Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Response of Earthworm Exposed to a Lignin-Modified Crosslinked Hydrogel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents for Hydrogel Synthesis
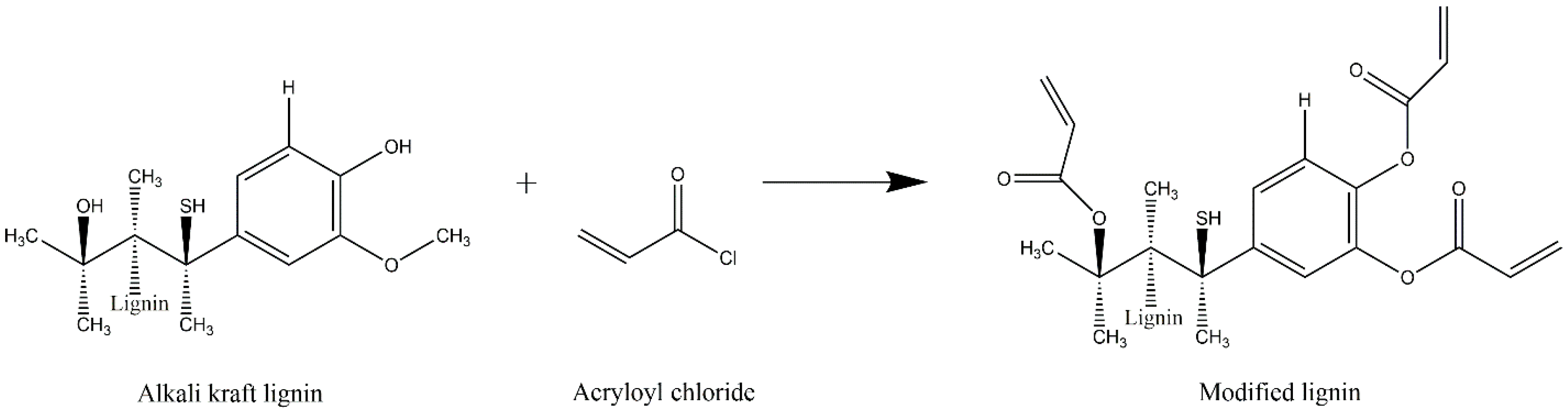
2.2. Modification of Kraft Lignin
2.3. Hydrogel Synthesis
2.4. Hydrogel Characterization
2.4.1. Elemental Analysis
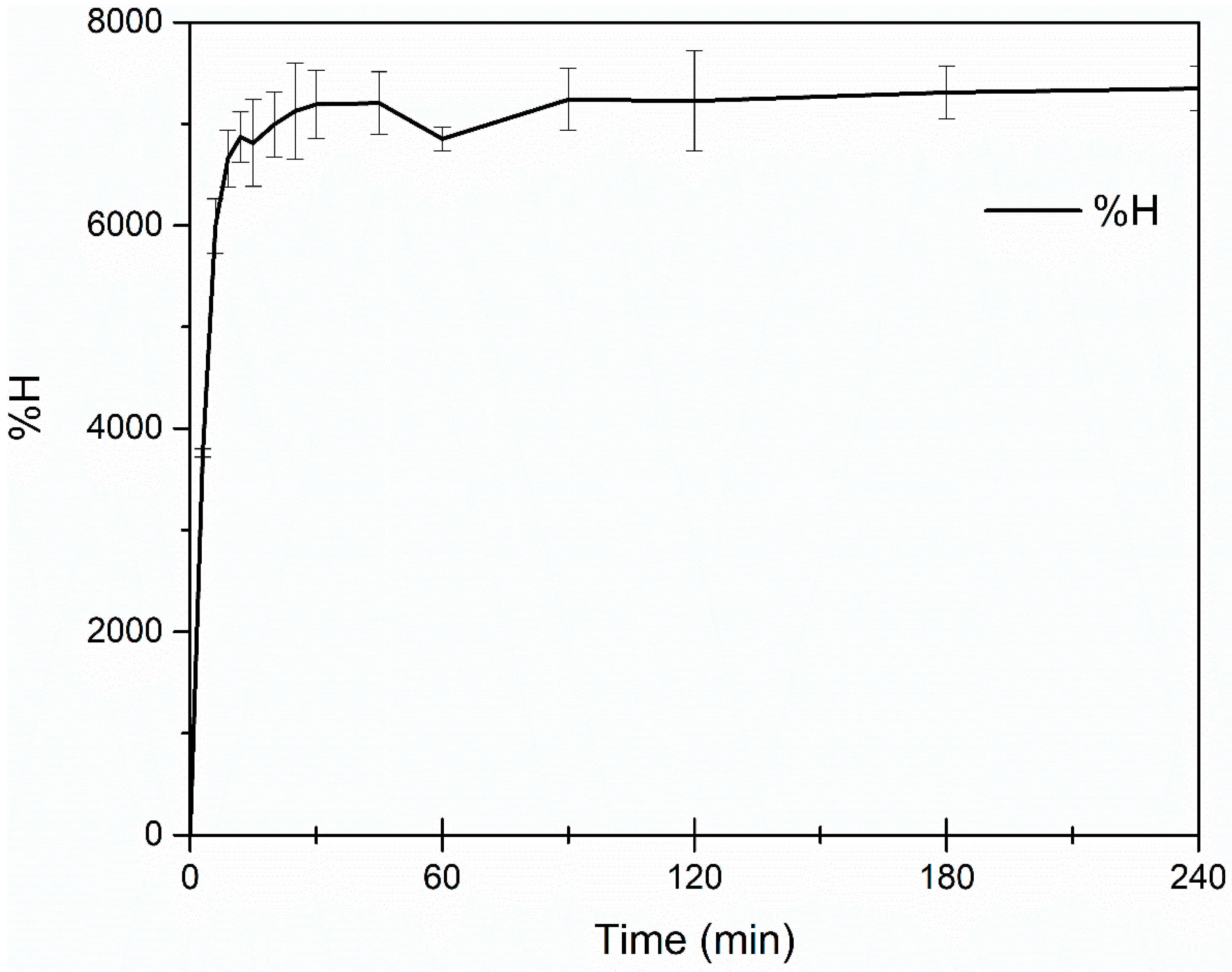
2.4.2. Swelling Kinetics
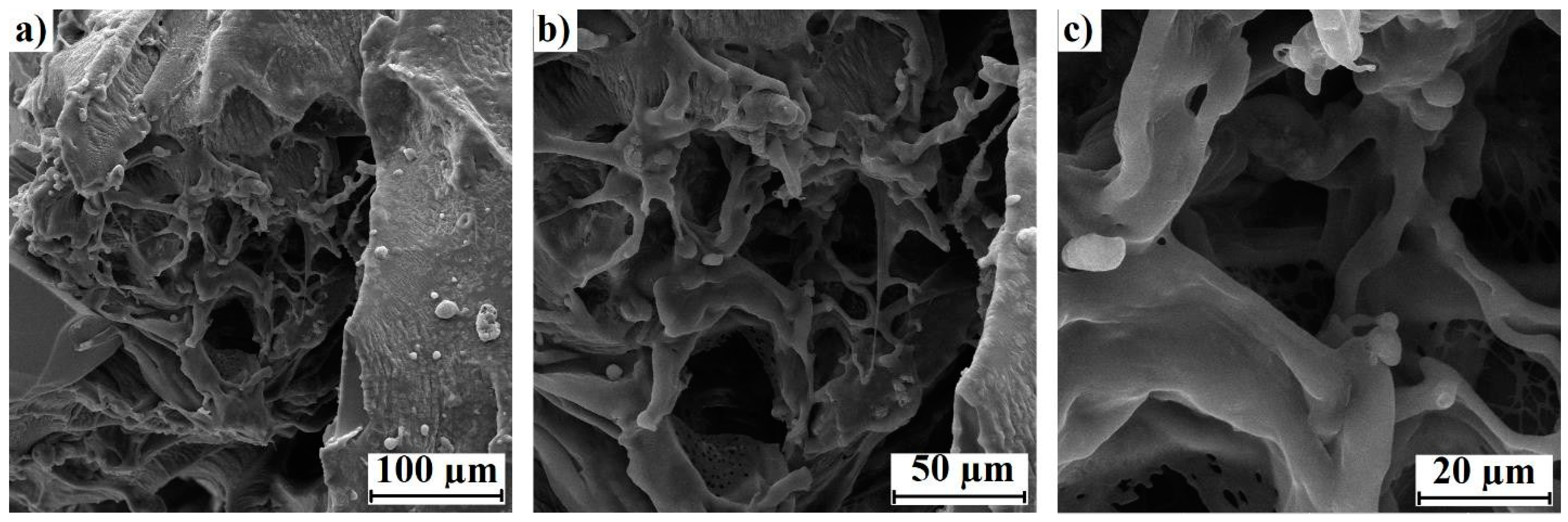
2.4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.5. Organism of Study: Eisenia fetida
2.6. Acute Toxicity Test
2.6.1. Contact Toxicity Test (Contact Test)
2.6.2. Test on Artificial Substrate (PSA)
2.7. Clinical Observations and Acute Toxicity Determinations
2.8. Euthanasia
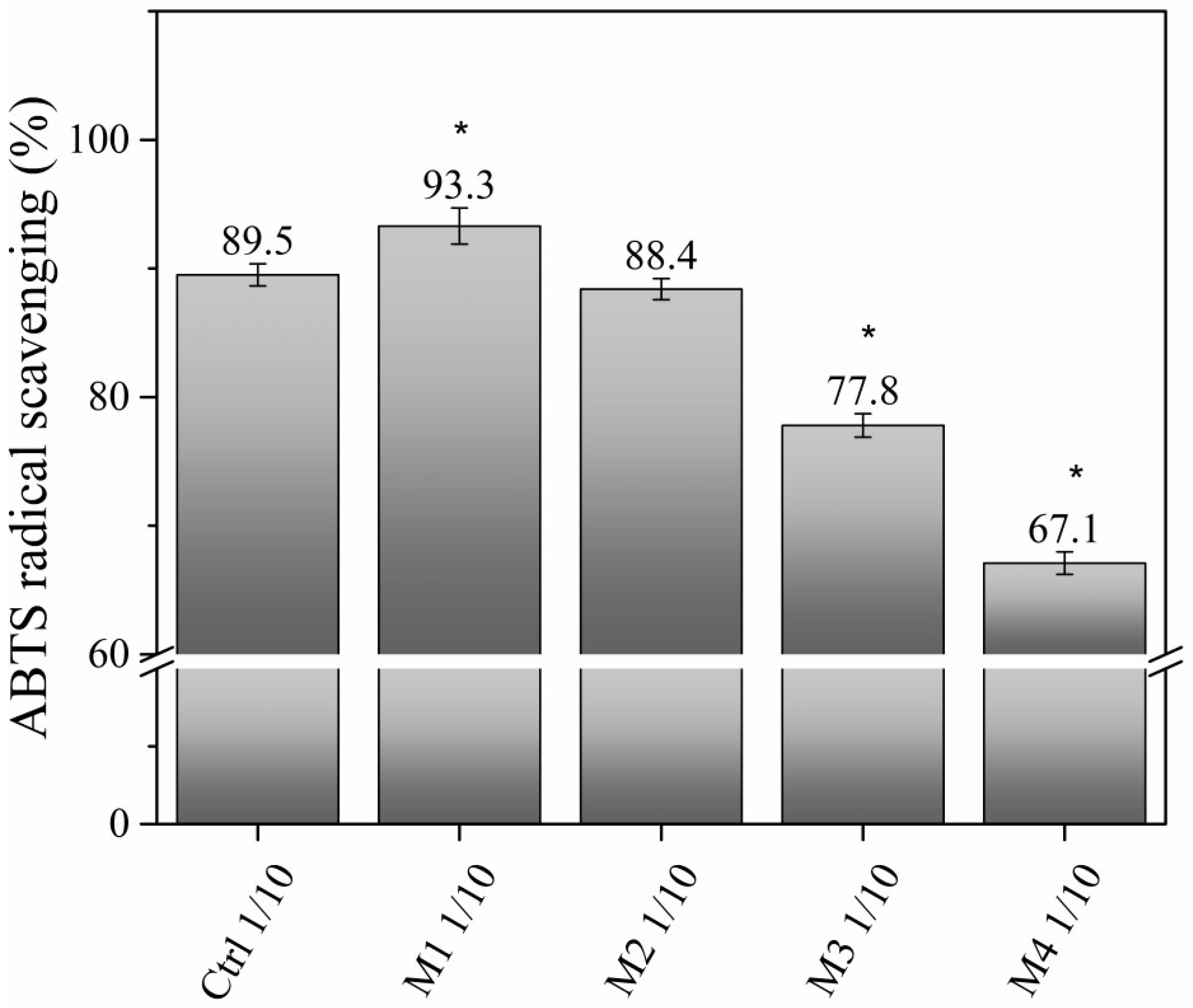
2.9. Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay: ABTS●+ Radical Scavenging Activity of Earthworms Exposed to Hydrogel
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Hydrogel Crosslinked with Modified Kraft Lignin
3.1.1. Elemental Analysis Results
3.1.2. Determination of Hydrogel Swelling
3.1.3. SEM Analysis
3.1.4. FTIR Analysis
3.2. Acute Toxicity Test on Earthworms (Contact Test)
3.2.1. Test Validity
3.2.2. Mortality Rate
3.2.3. Growth Inhibition and Physiological and Behavioral Alterations
3.2.4. Total Antioxidant Capacity Assay: ABTS●+ Radical Scavenging Activity of Earthworms Exposed to Hydrogel
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramirez, A.; Benítez, J.L.; Rojas de Astudillo, L.; Rojas de Gáscue, B. Materiales Polimeros de Tipo Hidrogeles: Revisión Sobre Su Caracterización Mediante Ftir, Dsc, Meb y Met. Rev. Latinoam. Metal. Mater. 2016, 36, 108–130. [Google Scholar]
- Aguero Luztonó, L.; Zaldivar Silva, D.; Escobar Ivirico, J.L. Liberación de Cefalexina a Partir de Hidrogeles de Poli(Acrilamida-Co-Ácido Metacrílico). Biomecánica 2000, 8, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, K.; Banthia, A.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Polymeric Hydrogels: Characterization and Biomedical Applications. Des. Monomers Polym. 2009, 12, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotoudeh, S.; Pourfallah, G.; Barati, A.; Davarnejad, R.; Farahani, M.A.; Memar, A. Dynamical Modeling and Experimental Analysis on the Swelling Behavior of the SIPN Hydrogels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 10111–10115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirani, N.; Yahia, L.H. History and Applications of Hydrogels. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 4, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzinski, W.E.; Dave, A.M.; Vaishnav, U.H.; Kumbar, S.G.