Multi-Objective Decision Support Model for Operating Theatre Resource Allocation: A Post-Pandemic Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Operating Room Resource Management
2.2. Patient Waiting List Management
3. Methodology
3.1. Indices, Parameters, and Decision Variables
3.2. Deterministic OR Resource Allocation (DORA) Model
3.2.1. Objective Function
3.2.2. Constraints
3.3. Numerical Case Study: Overview of Hospital Dataset
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
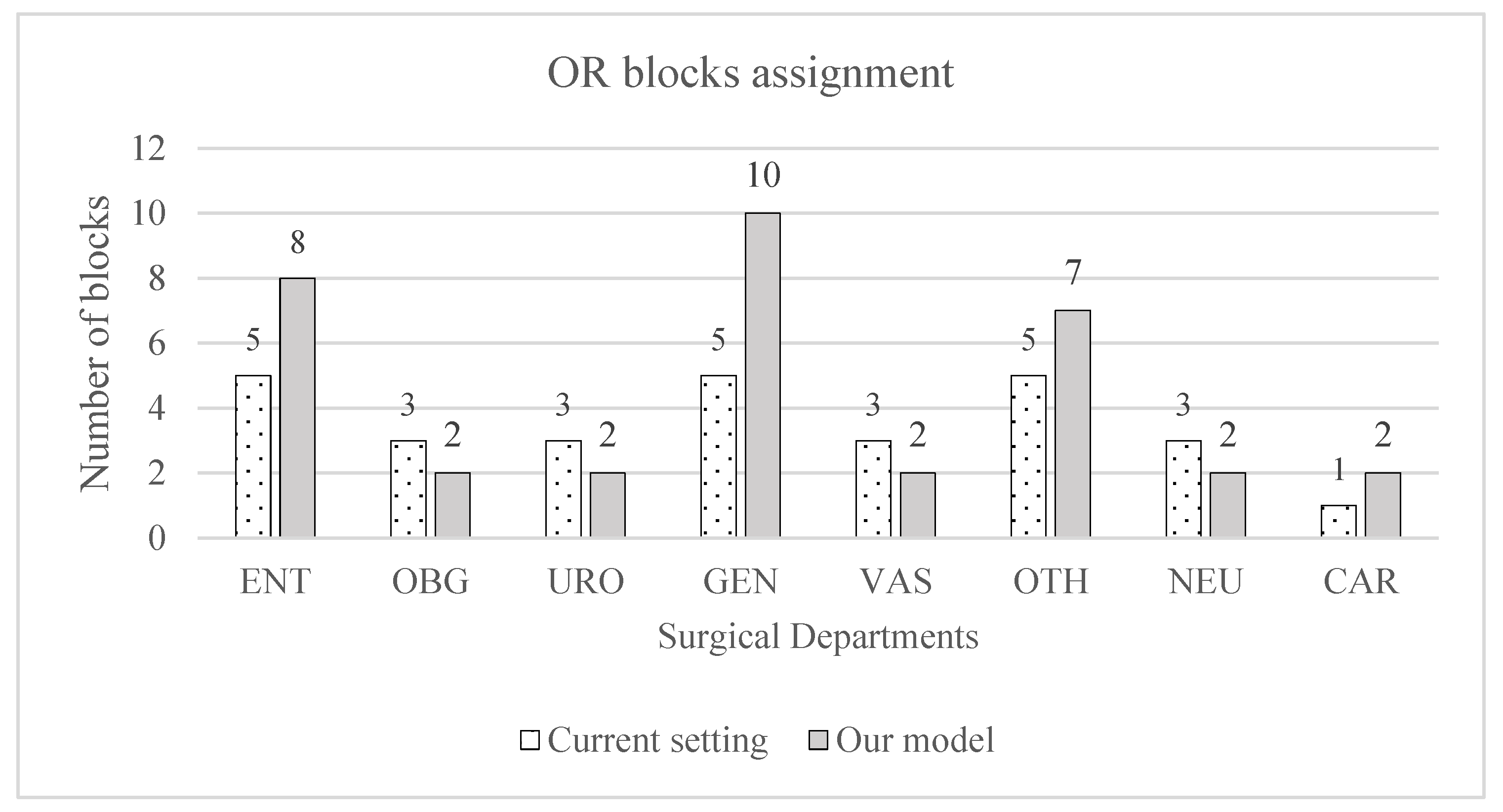
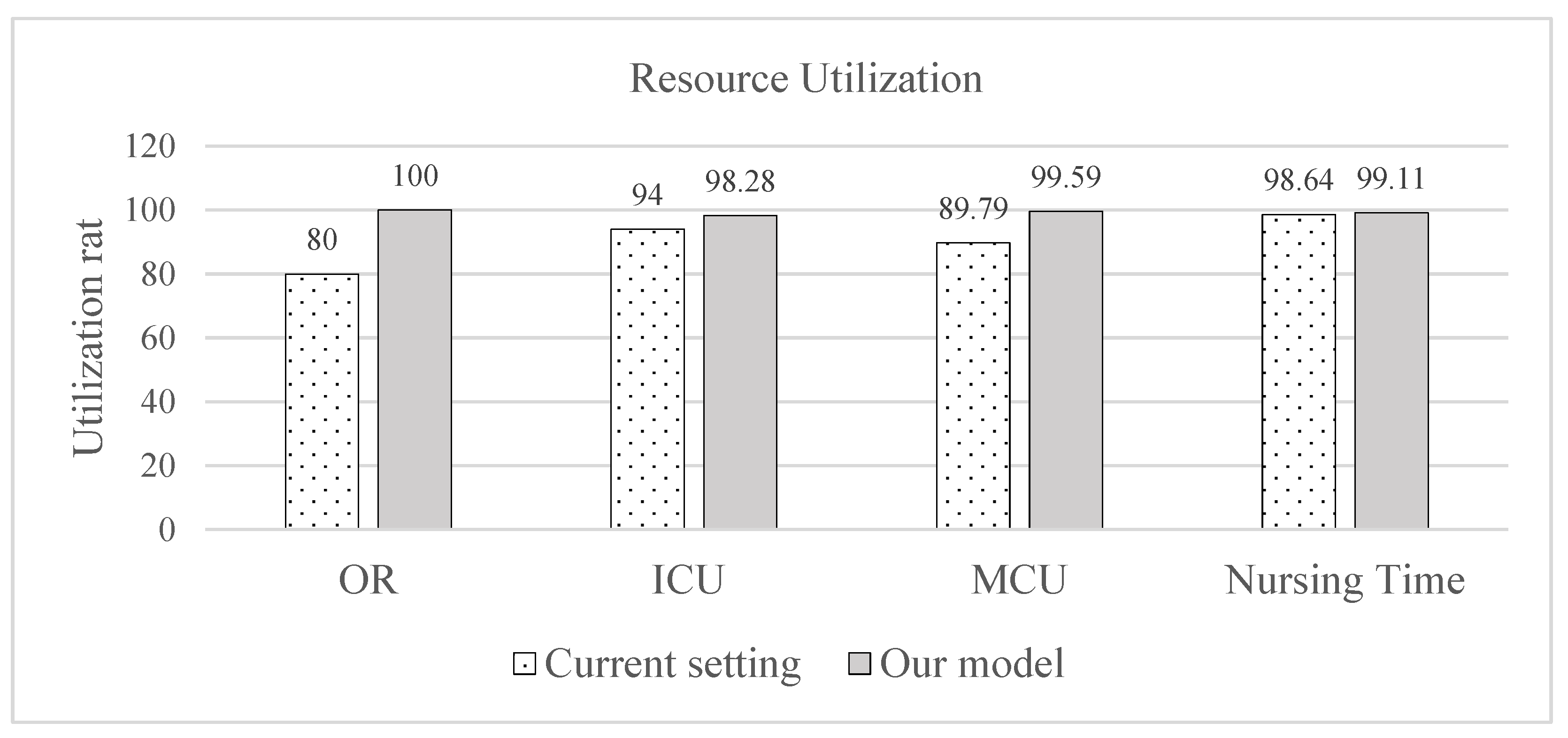
4.1. Comparative Analysis: Model Solution Versus Current Hospital Setting
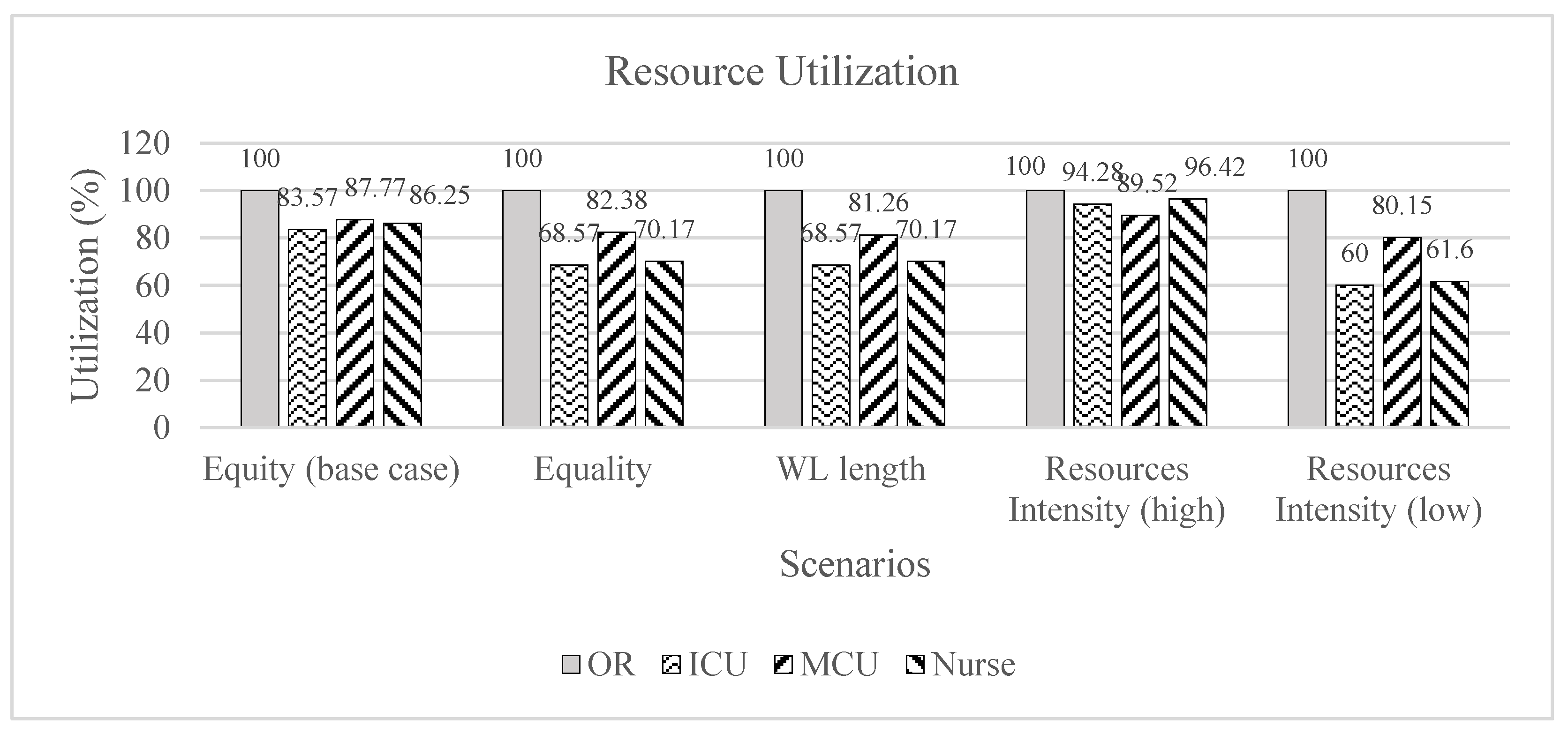
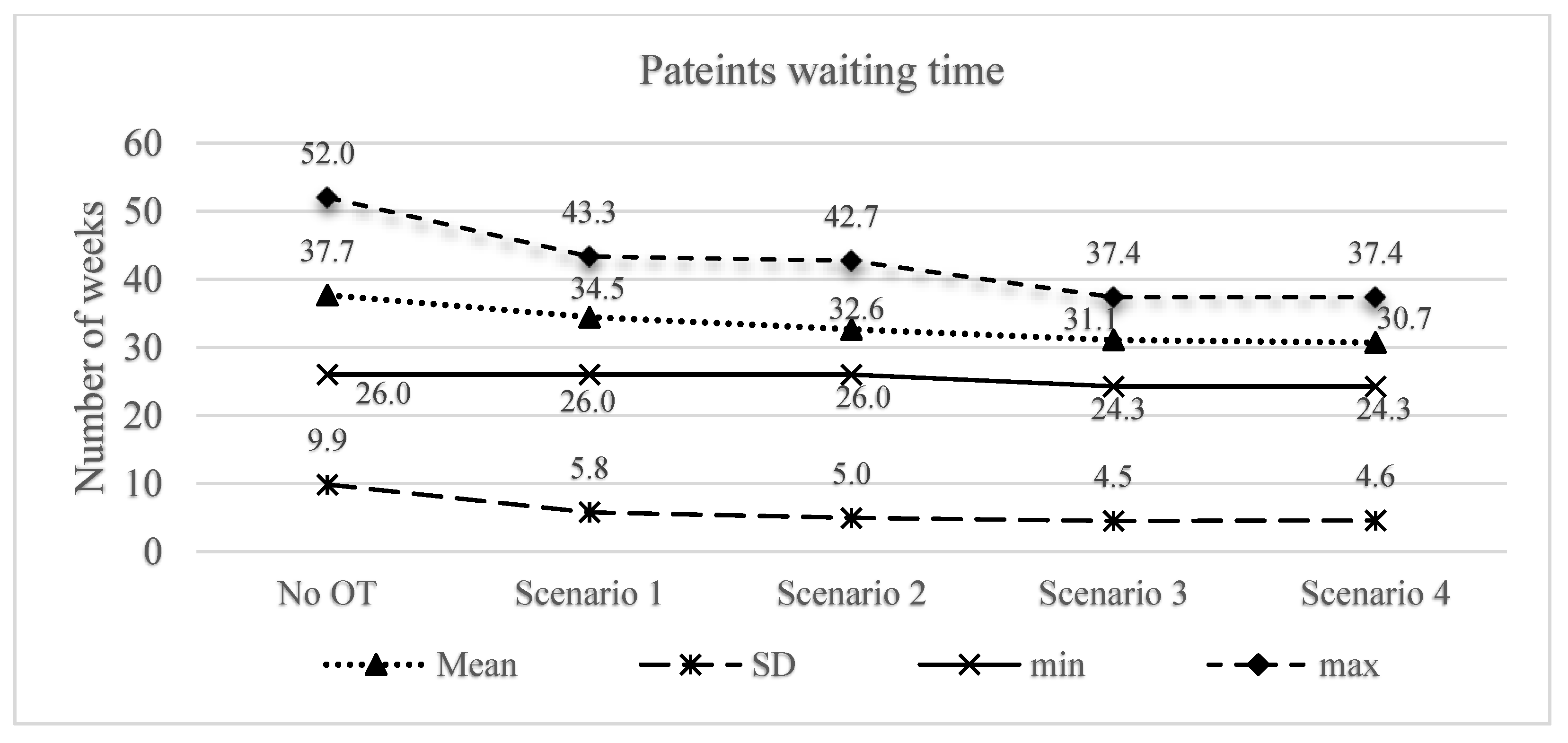
4.2. Sensitivity Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Freeman, N.; Zhao, M.; Melouk, S. An iterative approach for case mix planning under uncertainty. Omega 2018, 76, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehadeh, K.S.; Padman, R. Stochastic optimization approaches for elective surgery scheduling with downstream capacity constraints: Models, challenges, and opportunities. Comput. Oper. Res. 2022, 137, 105523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfelder, J.; Kohl, S.; Glaser, M.; McRae, S.; Brunner, J.O.; Koperna, T. Simulation-based evaluation of Operating Room Management Policies. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2021, 21, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihalj, M.; Corona, A.; Andereggen, L.; Urman, R.D.; Luedi, M.M.; Bello, C. Managing bottlenecks in the perioperative setting: Optimizing Patient Care and reducing costs. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2022, 36, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, S.; Anberber, E.; Ayele, B.; Ashebir, Z.; Abate, A.; Bitew, S.; Derbew, M.; Weiser, T.G.; Starr, N.; Mammo, T.N. Operating room efficiency in a low resource setting: A pilot study from a large tertiary referral center in Ethiopia. Patient Saf. Surg. 2022, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Karim, R.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Younes, H. Modeling Hospital Operating Theater Services: A system dynamics approach. Logistics 2023, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, H.R.; Lam, S.S.W.; Ang, B.Y.; Pourghaderi, A.; Nguyen, F.N.H.L.; Matchar, D.B.; Tan, H.K.; Ong, M.E.H. Resuming elective surgery after COVID-19: A simulation modelling framework for guiding the phased opening of Operating Rooms. