MIMIX Microneedle Array Patch (MAP) System | Influenza | Vaxess Technologies |
| NCT01813604 | 3 | Immunogenicity of Inactivated and Live Polio Vaccines | Group A: Trivalent Oral Polio Vaccine Group B: Bivalent Oral Polio Vaccine Group C: Inactivated Polio Vaccine Group D: fractional IPV (f-IPV) Arm E: f-IPV and bOPV | MicroJet 600 microneedle | Poliomyelitis | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| NCT03607903 | 1, 2 | Adalimumab Microneedles in Healthy Volunteers | Adalimumab ID Adalimumab SC Saline ID Saline SC | MicroJet 600 microneedle | Pain Injection Site | Centre for Human Drug Research, Netherlands |
| NCT00703651 | 2 | Study of Inactivated, Split-Virion Influenza Vaccine Administered by Intradermal Route Versus Vaxigrip® in Adults | Biological: Inactivated, split-virion influenza vaccine Trivalent Influenza vaccine, (Inactivated, split-virion vaccine) | Microprojection system | Influenza Orthomyxoviridae Infection Myxovirus Infection | Sanofi Pasteur, a Sanofi Company |
| NCT04064554 | NA | Clinical Study to Evaluate Safety and Immunogenicity of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Delivery Via Novel Micronjet600 Device Compared to Those Via Conventional Needle | Device: Bacillus Calmette–Guerin vaccination with MicronJet600 Device: BCG vaccination with conventional needle | MicronJet 600® | Tuberculosis BCG Vaccination | Yonsei University |
| NCT01049490 | NA | Dose Sparing Intradermal S-OIV H1N1 Influenza Vaccination Device | Biological: S-OIV H1N1 vaccine | Micron Jet 600® | Influenza Infection | The University of Hong Kong Hospital Authority, Hong Kong |
| NCT01304563 | NA | 2010/2011 Trivalent Influenza Vaccination | Biological: TIV 2010/2011 influenza vaccine Biological: INT | Micron Jet | Influenza | The University of Hong Kong Hospital Authority, Hong Kong |
| NCT01686503 | 2 | Intradermal Versus Intramuscular Polio Vaccine Booster in HIV-Infected Subjects | Drug: IPOL (Sanofi Pasteur) inactivated polio vaccine booster dose | NanoPass MicronJet 600® microneedles device | Polio Immunity | Eastern Virginia Medical School NanoPass Technologies Ltd. |
| NCT04394689 | 1 and 2 | Measles and Rubella Vaccine Microneedle Patch Phase 1–2 Age De-escalation Trial | Biological: Measles Rubella vaccine (MRV-SC) Biological: MRV-MNP | Dissolving microneedle patch | Measles Rubella Vaccination Healthy | Micron Biomedical, Inc. Medical Research Council Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| NCT02438423 | 1 | Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Delivered by Microneedle Patch or by Hypodermic Needle | Biological: Inactivated influenza vaccine | Dissolvable microneedle patch | Influenza | Mark Prausnitz Emory University Georgia Institute of Technology |
| NCT02621112 | 2 and 3 | HBV Vaccine in Renal Failure Patients | Biological: Intradermal HBVv with imiquimod Biological: Intradermal HBVv with aqueous cream Biological: Intramuscular HBVv with aqueous cream | Microneedles | Renal Failure | The University of Hong Kong |
| NCT02329457 | 2 and 3 | VZV Vaccine for Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation | Biological: Zostavax | Microneedles | Varicella Zoster Infection | The University of Hong Kong |
| NCT01707602 | 1 and 2 | Routes of Immunization and Flu Immune Responses | Biological: INTANZA® 15 Biological: Vaxigrip® Biological: INTANZ® 15 T | Microneedles | Influenza | Assistance Publique–Hôpitaux de Paris Institut National de la Santé Et de la Recherche Médicale, France |
| NCT03207763 | NA | Microneedle Patch Study in Healthy Infants/Young Children | Device: Microneedle Formulation 1 Device: Microneedle Formulation 2 | Microneedles | Vaccination Skin Absorption | Emory University Micron Biomedical, Inc. |
| NCT05315362 | 2 | Establishing Immunogenicity and Safety of Needle-free Intradermal Delivery of mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine | Device: Solid microneedle skin patch | Solid microneedle patch | Vaccination; Infection COVID-19 | Leiden University Medical Center |
| NCT00558649 | NA | A Pilot Study to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of Low-Dose Flu Vaccines | Biological: Flu Vaccine (FLUARIX®) | Microneedle Injectors | Influenza, Human | NanoPass Technologies Ltd. |
| NCT01767324 | NA | Site Selection for Intracutaneous Saline Delivery | Device: Injection to deltoid Device: Injection to the forearm Device: Injection to thigh | FLUGEN 101.2 microneedle-based device | Intracutaneous Drug Delivery | FluGen Inc. Accelovance |
| NCT01039623 | NA | Assessment of Safety and Immunogenicity of Intradermal Unadjuvanted Portion of Pandemrix® Via a Microneedles Device With Intramuscular Adjuvanted Pandemrix® as Reference | Biological: Pandemrix® (H1N1 pandemic influenza) | Microneedles | Healthy | Hadassah Medical Organization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, H.X. Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination. Medicines 2025, 12, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12010004
Nguyen HX. Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination. Medicines. 2025; 12(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Hiep X. 2025. "Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination" Medicines 12, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12010004
APA StyleNguyen, H. X. (2025). Beyond the Needle: Innovative Microneedle-Based Transdermal Vaccination. Medicines, 12(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines12010004





