A Systematic Review of Strategic Supply Chain Challenges and Teaching Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- (1)
- Must be published in peer-reviewed journals or conferences and written in English.
- (2)
- Publications must reference strategic supply chain management and its teaching strategies in high schools.
- (3)
- Publications must reference one or more supply chain challenges.
- (4)
- Papers published after the year 2000 are of interest.
- (1)
- Non-English papers.
- (2)
- Papers that focus on supply chain curricula without any aspect of pedagogy.
- (3)
- Non-peer-reviewed and review papers.
- (4)
- Books, thesis, reports, and book chapters.
- (5)
- Publications with no direct relation to supply chain management challenges and supply chain educational strategies.
3. Results
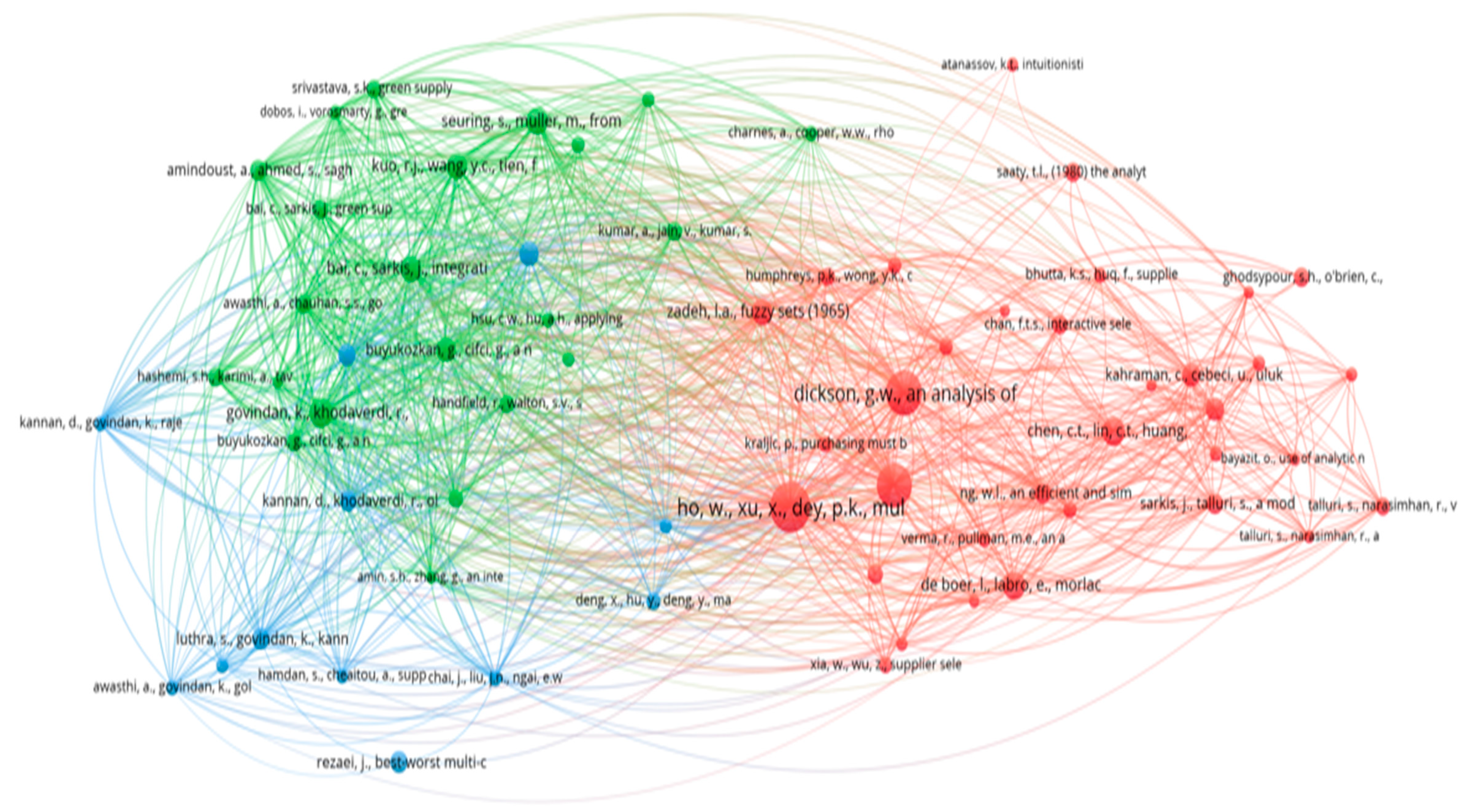
3.1. Thematic Analysis with Co-Citation Analysis
3.2. Strategic Supply Chain Concepts-Based Content Analysis
3.3. Strategic Supply Chain Pedagogical Activities and Teaching Innovative Strategies
4. Implications and Further Development
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bodendorf, F.; Wonn, F.; Simon, K.; Franke, J. Indicators and Countermeasures of Modern Slavery in Global Supply Chains: Pathway to a Social Supply Chain Management Framework. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 32, 2049–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhani, P.M. Strategic Supply Chain Management for Enhancing Competitive Advantages: Developing Business Value Added Framework. Int. J. Value Chain Manag. 2019, 10, 316–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, M.; Srivastava, A.K. Leadership and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Model. Manag. 2023, 18, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, A.; Rejeb, K.; Simske, S.J.; Treiblmaier, H. Drones for Supply Chain Management and Logistics: A Review and Research Agenda. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2023, 26, 708–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammelgaard, B.; Nowicka, K. Next Generation Supply Chain Management: The Impact of Cloud Computing. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2023; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abston, K.A.; Soter, H.A. A Professionalism Conundrum: Development of Business Students. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/3285 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Léger, P.; Cronan, P.; Charland, P.; Pellerin, R.; Babin, G.; Robert, J. Authentic OM Problem Solving in an ERP Context. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2012, 32, 1375–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- William, L.; Rahim, Z.A.B.A.; Wu, L.; de Souza, R. Effectiveness of Supply Chain Games in Problem-Based Learning Environment. In Game-Based Assessment Revisited; Ifenthaler, D., Kim, Y.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 257–280. ISBN 978-3-030-15569-8. [Google Scholar]
- Gravier, M.J.; Farris, T.M. An Analysis of Logistics Pedagogical Literature: Past and Future Trends in Curriculum, Content, and Pedagogy. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2008, 19, 233–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, R.; Kaneko, T.; Hiji, M. Development of BASE Supply Chain Collaboration Game by Using Tangible Blocks. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/3190 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Tajima, E.; Ishigaki, A.; Takashima, R.; Nishida, H.; Okammoto, T. Effectiveness of a Multi-Agent Cooperation Game in a Multi-Stage Supply Chain. J. Jpn. Ind. Manag. Assoc. 2023, 73, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuttke, D.; Mohadikar, M.; Eichhorn, C. Serious VR Simulation: J. Forrester’s Beer Game in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality Adjunct (ISMAR-Adjunct), Singapore, 17–21 October 2022; pp. 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Loaiza-Velez, C.; PACHECO, E.; Ramirez-Echeverri, S.; Vieira-Mejia, C. Using Game-Based Learning for Supply Chain Education. In Proceedings of the 2021 The 2nd International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Industrial Management, New York, NY, USA, 8–11 January 2021; pp. 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, M.