Polystyrene Nanoplastics Elicit Multiple Responses in Immune Cells of the Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. PS NPs
2.2. Earthworm Maintenance and Cell Extraction
2.3. Cellular Uptake of NPs
2.4. Cytotoxicity of NPs
2.5. Determination of Oxidative-Stress-Related Indicators
2.6. Test for the Integrity of the Cell Membrane
2.7. Detection of Immune-Related Indicators
2.8. Testing of MMP
2.9. Apoptosis Assays
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of NPs
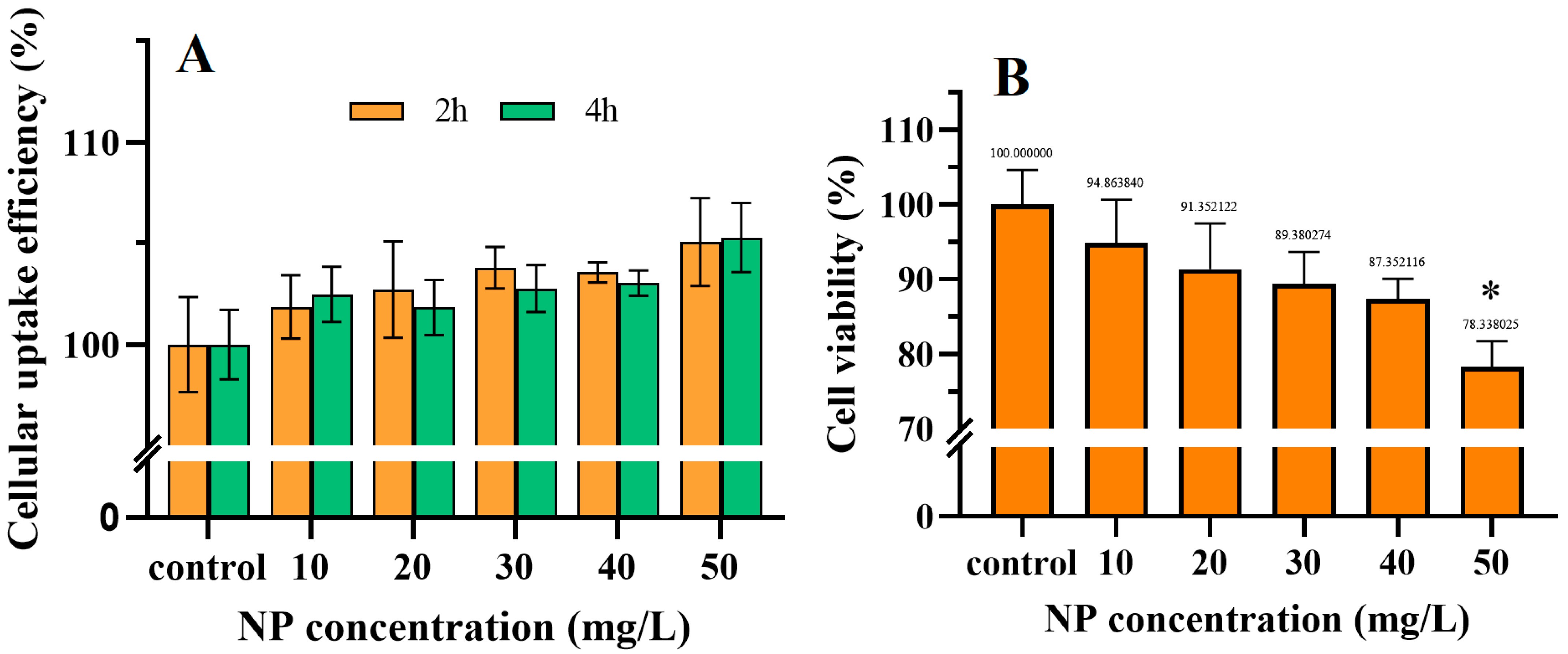
3.2. The Accumulation of NPs in Cells and Their Cytotoxicity
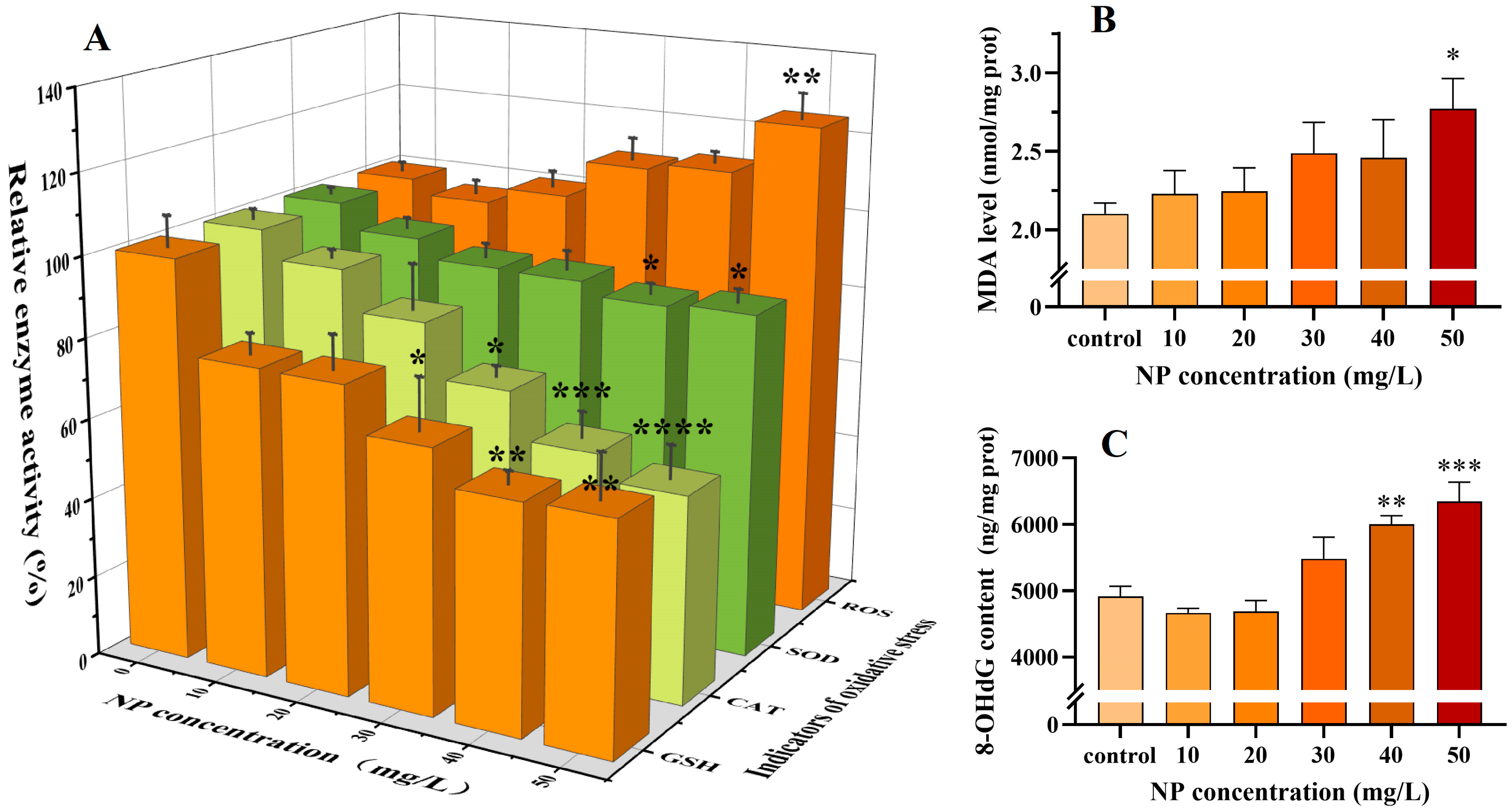
3.3. The Oxidative Stress Induced by NPs
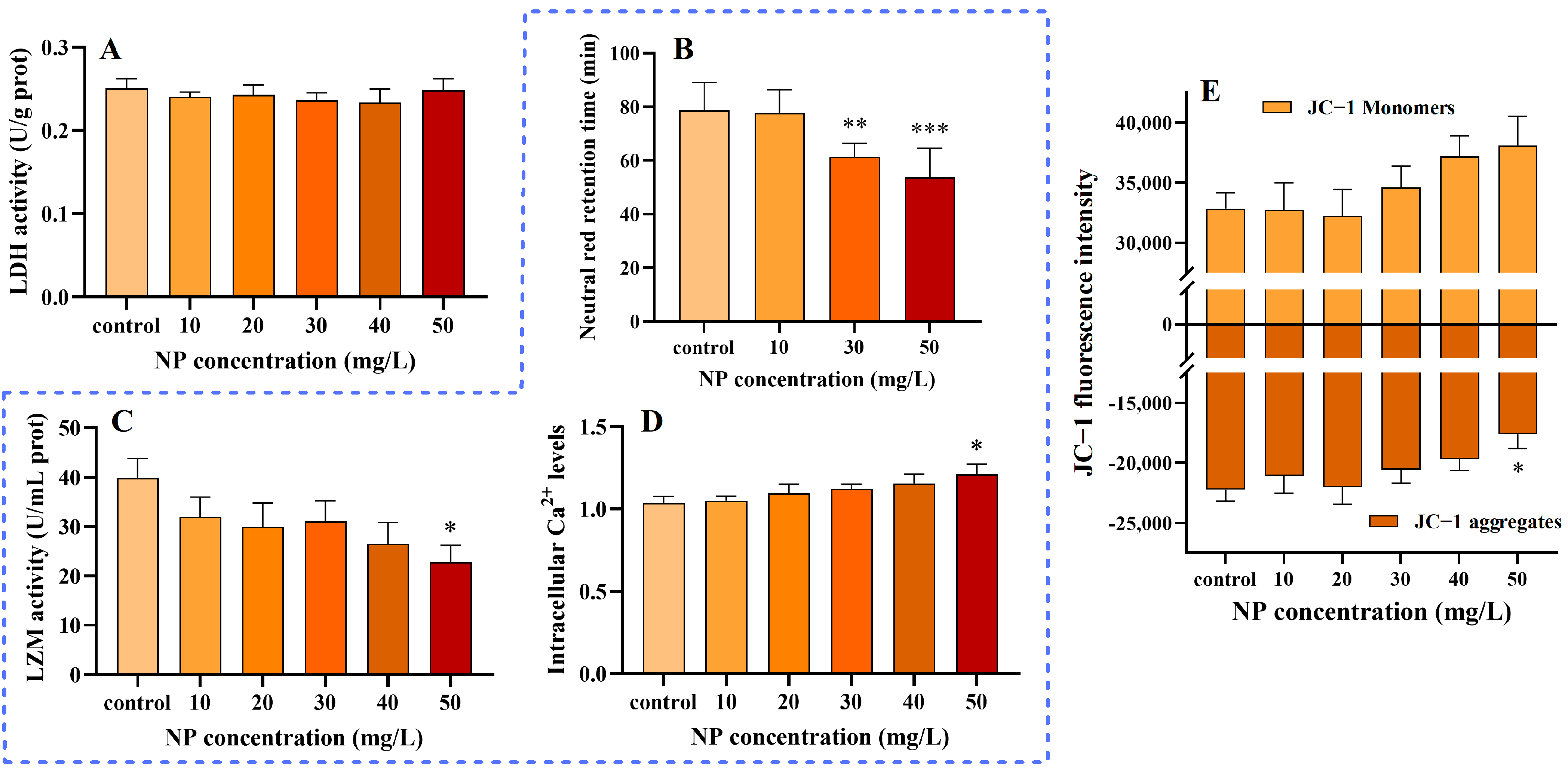
3.4. NPs Without Effect on Cell Membranes
3.5. Influence of NPs on the Immune System
3.6. Impact of NPs on MMPs
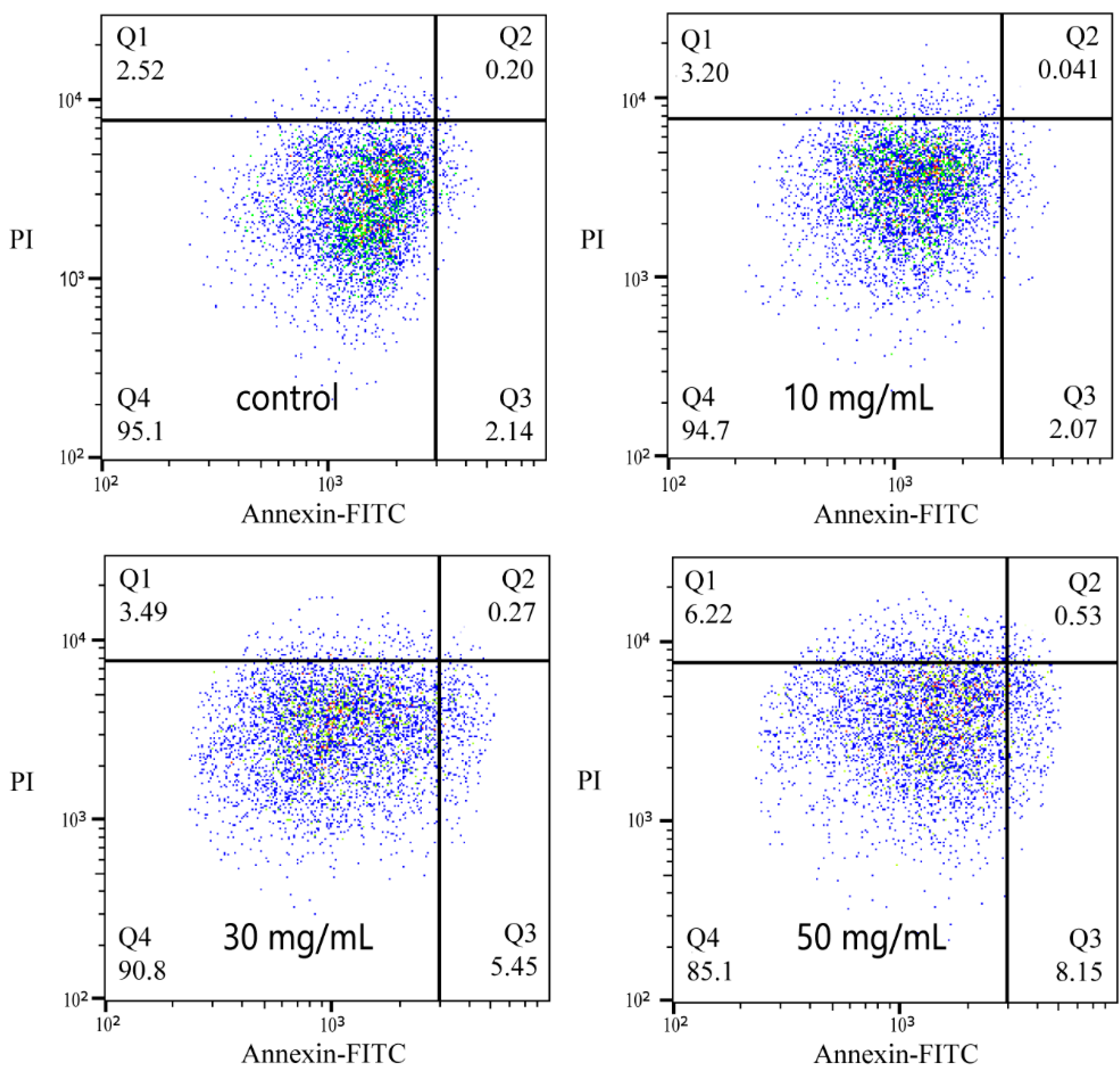
3.7. Apoptosis Induced by NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Caballero, M.C.; de Alba González, M.; Torres-Ruiz, M.; Iglesias-Hernández, P.; Zapata, V.; Terrón, M.C.; Sachse, M.; Morales, M.; Martin-Folgar, R.; Liste, I.; et al. Internalization and toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics on inmortalized human neural stem cells. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbins, A.; Law, K.L.; Muñoz, S.E.; Bianchi, T.S.; Zhu, L.X. Plastics in the Earth system. Science 2021, 373, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadare, O.O.; Wan, B.; Guo, L.H.; Xin, Y.; Qin, W.P.; Yang, Y. Humic acid alleviates the toxicity of polystyrene nanoplastic particles to Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Nano 2019, 6, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.Z.; Gao, P.P.; Zhang, M.Y.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.W.; Liu, C.G. Adverse effects of microplastics on earthworms: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Song, Z.; Zong, C.; Wei, N.; Li, D. Consistent Transport of Terrestrial Microplastics to the Ocean through Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 10612–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofty, J.; Muhawenimana, V.; Wilson, C.A.M.E.; Ouro, P. Microplastics removal from a primary settler tank in a wastewater treatment plant and estimations of contamination onto European agricultural land via sewage sludge recycling. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 304, 119198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, S.I.; Arfaioli, P.; Bardelli, T.; Ceccherini, M.T.; Nannipieri, P.; Pietramellara, G. Soil Pollution from Micro- and Nanoplastic Debris: A Hidden and Unknown Biohazard. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Sun, S.; Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, G. Microplastics hamper the fertilization success of a broadcast spawning bivalve through reducing gamete collision and gamete fusion efficiency. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 242, 106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.R.; Sheen, J.M.; Tiao, M.M. The Impact of Maternal Nanoplastic and Microplastic Particle Exposure on Mammal’s Offspring. Cells 2024, 13, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Wang, M.X.; Feng, Z.H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Lv, M.X.; Chang, J.H.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, C. Human Microplastics Exposure and Potential Health Risks to Target Organs by Different Routes: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2023, 9, 468–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Marbach, S.; Zimba, P.; Liu, Q.; Xu, W. Uptake of Nanoplastic particles by zebrafish embryos triggers the macrophage response at early developmental stage. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Yuan, X.Z.; Jia, Y.B.; Feng, L.J.; Zhu, F.P.; Dong, S.S.; Liu, J.J.; Kong, X.P.; Tian, H.Y.; Duan, J.L.; et al. Differentially charged nanoplastics demonstrate distinct accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzierski, M.; Cirederf-Boulant, D.; Palazot, M.; Yvin, M.; Bruzaud, S. Continents of plastics: An estimate of the stock of microplastics in agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayling, K.M.; Young, S.D.; Roberts, C.J.; de Heer, M.I.; Shirley, I.M.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mooney, S.J. The application of X-ray micro Computed Tomography imaging for tracing particle movement in soil. Geoderma 2018, 321, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, J.; Han, L.; Liu, W.; Ding, Y. Microplastics regulate soil microbial activities: Evidence from catalase, dehydrogenase, and fluorescein diacetate hydrolase. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Zhu, D.; Luo, Y.; He, D.; Zhang, H.; El-Naggar, A.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Chen, K.; Yan, Y.; Lu, X.; et al. Nanoplastics induce molecular toxicity in earthworm: Integrated multi-omics, morphological, and intestinal microorganism analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Kloas, W.; Bergmann, J.; Bachelier, J.B.; Faltin, E.; Becker, R.; Görlich, A.S.; Rillig, M.C. Microplastics Can Change Soil Properties and Affect Plant Performance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6044–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.F.; Lu, T.; Qu, Q.; Du, B.B.; Pan, X.L. Effects of Soil Residual Plastic Film on Soil Microbial Community Structure and Fertility. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, X.; Jia, W.; Chai, L.; Huang, M.; Huang, Y. Microplastics from mulching film is a distinct habitat for bacteria in farmland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pignattelli, S.; Broccoli, A.; Renzi, M. Physiological responses of garden cress (L. sativum) to different types of microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Zhu, D.; Qiao, M. Effects of polyethylene microplastics on the gut microbial community, reproduction and avoidance behaviors of the soil springtail, Folsomia candida. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, X.X.; Liu, J.W.; Cao, B.; Zou, G.Y.; et al. Ecological risk of microplastic toxicity to earthworms in soil: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1126847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Liu, Y.F. The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Tomar, S.; Chakraborty, D. Role of earthworm in improving soil structure and functioning. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahive, E.; Cross, R.; Saarloos, A.I.; Horton, A.A.; Svendsen, C.; Hufenus, R.; Mitrano, D.M. Earthworms ingest microplastic fibres and nanoplastics with effects on egestion rate and long-term retention. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Qiao, Y.; Klobučar, G.; Li, M. Toxicological effects of polystyrene microplastics on earthworm (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ren, S.; Pei, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, F. Ecotoxicological effects of polyethylene microplastics and ZnO nanoparticles on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 176, 104469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y. Size effects of polystyrene microplastics on the accumulation and toxicity of (semi-)metals in earthworms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.I.; An, Y.-J. Microplastic digestion generates fragmented nanoplastics in soils and damages earthworm spermatogenesis and coelomocyte viability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 124034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Guo, S.Q.; He, F.L.; Li, X.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, T.T.; Tian, G.; Liu, R.T. The combined effects of polystyrene nanoplastics with nickel on oxidative stress and related toxic effects to earthworms from individual and cellular perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.L.; Shi, H.J.; Guo, S.Q.; Li, X.X.; Tan, X.J.; Liu, R.T. Molecular mechanisms of nano-sized polystyrene plastics induced cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity in Eisenia fetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 465, 133032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Piao, J.; Kang, B.; Eom, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Song, J.S. The toxic effects of polystyrene microplastic/nanoplastic particles on retinal pigment epithelial cells and retinal tissue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 54950–54961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Shen, H.; Mahati, S.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Ou, R.; Liu, Z.; et al. Identification and analysis of microplastic aggregation in CAR-T cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesci, A.; Capillo, G.; Fumia, A.; Albano, M.; Messina, E.; Spanò, N.; Pergolizzi, S.; Lauriano, E.R. Coelomocytes of the Oligochaeta earthworm Lumbricus terrestris (Linnaeus, 1758) as evolutionary key of defense: A morphological study. Zool. Lett. 2023, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, G.; Yu, Y. Effects of polystyrene microplastics on accumulation of pyrene by earthworms. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 134059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Shi, H.; Liu, R.; Tian, G.; Qi, Y.; Wang, T. Randomly-shaped nanoplastics induced stronger biotoxicity targeted to earthworm Eisenia fetida species: Differential effects and the underlying mechanisms of realistic and commercial polystyrene nanoplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Gooren, H.; Peters, P.; Salánki, T.; van der Ploeg, M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Geissen, V. Microplastics in the Terrestrial Ecosystem: Implications for Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Guo, W.-B.; Yang, L.; Ji, R.; Pan, K.; Miao, A.-J. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Inhibit the Transformation of Tetrabromobisphenol A by the Bacterium Rhodococcus jostii. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L.; Neal, M.A. Applications and societal benefits of plastics. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 1977–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar, M.R.; Ghazi-Khansari, M. Determination of migration monomer styrene from GPPS (general purpose polystyrene) and HIPS (high impact polystyrene) cups to hot drinks. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2009, 19, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.Q.; Shi, H.J.; Qi, Y.T.; Tian, G.; Wang, T.T.; He, F.L.; Li, X.X.; Liu, R.T. Environmental relevant concentrations of polystyrene nanoplastics and lead co-exposure triggered cellular cytotoxicity responses and underlying mechanisms in Eisenia fetida. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.A.; Feng, S.S. Effects of Particle Size and Surface Modification on Cellular Uptake and Biodistribution of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2512–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wan, J.; Chu, S.; Li, X.; Zong, W.; Liu, R. Toxic mechanism on phenanthrene-triggered cell apoptosis, genotoxicity, immunotoxicity and activity changes of immunity protein in Eisenia fetida: Combined analysis at cellular and molecular levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florance, I.; Ramasubbu, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Polystyrene nanoplastics dysregulate lipid metabolism in murine macrophages in vitro. Toxicology 2021, 458, 152850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Engelmann, P.; Foldbjerg, R.; Szabó, M.; Somogyi, I.; Pollák, E.; Molnár, L.; Autrup, H.; Sutherland, D.S.; Scott-Fordsmand, J.; et al. Earthworms and Humans in Vitro: Characterizing Evolutionarily Conserved Stress and Immune Responses to Silver Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4166–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanyuk, B.; Vántus, V.B.; Radnai, B.; Vámos, E.; Kajner, G.; Galbács, G.; Telek, E.; Mészáros, M.; Deli, M.A.; Németh, P.; et al. Distinct Uptake Routes Participate in Silver Nanoparticle Engulfment by Earthworm and Human Immune Cells. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanzadeh, A.; Oyunbaatar, N.