The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Assessment of Bias Risk and Evidence Quality
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Subgroup and Sensitivity Analyses
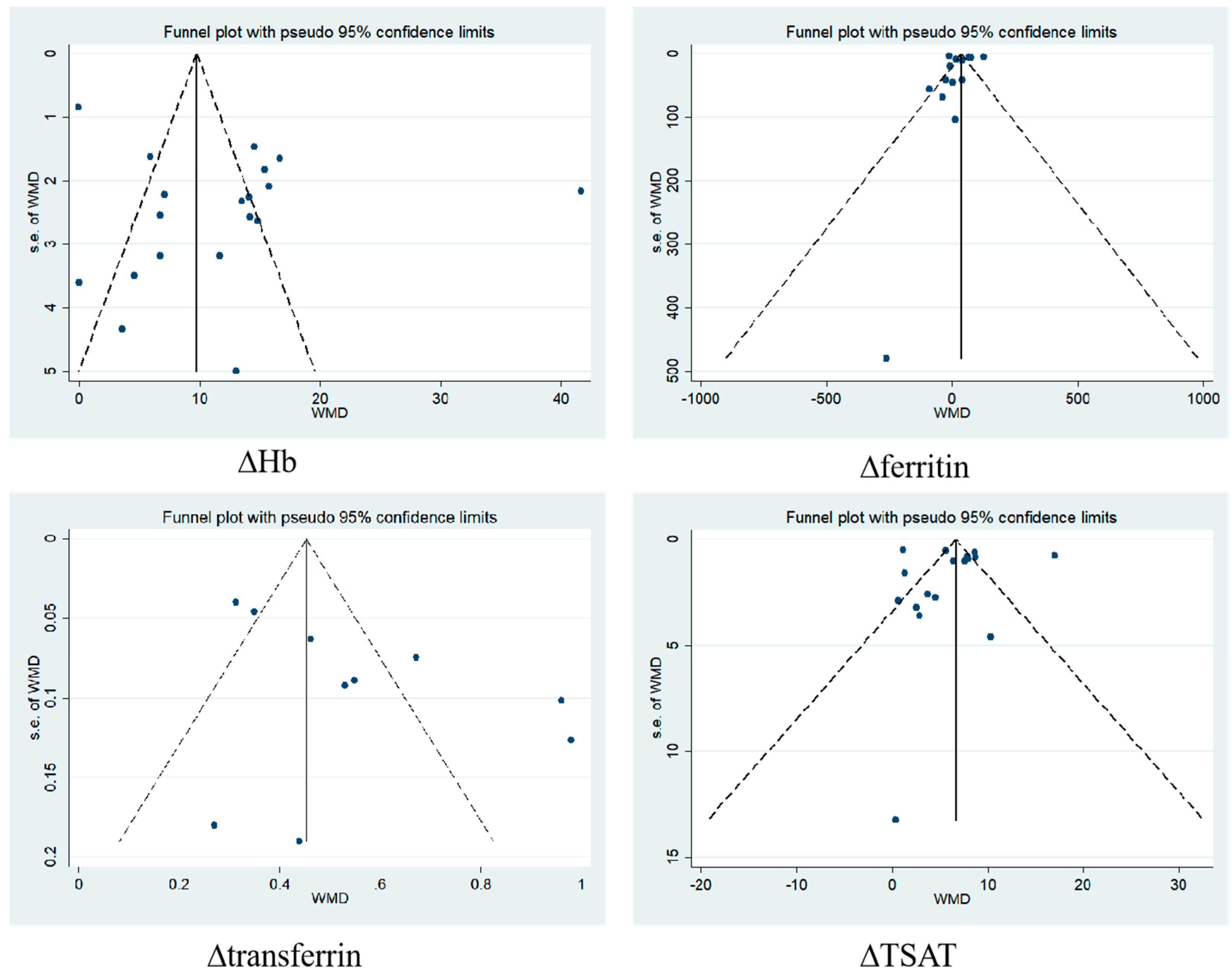
2.7. Publication Bias Analysis
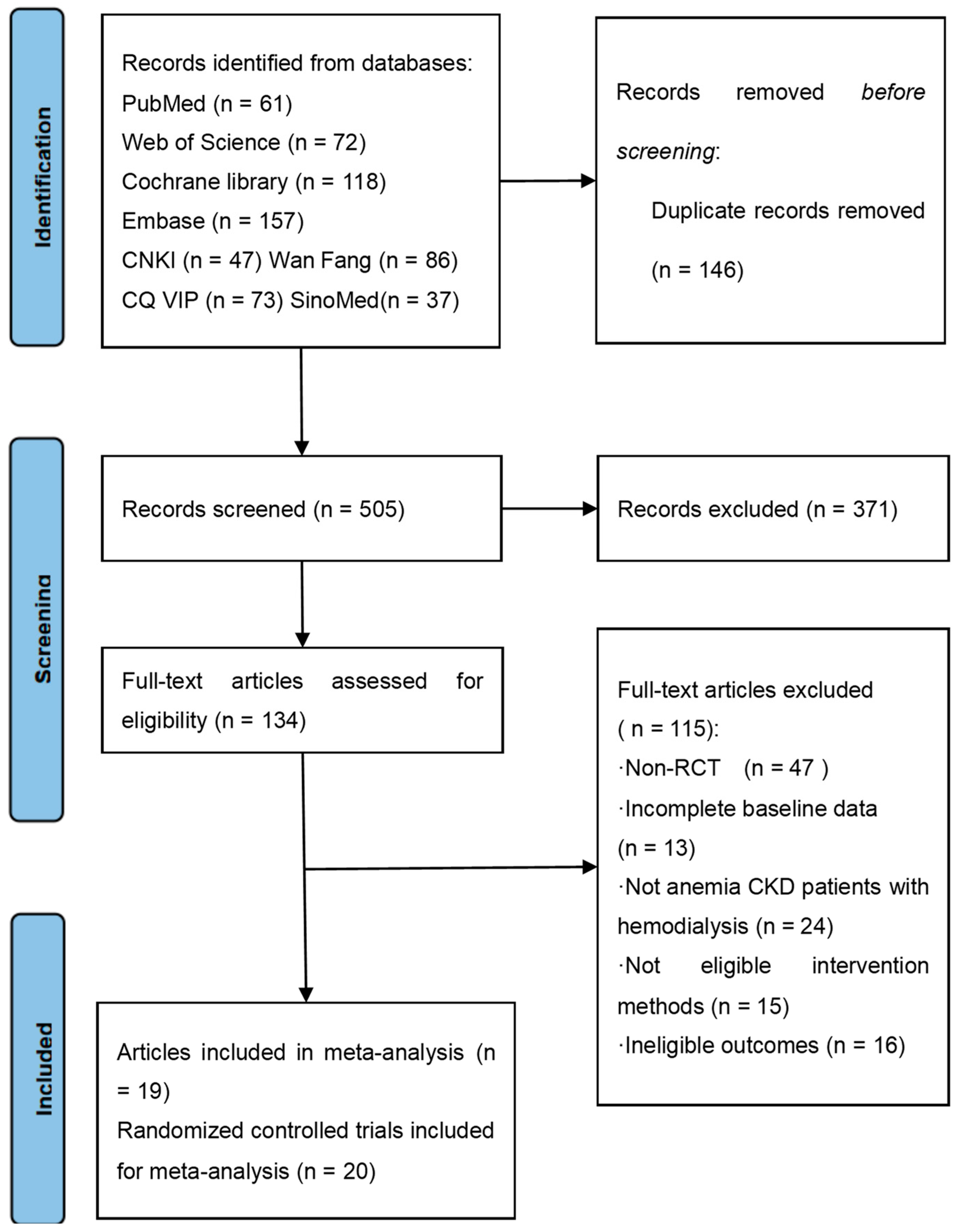
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
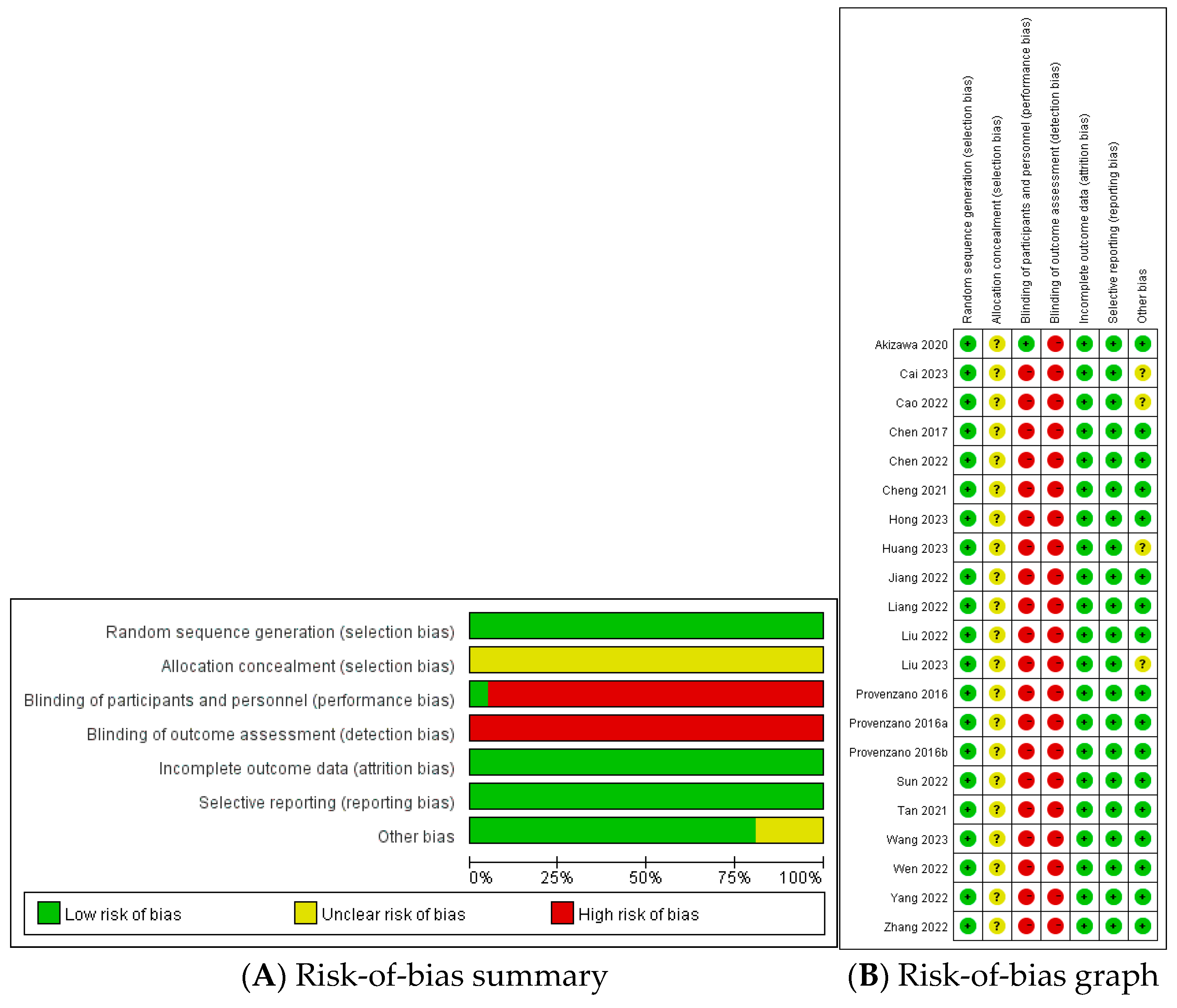
3.2. Evaluation of the Risk of Bias
3.3. Meta-Analysis
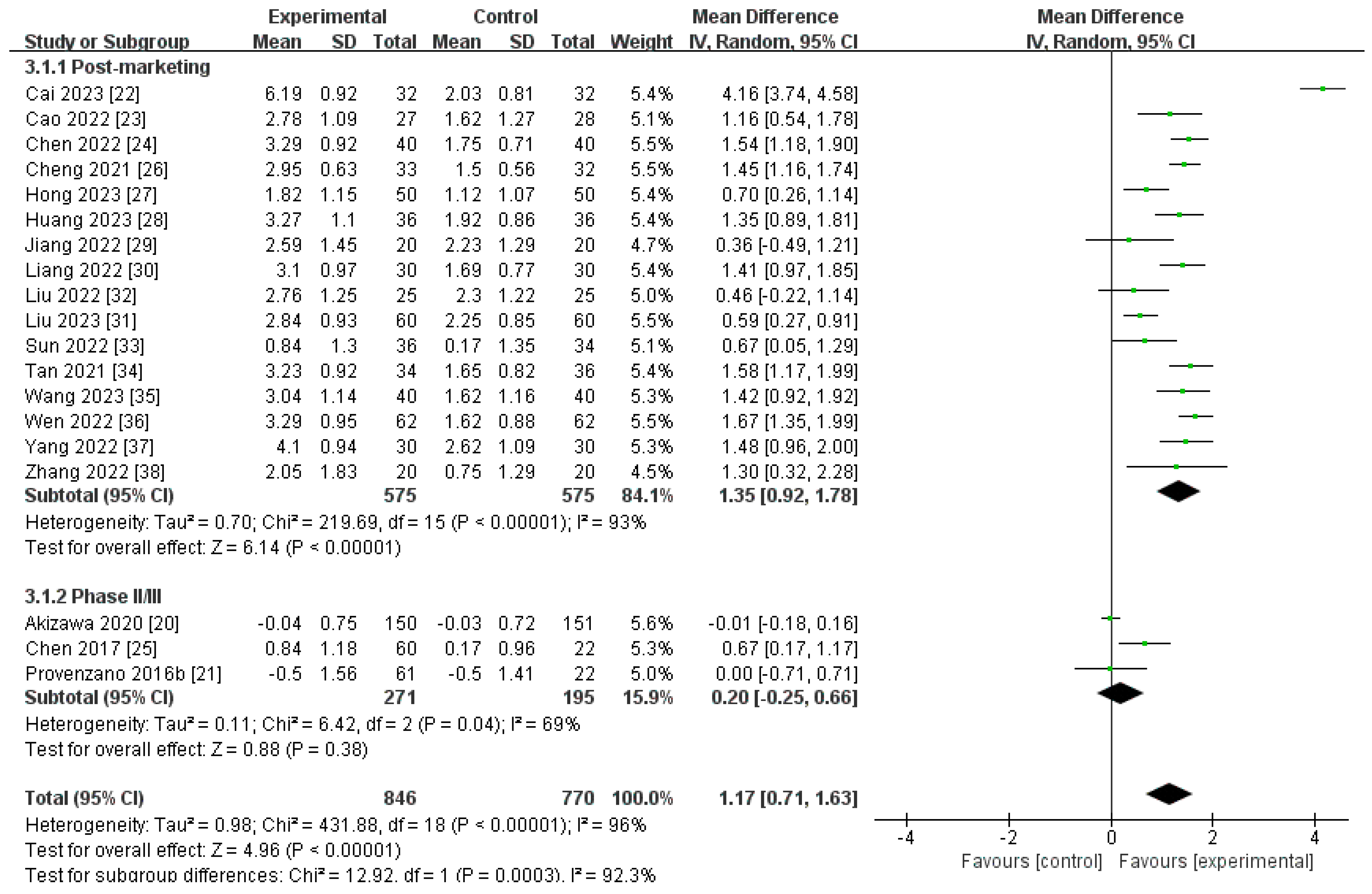
3.3.1. Primary Outcome
Changes in Hb Level from Baseline (∆Hb)
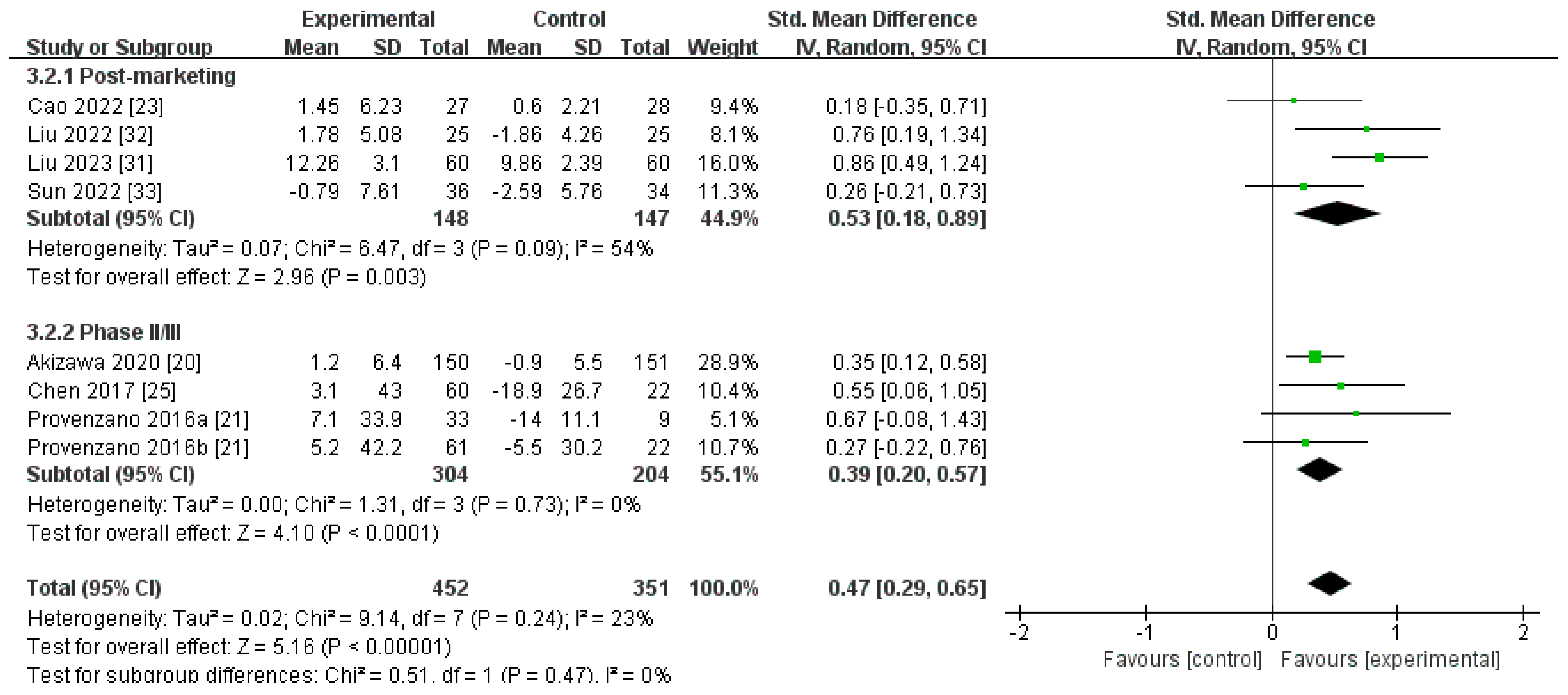
3.3.2. Secondary Outcomes
Changes in SI Levels from Baseline (∆SI)
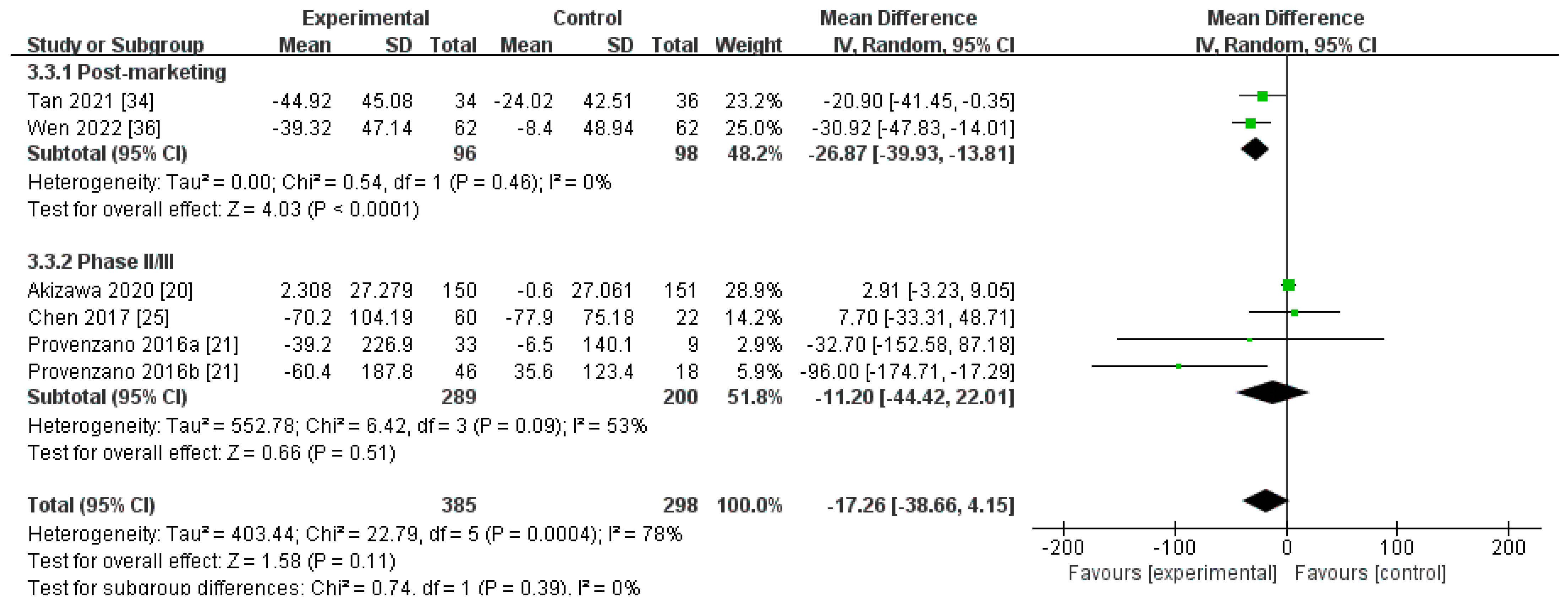
Changes in Hepcidin Levels from Baseline (∆Hepcidin)
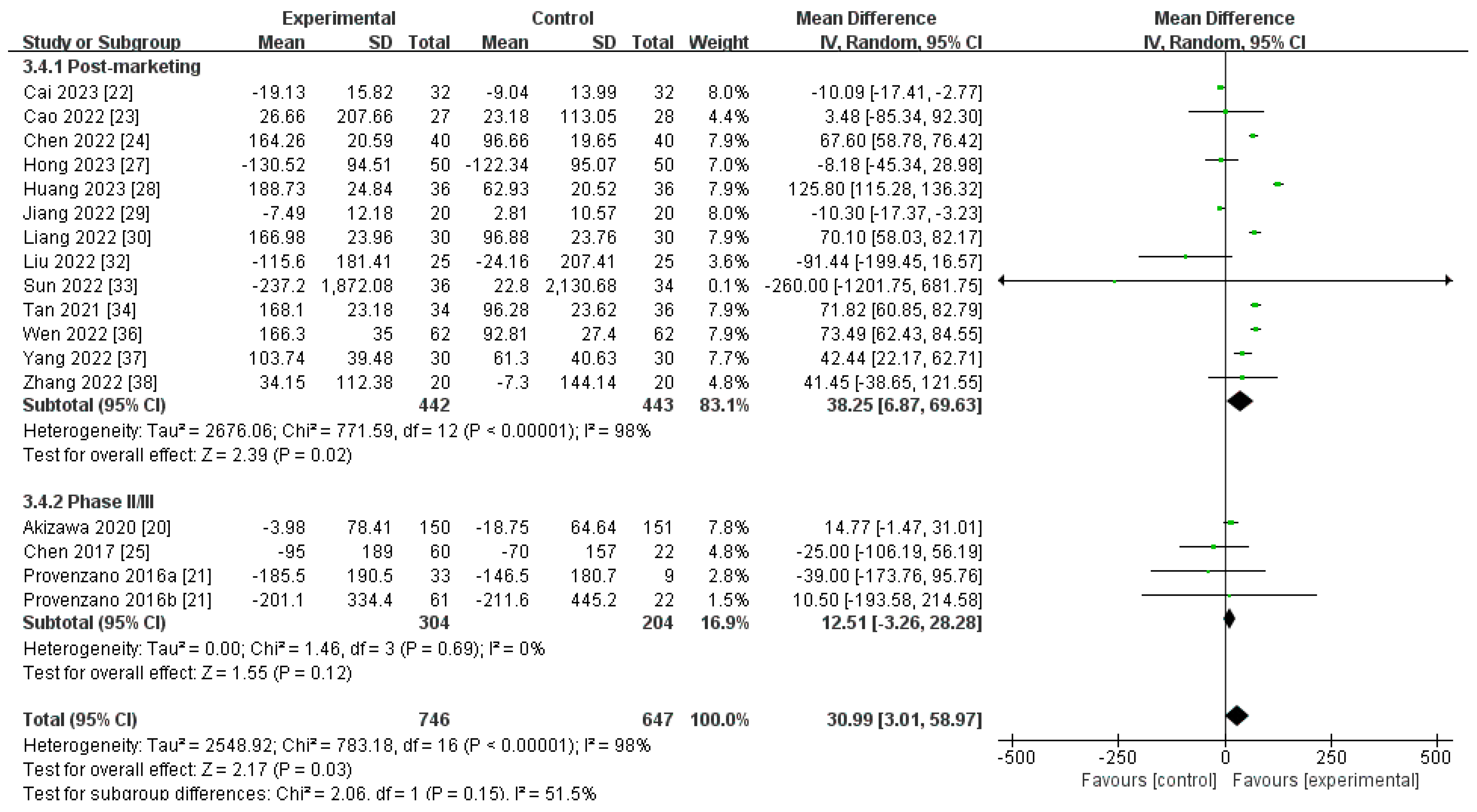
Changes in Ferritin Levels from Baseline (∆Ferritin)
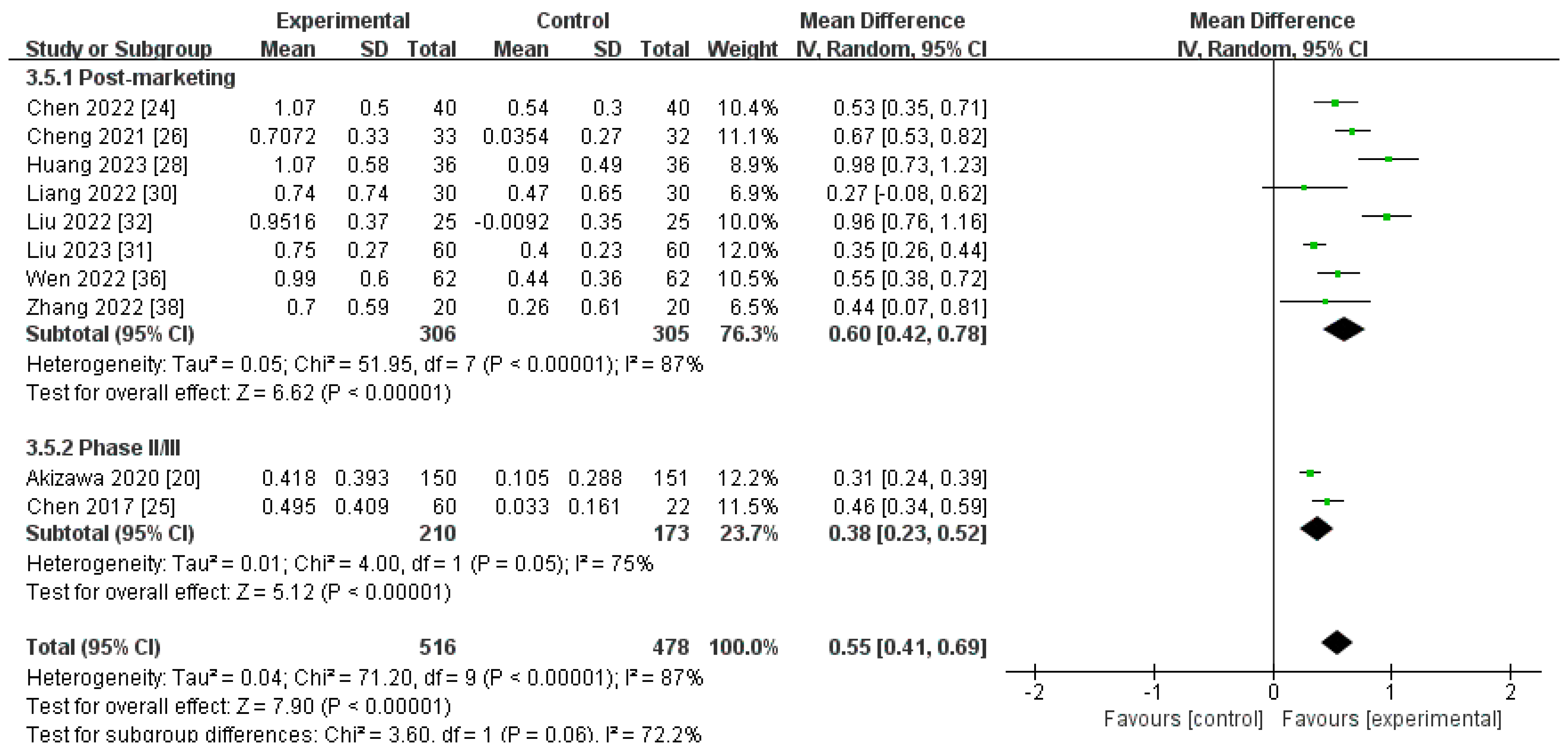
Changes in Transferrin Levels from Baseline (∆Transferrin)
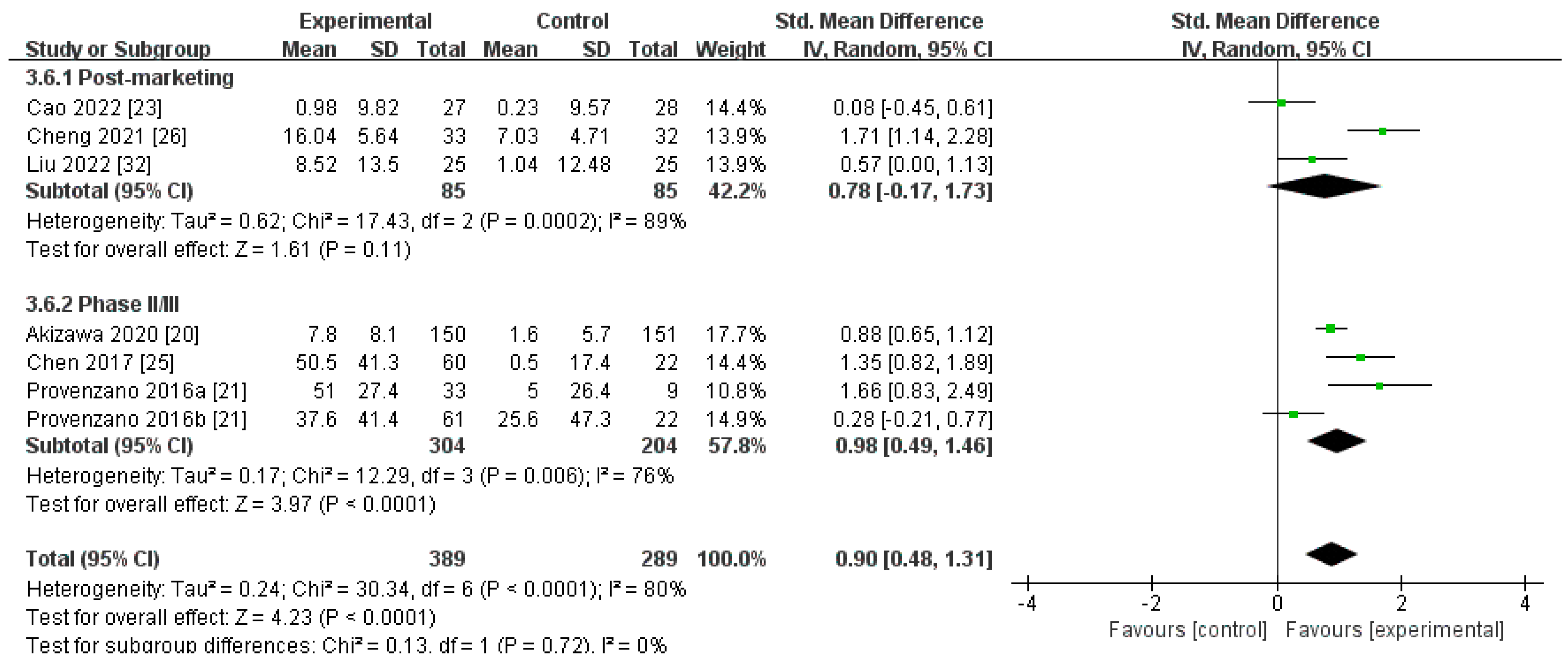
Changes in TIBC Levels from Baseline (∆TIBC)
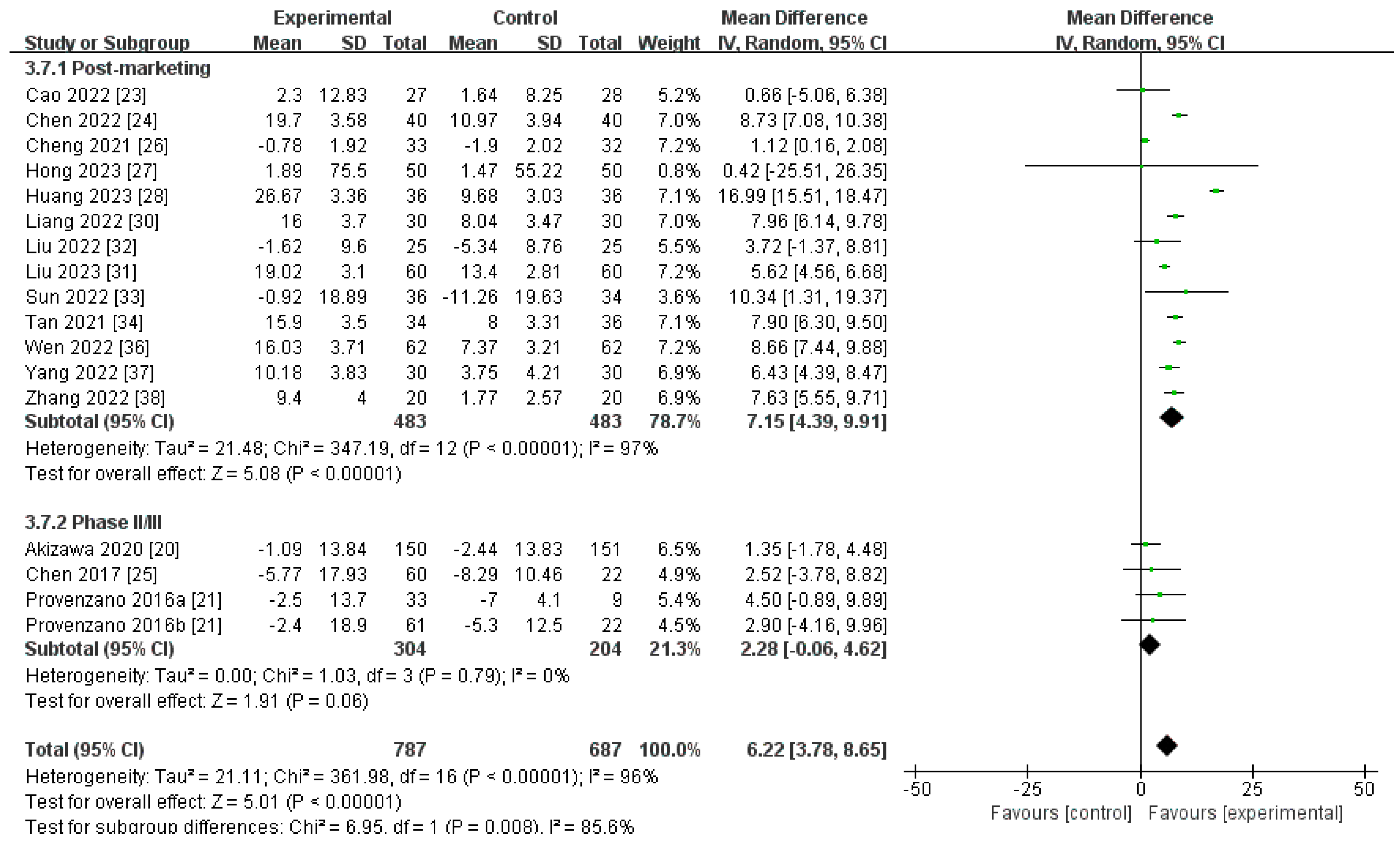
Changes in TSAT Levels from Baseline (∆TSAT)
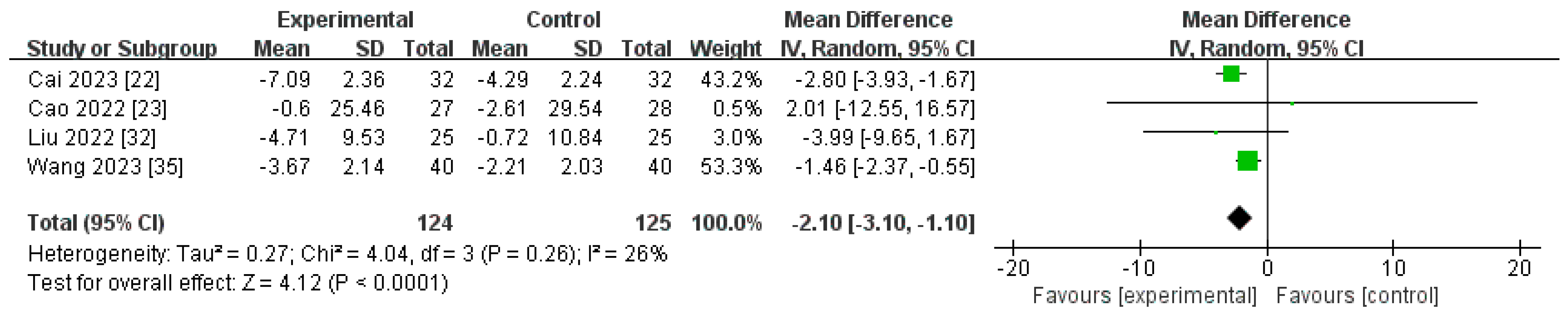
Changes in CRP Levels from Baseline (∆CRP)
3.4. The Safety
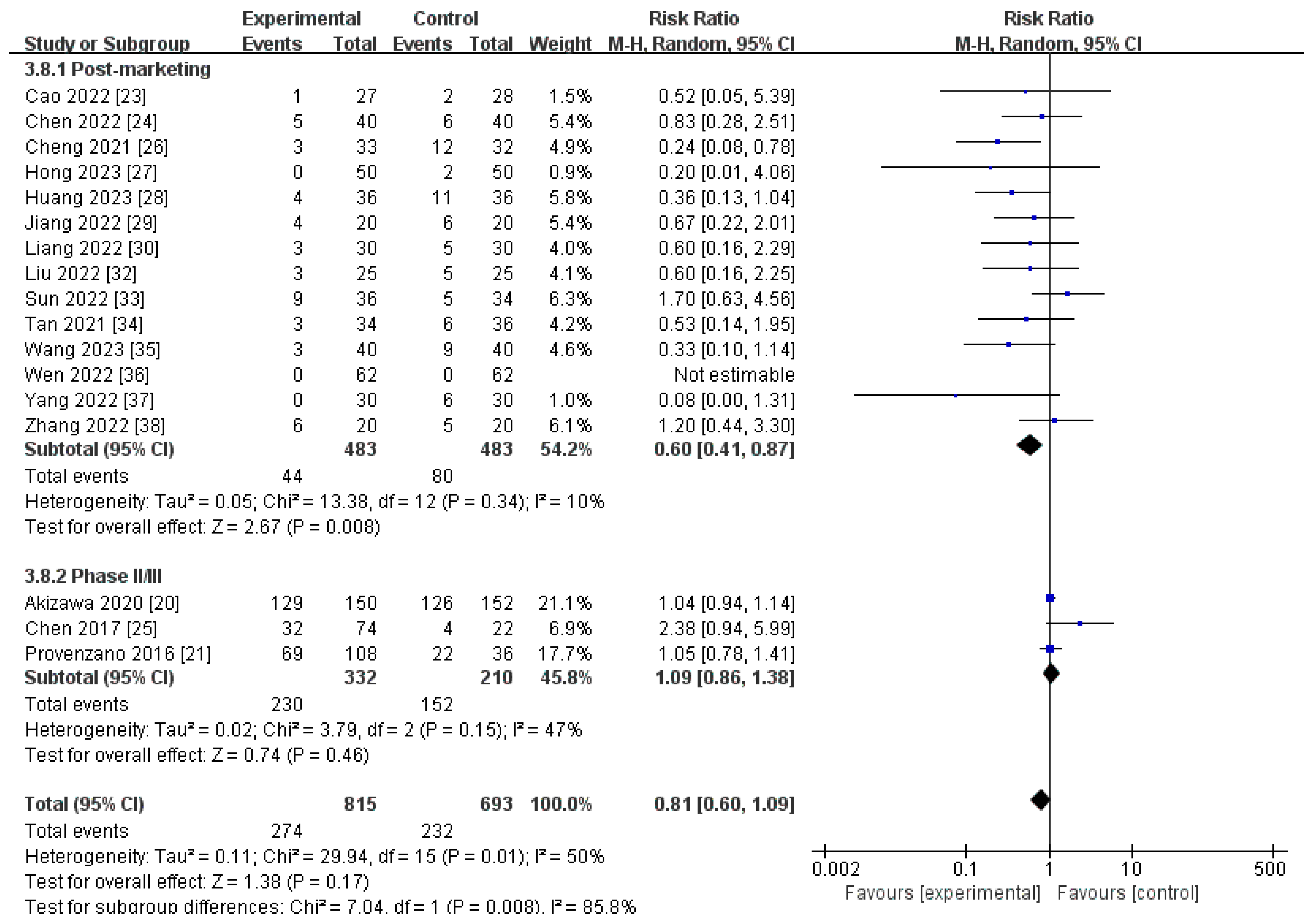
3.4.1. AEs
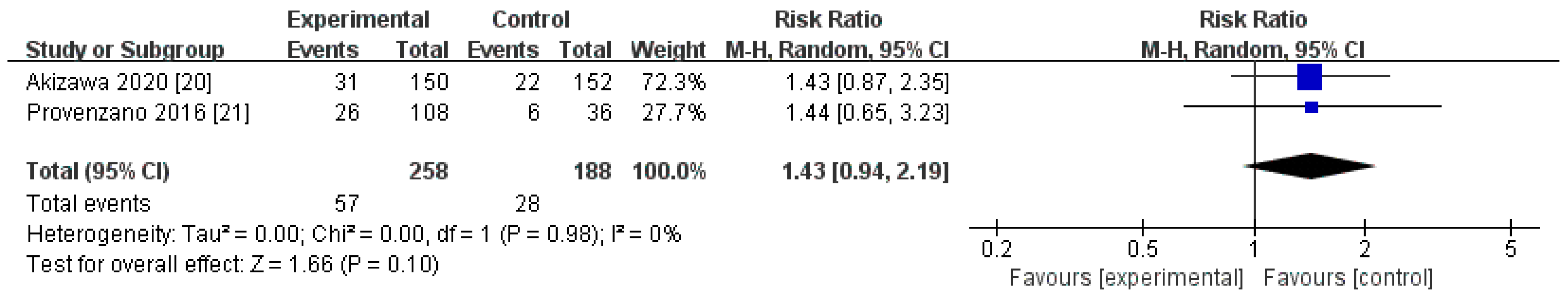
3.4.2. SAEs
3.5. Publication Bias
3.6. Quality of Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsushita, K.; Ballew, S.H.; Wang, A.Y.; Kalyesubula, R.; Schaeffner, E.; Agarwal, R. Epidemiology and risk of cardiovascular disease in populations with chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babitt, J.L.; Lin, H.Y. Mechanisms of anemia in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1631–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stauffer, M.E.; Fan, T. Prevalence of anemia in chronic kidney disease in the United States. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Covic, A.; Eckardt, K.U.; Wiecek, A.; Vanholder, R. Anaemia management in patients with chronic kidney disease: A position statement by the Anaemia Working Group of European Renal Best Practice (ERBP). Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babitt, J.L.; Eisenga, M.F.; Haase, V.H.; Kshirsagar, A.V.; Levin, A.; Locatelli, F.; Małyszko, J.; Swinkels, D.W.; Tarng, D.C.; Cheung, M.; et al. Controversies in optimal anemia management: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Conference. Kidney Int. 2021, 99, 1280–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.L.; Finkelstein, F.O.; Revicki, D.A.; Evans, C.; Wan, S.; Gitlin, M.; Agodoa, I.L. Systematic review of the impact of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents on fatigue in dialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2012, 27, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Hamano, T.; Wada, A.; Masakane, I. Types of Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents and Mortality among Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 30, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minutolo, R.; Garofalo, C.; Chiodini, P.; Aucella, F.; Del Vecchio, L.; Locatelli, F.; Scaglione, F.; De Nicola, L. Types of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and risk of end-stage kidney disease and death in patients with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2021, 36, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Szczech, L.; Tang, K.L.; Barnhart, H.; Sapp, S.; Wolfson, M.; Reddan, D. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2085–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, M.R. Managing Anemia across the Stages of Kidney Disease in Those Hyporesponsive to Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 450–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, J.; Martín, L.; Broseta, J.J.; Cases, A. Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: From Pathophysiology and Current Treatments, to Future Agents. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 642296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umanath, K.; Jalal, D.I.; Greco, B.A.; Umeukeje, E.M.; Reisin, E.; Manley, J.; Zeig, S.; Negoi, D.G.; Hiremath, A.N.; Blumenthal, S.S.; et al. Ferric Citrate Reduces Intravenous Iron and Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent Use in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbane, S.; Block, G.A.; Loram, L.; Neylan, J.; Pergola, P.E.; Uhlig, K.; Chertow, G.M. Effects of Ferric Citrate in Patients with Nondialysis-Dependent CKD and Iron Deficiency Anemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Wish, J.B. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: A Potential New Treatment for Anemia in Patients With CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Roxadustat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, H.; Fu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wei, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, W.J. The efficacy and safety of roxadustat for anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2021, 36, 1603–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Hao, C.; Liu, B.C.; Lin, H.; Wang, C.; Xing, C.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Roxadustat Treatment for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Long-Term Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Li, X.; Niu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Zuo, L. Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat in Chinese Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akizawa, T.; Iwasaki, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Majikawa, Y.; Reusch, M. Phase 3, Randomized, Double-Blind, Active-Comparator (Darbepoetin Alfa) Study of Oral Roxadustat in CKD Patients with Anemia on Hemodialysis in Japan. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 31, 1628–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Besarab, A.; Wright, S.; Dua, S.; Zeig, S.; Nguyen, P.; Poole, L.; Saikali, K.G.; Saha, G.; Hemmerich, S.; et al. Roxadustat (FG-4592) Versus Epoetin Alfa for Anemia in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis: A Phase 2, Randomized, 6- to 19-Week, Open-Label, Active-Comparator, Dose-Ranging, Safety and Exploratory Efficacy Study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Fu, T. Study on the efficacy and mechanism of action of roxadustat in patients with uremia on maintenance hemodialysis with renal anemia. Chin. Foreign Med. Res. 2023, 21, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Wang, F.; Mo, Y. Comparison of the clinical effects of roxadustat and erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 2022, 15, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N. Analysis of the clinical therapeutic effect of roxadustat on renal anemia in hemodialysis patients. China Foreign Med. Treat. 2022, 41, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Qian, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, X.; Mei, C.; Hao, C.; Jiang, G.; Lin, H.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, L.; et al. Phase 2 studies of oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG-4592 for treatment of anemia in China. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Wei, Z.; Shi, H.; Li, G.; Wu, X. Efficacy of roxadustat in the treatment of refractory renal anemia in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. J. Clin. Med. Pract. 