-L. A Web-Based Simulation Game for Teaching Supply Chain Management. Manag. Teach. Rev. 2020, 5, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, C.M.; Williams, S.K.; Hoefle, S. The Difficulties of Context: An Exploratory Study of Learning Transfer from a Business Simulation Game. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2022, 20, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deif, A. Going from 2D to 3D in Supply Chain 4.0 Education: An LSP Approach. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Oper. Manag. 2023, 5, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green Supply Chain Management: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Dolatabad, A.; Heidary Dahooie, J.; Antucheviciene, J.; Azari, M.; Razavi Hajiagha, S.H. Supplier Selection in the Industry 4.0 Era by Using a Fuzzy Cognitive Map and Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic VIKOR Methodology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 52923–52942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deghedi, G.A. Game-Based Learning for Supply Chain Management: Assessing the Complexity of Games. Int. J. Game-Based Learn. 2023, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on Conducting a Systematic Literature Review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2019, 39, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, H. Literature Review as a Research Methodology: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Péry, C.; Vuddaraju, L.N.R.; Corbett-Etchevers, I.; Tassabehji, R. Reducing Maritime Accidents in Ships by Tackling Human Error: A Bibliometric Review and Research Agenda. J. Shipp. Trade 2021, 6, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjørland, B. Citation Analysis: A Social and Dynamic Approach to Knowledge Organization. Inf. Process. Manag. 2013, 49, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Watson, R.T. Analyzing the Past to Prepare for the Future: Writing a Literature Review. MIS Q. 2002, 26, xiii–xxiii. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, G.W. An Analysis Of Vendor Selection Systems And Decisions. J. Purch. 1966, 2, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.; Xu, X.; Dey, P.K. Multi-Criteria Decision Making Approaches for Supplier Evaluation and Selection: A Literature Review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.A.; Current, J.R.; Benton, W.C. Vendor Selection Criteria and Methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1991, 50, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Sarkis, J. Green Supplier Development: Analytical Evaluation Using Rough Set Theory. J. Clean. Prod. 2010, 18, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Khodaverdi, R.; Jafarian, A. A Fuzzy Multi Criteria Approach for Measuring Sustainability Performance of a Supplier Based on Triple Bottom Line Approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S.; Müller, M. From a Literature Review to a Conceptual Framework for Sustainable Supply Chain Management. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Rajendran, S.; Sarkis, J.; Murugesan, P. Multi Criteria Decision Making Approaches for Green Supplier Evaluation and Selection: A Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 98, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Kumar, S.; Garg, D.; Haleem, A. Comparative Evaluation of GSCM Practices in Automotive Components Manufacturing Firms of India: A Fuzzy TOPSIS Approach. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2016, 25, 358–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, J. Best-Worst Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Method. Omega 2015, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, L.; Labro, E.; Morlacchi, P. A Review of Methods Supporting Supplier Selection. Eur. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 2001, 7, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.T.S.; Kumar, N. Global Supplier Development Considering Risk Factors Using Fuzzy Extended AHP-Based Approach. Omega 2007, 35, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, C.; Gürpinar, D. Analytic Network Process in Supplier Selection: A Case Study in an Electronic Firm. Appl. Math. Model. 