Emission Characteristics of Air Pollutants and CO2 from 11 Cities with Different Economic Development around the Bohai Sea in China from 2008–2017
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Description of Studied Cities
2.2. Emission Dataset
2.3. Socioeconomic Data
2.4. Statistics Analysis
3. Results
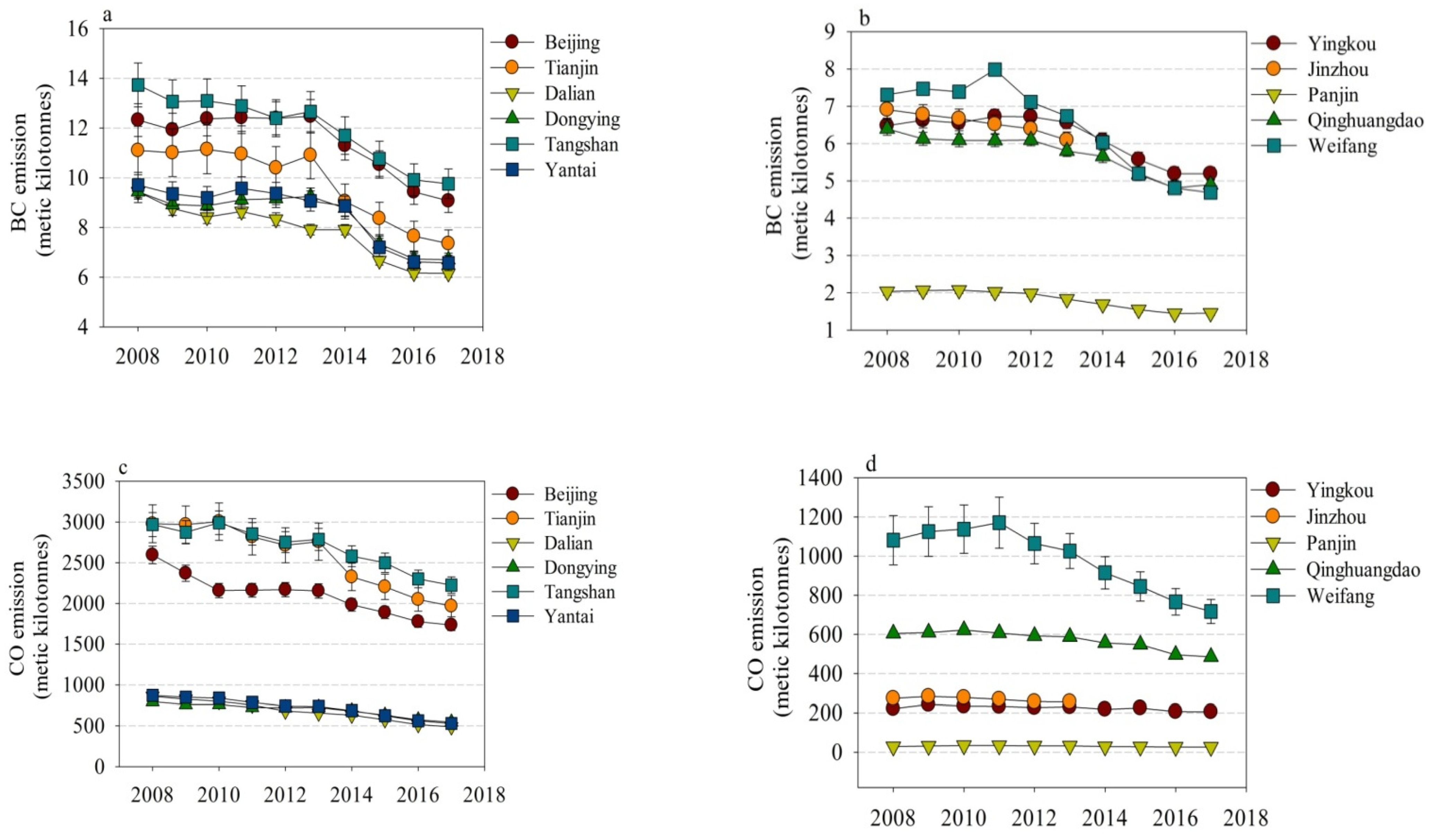
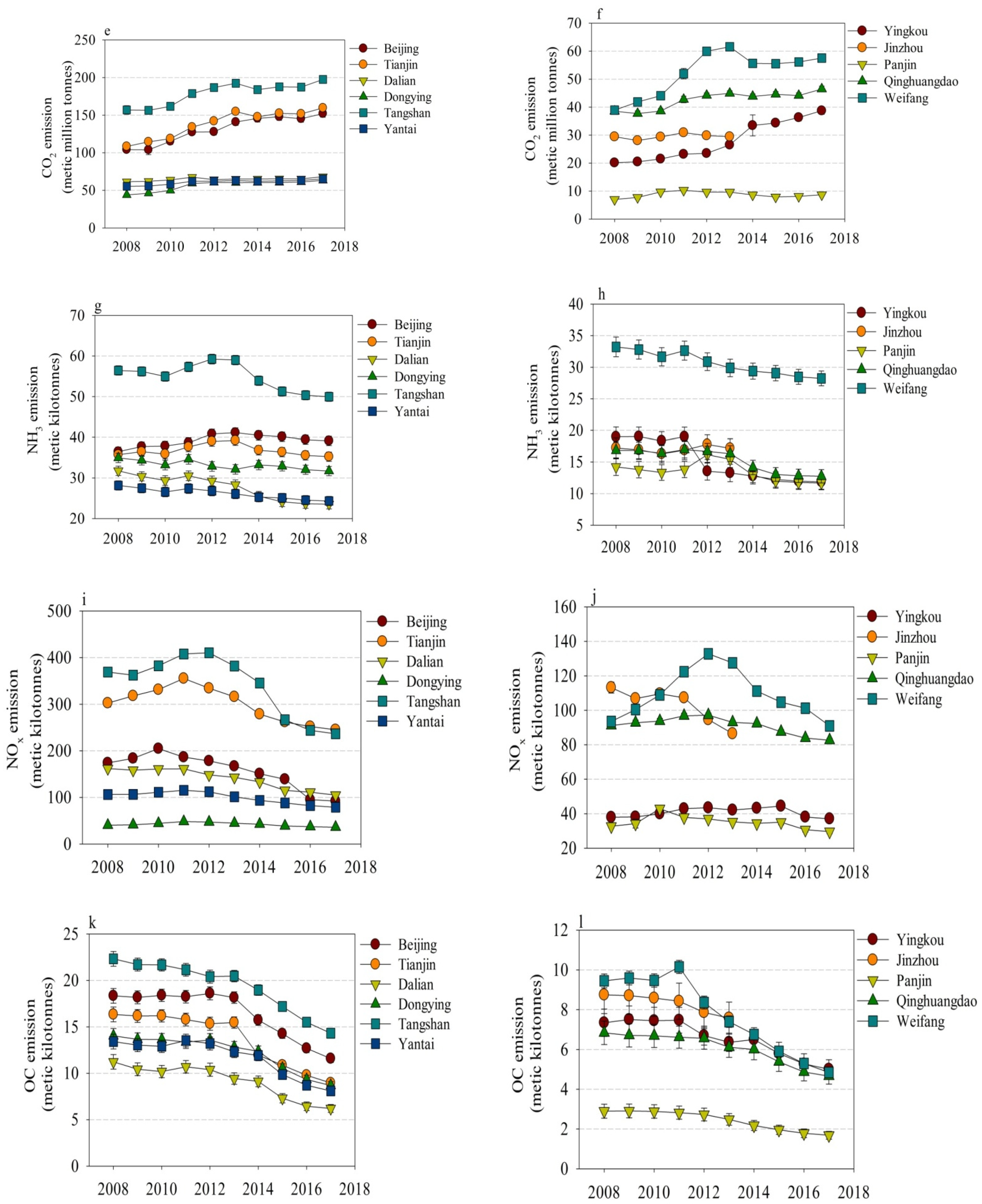
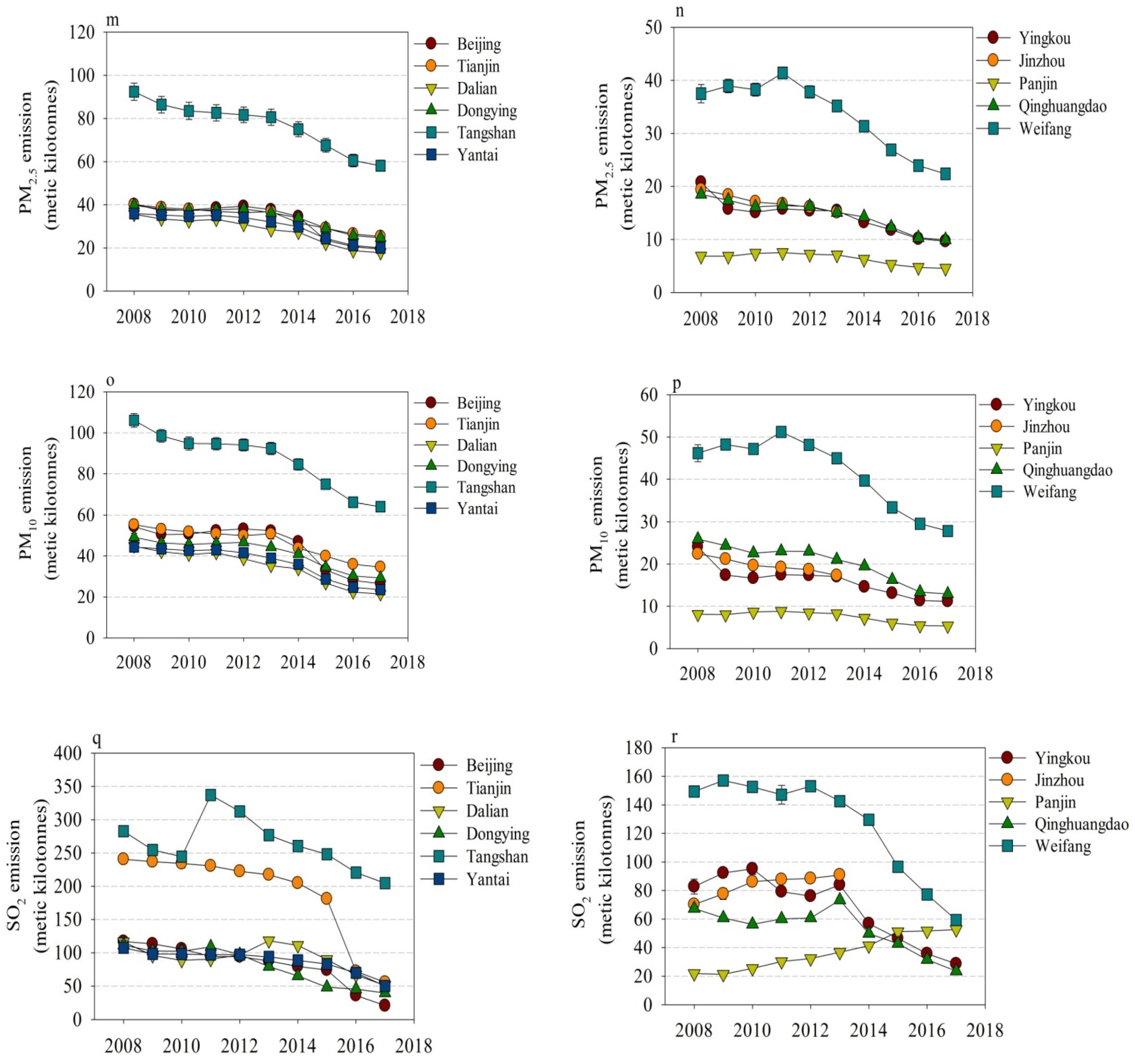
3.1. Monthly Trends in Emissions
3.2. Annual Trends in Emissions
3.3. Economic Metrics
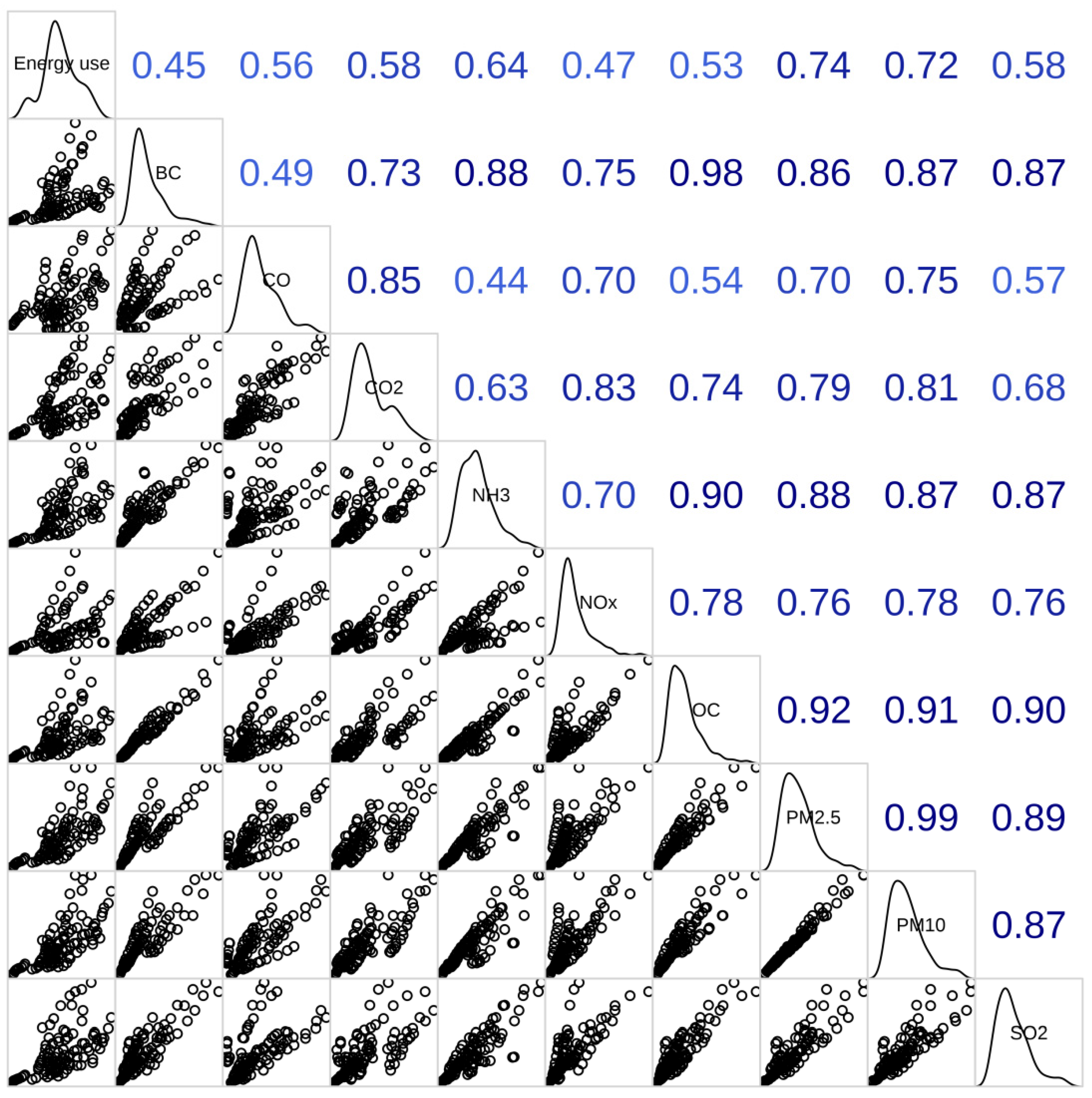
3.4. Associations between Economic Metrics and Emissions of Ambient Species
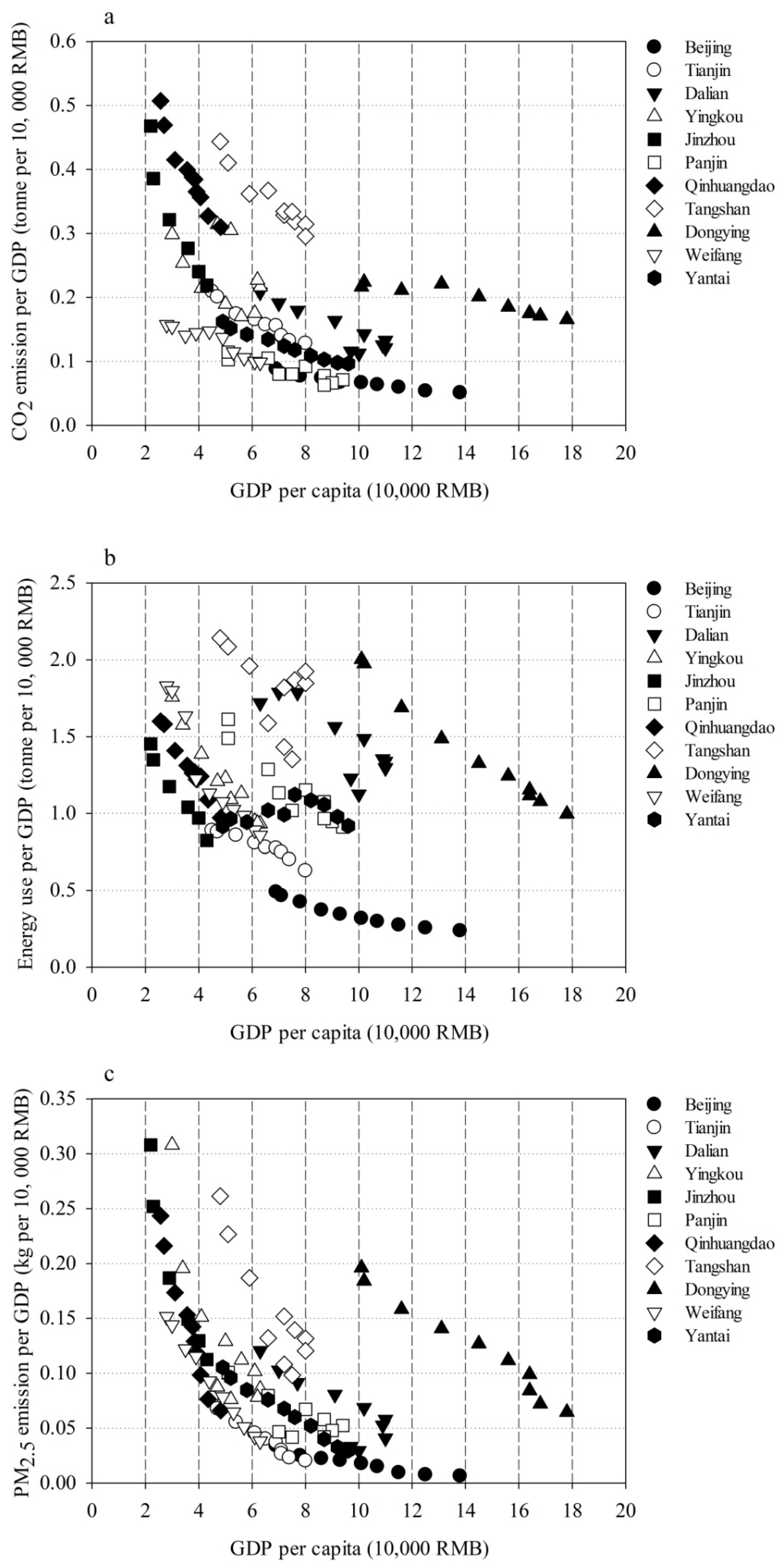
3.5. Energy Use and Emission per GDP for Cities with Different Development Levels
4. Discussion
4.1. Disparities in Emissions and Economic Development across Cities
4.2. Mitigation of Air Pollution and CO2 Emission at a City Level
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shindell, D.; Borgford-Parnell, N.; Brauer, M.; Haines, A.; Kuylenstierna, J.C.I.; Leonard, S.A.; Ramanathan, V.; Ravishankara, A.; Amann, M.; Srivastava, L. A climate policy pathway for near- and long-term benefits. Science 2017, 356, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, N.; Adger, W.N.; Agnolucci, P.; Blackstock, J.; Byass, P.; Cai, W.; Chaytor, S.; Colbourn, T.; Collins, M.; Cooper, A.; et al. Health and climate change: Policy responses to protect public health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1861–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgartner, J.; de Foy, B.; Schauer, J.J. A global perspective on national climate mitigation priorities in the context of air pollution and sustainable development. City Environ. Interact. 2019, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stott, P.A.; Stone, D.A.; Allen, M.R. Human contribution to the European heatwave of 2003. Nature 2004, 432, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, M.; Colombo, E.; Pavarini, C. Energy and Air Pollution World Energy Outlook Special Report—Spotlight; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, H.E.; Walton, M.A. Energy Access Outlook: From Poverty to Prosperity, World Energy Outlook-2017 Special Report; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Achakulwisut, P.; Brauer, M.; Moran, D.; Apte, J.S.; Henze, D.K. Particulate matter-attributable mortality and relationships with carbon dioxide in 250 urban areas worldwide. