Analysis of Supply Chain Response Frameworks: A Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
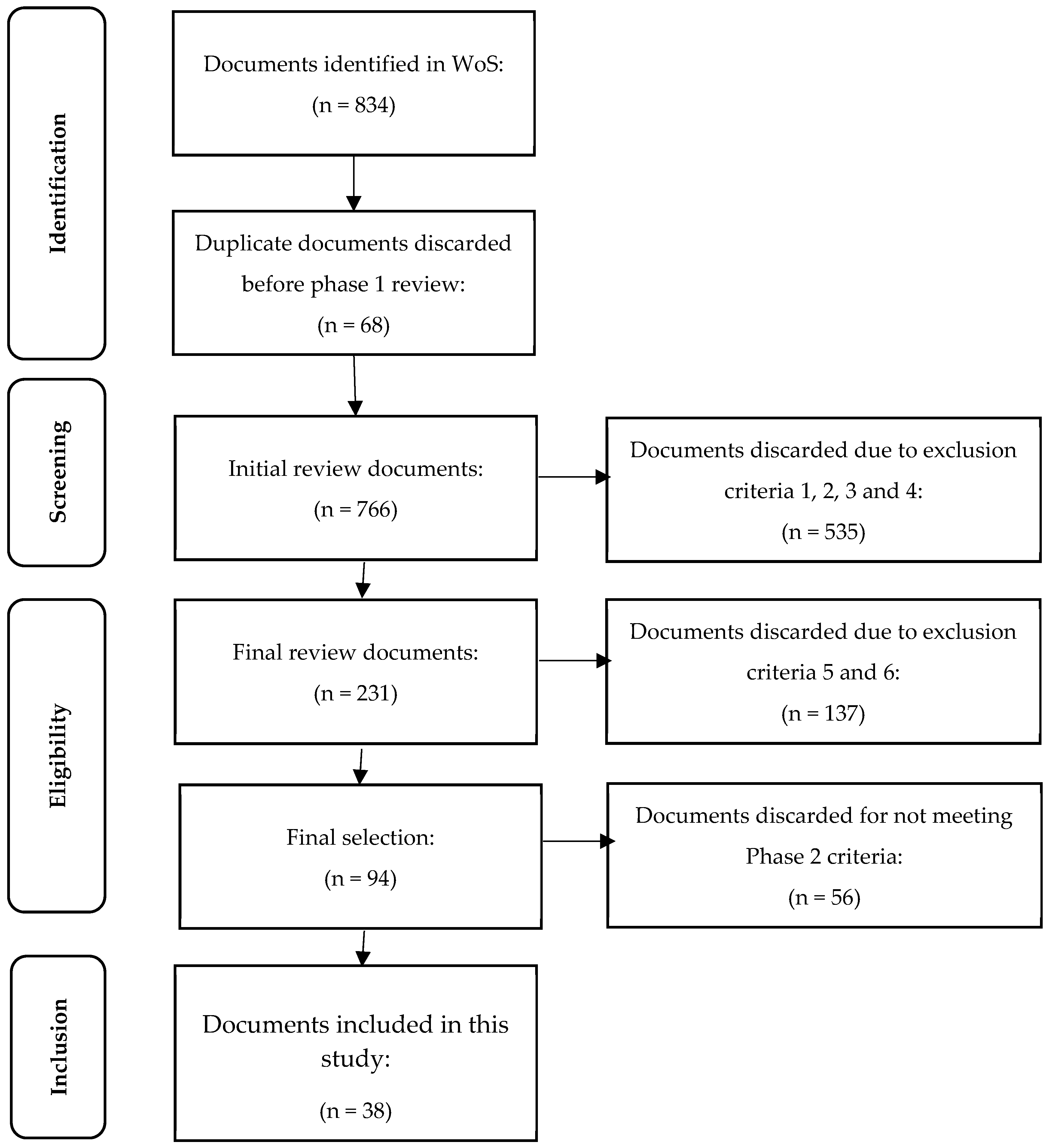
2. Methodology
3. Description of SCRFs
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sinha, A.; Swati, A.; Anand, P. Responsive supply chain: Modeling and simulation. Manag. Sci. Lett. 2015, 5, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Sarathy, R.; Mishra, V.; Bhattacharya, S.; Dastidar, S.G. Supply chain responsiveness: A relational capability perspective. J. Appl. Manag. Sci. 2015, 5, 244–268. [Google Scholar]
- Reichart, M.; Holweg, A. Creating the customer-responsive supply chain: A reconciliation of concepts. IJOPM 2007, 27, 1144–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chavez, W.; Jacobs, R.; Feng, M.A. Data-driven supply chain capabilities and performance: A resource-based view. Transp. Res. E. Logist. Transp. Rev. 2018, 114, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, G.; Kodali, R. A critical review of supply chain management frameworks: Proposed frame-work. Benchmarking Int. J. 2013, 20, 263–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tierney, K. Disaster response—Research findings and their implications for resilience measures. Caries Res. 2009, 59, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, C.Y.; Stentoft Arlbjørn, J.; Hvolby, H.H.; Johansen, J. Assessing responsiveness of a volatile and seasonal supply chain: A case study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2006, 104, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritchanchai, D.; MacCarthy, B.L. Responsiveness of the order fulfillment process. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1999, 19, 812–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, O. Understanding the stimuli, scope, and impact of organizational transformation: The context of eBusiness technologies in supply chains. Strateg. Chang. 2021, 5, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, R.; Lauras, M.; Montreuil, B.; Benaben, F. A decision support system for strategic supply chain capacity planning under uncertainty: Conceptual framework and experiment. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 16, 1793390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, C. Supply Chain Management: Strategy, Planning, and Operation, 7th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Corominas, A. Supply chains: What they are and the new problems they raise. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 6828–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Dhir, S.; Taggar, R.; Bindra, S. Retailer responsiveness: A total interpretive structural modelling approach. J. Glob. Bus. Adv. 2020, 13, 336–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blome, D.; Schoenherr, T.; Rexhausen, C. Antecedents and enablers of supply chain agility and its effect on performance: A dynamic capabilities perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 1295–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisna, T.; Marimin, M.; Arkeman, Y.; Sunarti, T.C. Multi-objective optimization for supply chain management problem: A literature review. Decis. Sci. Lett. 2016, 5, 283–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnyk, J.; Davis, S.; Spekman, E.; Sandor, R. Outcome-driven supply chains. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2010, 51, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Jermsittiparsert, K.; Sutduean, J.; Sriyakul, T.; Khumboon, R. The role of customer responsiveness in improving the external performance of an agile supply chain. Pol. J. Manag. Stud. 2019, 19, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldórsson, Á.; Arlbjorn, J.S. Research methodologies in supply chain management—What do we know? In Research Methodologies in Supply Chain Management: In Collaboration with Magnus Westhaus; Physica-Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.J.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, L.F.; Scavarda, G.; Vidal, D.; de Mattos Nascimento, L.; Garza-Reyes, J.A. A taxonomy of critical factors towards sustainable operations and supply chain management 4.0 in developing countries. Oper. Manag. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szablewska, N.; Kubacki, K. Empirical business research on modern slavery in supply chains: A systematic review. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 164, 113988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarski, L.; Roscoe, S.; Blome, C.; Schleper, M.C. Geopolitical disruptions in global supply chains: A state-of-the-art literature review. Prod. Plan. Control 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfeldt-Berg, M.; Olhager, J. The customer order decoupling point in empirical operations and supply chain management research: A systematic literature review and framework. Int. J. Product. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadegani, A.A.; Salehi, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ebrahim, N.A. A Comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of Science and Scopus databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013, 9, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Rollins, J.; Yan, E. Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997–2017: A selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, O.; Kocaman, R.; Kanbach, D.K. How to design bibliometric research: An overview and a framework proposal. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalan, M.; Kotzab, H. Assessing the responsiveness in the Danish mobile phone supply chain. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2003, 33, 668–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salam, M.A.; Banomyong, R. An investigation of supply chain responsiveness in the Thai textile industry supply view project quick scan view project. In Proceedings of the 8th Logistics Research Network Conference, London, UK, 10–12 September 2003; pp. 29–36. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229005387 (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- Eng, T.Y. The influence of a firm’s cross-functional orientation on supply chain performance. J. Supply Chain. Manag. 2005, 41, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Cavusgil, S.T.; Calantone, R.J. Information system innovations and supply chain management: Channel relationships and firm performance. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2006, 34, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homburg, C.; Grozdanovic, M.; Klarmann, M. Responsiveness to customers and competitors: The role of affective and cognitive organizational systems. J. Mark. 2007, 71, 318–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.M.; Gindy, N.N.Z. Future shape of the responsive manufacturing enterprise. Benchmarking Int. J. 2007, 14, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Lai, K.H.; Cheng, T.C.E. Responsive supply chain: A competitive strategy in a networked economy. Omega Westport 2008, 36, 549–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, R.P. Systems collaboration and strategic collaboration: Their impacts on supply chain responsiveness and market performance. Decis. Sci. 2010, 41, 955–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, C.; Wagner, S.M.; Petersen, K.J.; Ellram, L.M. Understanding responses to supply chain disruptions: Insights from information processing and resource dependence perspectives. Acad. Manag. J. 2010, 54, 833–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkovics, R.R.; Jean, R.J.B.; Roath, A.S.; Cavusgil, S.T. Does IT integration really enhance supplier responsiveness in global supply chains? Manag. Intern. Rev. 2011, 51, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, K.; Abbas, A.; Siddique, M.; Ur, K.; Cheema, R. A study of the different factors that affecting the supply chain responsiveness. J. Adv. Manuf. Sys. 2012, 3, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Suresh, N.C.; Kocabasoglu-Hillmer, C. An impact of manufacturing flexibility and technological dimensions of manufacturing strategy on improving supply chain responsiveness: Business environment perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 5597–5611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatte, A.A. Supply chain responsiveness through modularity based manufacturing practices: An exploratory study. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2013, 29, 743–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatte, A.A.; Rao, S.S.; Ragu-Nathan, T.S. Impact of SCM practices of a firm on supply chain responsiveness and competitive advantage of a firm. J. Appl. Bus. Res. 2013, 29, 2499–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qrunfleh, S.; Tarafdar, M. Lean and agile supply chain strategies and supply chain responsiveness: The role of strategic supplier partnership and postponement. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2013, 18, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.P.S.; Mahanty, M.K.; Jenamani, B.M. Supply chain responsiveness. In Modeling of Responsive Supply Chain; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehzati, T.; Dreyer, H.; Strandhagen, C.; Haartveit, J.O.; Romsdal, D.E.G. Exploring responsiveness and flexibility in multi-site production environments: The case of Norwegian dairy production. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 1039, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Das, S.; Deshpande, A. Effect of responsiveness and process integration in supply chain coordination. Adv. Manag. Account. 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rana, S.M.S.; Osman, A.; Abdul Manaf, A.H.; Solaiman, M.; Abdullah, M.S. Supply chain strategies and responsiveness: A study on retail chain stores. Int. Bus. Manag. 2016, 10, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, P.; Azar, N.A.Z.; Bahrin, A.S.; Appasamy, G.; Sundram, V.P.K. Determinants of supply chain responsiveness among firms in the manufacturing industry in Malaysia. Int. J. Sup. Chain Manag. 2016, 5, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, C.; Macdonald, J.R. Stages of supply chain disruption response: Direct, constraining, and mediating factors for impact mitigation. Decis. Sci. 2017, 48, 836–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilal, F.G.; Zhang, J.; Gilal, R.G.; Gilal, R.G.; Gilal, N.G. Supply Chain Management Practices and Product Development: A Moderated Mediation Model of Supply Chain Responsiveness, Organization Structure, and Research and Development. J. Adv. Manuf. Sys. 2017, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradlou, H.; Backhouse, C.; Ranganathan, R. Responsiveness, the primary reason behind re-shoring manufacturing activities to the UK: An Indian industry perspective. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. 2017, 47, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Chavez, R.; Jacobs, M.; Wong, C.Y.; Yuan, C. Environmental scanning, supply chain integration, responsiveness, and operational performance: An integrative framework from an organizational information processing theory perspective. Int. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2019, 39, 787–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis-Sramek, B.; Omar, A.; Germain, R. Leveraging supply chain orientation for global supplier responsiveness: The impact of institutional distance. Int. J. Appl. Logist. 2019, 30, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.M.S. Supply chain drivers and retail supply chain responsiveness: Strategy as moderator. Int. J. Manag. Prac. 2020, 13, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Taggar, R.; Bindra, S.; Dhir, S. A systematic review of responsiveness to develop future research agenda: A TCCM and bibliometric analysis. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 27, 2649–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asamoah, D.; Nuertey, D.; Agyei-Owusu, B.; Akyeh, J. The effect of supply chain responsiveness on customer development. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2021, 32, 1190–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghuram, P.; Saleeshya, P.G. Responsiveness model of textile supply chain-a structural equation modelling-based investigation. IJSOM 2021, 38, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, R.G.; Roath, A.S.; Adams, F.G.; Wieland, A. A responsiveness view of logistics and supply chain management. J. Bus. Logist. 2022, 43, 62–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saïah, F.; Vega, D.; de Vries, H.; Kembro, J. Process modularity, supply chain responsiveness, and moderators: The Médecins Sans Frontières response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 32, 1490–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sethi, S.P.; Chung, S.H.; Choi, T.M. Reforming global supply chain management under pandemics: The Great-3Rs framework. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2022, 32, 524–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easterby-Smith, M.; Jaspersen, L.J.; Thorpe, R.; Valizade, D. Management and Business Research, 7th ed.; SAGE: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yusof, S.M.; Aspinwall, E. Total quality management implementation frameworks: Comparison and review. Total Qual. Manag. 2000, 11, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghi, S.; Hosseini-Motlagh, S.M. Responsive and reliable injured-oriented blood supply chain for disaster relief: A real case study. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 291, 129–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, D.M.; Enz, M.G. Issues in supply chain management: Progress and potential. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2017, 62, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramshahgol, R.; Al-Husain, R. A GP-AHP approach to design responsive supply chains for Pareto customers. Oper. Res. Perspect. 2021, 8, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, R.J.; Lundholm, M.K.; Brierton, D.; Chapman, N.R.M. Responding to unforeseen disasters in a large health system. Am. J. Health-Sys. Pharm. 2021, 78, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahre, N.; Fabbe-Costes, M. How standards and modularity can improve humanitarian supply chain responsiveness: The case of emergency response units. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain. Manag. 2015, 5, 348–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Aros-Vera, F.; Browne, M. Agent interactions and the response of supply chains to pricing and incentives. Econ. Transp. 2015, 4, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y. Improving warehouse responsiveness by job priority management: A European distribution centre field study. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 139, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takawira, B.; Pooe, R.I.D. Supply chain disruptions during COVID-19 pandemic: Key lessons from the pharmaceutical industry. S. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2024, 55, 4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, U.; Aluko, O.; Ramanathan, R. Supply chain resilience and business responses to disruptions of the COVID-19 pandemic. Benchmarking Int. J. 2022, 29, 2275–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Tiwana, A.; Rai, A. Complementarities between product design modularity and IT infrastructure flexibility in IT-enabled supply chains. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2010, 57, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azyabi, N.G. How do information technology and knowledge management affect SMEs’ responsiveness to the COVID-19 crisis? Bus. Inform. 2021, 15, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.P.; Dixit, V. Disaster supply chain with information and digital technology integrated in its institutional framework. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 3003–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahiluoto, H.; Mäkinen, H.; Kaseva, J. Supplying resilience through assessing diversity of responses to disruption. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2020, 3, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Pacheco, R.A.; Benedito, R.A. Supply chain response during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A multiple-case study. Processes 2023, 11, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar Singh, R. Coordination and responsiveness issues in SME supply chains: A review. Benchmarking Int. J. 2017, 24, 635–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz Pacheco, R.A.; Benedito, E. Supply chain response framework. Systematic literature review and framework to respond to stimuli. Cogent Bus. Mang. 2024, 11, 2308083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Topic | Purpose of the SCRF |
|---|---|---|
| [8] | Order fulfillment process | Discuss evidence from field studies undertaken to investigate responsiveness. |
| [28] | Assessing responsiveness | Evaluate the SCR using four variables: delivery times, postponement strategies, bullwhip effect, and exchange of information. |
| [29] | Appraising determinants of SCR | Appraise the determinants of SCR concerning demand uncertainties in the Thai textile industry. |
| [30] | Cross-functional orientation | Examine the influence of cross-functional orientation on customer satisfaction and SCR in SCM. |
| [7] | Assessing responsiveness | Describe a structural approach to assess the responsiveness of a volatile and seasonal SC. |
| [31] | Responsiveness of the partnership of SC | Explore how innovations in SC communication systems affect channel relationships and market performance. |
| [32] | Responsiveness to customers and competitors | Identify the differential mechanisms that drive responsiveness to customers and responsiveness to competitors. |
| [33] | Manufacturing response | Develop an overall framework for capturing the main attributes of a responsive enterprise. |
| [3] | Customer responsiveness | Propose a clear definition of SCR and its relationship to flexibility and develop a holistic framework. |
| [34] | Competitive strategy | Analyze both advanced manufacturing and SC management to develop a framework for responsive SC. |
