Discharge Patterns of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) from Coking Plants and Its Relationship with Soil PHE Contents in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
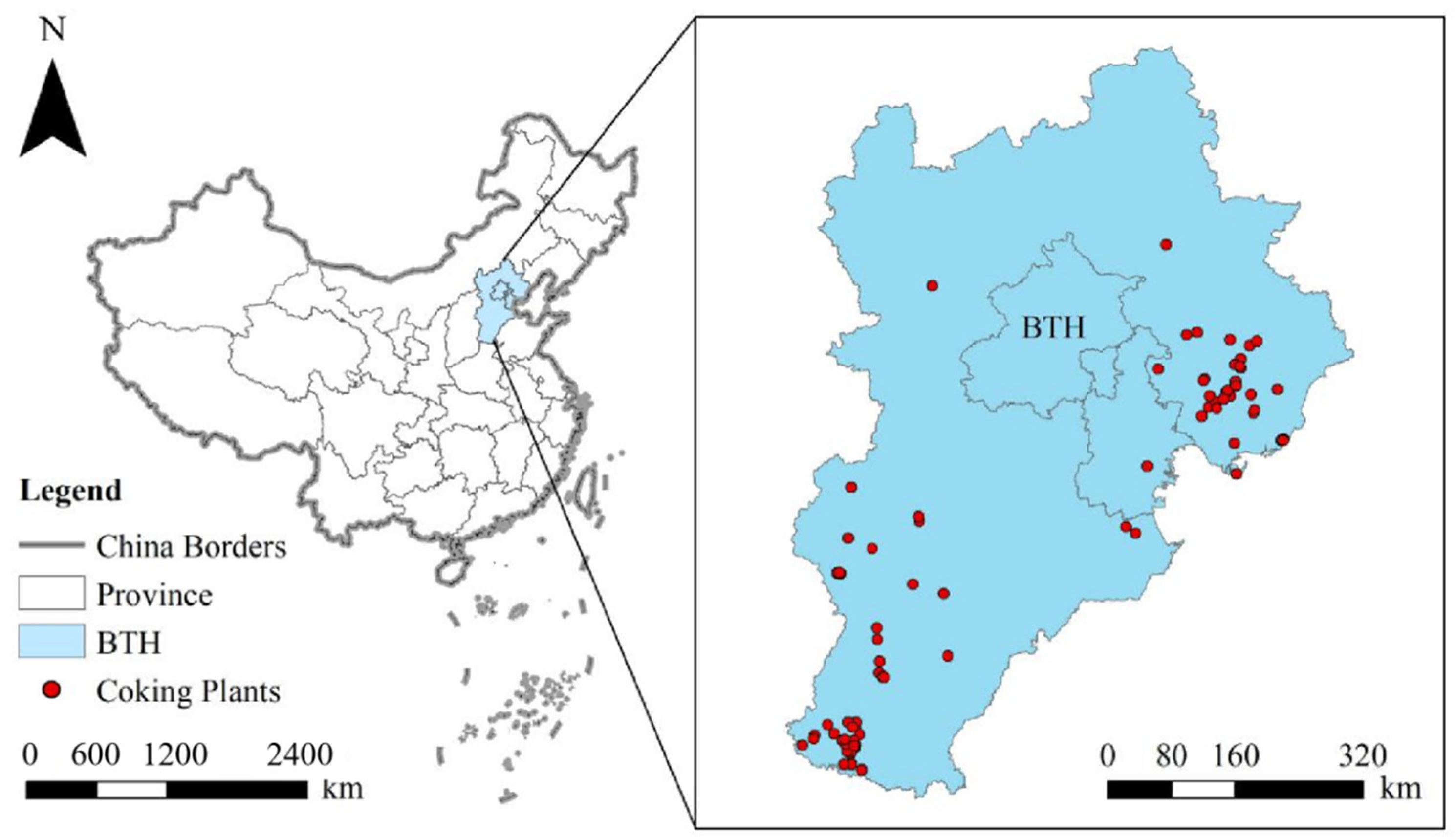
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Data of Coking Enterprises and Their PHE Emissions
2.2.2. Coal Consumption by Enterprises in BTH
2.2.3. Soil Environmental Quality Data in BTH