2007, 31, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Talluri, S. A Model for Strategic Supplier Selection. J. Supply Chain Manag. 2002, 38, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryadi, A.; Rau, H. Considering Region Risks and Mitigation Strategies in the Supplier Selection Process for Improving Supply Chain Resilience. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 181, 109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Ngai, E.W.T. Multi-Perspective Strategic Supplier Selection in Uncertain Environments. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 166, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amid, A.; Ghodsypour, S.H.; O’Brien, C. A Weighted Max–Min Model for Fuzzy Multi-Objective Supplier Selection in a Supply Chain. Innsbr. 2011, 131, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boran, F.E.; Genç, S.; Kurt, M.; Akay, D. A Multi-Criteria Intuitionistic Fuzzy Group Decision Making for Supplier Selection with TOPSIS Method. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 11363–11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Hu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Mahadevan, S. Supplier Selection Using AHP Methodology Extended by D Numbers. 21st Century Logist. Supply Chain Manag. 2014, 41, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.; Chauhan, S.S.; Goyal, S.K. A Fuzzy Multicriteria Approach for Evaluating Environmental Performance of Suppliers. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2010, 126, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobos, I.; Vörösmarty, G. Green Supplier Selection and Evaluation Using DEA-Type Composite Indicators. Int. Soc. Inventory Res. 2012 2014, 157, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Kumar Paul, S.; Chowdhury, P.; Agarwal, R.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Jose Chiappetta Jabbour, C.; Luthra, S. Modelling of Supply Chain Disruption Analytics Using an Integrated Approach: An Emerging Economy Example. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 173, 114690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, E.; Shahin, A. The Influence of the Quality Criteria on the Quality Cost of Suppliers in SMEs. Benchmarking Int. J. 2022, 29, 2313–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Cheng, T.C.E.; Shen, H.; Xu, L. Incentives for Quality Improvement Efforts Coordination in Supply Chains with Partial Cost Allocation Contract. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 6216–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lu, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, C. Quality and Pricing Decisions in a Two-Echelon Supply Chain with Nash Bargaining Fairness Concerns. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 2018, 4267305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, L.M.; Teli, S.N.; Majali, V.S.; Bhushi, U.M. An Application of Six Sigma to Reduce Supplier Quality Cost. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C 2016, 97, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surange, V.G. Implementation of Six Sigma to Reduce Cost of Quality: A Case Study of Automobile Sector. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2015, 15, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, H.; Schiffauerova, A. Analysing Barriers to Supplier Quality Management via Interpretive Structural Modelling: The Case of Saudi Industry. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2016, 24, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrighetti, R.; Battini, D.; Persona, A.; Zennaro, I. Disruption Cost Evaluation Methods in Supply Chain Network Design: State of the Art and Future Steps. In Proceedings of the Summer School Francesco Turco; Perona, M., Zanoni, S., Eds.; AIDI-Italian Association of Industrial Operations Professors: Brescia, Italy, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, K.; Fattahi, M.; Keyvanshokooh, E. Supply Chain Network Design under Uncertainty: A Comprehensive Review and Future Research Directions. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 263, 108–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.H.; Zhang, G. An Integrated Model for Closed-Loop Supply Chain Configuration and Supplier Selection: Multi-Objective Approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 6782–6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Wang, Z. The Collaborative Networks and Thematic Trends of Research on Purchasing and Supply Management for Environmental Sustainability: A Bibliometric Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Omoush, K.S.; de Lucas, A.; del Val, M.T. The Role of E-Supply Chain Collaboration in Collaborative Innovation and Value-Co Creation. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 158, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prataviera, L.B.; Creazza, A.; Dallari, F.; Melacini, M. How Can Logistics Service Providers Foster Supply Chain Collaboration in Logistics Triads? Insights from the Italian Grocery Industry. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2023, 28, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukamuhabwa, B.R.; Stevenson, M.; Busby, J.; Zorzini, M. Supply Chain Resilience: Definition, Review and Theoretical Foundations for Further Study. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 5592–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharia, Z.G.; Sanders, N.R.; Nix, N.W. The Emerging Role of the Third-Party Logistics Provider (3PL) as an Orchestrator. J. Bus. Logist. 2011, 32, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.J.; Schlachter, J.T. A Virtue-Ethics Analysis of Supply Chain Collaboration. J. Bus. Ethics 2008, 82, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh, A.; Haughton, M.; Khosrojerdi, A. Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Design under Disruption Risks: A Robust Approach with Real World Application. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 116, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snoeck, A.; Udenio, M.; Fransoo, J.C. A Stochastic Program to Evaluate Disruption Mitigation Investments in the Supply Chain. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 274, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Zhong, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. An Approach for Resilient-Green Supplier Selection Based on WASPAS, BWM, and TOPSIS under Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1761893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.M.; Ghezavati, V.; Bidhandi, H.M.; Al-e-Hashem, S.M.J.M. Green-Resilient Supplier Selection and Order Allocation Under Disruption by Utilizing Conditional Value at Risk: Mixed Response Strategies. Process Integr. Optim. Sustain. 2023, 7, 359–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei-Kordshouli, F.; Paydar, M.M.; Nayeri, S. Designing a Dairy Supply Chain Network Considering Sustainability and Resilience: A Multistage Decision-Making Framework. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 2903–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Feliu, J.; Chong, M.; Vargas-Florez, J.; de Brito, I.; Osorio-Ramirez, C.; Piatyszek, E.; Quiliche Altamirano, R. The Maturity of Humanitarian Logistics against Recurrent Crises. Soc. Sci. 2020, 9, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, S.; El Baz, J.; Ivanov, D.; Das, A. Supply Chain Viability: Conceptualization, Measurement, and Nomological Validation. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.J.; Griffin, P.M. Coordinated Supply Chain Management. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 94, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.A.; Scudder, G.D. The Use of Electronic Data Interchange for Supply Chain Coordination in the Food Industry. J. Oper. Manag. 2002, 20, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.P. A Hierarchical Model of the Impact of RFID Practices on Retail Supply Chain Performance. 21st Century Logist. Supply Chain Manag. 2014, 41, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.; Hamdy, W.; Alawady, H. Impacts of Internet of Things on Supply Chains: A Framework for Warehousing. Soc. Sci. 2019, 8, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, R. Chapter 9-The Application of Blockchain in Talent Supply Chain Management. In Blockchain in a Volatile-Uncertain-Complex-Ambiguous World; Mathiyazhagan, K., Sreedharan, V.R., Mathivathanan, D., Sunder M, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar]