2021, 25, 75–77, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, H.; Xu, F. Efficacy of roxadustat versus erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia combined with hemodialysis in the elderly and the effect on cardiovascular indicators. Chin. J. Gerontol. 2023, 43, 2903–2906. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Wei, F. Comparison of oral roxadustat and recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of patients with renal anemia combined with chronic maintenance dialysis. China Mod. Med. 2023, 30, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Hong, D.; Du, Y.; Gan, C.; Chen, Q.; Guan, X.; Deng, F. Observation on the efficacy and safety of roxadustat in the treatment of hemodialysis patients with renal anemia. Pract. Pharm. Clin. Remedies 2022, 25, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Li, W.; Wu, M. Effect of roxadustat on anemia-related indicators and iron metabolism indicators in patients with renal anemia combined with hemodialysis. Int. J. Transplant. Hemopurif. 2022, 20, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Feng, L.; Wu, L.; Lai, Y.; Hong, R. Effectiveness of roxadustat capsules in the treatment of renal anemia in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis and the effect on biochemical indexes. MedicaI Innov. China 2023, 20, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Wan, Y.; Bai, Y. Efficacy and safety of roxadustat in the treatment of renal anemia in elderly patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Anhui Med. J. 2022, 43, 747–752. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, W.; Tong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J.; He, H.; Xu, X. Comparison of the efficacy of roxadustat and recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia in patients on maintenance hemodialysis. Int. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 42, 867–871. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, P.; Luo, L.; Deng, W.; Tan, X. A comparative study of the clinical efficacy of roxadustat and recombinant human erythropoietin in the treatment of renal anemia on hemodialysis. Chin. J. Clin. Ration. Drug Use 2021, 14, 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yang, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, L. Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of roxadustat in hemodialysis patients with renal anemia based on the maximum difference between pre- and post-treatment changes in erythropoietin and interleukin-6 levels and hemoglobin. J. Clin. Nephrol. 2023, 23, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X.; Yang, J. Comparison of the clinical effects of roxadustat and erythropoietin in the treatment of patients with renal anemia complicated by maintenance hemodialysis. Intern. Med. 2022, 17, 83–85, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L. Analysis of the efficacy of roxadustat in the treatment of renal anemia in patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis. Mod. Diagn. Treat. 2022, 33, 1769–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, j.; Zhou, h.; Qiu, x.; Tu, Y. Efficacy and safety of roxadustat capsules versus recombinant human erythropoietin injection in the treatment of renal anemia on maintenance hemodialysis. Int. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 42, 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- Del Balzo, U.; Signore, P.E.; Walkinshaw, G.; Seeley, T.W.; Brenner, M.C.; Wang, Q.; Guo, G.; Arend, M.P.; Flippin, L.A.; Chow, F.A.; et al. Nonclinical Characterization of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor Roxadustat, a Novel Treatment of Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 374, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenendaal-van de Meent, D.; Kerbusch, V.; Kaspera, R.; Barroso-Fernandez, B.; Galletti, P.; Klein, G.K.; den Adel, M. Effect of Kidney Function and Dialysis on the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Roxadustat, an Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 46, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, R.; Tumlin, J.; Zabaneh, R.; Chou, J.; Hemmerich, S.; Neff, T.B.; Yu, K.P. Oral Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitor Roxadustat (FG-4592) for Treatment of Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Placebo-Controlled Study of Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Profiles in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 60, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hou, J.; Li, J.; Su, S.S.; Xue, S. Roxadustat for the treatment of anemia in patients with chronic kidney diseases: A meta-analysis. Aging 2021, 13, 17914–17929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Fu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Chi, K.; Geng, X.; Mao, Z.; Song, C.; Sun, G.; Hong, Q.; Cai, G.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Roxadustat for Anemia in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 724456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gafter-Gvili, A.; Schechter, A.; Rozen-Zvi, B. Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Acta. Haematol. 2019, 142, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, B.; Meindl, E.; Wagner, S.; Tilg, H.; Zoller, H. Intravenous iron supplementation therapy. Mol. Aspects Med. 2020, 75, 100862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakesmith, H.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Ironing out Ferroportin. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Erythropoietic regulators of iron metabolism. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrighting, D.M.; Andrews, N.C. Interleukin-6 induces hepcidin expression through STAT3. Blood 2006, 108, 3204–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, C.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tomosugi, N.; Maeda, K. A Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Stabilizer Improves Hematopoiesis and Iron Metabolism Early after Administration to Treat Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, C.; Tsuchiya, K.; Maeda, K. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors and Iron Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Geng, X.; Chi, K.; Song, C.; Wu, D.; Liu, C.; Hong, Q. Efficacy and Safety of Daprodustat Vs rhEPO for Anemia in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 746265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishbane, S.; Pollock, C.A.; El-Shahawy, M.; Escudero, E.T.; Rastogi, A.; Van, B.P.; Frison, L.; Houser, M.; Pola, M.; Little, D.J.; et al. Roxadustat Versus Epoetin Alfa for Treating Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease on Dialysis: Results from the Randomized Phase 3 ROCKIES Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Yang, H.; Geng, Y.; Tang, J.; Kang, Y.; Qi, A.; Li, S. Effects of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors versus erythropoiesis-stimulating agents on iron metabolism and inflammation in patients undergoing dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locatelli, F.; Del Vecchio, L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl Hydroxyl Domain Inhibitors: From Theoretical Superiority to Clinical Noninferiority Compared with Current ESAs? J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 1966–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besarab, A.; Chernyavskaya, E.; Motylev, I.; Shutov, E.; Kumbar, L.M.; Gurevich, K.; Chan, D.T.; Leong, R.; Poole, L.; Zhong, M.; et al. Roxadustat (FG-4592): Correction of Anemia in Incident Dialysis Patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.N.