The Relative Contributions of Different Wheat Leaves to the Grain Cadmium Accumulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling Methods and Sample Pre-treatment
2.3. Analytical Methods
- Physico-chemical analyzes of the samples
- 2.
- Plant morphology
2.4. Grain Filling Rate and Grain Cd Accumulation Rate Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
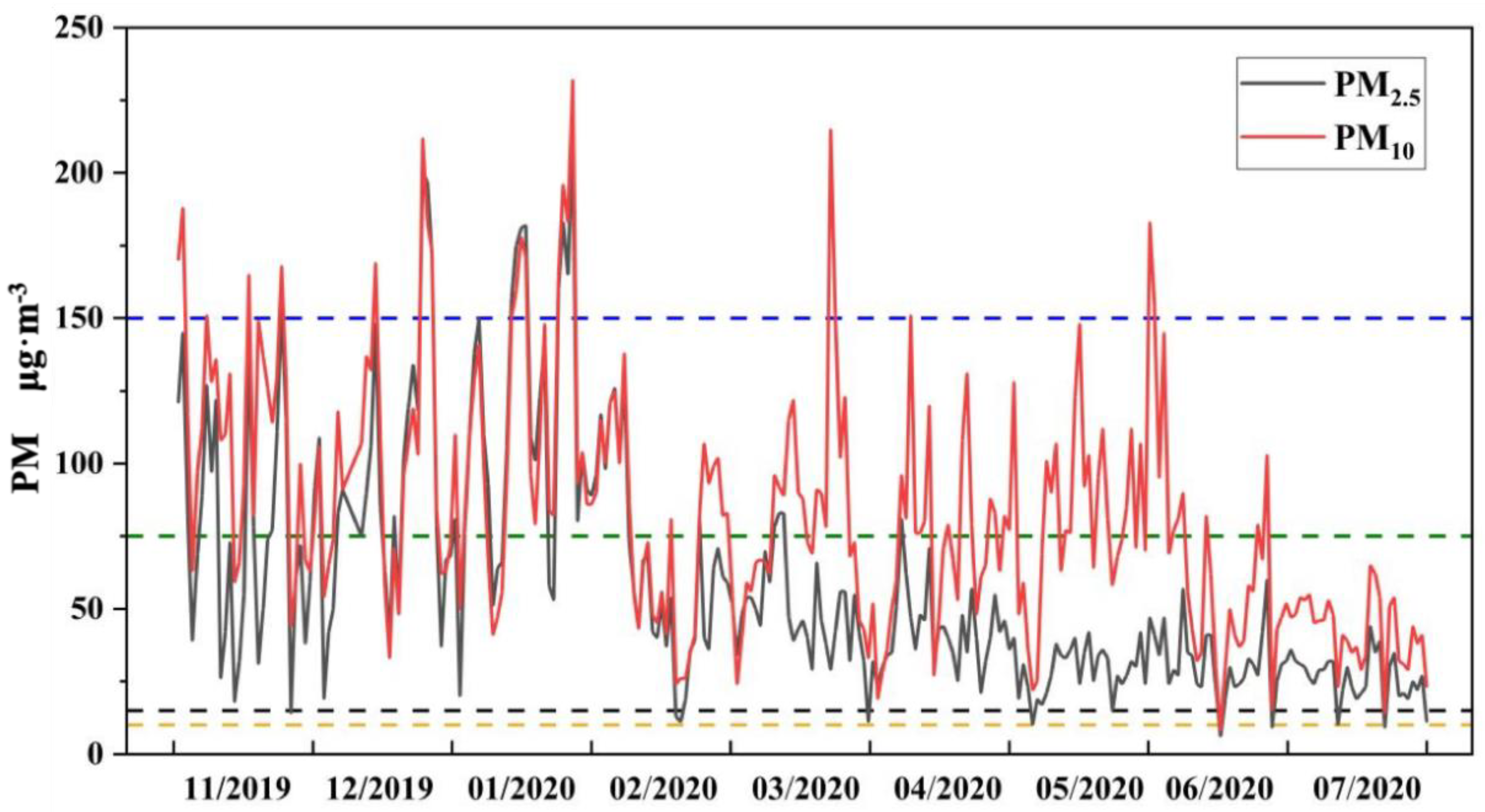
3.1. Regional Atmospheric Particulate Matter and Soil Cd Pollution
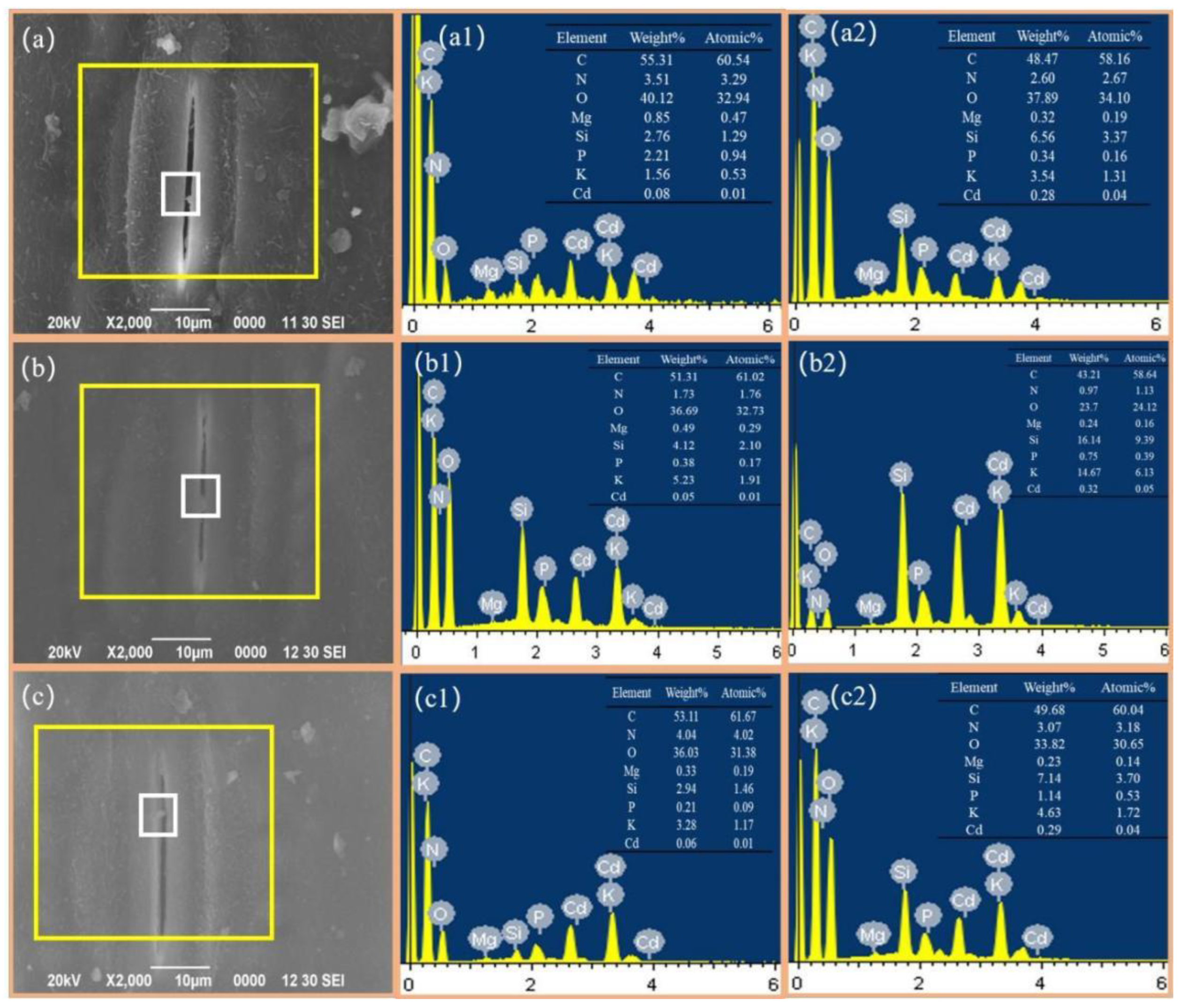
3.2. Mechanisms of Cd Uptake in Leaves Based on SEM-EDS
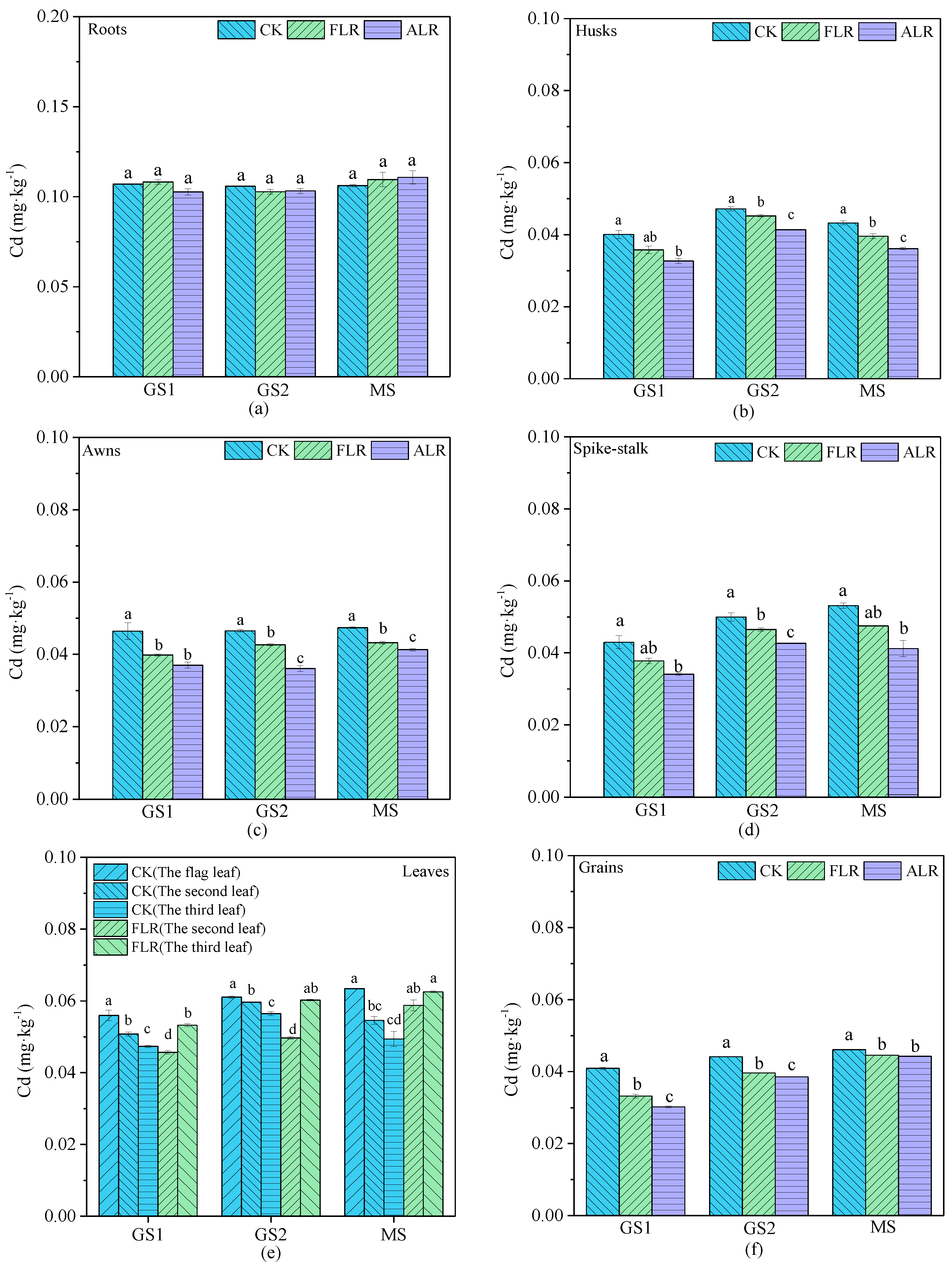
3.3. Cd Concentrations in Wheat Tissues and Grains
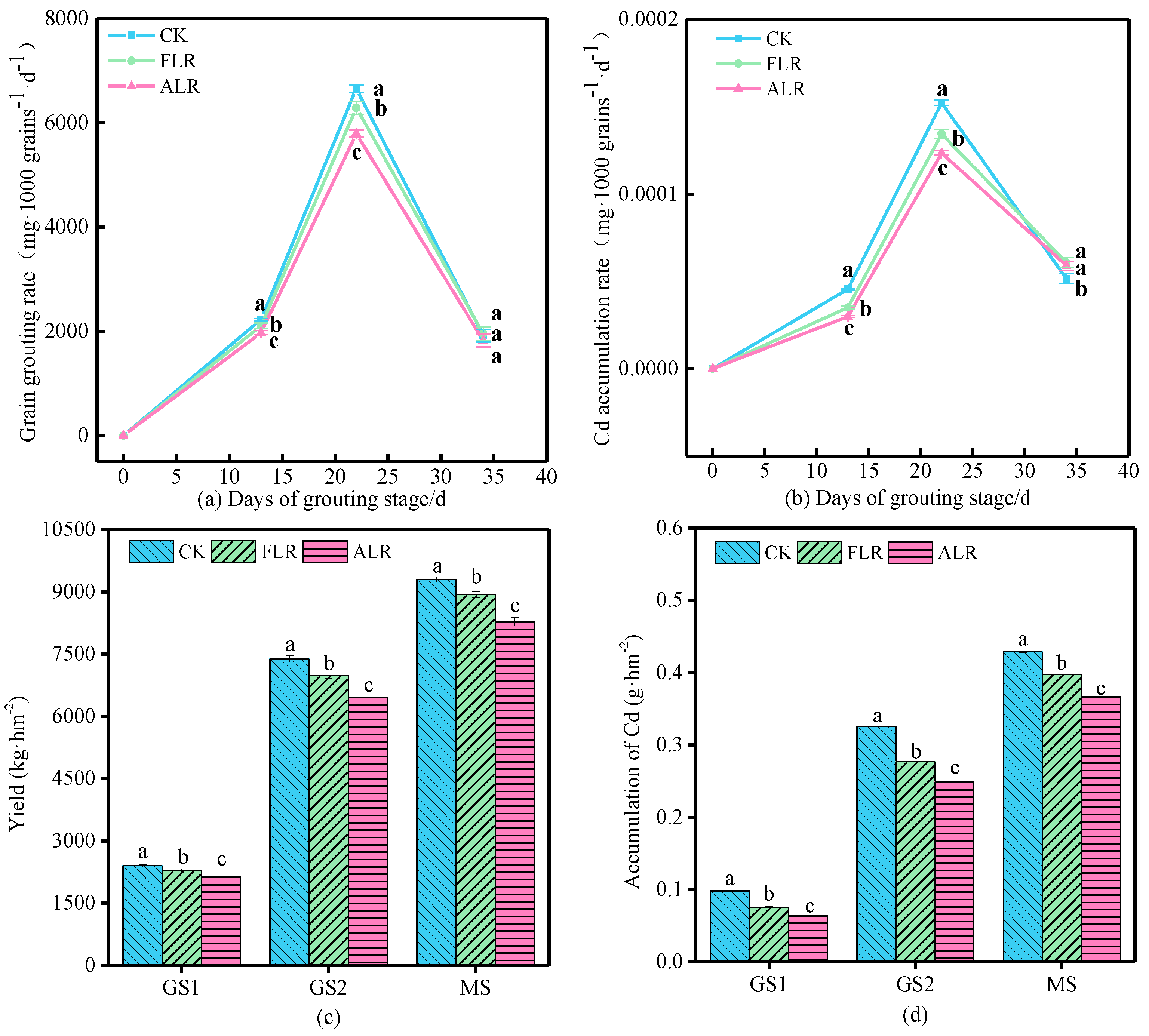
3.4. Grain Cd Accumulation Characteristics during the Filling Stage
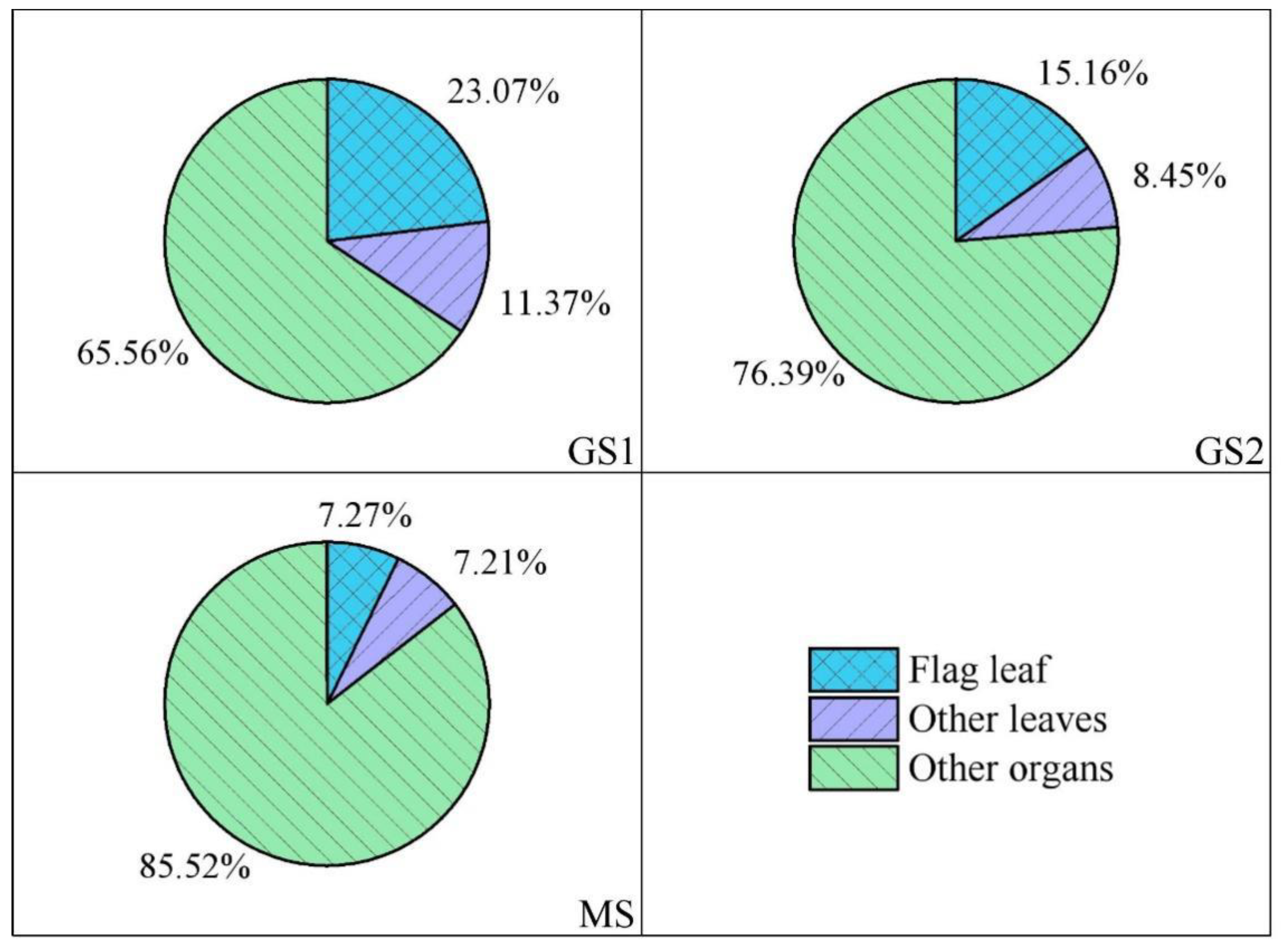
3.5. Relative Contributions of Wheat Leaves-to-Grain Cd Accumulation
3.6. Future Applications of Research
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, G.L.; Zhu, S.; Bai, S.N.; Xia, Y.; Lou, L.Q.; Cai, Q.S. The transportation and accumulation of arsenic, cadmium, and phosphorus in 12 wheat cultivars and their relationships with each other. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.G.; Zhang, C.; Du, B.Y.; Lu, B.X.; Zhou, D.M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J. Effects of node restriction on cadmium accumulation in eight Chinese wheat (Triticum turgidum) cultivars. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, I.M.; Micle, V.; Polyak, E.T.; Gabor, T. Assessment of Soil Quality Status and the Ecological Risk in the Baia Mare, Romania Area. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, F.Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Mechanism of Pb absorption in wheat grains. