Logistics Information Technology and Its Impact on SME Network and Distribution Performance: A Structural Equation Modelling Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
“To what extent does the adoption of LIT enhance the relationships between the supply chain networks and the performance of the distribution among SMEs in South Africa?”
2. Review of Concepts and Literature
2.1. SMEs and the Role of Distribution Information Technology
2.2. Relational View Theory
2.3. Key Dimensions of Physical Distribution Performance
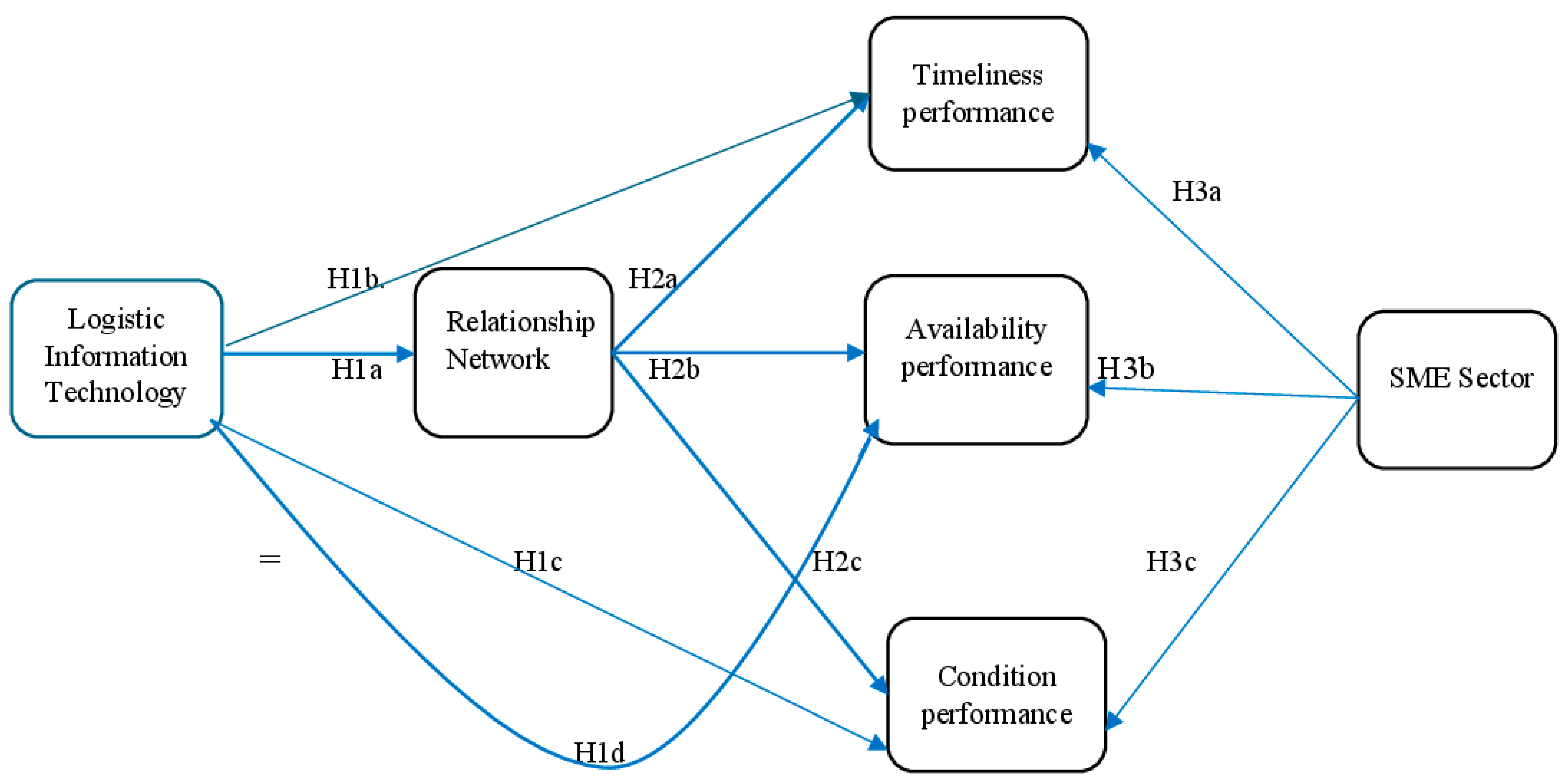
2.4. Research Hypothesis
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Approach, Sampling, and Questionnaire Design
3.2. Measurement and Structural Models
4. Data Analysis and Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics and Data Analysis
4.1.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.1.2. Exploratory and Confirmatory Factor Analysis
4.1.3. Diagnostics Test for Estimated Structural Models
4.2. Pathway Model and Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Theoretical Implications
5.2. Practical Implications
5.3. Key Recommendations
5.4. Limitations and Suggestions for Future Research
5.5. Ethical Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raji, M.A.; Olodo, H.B.; Oke, T.T.; Addy, W.A.; Ofodile, O.C.; Oyewole, A.T. The digital transformation of SMES: A comparative review between the USA and Africa. Int. J. Manag. Entrep. Res. 2024, 6, 737–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabalala, K.; Boyana, S.; Kolisi, L.; Thango, B.; Matshaka, L. Digital Technologies and Channels for Competitive Advantage in SMEs: A Systematic Review, Available at SSRN 4977280 [Preprint]. 2024. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4977280 (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Tetouani, S.; Chouar, A.; Lmariouh, J.; Soulhi, A.; Elalami, J. A “Push-Pull” rearrangement while routing for a driverless delivery vehicle. Cogent Eng. 2019, 6, 1567662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, L.; Human, L.I.; Rossouw, M.E.; Nel, J.D. A framework to drive business growth in developing countries using omni-channel strategies. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2023, 24, 344–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriani, A.; Sopha, B.M.; Wibisono, M.A. Dynamic capabilities for omnichannel transformation in MSMEs: A comparative case study of fashion and furniture sectors. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2025, 11, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrutzek-Hartmann, B.; Kotzab, H.; Yumurtacı Hüseyinoğlu, I.Ö.; Kühling, S. Omni-channel retailing resources and capabilities of SME specialty retailers–insights from Germany and Turkey. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2022, 50, 1129–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edison, H.; Wang, X.; Conboy, K. Comparing methods for large-scale agile software development: A systematic literature review. IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. 2021, 48, 2709–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrugalska, B.; Ahmed, J. Organizational agility in industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, T.; Xu, W. Sooner or Later? The Role of Adoption Timing in New Technology Introduction. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 31, 1663–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulka, B.M.; Gawuna, M.S. Contributions of SMEs to employment, gross domestic product, economic growth and development. Jalingo J. Soc. Manag. Sci. 2022, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Enaifoghe, A.; Vezi-Magigaba, M.F. Conceptualizing the role of entrepreneurship and SME in fostering South Africa’s local economic development. Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2023, 12, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cant, M.C.; Wiid, J.A. Establishing the challenges affecting South African SMEs. Int. Bus. Econ. Res. J. (Online) 2013, 12, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cant, M.C.; Erdis, C.; Sephapo, C.M. Business survival: The constraints experienced by South African SMEs in the financial sector. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. 2014, 4, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghiri, S.; Bernon, M.; Bourlakis, M.; Wilding, R. Omni-channel logistics special issue. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2018, 48, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Steenkamp, E. Strategic intra-regional trade in Sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons from Southeast Asia. Afr. J. Dev. Stud. 2025, 15, 187–213. [Google Scholar]
- Masongsong, A.C.; Ulep, S.J.; Abante, M.V.; Cagang, M.L.; Vigonte, F. Digital Transformation of International Trade for SMEs in Developing Countries: Opportunities, Challenges. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4740033 (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Mer, A.; Virdi, A.S. Decoding the challenges and skill gaps in small-and medium-sized enterprises in emerging economies: A review and re-search agenda. In Contemporary Challenges in Social Science Management: Skills Gaps and Shortages in the Labour Market; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2024; pp. 115–134. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Singh, R. Economic Imperatives of Evolving National Digital Policy: A Call for a Modern Industrial Policy Framework in India. Int. Trade J. 2022, 36, 572–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z. Strategies for SMEs to develop international business in the context of internet plus. Acad. J. Bus. Manag. 2023, 5, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.E.; Tavares-Lehmann, A.T.C. Industry 4.0 in the European union: Policies and national strategies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 180, 121664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaichon, P.; Phau, I.; Weaven, S. Moving from multi-channel to Omni-channel retailing: Special issue introduction. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2022, 65, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, N.H.; Hung-Anh, D.B.; Thuc, T.D. Global Supply Chain And Logistics Management; Academic Publications: Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrsai, A.; Karimi, H.R.; Thoben, K.D.; Scholz-Reiter, B. Using Metaheuristic and Fuzzy System for the Optimization of Material Pull in a Push-Pull Flow Logistics Network. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013, 359074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, H.; Budiman, S.D.; Monteiro, C.N. Improving the sustainability of a reverse supply chain system under demand uncertainty by using postponement strategies. Waste Manag. 2021, 131, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Vilkas, M.; Grybauskas, A.; Amran, A. Drivers and barriers of Industry 4.0 technology adoption among manufacturing SMEs: A systematic review and transformation roadmap. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2022, 33, 1029–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahadat, M.H.; Nekmahmud Argon, N.; Pejman Ebrahimi, P.; Fekete-Farkas, M. Digital Technology Adoption in SMEs: What Technological, Environmental and Organizational Factors Influence in Emerging Countries? Glob. Bus. Rev. 2023, 24, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuliawati, E.; Brilliana, C.; Rahmawati, N.; Trihastuti, D. Performance Evaluation of Logistics Service Provider (LSP) in FMCG Companies Using Physical Distribution Service Quality (PDSQ) Dimension: Case Study. J. Appl. Eng. Technol. Sci. (JAETS) 2023, 5, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, A.; Croucher, P.; Baker, P. The Handbook of Logistics and Distribution Management: Understanding the Supply Chain; Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK; New York, NY, USA; New Delhi, India, 2022; Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=-jlUEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR1&dq=physical+distribution+activities&ots=w_obrrYlGC&sig=pD38JMvyKq5IXddgtL3NSHeBG8g (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Raja Santhi, A.; Muthuswamy, P. Influence of blockchain technology in manufacturing supply chain and logistics. Logistics 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkonyan, A.; Gruchmann, T.; Lohmar, F.; Kamath, V.; Spinler, S. Sustainability assessment of last-mile logistics and distribution strategies: The case of local food networks. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 228, 107746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, R.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Nudurupati, S.S. Impact of inventory management on SME performance: A systematic review. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2024, 73, 2901–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Yang, L.; Huo, B. The impact of information technology usage on supply chain resilience and performance: An ambidextrous view. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2021, 232, 107956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaikho, I.; Salhied, L.; Towers, N. Improving distribution and business performance through lean warehousing. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2018, 46, 780–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G.; Seng, D. A combined method for short-term traffic flow prediction based on recurrent neural network. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.M.; Lv, Y.; Ng, K.K.H.; Ho, W.; Choy, K.L. Design and application of Internet of Things based Warehouse Management System for Smart Logistics. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 2753–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruffaldi, G.; Accorsi, R.; Manzini, R. Warehouse management system customization and information availability in 3pl companies: A decision-support tool. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2018, 119, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyan, J.C.; Wang, F.; Du, T.C. An evaluation of freight consolidation policies in global third party logistics. Omega 2003, 31, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Wee, H.M.; Zhou, Y.; Tjoeng, L. Freight consolidation and containerization strategy under business as usual scenario & carbon tax regulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, D.H.; Lankton, N.K.; Nicolaou, A.; Price, J. Distinguishing the effects of B2B information quality, system quality, and service outcome quality on trust and distrust. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2017, 26, 118–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, J.L.; He, W.; Shen, J. Big data analytics for supply chain relationship in banking. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2020, 86, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumah, B.; Masudin, I.; Zulfikarijah, F.; Restuputri, D.P. Logistics Management and Electronic Data Interchange Effects on Logistics Service Providers’ Competitive Advantage. J. Bus. Econ. Anal. 2020, 3, 171–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Papadopoulos, T.; Dubey, R.; Wamba, S.F.; Childe, S.J.; Hazen, B.; Akter, S. Big data and predictive analytics for supply chain and organizational performance. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez, G.B.; Ayala, N.F.; Frank, A.G. Chapter 19 - How Can SMEs Participate Successfully in Industry 4.0 Ecosystems? The Digital Supply Chain, MacCarthy, B.L., Ivanov, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 325–339. ISBN 9780323916141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moufaddal, M.; Benghabrit, A.; Bouhaddou, I. A Cyber-Physical Warehouse Management System Architecture in an Industry 4.0 Context. Artif. Intell. Ind. Appl. 2020, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, J.; Salazar-Arrieta, F.; Gómez-Montoya, R.; Cortés, P. Disruptive and Conventional Technologies for the Support of Logistics Processes: A Literature Review. Int. J. Technol. 2021, 12, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuorio, A.; Torkkeli, L.; Sainio, L.M. Service innovation and internationalization in SMEs: Antecedents and profitability outcomes. J. Int. Entrep. 