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. PHE Emissions from Coal-Consuming Enterprises in BTH
2.3.2. Relationship between PHEs Discharged from Coking Plants with the Soil PHE Concentrations in BTH
2.3.3. Soil Pollutant Accumulation from Coking Emissions
2.3.4. Calculation of Potential Ecological Risk
2.3.5. Prediction of Ecological Risk Caused by Coking Plants
3. Results
3.1. Discharge Patterns of PHEs from Coking Plants
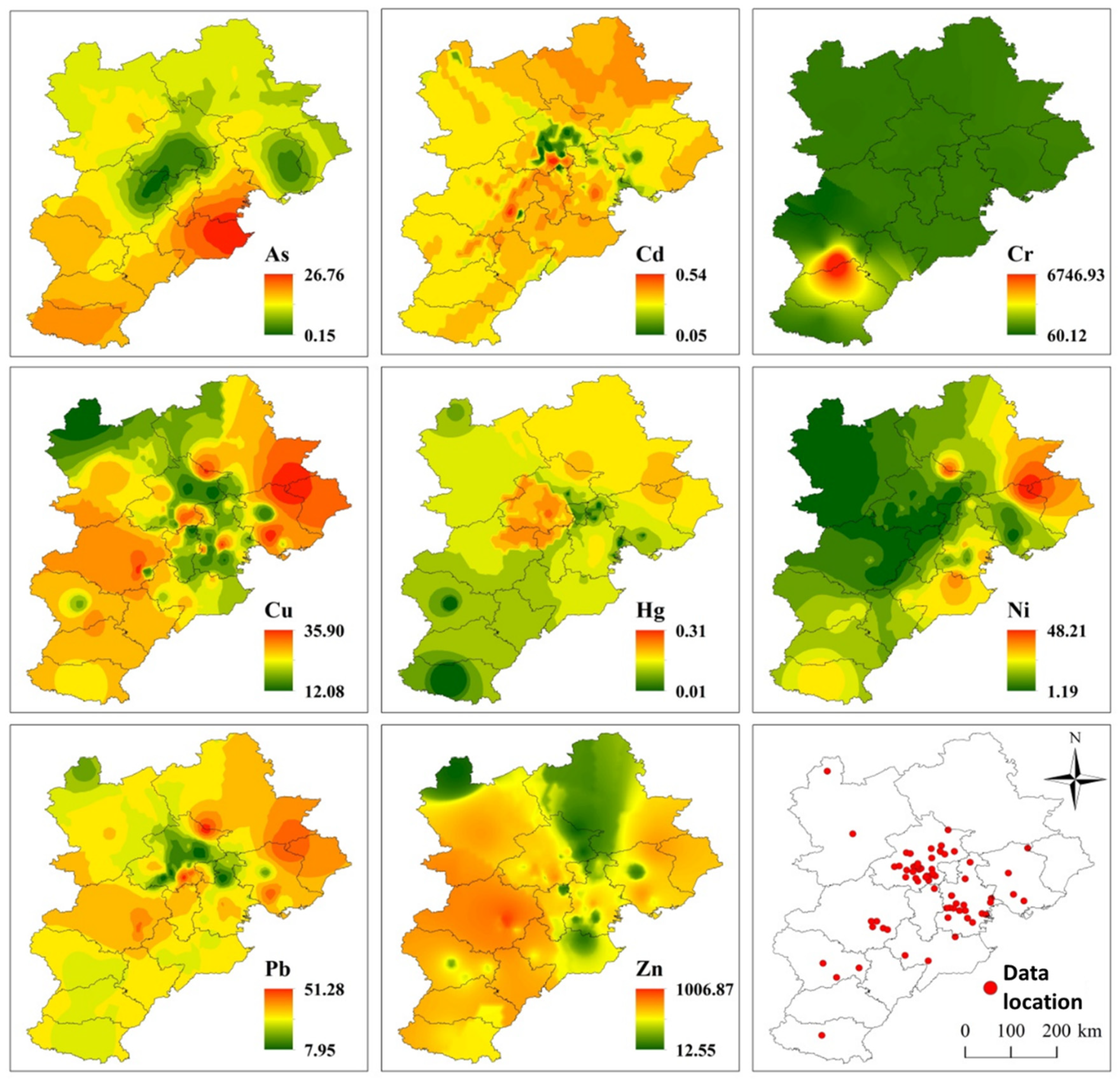
3.2. Relationship between Soil PHE Concentration and PHE Discharge from Coking Plants in BTH
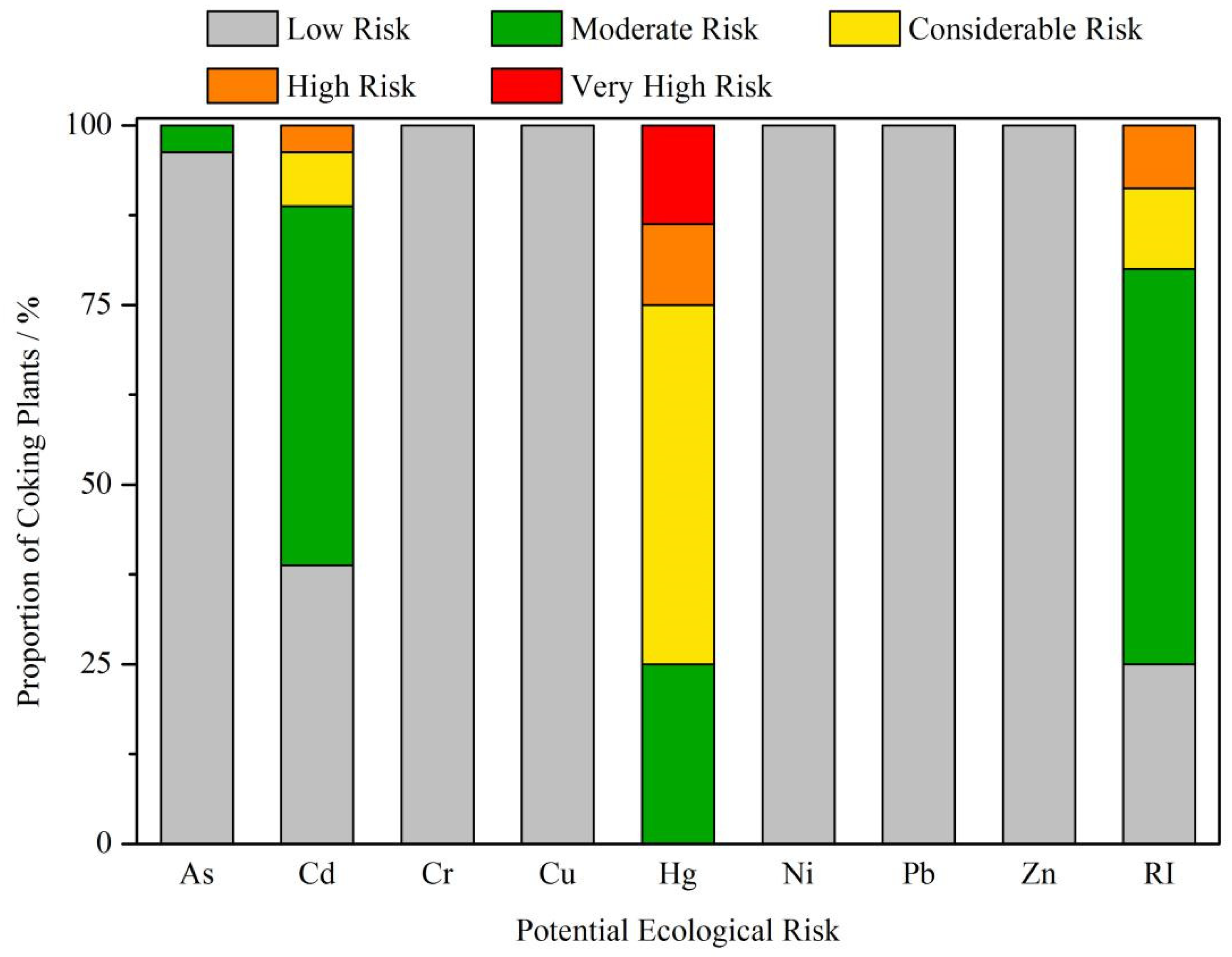
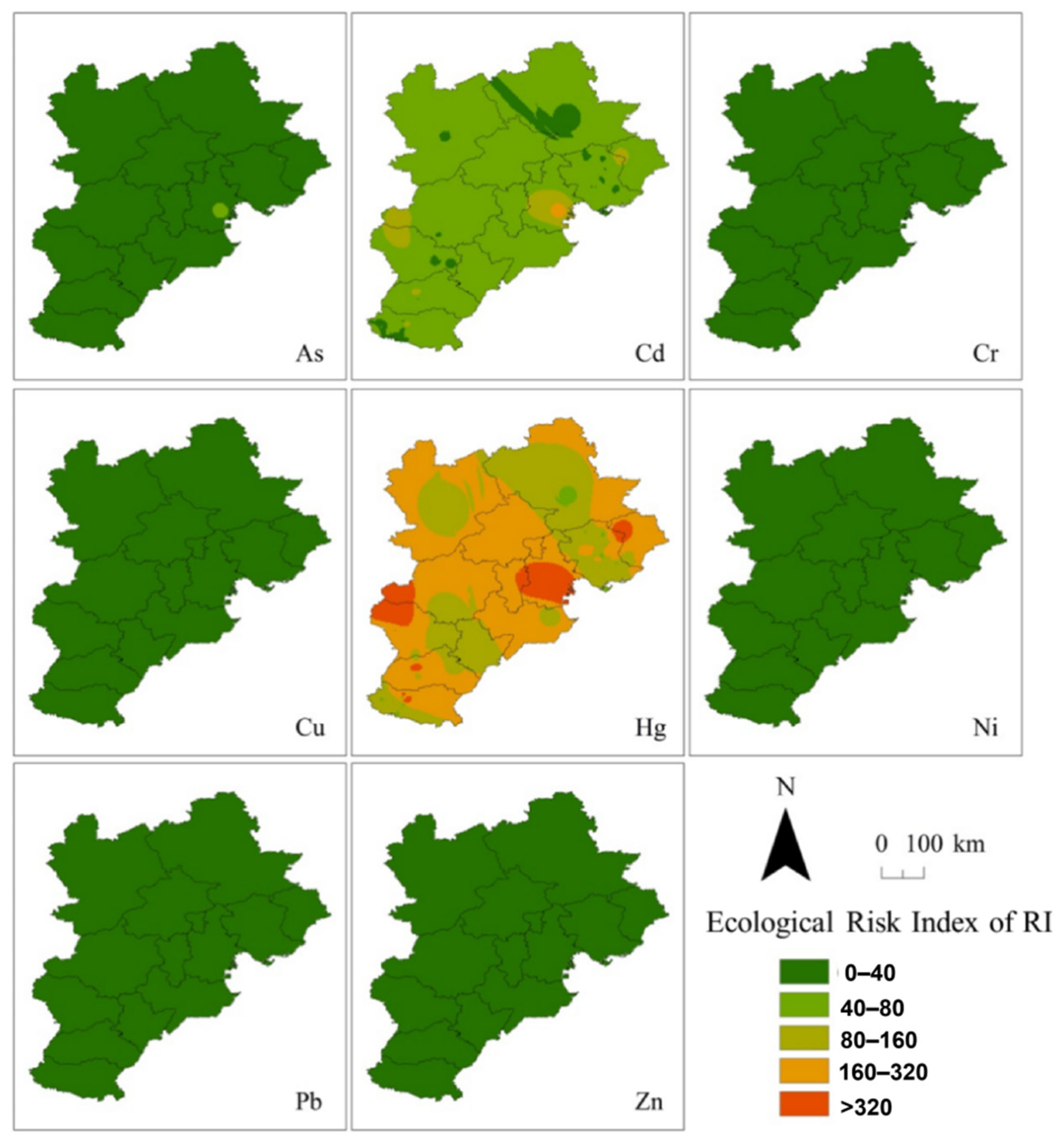
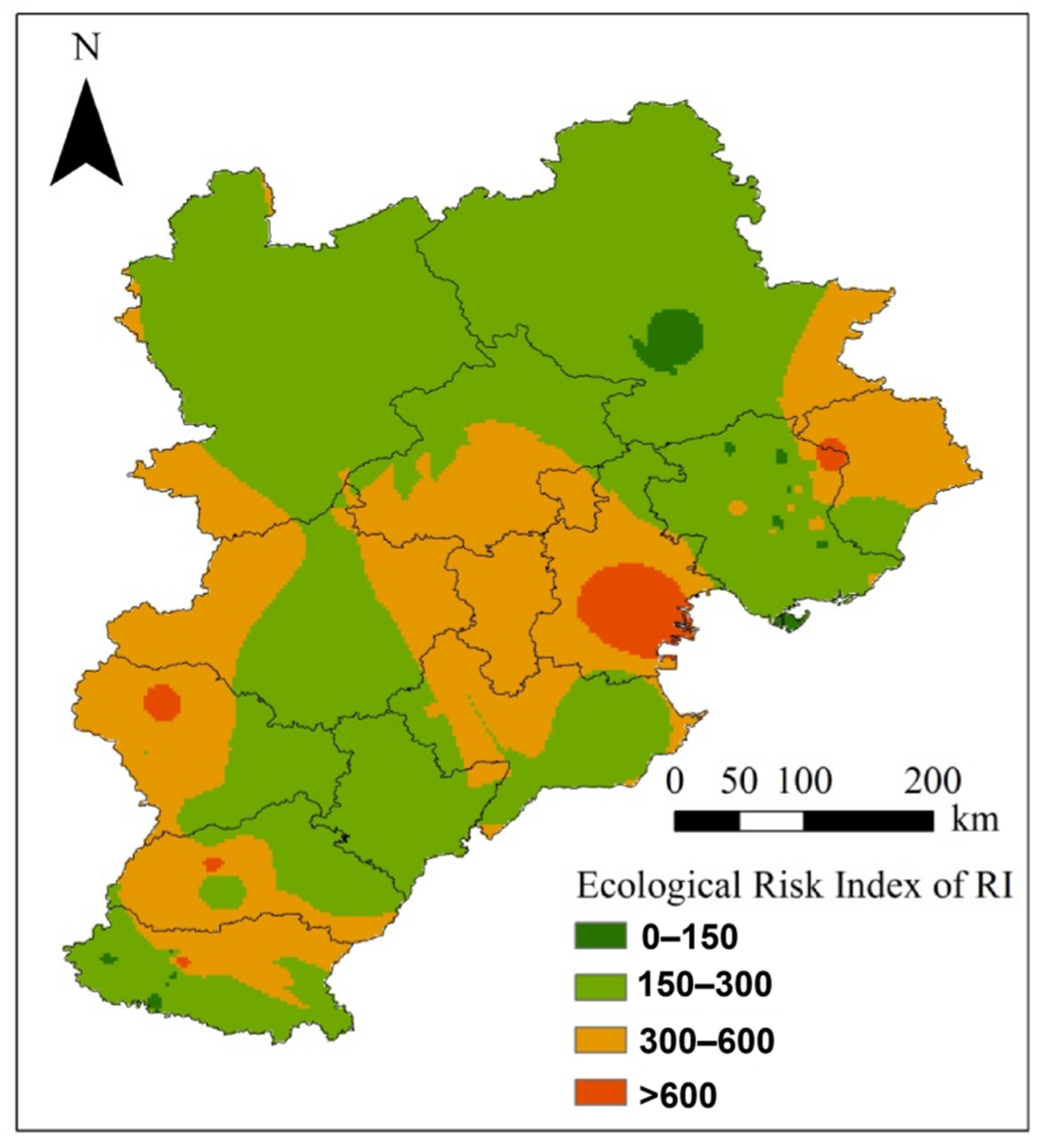
3.3. PHE Accumulation in Soil from Coking Emissions and Depositions, and Its Associated Ecological Risk