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2021, 158, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabir, A.; Kerwan, A.; Nicola, M.; Alsafi, Z.; Khan, M.; Sohrabi, C.; O’NEill, N.; Iosifidis, C.; Griffin, M.; Mathew, G.; et al. Impact of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on Surgical Practice—Part 2 (surgical prioritisation). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 79, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovers, M.M.; Wijn, S.R.; Grutters, J.P.; Metsemakers, S.J.; Vermeulen, R.J.; van der Pennen, R.; Berden, B.J.; Gooszen, H.G.; Scholte, M.; Govers, T.M. Development of a decision analytical framework to prioritise operating room capacity: Lessons learnt from an empirical example on delayed elective surgeries during the COVID-19 pandemic in a hospital in the Netherlands. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e054110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamon, B.M.; Balcik, B. Performance measurement in humanitarian relief chains. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2008, 21, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapukaya, E.N.; Satoglu, S.I. A Multi-Objective Dynamic Resource Allocation Model for search and rescue and first aid tasks in disaster response by employing volunteers. Logistics 2025, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Bélanger, V.; Ruiz, A.; Santos, D. A systematic literature review on the utilization of extended operating room hours to reduce surgical backlogs. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1118072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, H.; Boyle, J.; Khanna, S.; Biki, B.; Syed, F. Daily surgery caseload prediction: Towards improving operating theatre efficiency. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebali, A.; Diabat, A. A Chance-constrained operating room planning with elective and emergency cases under downstream capacity constraints. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 114, 329–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoen, B.; Demeulemeester, E.; Beliën, J. Operating room planning and scheduling: A literature review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 201, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.G.; Michaels, A.D.; Mehaffey, J.H.; Guidry, C.A.; Turrentine, F.E.; Hedrick, T.L.; Friel, C.M. Risk