Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Questionnaire Survey
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Microplastic Extraction
2.5. Microplastic Detection
2.6. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Participants
3.2. Microplastics in the Placenta, Cord Blood, and Meconium
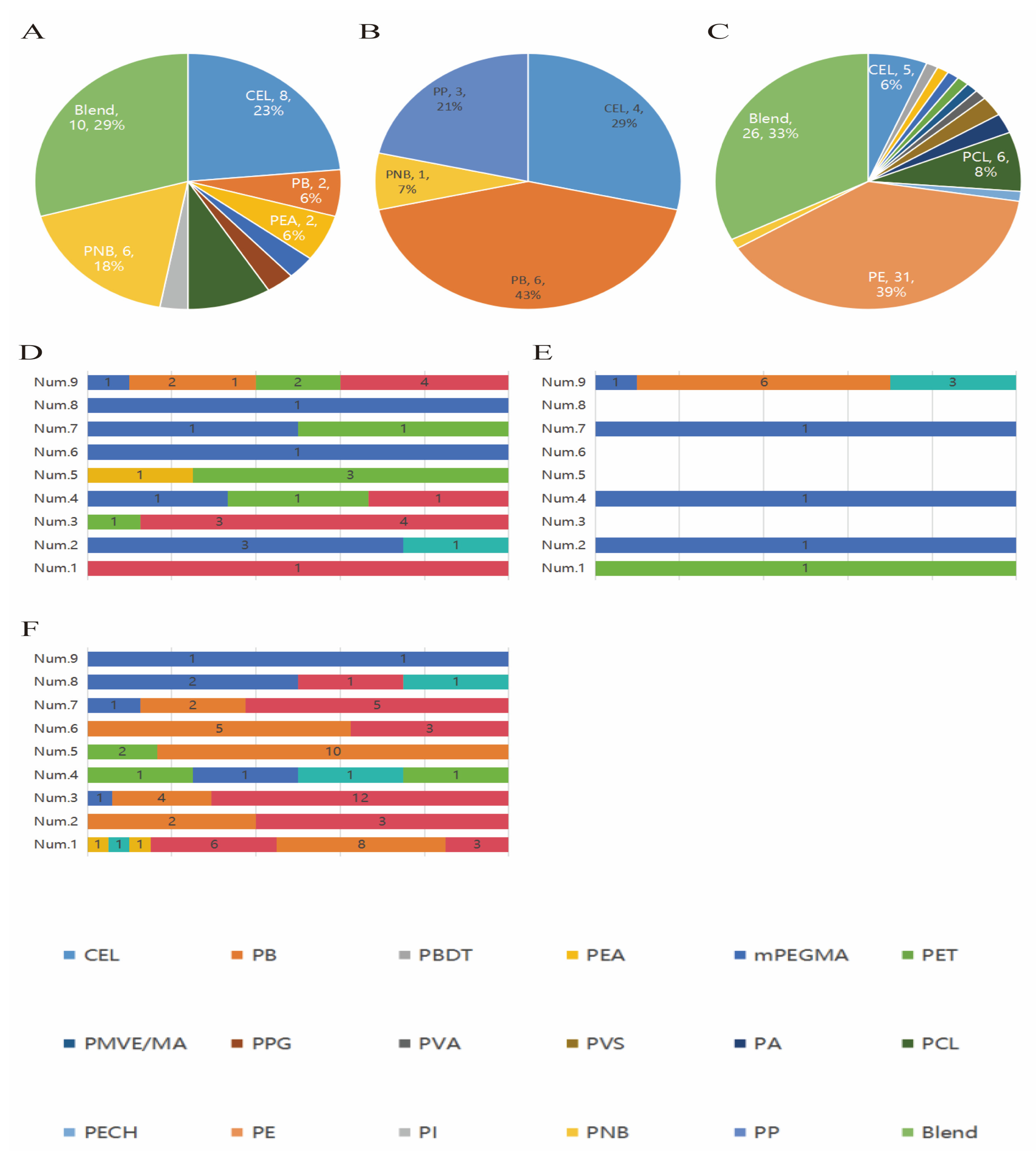
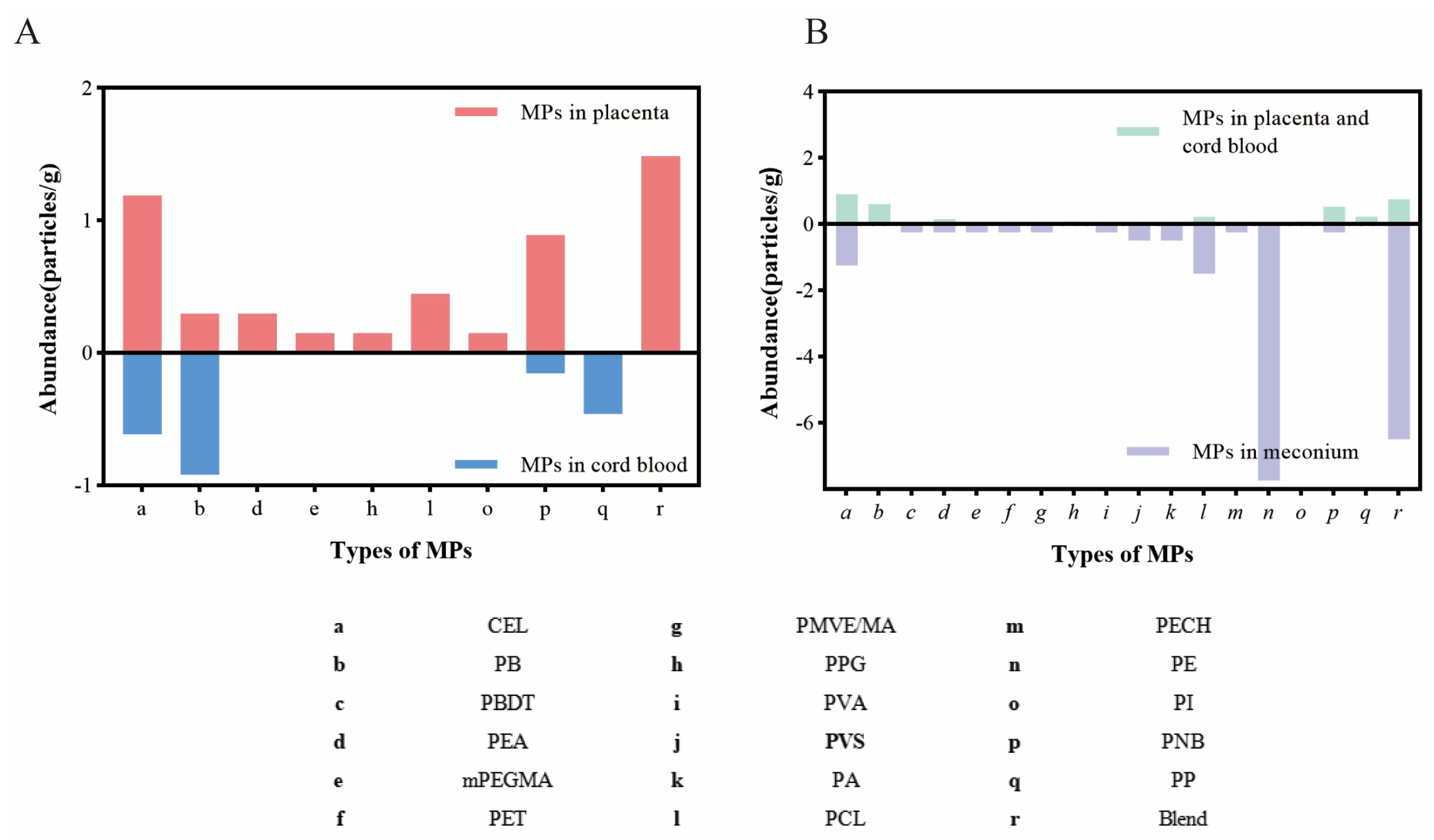
3.3. Characteristics of Microplastics in Placenta, Cord Blood, and Meconium
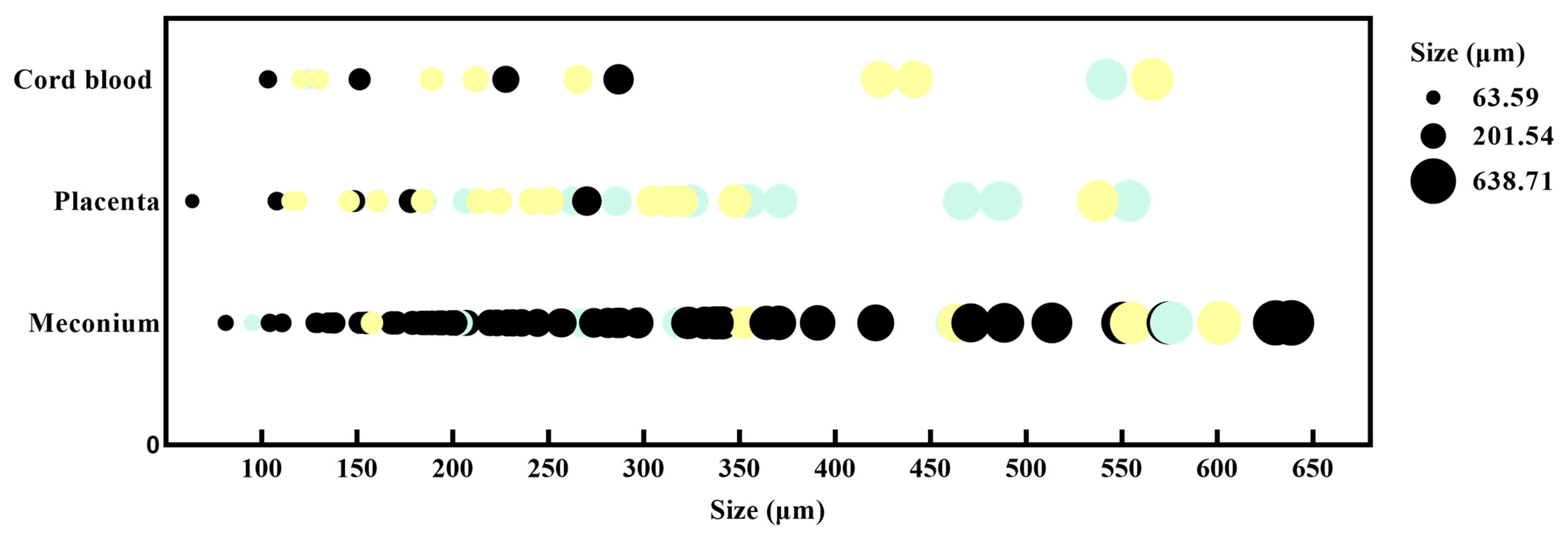
3.4. Particle Size and Color
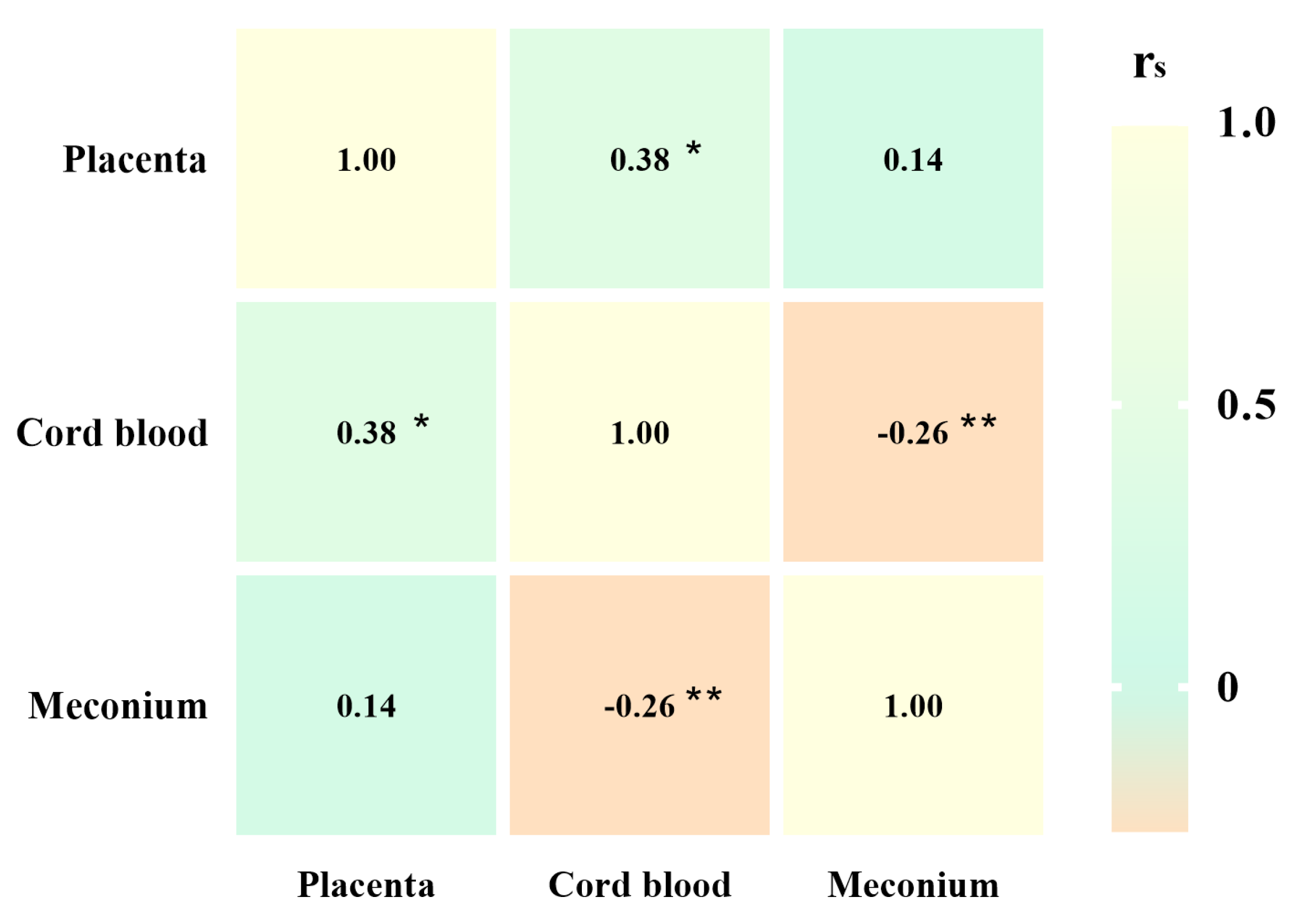
3.5. Associations Between the Abundance of Different Microplastics in the Placenta, Cord Blood, and Meconium
3.6. Relationship of the Presence of MPs in Placenta, Cord Blood, and Meconium Stratified by Living Environment and Lifestyles During Pregnancy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberghini, L.; Truant, A.; Santonicola, S.; Colavita, G.; Giaccone, V. Microplastics in Fish and Fishery Products and Risks for Human Health: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J.; John, A.W.G.; McGonigle, D.; Russell, A.E. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Sanganyado, E.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Liu, W. Organic pollutants in sedimentary microplastics from eastern Guangdong: Spatial distribution and source identification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 193, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Microplastics are everywhere—We need to understand how they affect human health. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 913. [CrossRef]
- Marfella, R.; Prattichizzo, F.; Sardu, C.; Fulgenzi, G.; Graciotti, L.; Spadoni, T.; D’onofrio, N.; Scisciola, L.; La Grotta, R.; Frigé, C.; et al. Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Duan, X.; Liang, B.; Xu, E.G.; Huang, Z. Micro- and nanoplastics: A new cardiovascular risk factor? Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Tan, H.; Chen, D. Large polystyrene microplastics results in hepatic lipotoxicity in mice. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Peng, C.; Cui, G.; Shao, H.; Du, Z. Activation of pyroptosis and ferroptosis is involved in the hepatotoxicity induced by polystyrene microplastics in mice. Chemosphere 2022, 291 Pt 2, 132944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Shen, L.; Ye, X.; Bai, G.; Liao, C.; Chen, Z.; Peng, T.; Li, X.; Kang, X.; An, G. Prenatal and postnatal exposure to polystyrene microplastics induces testis developmental disorder and affects male fertility in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhuan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Fu, X.; Hou, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induced female reproductive toxicity in mice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424 Pt C, 127629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced reproductive toxicities induced by phthalates contaminated microplastics in male mice (Mus musculus). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingaro, F.; Gianoncelli, A.; Ceccone, G.; Birarda, G.; Cassano, D.; La Spina, R.; Agostinis, C.; Bonanni, V.; Ricci, G.; Pascolo, L. Morphological and lipid metabolism alterations in macrophages exposed to model environmental nanoplastics traced by high-resolution synchrotron techniques. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1247747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Hale, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Environmentally Relevant Doses of Large Polystyrene Microplastics Disturbs Lipid Homeostasis via Bowel Function Interference. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15805–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Yan, Z.; Shen, R.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B. Microplastics release phthalate esters and cause aggravated adverse effects in the mouse gut. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zeng, W.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X. Polystyrene microplastics disturb maternal-fetal immune balance and cause reproductive toxicity in pregnant mice. Reprod. Toxicol. 2021, 106, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, Z.; Mercer, G.V.; Schneider, C.M.; Sled, J.G.; Macgowan, C.K.; Baschat, A.A.; Kingdom, J.C.; Helm, P.A.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J.; et al. Maternal exposure to polystyrene microplastics alters placental metabolism in mice. Metabolomics Off. J. Metabolomic Soc. 2022, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibbon, K.C.; Mercer, G.V.; Maekawa, A.S.; Hanrahan, J.; Steeves, K.L.; Ringer, L.C.M.; Simpson, A.J.; Simpson, M.J.; Baschat, A.A.; Kingdom, J.C.; et al. Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics cause placental dysfunction in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2024, 110, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, N.E.; Mercer, G.V.; Stapleton, D.; Steeves, K.L.; Hanrahan, J.; Cui, M.; Aghaei, Z.; Spring, S.; Helm, P.A.; Simpson, A.J.; et al. Maternal exposure to polystyrene nanoplastics impacts developmental milestones and brain structure in mouse offspring. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Shen, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Maternal exposure to different sizes of polystyrene microplastics during gestation causes metabolic disorders in their offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255 Pt 1, 113122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, Z.; Sled, J.G.; Kingdom, J.C.; Baschat, A.A.; Helm, P.A.; Jobst, K.J.; Cahill, L.S. Maternal Exposure to Polystyrene Micro- and Nanoplastics Causes Fetal Growth Restriction in Mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2022, 9, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D. Three ways to solve the plastics pollution crisis. Nature 2023, 616, 234–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ye, K.; Lu, Y.; Deng, H.; Yang, J.