Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Involvement in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Damage in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
2.2. Histopathologic Evaluation
2.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.4. Biochemical Evaluation
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. RNA Preparation and mRNA Quantification
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Body and Organ Weights
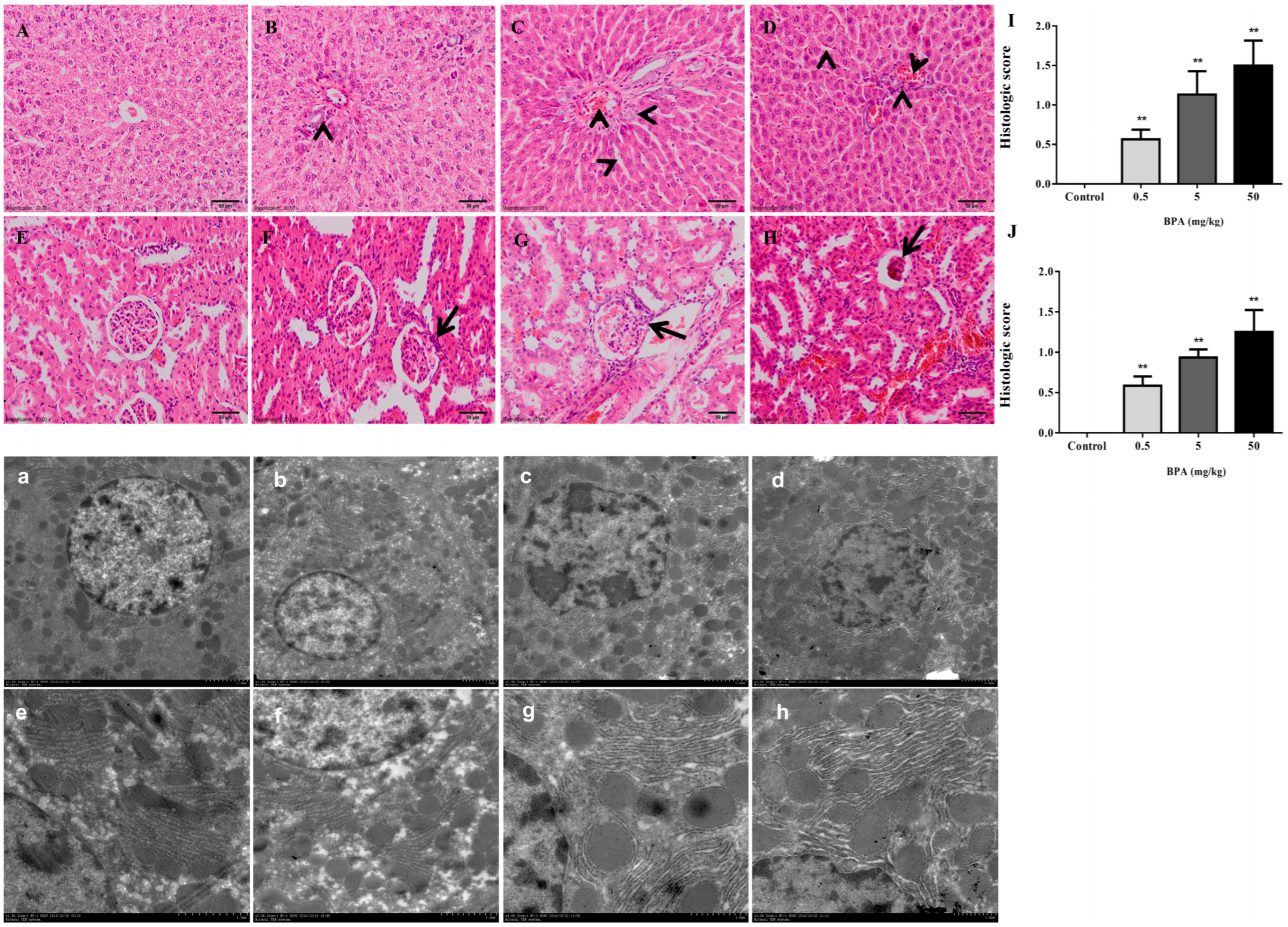
3.2. Histopathological Evaluation
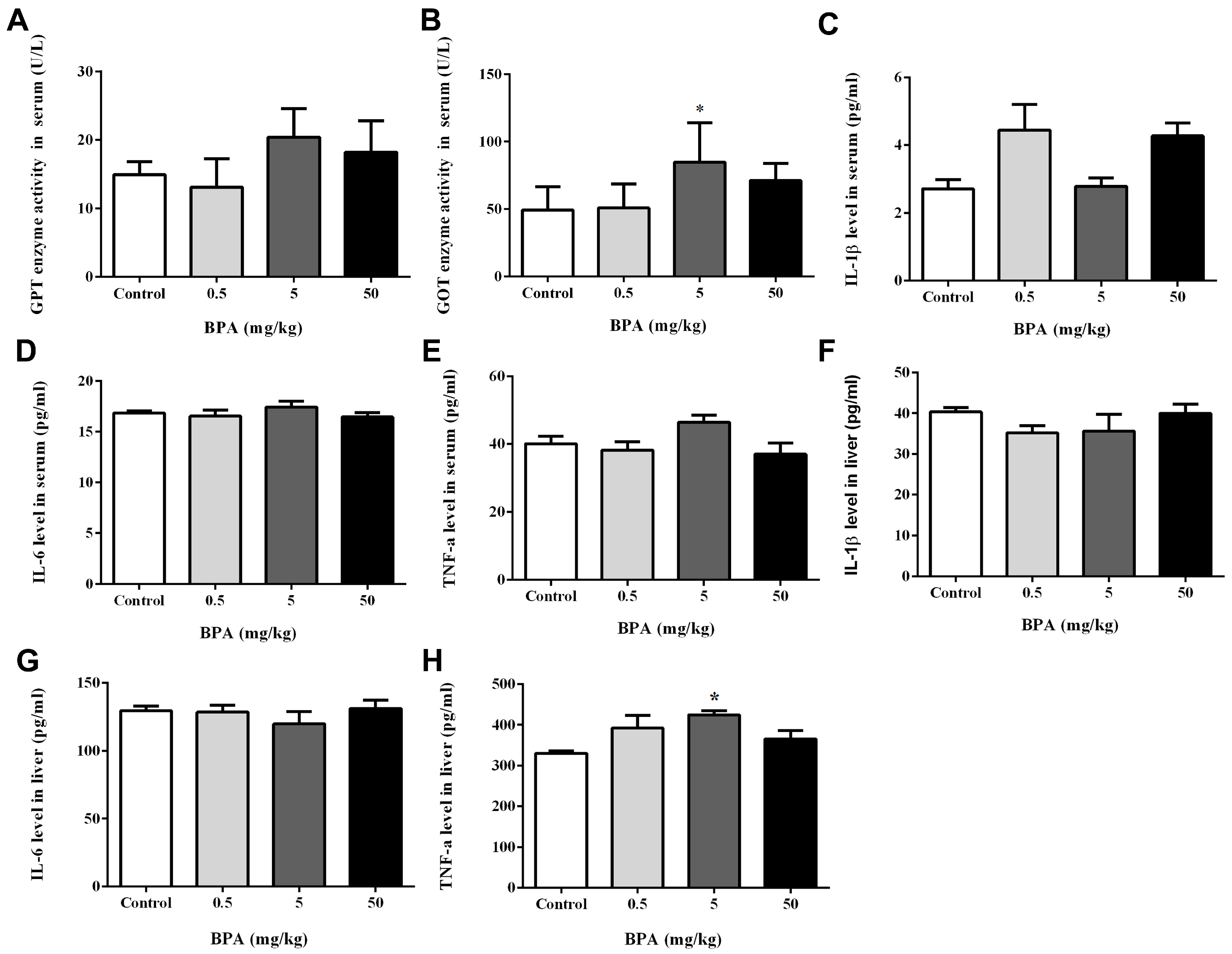
3.3. Assessment of Liver Function and IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α Levels in Serum and Liver
3.4. Evaluation of Serum, Liver, and Kidney Enzyme Levels to Analyze Oxidative Stress
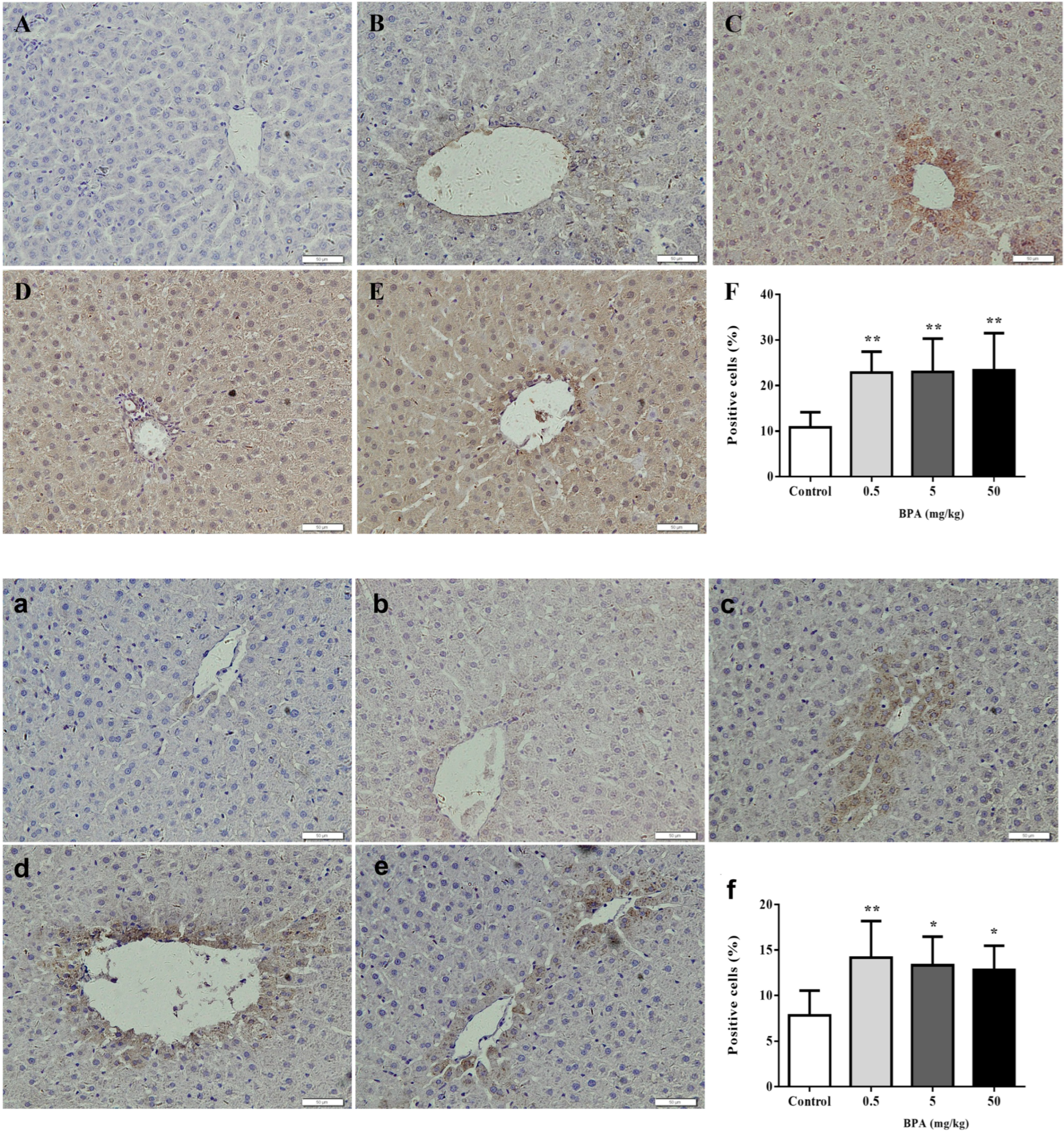
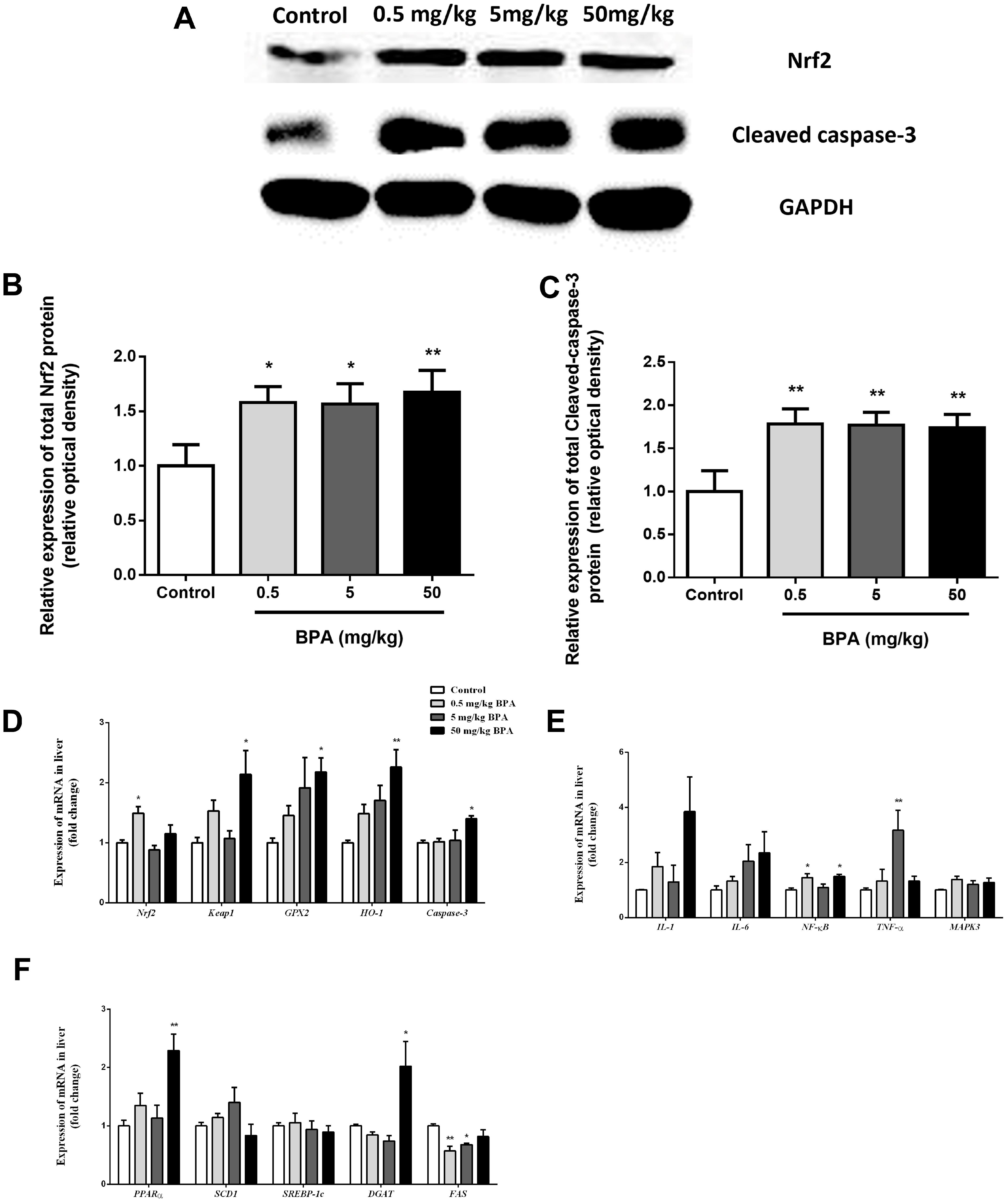
3.5. Immunohistochemistry of Nrf2 and Cleaved Caspase-3 in Liver
3.6. Nrf2 Involved in BPA-Induced Liver Oxidative Damage in Rats
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres-Garcia, J.L.; Ahuactzin-Perez, M.; Fernandez, F.J.; Cortes-Espinosa, D.V. Bisphenol A in the environment and recent advances in biodegradation by fungi. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Tariq, T.; Fatima, B.; Sahar, A.; Tariq, F.; Munir, S.; Khan, S.; Ranjha, M.M.A.N.; Sameen, A.; Zeng, X.A.; et al. An insight into bisphenol A, food exposure and its adverse effects on health: A review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1047827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Stegeman, J.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Allemand, D.; Anderson, D.M.; Backer, L.C.; Brucker-Davis, F.; Chevalier, N.; Corra, L.; Czerucka, D.; et al. Human Health and Ocean Pollution. Ann. Glob. Health 2020, 86, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrantes-Soares, F.; Lorigo, M.; Cairrao, E. Effects of BPA substitutes on the prenatal and cardiovascular systems. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2022, 52, 469–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenberg, L.N.; Hauser, R.; Marcus, M.; Olea, N.; Welshons, W.V. Human exposure to bisphenol A (BPA). Reprod. Toxicol. 2007, 24, 139–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, T.T.; Janesick, A.; Blumberg, B.; Heindel, J.J. Endocrine disrupting chemicals and disease susceptibility. J. Steroid Biochem. 