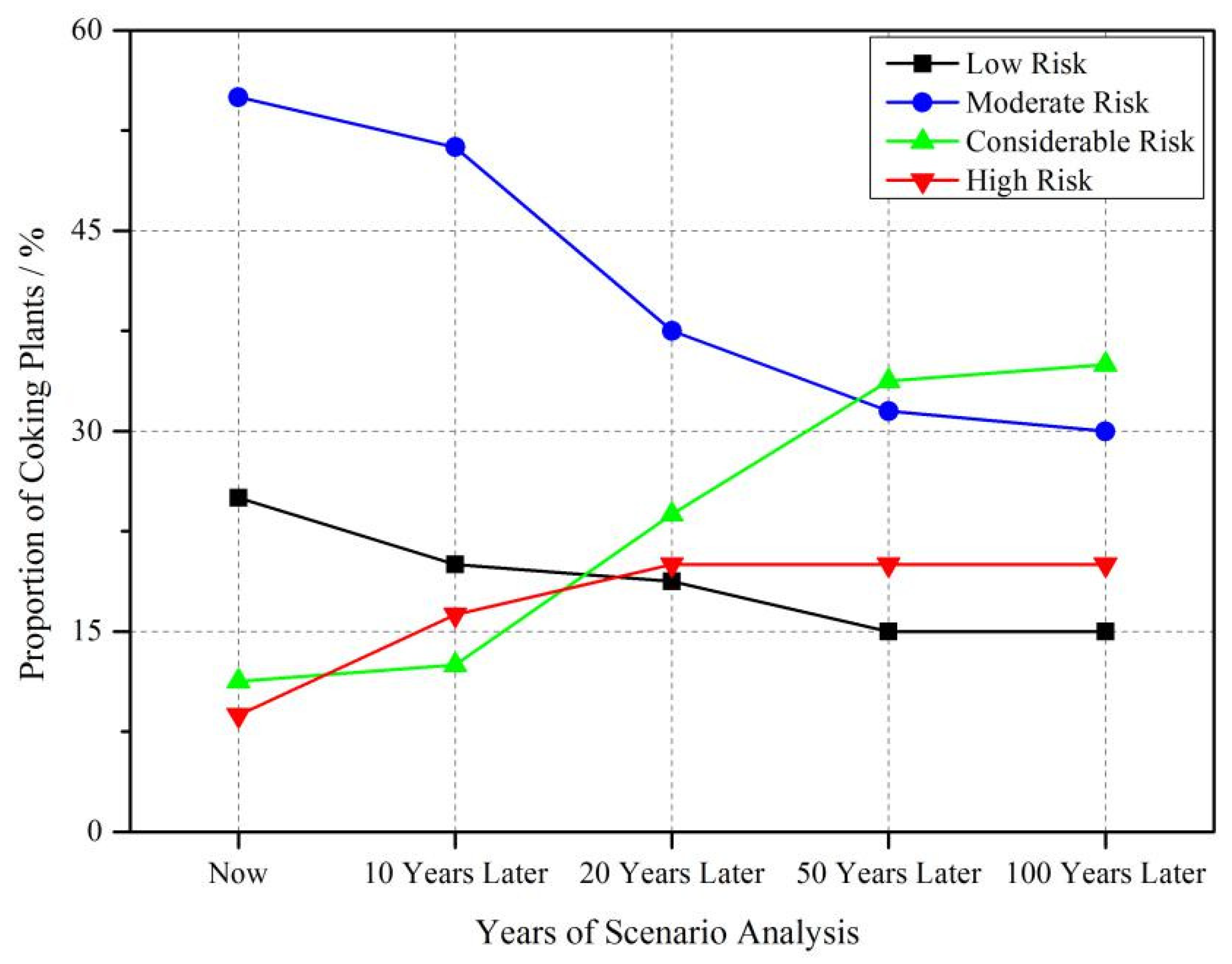
3.4. Prediction of the Potential Ecological Risk in the Future by Scenario Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Coking Was an Important Source for the PHE Discharge in BTH
4.2. Coking Contributed to the Accumuation of PHEs in Soil
4.3. Ecological Risk Analysis and Its Environmental Implications
4.4. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics in China (NBSC). Chinese Statistical Yearbook; Chinese Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2020. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2020/indexch.htm (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- National Bureau of Statistics in China (NBSC). Chinese Statistical Yearbook; Chinese Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2019/indexch.htm (accessed on 10 April 2021).
