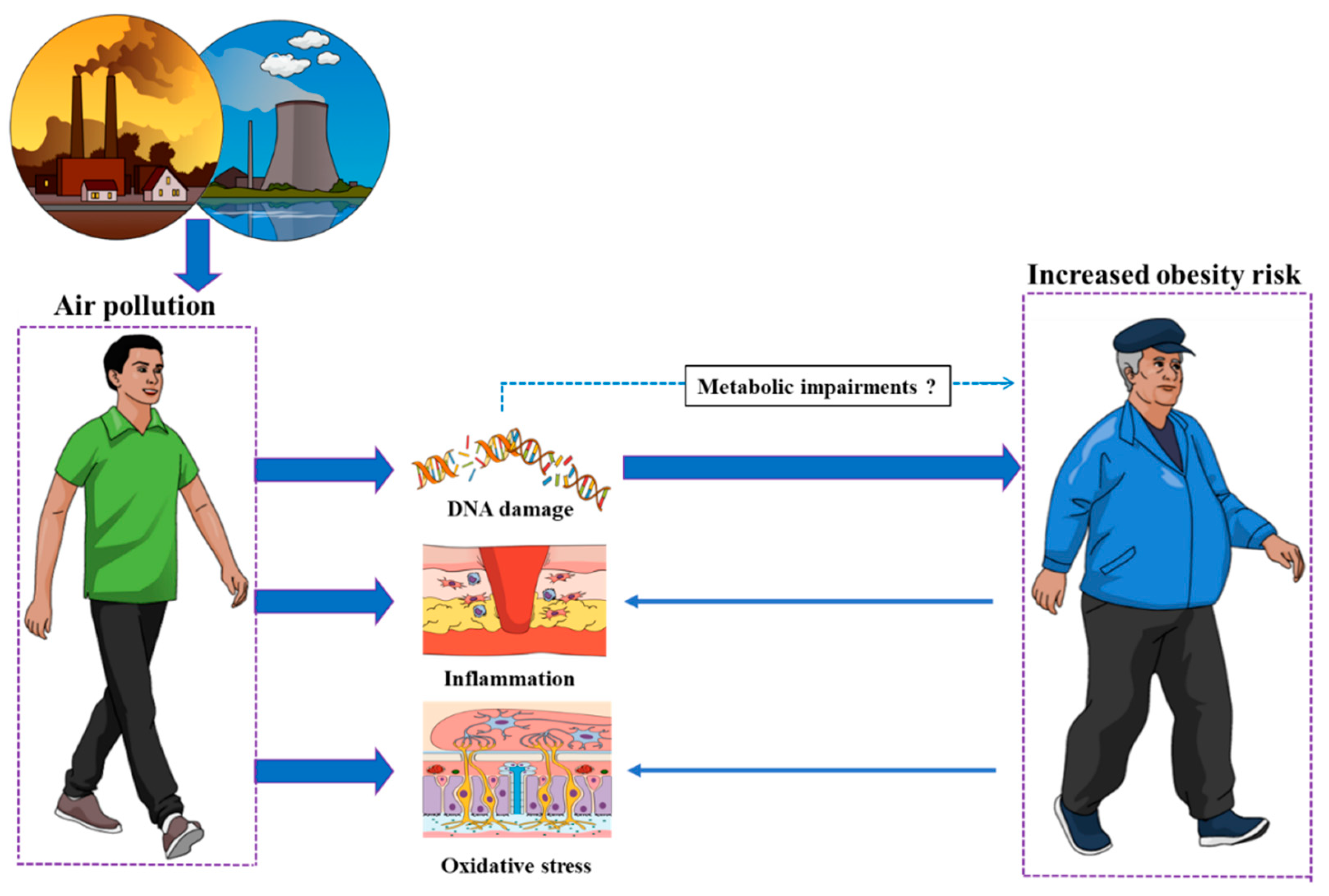
DNA Damage as a Mechanistic Link between Air Pollution and Obesity?