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Hydrogels as Controlled Release Devices in Agriculture. Des. Monomers Polym. 2002, 5, 39–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.C.L. Desarrollo de Hidrogeles Biodegradables Como Acarreadores de Inulina para el Control de la Infección de Phytophthora Capsici en Chile; Centro de Investigación y Asistencia en Tecnología y Diseño del Estado de Jalisco A.C: Zapopan, Jalisco, Mexico, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sannino, A.; Demitri, C.; Madaghiele, M. Biodegradable Cellulose-Based Hydrogels: Design and Applications. Materials 2009, 2, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, T. Polymers and the Environment. In Polymer Science; Ylmaz, F., Ed.; InTech: Manila, Philippines, 2013; ISBN 978-953-51-0941-9. [Google Scholar]
- Naaz, I.; Ali, S. Earthworm Biomarkers: The New Tools of Environmental Impact Assessment. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Commun. 2013, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Trestrail, C.; Nugegoda, D.; Shimeta, J. Invertebrate Responses to Microplastic Ingestion: Reviewing the Role of the Antioxidant System. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, N.B.; Hüffer, T.; Thompson, R.C.; Hassellöv, M.; Verschoor, A.; Daugaard, A.E.; Rist, S.; Karlsson, T.; Brennholt, N.; Cole, M.; et al. Are We Speaking the Same Language? Recommendations for a Definition and Categorization Framework for Plastic Debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chávez-Sifontes, M.; Domine, M. Lignina, Estructura Y Aplicaciones: Métodos De Despolimerización Para La Obtención De Derivados Aromáticos De Interés Industrial. Av. En Cienc. Ing. 2013, 4, 15–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, S.; Bembridge, J.; Holmstrup, M.; Posthuma, L.; SETAC (Society). Advances in Earthworm Ecotoxicology; SETAC: Duluth, MN, USA, 1998; p. 472. ISBN 978-1-880611-25-8. [Google Scholar]
- ISO: International Organization for Standardization. ISO (1993) Soil Quality—Effects of Pollutants on Earthworms (Eisenia fetida)—Part 1: Determination of Acute Toxicity Using Artificial Soil Substrate ISO 11268-1; International Standardization Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Ecotoxicological Effects of Microplastics and Cadmium on the Earthworm Eisenia Foetida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 392, 122273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartell, S.M. Biomarkers, Bioindicators, and Ecological Risk Assessment—A Brief Review and Evaluation. Environ. Bioindic. 