| [35] | Market performance | Examine the multiple roles of system collaboration and strategic collaboration and how they, directly and indirectly, influence a firm’s SCR and market performance. |
| [36] | Response to SC disruptions | Identify the repertoire of strategic responses to SC disruptions and devise and test a model that explains the occurrence of alternative responses. |
| [37] | IT integration | Examine the influence of information technology integration and trust on SCR in varied cultural distance conditions. |
| [38] | Factors that affect the SCR | Develop a theoretical framework to improve coordination in the SC and test it empirically. |
| [39] | Manufacturing flexibility and technological dimensions | Investigate the impact of manufacturing flexibility and technological dimensions of manufacturing strategy on SCR. |
| [40] | Modularity-based manufacturing practices | Extend previous research on manufacturing practices exploring dimension-level and item-level relationships between manufacturing practices based on modularity and SCR. |
| [41] | Impact of SCM practices | Conceptualize three dimensions of SCR and develop a reliable and valid instrument to measure this concept. |
| [42] | Strategic supplier partnership and postponement | Examine the role of strategic supplier partnership and postponement, respectively, on the relation between lean and agile SC strategy and SCR. |
| [43] | Several topics | Not specified. |
| [44] | Responsiveness and flexibility in multisite production environments | Explore responsiveness and flexibility in multisite production systems to identify the factors that require and enable responsiveness in a production network system. |
| [45] | Responsiveness and process integration in SC coordination | Present an integrative framework related to chain responsiveness, process integration, SC coordination, and performance. |
| [2] | SCR: a relational capability perspective | Conceptually explore trust, commitment, communication, cooperation, adaptation, and interdependence as relational resources in developing SCR. |
| [1] | Responsive SC | Develop a model of responsive SC management. |
| [46] | Retail SCR | Empirically analyze the impacts of SC strategies on retail SCR. |
| [47] | Determinants of SCR | Verify the significance of SC strategies (lean and agile SC, strategic supplier partnership, and postponement) on achieving SCR. |
| [48] | Stages of response to SC disruption | Not specified |
| [49] | SCM practices and product development | Develop a moderated mediation model, investigate the influence of SCM practices on product development, explore the mediating role of SCR, and examine the moderating influence of organization structure and research and development. |
| [50] | Responsiveness manufacturing | Understand the main motivation behind the re-shoring strategy of UK companies located in India. |
| [4] | SC | Explore the effect of data-driven SC capabilities on financial performance. |
| [51] | Environmental scanning, SC integration, responsiveness, and operational performance | Investigate the effects of environmental scanning on operational performance through SC integration and SCR. |
| [52] | SC orientation for global supplier responsiveness | Utilize middle-range theorizing to examine whether a US manufacturer can leverage SC orientation to garner responsiveness from a global supplier. |
| [53] | SC drivers and retail SCR | Explore important drivers of retail SCR. |
| [54] | SC | Epistemologically extend and explore the present theories from prior research conducted in the area of responsiveness. |
| [55] | SCR and customer development | Examine how SCR impacts the ability of firms to attract, satisfy, and retain customers. |
| [56] | Responsiveness model of textile SC | Examine the effect of the combination of material flow, information flow, lead time, and overall capability on the responsiveness of a textile SC. |
| [57] | SC | Show the potential of defined responsiveness based on SC and logistics management. |
| [58] | Process modularity and SCR | Extend the literature on SCR processes. |
| [59] | Global SCM | Guide both scholars and industrialists on reforming global SCM to achieve responsiveness, resilience, and restoration and to seek survival under a pandemic. |
| Reference | Assessed Components | Stimulus | Activity | Objective | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [8] | Stimuli, goals, capabilities | X | X | X | |
| [28] | Lead time, postponement strategies, bullwhip effect, and information exchange | X | X | X | |