2020, 18, 92–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdecker, B. Building the E-Commerce Supply Chain of the Future: What Influences Consumer Acceptance of Alternative Places of Delivery on the Last-Mile. Logistics 2021, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shretta, R.; Johnson, B.; Smith, L.; Doumbia, S.; De Savigny, D.; Anupindi, R.; Yadav, P. Costing the supply chain for delivery of ACT and RDTs in the public sector in Benin and Kenya. Malar. J. 2015, 14, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarouk, Y.; Mahdavi, I.; Rezaeian, J.; Santos-Arteaga, F.J. A novel multi-objective green vehicle routing and scheduling model with stochastic demand, supply, and variable travel times. Comput. Oper. Res. 2022, 141, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhide, S.; Chakurkar, P. Decentralized Deep Reinforcement Learning for Intelligent Transportation Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advancements in Smart, Secure and Intelligent Computing (ASSIC), Bhubaneswar, India, 27–29 January 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S.; Soeanu, A.; Berger, J.; Debbabi, M. The multi-depot split-delivery vehicle routing problem: Model and solution algorithm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 71, 238–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehmke, J.F.; Mattfeld, D.C. Vehicle Routing for Attended Home Delivery in City Logistics. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 39, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, G.N.; Greis, N.P.; Kasarda, J.D. Enterprise Logistics and Supply Chain Structure: The Role of Fit. J. Oper. Manag. 2000, 18, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Sánchez-Díaz, I. Freight Demand Management and the Potential of Receiver-Led Consolidation programs. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 84, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guastaroba, G.; Speranza, M.G.; Vigo, D. Intermediate Facilities in Freight Transportation Planning: A Survey. Transp. Sci. 2016, 50, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, R.L. Reinventing the Warehouse: World Class Distribution Logistics; Simon and Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Leal, J.A.; Sanchez-Diaz, I.; Browne, M.; Wojtowicz, J. State of the art and practice of urban freight management Part II: Financial approaches, logistics, and demand management. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2020, 137, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.C.; Huge-Brodin, M.; Ammenberg, J.; Karlsson, J. Exploring green logistics practices in freight transport and logistics: A study of biomethane use in Sweden. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2022, 26, 548–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantakopoulos, G.D.; Gayialis, S.P.; Kechagias, E.P. Vehicle routing problem and related algorithms for logistics distribution: A literature review and classification. Oper. Res. 2022, 22, 2033–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelhaus, S.; Grosse, E.H. Logistics 4.0: A systematic review towards a new logistics system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Huang, G.; Lan, S.; Dai, Q.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, T. A big data approach for logistics trajectory discovery from RFID-enabled production data. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 165, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, J.H.; Singh, H. The relational view: Cooperative strategy and sources or interorganisaitonal competitive advantage. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1998, 23, 600–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Z.; King, B.; Ben Miled, Z.; Wassick, J.; Tazelaar, J.A. Distributed Ledger for Supply Chain Physical Distribution Visibility. Information 2017, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussaoui, I.; Williams, B.D.; Hofer, C.; Aloysius, J.A.; Waller, M.A. Drivers of Retail On-Shelf Availability: Systematic Review, Critical Assessment, and Reflections on the Road Ahead. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2016, 46, 516–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaswengi, J.; Lambey-Checchin, C. How logistics service quality and product quality matter in the retailer–customer relationship of food drive-throughs: The role of perceived convenience. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2020, 50, 535–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis-Sramek, B.; Ishfaq, R.; Gibson, B.J.; Defee, C. Examining retail business model transformation: A longitudinal study of the transition to omnichannel order fulfilment. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2020, 50, 557–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, H.; Zailani, S.; Fernando, Y. Moderating Role of Logistics Information Technology on the Logistics Relationships and Logistics Service Quality. Oper. Supply Chain. Manag. 2010, 3, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienstock, C.C.; Mentzer, J.T.; Bird, M.M. Measuring Physical Distribution Service Quality. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 1997, 25, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Depaoli, S. Bayesian structural equation modeling. In Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling; Hoyle, R.H., Ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 650–673. [Google Scholar]
- Merkle, E.C.; Rosseel, Y. blavaan: Bayesian Structural Equation Models via Parameter Expansion. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 85, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; MacKinnon, D.P. Bayesian mediation analysis. Psychol. Methods 2009, 14, 301–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Vispoel, W.P.; Martinez, A.J. Applying SEM, Exploratory SEM, and Bayesian SEM to Personality Assessments. Psych 2024, 6, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Nathoo, F.S.; Masson, M.E.J. Investigating the Relationship Between the Bayes Factor and the Separation of Credible Intervals. University of Victoria. 2023. Available online: https://onlineacademiccommunity.uvic.ca/lindsaylab/wp-content/uploads/sites/4861/2023/03/Bayesian-Credible-Intervals.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2024).
- Hair, J.F.; Babin, B.J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. Covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM): A SmartPLS 4 software tutorial. J. Mark. Anal. 2025, June, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; SAGE Publications: Los Angeles, LA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Amoako, T.; Sheng, Z.H.; Dogbe, C.S.K.; Pomegbe, W.W.K. Assessing the Moderation Role of ICT in the Relationship Between Supply Chain Integration and SME Performance. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2022, 7, 203–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubihlela, J.; Omoruyi, O. Barriers to effective supply chain management, implementation, and impact on business performance of SMEs in South Africa. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2014, 30, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghiri, S.; Mirzabeiki, V. Omni-channel integration: The matter of information and digital technology. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2021, 41, 1660–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugos, M.H. Essentials of Supply Chain Management, 5th ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, D.B.; Trautrims, A.; Wong, C.Y. Sustainable Logistics and Supply Chain Management: Principles and Practices for Sustainable Operations and Management, 2nd ed.; Kogen Page: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Keshipour, B.; Kangaarloye, S.J.; Sales, J.B. Study of ranking factors affecting the implementation of timely management of goods and equipment and its evaluation criteria in the power distribution company of the whole country using fuzzy AHP and fuzzy DEMATEL. Adv. Math. Financ. Appl. 2023, 8, 1239–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Reaidy, P.J.; Gunasekaran, A.; Spalanzani, A. Bottom-up approach based on Internet of Things for order fulfilment in a collaborative warehousing environment. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 159, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vass, T.; Shee, H.; Miah, S.J. The effect of “Internet of Things” on supply chain integration and performance: An organisational capability perspective. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2018, 22. Available online: http://journal.acs.org.au/index.php/ajis/article/view/1734 (accessed on 4 December 2024). [CrossRef]
- Ozili, P.K. The Acceptable R-Square in Empirical Modelling for Social Science Research. In Advances in Knowledge Acquisition. Transfer, and Management; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 134–143. Available online: https://www.irma-international.org/viewtitle/320215/?isxn=9781668468593 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Al Shukaili, S.M.S.; Jamaluddin, Z.; Zulkifli, N. The impact of strategic inventory management on logistics organization’s performance. Int. J. Bus. Technol. Manag. 2023, 5, 288–298. [Google Scholar]
- Pasupuleti, V.; Thuraka, B.; Kodete, C.S.; Malisetty, S. Enhancing supply chain agility and sustainability through machine learning: Optimization techniques for logistics and inven-tory management. Logistics 2024, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Technology | Impact on Timeliness | Impact on Availability | Impact on Condition | Key References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warehouse Management System (WMS) | Reduces lead times through automated storage/retrieval and real-time tracking. | Improves inventory accuracy and reduces stockouts via cloud-based monitoring. | Ensures proper handling and storage conditions (e.g., IoT-enabled climate control). | [32,35,37,44] |
| Freight Consolidation Systems | Optimises transport routes, reducing delays via load consolidation. | Enhances stock replenishment efficiency by reducing fragmented shipments. | Minimises product damage through reduced handling and optimised packaging. | [22,37,38,54] |
| Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) | Accelerates order processing and updates delivery schedules in real time. | Improves demand forecasting and inventory synchronisation with suppliers. | Ensures accurate order fulfilment, reducing errors in product handling. | [39,41,43] |
| Bar Coding Systems | Speeds up scanning and sorting processes, reducing delays in dispatch. | Enhances inventory tracking, reducing misplacements and stock discrepancies. | Reduces human error in picking/packing, maintaining product integrity. | [44,45,46] |
| Vehicle Routing/Scheduling | Optimises delivery routes using AI, ensuring on-time deliveries. | Balances load distribution, improving last-mile availability. | Reduces transit time, preserving product quality (e.g., perishables). | [47,49,51,52] |
| Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) | Enables real-time tracking, reducing delays from lost shipments. | Provides exact inventory visibility, preventing stockouts. | Monitors environmental conditions (e.g., temperature for sensitive goods). | [36,42,43,44] |
| Number of SMEs | Sample Percentage | |
|---|---|---|
| Province of SME | ||
| Northern Cape | 131 | 41.9 |
| Eastern Cape | 97 | 31 |
| Free State | 74 | 23.6 |
| Gauteng | 11 | 3.5 |
| Years SME has been in operation | ||
| Less than a year | 30 | 9.6 |
| Between 1 and 5 years | 87 | 27.8 |
| More than 5 years | 196 | 62.6 |
| Annual turnover | ||
| Less than ZAR 500,000 | 75 | 24 |
| Between ZAR 500,000 and 2 million | 123 | 39.3 |
| More than ZAR 2 million | 115 | 36.7 |
| Size of SME | ||
| Small | 66 | 21.1 |
| Medium | 247 | 78.9 |
| Sector | ||
| Food (food, beverages, and tobacco in specialised stores) | 111 | 35.5 |
| Medical (pharmaceutical and medical goods, cosmetics, and toiletries) | 33 | 10.5 |
| Clothing (textiles, clothing, footwear, and leather goods) | 92 | 29.4 |