- Mafakheri, F.; Breton, M.; Ghoniem, A. Supplier Selection-Order Allocation: A Two-Stage Multiple Criteria Dynamic Programming Approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 132, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, B.R. Role of Green Policy on Sustainable Supply Chain Management. Benchmarking Int. J. 2016, 23, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.R.; Bushuev, M.A.; Kretinin, A.A.; Guiffrida, A.L. Recent Developments in Green Supply Chain Management: Sourcing and Logistics. Green Supply Chain Manag. Sustain. Bus. Pract. 2017, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.H.; Karimi, A.; Tavana, M. An Integrated Green Supplier Selection Approach with Analytic Network Process and Improved Grey Relational Analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 159, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handfield, R.; Walton, S.V.; Sroufe, R.; Melnyk, S.A. Applying Environmental Criteria to Supplier Assessment: A Study in the Application of the Analytical Hierarchy Process. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 141, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, D.; Khodaverdi, R.; Olfat, L.; Jafarian, A.; Diabat, A. Integrated Fuzzy Multi Criteria Decision Making Method and Multi-Objective Programming Approach for Supplier Selection and Order Allocation in a Green Supply Chain. Clean. Prod. Initiat. Chall. Sustain. World 2013, 47, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Govindan, K.; Kannan, D.; Mangla, S.K.; Garg, C.P. An Integrated Framework for Sustainable Supplier Selection and Evaluation in Supply Chains. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Agrawal, A.; Kumar, N.; Shah, M.A.; Jawla, P.; Priyan, S. Benchmarking the Interactions among Green and Sustainable Vendor Selection Attributes. Adv. Oper. Res. 2022, 2022, 8966856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-W.; Hu, A.H. Applying Hazardous Substance Management to Supplier Selection Using Analytic Network Process. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jain, V.; Kumar, S. A Comprehensive Environment Friendly Approach for Supplier Selection. Omega 2014, 42, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoomi, B.; Sahebi, I.G.; Fathi, M.; Yıldırım, F.; Ghorbani, S. Strategic Supplier Selection for Renewable Energy Supply Chain under Green Capabilities (Fuzzy BWM-WASPAS-COPRAS Approach). Energy Strategy Rev. 2022, 40, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnourani, S.; Mejjaouli, S. The Impact of Carbon Cap Policy on Supply Chain Network. In Proceedings of the 2022 9th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Applications (Europe), Barcelona, Spain, 12–14 January 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wei, X.; Lin, J.; Tian, X.; Lev, B.; Wang, S. Supply Chain Management under Carbon Taxes: A Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Omega 2021, 98, 102295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, V.L.; Alves, A.C.; Leão, C.P. Lean Thinking Contributions for Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 904–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, D.; Zühlke, D. Lean Automation Enabled by Industry 4.0 Technologies. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2015, 48, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, M.; Powell, D.J.; Kundu, K. Lean Supply Chain Management and Industry 4.0: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Lean Six Sigma 2023, 14, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdirad, M.; Krishnan, K. Industry 4.0 in Logistics and Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Eng. Manag. J. 2021, 33, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdirad, M.; Krishnan, K. Examining the Impact of E-Supply Chain on Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction: A Case Study. Int. J. Qual. Serv. Sci. 2022, 14, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Merino, M.; Maqueira-Marín, J.M.; Moyano-Fuentes, J.; Martínez-Jurado, P.J. Information and Digital Technologies of Industry 4.0 and Lean Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 5034–5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxby, R.; Cano-Kourouklis, M.; Viza, E. An Initial Assessment of Lean Management Methods for Industry 4.0. TQM J. 2020, 32, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sony, M. Industry 4.0 and Lean Management: A Proposed Integration Model and Research Propositions. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2018, 6, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, G.L.; Miorando, R.; Marodin, G. Lean Supply Chain Management: Empirical Research on Practices, Contexts and Performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 193, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labonte-LeMoyne, E.; Leger, P.-M.; Robert, J.; Babin, G.; Charland, P.; Michon, J.-F. Business Intelligence Serious Game Participatory Development: Lessons from ERPsim for Big Data. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2017, 23, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, P.-M.; Charland, P.; Feldstein, H.D.; Robert, J.; Babin, G.; Lyle, D. Business Simulation Training in Information Technology Education: Guidelines for New Approaches in IT Training. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2011, 10, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.-D. Physical and Virtual Game Based Experiential Learning for Supply Chain and Operations Management Teaching Practice and Effectiveness. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON), Gammarth, Tunisia, 28–31 March 2022; pp. 1113–1120. [Google Scholar]
- William, L.; Rahim, Z.B.A.; Boo, I.; De Souza, R. Embedding Mixed Reality in Humanitarian Logistics Gaming. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Teaching, Assessment, and Learning for Engineering (TALE), Wollongong, NSW, Australia, 4–7 December 2018; Lee, M.J.W., Nikolic, S., Wong, G.K.W., Shen, J., Ros, M., Lei, L.C.U., Venkatarayalu, N., Eds.; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 710–715. [Google Scholar]
- Balaban, M.; Russell, S.; Mastaglio, T.W.; Dykes, P. The Evaluation of a Constructive Modeling and Simulation Approach in Teaching Port Management Skills. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Simulation Symposium, Alexandria, VA, USA, 12–15 April 2015; Society for Computer Simulation International: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, M.; Voordijk, H.; Adriaanse, A.; Hartmann, T. Experiencing Supply Chain Optimizations: A Serious Gaming Approach. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2017, 143, 04017082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L. Using a Video Game to Teach Supply Chain and Logistics Management. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2017, 25, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seethamraju, R. Enhancing Student Learning of Enterprise Integration and Business Process Orientation through an ERP Business Simulation Game. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2011, 22, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Park, A.; Rudna, O.; Song, J.M. FloraPark (the Flower Game): A Supply Chain Contract and Collaboration Simulation. Inf. Trans. Educ. 2023, 24, 1–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P. The Use of Classroom Games in Management Science and Operations Research. Inf. Trans. Educ. 2007, 8, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lau, A.K.W. Teaching Supply Chain Management Using a Modified Beer Game: An Action Learning Approach. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2015, 18, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.T.; Lui, R.W.; Chau, M. How Does Competition Help Future Learning in Serious Games? An Exploratory Study in Learning Search Engine Optimization. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2019, 30, 167–177. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney Jr, E.; Niese, B.; Bhatia, M.S. Teaching Tip: Active Learning in the IS Classroom: A Student Crowdpolling Exercise for IS Courses. J. Inf. Syst. Educ. 2023, 34, 118–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.A.; Maylor, H.R. Game Playing and Operations Management Education. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2007, 105, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, C.M. The Juice Supply Game: An Excel Based Simulation. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/3382/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Stefan, I.A.; Hauge, J.B.; Hasse, F.; Stefan, A. Using Serious Games and Simulations for Teaching Co-Operative Decision-Making. In Procedia Computer Science; Herrera-Viedma, E., Shi, Y., Berg, D., Tien, J., Cabrerizo, F.J., Li, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 162, pp. 745–753. [Google Scholar]
