Accumulation, Depuration, and Biological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic Spheres and Adsorbed Cadmium and Benzo(a)pyrene on the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mussels
2.2. Microplastics
2.3. Experiment 1: 1-Day Exposure and 3-Day Depuration of Pristine MPs
2.4. Experiment 2: 3-Day Exposure to Pristine and Contaminant Adsorbed MPs
2.4.1. Chemical Analysis of the Mussel and Water Samples
2.4.2. Biochemical Analysis of the Antioxidant and Peroxisomal Enzyme Activity
2.4.3. Lysosomal Membrane Stability
2.4.4. Tissue Metal Accumulation after Autometallography
2.4.5. Quantitative Histological Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Accumulation and Depuration of MPs in Mussel Tissue
3.2. Metal and PAH Accumulation in Mussels and Concentration in Exposure Media
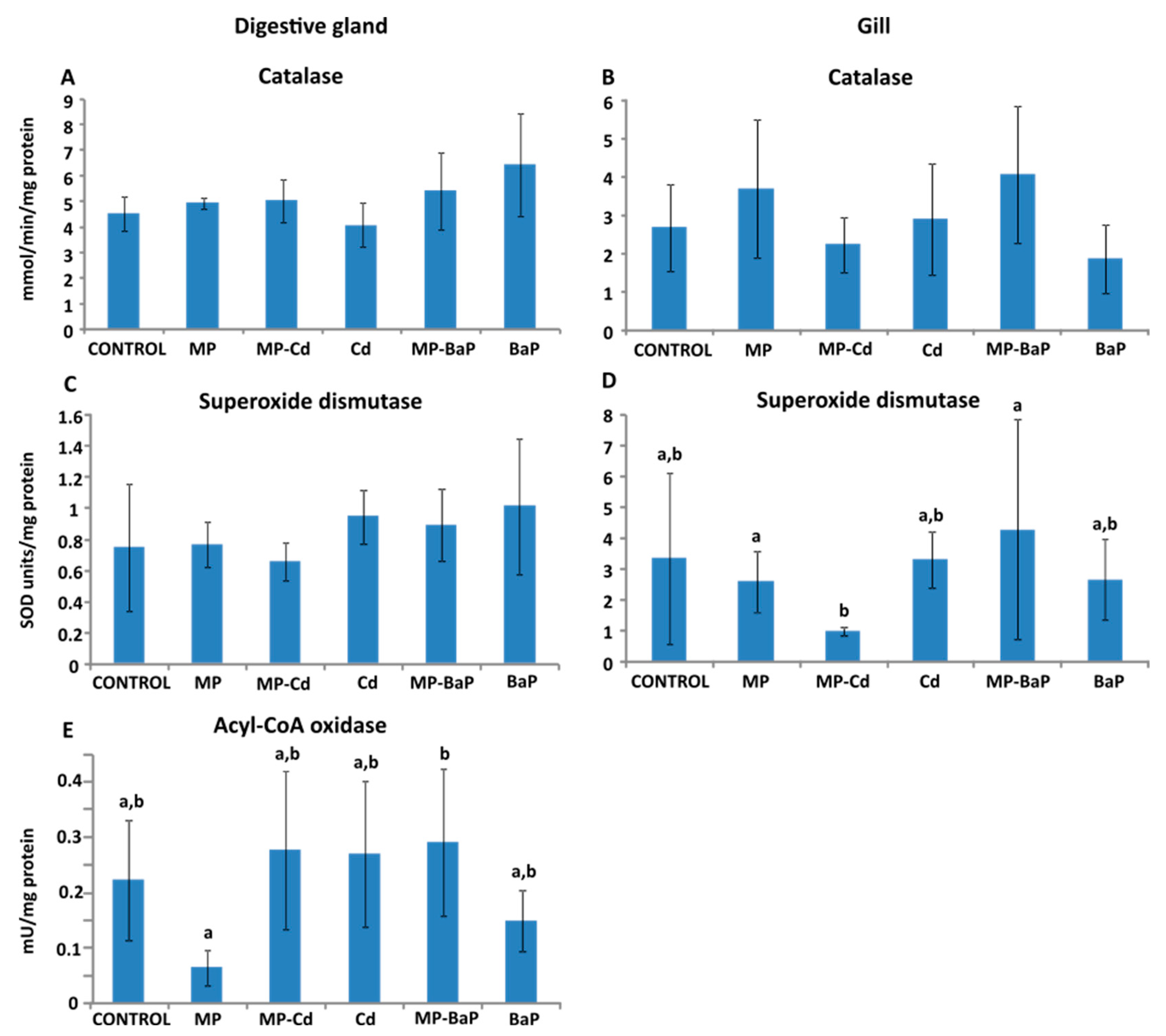
3.3. Activity of Antioxidant and Peroxisomal Enzymes
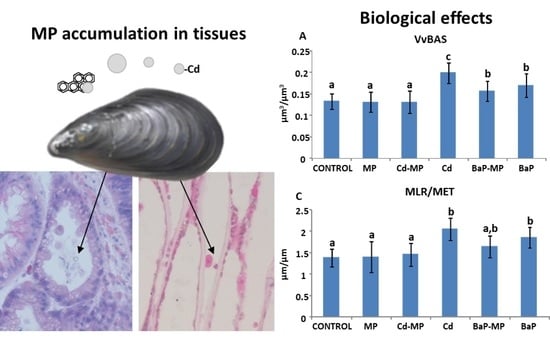
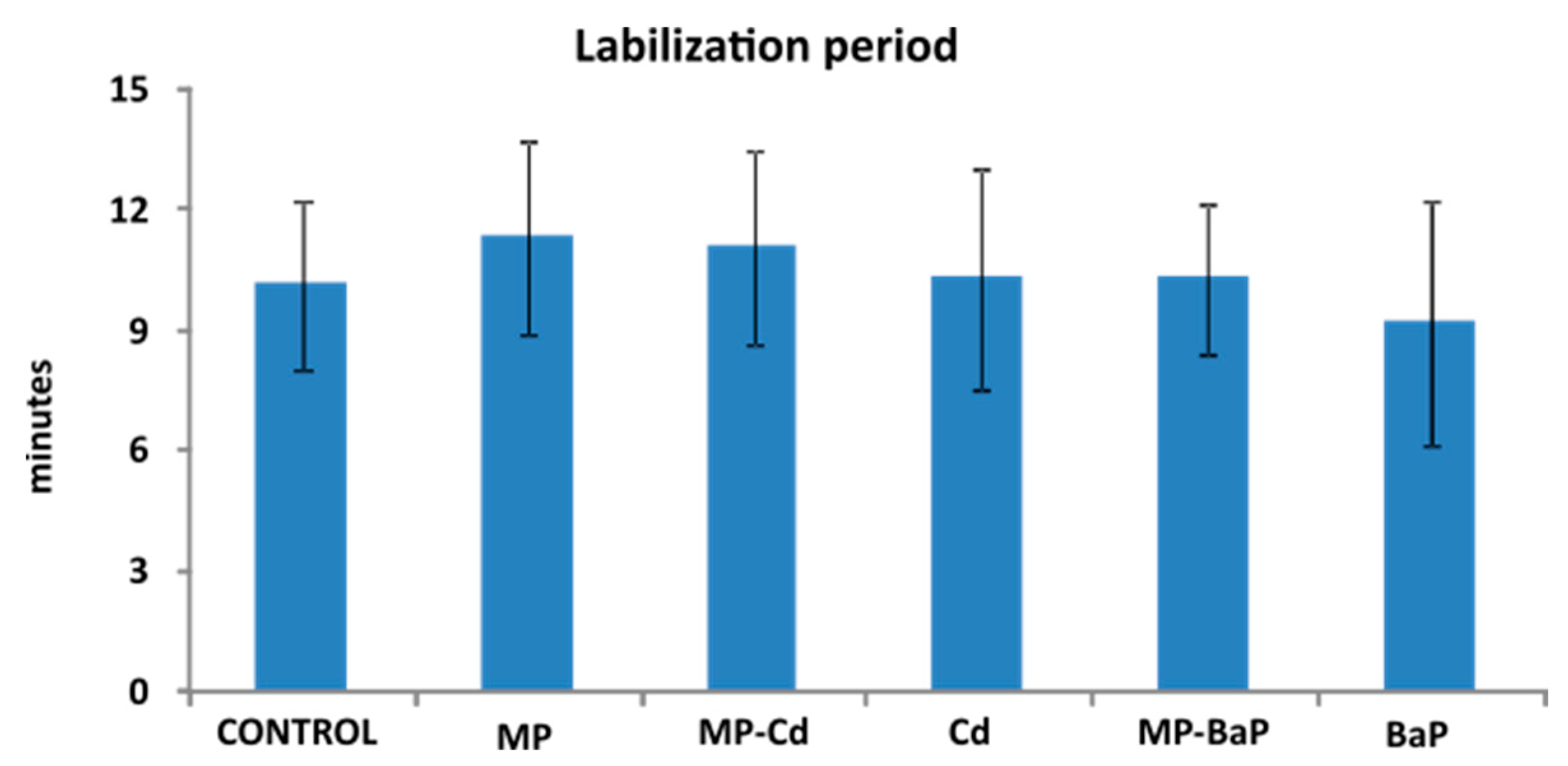
3.4. Lysosomal Membrane Stability
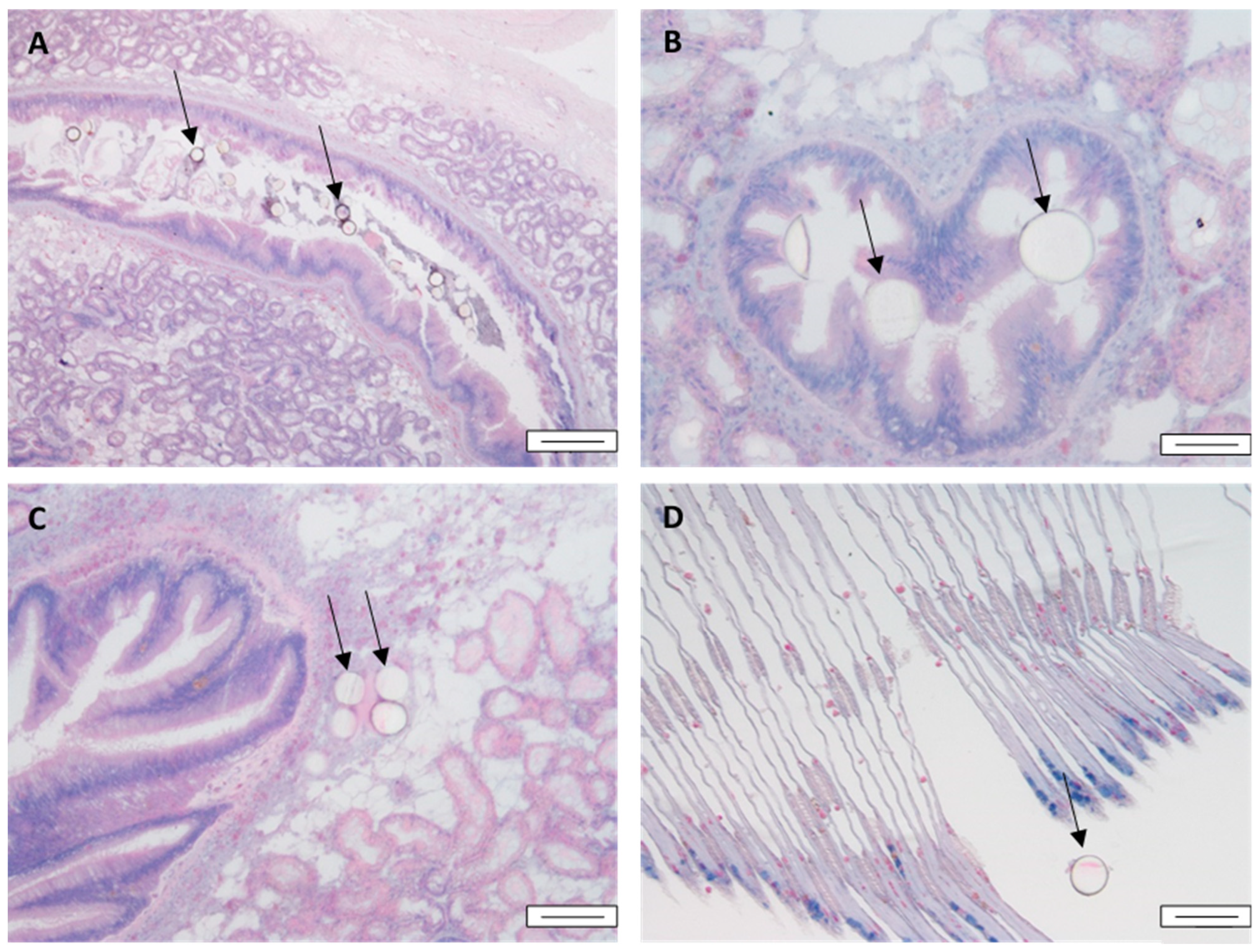
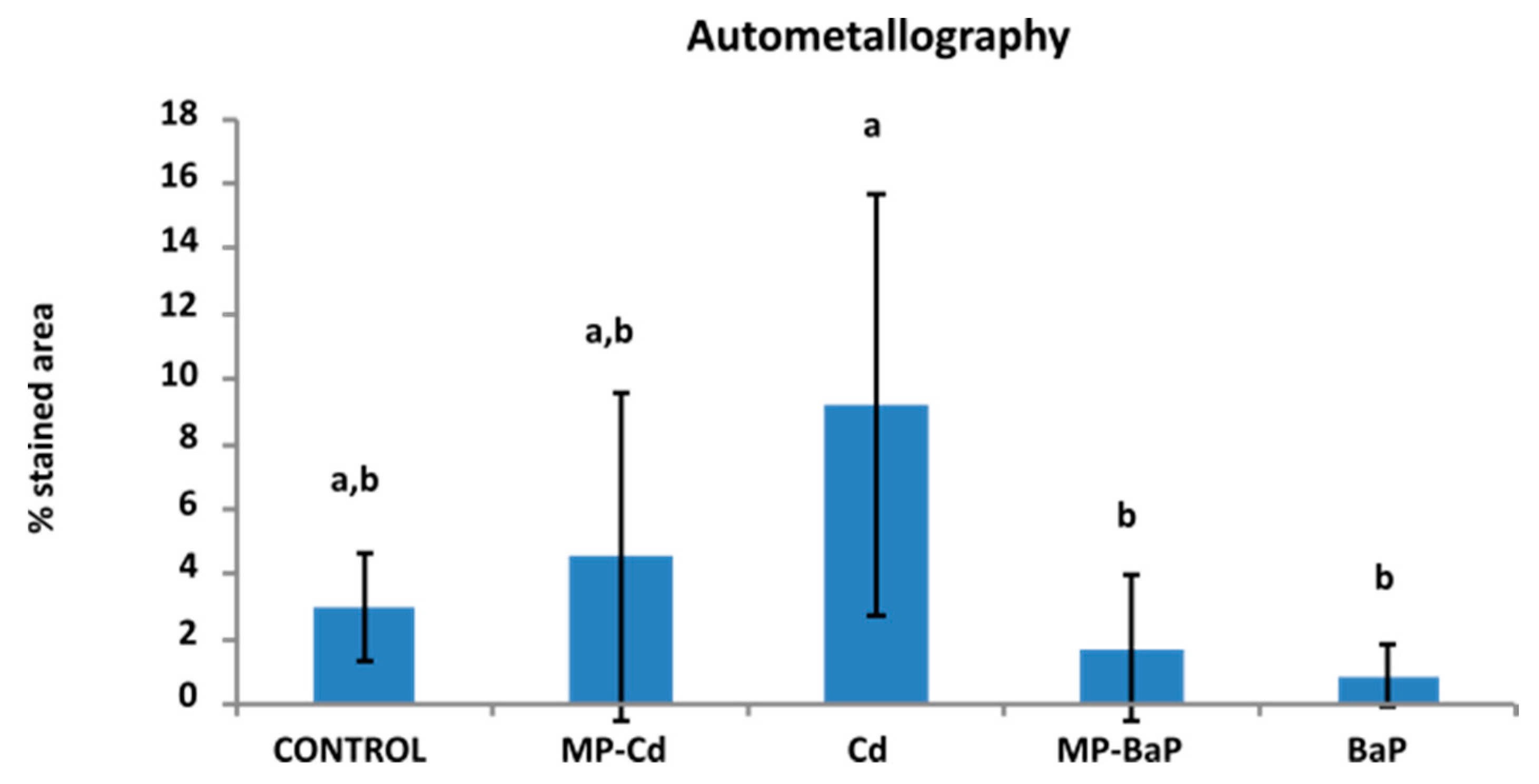
3.5. Tissue Metal Distribution and Accumulation after Autometallography
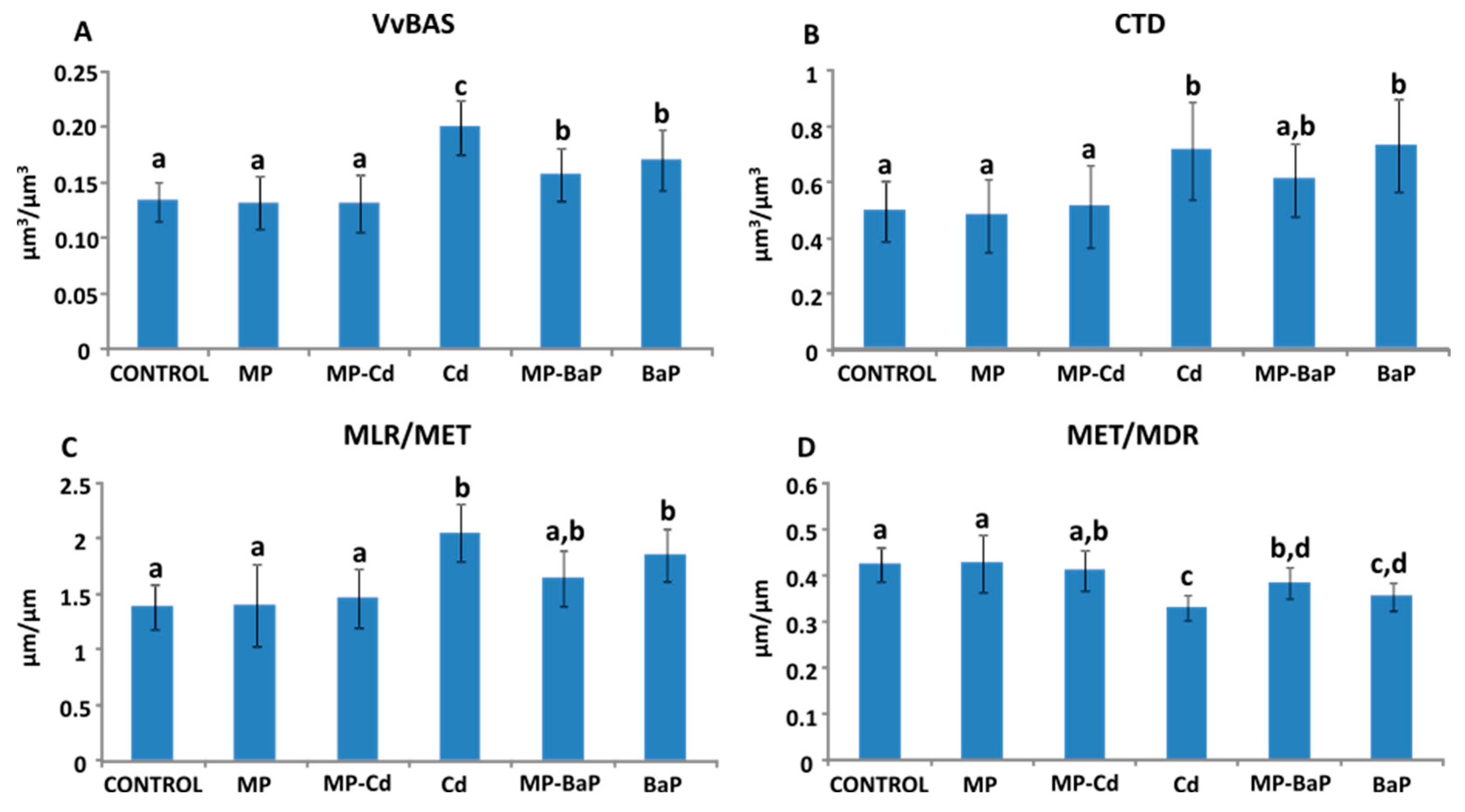
3.6. Quantitative Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantitative Histological Analysis
4.2. Accumulation and Effects of Contaminated MPs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastics Europe Plastics—The Facts 2020. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Plastics_the_facts-WEB-2020_versionJun21_final.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Sharma, S.; Chatterjee, S. Microplastic pollution, a threat to marine ecosystem and human health: A short review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21530–21547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A. Sources and pathways of microplastics to Habitats. In Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2015; pp. 229–244. ISBN 978-3-319-16510-3. [Google Scholar]
- Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.M.; Van Franeker, J.A.; Leopold, M.F.; Kühn, S.; Bravo Rebolledo, E.L.; Heße, E.; Mielke, L.; IJzer, J.; Kamminga, P.; et al. Microplastic in a macro filter feeder: Humpback whale Megaptera novaeangliae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, L.; Peng, G.; Xu, P.; Li, D. Food-web transfer of microplastics between wild caught fish and crustaceans in East China Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 146, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, D.K.A.; Milner, P. Drifting plastic and its consequences for sessile organism dispersal in the Atlantic Ocean. Mar. Biol. 2005, 146, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galgani, F.; Hanke, G.; Werner, S.; De Vrees, L. Marine litter within the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2013, 70, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeiren, P.; Muñoz, C.; Ikejima, K. Microplastic identification and quantification from organic rich sediments: A validated laboratory protocol. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, K.; Herrera, A.; Gómez, M. Microplastics in marine biota: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 169, 112540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziccardi, L.M.; Edgington, A.; Hentz, K.; Kulacki, K.J.; Kane Driscoll, S. Microplastics as vectors for bioaccumulation of hydrophobic organic chemicals in the marine environment: A state-of-the-science review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1667–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotopoulou, K.N.; Karapanagioti, H.K. Surface properties of beached plastic pellets. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 81, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Hentschel, B.T.; Kaye, S. Long-term field measurement of sorption of organic contaminants to five types of plastic pellets: Implications for plastic marine debris. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1646–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velzeboer, I.; Kwadijk, C.J.A.F.; Koelmans, A.A. Strong sorption of PCBs to nanoplastics, microplastics, carbon nanotubes, and fullerenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Shim, W.J.; Kwon, J.-H. Sorption capacity of plastic debris for hydrophobic organic chemicals. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, L.; Hobson, K.A.; Welch, H.E. Biomagnification and bioaccumulation of mercury in an arctic marine food web: Insights from stable nitrogen isotope analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, K.J.; Hall, A.J.; Debier, C.; Eppe, G.; Thomé, J.-P.P.; Bennett, K.A. Persistent organic pollutant burden, experimental POP exposure, and tissue properties affect metabolic profiles of blubber from Gray Seal pups. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13523–13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, S.D.; Brenner, D.; Bourakovsky, A.; Mahaffey, C.A.; Perkins, C.R. Polychlorinated biphenyls and chlorinated pesticides in harbor seals (Phoca vitulina concolor) from the northwestern Atlantic coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, A.H.; Veldhoen, N.; Ellis, G.; Ford, J.K.B.; Helbing, C.C.; Ross, P.S. PCB-associated changes in mRNA expression in Killer Whales (Orcinus orca) from the NE Pacific Ocean. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10194–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeersch, G.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R.; Marques, A.; Granby, K.; Fait, G.; Kotterman, M.J.J.; Diogène, J.; Bekaert, K.; Robbens, J.; et al. A critical view on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M.; Thompson, R.C. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis (L.). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, J.; Green, N.W.; Brooks, S.; Allan, I.J.; Ruus, A.; Gomes, T.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Schøyen, M. Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis spp.) as sentinel organisms in coastal pollution monitoring: A review. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 130, 338–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.; Martins, M.; Sobral, P.; Costa, P.M.; Costa, M.H. An assessment of the ability to ingest and excrete microplastics by filter-feeders: A case study with the Mediterranean mussel. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lusher, A.L.; Rotchell, J.M.; Deudero, S.; Turra, A.; Bråte, I.L.N.; Sun, C.; Shahadat Hossain, M.; Li, Q.; Kolandhasamy, P.; et al. Using mussel as a global bioindicator of coastal microplastic pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, G.M.; Nina Steffani, C. Can we predict the effects of alien species? A case-history of the invasion of South Africa by Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 300, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccherelli, V.U.; Rossi, R. Settlement, growth and production of the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1984, 16, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Bebianno, M.J.; Blasco, J.; Porte, C.; Sarasquete, C.; Viarengo, A. The use of biomarkers to assess the impact of pollution in coastal environments of the Iberian Peninsula: A practical approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 247, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Köhler, A. Uptake and effects of microplastics on cells and tissue of the Blue Mussel Mytilus edulis L. after an experimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, B.; Albentosa, M. Insights into the uptake, elimination and accumulation of microplastics in mussel. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avio, C.G.; Gorbi, S.; Milan, M.; Benedetti, M.; Fattorini, D.; D’Errico, G.; Pauletto, M.; Bargelloni, L.; Regoli, F. Pollutants bioavailability and toxicological risk from microplastics to marine mussels. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 198, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Soto, N.; Hatfield, J.; Katsumiti, A.; Duroudier, N.; Lacave, J.M.; Bilbao, E.; Orbea, A.; Navarro, E.; Cajaraville, M.P. Impacts of dietary exposure to different sized polystyrene microplastics alone and with sorbed benzo[a]pyrene on biomarkers and whole organism responses in mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 548–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Weinstein, J.E.; van den Hurk, P.; Klaine, S.J. Trophic transfer of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems: Identifying critical research needs. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Bakir, A.; Burton, G.A.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastic as a vector for chemicals in the aquatic environment: Critical review and model-supported reinterpretation of empirical studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3315–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Sun, S.; Du, X.; Han, Y.; Shi, W.; Liu, G. Immunotoxicity and neurotoxicity of bisphenol A and microplastics alone or in combination to a bivalve species, Tegillarca granosa. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Han, Y.; Sun, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Du, X.; Liu, G. Immunotoxicities of microplastics and sertraline, alone and in combination, to a bivalve species: Size-dependent interaction and potential toxication mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 396, 122603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Han, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shi, W.; Du, X.; Sun, S.; Liu, G. Microplastics aggravate the Bioaccumulation of two waterborne veterinary antibiotics in an edible bivalve species: Potential mechanisms and implications for human health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 8115–8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Jones, P.R.; Moore, C.; Narayan, U.V. Quantification of persistent organic pollutants adsorbed on plastic debris from the North Pacific Gyre’s “eastern garbage patch”. J. Environ. Monit. 2010, 12, 2226–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banni, M.; Negri, A.; Dagnino, A.; Jebali, J.; Ameur, S.; Boussetta, H. Acute effects of benzo[a]pyrene on digestive gland enzymatic biomarkers and DNA damage on mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Straif, K.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part F: Chemical agents and related occupations. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speciale, A.; Zena, R.; Calabrò, C.; Bertuccio, C.; Aragona, M.; Saija, A.; Trombetta, D.; Cimino, F.; Lo Cascio, P. Experimental exposure of blue mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) to high levels of benzo[a]pyrene and possible implications for human health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 150, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batel, A.; Linti, F.; Scherer, M.; Erdinger, L.; Braunbeck, T. Transfer of benzo[a]pyrene from microplastics to Artemia nauplii and further to zebrafish via a trophic food web experiment: CYP1A induction and visual tracking of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1656–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittura, L.; Avio, C.G.; Giuliani, M.E.; D’Errico, G.; Keiter, S.H.; Cormier, B.; Gorbi, S.; Regoli, F. Microplastics as vehicles of environmental PAHs to marine organisms: Combined chemical and physical hazards to the Mediterranean mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Chapman, E.C.; Shi, H.; Rotchell, J.M. PVC does not influence cadmium uptake or effects in the mussel (Mytilus edulis). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davarpanah, E.; Guilhermino, L. Single and combined effects of microplastics and copper on the population growth of the marine microalgae Tetraselmis chuii. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.R.; Syberg, K.; Shashoua, Y.; Bury, N.R. Influence of polyethylene microplastic beads on the uptake and localization of silver in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Yang, C.; Wu, L. Combined toxicity of microplastics and cadmium on the zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, B.; Bendell, L.I. Macro and micro plastics sorb and desorb metals and act as a point source of trace metals to coastal ecosystems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; Cajaraville, M.P. Peroxisome proliferation and antioxidant enzymes in transplanted mussels of four Basque estuaries with different levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and polychlorinated biphenyl pollution. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-B.; Kang, H.-M.; Lee, M.-C.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, J.; Hwang, D.-S.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Shin, K.-H.; Park, H.G.; et al. Adverse effects of microplastics and oxidative stress-induced MAPK/Nrf2 pathway-mediated defense mechanisms in the marine copepod Paracyclopina nana. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soto, M.; Marigómez, I. BSD Extent, an index for metal pollution screening based on the metal content within digestive cell lysosomes of mussels as determined by autometallography. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 37, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubaish, F.; Liebezeit, G. Suspended microplastics and black carbon particles in the jade system, southern north sea. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marigómez, I.; Izagirre, U.; Lekube, X. Lysosomal enlargement in digestive cells of mussels exposed to cadmium, benzo[a]pyrene and their combination. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, G.M.; Burdett, K.; Connock, M.J. A sensitive spectrophotometric assay for peroxisomal acyl-CoA oxidase. Biochem. J. 1985, 227, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebi, H. Catalase Methods of Enzymatic Analysis, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Porte, C.; Sole, M.; Albaigés, J.; Livingstone, D.R. Responses of mixed-function oxygenase and antioxidase enzyme system of Mytilus sp. to organic pollution. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1991, 100, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. UNEP/RAMOGE: Manual on the Biomarkers Recommended for the MED POL Biomonitoring Programme; UNEP: Athens, Greece, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Garmendia, L.; Soto, M.; Vicario, U.; Kim, Y.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Marigómez, I. Application of a battery of biomarkers in mussel digestive gland to assess long-term effects of the Prestige oil spill in Galicia and Bay of Biscay: Tissue-level biomarkers and histopathology. J. Environ. Monit. 2011, 13, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignell, J.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Marigómez, I. Background Document: Histopathology of Mussels (Mytilus spp.) for Health Assessment in Biological Effects Monitoring. In Integrated Marine Environmental Monitoring of Chemicals and Their Effects; Davies, I.M., Vethaak, A.D., Eds.; ICES Cooperative Research Report No. 315; ICEM: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2012; p. 277. Available online: https://www.ices.dk/sites/pub/Publication%20Reports/Cooperative%20Research%20Report%20(CRR)/CRR315.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Faggio, C.; Tsarpali, V.; Dailianis, S. Mussel digestive gland as a model tissue for assessing xenobiotics: An overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Browne, M.A.; Underwood, A.J.; van Franeker, J.A.; Thompson, R.C.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. The ecological impacts of marine debris: Unraveling the demonstrated evidence from what is perceived. Ecology 2016, 97, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Besseling, E.; Foekema, E.; Kooi, M.; Mintenig, S.; Ossendorp, B.C.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.E.; Verschoor, A.; van Wezel, A.P.; Scheffer, M. Risks of plastic debris: Unravelling fact, opinion, perception, and belief. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11513–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroja, E.; Christoforou, E.; Lindström, J.; Spatharis, S. Effects of microplastics on bivalves: Are experimental settings reflecting conditions in the field? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 171, 112696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Hansson, L.-A.; Lard, M.; Frohm, B.; Linse, S. Food chain transport of nanoparticles affects behaviour and fat metabolism in fish. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fossi, M.C.; Coppola, D.; Baini, M.; Giannetti, M.; Guerranti, C.; Marsili, L.; Panti, C.; de Sabata, E.; Clò, S. Large filter feeding marine organisms as indicators of microplastic in the pelagic environment: The case studies of the Mediterranean basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) and fin whale (Balaenoptera physalus). Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 100, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios Mendoza, L.M.; Jones, P.R. Characterisation of microplastics and toxic chemicals extracted from microplastic samples from the North Pacific Gyre. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sıkdokur, E.; Belivermiş, M.; Sezer, N.; Pekmez, M.; Bulan, Ö.K.; Kılıç, Ö. Effects of microplastics and mercury on manila clam Ruditapes philippinarum: Feeding rate, immunomodulation, histopathology and oxidative stress. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.M.; Fero, K.; Arrenberg, A.B.; Bergeron, S.A.; Driever, W.; Burgess, H.A. Deep brain photoreceptors control light-seeking behavior in zebrafish larvae. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trestrail, C.; Nugegoda, D.; Shimeta, J. Invertebrate responses to microplastic ingestion: Reviewing the role of the antioxidant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 138559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Châtel, A.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B.; et al. Realistic environmental exposure to microplastics does not induce biological effects in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 150, 110627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Wei, S.; Shang, Y.; Gu, H.; Wu, F.; Lan, Z.; Hu, M.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y. Microplastics impair digestive performance but show little effects on antioxidant activity in mussels under low pH conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbea, A.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Cajaraville, M.P. Interactive effects of benzo(a)pyrene and cadmium and effects of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on antioxidant and peroxisomal enzymes and peroxisomal volume density in the digestive gland of mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis Lmk. Biomarkers 2002, 7, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revel, M.; Lagarde, F.; Perrein-Ettajani, H.; Bruneau, M.; Akcha, F.; Sussarellu, R.; Rouxel, J.; Costil, K.; Decottignies, P.; Cognie, B.; et al. Tissue-specific biomarker responses in the Blue Mussel Mytilus spp. exposed to a mixture of microplastics at environmentally relevant concentrations. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kögel, T.; Bjorøy, Ø.; Toto, B.; Bienfait, A.M.; Sanden, M. Micro- and nanoplastic toxicity on aquatic life: Determining factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancio, I.; Orbea, A.; Völkl, A.; Fahimi, H.D.; Cajaraville, M.P. Induction of peroxisomal oxidases in mussels: Comparison of effects of lubricant oil and benzo(a)pyrene with two typical peroxisome proliferators on peroxisome structure and function in Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 149, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschino, V.; Da Ros, L. Biochemical and lysosomal biomarkers in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Mar Piccolo of Taranto (Ionian Sea, Southern Italy). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 12770–12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimbrough, K.L.; Johnson, W.E.; Lauenstein, G.G.; Christensen, J.D.; Apeti, D.A. An Assessment of Two Decades of Contaminant Monitoring in the Nation’s Coastal Zone; NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS 74; NCCOS: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2008; 105p. Available online: https://coastalscience.noaa.gov/data_reports/an-assessment-of-two-decades-of-contaminant-monitoring-in-the-nations-coastal-zone/ (accessed on 12 March 2020).