2006, 1, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Hernandez, J.C. Earthworm Biomarkers in Ecological Risk Assessment. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Ware, G.W., Whitacre, D.M., Albert, L.A., de Voogt, P., Gerba, C.P., Hutzinger, O., Knaak, J.B., Mayer, F.L., Morgan, D.P., Park, D.L., et al., Eds.; Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 85–126. ISBN 978-0-387-32964-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gastaldi, L.; Ranzato, E.; Caprì, F.; Hankard, P.; Pérès, G.; Canesi, L.; Viarengo, A.; Pons, G. Application of a Biomarker Battery for the Evaluation of the Sublethal Effects of Pollutants in the Earthworm Eisenia Andrei. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 146, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaete, H.; Hidalgo, M.E.; Neaman, A.; Ávila, G. Evaluación de la toxicidad de cobre en suelos a través de biomarcadores de estrés oxidativo en eisenia foetida. Quím. Nova 2010, 33, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez Romero, P.; Mendoza Cantú, A. Ensayos Toxicológicos Para La Evaluación de Sustancias Químicas En Agua y Suelo: La Experiencia En México; Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales Instituto Nacional de Ecología: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gaupp-Berghausen, M.; Hofer, M.; Rewald, B.; Zaller, J.G. Glyphosate-Based Herbicides Reduce the Activity and Reproduction of Earthworms and Lead to Increased Soil Nutrient Concentrations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozo, L.; Fernández, M.; López, M.; Reyes, R.; Suárez, P. Biomarcadores de contaminación química en comunidades microbianas. Interciencia 2007, 32, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlahogianni, T.; Dassenakis, M.; Scoullos, M. Molecular Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Aquatic Organisms in Relation to Toxic Environmental Pollutants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2006, 64, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhan, H. Superabsorbent Nanocomposite Hydrogels Made of Carboxylated Cellulose Nanofibrils and CMC-g-p(AA-Co-AM). Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna Cock, L.; Guancha-Chalapud, M.A. Natural Fibers for Hydrogels Production and Their Applications in Agriculture. Acta Agronómica 2017, 66, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Seijo, A.; da Costa, J.P.