-E.; Ganjbakhsh, S.E.; Park, S.; Kim, D.-S.; Kanade, P.P.; Lee, S.; Lee, D.-W.; Kim, E.-S. Exposure to nanoplastics impairs collective contractility of neonatal cardiomyocytes under electrical synchronization. Biomaterials 2021, 278, 121175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaei, G.; Abass, D.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Martín-Pérez, J.; Gutiérrez, J.; Peng, G.; Reemtsma, T.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A.; García-Rodríguez, A. Teabag-derived micro/nanoplastics (true-to-life MNPLs) as a surrogate for real-life exposure scenarios. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, W.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Kwon, M.K.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, J.E.; et al. Microglial phagocytosis of polystyrene microplastics results in immune alteration and apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koner, S.; Florance, I.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Cellular response of THP-1 macrophages to polystyrene microplastics exposure. Toxicology 2023, 483, 153385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarkovic, N. Roles and Functions of ROS and RNS in Cellular Physiology and Pathology. Cells 2020, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, G.L.; Yin, H.; Hardy, K.D.; Davies, S.S.; Roberts, L.J., II. Isoprostane Generation and Function. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5973–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.H.; He, F.L.; Li, X.X.; Li, Y.Z.; Huo, C.Q.; Wang, H.; Qi, Y.T.; Tian, G.; Zong, W.S.; Liu, R.T. Response pathways of superoxide dismutase and catalase under theregulation of triclocarban-triggered oxidative stress in Eisenia foetida: Comprehensive mechanism analysis based on cytotoxicity andbinding model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Raihan, M.R.H.; Masud, A.A.C.; Rahman, K.; Nowroz, F.; Rahman, M.; Nahar, K.; Fujita, M. Regulation of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Salinity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.W.; Xu, G.H.; Yu, Y. In-vivo and in-vitro tests to assess toxic mechanisms of nano ZnO to earthworms. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaha, C.M.; Pandit, R.S. Biochemical and molecular changes mediated by plasticizer diethyl phthalate in Chironomus circumdatus (bloodworms). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 228, 108650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgstahl, G.E.O.; Oberley-Deegan, R.E. Superoxide Dismutases (SODs) and SOD Mimetics. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliakbarzadeh, F.; Rafiee, M.; Khodagholi, F.; Khorramizadeh, M.R.; Manouchehri, H.; Eslami, A.; Sayehmiri, F.; Mohseni-Bandpei, A. Adverse effects of polystyrene nanoplastic and its binary mixtures with nonylphenol on zebrafish nervous system: From oxidative stress to impaired neurotransmitter system. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodega, G.; Alique, M.; Puebla, L.; Carracedo, J.; Ramírez, R.M. Microvesicles: ROS scavengers and ROS producers. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1626654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolwell, G.P.; Bindschedler, L.V.; Blee, K.A.; Butt, V.S.; Davies, D.R.; Gardner, S.L.; Gerrish, C.; Minibayeva, F. The apoplastic oxidative burst in response to biotic stress in plants: A three-component system. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, X.C.; Tang, H.Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Ge, X.; Hu, S.Y.; Li, X.X.; Guo, S.Q.; Liu, R.T. The size-dependent effects of nanoplastics in mouse primary hepatocytes from cells to molecules. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.C.; Xu, M.C.; Cui, Z.H.; Xiao, Y.H.; Liu, C.Q.; Liu, R.T.; Zhang, G.M. Probing the molecular mechanism of interaction between polystyrene nanoplastics and catalase by multispectroscopic techniques. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 382, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chu, S.; Song, Z.; He, F.; Cui, Z.; Liu, R. Discrepancy of apoptotic events in mouse hepatocytes and catalase performance: Size-dependent cellular and molecular toxicity of ultrafine carbon black. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.; Vietti, D.E.; Cooper, C.S. Degenerative Chemistry Of Malondialdehyde–Structure, Stereochemistry, and Kinetics of Formation of Enaminals from Reaction with Amino-Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 103, 3030–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-J.; Hudson, L.G.; Liu, W.; Ding, W.; Cooper, K.L.; Liu, K.J. Dual Actions Involved in Arsenite-Induced Oxidative DNA Damage. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, D.; Takaki, A.; Nakatsuka, A.; Wada, J.; Tamaki, N.; Yasunaka, T.; Koike, K.; Tsuzaki, R.; Matsumoto, K.; Miyake, Y.; et al. Hydrogen-rich water prevents progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and accompanying hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Liu, G.; Li, M.; Huo, M.; Zong, W.; Liu, R. Probing the Cell Apoptosis Pathway Induced by Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate at the Subcellular and Molecular Levels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ye, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L. Hydrogen bonding-mediated interaction underlies the enhanced membrane toxicity of chemically transformed polystyrene microplastics by cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, C. Lysosomes and lysosome-related organelles in immune responses. FEBS Open Bio 2022, 12, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mei, A.; Wang, X.; Shi, Q. Cellular absorption of polystyrene nanoplastics with different surface functionalization and the toxicity to RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandts, I.; Solà, R.; Garcia-Ordoñez, M.; Gella, A.; Quintana, A.; Martin, B.; Esteve-Codina, A.; Teles, M.; Roher, N. Polystyrene nanoplastics target lysosomes interfering with lipid metabolism through the PPAR system and affecting macrophage functionalization. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2245–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, R.; Yang, S.; Cho, S.; Sabean, M.; Roberts, E.A. In vitro assessment of copper-induced toxicity in the human hepatoma line, Hep G. Toxicol. In Vitro 2004, 18, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, G.; Jiang, H.; Pan, K.; Liu, W. Nanoplastics induces oxidative stress and triggers lysosome-associated immune-defensive cell death in the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Environmental pollutants, pathogens and immune system in earthworms. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6196–6208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, F.; Li, X.-N.; Diao, J.-X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Yang, X.-L.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y. Potential toxicity and affinity of triphenylmethane dye malachite green to lysozyme. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 78, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.K.; Na, D.H.; Bae, J.S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lysozyme Against HMGB1 in Human Endothelial Cells and in Mice. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, M.; Khan, F.U.; Younas, W.; Noorullah, M.; Ullah, I.; Li, L.; Zuberi, A.; Wang, Y. Physiological and histopathological effects of polystyrene nanoparticles on the filter-feeding fish Hypophthalmichthys molitrix. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Ciacci, C.; Bergami, E.; Monopoli, M.P.; Dawson, K.A.; Papa, S.; Canonico, B.; Corsi, I. Evidence for immunomodulation and apoptotic processes induced by cationic polystyrene nanoparticles in the hemocytes of the marine bivalve Mytilus. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, A.; Zhou, X.; He, J.; Zhang, N.; Shen, X.; Sun, C.; Yan, B.; Shao, Y. Toxic effects of acute exposure to polystyrene microplastics and nanoplastics on the model insect, silkworm Bombyx mori. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; He, F.; Guo, S.; Du, F.; Song, H.; Liu, R. Valence-dependent immune responses of earthworm coelomocytes: Toxicity pathways and molecular mechanisms of As (III) and As (V)-induced immunotoxicity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opper, B.; Nemeth, P.; Engelmann, P. Calcium is required for coelomocyte activation in earthworms. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Yi, Y.; Moon, S.; Yoon, H.; Park, Y.S. Impact of Micro- and Nanoplastics on Mitochondria. Metabolites 2022, 12, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Halimu, G.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Gu, W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, X. In vitro study on the toxicity of nanoplastics with different charges to murine splenic lymphocytes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Fu, M.; Bi, R.; Zheng, X.; Fu, B.