- Blanco-Rayón, E.; Ivanina, A.V.; Sokolova, I.M.; Marigómez, I.; Izagirre, U. Food-type may jeopardize biomarker interpretation in mussels used in aquatic toxicological experimentation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izagirre, U.; Ramos, R.; Marigómez, I. Natural variability in size and membrane stability of lysosomes in mussel digestive cells: Seasonal and tidal zonation. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 372, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Ríos, A.; Pérez, L.; Ortiz-Zarragoitia, M.; Serrano, T.; Barbero, M.C.; Echavarri-Erasun, B.; Juanes, J.A.; Orbea, A.; Cajaraville, M.P. Assessing the effects of treated and untreated urban discharges to estuarine and coastal waters applying selected biomarkers on caged mussels. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Garmendia, L.; Orbea, A.; Werding, R.; Gómez-Mendikute, A.; Izagirre, U.; Soto, M.; Marigómez, I. Signs of recovery of mussels health two years after the Prestige oil spill. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 62, S337–S341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cajaraville, M.P.; Marigómez, J.A.; Díez, G.; Angulo, E. Comparative effects of the water accommodated fraction of three oils on mussels—2. Quantitative alterations in the structure of the digestive tubules. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. 1992, 102, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimeno-Romero, A.; Bilbao, E.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Soto, M.; Marigómez, I. Bioaccumulation, tissue and cell distribution, biomarkers and toxicopathic effects of CdS quantum dots in mussels, Mytilus galloprovincialis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Group | Digestive Gland | Gills | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | F | Stomach Lumen | Duct Lumen | Tubule Lumen | Connective Tissue | n | F | within Filaments | outside Filaments | |||
| 45 µm particles | C1 | E | 10 | 50 | 0.3 ± 0.67 | n.o. | n.o. | 0.1 ± 0.3 | 10 | 20 | n.o. | 0.3 ± 0.67 |
| D1 | 10 | 10 | 0.3 ± 0.95 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | 9 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | ||
| D2 | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | ||
| D3 | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | ||
| C2 | E | 8 | 100 | 8.1 ± 7.41 | 3.5 ± 8.75 | 0.25 ± 0.71 | 1.37 ± 2.39 | 10 | 30 | n.o. | 0.8 ± 1.62 | |
| D1 | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 20 | n.o. | 0.2 ± 0.42 | ||
| D2 | 10 | 20 | 1.1 ± 2.33 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | ||
| D3 | 10 | 20 | 0.2 ± 0.63 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 10 | n.o. | 0.1 ± 0.32 | ||
| C3 | E | 10 | 100 | 83.6 ± 112.32 | 13 ± 27.02 | 1.1 ± 1.91 | 11.7 ± 31.60 | 10 | 40 | n.o. | 1.1 ± 2.18 | |
| D1 | 10 | 90 | 16.7 ± 21.71 | 2.4 ± 3.47 | n.o. | 0.3 ± 0.67 | 10 | 20 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.4 ± 0.97 | ||
| D2 | 10 | 60 | 9.1 ± 21.75 | 3.2 ± 9.77 | 0.7 ± 2.21 | 2.3 ± 5.66 | 10 | 20 | n.o. | 0.3 ± 0.67 | ||
| D3 | 10 | 40 | 5.1 ± 11.73 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 10 | n.o. | 0.1 ± 0.32 | ||
| 4.5 µm particles | C1 | E | 10 | 50 | 0.4 ± 0.63 | 0.3 ± 0.67 | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 50 | 0.4 ± 0.7 | 1 ± 1.05 |
| D1 | 10 | 30 | 0.3 ± 0.48 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 40 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.9 ± 1.29 | ||
| D2 | 10 | 20 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 20 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.5 ± 0.97 | ||
| D3 | 9 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 20 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | ||
| C2 | E | 9 | 70 | 1.7 ± 1.41 | 0.9 ± 0.93 | 0.7 ± 0.71 | n.o. | 10 | 80 | 0.5 ± 0.71 | 2.7 ± 1.95 | |
| D1 | 10 | 50 | 0.6 ± 0.84 | 0.3 ± 0.48 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 10 | 70 | 0.4 ± 0.70 | 1.9 ± 1.59 | ||
| D2 | 10 | 50 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | n.o. | 10 | 40 | 0.3 ± 0.67 | 0.6 ± 0.97 | ||
