Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategy
2.1.1. Ovid MEDLINE Search
2.1.2. EMBASE Search
2.1.3. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Search
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Abstraction
2.4. Analysis of Bias Risk
2.4.1. Bias Risk in Case Reports
2.4.2. Bias Risk in Case Series
2.4.3. Bias Risk in Observational Studies
2.5. Statistical Analysis
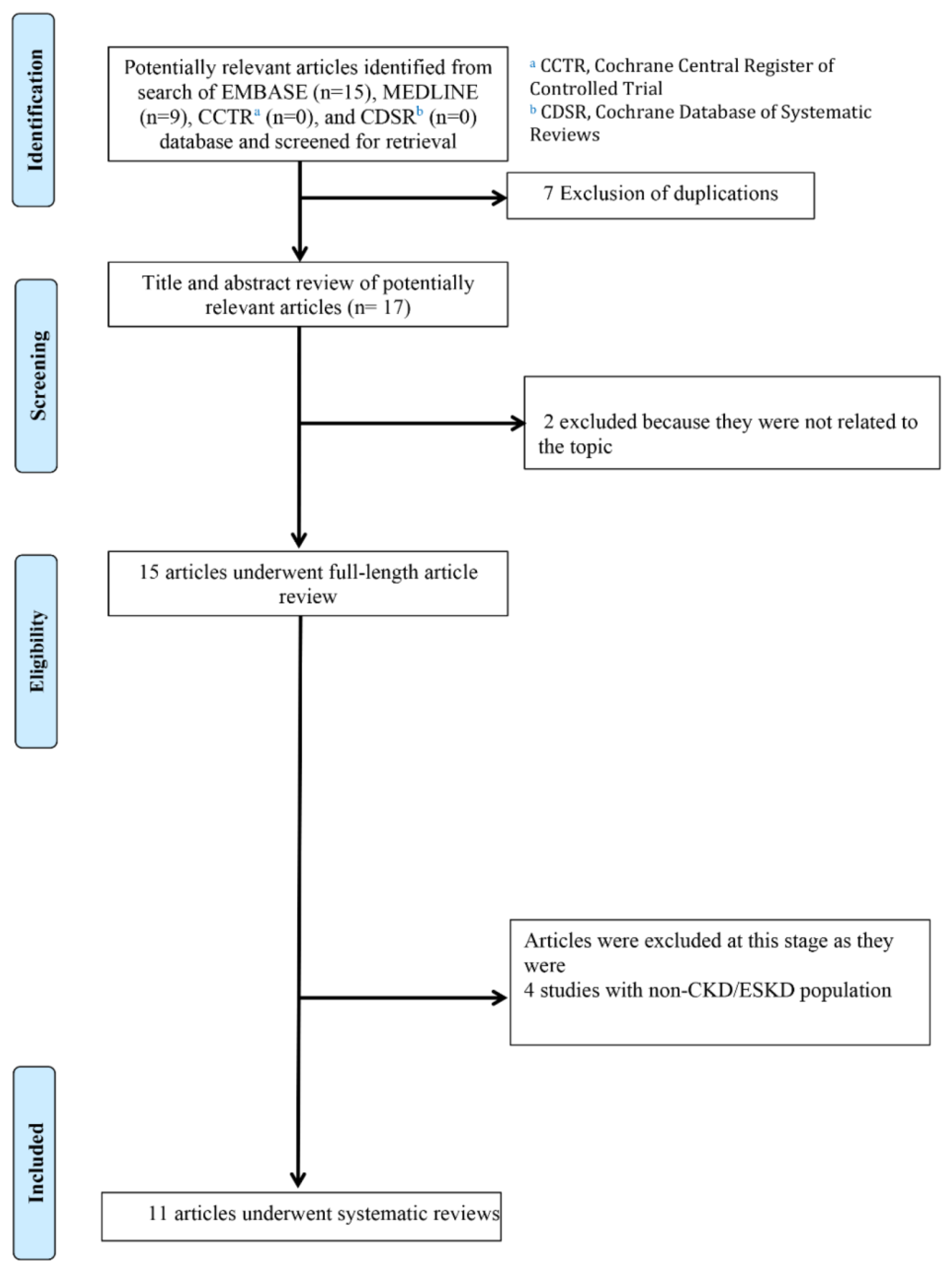
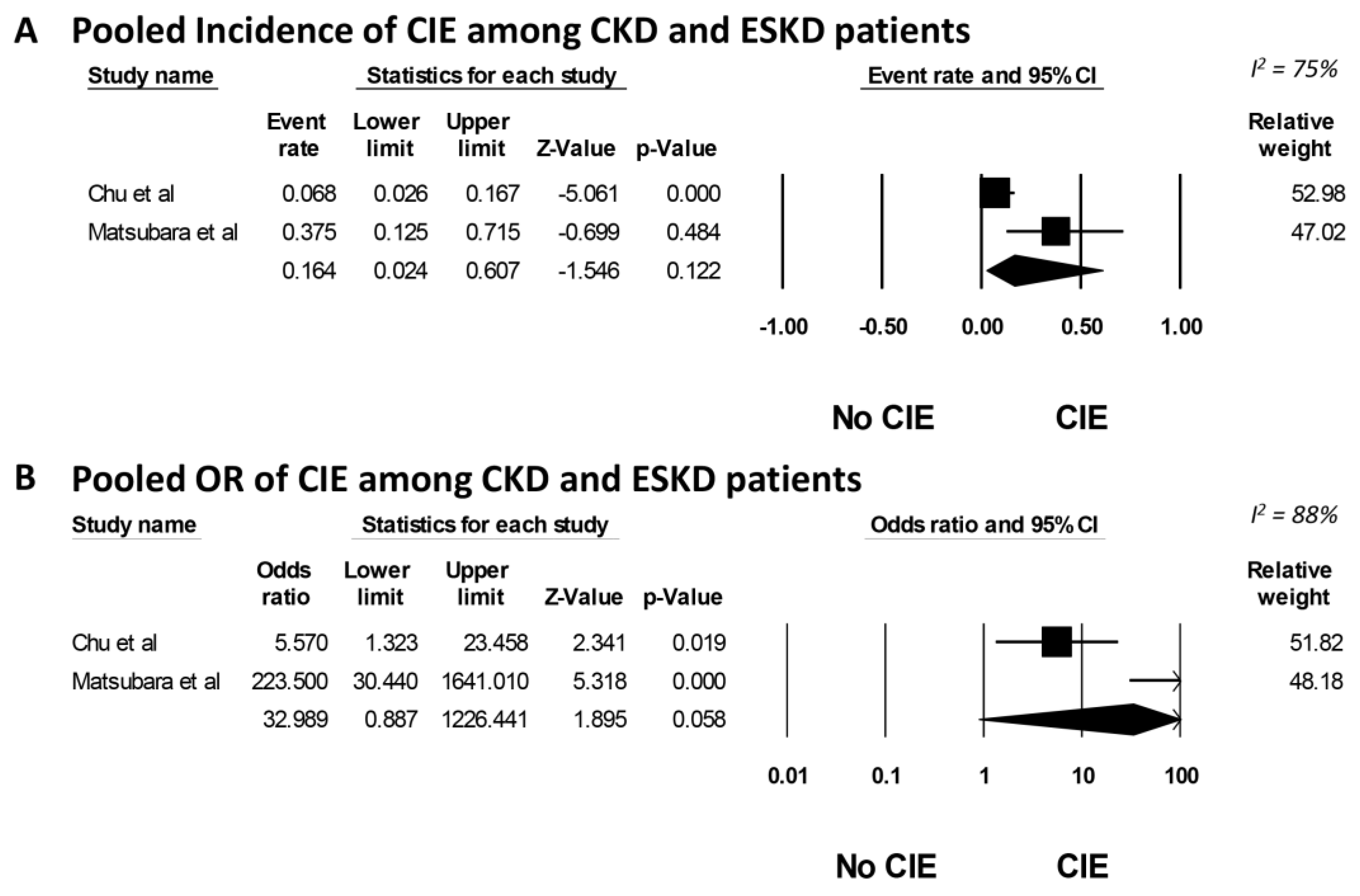
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Babalova, L.; Ruzinak, R.; Ballova, J.; Sivak, S.; Kantorova, E.; Kurca, E.; Zelenak, K.; Nosal, V. Contrast-induced encephalopathy. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2021, 122, 618–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.T.; Lee, K.P.; Chen, C.H.; Sung, P.S.; Lin, Y.H.; Lee, C.W.; Tsai, L.K.; Tang, S.C.; Jeng, J.S. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy After Endovascular Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2020, 51, 3756–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monforte, M.; Marca, G.D.; Lozupone, E. Contrast-induced Encephalopathy. Neurol. India 2020, 68, 718–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Pardo, O.; Ordoñez, A.; Roa, C. Contrast-induced encephalopathy in an infant. Radiol. Case Rep. 2021, 16, 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Wei, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S. Contrast-induced encephalopathy following cerebral angiography: A case report. Med. Int. 2022, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Du, X.; Liu, K. Contrast-induced encephalopathy following bronchial arteriography and endovascular procedure. Acta Neurol. Belgica 2023, 123, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Caranci, F.; Conforti, R.; Rinaldi, F.O.; Pinto, A. Contrast-induced encephalopathy after abdominal CT examination. Acta Neurol. Belgica 2021, 121, 1325–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, T.