2011, 127, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczna, A.; Rutkowska, A.; Rachon, D. Health risk of exposure to Bisphenol A (BPA). Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2015, 66, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carwile, J.L.; Michels, K.B. Urinary bisphenol A and obesity: NHANES 2003–2006. Environ. Res. 2011, 111, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasande, L.; Attina, T.M.; Blustein, J. Association between urinary bisphenol A concentration and obesity prevalence in children and adolescents. JAMA 2012, 308, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.T.; Chang, V.C.; Mendez, M.A.; de Groh, M. Urinary bisphenol A and obesity in adults: Results from the Canadian Health Measures Survey. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2017, 37, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeker, J.D.; Ehrlich, S.; Toth, T.L.; Wright, D.L.; Calafat, A.M.; Trisini, A.T.; Ye, X.; Hauser, R. Semen quality and sperm DNA damage in relation to urinary bisphenol A among men from an infertility clinic. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, S.; Williams, P.L.; Missmer, S.A.; Flaws, J.A.; Berry, K.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Petrozza, J.C.; Wright, D.; Hauser, R. Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and implantation failure among women undergoing in vitro fertilization. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, H.S. Impact of bisphenol a on the cardiovascular system—Epidemiological and experimental evidence and molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 8399–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.G.; Correia, J.; Adiga, D.; Rai, P.S.; Dsouza, H.S.; Chakrabarty, S.; Kabekkodu, S.P. A comprehensive review on the carcinogenic potential of bisphenol A: Clues and evidence. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 19643–19663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salamanca-Fernandez, E.; Rodriguez-Barranco, M.; Amiano, P.; Delfrade, J.; Chirlaque, M.D.; Colorado, S.; Guevara, M.; Jimenez, A.; Arrebola, J.P.; Vela, F.; et al. Bisphenol-A exposure and risk of breast and prostate cancer in the Spanish European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study. Environ. Health 2021, 20, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Braver-Sewradj, S.P.; van Spronsen, R.; Hessel, E. Substitution of bisphenol A: A review of the carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity, and endocrine disruption potential of alternative substances. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 128–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierello, W.; Maruszewska, A.; Skorka-Majewicz, M.; Goschorska, M.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I.; Dec, K.; Styburski, D.; Nowakowska, A.; Gutowska, I. The influence of polyphenols on metabolic disorders caused by compounds released from plastics—Review. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimpi, P.C.; More, V.R.; Paranjpe, M.; Donepudi, A.C.; Goodrich, J.M.; Dolinoy, D.C.; Rubin, B.; Slitt, A.L. Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Nrf2 Expression following Perinatal and Peripubertal Exposure to Bisphenol A in a Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Liver Disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 087005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavin, C.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Langouet, S.; Bezencon, C.; Guignard, G.; Verguet, C.; Piguet, D.; Holzhauser, D.; Cornaz, R.; Schilter, B. Induction of Nrf2-mediated cellular defenses and alteration of phase I activities as mechanisms of chemoprotective effects of coffee in the liver. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansanen, E.; Kivela, A.M.; Levonen, A.L. Regulation of Nrf2-dependent gene expression by 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansanen, E.; Jyrkkanen, H.K.; Levonen, A.L. Activation of stress signaling pathways by electrophilic oxidized and nitrated lipids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.; Win-Shwe, T.T.; Li, C. Ion Imbalance Is Involved in the Mechanisms of Liver Oxidative Damage in Rats Exposed to Glyphosate. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, M. Histological Grading and Staging of Chronic Hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2021, 17, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Fang, X.; Shi, Z.; Xu, M.; Dai, J. Effects of PFNA exposure on expression of junction-associated molecules and secretory function in rat Sertoli cells. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochester, J.R. Bisphenol A and human health: A review of the literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2013, 42, 132–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, F.; Aquilina, A.; Vassallo, J.; Pace, N.P. Bisphenol A and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Epidemiologic, Functional, and Early Life Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Bermejo, M.; Mas-Perez, I.; Murillo-Llorente, M.T. The Role of the Bisphenol A in Diabetes and Obesity. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Prabhu, N.B.; Kabekkodu, S.P.; Rai, P.S. Review on bisphenol A and the risk of polycystic ovarian syndrome: An insight from endocrine and gene expression. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32631–32650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, C.; Mulligan, K. Does Bisphenol A Confer Risk of Neurodevelopmental Disorders? What We Have Learned from Developmental Neurotoxicity Studies in Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, R.E.; Adams, J.; Boekelheide, K.; Gray, L.J.; Hayward, S.W.; Lees, P.S.; McIntyre, B.S.; Portier, K.M.; Schnorr, T.M.; Selevan, S.G.; et al. NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of bisphenol A. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2008, 83, 157–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmugi, A.; Ducheix, S.; Lasserre, F.; Polizzi, A.; Paris, A.; Priymenko, N.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Pineau, T.; Guillou, H.; Martin, P.G.; et al. Low doses of bisphenol A induce gene expression related to lipid synthesis and trigger triglyceride accumulation in adult mouse liver. Hepatology 2012, 55, 395–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, R. Advances in BPA-induced Oxidative Stress and Related Effects and Mechanisms in Liver, 1991–2017. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Dong, Z. Long-term exposure to bisphenol A and its analogues alters the behavior of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma) and causes hepatic injury. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Shahab, M.S.; Samad, A.; Ashraf, A.; Al-Ghanim, K.; Mruthinti, S.S.; Mahboob, S. Tangeretin ameliorates bisphenol induced hepatocyte injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baralic, K.; Pavic, A.; Javorac, D.; Zivancevic, K.; Bozic, D.; Radakovic, N.; Miljaković, E.A.