- Mu, L.; Peng, L.; Liu, X.F.; Bai, H.L.; Song, C.F.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Emission characteristics of heavy metals and their behavior during coking processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6425–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, P.W.; Dong, N.; Yang, S.C.; Gou, Y.L. Quantitative analysis of the main sources of pollutants in the soils around key areas based on the positive matrix factorization method. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, C.; Fan, W.Y.; Li, M.Z.; Mao, X.G.; Bao, G.D. Surface soil geochemical quality evaluation based on the space analysis of GIS. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress (WAC), Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 24–28 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Tian, H.Z.; Hao, Y.; Gao, J.J.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Hua, S.B.; Wang, K.; Liu, H.J. A high-resolution emission inventory of anthropogenic trace elements in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei (BTH) region of China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.F.; Li, J.N.; Chen, L.G.; Xu, Z.C.; He, D.C.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wei, F.S.; Li, J.H. Biomass fuels and coke plants are important sources of human exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, benzene and toluene. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Mi, W.Y.; Xie, Z.Y.; Tang, J.H.; Apel, C.; Joerss, H.; Ebinghaus, R.; Zhang, Q.H. Overall comparison and source identification of PAHs in the sediments of European Baltic and North Seas, Chinese Bohai and Yellow Seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, B.F.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, J.; Chen, P.; Liu, W.Z.; Wang, X.M. A complete atmospheric emission inventory of F, As, Se, Cd, Sb, Hg, Pb, and U from coal-fired power plants in Anhui Province, eastern China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 43, 1817–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, A.Z.; Zhang, H.F.; Islam, A.; Yang, M. Occurrence, fates, and carcinogenic risks of substituted polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in two coking wastewater treatment systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 147808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.Z.; Zhu, C.Y.; Gao, J.J.; Cheng, K.; Hao, J.M.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.R. Quantitative assessment of atmospheric emissions of toxic heavy metals from anthropogenic sources in China: Historical trend, spatial distribution, uncertainties, and control policies. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 12107–12166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- USEPA. Compilation of Air Emissions Factors; United States Environmental Protection Agency (US, EPA): Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-factors-and-quantification/ap-42-compilation-air-emissions-factors (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Zhu, C.Y.; Tian, H.Z.; Cheng, K.; Liu, K.J.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.B.; Gao, J.J.; Zhou, J.R. Potentials of whole process control of heavy metals emissions from coal-fired power plants in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 114, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China SEPA. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. In 2013 China Statistical Yearbook China; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, S.L.; Jia, Z.Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, G.M. Temporal and spatial distributions and sources of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in western Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.-M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minkina, T.; Konstantinova, E.; Bauer, T.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sushkova, S.; Chaplygin, V.; Burachevskaya, M.; Nazarenko, O.; Kizilkaya, R.; Gülser, C.; et al. Environmental and human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soils around the largest coal-fired power station in Southern Russia. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2285–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachwał, M.; Magiera, T.; Wawer, M. Coke industry and steel metallurgy as the source of soil contamination by technogenic magnetic particles, heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Singh, J.; Taneja, P.K.; Mandal, A. Remediation techniques for removal of heavy metals from the soil contaminated through different sources: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, Q.S.; Zhu, Y.M.; Fan, S.S.; He, P.J. Review of source identification methodologies for heavy metals in solid waste. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.W.; Xu, W.; Zong, S.; Yao, L.Y.; Liu, J.L.; Lu, F.; Yi, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.G.; Shi, Z.Y.; Zhang, B.; et al. The Pollution Characteristics and Full-Scale Risk Assessment of Coking Plant Soil Co-Contaminated with Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Heavy Metals. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 38, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.J.; Wei, C.Y.; Feng, C.H.; Ren, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, C.F. States distribution of heavy metals in coking wastewater sludge and its potential environmental risks. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2013, 7, 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Y.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; Qin, Z.R.; Jiao, W.T. Spatial distribution and assessment of the human health risks of heavy metals in a retired petrochemical industrial area, south China. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Radko, T.; Mainka, A. Fractionation of trace elements and human health risk of submicron particulate matter (PM1) collected in the surroundings of coking plants. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hou, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.X.; Wu, D.; Li, X.J.; Ji, L.; Ma, X.P. Health risk assessment of heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil at coke oven gas plants. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2015, 14, 487–496. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Xiang, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Sushkova, S.; Minkina, T.; Duan, R. Implications of Soil Potentially Toxic Elements Contamination, Distribution and Health Risk at Hunan’s Xikuangshan Mine. Processes 2021, 9, 1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.T.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.Y.; Lei, K.G.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Zheng, D.F.; Fang, X.Q.; Cao, Y. Heavy metal contamination risk assessment and correlation analysis of heavy metal contents in soil and crops. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, B.; Agrawal, M.; Singh, S. Assessment of air pollution around coal mining area: Emphasizing on spatial distributions, seasonal variations and heavy metals, using cluster and principal component analysis. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2014, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstantinova, E.; Minkina, T.; Nevidomskaya, D.; Mandzhieva, S.; Bauer, T.; Zamulina, I.; Burachevskaya, M.; Sushkova, S. Exchangeable form of potentially toxic elements in floodplain soils along the river-marine systems of Southern Russia. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2021, 10, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Li, X.M.; Liu, X.F.; Bai, H.L.; Peng, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Tian, M.; Zheng, L.R. Characterization and emission factors of carbonaceous aerosols originating from coke production in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Peng, L.; Cao, J.; He, Q.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, H. Emissions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from coking industries in China. Particuology 2013, 11, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, P.W.; Lai, D.L.; Yang, S.C.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wang, H.Q. Effectiveness of predicting the spatial distributions of target contaminants of a coking plant based on their related pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahado, S.K.; Nwaogu, C.; Sarkodie, V.Y.O.; Borůvka, L. Modeling and Assessing the Spatial and Vertical Distributions of Potentially Toxic Elements in Soil and How the Concentrations Differ. Toxics 2021, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerizghi, T.; Guo, Q.; Tian, L.; Wei, R.; Zhao, C. An integrated approach to quantify ecological and human health risks of soil heavy metal contamination around coal mining area. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, C. Does environmental decentralization aggravate pollution emissions? Microscopic evidence from Chinese industrial enterprises. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Ren, J. Environmental quality and anthropogenic pollution assessment of heavy metals in topsoil of Hebei plain. Geol. China 2011, 38, 218–225. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.-N.; Li, H.; Sun, D.-F.; Zhou, L.-D.; Li, B.-G. Combining geostatistics with Moran’s I analysis for mapping soil heavy metals in Beijing, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 995–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Lu, A.; Wang, J.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, C. Analysis and assessment of soil environmental quality of some farmlands in Beijing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2006, 22, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, Z. Pollution evaluation and source apportionment of heavy metals in soils from Tianjin suburbs, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Y.; Wu, S.T. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Cu, Zn and Cd Pollution in Beijing, China. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 356–360, 730–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, W.; Luan, Y. Pollution assessment of heavy metal accumulation in the farmland soils of Beijing’s suburbs. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 27483–27492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenay, Ç.; Aykan, K.; Beyhan, P.; Savaş, A. Inventory of emissions of primary air pollutants in the city of Kocaeli, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 128, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Yu, T.; Xia, X.Q.; Cheng, H.X.; Zhou, G.H. Soil Geochemical Parameters of China; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.R. Environmental Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Nanjing University Press: Nanjing, China, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control—A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, E.P.; Custodio, M.; Bastos, M.C.; Ascencion, J.C. Heavy Metals in Agriculture Soils from High Andean Zones and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment in Peru’s Central Andes. J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihal, G.; Latha, R.; Sudip, M. Occurrence, geochemical fraction, ecological and health risk assessment of cadmium, copper and nickel in soils contaminated with municipal solid wastes. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129573. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, Y.S. Evaluation of sediment contamination in the Red Sea coastal area combining multiple pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, W.X.; Zhao, H.Q.; Yang, Q.C.; Yang, Z.P. Potential ecological risk assessment and prediction of soil heavy-metal pollution around coal gangue dump. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 14, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- China SEPA. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. In Soil Environmental Quality, Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land (GB15618-2018); China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Coralie, B.; Pierre, F.; Laurence, M.; Aurélie, C.; Thierry, B.; Corinne, L. Biodegradation of the organic matter in a coking plant soil and its main constituents. Org. Geochem. 2013, 56, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatial and temporal characteristics of different types of pollution-intensive industries in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region in China by using land use data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhu, C.