Modulation of Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Acute and Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice: A Study Pilot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethical Care
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Serum Inflammatory Mediators
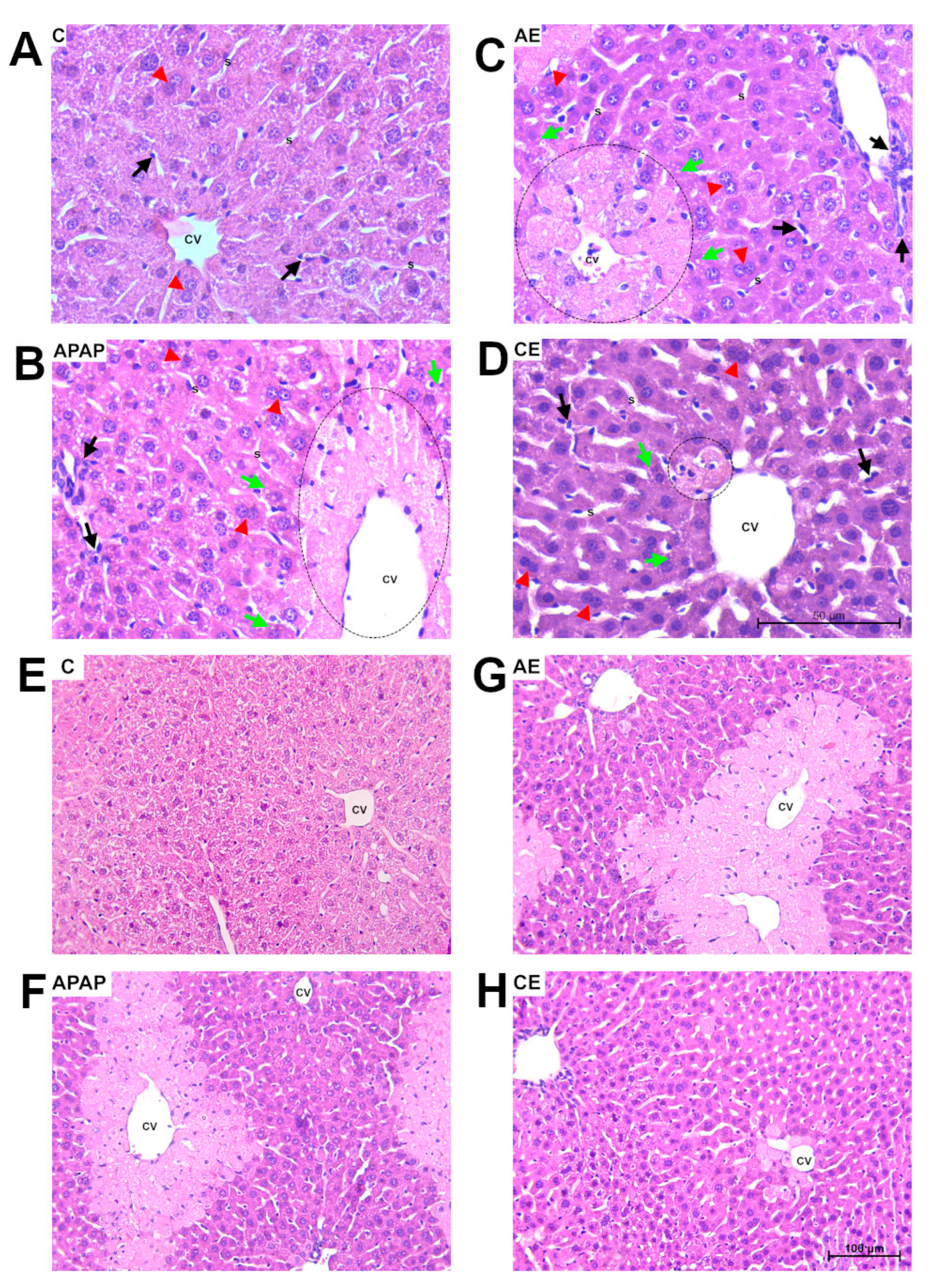
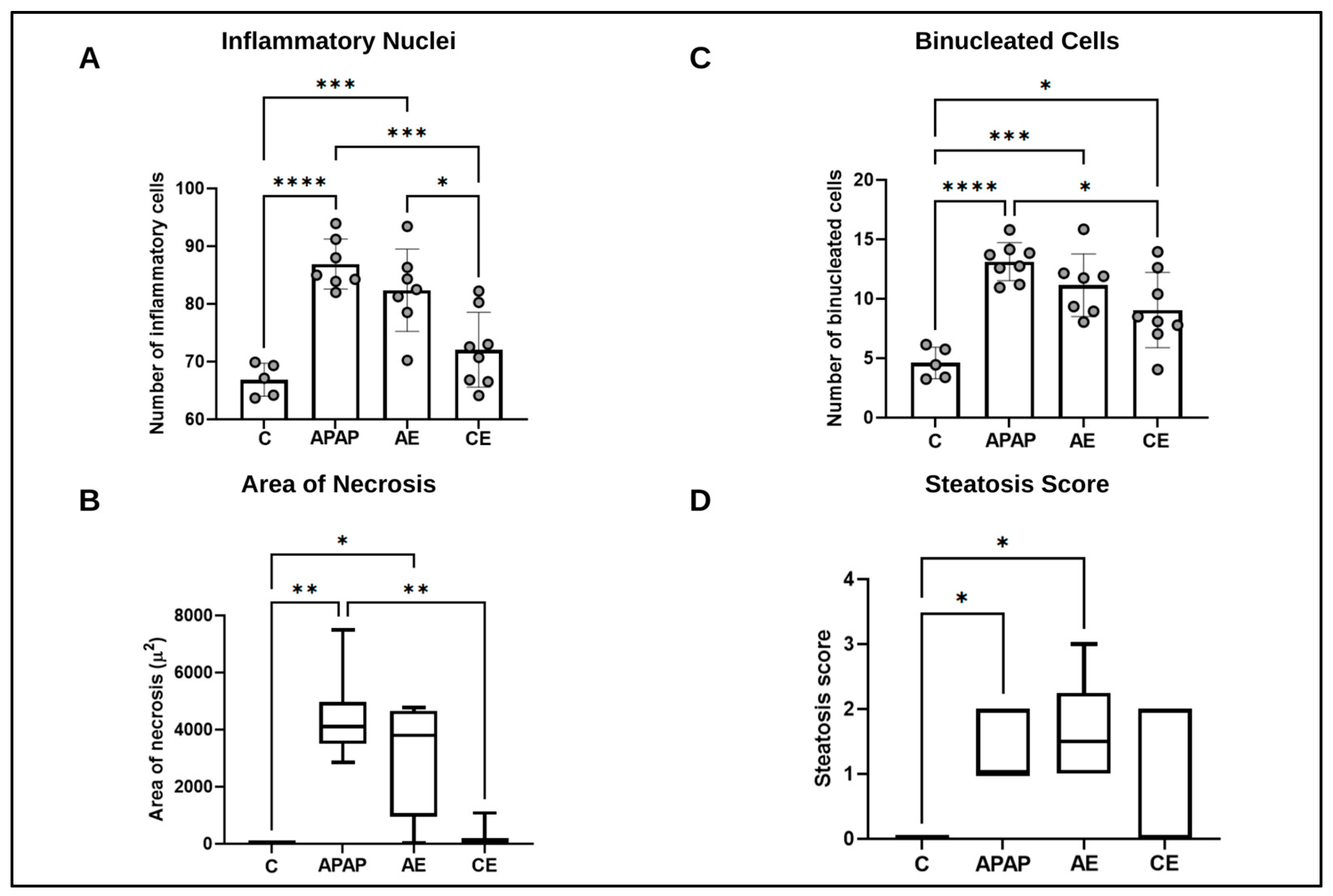
2.4. Histological and Morphometric Analysis
2.5. Assessment of Liver Injury Biomarkers
2.5.1. Measurement of ALT and AST Levels
2.5.2. Quantification of Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances (TBARS)
2.5.3. Carbonylated Protein
2.5.4. Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) Activity
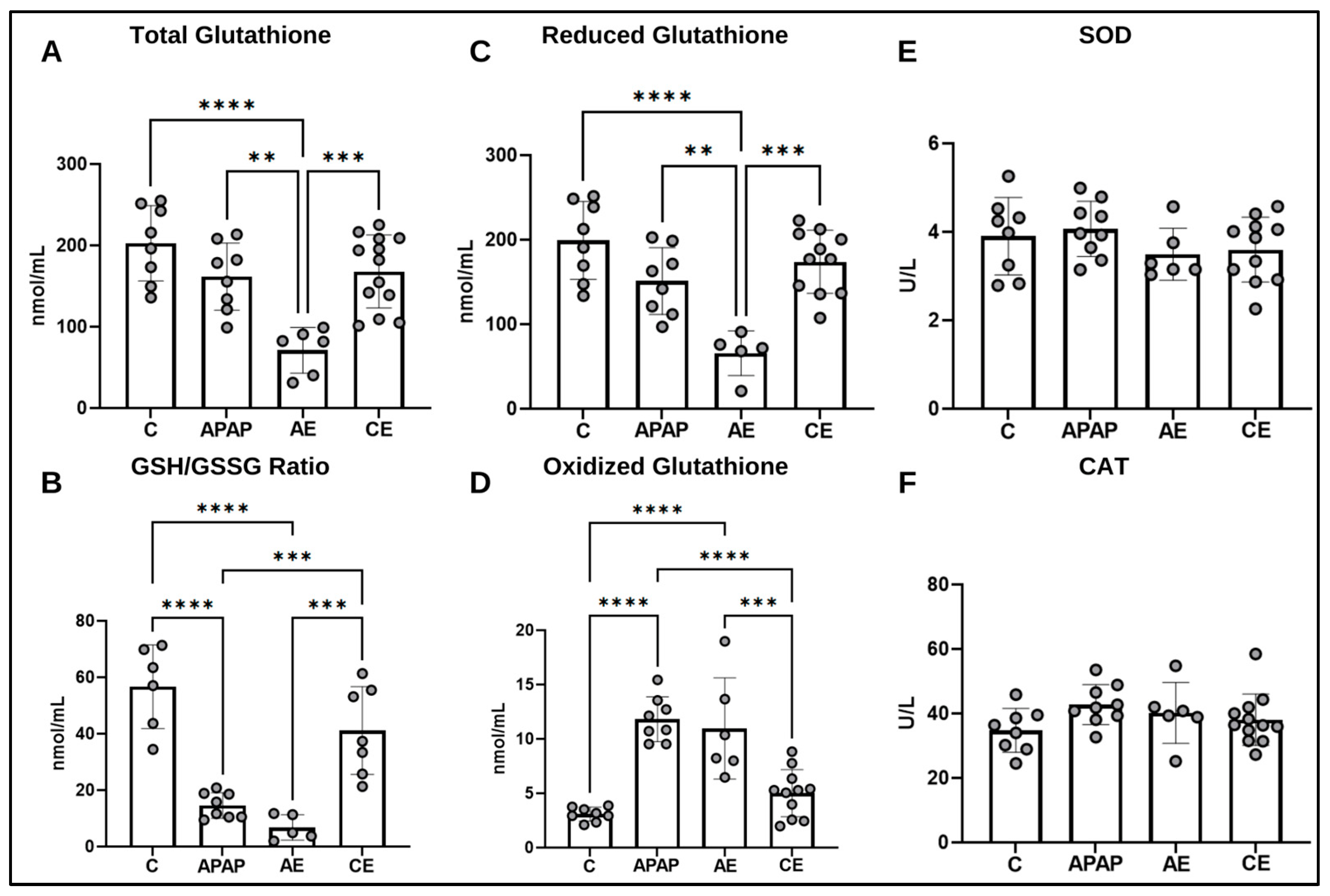
2.6. Assessment of the Antioxidant Profile
2.6.1. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
2.6.2. Catalase (CAT)
2.6.3. Total Glutathione (GSHt) and Oxidized (GSSG) and Reduced (GSH) Fractions
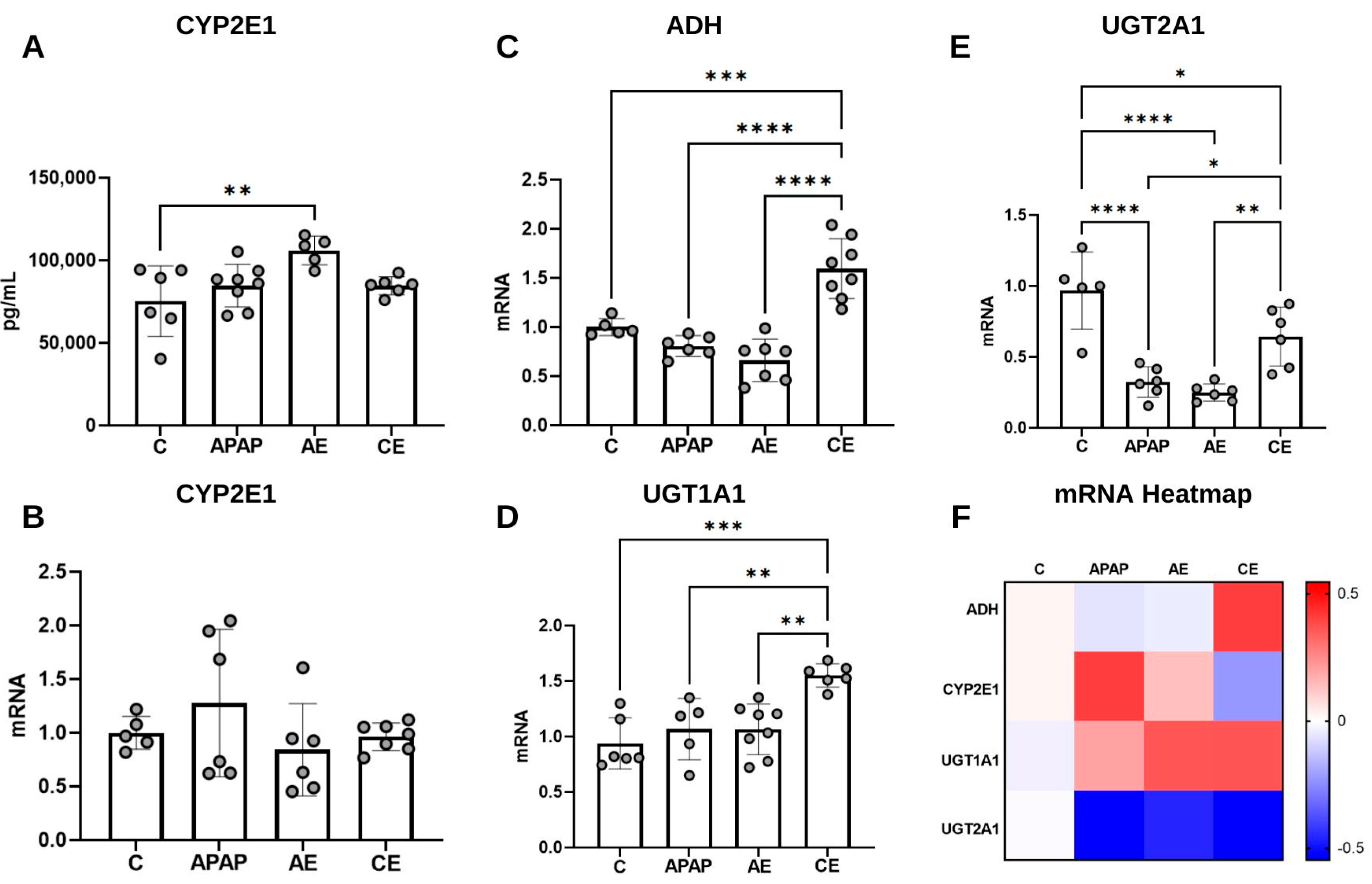
2.6.4. Quantification of Cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1)
2.6.5. Gene Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
2.6.6. Proteomic Analysis
2.6.7. Statistical Analyzes
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Serum Inflammatory Profile
3.2. Histological and Morphometric Analysis
3.3. Assessment of Liver Injury Markers
3.4. Assessment of the Hepatic Antioxidant Profile
3.5. Assessment of CYP2E1 Levels and Expression of Genes Related to APAP and Ethanol Metabolism
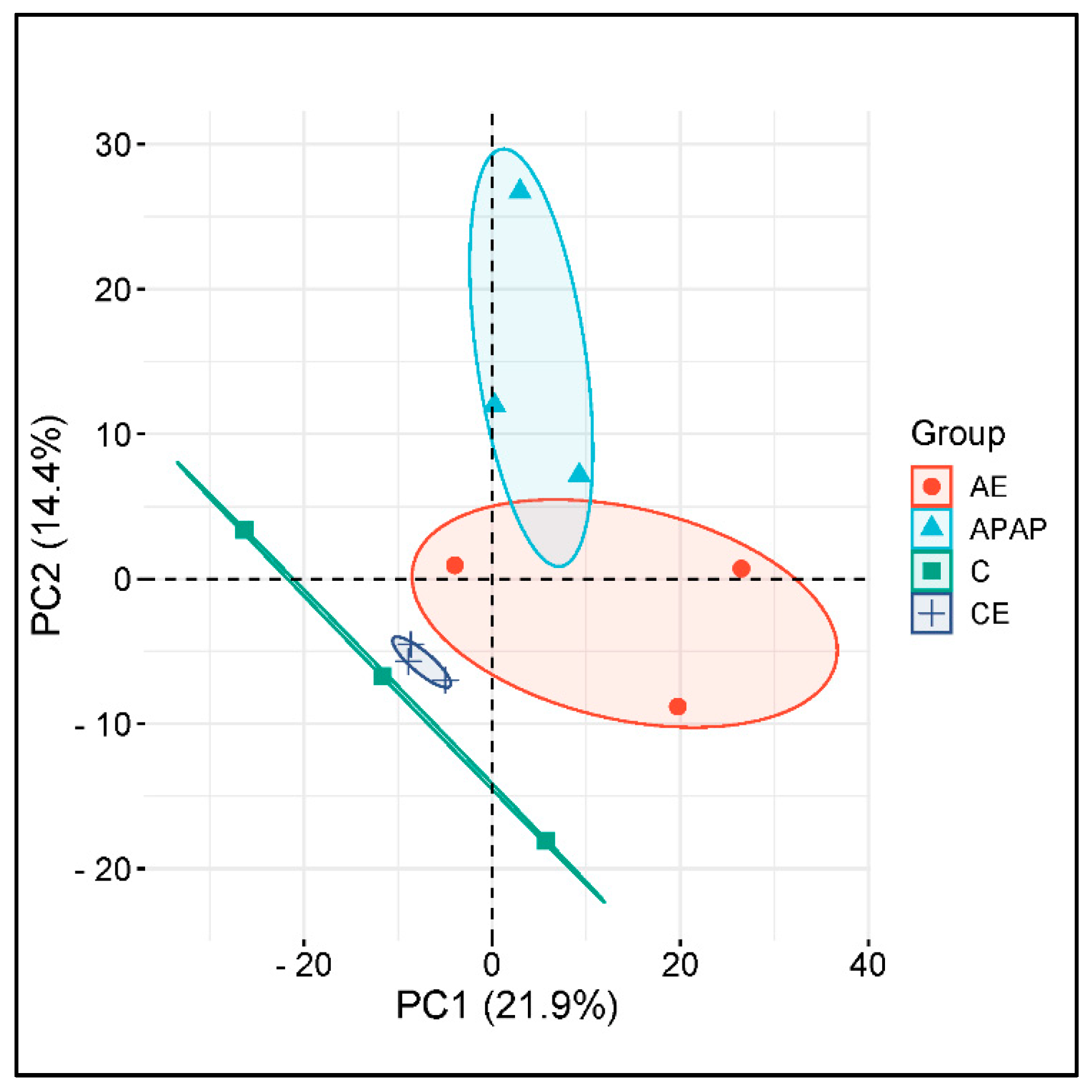
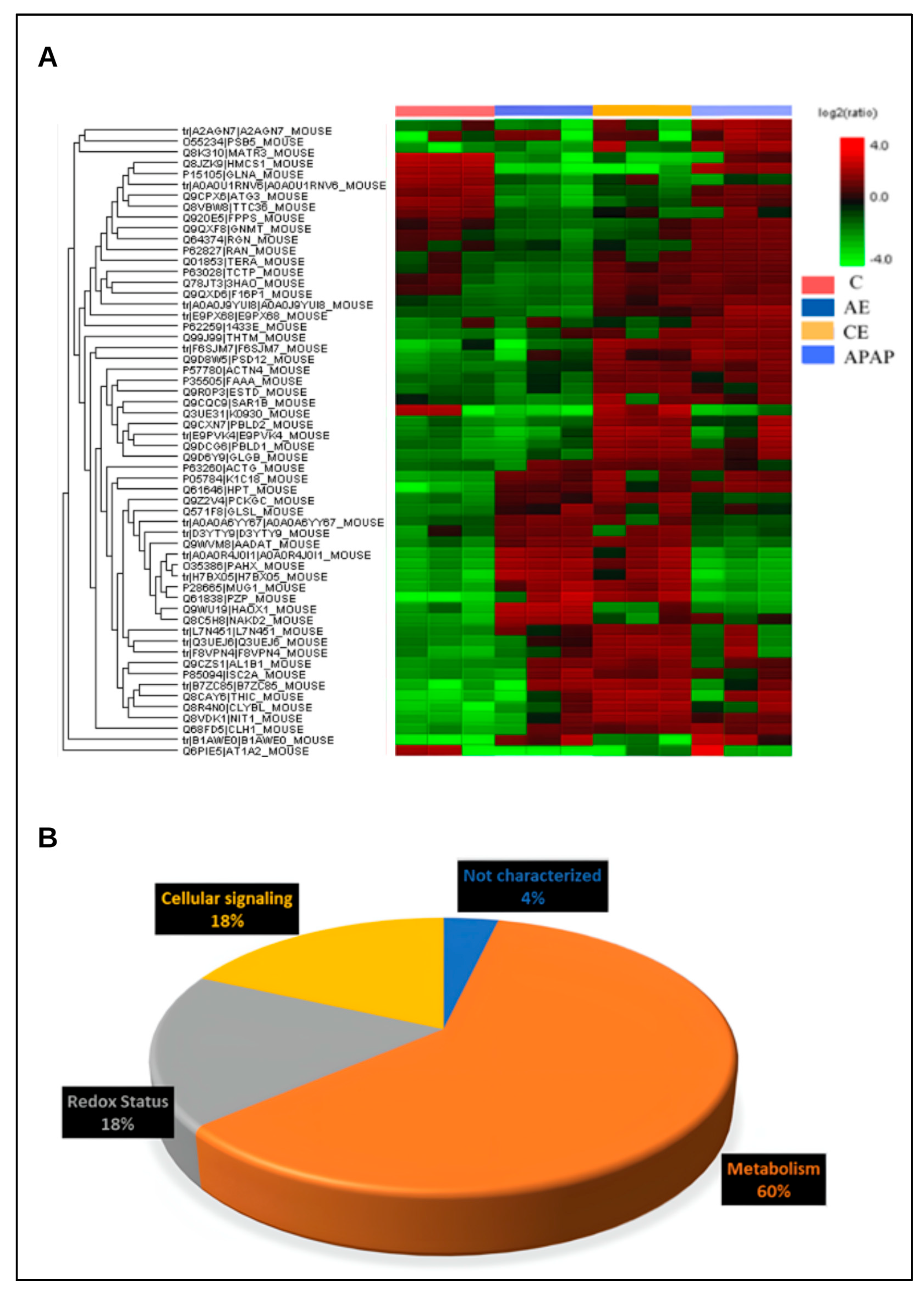
3.6. The Hepatic Proteome Is Altered During Acute and Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Acetaminophen Overdose
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rotundo, L.; Pyrsopoulos, N. Liver injury induced by paracetamol and challenges associated with intentional and unintentional use. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity. Semin Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittarelli, R.; Pellegrini, M.; Scarpellini, M.G.; Marinelli, E.; Bruti, V.; Di Luca, N.M.; Busardò, F.P.; Zaami, S. Hepatotoxicity of paracetamol and related fatalities. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21 (Suppl. 