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Curcic, M.; Bulat, Z.; et al. Comprehensive investigation of hepatotoxicity of the mixture containing phthalates and bisphenol A. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elswefy, S.E.; Abdallah, F.R.; Atteia, H.H.; Wahba, A.S.; Hasan, R.A. Inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis cascade implications in bisphenol A-induced liver fibrosis in male rats. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2016, 97, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoene, M.; Rytel, L.; Dzika, E.; Wlodarczyk, A.; Kruminis-Kaszkiel, E.; Konrad, P.; Wojtkiewicz, J. Bisphenol A Causes Liver Damage and Selectively Alters the Neurochemical Coding of Intrahepatic Parasympathetic Nerves in Juvenile Porcine Models under Physiological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eweda, S.M.; Newairy, A.; Abdou, H.M.; Gaber, A.S. Bisphenol A-induced oxidative damage in the hepatic and cardiac tissues of rats: The modulatory role of sesame lignans. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 19, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, Z.K.; Elobeid, M.A.; Virk, P.; Omer, S.A.; ElAmin, M.; Daghestani, M.H.; AlOlayan, E.M. Bisphenol A induces hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in rat model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012, 2012, 194829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Feng, X.; Su, R.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Epigallocatechin 3-gallate ameliorates bile duct ligation induced liver injury in mice by modulation of mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, D.W.; Goedken, M.J.; Rommelaere, S.; Chasson, L.; Galland, F.; Naquet, P.; Manautou, J.E. Enhanced hepatotoxicity by acetaminophen in Vanin-1 knockout mice is associated with deficient proliferative and immune responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, P.; Unni, S.; Krishnappa, G.; Padmanabhan, B. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: Promising therapeutic target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, H.