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Duarte, A.C.; Pereira, R. Oxidative Stress, Energy Metabolism and Molecular Responses of Earthworms (Eisenia Fetida) Exposed to Low-Density Polyethylene Microplastics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 33599–33610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givaudan, N.; Binet, F.; Le Bot, B.; Wiegand, C. Earthworm Tolerance to Residual Agricultural Pesticide Contamination: Field and Experimental Assessment of Detoxification Capabilities. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 192, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.P.; Hernández-Ruiz, J.; Martinez-Subiela, S.; Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Ceron, J.J. Spectrophotometric Assays for Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) in Dog Serum: An Update. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abele, D.; Vázquez-Medina, J.P.; Zenteno-Savín, T. Oxidative Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems: Abele/Oxidative Stress in Aquatic Ecosystems; Willey-Blackwel: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-García, D.; Guerrero, L.G.; Orozco-Guareño, E. Development of Kraft Lignin chemically modified as a novel crosslinking agent for the synthesis of active hydrogels. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Guideline for the Testing of Chemicals No. 207. Earthworm, Acute Toxicity; OECD: París, France, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Jovana, M.; Tanja, M.; Mirjana, S. Effects of Three Pesticides on the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida (Savigny 1826) under Laboratory Conditions: Assessment of Mortality, Biomass and Growth Inhibition. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 62, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.; Lin, K. Biological Effects of Decabromodiphenyl Ether (BDE209) and Pb on Earthworm (Eisenia Fetida) in a Soil System. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 207, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yan, S. Comparative Effects of Lindane and Deltamethrin on Mortality, Growth, and Cellulase Activity in Earthworms (Eisenia Fetida). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2007, 89, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Pan, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Chen, Z.; Dong, W.; Xie, A.; Qi, X. Dendritic Hydrogels with Robust Inherent Antibacterial Properties for Promoting Bacteria-Infected Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022, 14, 11144–11155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, Y.; Pan, W.; Tong, X.; Zeng, Q.; Su, T.; Qi, X.; Shen, J. Polydopamine-incorporated dextran hydrogel drug carrier with tailorable structure for wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, C.; Dai, X.; Zhu, F.; Ge, C. Ultrasonic Synthesis and Properties of a Sodium Lignosulfonate–Grafted Poly(Acrylic Acid-Co-Acryl Amide) Composite Super Absorbent Polymer. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 6057–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Liang, H.; Sun, R.; Peng, P.; Jiang, Y.; She, D. Hydrogel Synthesis Based on Lignin/Sodium Alginate and Application in Agriculture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Yang, H.; Dong, X.; Lei, H.; Chen, D. PH-Sensitive Polymeric Particles as Smart Carriers for Rebar Inhibitors Delivery in Alkaline Condition: Research Article. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Chakma, S. Synthesis and Evaluation of CMC-g-AMPS/Fe/Al/AC Composite Hydrogel and Their Use in Fluoride Removal from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Heavy Metals Removal Using Hydrogel-Supported Nanosized Hydrous Ferric Oxide: Synthesis, Characterization, and Mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 580, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-B.; Yuan, C.-H.; Ke, A.-R.; Quan, Z.-L. Electrical Response Characterization of PVA–P(AA/AMPS) IPN Hydrogels in Aqueous Na2SO4 Solution. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 134, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrescu, A.M.; Lisa, G.; Iordan, A.R.; Tudorache, F.; Petrila, I.; Borhan, A.I.; Palamaru, M.N.; Mihailescu, C.; Leontie, L.; Munteanu, C. Ni Ferrite Highly Organized as Humidity Sensors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015, 156, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, H. Synthesis and Application of a Polyacrylate Dispersant on the Preparation of Ultrafine Ground Calcium Carbonate in a Laboratory Stirred Media Mill. Powder Technol. 2014, 266, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozay, H.; Ilgin, P.; Sezgintürk, M.K.; Ozay, O. Ruthenium Nanoparticles Supported in the Network of HES-p(AMPS) IPN Hydrogel as Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Production from the Hydrolysis of Ethylenediamine Bisborane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 9892–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, A.B.; Ramírez, I.X.B.; Eslava, L.F.B.; Niño, G.R. Evaluación de hidrogeles para aplicaciones agroforestales. Ing. Investig. 