associated with complications and mortality after urgent surgery vs elective and emergency surgery. JAMA Surg. 2017, 152, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Yih, Y. Scheduling elective surgery under uncertainty and downstream capacity constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 206, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyshabouri, S.; Berg, B.P. Two-stage robust optimization approach to elective surgery and downstream capacity planning. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fügener, A.; Hans, E.W.; Kolisch, R.; Kortbeek, N.; Vanberkel, P.T. Master surgery scheduling with consideration of multiple downstream units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 239, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dridi, M.; El Moudni, A. A two-level optimization model for elective surgery scheduling with downstream capacity constraints. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 276, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, B.T.; Miller, A.J.; Balasubramanian, H.J.; Huschka, T.R. Optimal allocation of surgery blocks to operating rooms under uncertainty. Oper. Res. 2010, 58, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Li, M.-Y. Solving operating room scheduling problem using artificial bee colony algorithm. Healthcare 2021, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fügener, A. An Integrated Strategic and Tactical Master Surgery Scheduling Approach With Stochastic Resource Demand. J. Bus. Logist. 2015, 36, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaei, R.; Mozdgir, A. Master surgical scheduling problem with multiple criteria and robust estimation. Sci. Iran. 2018, 26, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wei, D.; Bai, K.; Gao, J.; Zhang, R. Multi-phase and integrated multi-objective cyclic operating room scheduling based on an improved NSGA-II approach. Symmetry 2019, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrão, R.L.; Garcia, R.C.; da Silva, J.M. An integrated two-level integer linear program (ILP) model for elective surgery scheduling: A case study in an Italian hospital. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalkareem, Z.A.; Amir, A.; Al-Betar, M.A.; Ekhan, P.; Hammouri, A.I. Healthcare Scheduling in Optimization Context: A Review. HEAL Technol. 