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, S.; You, L.L. Roxadustat alleviates the inflammatory status in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis with erythropoiesis-stimulating agent resistance by increasing the short-chain fatty acids producing gut bacteria. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, A.F.; Liang, J.X.; Yao, L.; Han, J.L.; Zhou, L.J. Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor roxadustat (FG-4592) protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting inflammation. Ren. Fail. 2021, 43, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M. Roxadustat (FG-4592) protects against ischaemia-induced acute kidney injury via improving CD73 and decreasing AIM2 inflammasome activation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2023, 38, 858–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besarab, A.; Provenzano, R.; Hertel, J.; Zabaneh, R.; Klaus, S.J.; Lee, T.; Leong, R.; Hemmerich, S.; Yu, K.H.; Neff, T.B. Randomized placebo-controlled dose-ranging and pharmacodynamics study of roxadustat (FG-4592) to treat anemia in nondialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (NDD-CKD) patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2015, 30, 1665–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckardt, K.U.; Agarwal, R.; Aswad, A.; Awad, A.; Block, G.A.; Bacci, M.R.; Farag, Y.M.K.; Fishbane, S.; Hubert, H.; Jardine, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Vadadustat for Anemia in Patients Undergoing Dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chertow, G.M.; Pergola, P.E.; Farag, Y.M.K.; Agarwal, R.; Arnold, S.; Bako, G.; Block, G.A.; Burke, S.; Castillo, F.P.; Jardine, A.G.; et al. Vadadustat in Patients with Anemia and Non-Dialysis-Dependent CKD. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yin, H.; Yang, L.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Liao, D. The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 779694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiky, B.; Schömig, M.; Esposito, C.; Barratt, J.; Reusch, M.; Valluri, U.; Sulowicz, W. Roxadustat for the Maintenance Treatment of Anemia in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease on Stable Dialysis: A European Phase 3, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Controlled Study (PYRENEES). Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 5361–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study ID | Country | Single/Multicenter | Phase | Sample Size (T/C) | Gender Ratio (Male/Female) | Age (Years) Mean ± SD | Baseline Hb (g/dL) | Interventions | Dosage of Medication | Control | Dosage of Medication | Study Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akizawa 2020 [20] | Japan | multicenter | phase III | 150/151 | T:101/49 (2.06) C:107/44 (2.43) | T:64.6 ± 11.7 C:64.9 ± 10.1 | T:11.02 ± 0.56 C:11.01 ± 0.60 | roxadustat | 70 mg or 100 mg, TIW | darbepoetin alfa | 10–60 ug, QIW | 24 weeks |
| Chen 2017 [25] | China | multicenter | phase II | 74/22 | T:45/29 (1.55) C:13/9 (1.44) | 50.8 ± 12.6 | 10.7 ± 0.8 | FG-4592 | 1.1–1.8 mg/kg, 1.5–2.3 mg/kg or 1.7–2.3 mg/kg, TIW | epoetin alfa | 3000 to 20,000 IU/week | 6 weeks |
| Provenzano 2016a [21] | USA | multicenter | phase II | 41/13 | T:27/14 (1.93) C:9/4 (2.25) | T:55.8 ± 13.4 C:59.5 ± 10.1 | T:11.3 ± 0.6 C:11.5 ± 0.6 | roxadustat | 1.0 mg/kg, 1.5 mg/kg, 2.0 mg/kg, or 1.8 mg/kg, TIW | epoetin alfa | 136.3 ± 47.7 IU/kg/wk | 6 weeks |