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Abe, T.; Baba, K.; Arao, T.; Terada, Y. Role of the node in controlling traffic of cadmium, zinc, and manganese in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Fujita, M.; Ota, T.; Minamiyama, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Shinano, T. Varietal differences in the absorption and partitioning of cadmium in common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 124, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Niazi, N.K.; Xiong, T.T.; Farooq, A.B.U.; Khalid, S. Ecotoxicology of heavy metal (loid)-enriched particulate matter: Foliar accumulation by plants and health impacts. Rev. Environ Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 253, 65–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Guo, M.Y.; Li, X.H.; Luo, X.X.; Pan, R.K.; Ouyang, T.P. Spatial distribution, pollution, and health risk assessment of heavy metal in agricultural surface soil for the Guangzhou-Foshan urban zone, South China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J. Study of the bioavailability of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition on the soil-pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 362, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, P.; Yang, J.; Lin, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.Z. Evaluating the contributions of leaf organ to wheat grain cadmium at the filling stage. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Xu, Z.Q.; Peng, J.W.; Fei, J.C.; Yu, P.Y.; Wang, M.D.; Tan, Y.F.; Huang, Y.; Zhran, M.; Fahmy, A. The contribution of atmospheric deposition of cadmium and lead to their accumulation in rice grains. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Wang, W.Q.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, F.W.; He, D.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Chang, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; et al. Effects of simulated Cd deposition on soil Cd availability, microbial response, and crop Cd uptake in the passivation-remediation process of Cd-contaminated purple soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olszewski, J.; Makowska, M.; Pszczółkowska, A.; Okorski, A.; Bieniaszewski, T. The effect of nitrogen fertilization on flag leaf and ear photosynthesis and grain yield of spring wheat. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xie, P.; Zhang, K.; Yang, J.X.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, F.Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, H.Z. Contribution of the flag leaf to lead absorption in wheat grain at the grain-filling stage. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2021, 225, 112722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.S.; Taylor, G.J. Cadmium uptake and partitioning in durum wheat during grain filling. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bragado, R.; Molero, G.; Reynolds, M.P.; Araus, J.L. Relative contribution of shoot and ear photosynthesis to grain filling in wheat under good agronomical conditions assessed by differential organ δ13C. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5401–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maydup, M.L.; Antonietta, M.; Graciano, C.; Guiamet, J.J.; Tambussi, E.A. The contribution of the awns of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) to grain filling: Responses to water deficit and the effects of awns on ear temperature and hydraulic conductance. Field Crops Res. 2014, 167, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Xiao, X.Y.; Peng, C.; Shi, L.; Ran, H.Z.; Xu, W.X. Atmospheric deposition as a source of cadmium and lead to soil-rice system and associated risk assessment. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.R.; Rong, H.; Zhang, X.B.; Shi, W.J.; Hong, X.; Liu, W.C.; Cao, T.; Yu, X.X.; Yu, Q.F. Effects and mechanisms of foliar application of silicon and selenium composite sols on diminishing cadmium and lead translocation and affiliated physiological and biochemical responses in hybrid rice (Oryza sativa L.) exposed to cadmium and lead. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, W.C.; Chen, R.C.; Liu, M.N.; Yao, H.L.; Li, J.H.; Hong, J.L.; Mao, X.Y. Reducing Cd accumulation in rice grain with foliar application of glycerol and its mechanisms of Cd transport inhibition. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, F.Y.; Hu, B.; Wei, M.B.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Quantitative analysis of lead sources in wheat tissue and grain under different lead atmospheric deposition areas. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 36710–36719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Liu, F.Y.; Hu, B.; Wei, M.B.; Zhao, J.H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.Z. Direct evidence of lead contamination in wheat tissues from atmospheric deposition based on atmospheric deposition exposure contrast tests. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 185, 109688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igalavithana, A.D.; Farooq, M.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Qayyum, M.F.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Determining soil quality in urban agricultural regions by soil enzyme-based index. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1531–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, F.; Xuan, X. Impacts of industrial restructuring and technological progress on PM2.5 Pollution: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Cheng, C.X. Temporal and Spatial Heterogeneity of PM2.5 Related to Meteorological and Socioeconomic Factors across China during 2000–2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.S.; Zhu, J.; Li, W.F.; Xu, D.; Liu, J.Z. Estimation of the PM2.5 health effects in China during 2000–2011. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 10695–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edlund, K.K.; Killman, F.; Molnár, P.; Boman, J.; Stockfelt, L.; Wichmann, J. Health risk assessment of PM2.5 and PM2.5-bound trace elements in Thohoyandou, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Gui, H.R.; Lin, M.L.; Peng, W.H. Chemical speciation distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soil from Sunan mining area, Anhui Province, China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. 