| Furniture (household furniture, appliances, and equipment) | 33 | 10.5 |
| Hardware (hardware, paint, and glass) | 34 | 10.9 |
| Other | 10 | 3.2 |
| Position of respondent | ||
| CEO/director/owner | 93 | 29.71 |
| Manager | 142 | 45.37 |
| Supervisor | 33 | 10.54 |
| Salesperson | 7 | 2.24 |
| Administrator or officer | 6 | 7.35 |
| General worker | 23 | 4.79 |
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin | Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Determinant | Shapiro–Wilk Test |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.93 | <0.00001 | 4.3 × 10−28 | 2.3 × 10−16 |
| Construct | Item | Factor Loadings | Cronbach Alpha | Composite Reliability | Average Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Logistic Information Technology (LIT) | LIT2 | 0.6710 | 0.8863 | 0.8940 | 0.6843 |
| LIT2 | 0.8774 | ||||
| LIT3 | 0.8667 | ||||
| LIT4 | 0.8426 | ||||
| Distribution Network Relations (DNL) | DNR3 | 0.8147 | 0.9479 | 0.9470 | 0.8173 |
| DNR4 | 0.9064 | ||||
| DNR5 | 0.9609 | ||||
| DNR6 | 0.9505 | ||||
| Timeline Performance (TIMEP) | TIMEP10 | 0.8384 | 0.9301 | 0.9303 | 0.7275 |
| TIMEP11 | 0.8399 | ||||
| TIMEP13 | 0.8364 | ||||
| TIMEP14 | 0.8628 | ||||
| TIMEP15 | 0.8482 | ||||
| Availability Performance (AVALP) | AVALP12 | 0.8011 | 0.8769 | 0.8813 | 0.6545 |
| AVALP13 | 0.7730 | ||||
| AVALP15 | 0.7555 | ||||
| AVALP19 | 0.7588 | ||||
| Condition Performance (CONDP) | CONDP4 | 0.7696 | 0.9171 | 0.9172 | 0.7357 |
| CONDP5 | 0.8416 | ||||
| CONDP6 | 0.8234 | ||||
| CONDP7 | 0.8649 |
| Heterotrait/Monotrait Ratio | |||||
| Construct | LIT | DNL | TIMEP | AVALP | CONDP |
| LIT | 1.000 | ||||
| DNL | 0.569 | 1.000 | |||
| TIMEP | 0.408 | 0.493 | 1.000 | ||
| AVALP | 0.265 | 0.357 | 0.576 | 1.000 | |
| CONDP | 0.365 | 0.409 | 0.554 | 0.571 | 1.000 |
| Fit indices for constructs | |||||
| Fit index/test | Chi-square test | CFI | TLI | SRMR | RMSEA ≤ 0.050 |
| Value | <0.0001 | 0.920 | 0.907 | 0.058 | <0.0001 |
| Model | R-Square | Rhat for All Parameters | PPP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timeliness Performance | 0.278 | [0.999, 1.004] | 0.299 |
| Availability Performance | 0.227 | ||
| Condition Performance | 0.139 | ||
| Network Relationship | 0.176 |
| Relationship Network | Timeliness Performance | Availability Performance | Condition Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNL | 0.388 [0.242, 0.531] | 0.240 [0.120, 0.358] | 0.241 [0.134, 0.353] | |
| LIT usage | 0.524 [0.434, 0.613] | 0.237 [0.098, 0.372] | 0.085 [−0.030, 0.199] | 0.175 [0.065, 0.283] |
| Sector variation | 0.179 [−0.100, 0.445] | 0.430 [0.202, 0.655] | 0.154 [−0.043, 0.358] | |
| DNL mediation | 0.203 [0.119, 0.287] | 0.126 [0.059, 0.193] | 0.126 [0.065, 0.188] | |
| Total DNL impact | 0.440 [0.321, 0.560] | 0.211 [0.110, 0.311] | 0.302 [0.210, 0.394] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omoruyi, O.; Antwi, A.; Mwanza, A.; Mabugu, R.E.; Dakora, E.A.N. Logistics Information Technology and Its Impact on SME Network and Distribution Performance: A Structural Equation Modelling Analysis. Logistics 2025, 9, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040142
Omoruyi O, Antwi A, Mwanza A, Mabugu RE, Dakora EAN. Logistics Information Technology and Its Impact on SME Network and Distribution Performance: A Structural Equation Modelling Analysis. Logistics. 2025; 9(4):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040142
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmoruyi, Osayuwamen, Albert Antwi, Alfred Mwanza, Ramos E. Mabugu, and Edward A. N. Dakora. 2025. "Logistics Information Technology and Its Impact on SME Network and Distribution Performance: A Structural Equation Modelling Analysis" Logistics 9, no. 4: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040142
APA StyleOmoruyi, O., Antwi, A., Mwanza, A., Mabugu, R. E., & Dakora, E. A. N. (2025). Logistics Information Technology and Its Impact on SME Network and Distribution Performance: A Structural Equation Modelling Analysis. Logistics, 9(4), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9040142