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wu, B.; Liu, X.; Hao, Y.; Liu, W.; Bai, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variations of Ambient Concentrations of Trace Elements in a Highly Polluted Region of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 4186–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.R.; Gao, W.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M. Updated atmospheric speciated mercury emissions from iron and steel production in China during 2000–2015. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10423–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.F.; Zhang, L.X.; Lv, J.S. Spatial assessment models to evaluate human health risk associated to soil potentially toxic elements. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.P.; Tian, S.L.; Li, X.R.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Wentworth, G.R.; Wang, Y. Trace elements in particulate matter from metropolitan regions of Northern China: Sources, concentrations and size distributions. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 537, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.G.; Fu Joshua, S.; Jang Carey, J.; Hao, J.M.; He, K.B. Air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 41, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. PM2.5-bound elements in Hebei Province, China: Pollution levels, source apportionment and health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Ussher, S.J.; Lv, W.; Li, J.; Gao, J.; Luo, Y.; Meng, F. The characteristics of atmospheric particles and metal elements during winter in Beijing: Size distribution, source analysis, and environmental risk assessment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.W.; Geng, Y.; Sun, R.R.; Xie, M.; Feng, X.W.; Li, X.X.; Cui, Z.J. Distribution, speciation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Jinan Iron & Steel Group soils from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.H.; Sun, R.R.; Cui, M.H.; Sun, N.; Zhang, S.W. Evaluation and analysis of heavy metals in iron and steel industrial area. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafka, Z.; Puncocharova, J. Toxicity of heavy metals in nature. Chem. Listy 2002, 96, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.Y.; Song, Z.F.; Cai, K.Z. Source apportionment of topsoil heavy metals and associated health and ecological risk assessments in a typical hazy city of the North China plain. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.L.; Lin, T.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.R.; Deng, N.; Tang, M.Q.; Xiao, Y.M.; Guo, H.; Deng, Q.F. Co-exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and metals, four common polymorphisms in microRNA genes, and their gene-environment interactions: Influences on oxidative damage levels in Chinese coke oven workers. Environ. Int. 2019, 132, 105055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Meng, J.; Su, G.J.; Liu, Z.L.; Shi, B.; Wang, T.Y. Source apportionment and risk assessment for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soils at a typical coking plant. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Sun, D. Early warning of heavy metals potantial risk governance in Beijing. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2015, 52, 731–746. [Google Scholar]
- Eyrikh, S.; Shol, L.; Shinkaruk, E. Assessment of Mercury Concentrations and Fluxes Deposited from the Atmosphere on the Territory of the Yamal-Nenets Autonomous Area. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PHE | Max (mg·kg−1) | Min (mg·kg−1) | Screening Value (mg·kg−1) * | Over-Screening-Value Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 27.6 | 4.70 | 20 | 4.55 |
| Cd | 1.45 | 0.06 | 20 | 0.00 |
| Cr | 6929 | 14.6 | 200 | 1.52 |
| Cu | 85.0 | 12.5 | 2000 | 0.00 |
| Hg | 1.62 | 0.01 | 8 | 2.38 |
| Ni | 69.0 | 12.0 | 150 | 0.00 |
| Pb | 117 | 2.15 | 400 | 0.00 |
| Zn | 1670 | 30.0 | 250 | 6.25 |
| PHE in Soil | PHE Released by Coking Plant | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sig. | Phi Value | V Value | |
| As | 0.252 | 8.367 | 1.000 |
| Cd | 0.364 | 4.243 | 1.000 |
| Cr | 0.252 | 8.367 | 1.000 |
| Cu | 0.367 | 4.123 | 1.000 |
| Hg | 0.367 | 4.123 | 1.000 |
| Ni | 0.252 | 8.367 | 1.000 |
| Pb | 0.283 | 7.141 | 1.000 |
| Zn | 0.367 | 4.123 | 1.000 |
| Index of Risk | Maximum | Minimum | Mean | Standard | CV * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-Ei | 52.29 | 10.03 | 15.30 | 7.88 | 51.48 |
| Cd-Ei | 209.57 | 30.14 | 52.51 | 33.44 | 63.69 |
| Cr-Ei | 2.50 | 2.00 | 2.06 | 0.09 | 4.52 |
| Cu-Ei | 11.03 | 5.00 | 5.76 | 1.12 | 19.51 |
| Hg-Ei | 1199.75 | 40.88 | 185.36 | 216.00 | 116.53 |
| Ni-Ei | 12.69 | 5.01 | 5.96 | 1.43 | 24.00 |
| Pb-Ei | 17.21 | 5.01 | 6.53 | 2.27 | 34.82 |
| Zn-Ei | 2.52 | 1.00 | 1.19 | 0.28 | 23.82 |
| RI | 1507.55 | 99.07 | 274.68 | 262.53 | 95.58 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, X.; Zeng, W.; Gu, G.; Wang, L.; Lei, M. Discharge Patterns of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) from Coking Plants and Its Relationship with Soil PHE Contents in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Toxics 2022, 10, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050240
Wan X, Zeng W, Gu G, Wang L, Lei M. Discharge Patterns of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) from Coking Plants and Its Relationship with Soil PHE Contents in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Toxics. 2022; 10(5):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050240
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Xiaoming, Weibin Zeng, Gaoquan Gu, Lingqing Wang, and Mei Lei. 2022. "Discharge Patterns of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) from Coking Plants and Its Relationship with Soil PHE Contents in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China" Toxics 10, no. 5: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050240
APA StyleWan, X., Zeng, W., Gu, G., Wang, L., & Lei, M. (2022). Discharge Patterns of Potentially Harmful Elements (PHEs) from Coking Plants and Its Relationship with Soil PHE Contents in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region, China. Toxics, 10(5), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10050240