1), 95–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Ren, S.; Jiang, H.; Yan, R.; Chen, W.; Yan, R.; Dong, J.; Shao, L.; Yu, Y. The oral administration of Lacticaseibacillus casei Shirota alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury through accelerated acetaminophen metabolism via the liver-gut axis in mice. mSphere 2024, 9, e0067223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, A.; Pingali, P.; Faber, A.; Landry, J.; Akakpo, J.Y.; Jaeschke, H.; Li, H.; Lee, W.S.; May, L.; Patel, B.; et al. High dose acetaminophen with concurrent CYP2E1 inhibition has profound anti-cancer activity without liver toxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024, 388, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maideen, N.M.P. Drug Interactions of Acetaminophen (Paracetamol) involving CYP and UGT Enzymes. Eur. J. Med. 2019, 7, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breslow, R.A.; Dong, C.; White, A. Prevalence of Alcohol-Interactive Prescription Medication Use Among Current Drinkers: United States, 1999 to 2010. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Mathurin, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Han, J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, M.; Jung, Y. Pathophysiological Aspects of Alcohol Metabolism in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Zentella, M.L.; Villalobos-García, D.; Hernández-Muñoz, R. Ethanol Metabolism in the Liver, the Induction of Oxidant Stress, and the Antioxidant Defense System. Antioxidants. 2022, 11, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iturrospe, E.; da Silva, K.M.; Robeyns, R.; van de Lavoir, M.; Boeckmans, J.; Vanhaecke, T.; van Nuijs, A.L.; Covaci, A. Metabolic Signature of Ethanol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in HepaRG Cells by Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Singla, B.; Singh, A.K.; Thomas-Gooch, S.M.; Zhi, K.; Singh, U.P. Hepatic, Extrahepatic and Extracellular Vesicle Cytochrome P450 2E1 in Alcohol and Acetaminophen-Mediated Adverse Interactions and Potential Treatment Options. Cells 2022, 11, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaber, M.A.; Ghanim, B.Y.; Al-Natour, M.; Arqoub, D.A.; Abdallah, Q.; Abdelrazig, S.; Alkrad, J.A.; Kim, D.H.; Qinna, N.A. Potential biomarkers and metabolomics of acetaminophen-induced liver injury during alcohol consumption: A preclinical investigation on C57/BL6 mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 465, 116451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.M.; Queiroz, I.F.; Lima, W.G.; Talvani, A.; Perucci, L.O.; de Souza, M.O.; Costa, D.C. Temporal analysis of paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 46, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, A.M.; Queiroz, I.F.; Perucci, L.O.; de Souza, M.O.; Lima, W.G.; Talvani, A.; Costa, D.C. Piperine as Therapeutic Agent in Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, A.C.B.; da Silva, R.C.; Rossoni, J.V.; Figueiredo, V.P.; Talvani, A.; Cangussú, S.D.; Bezerra, F.S.; Costa, D.C. Lycopene pretreatment improves hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen in C57BL/6 mice. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandeira, A.C.B.; da Silva, T.P.; de Araujo, G.R.; Araujo, C.M.; da Silva, R.C.; Lima, W.G.; Bezerra, F.S.; Costa, D.C. Lycopene inhibits reactive oxygen species production in SK-Hep-1 cells and attenuates acetaminophen-induced liver injury in C57BL/6 mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 263, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneru, M.; Sahu, B.D.; Kumar, J.M.; Kuncha, M.; Kadari, A.; Kilari, E.K.; Sistla, R. Fisetin protects liver from binge alcohol-induced toxicity by mechanisms including inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and oxidative stress. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 22, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Bhardwaj, M.; Shukla, S.; Min, S.-H.; Choi, D.K.; Bajpai, V.K.; Huh, Y.S.; Kang, S.C. Carvacrol inhibits cytochrome P450 and protects against binge alcohol-induced liver toxicity. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.F.A.; Machado-Junior, P.A.; Souza, A.B.F.; Castro, T.D.F.; Costa, G.D.P.; Talvani, A.; Bezerra, F.S.; Cangussú, S.D. Lycopene Ameliorates Liver Inflammation and Redox Status in Mice Exposed to Long-Term Cigarette Smoke. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7101313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado-Junior, P.A.; Araújo, N.P.S.; Souza, A.B.F.; Castro, T.F.; Oliveira, M.; Costa, G.P.; Matos, N.A.; Vieira, P.M.A.; Talvani, A.; Bezerra, F.S.; et al. Protective Effects of Quercetin on Livers from Mice Exposed to Long-Term Cigarette Smoke. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2196207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Yao, Y.; Wei, Z.Y.; Wang, S.X.; Wu, Y.C.; Hu, Y.; Yang, C.C.; Min, J.L.; Li, L.Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Deletion of p38γ attenuates ethanol consumption- and acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice through promoting Dlg1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, H.; Kwon, D.; Yun, J.; Jung, Y.