2018, 24, 1694–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirasophon, S.; Pochanart, P. The Long-term Characteristics of PM10 and PM2.5 in Bangkok, Thailand. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 14, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.P.; Zhang, X.M.; Xue, P.Y.; Dong, J.W.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, Q.L.; Geng, L.P.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, W.J. Mechanism of Pb accumulation in Chinese cabbage leaves: Stomata and trichomes regulate foliar uptake of Pb in atmospheric PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 293, 118585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcen, N. Stomatal parameters and growth responses of nicotiana and atriplex to Cd, Pb and Cd–Pb-contaminated soil. Fresen. Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 6340–6345. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.L.; Chi, M.C.; Guo, S.E.; Lin, Y.C.; Chou, C.T.; Lin, C.M. Seasonal variation and source apportionment of PM2.5-bound trace elements at a coastal area in southwestern Taiwan. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 9101–9113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.L.; Lyu, Y.L.; Yang, Y.Y. Concentrations and chemical forms of heavy metals in the bulk atmospheric deposition of Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 27356–27365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, E.; Foucault, Y.; Sarret, G.; Sobanska, S.; Cécillon, L.; Castrec-Rouelle, M.; Uzu, G.; Dumat, C. Metal and metalloid foliar uptake by various plant species exposed to atmospheric industrial fallout: Mechanisms involved for lead. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenele, N.M.B.; Otoch, M.D.L.O.; Gomes-Rochette, N.F.; de Menezes Sobreira, A.C.; Barreto, A.A.G.C.; de Oliveira, F.D.B.; Costa, J.H.; da Silveira Sa Borges, S.; do Nascimento, R.F.; de Melo, D.F. Effect of lead on physiological and antioxidant responses in two Vigna unguiculata cultivars differing in Pb-accumulation. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichert, T.; Kurtz, A.; Steiner, U.; Goldbach, H.E. Size exclusion limits and lateral heterogeneity of the stomatal foliar uptake pathway for aqueous solutes and water-suspended nanoparticles. Physiol. Plantarum. 2008, 134, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Eichert, T. Uptake of hydrophilic solutes through plant leaves: Current state of knowledge and perspectives of foliar fertilization. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2009, 28, 36–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajbhiye, T.; Pandey, S.K.; Kim, K.H.; Szulejko, J.E.; Prasad, S. Airborne foliar transfer of PM bound heavy metals in Cassia siamea: A less common route of heavy metal accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, J.W.; Li, Z.G.; Liu, B.X.; Cheng, G.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, Y.C.; Zhou, S.Q.; Yuan, W.Y. Source apportionment of heavy metal and their health risks in soil-dustfall-plant system nearby a typical non-ferrous metal mining area of Tongling, Eastern China. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelstein, M.; Ben-Hur, M. Heavy metals and metalloids: Sources, risks and strategies to reduce their accumulation in horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 234, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Ghafoor, A.; Farooq, M. Suppression of cadmium concentration in wheat grains by silicon is related to its application rate and cadmium accumulating abilities of cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agr. 2015, 95, 2467–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oropeza, G.N.; Hausler, R.; Glaus, M.; Vega, A.R.; Romero, L.R. Transport of heavy metals in materials with diameter analogous to xylem vessels. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2014, 8, 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrut, B.; Shahid, M.; Dumat, C.; Winterton, P.; Pinelli, E. Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 213, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, Q.S.; Zhang, L.L.; Chen, S.X.; Li, G.P.; Wang, W.L. Effects of foliar application of magnesium sulfate on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter accumulation and its translocation, and carbohydrate metabolism in grain during wheat grain filling. Cereal Res. Commun. 2020, 48, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xia, H.Y.; Fan, S.J.; Song, J.; Lv, X.M.; Kong, L.G. Photosynthetic characteristics of non-foliar organs in main C3 cereals. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 166, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, L.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Mao, P.S. Contribution of the pod wall to seed grain filling in alfalfa. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.R.; Wang, C.R.; Huang, Y.C.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.Q.; Huang, Y.Z.; Cheng, L.L.; Huang, Y.F.; Zhang, C.B. Foliar application of the sulfhydryl compound 2, 3-dimercaptosuccinic acid inhibits cadmium, lead, and arsenic accumulation in rice grains by promoting heavy metal immobilization in flag leaves. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, L.L.; Li, X.R.; Chen, J.X.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y.; Lv, J.Y. Photosynthetic and ascorbate-glutathione metabolism in the flag leaves as compared to spikes under drought stress of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.Y.; Hou, P.; Duan, F.Y.; Niu, L.; Dai, T.B.; Wang, K.R.; Zhao, M.; Li, S.K.; Zhou, W.B. Improving photosynthesis to increase grain yield potential: An analysis of maize hybrids released in different years in China. Photosynt. Res. 2021, 150, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.X.; Ding, C.F.; Guo, F.Y.; Li, X.G.; Zhou, Z.G.; Zhang, T.L.; Wang, X.X. The role of node restriction on cadmium accumulation in the brown rice of 12 Chinese rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10157–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. The node, a hub for mineral nutrient distribution in graminaceous plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Moore, K.L.; Miller, A.J.; McGrath, S.P.; Ma, J.F.; Zhao, F.J. The role of nodes in arsenic storage and distribution in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 3717–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Environmental Medium | Cd (mg·kg−1) | Acid Soluble State | Reducible State | Oxidizable State | Residual State |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 0.25 ± 0.04 | 15.22% ± 1.35% | 20.83% ± 0.66% | 22.34% ± 1.01% | 41.60% ± 2.75% |
| Atmospheric particles | 3.1 ± 0.25 | 24.70% ± 1.68% | 16.63% ± 1.96% | 17.56% ± 1.93% | 41.11% ± 5.05% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, C.; Lin, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, H. The Relative Contributions of Different Wheat Leaves to the Grain Cadmium Accumulation. Toxics 2022, 10, 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110637
Ma C, Lin L, Yang J, Zhang H. The Relative Contributions of Different Wheat Leaves to the Grain Cadmium Accumulation. Toxics. 2022; 10(11):637. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110637
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Chuang, Lin Lin, Jun Yang, and Hongzhong Zhang. 2022. "The Relative Contributions of Different Wheat Leaves to the Grain Cadmium Accumulation" Toxics 10, no. 11: 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110637
APA StyleMa, C., Lin, L., Yang, J., & Zhang, H. (2022). The Relative Contributions of Different Wheat Leaves to the Grain Cadmium Accumulation. Toxics, 10(11), 637. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10110637