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dentener, F.; van Dingenen, R.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaddick, G.; Thomas, M.L.; Amini, H.; Broday, D.; Cohen, A.; Frostad, J.; Green, A.; Gumy, S.; Liu, Y.; Martin, R.V.; et al. Data Integration for the Assessment of Population Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution for Global Burden of Disease Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9069–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogelj, J.; den Elzen, M.; Höhne, N.; Fransen, T.; Fekete, H.; Winkler, H.; Schaeffer, R.; Sha, F.; Riahi, K.; Meinshausen, M. Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2 °C. Nature 2016, 534, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, A.M.; Azam, M. Evaluating the impact of GDP per capita on environmental degradation for G-20 economies: Does N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve exist? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 11103–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T. Economic growth, income inequality and environment: Assessing the applicability of the Kuznets hypotheses to Asia. Palgrave Commun. 2017, 3, 17069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, M.; Shindell, D.T.; Seltzer, K.M.; Tao, S.; Zhong, Q. The long-term relationship between emissions and economic growth for SO2, CO2, and BC. Environ. Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 124021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soergel, B.; Kriegler, E.; Weindl, I.; Rauner, S.; Dirnaichner, A.; Ruhe, C.; Hofmann, M.; Bauer, N.; Bertram, C.; Bodirsky, B.L.; et al. A sustainable development pathway for climate action within the UN 2030 Agenda. Nat. Clim. Change 2021, 11, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Traub, G.; Kroll, C.; Teksoz, K.; Durand-Delacre, D.; Sachs, J.D. National baselines for the Sustainable Development Goals assessed in the SDG Index and Dashboards. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, M.; Lessmann, K.; Jakob, M.; Steckel, J.C.; Edenhofer, O. Mobilizing domestic resources for the Agenda 2030 via carbon pricing. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Deng, Z.; He, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.; Qi, Y.; Liang, X. Challenges and opportunities for carbon neutrality in China. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 3, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, R.A. China’s coal burning cutting lives short by years. Nature news 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nansai, K.; Tohno, S.; Chatani, S.; Kanemoto, K.; Kagawa, S.; Kondo, Y.; Takayanagi, W.; Lenzen, M. Consumption in the G20 nations causes particulate air pollution resulting in two million premature deaths annually. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Zhan, A. Anthropogenic pollutant-driven geographical distribution of mesozooplankton communities in estuarine areas of the Bohai Sea, China. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ma, X. Vertical distributions of mercury in marine sediment cores from central and southern part of Bohai Sea, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, X.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y. Temporal and spatial variation, input fluxes and risk assessment of cyclic methylsiloxanes in Rivers-Bohai Sea System. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Diamond, J. China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 2005, 435, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Luan, X.; Liao, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, G.; Chen, L. Human impacts on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon distribution in Chinese intertidal zones. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 878–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Xue, Q.; Hubacek, K.; Fan, J.; Shan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Coffman, D.M.; Managi, S.; Zhang, X. Inclusive wealth index measuring sustainable development potentials for Chinese cities. Glob. Environ. Change 2022, 72, 102417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, S.; Wen, T.; Meng, F.; Chen, G.; Qian, X. Influence of ferrous-metal production on mercury contamination and fractionation in farmland soil around five typical iron and steel enterprises of Tangshan, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 188, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Cui, F.; Xiang, N. Roadmap of green transformation for a steel-manufacturing intensive city in China driven by air pollution control. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 283, 124643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cai, Y.; Lin, G. Pathways for sustainable municipal energy systems transition: A case study of Tangshan, a resource-based city in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Xue, X.; Jia, M.; Jing, H.; Wang, T.; Zhen, R.; Huang, M.; Tian, J.; Guo, J.; Li, L.; et al. Iron and steel industry emissions and contribution to the air quality in China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 237, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel slag in China: Treatment, recycling, and management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Lan, G.Z.; Kraeger, P.; Wei, M. Tangshan—China’s one time industrial pioneer striving for ecological excellence. Cities 2017, 65, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Baumgarnter, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, M. Oxidative potential and inflammatory impacts of source apportioned ambient air pollution in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 12920–12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Du, L.; Chen, H. Impact of industrial agglomeration on haze pollution: New evidence from Bohai Sea Economic Region in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Du, H.; Zhao, Z.; Russo, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. The impact of potential recirculation on the air quality of Bohai Bay in China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Cui, H.; Man, H.; et al. Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; He, K.B.; Cheng, Y.F.; Emmons, L.K.; Huo, H.; Kang, S.C.; Lu, Z.; Shao, M.; et al. Mapping Asian anthropogenic emissions of non-methane volatile organic compounds to multiple chemical mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 5617–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Huo, H.; He, K.B. High-resolution inventory of technologies, activities, and emissions of coal-fired power plants in China from 1990 to 2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 13299–13317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmüller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A mosaic of regional and global emission grid maps for 2008 and 2010 to study hemispheric transport of air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.