-S. Downregulation of Glutathione-Mediated Detoxification Capacity by Binge Drinking Aggravates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury through IRE1α ER Stress Signaling. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, P.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, M.; Quan, J.; Hu, X. The Hepatic Nerves Regulated Inflammatory Effect in the Process of Liver Injury: Is Nerve the Key Treating Target for Liver Inflammation? Inflammation 2023, 46, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas Souza, B.S.; Nascimento, R.C.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Vasconcelos, J.F.; Kaneto, C.M.; de Carvalho, L.F.P.P.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, R.; Soares, M.B.P.; de Freitas, L.A.R. Transplantation of bone marrow cells decreases tumor necrosis factor-α production and blood–brain barrier permeability and improves survival in a mouse model of acetaminophen-induced acute liver disease. Cytotherapy 2012, 14, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.L.; Guo, Y.N.; Lu, M.H.; Ding, K.N.; Liang, S.S.; Mou, R.W.; Yuan, S.; He, Y.M.; Tang, L.P. Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity predominantly via inhibiting Nrf2 antioxidative pathway and activating TLR4-NF-κB-MAPK inflammatory response in mice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederbaum, A.I. CYP2E1- and TNFalpha/LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2015, 3, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdi, M.; Eiras, D.P.; Holt, M.P.; Webster, M.R.; Reilly, T.P.; Welch, K.D.; Pohl, L.R. Role of IL-6 in an IL-10 and IL-4 Double Knockout Mouse Model Uniquely Susceptible to Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2007, 20, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yin, M. Protective and Alleviative Effects from 4 Cysteine-Containing Compounds on Ethanol-Induced Acute Liver Injury through Suppression of Oxidation and Inflammation. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, S511–S515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavia, L. The influence of genetic background of C57Bl/6 and A/J mice on the development of acute inflammatory response induced by alcohol. Rev. Soc. Bras. Ciências Animais Laboratório 2013, 2, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ming, Y.; Hong, W.; Tang, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, X.; Mao, Y. Comparison of hepatic transcriptome profiling between acute liver injury and acute liver failure induced by acetaminophen in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 283, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M.; Vinken, M.; Jaeschke, H. Experimental models of hepatotoxicity related to acute liver failure. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 290, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavia, L. A/J mice are more susceptible than C57BL/6 to acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2021, 108, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, A.; Anadón, A.; Rodríguez, J.L.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Yuan, Z.; Martínez, M.A. Paracetamol: Overdose-induced oxidative stress toxicity, metabolism, and protective effects of various compounds in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 395–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Bing, S.J.; Cho, J.; Kim, A.; Kim, G.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.B.; Doh, Y.H.; Jee, Y. Sasa quelpaertensis leaves ameliorate alcohol-induced liver injury by attenuating oxidative stress in HepG2 cells and mice. Acta Histochem. 2018, 120, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.R.; Kim, Y.H.; Gang, G.T.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Ly, S.Y.; Oh, W.K.; Song, K.S.; Lee, C.H. Hepatoprotective effects of chestnut (Castanea crenata) inner shell extract against chronic ethanol-induced oxidative stress in C57BL/6 mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smathers, R.L.; Galligan, J.J.; Shearn, C.T.; Fritz, K.S.; Mercer, K.; Ronis, M.; Orlicky, D.J.; Davidson, N.O.; Petersen, D.R. Susceptibility of L-FABP−/− mice to oxidative stress in early-stage alcoholic liver. J. Lipid. Res. 2013, 54, 1335–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.K.; Chava, S.; Perumal, S.K.; Paal, M.C.; Rasineni, K.; Ganesan, M.; Donohue, T.M.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Acute ethanol-induced liver injury is prevented by betaine administration. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 940148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobariya, P.; Xie, W.; Rao, S.P.; Xie, J.; Seelig, D.M.; Vince, R.; Lee, M.K.; More, S.S. Deletion of Glyoxalase 1 Exacerbates Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, E.I.; Babenka, A.S.; Shchastniy, A.T. MMP-9 mRNA Expression and Bridging Fibrosis Progression in Toxic Liver Injury. Acta Naturae 2023, 15, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Abril, E.R.; Bethea, N.W.; McCuskey, R.S. Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinases Minimizes Hepatic Microvascular Injury in Response to Acetaminophen in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 83, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCuskey, R.S. Sinusoidal endothelial cells as an early target for hepatic toxicants. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2006, 34, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Abril, E.R.; Bethea, N.W.; Mccuskey, R.S. Ethanol Binging Enhances Hepatic Microvascular Responses to Acetaminophen in Mice. Microcirculation 2004, 11, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, L.; Piao, R. Orientin reverses acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure by inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 149, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogaru, G.; Bulboaca, A.E.; Gheban, D.; Boarescu, P.M.; Rus, V.; Festila, D.; Sitar-Taut, A.-V.; Stanescu, I. Effect of Liposomal Curcumin on Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by Down-regulation of Oxidative Stress and Matrix Metalloproteinases. In Vivo 2020, 34, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Cho, T.-S.; Kim, D.-J.; Cha, Y.-N. Protective effect of ethanol against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice: Role of role of NADH: Quinone reductase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, C.; Mella, L.; Godoy, K.; Adeli, K.; Farías, J. β-Carotene Increases Activity of Cytochrome P450 2E1 during Ethanol Consumption. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganov, P.; Durrence, H.; Cox, C.; Reuben, A. Alcohol-acetaminophen syndrome. Postgrad. Med. 2000, 107, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.M.; McElligott, T.F.; Power, E.M.; Massey, T.E.; Racz, W.J. Increased acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity after chronic ethanol consumption in mice. Toxicology 1983, 28, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, L.E.; Dalhoff, K.; Poulsen, H.E. Acute versus chronic alcohol consumption in acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 2002, 35, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.P.; Mowat, C.; Muir, D.F.; Tredger, J.M.; Williams, R. The Effect of Chronic Alcohol Intake on Prognosis and Outcome in Paracetamol Overdose. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1991, 10, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, L.F. Paracetamol, alcohol and the liver. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 49, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Metabolism and Disposition of Acetaminophen: Recent Advances in Relation to Hepatotoxicity and Diagnosis. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 2174–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, W.S.; Stephen, A.F.; Malkowska, A.M.; Robinson, O.D. Acute Ethanol Coingestion Confers a Lower Risk of Hepatotoxicity after Deliberate Acetaminophen Overdose. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2008, 15, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromer, M.Q.; Black, M. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 2003, 7, 351–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, N.; Nalpas, B.; Yang, C.S.; Beaune, P.H. Modulation of cytochrome P450 isozymes in human liver, by ethanol and drug intake. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 19, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liangpunsakul, S.; Kolwankar, D.; Pinto, A.; Gorski, J.C.; Hall, S.D.; Chalasani, N. Activity of CYP2E1 and CYP3A enzymes in adults with moderate alcohol consumption: A comparison with nonalcoholics. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Duan, Y.; Han, J.; Yang, X. MEK1/2 inhibitors induce class I alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH1) expression by regulating farnesoid X receptor in hepatic cell lines and C57BL/6J mouse. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 5843–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedgpeth, B.; Missall, R.; Bambaci, A.; Smolen, M.; Yavuz, S.; Cottrell, J.; Chu, T.; Chang, S.L. A Review of Bioinformatics Tools to Understand Acetaminophen-Alcohol Interaction. Medicines 2019, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutsuno, Y.; Itoh, T.; Tukey, R.H.; Fujiwara, R. Glucuronidation of Drugs and Drug-Induced Toxicity in Humanized UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase 1 Mice. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiratani, H.; Katoh, M.; Nakajima, M.; Yokoi, T. Species Differences in UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Activities in Mice and Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Wu, J.; Tang, B.