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Zheng, H.; Sun, K.; Jiang, Y. Occurrence and risk assessment of microplastics on the Shenzhen coast, South China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 286, 117227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Ouyang, F.; Peng, D.; You, J.; Ding, L.; Ouyang, Z.; Liu, P.; Guo, X. A case study of distribution and characteristics of microplastics in surface water and sediments of the seas around Shenzhen, southern coastal area of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838 Pt 1, 156063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhumitha, C.T.; Karmegam, N.; Biruntha, M.; Arun, A.; Al Kheraif, A.A.; Kim, W.; Kumar, P. Extraction, identification, and environmental risk assessment of microplastics in commercial toothpaste. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Kumar, G.; Yang, Y.-H. Understanding microplastic pollution: Tracing the footprints and eco-friendly solutions. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, T.; Ehrlich, L.; Henrich, W.; Koeppel, S.; Lomako, I.; Schwabl, P.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Microplastic in Human Placenta and Meconium in a Clinical Setting. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuth, M.; Mason, S.A.; Wattenberg, E.V. Anthropogenic contamination of tap water, beer, and sea salt. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wu, Q.; Wei, X.-F.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Crittenden, J.C.; Liu, B. Tracing microplastics in rural drinking water in Chongqing, China: Their presence and pathways from source to tap. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 459, 132206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhib, I.; Uddin, K.; Rahman, M.; Malafaia, G. Occurrence of microplastics in tap and bottled water, and food packaging: A narrative review on current knowledge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadac-Czapska, K.; Knez, E.; Grembecka, M. Food and human safety: The impact of microplastics. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 3502–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G. Impacts of microplastic on fisheries and seafood security—Global analysis and synthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, M.; Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Wang, J.; Shan, J. Microplastics contamination in food and beverages: Direct exposure to humans. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 2816–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruti, V.; Pérez-Guevara, F.; Elizalde-Martínez, I.; Kutralam-Muniasamy, G. First study of its kind on the microplastic contamination of soft drinks, cold tea and energy drinks—Future research and environmental considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Luo, Y.; Ding, Y.; Huang, J.; Wu, H.; Han, J.; Du, L.; Kang, A.; Jia, M.; et al. Plastic bottles for chilled carbonated beverages as a source of microplastics and nanoplastics. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabl, P.; Köppel, S.; Königshofer, P.; Bucsics, T.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T.; Liebmann, B. Detection of Various Microplastics in Human Stool: A Prospective Case Series. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenner, L.C.; Rotchell, J.M.; Bennett, R.T.; Cowen, M.; Tentzeris, V.; Sadofsky, L.R. Detection of microplastics in human lung tissue using μFTIR spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, E.; Du, Z.; Peng, Z.; Han, Z.; Li, L.; Zhao, R.; Qin, Y.; Xue, M.; Li, F.; et al. Detection of Various Microplastics in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10911–10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfar, J.; Čabanová, K.; Vávra, K.; Delongová, P.; Motyka, O.; Špaček, R.; Kukutschová, J.; Šimetka, O.; Heviánková, S. Microplastics and additives in patients with preterm birth: The first evidence of their presence in both human amniotic fluid and placenta. Chemosphere 2023, 343, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. The Association Between Microplastics and Microbiota in Placentas and Meconium: The First Evidence in Humans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 17774–17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sui, M.; Wang, T.; Teng, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, M. Detection and quantification of various microplastics in human endometrium based on laser direct infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Weng, J.; Jin, Z.; Cao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z. Detection and characterization of microplastics in the human testis and semen. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, H.A.; van Velzen, M.J.; Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Lamoree, M.H. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ. Int. 2022, 163, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Huang, X.; Bi, R.; Bi, R.; Guo, Q.; Guo, Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, X.; et al. Detection and Analysis of Microplastics in Human Sputum. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Notarstefano, V.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Giorgini, E.; Montano, L. First Evidence of Microplastics in Human Urine, a Preliminary Study of Intake in the Human Body. Toxics 2022, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Bin Li, Y.; He, H.R.; Zhang, J.F.; Ma, G.S. You are what you eat: Microplastics in the feces of young men living in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, B.; Dong, R. Detection of various microplastics in placentas, meconium, infant feces, breastmilk and infant formula: A pilot prospective study. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zuo, R.; Xu, Q.; Qian, Y.; An, L. Identification of microplastics in human placenta using laser direct infrared spectroscopy. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856 Pt 1, 159060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Feng, Y.; Wang, R.; Jiang, J.; Guan, Q.; Yang, X.; Wei, H.; Xia, Y.; Luo, Y. Pigment microparticles and microplastics found in human thrombi based on Raman spectral evidence. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 49, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, A.; Svelato, A.; Santacroce, C.; Catalano, P.; Notarstefano, V.; Carnevali, O.; Papa, F.; Rongioletti, M.C.A.; Baiocco, F.; Draghi, S.; et al. Plasticenta: First evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, F.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of Microplastics in Human Feces Reveals a Correlation between Fecal Microplastics and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Status. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massardo, S.; Verzola, D.; Alberti, S.; Caboni, C.; Santostefano, M.; Verrina, E.E.; Angeletti, A.; Lugani, F.; Ghiggeri, G.M.; Bruschi, M.; et al. MicroRaman spectroscopy detects the presence of microplastics in human urine and kidney tissue. Environ. Int. 2024, 184, 108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lemos, B.; Ren, H. Tissue accumulation of microplastics in mice and biomarker responses suggest widespread health risks of exposure. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Qiao, R.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. An efficient method for extracting microplastics from feces of different species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Su, X.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, G.; Du, Q. Microplastics in maternal blood, fetal appendages, and umbilical vein blood. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 287, 117300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneman, W.J.; Spaink, H.P.; Brun, N.R.; Bosker, T.; Vijver, M.G. Pathway analysis of systemic transcriptome responses to injected polystyrene particles in zebrafish larvae. Aquat. Toxicol. 2017, 190, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, W.; Liu, P.; Ji, X. Effect of Annealing Process and Molecular Weight on the Polymorphic Transformation from Form II to Form I of Poly(1-butene). Polymers 2023, 15, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariou, R.; Veyrand, B.; Yamada, A.; Berrebi, A.; Zalko, D.; Durand, S.; Pollono, C.; Marchand, P.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Antignac, J.-P.; et al. Perfluoroalkyl acid (PFAA) levels and profiles in breast milk, maternal and cord serum of French women and their newborns. Environ. Int. 2015, 84, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marie, C.; Vendittelli, F.; Sauvant-Rochat, M.-P. Obstetrical outcomes and biomarkers to assess exposure to phthalates: A review. Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 116–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafmueller, S.; Manser, P.; Diener, L.; Diener, P.-A.; Maeder-Althaus, X.; Maurizi, L.; Jochum, W.; Krug, H.F.; Buerki-Thurnherr, T.; Von Mandach, U.; et al. Bidirectional Transfer Study of Polystyrene Nanoparticles across the Placental Barrier in an ex Vivo Human Placental Perfusion Model. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M.M.; Hirschmugl, B.; Berger, N.; Holter, M.; Radulović, S.; Leitinger, G.; Liesinger, L.; Berghold, A.; Roblegg, E.; Birner-Gruenberger, R.; et al. Plasma proteins facilitates placental transfer of polystyrene particles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Kenneally, D.; Odio, M.; Hatzopoulos, I. Modern diaper performance: Construction, materials, and safety review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55 (Suppl. S1), 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonicola, S.; Volgare, M.; Cocca, M.; Dorigato, G.; Giaccone, V.; Colavita, G. Impact of Fibrous Microplastic Pollution on Commercial Seafood and Consumer Health: A Review. Animals 2023, 13, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, J.; Steeves, K.L.; Locke, D.P.; O’brien, T.M.; Maekawa, A.S.; Amiri, R.; Macgowan, C.K.; Baschat, A.A.; Kingdom, J.C.; Simpson, A.J.; et al. Maternal exposure to polyethylene micro- and nanoplastics impairs umbilical blood flow but not fetal growth in pregnant mice. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Gong, Z.; Wang, L. Barrier function of zebrafish embryonic chorions against microplastics and nanoplastics and its impact on embryo development. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, M.V.; Kumar, M.; Sacanna, S.; Thutupalli, S.; Bogaart, G.v.D. Modulation of Immune Responses by Particle Size and Shape. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 607945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Bang, J.; Kim, T.; Oh, Y.; Hwang, Y.; Hong, J. In vitro chemical and physical toxicities of polystyrene microfragments in human-derived cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 400, 123308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barboza, L.G.A.; Vethaak, A.D.; Lavorante, B.R.; Lundebye, A.-K.; Guilhermino, L. Marine microplastic debris: An emerging issue for food security, food safety and human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 336–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Golieskardi, A.; Choo, C.K.; Larat, V.; Galloway, T.S.; Salamatinia, B.; Bin Ho, Y. The presence of microplastics in commercial salts from different countries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.; Hong, S.; Jung, J.; Kwon, J.-H. Analysis of microplastics in various foods and assessment of aggregate human exposure via food consumption in Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 322, 121153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banaei, G.; García-Rodríguez, A.; Tavakolpournegari, A.; Martín-Pérez, J.; Villacorta, A.; Marcos, R.; Hernández, A. The release of polylactic acid nanoplastics (PLA-NPLs) from commercial teabags. Obtention, characterization, and hazard effects of true-to-life PLA-NPLs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, L.-Y.; Li, Z.; Zeng, E.Y. Drinking Boiled Tap Water Reduces Human Intake of Nanoplastics and Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Tamminga, M.; Liu, B.; Sebode, M.; Carambia, A.; Fischer, L.; Püschel, K.; Huber, S.; Fischer, E.K. Microplastics detected in cirrhotic liver tissue. EBioMedicine 2022, 82, 104147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Categories | N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| BMI before pregnancy (kg/m2), median (IQR) | - | 21.3 (18.7, 23.8) |
| Age (year), median (IQR) | - | 31.8 (28.5, 37.0) |
| Education | High school and below | 1 (11.1) |
| Bachelor’s degree | 7 (77.8) | |
| Postgraduate and above | 1 (11.1) | |
| Occupation | Governmental official | 0 (0.0) |
| Profession and technology | 1 (11.1) | |
| General office | 4 (44.4) | |
| Business services | 3 (33.3) | |
| Others | 1 (11.1) | |
| Annual income per capita (CNY) | <100 thousand | 4 (44.4) |
| 100–200 thousand | 3 (33.3) | |
| >200 thousand | 2 (22.2) | |
| Parity | Primipara | 4 (44.4) |
| Multipara | 5 (55.6) | |