- Schaedler Uhlmann, T.; Battaiola, A.L. Applications of a Roleplaying Game for Qualitative Simulation and Cooperative Situations Related to Supply Chain Management. In Proceedings of the HCI in Business, Crete, Greece, 22–27 June 2014; Nah, F.F.-H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 429–439. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.C. Online Games to Teach Operations. Inf. Trans. Educ. 2007, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, R.; Sadeh, N. The 2003 Supply Chain Management Trading Agent Competition. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Electronic Commerce, Plymouth, UK, 27–29 April 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Tobail, A.; Crowe, J.; Arisha, A. Learning by Gaming: Supply Chain Application. In Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 11–14 December 2011; Winter Simulation Conference: Phoenix, Arizona, 2011; pp. 3940–3951. [Google Scholar]
- Corsi, T.M.; Boyson, S.; Verbraeck, A.; Van Houten, S.-P.; Han, C.; Macdonald, J.R. The Real-Time Global Supply Chain Game: New Educational Tool for Developing Supply Chain Management Professionals. Transp. J. 2006, 45, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherpereel, C.M.; Williams, S.K.; Hoefle, S.E. Learning Transfer from a Business Simulation: How Are You Situated? Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/3238 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Kandanaarachchi, T.; Perera, H.N. Gamified Learning of Supply Chain Optimization Through the Beer Distribution Game. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management (IEEM), Singapore, 13–16 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 503–507, ISBN 978-1-66543-771-4. [Google Scholar]
- Shovityakool, P.; Jittam, P.; Sriwattanarothai, N.; Laosinchai, P. A Flexible Supply Chain Management Game. Simul. Gaming 2019, 50, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weenk, E. Mastering the Supply Chain: Principles, Practice and Real-Life Applications; Kogan Page Publishers: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 0-7494-8449-7. [Google Scholar]
- Maisiri, W.; Hattingh, T. Integrating Game-Based Learning in an Industrial Engineering Module at a South African University. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE IFEES World Engineering Education Forum—Global Engineering Deans Council (WEEF-GEDC), Cape Town, South Africa, 28 November–1 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–5, ISBN 978-1-66547-528-0. [Google Scholar]
- De Leeuw, S.; Schippers, M.C.; Hoogervorst, S.J. The Fresh Connection. In The Handbook of Behavioral Operations Management; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 359–377. [Google Scholar]
- Shaltayev, D. Mixed-Integer Linear Programming Optimization for the Supply Chain Game. Decis. Sci. J. Innov. Educ. 2021, 19, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, M.P.; Estelle, J.; Singh, S.; Vorobeychik, Y.; Kiekintveld, C.; Soni, V. Strategic interactions in a supply chain game. Comput. Intell. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.G., Jr.; Morrice, D.J. A Simulation Game for Teaching Services-Oriented Supply Chain Management: Does Information Sharing Help Managers with Service Capacity Decisions? Prod. Oper. Manag. 2000, 9, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, M.; Koyama, Y.; Deguchi, H. Human and Agent Playing the “Beer Game”. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/410 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Oe, A.; Kawai, A. Educational Effect of a Supply Chain Management Game: Simulation Results for Supply Chain Experts. In Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems: “Societal Transformation Through IS/IT”, PACIS, Langkawi, Malaysia, 16–20 July 2017; Association for Information Systems: Atlanta, Georgia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sparling, D. Simulations and Supply Chains: Strategies for Teaching Supply Chain Management. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2002, 7, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xie, Y.; Wild, N.; Hunt, C. Learning and Practising Supply Chain Management Strategies from a Business Simulation Game: A Comprehensive Supply Chain Simulation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 40th Conference on Winter Simulation, Miami, FL, USA, 7–10 December 2008; Winter Simulation Conference: Miami, Florida, 2008; pp. 2534–2542. [Google Scholar]