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, D.; Lin, X. Constitutive androstane receptor activation promotes bilirubin clearance in a murine model of alcoholic liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3459–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Welch, K.D.; Wen, B.; Goodlett, D.R.; Yi, E.C.; Lee, H.; Reilly, T.P.; Nelson, S.D.; Pohl, L.R. Proteomic Identification of Potential Susceptibility Factors in Drug-Induced Liver Disease. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2005, 18, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Huang, E.; Pathak, V.; Willard, B.B.; Allende, D.S.; Nagy, L.E. Phosphoproteomics identifies pathways underlying the role of receptor-interaction protein kinase 3 in alcohol-associated liver disease and uncovers apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 as a target. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2022–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, A.C.; Coelho, A.M.; da Cruz Castro, M.L.; Pereira, R.R.; da Silva Araújo, N.P.; Ferreira, F.M.; Machado Júnior, P.A.; Pio, S.; Vital, C.E.; Bezerra, F.S.; et al. Modulation of Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Acute and Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice: A Study Pilot. Toxics 2024, 12, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120857
Gonçalves AC, Coelho AM, da Cruz Castro ML, Pereira RR, da Silva Araújo NP, Ferreira FM, Machado Júnior PA, Pio S, Vital CE, Bezerra FS, et al. Modulation of Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Acute and Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice: A Study Pilot. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120857
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Allan Cristian, Aline Meireles Coelho, Maria Laura da Cruz Castro, Renata Rebeca Pereira, Natalia Pereira da Silva Araújo, Flávia Monteiro Ferreira, Pedro Alves Machado Júnior, Sirlaine Pio, Camilo Elber Vital, Frank Silva Bezerra, and et al. 2024. "Modulation of Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Acute and Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice: A Study Pilot" Toxics 12, no. 12: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120857
APA StyleGonçalves, A. C., Coelho, A. M., da Cruz Castro, M. L., Pereira, R. R., da Silva Araújo, N. P., Ferreira, F. M., Machado Júnior, P. A., Pio, S., Vital, C. E., Bezerra, F. S., Talvani, A., de Castro Borges, W., de Oliveira, E. C., & Costa, D. C. (2024). Modulation of Paracetamol-Induced Hepatotoxicity by Acute and Chronic Ethanol Consumption in Mice: A Study Pilot. Toxics, 12(12), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120857