2021, 11, 445–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, N.C.; Wood, R.M. Modeling the recovery of elective waiting lists following COVID-19: Scenario projections for england. Value Health 2022, 25, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaid, A.A.; Asaad, A.R.; Othman, M.; Mohammad, A.H. Multi-objective technology-based approach to home healthcare routing problem considering sustainability aspects. Logistics 2024, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBerkel, P.T.; Blake, J.T. A comprehensive simulation for wait time reduction and capacity planning applied in general surgery. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2007, 10, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Ye, H.; Li, W. Operating room planning under surgery type and priority constraints. Procedia Manuf. 2016, 5, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spratt, B.; Kozan, E. Waiting List Management Through Master Surgical Schedules: A Case Study. Oper. Res. Health Care 2016, 10, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, J.A. Simulating waiting list management. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2011, 14, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.; McGree, J.M.; Grieve, D.; Aseervatham, R.; Ryan, S.; Corry, P. Managing surgical waiting lists through dynamic priority scoring. Health Care Manag. Sci. 2023, 26, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Vahid, S.; Eberg, M.; Milroy, S.; Milkovich, J.; Wright, F.C.; Hunter, A.; Kalladeen, R.; Zanchetta, C.; Wijeysundera, H.C.; et al. Clearing the surgical backlog caused by COVID-19 in Ontario: A time series modelling study. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2020, 192, E1347–E1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussedik, S.; MacIntyre, S.; Gray, J.; McMeekin, P.; Clement, N.D.; Deehan, D.J. Elective orthopaedic cancellations due to the COVID-19 pandemic: Where are we now, and where are we heading? Bone Jt. Open 2021, 2, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, D.; Jalali, A.; Whipple, T.; Rehman, M.; Ahumada, L.M. “P3”: An adaptive modeling tool for post-COVID-19 restart of surgical services. JAMIA Open 2021, 4, ooab016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, S.; Corradi, L.; Goyet, J.d.V.d.; Iannucci, M.; Porro, I.; Rosso, N.; Tanfani, E.; Testi, A. Optimization and Planning of Operating Theatre Activities: An Original Definition of Pathways and Process Modeling. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanantong, T.; Pannakkong, W.; Chemkomnerd, N. Resource management framework using simulation modeling and multi-objective optimization: A case study of a front-end department of a public hospital in Thailand. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jittamai, P.; Kangwansura, T. A hospital admission planning model for operating room allocation under uncertain demand requirements. Int. J. Serv. Oper. Manag. 2016, 23, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Study | Decision Level | Cost Consideration | Objective Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fugener [19] | Tactical level | Fixed cost and downstream costs |
|
| Zhang et al. [20] | Operational level | Cost incurred by performing and delaying procedures, fixed OR cost and overtime cost |
|
| Denton et al. [21] | Operational level | Fixed cost and overtime cost |
|
| Lin and Li [22] | Tactical level | Waste cost and overtime cost |
|
| Fugener [23] | Integrated strategic and tactical | Downstream costs |
|
| Shafaei and Mozdgir [24] | Tactical MSS | None |
|
| Lu et al. [25] | Two stages, strategic and tactical | Overtime costs |
|
| Patrão et al. [26] | Integrated strategic and tactical | Cost of misplacing patients |
|
| This Study | Integrated strategic and tactical | Waiting cost and overtime cost |
|
| Study | Strategies | Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| VanBerkel and Blake [30] | Increasing Capacity | Discrete-event simulation | Increasing bed capacity and OR time can significantly impact throughput and reduce waiting times using discrete-event simulation |
| Spratt and Kozan [32] | Improving Efficiency | Mixed-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) | Ensured timely treatment of patients while managing resources |
| Bowers [33] | Demand-Side Management | Model simulation | Estimated number of patients treated within target waiting time |
| Powers et al. [34] | Demand-Side Management | Dynamic priority scoring (DPS) | Focused on equitable ranking of patients |
| This study | Considering All Three Strategies | Mathematical modeling (MINLP) | Allocate optimal resources, provide fair access time to surgical service across department, minimize total cost |
| Study | Objectives | Methodology | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al. [35] | Estimate surgery backlog size and clearance time resulting from COVID-19 | Forecasting and queuing models | Provided estimates for backlog size and project time for clearance, aiding in recovery planning |