-I.; Woo, J.-H.; He, K.; Lu, Z.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Bond, T.C.; Carmichael, G.R.; Fernandes, S.D.; Fu, Q.; He, D.; Klimont, Z.; Nelson, S.M.; Tsai, N.Y.; Wang, M.Q.; et al. An inventory of gaseous and primary aerosol emissions in Asia in the year 2000. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Wang, L. Per capita renewable energy consumption in 116 countries: The effects of urbanization, industrialization, GDP, aging, and trade openness. Energy 2022, 254, 124289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pata, U.K.; Aydin, M. Testing the EKC hypothesis for the top six hydropower energy-consuming countries: Evidence from Fourier Bootstrap ARDL procedure. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Buonocore, J.J.; Levy, J.I.; Lambert, K.F.; Burtraw, D.; Reid, S.B.; Fakhraei, H.; Schwartz, J. US power plant carbon standards and clean air and health co-benefits. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2015, 5, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Lei, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D. Co-benefits from energy policies in China. Energy 2010, 35, 4265–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatial and temporal characteristics of different types of pollution-intensive industries in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China by using land use data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yin, T.; Tian, J. Research on the impact of Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei electric power and thermal power industry on haze pollution. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Schwartz, J.; Shindell, D.; Amann, M.; Faluvegi, G.; Klimont, Z.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Pozzoli, L.; Van Dingenen, R.; Vignati, E.; et al. Global Air Quality and Health Co-benefits of Mitigating Near-Term Climate Change through Methane and Black Carbon Emission Controls. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 831–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Steinberger, J.; Gasson, B.; Hansen, Y.; Hillman, T.; Havránek, M.; Pataki, D.; Phdungsilp, A.; Ramaswami, A.; Mendez, G.V. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Global Cities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7297–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, C.; Steinberger, J.; Gasson, B.; Hansen, Y.; Hillman, T.; Havránek, M.; Pataki, D.; Phdungsilp, A.; Ramaswami, A.; Mendez, G.V. Methodology for inventorying greenhouse gas emissions from global cities. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 4828–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.A.G.; Staffell, I. Rapid fuel switching from coal to natural gas through effective carbon pricing. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, W. Modelling national, provincial and city-level low-carbon energy transformation pathways. Energy Policy 2020, 137, 111096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, W.-K.; Kahlor, L.A.; Olson, H.C. Understanding public support for carbon capture and storage policy: The roles of social capital, stakeholder perceptions, and perceived risk/benefit of technology. Energy Policy 2020, 139, 111312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P. Key areas and pathways for carbon emissions reduction in Beijing for the “Dual Carbon” targets. Energy Policy 2022, 164, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yuan, X.; Yao, X.; Lei, M. Carbon leakage and low-carbon performance: Heterogeneity of responsibility perspectives. Energy Policy 2022, 165, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Wang, Z. Spatial network structure of transportation carbon emission efficiency in China and its influencing factors. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 19, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Alexandroff, A. Current and future struggles to eliminate coal. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Huang, G.H.; Chen, J.P.; Li, Y.P.; He, C.Y. A chance-constrained urban agglomeration energy model for cooperative carbon emission management. Energy 2021, 223, 119885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Li, F.; Cao, X.; Tang, Z.; Bai, Y.; Yang, S. Reducing export-driven CO2 and PM emissions in China’s provinces: A structural decomposition and coordinated effects analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 274, 123101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Quan, M.; Li, H.; Hao, X. Is environmental regulation works on improving industrial resilience of China? Learning from a provincial perspective. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4695–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| City | Province | Area (km2) | Population a,b (10,000 Persons) | GDP a,b (Chinese Currency, Billion RMB) | GDP per Capita a,b (Chinese Currency, 10,000 RMB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | / | 16,410 | 1770–2200 | 1180–2990 | 6.9–13.8 |
| Tianjin | / | 11,966 | 1170–1440 | 520–1250 | 4.5–8.0 |
| Dalian | Liaoning | 12,574 | 613–700 | 295–605 | 6.3–10.0 |
| Yingkou | Liaoning | 5427 | 233–243 | 67–127 | 3.0–5.4 |
| Panjin | Liaoning | 4102 | 139–143 | 67–125 | 5.1–7.6 |
| Jinzhou | Liaoning | 10,301 | 312–305 | 63–107 | 2.2–3.5 |
| Qinhuangdao | Hebei | 7802 | 295–311 | 76–130 | 2.7–4.8 |
| Tanshan | Hebei | 13,472 | 746–789 | 354–592 | 4.8–7.5 |
| Dongying | Shandong | 8243 | 200–215 | 202–381 | 10.0–17.8 |
| Weifang | Shandong | 16,167 | 890–936 | 248–585 | 2.8–6.2 |
| Yantai | Shandong | 13,864 | 701–706 | 341–676 | 4.0–9.5 |
| Item | Period | Unit | Data Source | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 2008–2017 | Metric tonnes | Multi-resolution Emission Inventory for China (MEIC) | MEIC model generates a database of air pollutants and CO2 over China with regular updates using the bottom-up technical method based on a series of improved emission inventory models, which includes unit-based emission inventories for power plants and cement plants, a high-resolution county-level vehicle emission inventory, a residential combustion emission inventory based on national-wide survey data, and an explicit profile-based non-methanevolatile organic compound (NMVOC) speciationframework. The data areavailable at http://www.meicmodel.org (accessed on 1 November 2021). |
| CO | ||||
| CO2 | ||||
| NH3 | ||||
| NOx | ||||
| OC | ||||
| PM2.5 | ||||
| PM10 | ||||
| SO2 |
| City | BC | CO | CO2 | NH3 | NOx | OC | PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.6–1.5 | 148–260 | 8.0–16 | 2.0–6.0 | 5.0–18 | 1.0–2.8 | 1.8–4.2 | 2.0–5.6 | 2.0–12.3 |
| Tianjin | 0.8–1.8 | 80–200 | 6.0–16 | 2.0–5.0 | 22–32 | 0.8–2.6 | 1.2–2.2 | 3.0–5.8 | 5.0–22.0 |
| Dalian | 0.8–1.0 | 80–100 | 4.2–5.5 | 1.8–4.0 | 11–14 | 0.5–2.0 | 2.0–3.2 | 2.4–4.0 | 4.8–11.6 |