| Mode of conception | Natural conception | 9 (100.0) |
| Assisted reproduction | 0 (0.0) | |
| Birth outcome | Preterm | 4 (44.4) |
| Full-term | 5 (55.6) | |
| Mode of delivery | Vaginal delivery | 7 (77.8) |
| Cesarean delivery | 2 (22.2) | |
| Sex of newborns | Male | 5 (55.6) |
| Female | 4 (44.4) | |
| Newborn weight (g), median (IQR) | - | 2980 (2200, 3210) |
| Participants | Frequency of Microplastic Particles (Particle) | Samples’ Dry Weight (g) | Abundance (Particle/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placenta | Cord Blood | Meconium | Placenta | Cord Blood | Meconium | Placenta | Cord Blood | Meconium | |
| Num.1 | 1 | 1 | 20 | 0.4381 | 0.9058 | 0.3076 | 2.28 | 1.10 | 65.02 |
| Num.2 | 4 | 1 | 5 | 0.8032 | 0.6789 | 0.2410 | 4.98 | 1.47 | 20.75 |
| Num.3 | 8 | - | 17 | 0.8740 | 0.4166 | 0.2203 | 9.15 | 0 | 77.17 |
| Num.4 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0.9531 | 0.7687 | 0.7481 | 3.15 | 1.30 | 5.35 |
| Num.5 | 4 | - | 12 | 0.6093 | 0.8135 | 0.7527 | 6.56 | 0 | 15.94 |
| Num.6 | 1 | - | 8 | 0.8073 | 0.8213 | 0.2224 | 1.24 | 0 | 35.98 |
| Num.7 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 0.7689 | 0.6111 | 0.1221 | 2.60 | 1.63 | 65.52 |
| Num.8 | 1 | - | 4 | 0.7342 | 0.8570 | 0.4901 | 1.37 | 0 | 8.16 |
| Num.9 | 10 | 10 | 2 | 0.7459 | 0.6409 | 0.8963 | 13.41 | 15.60 | 2.23 |
| Median (Interquartile range) | 3 (1, 6) | 1 (0, 1) | 8 (4, 15) | - | - | - | 3.15 (1.82, 7.85) | 1.1 (0, 1.55) | 20.75 (6.75, 65.27) |
| Total | 34 | 14 | 80 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| P a | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.001 b | ||
| Questions | Options | N (%) | Placenta | Cord Blood | Meconium | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Living environment | Having sites of air pollution around your home or not | no | 8 (88.9) | 2.9 (1.6, 8.1) | 1.2 (0, 1.6) | 28.4 (6.1, 65.4) |
| yes | 1 (11.1) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | 0.667 | 0.444 | 0.889 | |||
| Distance of residence from major transportation arteries (two-way, four-lane roads) | ≤100 m | 5 (55.6) | 2.3 (1.3, 8.0) | 1.1 (0, 8.6) | 36.0 (5.2, 65.3) | |
| >100 m | 4 (44.6) | 5.8 (3.6, 8.5) | 0.6 (0, 1.4) | 18.3 (8.0, 63.1) | ||
| P a | 0.190 | 0.730 | 1.000 | |||
| Frequency of using air purifiers at home | never/seldom | 8 (88.9) | 4.1 (1.6, 8.5) | 0.5 (0, 1.4) | 18.3 (6.1, 57.8) | |
| often | 1 (11.1) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | 0.889 | 0.444 | 0.444 | |||
| Dietary and lifestyle during pregnancy | Drinking water | piped water | 5 (55.6) | 5.0 (2.7, 11.3) | 1.3 (0.5, 8.5) | 20.8 (3.8, 71.1) |
| barrel-loaded water | 4 (44.6) | 2.0 (1.3, 5.6) | 0 (0, 1.2) | 26.0 (10.1, 58.1) | ||
| P a | 0.190 | 0.286 | 1.000 | |||
| Passive smoking | no | 7 (77.8) | 5.0 (2.3, 9.1) | 1.1 (0, 1.6) | 20.7 (8.2, 65.5) | |
| yes | 2 (22.2) | 2.2 (1.2, 3.1) | 0.6 (0, 1.3) | 20.7 (5.3, 36.0) | ||
| P a | 0.333 | 0.667 | 0.667 | |||
| Drinking water in plastic cup/bottles | never/seldom | 7 (77.8) | 3.1 (2.3, 6.6) | 1.1 (0, 1.5) | 36.0 (15.9, 65.5) | |
| often | 2 (22.2) | 7.4 (1.4, 13.4) | 7.8 (0, 15.6) | 5.2 (2.2, 8.2) | ||
| P a | 1.000 | 0.667 | 0.111 | |||