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. Cadmium induced BEAS-2B cells apoptosis and mitochondria damage via MAPK signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.K.; Wang, X.Q.; Chen, W.N.; Wang, M.L.; Zhao, J.S.; Xu, Z.Y.; Wang, R.; Mi, C.Y.; Zheng, Z.D.; Zhang, H.D. Exposure to high dose of polystyrene nanoplastics causes trophoblast cell apoptosis and induces miscarriage. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Polymer Type | Size, μm | Soil Biology | Major Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polystyrene | 0.1, 10 | Eisenia fetida | The M/NPs disrupted the integrity of the earthworm intestine and promoted the accumulation of pyrene by the earthworms. | [36] |
| Polystyrene | 0.2 | Eisenia fetida | NPs exposure provoked oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and developmental and reproductive toxicity. | [37] |
| Polyethylene | 200~300 | Eisenia fetida | MPs cause weight loss, growth inhibition, and death in earthworms | [38] |
| Polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polyvinylchloride (PVC) | 0~125 | Garden cress (L. sativum) | In the chronic exposure experiment (21 days), PP and PE exerted a detrimental effect on the germination rate, number of leaves, and biomass of lettuce, while its height was predominantly influenced by PE + PVC. | [21] |
| Polystyrene | 0~500 | springtail (Folsomia candida) | The MPs altered the microbial community in the gut of the springtails, inhibiting their reproduction and causing them to exhibit avoidance behaviors. | [22] |
| Polystyrene | 0.02, 0.1 | Bacterium (Rhodococcus jostii) | NPs have the capacity to inhibit the transformation of tetrabromobisphenol A by the Gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus jostii. | [39] |
| Polyethylene | 180, 250 | Eisenia fetida | MPs caused damage to the male reproductive organs of earthworms, whereas the effect on the female reproductive organs was negligible. | [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Hu, S.; Liu, R. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Elicit Multiple Responses in Immune Cells of the Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). Toxics 2025, 13, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010018
Shi H, Wang Y, Li X, Wang X, Qi Y, Hu S, Liu R. Polystyrene Nanoplastics Elicit Multiple Responses in Immune Cells of the Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). Toxics. 2025; 13(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Huijian, Yaoyue Wang, Xiangxiang Li, Xiaoyang Wang, Yuntao Qi, Shaoyang Hu, and Rutao Liu. 2025. "Polystyrene Nanoplastics Elicit Multiple Responses in Immune Cells of the Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826)" Toxics 13, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010018
APA StyleShi, H., Wang, Y., Li, X., Wang, X., Qi, Y., Hu, S., & Liu, R. (2025). Polystyrene Nanoplastics Elicit Multiple Responses in Immune Cells of the Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). Toxics, 13(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13010018