| Provenzano 2016b [21] | USA | multicenter | phase II | 67/23 | T:45/22 (2.05) C:14/9 (1.56) | T:56.9 ± 12.1 C:57.0 ± 11.6 | T:11.2 ± 0.7 C:11.2 ± 1.0 | roxadustat | 1.3 mg/kg; 2.0 mg/kg; 70–120–200 mg (1.68 ± 0.65 mg/kg, TIW) | epoetin alfa | 173.4 ± 83.7 IU/kg/wk | 19 weeks |
| Cai 2023 [22] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 32/32 | T:18/14 (1.29) C:17/15 (1.13) | T:51.98 ± 9.20 C:52.15 ± 9.25 | T:132.5 ± 10.58 C:92.85 ± 9.15 | roxadustat | 70–120 mg, TIW | rhEPO | 2000 IU, BIW/TIW | 2 months |
| Cao 2022 [23] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 27/28 | T:14/13 (1.08) C:12/16 (0.75) | T:57.36 ± 7.75 C:58.94 ± 9.11 | T:105.11 ± 10.24 C:98.55 ± 12.11 | roxadustat | 100 mg (45–60 kg) or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–120 U/kg, TIW | 3 months |
| Chen 2022 [24] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 40/40 | T:18/22 (0.82) C:20/20 (1.00) | T:53.40 ± 3.07 C:53.33 ± 3.11 | T:103.55 ± 10.11 C:88.21 ± 5.68 | roxadustat | 100 mg (45–60 kg) or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–120 IU/kg, BIW/TIW | 3 months |
| Cheng 2021 [26] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 33/32 | T:20/13 (1.54) C:19/13 (1.46) | T:41.58 ± 2.15 C:41.52 ± 2.13 | T:109.63 ± 7.05 C:95.37 ± 5.88 | roxadustat | 100 mg (<60 kg), or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | Continued their previous doses | 6 weeks |
| Hong 2023 [27] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 50/50 | T:28/22 (1.27) C:26/24 (1.08) | T:69.52 ± 8.97 C:70.12 ± 9.45 | T:94.29 ± 12.41 C:85.54 ± 11.37 | roxadustat | 100 mg (≥45 kg and <60 kg), 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–150 IU/kg, TIW | 12 weeks |
| Huang 2023 [28] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 36/36 | T:20/16 (1.25) C:24/12 (2.00) | T:51.36 ± 1.72 C:51.25 ± 1.31 | T:112.91 ± 12.64 C:100.66 ± 9.44 | roxadustat | 100 mg (<60 kg), 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 80–150 U/kg, TIW | 3 months |
| Jiang 2022 [29] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 20/20 | T:10/10 (1.00) C:11/8 (1.38) | T:50.1 ± 20.6 C:47.5 ± 17.1 | T:95.38 ± 16.42 C:93.59 ± 14.73 | roxadustat | 100 mg (40–60 kg), 120 mg (>60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 10,000–20,000 U, QIW | 12 weeks |
| Liang 2022 [30] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 30/30 | T:19/11 (1.73) C:18/12 (1.50) | T:49.98 ± 2.86 C:50.01 ± 2.19 | T:102.83 ± 10.75 C:87.36 ± 8.12 | roxadustat | 100 mg (45–60 kg), 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–120 IU/kg, BIW/TIW | 3 months |
| Liu 2022 [32] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 25/25 | T:13/12 (1.08) C:14/11 (1.27) | T:70.8 ± 4.15 C:71.64 ± 4.8 | T:114.84 ± 10.04 C:109.04 ± 9.24 | roxadustat | 100 mg (45–60 kg) or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–150 IU/kg, BIW/TIW | 24 weeks |
| Liu 2023 [31] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 60/60 | T:33/27 (1.22) C:32/28 (1.14) | T:60.51 ± 7.66 C:60.36 ± 7.71 | T:115.32 ± 10.32 C:109.31 ± 9.1 | roxadustat | 100 mg (45–60 kg) or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 120 IU/kg, QIW | 6 months |
| Sun 2022 [33] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 36/34 | T:14/22 (0.64) C:13/21 (0.62) | T:51.65 ± 3.53 C:51.29 ± 2.02 | T:108.33 ± 14.11 C:100.86 ± 10.40 | roxadustat | 120 mg (≥60 kg), or 100 mg (<60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | Continued their previous doses | 24 weeks |
| Tan 2021 [34] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 34/36 | T:18/16 (1.13) C:18/18 (1.00) | T:45.6 ± 7.1 C:47.6 ± 6.7 | T:103.65 ± 10.01 C:87.12 ± 8.36 | roxadustat | 100 mg (40–60 kg) and following 120 mg, TIW | rhEPO | 100 U/kg, TIW | 3 months |