| Oussedik et al. [36] | Model orthopedic pathway to estimate elective surgery waiting lists and suggest recovery strategies | Pathway modeling | Proposed strategies for managing orthopedic surgery waiting list and optimizing resources |
| Joshi et al. [37] | Use machine learning for predictive analysis to estimate backlog clearance time and associated costs | Machine learning algorithm | Offered real-time estimations on clearance time and costs, facilitating resource optimization |
| This study | Formulate mathematical model for managing resources and waiting list | Math modeling technique (MINLP) | Optimal resource allocation results in minimum average waiting time and costs |
| Sets | Descriptions | |
|---|---|---|
| T | Set of days in weekly planning horizon | |
| r | Set of resources including operating room (or), intensive care unit (icu), medium care unit (mcu), and nursing hours (nh) | |
| Indices | ||
| t | Index of days, t = 1, 2, …, T | |
| s | Index of number of surgical departments, s = 1, 2, …, S | |
| Parameters | ||
| The average operation duration of surgical specialty s | ||
| Relative important weight of specialty s | ||
| Average number of patients per OR block for specialty s | ||
| Average LOS of surgical specialty s patients in MCU before surgery | ||
| Average LOS of surgical specialty s patients in MCU after surgery and ICU | ||
| Average LOS of surgical specialty s patients in ICU after surgery | ||
| Average nursing workload (in hours) required for specialty s patients in ICU | ||
| Available capacity of resource r on day t, rÎR = {or, icu, mcu, nh} | ||
| Maximum overtime of resources allowed for resources r over T | ||
| Target utilization of resources rÎR = {or} in planning horizon T | ||
| Weekly demand for surgical specialty s | ||
| Total patients waiting in each surgical department s | ||
| Maximum requirement number of OR blocks of specialty over T | ||
| Minimum requirement number of OR blocks of specialty over T | ||
| Resource utilization requirement of resource r over T | ||
| Cost of waiting for surgery for patients from specialty s | ||
| Cost of overcapacity resources r | ||
| Relative weight of patient waiting time | ||
| Relative weight of overtime cost | ||
| Decision variables | ||
| Number of OR blocks assigned to surgical department s in planning horizon T | ||
| Number of weeks required to clear patient waiting list of surgical department s | ||