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, L.; Hou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y. Sequestered SQSTM1/p62 crosstalk with Keap1/NRF2 axis in hPDLCs promotes oxidative stress injury induced by periodontitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 190, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, D.; Dallaglio, K.; Torquato, P.; Piroddi, M.; Galli, F. Nrf2-p62 autophagy pathway and its response to oxidative stress in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Res. 2018, 193, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Q. Signal amplification in the KEAP1-NRF2-ARE antioxidant response pathway. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, X. Hydrogen sulfide protects Sertoli cells against toxicant Acrolein-induced cell injury. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 176, 113784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Shang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J. BRG1 alleviates microglial activation by promoting the KEAP1-NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway and minimizing oxidative damage in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 119, 110201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene Symbol | Accession No. | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product Size (bp) | 40 PCR Cycles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | NM_031512.2 | F: GCCAACAAGTGGTATTCTCCA R: TGCCGTCTTTCATCACACAG | 120 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| IL-6 | NM_012589.2 | F: AGTTGCCTTCTTGGGACTGA R: ACTGGTCTGTTGTGGGTGGT | 102 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| MAPK3 | NM_017347.2 | F: CTACACGCAGCTGCAGTACATC R: GTGCGCTGACAGTAGGTTTGA | 153 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| NF-kB | NM_001276711.1 | F: CGACGTATTGCTGTGCCTTC R: TTGAGATCTGCCCAGGTGGTA | 198 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| TNF-α | NM_012675.3 | F: TTCCGTCCCTCTCATACACTG R: AGACACCGCCTGGAGTTCT | 149 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| Keap1 | NM_057152.2 | F: CATCGGCATCGCCAACTTC R: GCTGGCAGTGTGACAGGTTGA | 278 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| GPx2 | NM_183403.2 | F: CCGTGCTGATTGAGAATGTG R: AGGGAAGCCGAGAACCACTA | 113 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| Caspase-3 | NM_012922 | F: AAGCCGAAACTCTTCATC R: TGAGCATTGACACAATACAC | 349 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| PPARα | NM_001145367.1 | F: CTCGTGCAGGTCATCAAGAA R: CAGCCCTCTTCATCTCCAAG | 158 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| DGAT | NM_053437.1 | F: TCTTCCTACCGGGATGTCAATC R: TCCCTGCAGACACAGCTTG | 204 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| SREBP1c | NM_001271207.1 | F: GCCATGGATTGCACATTG R: TGTGTCTCCTGTCTCACCCC | 187 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| SCD1 | NM_009127.4 | F: CCTTAACCCTGAGATCCCGTAGA R: AGCCCATAAAAGATTTCTGCAAA | 237 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| FAS | NM_139194.2 | F: GGACATGGTCACAGACGATGAC R: GGAGGCGTCGAACTTGGA | 279 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| Nrf2 | NM_010902 | F: ACAGATGGCGTCACTTCG R: TGAGGACCCACTGGAGGA | 109 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| HO-1 | NM_010442 | F: ACAGATGGCGTCACTTCG R: TGAGGACCCACTGGAGGA | 128 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| β-actin | NM_031144.3 | F:AGCCATGTACGTAGCCATCC R:CTCTCAGCTGTGGTGGTGAA | 227 | 95 °C for 15 s 60 °C for 30 s 72 °C for 30 s |
| Control | GLP (mg/kg Body Weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 5 | 50 | |
| Number of animals | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Initial body weight (g) | 235.30 ± 5.65 | 232.70 ± 4.48 | 234.60 ± 5.04 | 236.90 ± 4.45 |
| Body weight (g) | 362.20 ± 16.82 | 360.20 ± 3.92 | 367.30 ± 11.10 | 357.10 ± 4.28 |
| Body weight gain (g) | 126.80 ± 11.50 | 127.50 ± 3.70 | 132.70 ± 9.72 | 120.30 ± 4.87 |
| Average daily gain(g) | 4.23 ± 0.384 | 4.25 ± 0.12 | 4.42 ± 0.32 | 4.01 ± 0.16 |
| Liver weight (g) | 13.34 ± 0.91 | 12.52 ± 0.20 | 11.90 ± 0.40 | 10.94 ± 0.30 * |
| Liver index (%) | 3.67 ± 0.11 | 3.48 ± 0.04 | 3.24 ± 0.06 ** | 3.07 ± 0.09 ** |
| Kidney weight (g) | 2.34 ± 0.14 | 2.42 ± 0.10 | 2.41 ± 0.07 | 2.47 ± 0.05 |
| Kidney index (%) | 0.65 ± 0.03 | 0.67 ± 0.03 | 0.66 ± 0.02 | 0.69 ± 0.02 |
| Spleen weight (g) | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 0.71 ± 0.07 | 0.74 ± 0.03 |
| Spleen index (%) | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.01 |
| Heart weight (g) | 1.38 ± 0.07 | 1.60 ± 0.09 | 1.50 ± 0.10 | 1.45 ± 0.08 |
| Heart index (%) | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.44 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.02 |
| Lung weight (g) | 1.69 ± 0.25 | 1.54 ± 0.06 | 1.47 ± 0.08 | 1.56 ± 0.09 |
| Lung index (%) | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.43 ± 0.02 | 0.40 ± 0.02 | 0.44 ± 0.03 |
| Adrenal weight (g) | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 0.069 ± 0.017 | 0.047 ± 0.006 | 0.049 ± 0.005 |