| Wang 2023 [35] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 40/40 | T:20/20 (1.00) C:21/19 (1.11) | T:52.85 ± 4.29 C:52.63 ± 4.17 | T:104.76 ± 12.23 C:90.45 ± 12.70 | roxadustat | 100 mg (≤60 kg) or 120 mg (>60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 80–120 IU/kg, TIW | 8 weeks |
| Wen 2022 [36] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 62/62 | T:34/28 (1.21) C:32/30 (1.07) | T:41.36 ± 8.92 C:43.43 ± 10.15 | T:104.3 ± 10.42 C:87.58 ± 9.24 | roxadustat | 500 mg (40–60 kg) or 120 mg (>60 kg), BIW/TIW | rhEPO | 100–150 U/kg, TIW | 3 months |
| Yang 2022 [37] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 30/30 | T:21/9 (2.33) C:19/11 (1.73) | T:57.17 ± 8.62 C:56.42 ± 8.37 | T:121.75 ± 10.08 C:108.38 ± 12.1 | roxadustat | 2 mg/kg, TIW | rhEPO | 30–50 IU/kg, TIW | 4 weeks |
| Zhang 2022 [38] | China | single-center | post-marketing | 20/20 | _ | T:53.05 ± 14.85 C:58.10 ± 13.87 | T:107.35 ± 20.72 C:100.75 ± 10.35 | roxadustat | 100 mg (<60 kg) or 120 mg (≥60 kg), TIW | rhEPO | 100–150 IU/kg, TIW | 12 weeks |
| Outcomes | Roxadustat | ESAs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | n | I2 | p | Meta-Analysis | |
| Primary outcome | |||||
| ∆Hb | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 575 | 575 | 93% | <0.00001 | MD 1.35[0.92, 1.78] |
| Phase II/III studies | 271 | 195 | 69% | 0.38 | MD 0.20[−0.25, 0.66] |
| Pooled results | 846 | 770 | 96% | <0.00001 | MD 1.17[0.71, 1.63] |
| Secondary outcomes | |||||
| ∆SI | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 148 | 147 | 54% | 0.003 | SMD 0.53[0.18, 0.89] |
| Phase II/III studies | 304 | 204 | 0% | <0.0001 | SMD 0.39[0.20, 0.57] |
| Pooled results | 452 | 351 | 23% | <0.00001 | SMD 0.47[0.29, 0.65] |
| ∆Hepcidin | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 96 | 98 | 0% | <0.0001 | MD −26.87[−39.93, −13.81] |
| Phase II/III studies | 289 | 200 | 53% | 0.51 | MD −11.20[−44.42, 22.01] |
| Pooled results | 385 | 298 | 78% | 0.11 | MD −17.26[−38.66, 4.15] |
| ∆Ferritin | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 442 | 443 | 98% | 0.02 | MD 38.25[6.87, 69.63] |
| Phase II/III studies | 304 | 204 | 0% | 0.12 | MD 12.51[−3.26, 28.28] |
| Pooled results | 746 | 647 | 98% | 0.03 | MD 30.99[3.01, 58.97] |
| ∆Transferrin | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 306 | 305 | 87% | <0.00001 | MD 0.60[0.42, 0.78] |
| Phase II/III studies | 210 | 173 | 75% | <0.00001 | MD 0.38[0.23, 0.52] |
| Pooled results | 516 | 478 | 87% | <0.00001 | MD 0.55[0.41, 0.69] |
| ∆TIBC | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 85 | 85 | 89% | 0.11 | SMD 0.78[−0.17, 1.73] |
| Phase II/III studies | 304 | 204 | 76% | <0.0001 | SMD 0.98[0.49, 1.46] |
| Pooled results | 389 | 289 | 80% | <0.0001 | SMD 0.90[0.48, 1.31] |
| ∆TSAT | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 483 | 483 | 97% | <0.00001 | MD 7.15[4.39, 9.91] |
| Phase II/III studies | 304 | 204 | 0% | 0.06 | MD 2.28[−0.06, 4.62] |
| Pooled results | 787 | 687 | 96% | <0.00001 | MD 6.22[3.78, 8.65] |
| ∆CRP | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 124 | 125 | 26% | <0.0001 | MD −2.10[−3.10, −1.10] |
| Safety | |||||
| AEs | |||||
| Post-marketing studies | 483 | 483 | 10% | 0.008 | RR 0.60[0.41, 0.87] |
| Phase II/III studies | 332 | 210 | 47% | 0.46 | RR 1.09[0.86, 1.38] |
| Pooled results | 815 | 693 | 50% | 0.17 | RR 0.81[0.60, 1.09] |
| SAEs | |||||
| Phase II/III studies | 258 | 188 | 0% | 0.10 | RR 1.43[0.94, 2.19] |
| Test | ∆Hb | ∆SI | ∆Hepcidin | ∆Ferritin | ∆Transferrin | ∆TIBC | ∆TSAT | ∆CRP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p Value | ||||||||
| Egger’s test | 0.131 | 0.051 | 0.153 | 0.852 | 0.06 | 0.174 | 0.942 | 0.87 |