2007, 27, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, F.; Brulle, F.; Dumez, S.; Lemiere, S.; Platel, A.; Nesslany, F.; Cuny, D.; Deram, A.; Vandenbulcke, F. Antioxidant Responses of Annelids, Brassicaceae and Fabaceae to Pollutants: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 114, 273–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.J.; Long, S.M.; Spurgeon, D.J.; Svendsen, C.; Hankard, P.K. Toxicological and Biochemical Responses of the Earthworm Lumbricus Rubellus to Pyrene, a Non-Carcinogenic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon. Chemosphere 2004, 57, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Carmen Cuevas Díaz, M.; Cerrato, R.F.; Martín, A.R.; Vázquez, R.R. Ensayos Toxicoló-Gicos Para la Evaluación de Sustancias Químicas en Agua y Suelo la Experiencia en México; Primera; Instituto Nacional de Ecología, Semarnat: Mexico City, Mexico, 2008; ISBN 978-968-817-882-9. [Google Scholar]
- EPA. Ecological Effects Test Guidelines OCSPP 850 3100: Earthworm Subchronic Toxicity Test, EPA 712-C-016, USEPA Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Vera, J.A. Bioremediation Treatments for Disposal of Waste Generated of Inorganic Salts General Chemistry Laboratory Using Technical Vermiculture. Rev. Ambient Agua Aire Suelo 2013, 4, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemtiri, A.; Colinet, G.; Alabi, T.; Cluzeau, D.; Zirbes, L.; Haubruge, É.; Francis, F. Impacts of Earthworms on Soil Components and Dynamics. A Review. BASE 2014, 18, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lemtiri, A.; Liénard, A.; Alabi, T.; Brostaux, Y.; Cluzeau, D.; Francis, F.; Colinet, G. Earthworms Eisenia Fetida Affect the Uptake of Heavy Metals by Plants Vicia Faba and Zea Mays in Metal-Contaminated Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 104, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P. Effects of Metal-Contaminated Soils on the Growth, Sexual Development, and Early Cocoon Pro- duction of the EarthwormEisenia Fetida, with Particular Reference to Zinc. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1996, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, D.J.; Hopkin, S.P.; Jones, D.T. Effects of Cadmium, Copper, Lead and Zinc on Growth, Reproduction and Survival of the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida (Savigny): Assessing the Environmental Impact of Point-Source Metal Contamination in Terres- trial Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 1994, 84, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukkari, T.; Aatsinki, M.; Väisänen, A.; Haimi, J. Toxicity of Copper and Zinc Assessed with Three Different Earthworm Tests. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2005, 30, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveque, T.; Capowiez, Y.; Schreck, E.; Mazzia, C.; Auffan, M.; Foucault, Y.; Austruy, A.; Dumat, C. Assessing Ecotoxicity and Uptake of Metals and Metalloids in Relation to Two Different Earthworm Species (Eiseina hortensis and Lumbricus terrestris). Environ. Pollut. 