| Milk tea consumption | never/seldom | 9 (100.0) | 3.1 (1.8, 7.9) | 1.1 (0, 1.5) | 20.7 (6.8, 65.3) | |
| often | 0 (0.0) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | - | - | - | |||
| Tea consumption | never/seldom | 6 (66.7) | 2.4 (1.3, 6.0) | 0.5 (0, 1.5) | 50.5 (17.6, 68.4) | |
| often | 3 (33.3) | 6.6 (3.1, 13.4) | 1.3 (0, 15.6) | 5.3 (2.2, 15.9) | ||
| P a | 0.167 | 0.548 | 0.048 b | |||
| Drinking beverages in plastic bottles | never/seldom | 9 (100.0) | 3.1 (1.8, 7.9) | 1.1 (0, 1.5) | 20.7 (6.8, 65.3) | |
| often | 0 (0.0) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | - | - | - | |||
| Microwave food using plastic tableware | never/seldom | 8 (88.9) | 2.9 (1.6, 6.2) | 1.2 (0, 1.6) | 18.3 (6.1, 57.8) | |
| often | 1 (11.1) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | 0.444 | 0.444 | 0.222 | |||
| Dietary and lifestyle during pregnancy | Takeout frequency | never/seldom | 9 (100.0) | 3.1 (1.8, 7.9) | 1.1 (0, 1.5) | 20.7 (6.8, 65.3) |
| often | 0 (0.0) | - | - | - | ||
| P a | - | - | - | |||
| Eating seafood (fish, shellfish) | never/seldom | 5 (55.6) | 5.0 (1.3, 10.0) | 0 (0, 8.5) | 15.9 (5.2, 28.4) | |
| often | 4 (44.6) | 2.9 (2.4, 7.6) | 1.2 (0.3, 1.5) | 65.3 (20.3, 74.3) | ||
| P a | 1.000 | 0.730 | 0.190 | |||
| Time for daily wear of the mask | <3 h/day | 6 (66.7) | 3.8 (1.3, 7.2) | 0 (0, 1.5) | 28.4 (14.0, 68.4) | |
| ≥3 h/day | 3 (33.3) | 3.1 (2.3, 13.4) | 1.3 (1.1, 15.6) | 5.3 (2.2, 65.0) | ||
| P a | 0.714 | 0.262 | 0.262 | |||
| Drinking boxed milk | never/seldom | 1 (11.1) | - | - | - | |
| often | 8 (88.9) | 2.9 (1.6, 8.1) | 1.2 (0, 1.6) | 28.4 (6.1, 65.4) | ||
| P a | 0.667 | 0.444 | 1.000 | |||
| Scrub cleanser | never/seldom | 1 (11.1) | - | - | - | |
| often | 8 (88.9) | 4.1 (2.4, 8.5) | 1.2 (0, 1.6) | 18.3 (6.1, 65.4) | ||
| P a | 0.222 | 0.444 | 0.889 | |||
| Toothpaste | <3 times/day | 7 (77.8) | 3.1 (1.4, 6.6) | 1.3 (0, 1.6) | 15.9 (5.3, 36.0) | |
| ≥3 times/day | 2 (22.2) | 5.7 (2.3, 9.1) | 0.5 (0, 1.1) | 71.1 (65.0, 77.2) | ||
| P a | 1.000 | 0.500 | 0.111 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Lin, W.; Zeng, D.; Yang, P.; Ni, W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Lai, L.; Ouyang, Z.; et al. Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China. Toxics 2024, 12, 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120850
Zhu M, Li X, Lin W, Zeng D, Yang P, Ni W, Chen Z, Lin B, Lai L, Ouyang Z, et al. Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):850. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120850
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Minting, Xiaotian Li, Wei Lin, Dan Zeng, Pan Yang, Weigui Ni, Zhijian Chen, Bingyi Lin, Lijuan Lai, Zhongai Ouyang, and et al. 2024. "Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China" Toxics 12, no. 12: 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120850
APA StyleZhu, M., Li, X., Lin, W., Zeng, D., Yang, P., Ni, W., Chen, Z., Lin, B., Lai, L., Ouyang, Z., & Fan, J. (2024). Microplastic Particles Detected in Fetal Cord Blood, Placenta, and Meconium: A Pilot Study of Nine Mother–Infant Pairs in South China. Toxics, 12(12), 850. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120850