| Average number of weeks required to clear patient waiting list in hospital | ||
| Overcapacity of resources r needed over T and T + 2 | ||
| Utilizations of resource r over T and T + 2 | ||
| Specialty | No. Blocks Assigned | Number of Patients on Waiting List | Expected Waiting Time (Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENT | 5 | 1092 | 36.4 |
| OBG | 3 | 468 | 31.2 |
| URO | 3 | 416 | 34.67 |
| GEN | 5 | 1144 | 31.77 |
| VAS | 3 | 416 | 52 |
| OTH | 5 | 1196 | 42.71 |
| NEU | 3 | 260 | 43.33 |
| CAR | 1 | 104 | 52 |
| Current Setting | Proposed Model | % Decrease (Proposed Model: Current Setting) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Objective value (unit cost) | 4,725,300 | 4,089,871 | 13.45% |
| Mean waiting time (weeks) | 41.32 | 37.67 | 8.81% |
| Sd waiting time (weeks) | 13.87 | 9.86 | 28.87% |
| Mean utilization (%) | 90.60 | 99.25 | 8.7% |
| Sd utilization (%) | 7.95 | 0.74 | 90% |
| Patient throughput | 140 | 148 | 5.71% |
| No. OT | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | Scenario 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average WL clearance time (weeks) | 37.7 | 34.5 | 32.6 | 31.1 | 30.7 |
| % decrease from base case (%) | - | 8.55% | 13.38% | 17.45% | 18.50% |
| % increase in overtime costs from 10% | - | - | 136.2% | 267.6% | 304.4% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jittamai, P.; Toek, S.; Kongkanjana, K.; Chanlawong, N. Multi-Objective Decision Support Model for Operating Theatre Resource Allocation: A Post-Pandemic Perspective. Logistics 2025, 9, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9030116
Jittamai P, Toek S, Kongkanjana K, Chanlawong N. Multi-Objective Decision Support Model for Operating Theatre Resource Allocation: A Post-Pandemic Perspective. Logistics. 2025; 9(3):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9030116
Chicago/Turabian StyleJittamai, Phongchai, Sovann Toek, Kingkan Kongkanjana, and Natdanai Chanlawong. 2025. "Multi-Objective Decision Support Model for Operating Theatre Resource Allocation: A Post-Pandemic Perspective" Logistics 9, no. 3: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9030116
APA StyleJittamai, P., Toek, S., Kongkanjana, K., & Chanlawong, N. (2025). Multi-Objective Decision Support Model for Operating Theatre Resource Allocation: A Post-Pandemic Perspective. Logistics, 9(3), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics9030116