| D3 | 10 | 20 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | n.o. | n.o. | 10 | 40 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | 0.4 ±0.70 | ||
| C3 | E | 10 | 90 | 1 ± 0.82 | 0.9 ± 0.74 | 0.9 ± 0.74 | 0.3 ± 0.48 | 10 | 90 | 0.8 ± 0.79 | 2.8 ± 1.75 | |
| D1 | 10 | 80 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | 0.7 ± 0.82 | 0.5 ± 0.53 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 10 | 70 | 0.8 ± 0.79 | 1.4 ± 1.43 | ||
| D2 | 10 | 50 | 0.4 ± 0.52 | 0.3 ± 0.48 | 0.2 ± 0.42 | n.o. | 10 | 60 | 0.3 ± 0.48 | 1.1 ± 1.20 | ||
| D3 | 10 | 30 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | 0.1 ± 0.32 | n.o. | 9 | 40 | 0.6 ± 1.01 | 0.6 ± 0.88 | ||
| Metal | µg/g dw |
| Fe | 141 ± 22.06 |
| Zn | 446.6 ± 93.75 |
| Cr | 1.72 ± 0.16 |
| Ni | 1.52 ± 0.34 |
| Cu | 4.62 ± 0.128 |
| Cd | 0.65 ± 0.07 |
| Pb | 1.95 ± 0.21 |
| PAH | ng/g dw |
| Naphthalene | 1555.8 ± 253.56 |
| Acenaphthylene | 5.6 ± 2.07 |
| Acenaphthalene | bdl |
| Fluorene | 5 ± 2 |
| Phenanthrene | 25.6 ± 1.52 |
| Anthracene | 111.6 ± 168.45 |
| Fluoranthene | 54 ± 5.48 |
| Pyrene | 63.6 ± 9.96 |
| Benzo(a)anthracene | 31 ± 3.16 |
| Chrysene | 57.2 ± 4.44 |
| Benzo(b)fluoranthene | 33 ± 4.64 |
| Benzo(k)fluoranthene | 26.2 ± 4.33 |
| Benzo(a)pyrene | 81.8 ± 35.05 |
| Indeno pyrene | <6 ± 2 * |
| Dibenzo(a,h)anthracene | <3.67 ± 1.5 * |
| Benzo(ghi)perylene | 14.4 ± 4.16 |
| TOTAL PAHs | <2071.5 |
| Group | Cd (µg/g dw) | BaP (ng/g dw) |
|---|---|---|
| MP | 0.59 ± 0.09 | 18.5 ± 16.25 |
| MP-Cd | 0.60 ± 0.16 | nm |
| Cd | 33 ± 7.85 | nm |
| MP-BaP | nm | 3050 ± 777.82 |
| BaP | nm | 192,450 ± 11,101.58 |
| Group | Cd (µg/L) | BaP (µg/L) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 min | 1 day | 30 min | 1 day | |
| MP | bdl | bdl | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.10 |
| MP-Cd | bdl | bdl | nm | nm |
| Cd | 112.33 ± 2.08 | 74.37 ± 7.99 | nm | nm |
| MP-BaP | nm | nm | 0.30 ± 0.29 | 0.29 ± 0.13 |
| BaP | nm | nm | 40.60 ± 31.71 | 1.72 ± 1.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
von Hellfeld, R.; Zarzuelo, M.; Zaldibar, B.; Cajaraville, M.P.; Orbea, A. Accumulation, Depuration, and Biological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic Spheres and Adsorbed Cadmium and Benzo(a)pyrene on the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxics 2022, 10, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010018
von Hellfeld R, Zarzuelo M, Zaldibar B, Cajaraville MP, Orbea A. Accumulation, Depuration, and Biological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic Spheres and Adsorbed Cadmium and Benzo(a)pyrene on the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxics. 2022; 10(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010018
Chicago/Turabian Stylevon Hellfeld, Rebecca, María Zarzuelo, Beñat Zaldibar, Miren P. Cajaraville, and Amaia Orbea. 2022. "Accumulation, Depuration, and Biological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic Spheres and Adsorbed Cadmium and Benzo(a)pyrene on the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis" Toxics 10, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010018
APA Stylevon Hellfeld, R., Zarzuelo, M., Zaldibar, B., Cajaraville, M. P., & Orbea, A. (2022). Accumulation, Depuration, and Biological Effects of Polystyrene Microplastic Spheres and Adsorbed Cadmium and Benzo(a)pyrene on the Mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Toxics, 10(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics10010018