| [29] | Buyer behavior, operational accuracy, lead time, organizational culture, and collaboration | X | |||
| [30] | Interfunctional cooperation, operational linkages, information exchange, participative management style, technology integration, length of Internet adoption, and customer satisfaction | X | X | ||
| [7] | Strategies and operational level of responsiveness, cluster, and indicators | X | X | X | |
| [31] | Information exchange and interfirm coordination | X | |||
| [32] | Customer orientation of the cognitive organizational system, customer orientation of the affective organizational system, customer-related responsiveness, and competitor-related responsiveness | X | |||
| [33] | Manufacturing responsiveness and response output | X | X | ||
| [3] | Operational factors, SC integration, external requirements, and relational factors | X | X | ||
| [34] | Virtual enterprise, strategic planning, knowledge and IT management, and outcome | X | X | ||
| [35] | System collaboration and strategic collaboration | X | |||
| [36] | Trust, dependence, SC disruption orientation, and prior experience | X | |||
| [37] | Disruption impact | ||||
| [38] | Top-level commitment, organizational factors, mutual under-standing, flow of information, and relationship- and deci-sion-making | X | |||
| [39] | New product flexibility, E-procurement, market flexibility, and advanced manufacturing technology | X | |||
| [40] | Modularity-based manufacturing practices and SCR | X | |||
| [41] | Strategic supplier partnership, customer relationship, information sharing, operation system responsiveness, logistics process responsiveness, supplier network responsiveness, price/cost, quality, delivery dependability, and time to market and product innovation | X | X | ||
| [42] | Lean SC strategy, agile SC strategy, strategic supplier partnership, postponement, and firm performance | X | |||
| [43] | Operational factors, SC integration, external determinants, strategic planning, virtual enterprise, knowledge and information technology management, and SCR | X | X | ||
| [44] | Operational factors, SC integration, external requirements, and relational factors | X | X | ||
| [45] | SCR, SC process integration, and SC coordination | X | |||
| [2] | Relational resources | X | |||
| [1] | Operational factors, SC integration, external determinants, strategic planning, virtual enterprise, knowledge and IT management, and SCR | X | |||
| [46] | Lean SC strategy, agile SC strategy, and hybrid strategies | X | |||
| [47] | Lean SC strategy, agile SC strategy, strategic supplier partnership, and postponement | X | |||
| [48] | Recognition, diagnosis, development, and implementation | X | |||
| [49] | SCM practices, organization structure, research and development, and product development | X | |||
| [50] | Human factors, manufacturing equipment, and IT solutions | X | |||
| [4] | SC data drives | X | |||
| [51] | Environmental scanning, SC integration | X | |||
| [52] | SC orientation, formal institutionaldistance, and informal institutional distance | X | |||
| [53] | Suppliers, inventory management, IT, transportation management, and coordination | X | |||
| [54] | Innovation, collaboration, flexibility, service performance, customer relationship management, and customer engagement | X | |||
| [55] | Operation system responsiveness, supplier network responsiveness, and logistics process responsiveness | X | |||
| [56] | Material flow, overall capability, information flow, and lead time | X | |||
| [57] | Flexibility, agility, resilience, and improvisation | X | |||
| [58] | Process modularity: architecture, interfaces, standards | X | |||
| [59] | Operational flexibilities and strategies, managerial attitudes, enhanced logistics, forecasting, and analytics | X |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz Pacheco, R.A.; Benedito, E. Analysis of Supply Chain Response Frameworks: A Literature Review. Logistics 2024, 8, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8030063
Díaz Pacheco RA, Benedito E. Analysis of Supply Chain Response Frameworks: A Literature Review. Logistics. 2024; 8(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz Pacheco, Raúl Antonio, and Ernest Benedito. 2024. "Analysis of Supply Chain Response Frameworks: A Literature Review" Logistics 8, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8030063
APA StyleDíaz Pacheco, R. A., & Benedito, E. (2024). Analysis of Supply Chain Response Frameworks: A Literature Review. Logistics, 8(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8030063