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, H.; Teng, G.; Chen, J.; Jian, Y.; et al. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy Resulting From Use of Ioversol and Iopromide. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 43, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.; Bogdan, G.; Radančević, D.; Pejanović-Škobić, N. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy following Cerebral Angiography in a Hemodialysis Patient. Case Rep. Neurol. Med. 2020, 2020, 3985231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, N.; Izumi, T.; Miyachi, S.; Ota, K.; Wakabayashi, T. Contrast-induced Encephalopathy Following Embolization of Intracranial Aneurysms in Hemodialysis Patients. Neurologia Medico-Chirurgica 2017, 57, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muruve, D.A.; Steinman, T.I. Contrast-induced encephalopathy and seizures in a patient with chronic renal insufficiency. Clin. Nephrol. 1996, 45, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olbrich, D.; Turk, G.; Helmberger, T. Severe contrast induced encephalopathy (CIE) with subsequent cerebral infarction after cardiac catheterization in a patient with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Neuroradiology 2017, 59, S78. [Google Scholar]
- Ozelsancak, R.; Erken, E.; Yildiz, I.; Giray, S.; Yildirim, T.; Micozkadioglu, H. A very rare case of encephalopathy in a patient with end-stage renal disease: Contrast agent, ioversol. Renal Fail. 2010, 32, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şimşek, E.; Ertürk, E.; Uçar, R.; Yilmaz, A.O.; Ekmekçi, C.; Mutlu, İ.; Sari, C. Transient Contrast Neurotoxicity After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Mimicking Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in a Patient With Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Med. Insights Case Rep. 2019, 12, 1179547619867671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Ramanathan, V. Severe encephalopathy following cerebral arteriogram in a patient with end-stage renal disease. Semin Dial. 2013, 26, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-C.; Yang, K.