| Adrenal index (%) | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.014 ± 0.001 * | 0.013 ± 0.002 * | 0.014 ± 0.001 * |
| Control | BPA (mg/kg Body Weight) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.5 | 5 | 50 | |
| Serum | ||||
| SOD (U/mL) | 655.50 ± 28.61 | 608.50 ± 9.19 | 681.00 ± 23.10 | 702.70 ± 23.05 |
| MDA (nmol/mL) | 7.57 ± 0.95 | 8.25 ± 0.96 | 10.60 ± 1.08 | 9.93 ± 1.28 |
| CAT (U/mL) | 36.10 ± 4.89 | 46.08 ± 4.40 | 71.39 ± 7.90 ** | 64.90 ± 6.58 ** |
| GSH-PX (U/L) | 85.26 ± 10.03 | 98.53 ± 15.54 | 103.80 ± 19.94 | 66.74 ± 22.16 |
| Liver | ||||
| SOD (U/mgprotein) | 287.30 ± 17.70 | 222.90 ± 23.79 | 210.50 ± 6.50 * | 235.1 ± 24.36 |
| MDA (nmol/mgprotein) | 1.30 ± 0.15 | 1.69 ± 0.17 | 1.97 ± 0.24 | 2.20 ± 0.38 * |
| CAT (U/mgprotein) | 42.03 ± 5.69 | 42.46 ± 11.21 | 26.83 ± 4.81 | 30.74 ± 7.18 |
| GSH-PX (U/mgprotein) | 610.40 ± 72.82 | 239.90 ± 45.61 * | 397.90 ± 87.11 | 427.80 ± 117.30 |
| Kidney | ||||
| SOD (U/mgprotein) | 147.00 ± 7.02 | 89.52 ± 5.74 ** | 86.15 ± 7.50 ** | 78.08 ± 2.06 ** |
| MDA (nmol/mgprotein) | 1.59 ± 0.26 | 1.85 ± 0.12 | 3.39 ± 0.49 ** | 2.44 ± 0.31 |
| CAT (U/mgprotein) | 45.55 ± 3.64 | 40.03 ± 1.22 | 39.56 ± 2.62 | 42.73 ± 1.91 |
| GSH-PX (U/mgprotein) | 962.90 ± 185.40 | 728.90 ± 116.00 | 805.10 ± 121.30 | 782.20 ± 207.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Wang, K.; Shen, D.; Li, C. Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Involvement in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Toxics 2024, 12, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120864
Tang J, Wang K, Shen D, Li C. Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Involvement in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120864
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Juan, Kai Wang, Dan Shen, and Chunmei Li. 2024. "Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Involvement in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Damage in Rats" Toxics 12, no. 12: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120864
APA StyleTang, J., Wang, K., Shen, D., & Li, C. (2024). Oxidative Stress and Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway Involvement in Bisphenol A-Induced Liver Damage in Rats. Toxics, 12(12), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120864