2013, 179, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.M.; Thai, A.C.; Larive, C.K. Metabolite Biomarkers of Chlorothalonil Exposure in Earthworms, Coelomic Fluid, and Coelomocytes. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.S.; Pathiratne, A.; van Gestel, C.A.M. Toxicity of Chlorpyrifos, Carbofuran, Mancozeb and Their Formulations to the Tropical Earthworm Perionyx Excavatus. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, D.; Inoue, K.; Ohto, K.; Oshima, T.; Murota, A.; Funaoka, M.; Makino, K. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on Crosslinked Lignocatechol: A Modified Lignin Gel. React. Funct. Polym. 2005, 62, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroza-Sandoval, A.; Yáñez-Chávez, L.G.; Sánchez-Cohen, I.; José, A. Samaniego-Gaxiola Efecto Del Hidrogel y Vermicomposta En La Producción de Maíz. Rev. Fitotec. Mex. 2015, 38, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Orozco-Guareño, E.; Hernández, S.L.; Gómez-Salazar, S.; Mendizábal, E.; Katime, I. Estudio del hinchamiento de hidrogeles acrílicos terpoliméricos en agua y en soluciones acuosas de ión plumboso. Rev. Mex. Ing. Quím. 2011, 10, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Domínguez-Rodríguez, V.I.; Adams, R.H.; Sánchez-Madrigal, F.; Pascual-Chablé, J.D.L.S.; Gómez-Cruz, R. Soil Contact Bioassay for Rapid Determination of Acute Toxicity with Eisenia Foetida. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Velasco, N.; Gandariasbeitia, M.; Irizar, A.; Soto, M. Uptake Route and Resulting Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles in Eisenia Fetida Earthworm Exposed through Standard OECD Tests. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagi, T.; Ose, K. Toxicity, Bioaccumulation and Metabolism of Pesticides in the Earthworm. J. Pestic. Sci. 2015, 40, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, S.; Barišić, J.; Malev, O.; Klobučar, G.; Popović, N.T.; Strunjak-Perović, I.; Krasnići, N.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Klobučar, R.S. Sewage Sludge Toxicity Assessment Using Earthworm Eisenia Fetida: Can Biochemical and Histopathological Analysis Provide Fast and Accurate Insight? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12150–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.L.; Wyman Dorough, H. Relative Toxicities of Chemicals to the Earthworm Eisenia foetida. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1984, 3, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y. Biochemical and Genotoxic Effect of Triclosan on Earthworms (Eisenia fetida) Using Contact and Soil Tests. Environ. Toxicol. 