-B.; Hsu, Y.-H. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease: A Case Report and Literature. Acta Nephrologica 2017, 31, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Alshaer, Q.; Najdawi, Z.; Peterson, R.; Bhatt, N. A Case of Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in The Setting of Acute Stroke Thrombolysis. Neurology 2022, 98 (Suppl. S18), 2201. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Lisy, K.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, SA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.S.; Barber, M.S.; Kienle, G.S.; Aronson, J.K.; von Schoen-Angerer, T.; Tugwell, P.; Kiene, H.; Helfand, M.; Altman, D.G.; Sox, H.; et al. CARE guidelines for case reports: Explanation and elaboration document. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 89, 218–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnier, J.J.; Kienle, G.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; Sox, H.; Riley, D.; Group*, C. The CARE Guidelines: Consensus-based Clinical Case Reporting Guideline Development. Glob. Adv. Health Med. 2013, 2, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, S.; Georgi, M.; McCluney, S.J. COVID-19 and Kawasaki Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Case-Reports and Case-Series. Lancet. 2020 preprint. [CrossRef]
- El Dib, R.; Nascimento Junior, P.; Kapoor, A. An alternative approach to deal with the absence of clinical trials: A proportional meta-analysis of case series studies. Acta Cir. Bras. 2013, 28, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, W.; Keighley, C.; Wolfe, R.; Lee, W.L.; Slavin, M.A.; Kong, D.C.M.; Chen, S.C. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological quality and synthesis of case series and case reports. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Quality Assessment Tool for Case Series Studies. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 9 June 2023).
- Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 25, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easterbrook, P.J.; Gopalan, R.; Berlin, J.; Matthews, D.R. Publication bias in clinical research. Lancet 1991, 337, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FONG, V.; Kamaruzaman, L.; Daud, W.W.; Mohd, R.; Tan, H.; Erica, Y.; Mustafar, R. POS-617 contrast-induced encephalopathy in a patient with end-stage renal disease. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, S264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murumkar, V.; Peer, S.; Jabeen, S.; Chauhan, R.S.; Saini, J.; Aravinda, R.H.; Lanka, V.; Kulkarni, G.B. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy—An Unusual Complication Following Endovascular Interventions in the Anterior Circulation. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2021, 24, 635–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamra, M.; Bakhit, Y.; Khan, M.; Moore, R. Case report and literature review on contrast-induced encephalopathy. Future Cardiol. 2017, 13, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokersnik, J.A.; Liu, L.; Simon, E.L. Contrast-induced encephalopathy presenting as acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 1122.e3–1122.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mescolotte, G.M.; Silva, F.R.D.; Afonso, S.; Pamplona, J.; Moreno, R. Reversible contrast-induced encephalopathy after coil embolization of epistaxis. Rev. Bras. Ter. Intensiva 2021, 33, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumaran, S.; Balamurugan, N.; Jena, N.N.; Thirumalaikolundusubramanian, P. Contrast-induced encephalopathy and diagnostic modalities—Can it make a difference? Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.; Semelka, R.C.; Ramalho, M.; Nunes, R.H.; AlObaidy, M.; Castillo, M. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Accumulation and Toxicity: An Update. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazella, M.A. Current status of gadolinium toxicity in patients with kidney disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.H.; Kanal, E.; Abu-Alfa, A.K.; Cowper, S.E. Gadolinium-based MR contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Radiology 2007, 242, 647–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattani, A.; Au, L.; Tay, K.H.; Davey, P. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy following Coronary Angiography with No Radiological Features: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cardiology 2018, 139, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.R.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.L.; Yang, P. Case Report and Literature Review on Low-Osmolar, Non-Ionic Iodine-Based Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy. Clin. Interv. Aging 2020, 15, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deray, G. Dialysis and iodi.inated contrast media. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2006, 69, S25–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, V.; Taroni, P.; Alvino, S.; Spinazzi, A. Pharmacokinetics and safety of iomeprol in healthy volunteers and in patients with renal impairment or end-stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis. Investig. Radiol 2001, 36, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rault, R.M. Hemodialysis for removal of iodinated contrast media. Int J. Artif. Organs 2001, 24, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davenport, M.S.; Perazella, M.A.; Yee, J.; Dillman, J.R.; Fine, D.; McDonald, R.J.; Rodby, R.A.; Wang, C.L.; Weinreb, J.C. Use of Intravenous Iodinated Contrast Media in Patients With Kidney Disease: Consensus Statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Med. 2020, 2, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morcos, S.K.; Thomsen, H.S.; Webb, J.A. Dialysis and contrast media. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 3026–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Mao, M.A.; Mao, S.A.; D’Costa, M.R.; Kittanamongkolchai, W.; Kashani, K.B. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Transplant. 2017, 7, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Podboy, A.J.; Gillaspie, E.A.; Greason, K.L.; Kashani, K.B. The effects of contrast media volume on acute kidney injury after transcatheter aortic valve replacement: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Evid.-Based Med. 2016, 9, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Author (Year) | Muruve et al. (1996) [11] | Ozelsancak et al. (2010) [13] | Yan et al. (2013) [15] | Olbrich et al. (2017) [12] | Yen et al.(2017) [16] | Simsek et al. (2019) [14] | Bender et al. (2020) [9] | Alshaer et al. (2022) [17] | Fong et al. (2022) [31] | Matsubara et al. (2017) [10] | Matsubara et al. (2017) [10] | Matsubara et al. (2017) [10] | Chu et al. (2020) [2] | Chu et al. (2020) [2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Publication type | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Case report | Cohort study | Cohort study | Cohort study | Cohort study | Cohort study |