| Yingkou | 0.5–0.7 | 15–22 | 1.4–4.2 | 1.0–2.4 | 2.4–4.8 | 0.5–1.1 | 0.8–1.8 | 1.0–2.2 | 3.0–8.2 |
| Panjin | 0.15–0.25 | 2.2–3.1 | 0.6–1.0 | 0.8–2.0 | 2.0–3.2 | 0.2–0.48 | 0.4–0.7 | 0.5–0.9 | 1.5–7.6 |
| Jinzhou | 0.5–0.7 | 20–25 | 1.8–3.0 | 1.2–2.2 | 6.4–10 | 0.5–1.4 | 1.5–1.8 | 1.6–2.0 | 2.5–14.0 |
| Qinghuangdao | 0.5–0.6 | 50–65 | 2.4–4.0 | 0.8–2.0 | 3.0–8.0 | 0.5–0.9 | 1.0–1.5 | 1.5–2.2 | 2.0–7.0 |
| Tanshan | 0.8–1.6 | 200–340 | 12–19 | 3.0–7.0 | 20–35 | 1.0–3.8 | 6.0–10.0 | 7.0–11.0 | 15.0–30.0 |
| Dongying | 0.7–1.0 | 60–80 | 2.5–6.0 | 1.8–4.2 | 2.8–4.8 | 0.6–2.2 | 1.6–4.8 | 2.0–6.0 | 3.0–12.0 |
| Weifang | 0.4–1.0 | 150–220 | 3.0–5.0 | 1.5–4.0 | 5.0–11 | 0.4–1.6 | 2.0–5.4 | 3.0–6.0 | 5.0–15.0 |
| Yantai | 0.6–1.1 | 60–120 | 4.0–5.6 | 1.2–3.8 | 9.0–11 | 0.6–2.0 | 1.8–3.8 | 2.0–4.4 | 4.0–11.0 |
| Types | City a | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Human capital-dominated development | Beijing | [26] |
| Produced capital-dominated development | Tianjin, Dalian, Yingkou, Jinzhou, and Panjin in Liaoning Province, as well as Weifang and Yantai in Shandong Province | [26] |
| Energy-producing city | Dongying in Shandong Province | [26] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lan, J.; Li, Y. Emission Characteristics of Air Pollutants and CO2 from 11 Cities with Different Economic Development around the Bohai Sea in China from 2008–2017. Toxics 2022, 10, 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090547
Zhao Z, Liu Q, Lan J, Li Y. Emission Characteristics of Air Pollutants and CO2 from 11 Cities with Different Economic Development around the Bohai Sea in China from 2008–2017. Toxics. 2022; 10(9):547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090547
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zongshan, Qingyang Liu, Jing Lan, and Yaru Li. 2022. "Emission Characteristics of Air Pollutants and CO2 from 11 Cities with Different Economic Development around the Bohai Sea in China from 2008–2017" Toxics 10, no. 9: 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090547
APA StyleZhao, Z., Liu, Q., Lan, J., & Li, Y. (2022). Emission Characteristics of Air Pollutants and CO2 from 11 Cities with Different Economic Development around the Bohai Sea in China from 2008–2017. Toxics, 10(9), 547. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10090547