Abstract
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Medanić, D.; Pucarin-Cvetković, J. Obesity—A public health problem and challenge. Acta Med. Croatica 2012, 66, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Broken Energy Homeostasis and Obesity Pathogenesis: The Surrounding Concepts. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Obesity as a Neuroendocrine Reprogramming. Medicina 2021, 57, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apovian, C.M. Obesity: Definition, comorbidities, causes, and burden. Am. J. Manag. Care 2016, 22, s176–s185. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. In Vitro Mimicking of Obesity-Induced Biochemical Environment to Study Obesity Impacts on Cells and Tissues. Diseases 2022, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubertakh, B.; Silvestri, C.; Di Marzo, V. Obesity: The Fat Tissue Disease Version of Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; St-Amand, J. Redefining obesity toward classifying as a disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2018, 55, 20–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S. Recognizing obesity as a disease. J. Am. Assoc. Nurse Pract. 2020, 32, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Tallis, J. Is obesity a risk factor for skeletal muscle ageing? Aging 2019, 11, 2183–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, J.L. Obesity-associated cardiovascular risk in women: Hypertension and heart failure. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 1523–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adalsteinsdottir, B. Obesity as a modifiable risk factor for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.A.A.; Saleem, K. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Failure to Wean from ECMO: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Can. Respir. J. 2021, 2021, 9967357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, A.; Ferrari, F.; Santini, F.; Elisei, R. Obesity as a risk factor for thyroid cancer. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandviwala, T.; Khalid, U.; Deswal, A. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Risk Factor or a Risk Marker? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2016, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pergola, G.; Silvestris, F. Obesity as a major risk factor for cancer. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 291546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Milani, R.V.; Ventura, H.O. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: Risk factor, paradox, and impact of weight loss. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1925–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Regeneration during Obesity: An Impaired Homeostasis. Animals 2020, 10, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Exercise, Diet and Sleeping as Regenerative Medicine Adjuvants: Obesity and Ageing as Illustrations. Medicines 2022, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lavie, C.J.; Mehra, M.R.; Henry, B.M.; Lippi, G. Obesity and Outcomes in COVID-19: When an Epidemic and Pandemic Collide. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Will an obesity pandemic replace the coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic? Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leeuw, A.J.M.; Luttikhuis, M.A.M.O.; Wellen, A.C.; Müller, C.; Calkhoven, C.F. Obesity and its impact on COVID-19. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 899–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Crisis: Losing Our Immunity When We Need It the Most. Biology 2021, 10, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanemi, A.; Melouane, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Exercise and High-Fat Diet in Obesity: Functional Genomics Perspectives of Two Energy Homeostasis Pillars. Genes 2020, 11, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.M.; Quigley, K.M.; Wadden, T.A. Dietary interventions for obesity: Clinical and mechanistic findings. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Diet Impact on Obesity beyond Calories and Trefoil Factor Family 2 (TFF2) as an Illustration: Metabolic Implications and Potential Applications. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, K.M.; Khoo, J. Diet and exercise in management of obesity and overweight. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28 (Suppl. 4), 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Song, Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y. Air Pollution as a Cause of Obesity: Micro-Level Evidence from Chinese Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bont, J.; Casas, M.; Barrera-Gómez, J.; Cirach, M.; Rivas, I.; Valvi, D.; Álvarez, M.; Dadvand, P.; Sunyer, J.; Vrijheid, M. Ambient air pollution and overweight and obesity in school-aged children in Barcelona, Spain. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rider, C.F.; Carlsten, C. Air pollution and DNA methylation: Effects of exposure in humans. Clin. Epigenetics 2019, 11, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.R.; Madugundu, G.S.; Cadet, J. Ozone-Induced DNA Damage: A Pandora’s Box of Oxidatively Modified DNA Bases. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Alves, N.; Pereira, G.M.; Di Domenico, M.; Costanzo, G.; Benevenuto, S.; de Oliveira Fonoff, A.M.; de Souza Xavier Costa, N.; Júnior, G.R.; Kajitani, G.S.; Moreno, N.C.; et al. Inflammation response, oxidative stress and DNA damage caused by urban air pollution exposure increase in the lack of DNA repair XPC protein. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.; Liou, S.H.; Lin, H.C.; Shih, T.S.; Tsai, P.J.; Chen, J.S.; Yang, T.; Jaakkola, J.J.; Strickland, P.T. Exposure to traffic exhausts and oxidative DNA damage. Occup. Environ. Med. 2005, 62, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Danielsen, P.H.; Karottki, D.G.; Jantzen, K.; Roursgaard, M.; Klingberg, H.; Jensen, D.M.; Christophersen, D.V.; Hemmingsen, J.G.; Cao, Y.; et al. Oxidative stress and inflammation generated DNA damage by exposure to air pollution particles. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2014, 762, 133–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, P.; Loft, S. Oxidative damage to DNA and lipids as biomarkers of exposure to air pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risom, L.; Møller, P.; Loft, S. Oxidative stress-induced DNA damage by particulate air pollution. Mutat. Res. 2005, 592, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Su, Z.; Yan, T.; Zhou, S.; Wang, T.; Wei, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, G.; et al. DNA damage, serum metabolomic alteration and carcinogenic risk associated with low-level air pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 297, 118763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görsdorf, S.; Appel, K.E.; Engeholm, C.; Obe, G. Nitrogen dioxide induces DNA single-strand breaks in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Carcinogenesis 1990, 11, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, P.; Folkmann, J.K.; Forchhammer, L.; Bräuner, E.V.; Danielsen, P.H.; Risom, L.; Loft, S. Air pollution, oxidative damage to DNA, and carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, D.L.; Tomei, G.; Tomei, F.; Sancini, A. Traffic air pollution and oxidatively generated DNA damage: Can urinary 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2-deoxiguanosine be considered a good biomarker? A meta-analysis. Biomarkers 2010, 15, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Ageing and Obesity Shared Patterns: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Epigenetics. Diseases 2021, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Włodarczyk, M.; Nowicka, G. Obesity, DNA Damage, and Development of Obesity-Related Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, B.M.; Keildson, S.; Lindgren, C.M. Genetics and epigenetics of obesity. Maturitas 2011, 69, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassan, F.L.; Kelly, R.S.; Kosheleva, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Vokonas, P.S.; Lasky-Su, J.A.; Schwartz, J.D. Metabolomic signatures of the long-term exposure to air pollution and temperature. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassan, F.L.; Kelly, R.S.; Koutrakis, P.; Vokonas, P.S.; Lasky-Su, J.A.; Schwartz, J.D. Metabolomic signatures of the short-term exposure to air pollution and temperature. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setayesh, T.; Mišík, M.; Langie, S.A.S.; Godschalk, R.; Waldherr, M.; Bauer, T.; Leitner, S.; Bichler, C.; Prager, G.; Krupitza, G.; et al. Impact of Weight Loss Strategies on Obesity-Induced DNA Damage. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1900045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Volpi, E.V. DNA damage in obesity: Initiator, promoter and predictor of cancer. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2018, 778, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompella, P.; Vasquez, K.M. Obesity and cancer: A mechanistic overview of metabolic changes in obesity that impact genetic instability. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 1531–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. Obese Animals as Models for Numerous Diseases: Advantages and Applications. Medicina 2021, 57, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doulberis, M.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Polyzos, S.A.; Katsinelos, P.; Grigoriadis, N.; Srivastava, D.S.; Kountouras, J. Rodent models of obesity. Minerva Endocrinol. 2020, 45, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghanemi, A.; Yoshioka, M.; St-Amand, J. DNA Damage as a Mechanistic Link between Air Pollution and Obesity? Medicines 2023, 10, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10010004
Ghanemi A, Yoshioka M, St-Amand J. DNA Damage as a Mechanistic Link between Air Pollution and Obesity? Medicines. 2023; 10(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhanemi, Abdelaziz, Mayumi Yoshioka, and Jonny St-Amand. 2023. "DNA Damage as a Mechanistic Link between Air Pollution and Obesity?" Medicines 10, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10010004
APA StyleGhanemi, A., Yoshioka, M., & St-Amand, J. (2023). DNA Damage as a Mechanistic Link between Air Pollution and Obesity? Medicines, 10(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines10010004