2012, 27, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, I.C.; Martínez, L.; Posada, E.; González, M.E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Efectos de La Lombriz Roja Californiana (Eisenia foetida), Sobre El Crecimiento de Microorganismos En Suelos Contaminados Con Mercurio de Segovia, Antoquia. Cienc. Ing. Neogranadina 2017, 27, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréa, M.M. de O uso de minhocas como bioindicadores de contaminaçao de solos. Acta Zool. Mex. 2010, 26, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Shen, L.; Zhu, J. Full-Color Photonic Hydrogels for PH and Ionic Strength Sensing. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 83, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, T.; Asami, N.; Uragami, T. A Reversibly Antigen-Responsive Hydrogel. Nature 1999, 399, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sample | %C | %H | %N | %S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthesized Hydrogel | 44.69 | 5.03 | 4.55 | 6.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiménez, H.D.; Orozco, E.; Hernández, S.L.; Ramírez, A.C.; Velázquez, J.M.; Velazquez, G.; Minjarez, A.d.C.; Zamudio, A.; Flores, M.M.; Velasco, S.F. Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Response of Earthworm Exposed to a Lignin-Modified Crosslinked Hydrogel. Toxics 2023, 11, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060476
Jiménez HD, Orozco E, Hernández SL, Ramírez AC, Velázquez JM, Velazquez G, Minjarez AdC, Zamudio A, Flores MM, Velasco SF. Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Response of Earthworm Exposed to a Lignin-Modified Crosslinked Hydrogel. Toxics. 2023; 11(6):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060476
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiménez, Humberto D., Eulogio Orozco, Saira L. Hernández, Ana C. Ramírez, José M. Velázquez, Gilberto Velazquez, Amelia del C. Minjarez, Adalberto Zamudio, Milagros M. Flores, and Sandra F. Velasco. 2023. "Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Response of Earthworm Exposed to a Lignin-Modified Crosslinked Hydrogel" Toxics 11, no. 6: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060476
APA StyleJiménez, H. D., Orozco, E., Hernández, S. L., Ramírez, A. C., Velázquez, J. M., Velazquez, G., Minjarez, A. d. C., Zamudio, A., Flores, M. M., & Velasco, S. F. (2023). Evaluation of Acute Toxicity and Antioxidant Response of Earthworm Exposed to a Lignin-Modified Crosslinked Hydrogel. Toxics, 11(6), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11060476