| Age (year) | 49 | 55 | 63 | 76 | 64 | 68 | 46 | 80 s | 28 | 63 | 74 | 63 | 84 | 61 |
| Comorbidities | Unstable angina, HTN, chronic glomerular nephritis | DM, HTN, CAD | HTN, DM, rheumatoid arthritis | CAD | HTN, CAD, DM | DM, HTN, CAD | HTN, hypothyroidism, PKD | Lupus nephritis | HTN, PKD | HTN, liver cirrhosis, mitral insufficiency, DM | HTN, PKD | HTN, recent myocardial infarct | HTN, HLD, HF, AF, prior ipsilateral MCA stroke | |
| Baseline kidney function (CKD, ESRD) | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | CKD | ESKD | CKD4 | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD | ESKD |
| Contrast profile | Coronary angiography | Abdominal angiography | Cerebral angiogram | Coronary angiography | Peripheral CT angiogram | Coronary angiography | Cerebral angiography | CTA head | CT angiogram and CT brain | Left internal carotid angiogram with coil embolization | Endovascular procedure for basilar tip, unruptured | Endovascular procedure for basilar tip, unruptured | Endovascular thrombectomy | Endovascular thrombectomy |
| Name | Meglumine/sodium diatrizoate | Ioversol | Iodixanol (Visipaque 320) | - | Iobitridol | Iohexol (Biemexol 300) | Iopamiro 370 | - | - | Iodixanol (Visipaque 270) | Ipamidol (Iopamilon 300) | Ipamidol (Iopamilon 300) | Iopromide | Iopromide |
| Route (IV, IA) | IA | IA | IA | IA | IA | IA | IA | IA | IV/IA | IA | IA | IA | IA | IA |
| Dose (mL) | 90, 610 | 100 | 910 | 280 | 100, 150 | 230 | 80 | - | - | 210 | 160 | 300 | 42 | 12 |
| Encephalopathy characteristic | Headache, seizures | Confusion, agitation | Somnolence and reduced spontaneous movement | LOC | Irritation, disorientation, anisocoria | Seizures | Blurring of vision to blindness, seizure | Seizures | LOC | Hemiparesis, convulsion | Blindness, consciousness disturbance | Blindness | Worsened NIHSS | Worsened NIHSS |
| Dialysis mode | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | - | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD | HD |
| Days dialysis after encephalopathy | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 1 | 0 | - | - |
| Response to treatment | Improvement | Improvement | Improvement after weaning sedation on day 3 | Multiple bilateral infarctions | Improvement | Improvement | Complete resolution | - | Improvement | Improvement | Resolution | Improvement | Deceased | - |
| Onset of improvement (day) | 1 | 15 | 3 | - | 0 | 1 | 5 | 1 | After > 1 HD session | 1 | 1 | - | - | - |
| Author (Year) | Study Design | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|
| Muruve et al. (1996) [11] | Case report | Low |
| Ozelsancak et al. (2010) [13] | Case report | Moderate |
| Yan et al. (2013) [15] | Case report | Low |
| Olbrich et al. (2017) [12] | Case report | Low |
| Yen et al. (2017) [16] | Case report | Moderate |
| Simsek et al. (2019) [14] | Case report | Low |
| Bender et al. (2020) [9] | Case report | Low |
| Alshaer et al. (2022) [17] | Case report | Moderate |
| Fong et al. (2022) [31] | Case report | Moderate |
| Matsubara et al. (2017) [10] | Cohort study | Low |
| Chu et al. (2020) [2] | Cohort study | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, P.W.; Krisanapan, P.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Miao, J.; Hassanein, M.; Acharya, P.; Mao, M.A.; Craici, I.M.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicines 2023, 10, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10080046
Davis PW, Krisanapan P, Tangpanithandee S, Thongprayoon C, Miao J, Hassanein M, Acharya P, Mao MA, Craici IM, Cheungpasitporn W. Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicines. 2023; 10(8):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10080046
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Paul W., Pajaree Krisanapan, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Charat Thongprayoon, Jing Miao, Mohamed Hassanein, Prakrati Acharya, Michael A. Mao, Iasmina M. Craici, and Wisit Cheungpasitporn. 2023. "Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Medicines 10, no. 8: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10080046
APA StyleDavis, P. W., Krisanapan, P., Tangpanithandee, S., Thongprayoon, C., Miao, J., Hassanein, M., Acharya, P., Mao, M. A., Craici, I. M., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2023). Contrast-Induced Encephalopathy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicines, 10(8), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10080046