| Outcomes | Certainty Assessment | № of Patients | Effect | Certainty | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| № of Studies | Study Design | Risk of Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Other Considerations | Continous | Placebo | Relative | Absolute | ||
| (95% CI) | (95% CI) | |||||||||||
| ∆Hb | 19 | randomised trials | very serious a | serious b | serious | not serious | none | 846 | 770 | - | MD 1.17 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.71 higher to 1.63 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆SI | 8 | randomised trials | very serious a | not serious | serious c | not serious | none | 452 | 351 | - | SMD 0.47 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.29 higher to 0.65 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆Hepcidin | 6 | randomised trials | very serious a | serious b | serious c | serious e | none | 385 | 298 | - | MD 17.26 lower | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (38.66 lower to 4.15 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆SF | 17 | randomised trials | very serious a | very serious d | serious c | not serious | none | 746 | 647 | - | MD 30.99 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (3.01 higher to 58.97 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆TRF | 10 | randomised trials | very serious a | serious b | serious c | not serious | none | 516 | 478 | - | MD 0.55 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.41 higher to 0.69 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆TIBC | 7 | randomised trials | very serious a | serious b | serious c | not serious | none | 389 | 289 | - | SMD 0.9 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.48 higher to 1.31 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆TSAT | 17 | randomised trials | very serious a | very serious d | serious c | not serious | none | 787 | 687 | - | MD 6.22 higher | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (3.78 higher to 8.65 higher) | Very low | |||||||||||
| ∆CRP | 4 | randomised trials | very serious a | not serious | not serious | serious f | none | 124 | 125 | - | MD 2.01 lower | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| GRAD | Very low | |||||||||||
| AEs | 17 | randomised trials | very serious a | not serious | serious c | not serious | none | 274/815 (33.6%) | 232/693 (33.5%) | RR 0.81 | 64 fewer per 1000 | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.60 to 1.09) | (from 134 fewer to 30 more) | Very low | ||||||||||
| SAEs | 2 | randomised trials | very serious a | not serious | serious c | serious g | none | 57/258 (22.1%) | 28/188 (14.9%) | RR 1.43 | 64 more per 1000 | ⨁◯◯◯ |
| (0.94 to 2.19) | (from 9 fewer to 177 more) | Very low | ||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Z.; Tang, J.; Cui, H.; Dong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W. The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxics 2024, 12, 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120846
Geng Y, Zhang S, Cao Z, Tang J, Cui H, Dong Z, Liu Y, Liu W. The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxics. 2024; 12(12):846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120846
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Yunling, Shuaixing Zhang, Zijing Cao, Jingyi Tang, Hailan Cui, Zhaocheng Dong, Yuning Liu, and Weijing Liu. 2024. "The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Toxics 12, no. 12: 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120846
APA StyleGeng, Y., Zhang, S., Cao, Z., Tang, J., Cui, H., Dong, Z., Liu, Y., & Liu, W. (2024). The Efficacy and Safety of Roxadustat for Anemia in Hemodialysis Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Toxics, 12(12), 846. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics12120846