- Pillay, R.; Laeequddin, M. Peer Teaching: A Pedagogic Method for Higher Education. Int. J. Innov. Technol. Explor. Eng. 2019, 9, 2907–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, K. Cash Beer Game. Found. Trends Technol. Inf. Oper. Manag. 2019, 12, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikovska, J. Developing an Integrated Approach for the Scenario-Based Management of Simulation Games. In Proceedings of the Open Conference of Electrical, Electronic and Information Sciences eStream-Proceedings, Vilnius, Lithuania, 25 April 2019; Navakauskas, D., Paulikas, S., Plonis, D., Udris, D., Eds.; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lindawati; Nugroho, E.; Fredericco, R.; Rahim, Z.B.A.; De Souza, R. ThinkLog: Interactive Learning for Supply Chain Management. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Teaching Assessment, and Learning for Engineering (TALE); Hong Kong, China, 12–14 December 2017, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, M.; Nakano, M.; Mizuyama, H.; Roser, C. Proposal of a Beer Distribution Game Considering Waste Management and the Bullwhip Effect; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2020; Volume 12434 LNCS, p. 84. ISBN 9783030618131. [Google Scholar]
- Super, J.F.; Betts, T.K.; Keller, H. Humphreys Joy Roach Simulation Game Outcomes: A Multilevel Examination of Knowledge Sharing Norms, Transactive Memory Systems, and Individual Learning Goal Orientations. Simul. Gaming 2020, 51, 830–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.K.; Tanabu, M.; Shirai, H.; Koji, K.; Managi, S. Cooperative Business Game with Framing Effect. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/375 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Delke, V.; Buchholz, W.; Schiele, H. Assessing Serious Games within Purchasing and Supply Management Education: An in-Class Experiment. In ECGBL 2021 15th European Conference on Game-Based Learning; Fotaris, P., Ed.; Dechema e.V.: Frankfurt, Germany, 2021; pp. 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Murff, E.; Teach, R.D. Partners or Competitors? A B2B Simulation. Available online: https://absel-ojs-ttu.tdl.org/absel/article/view/412 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Galli, M.; Mezzogori, D.; Reverberi, D.; Romagnoli, G.; Zammori, F. Experiencing the Role of Cooperation and Competition in Operations and Supply Chain Management with a Multiplayer Serious Game. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-85910-7_52 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Chang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Yang, Y.-N.; Chao, H.-C. A Flexible Web-Based Simulation Game for Production and Logistics Management Courses. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2009, 17, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, J.; Pillai, V.M.; Nath, H.V.; Shah, K.; Prajwal, P.G.; Manu, J.P.; Shirswar, M. Blockchain-Enabled Beer Game: A Software Tool for Familiarizing the Application of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2022, 122, 1025–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Ramirez, M.; Pacheco-Velazquez, E.; Thierry-Aguilera, R. Designing and Evaluating a Business Simulator for Sustainable Logistics Decisions. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/a84a2c67f328323598321aef4ee3eaef/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=51908 (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Gu, x.; Song, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, M. Research of the Supply Chain Inventory Manager Dynamic Simulation Training Based on HLA. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/4732094 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Merkuryev, Y.; Bikovska, J.; Merkuryeva, G. Supply Chain Dynamics: Simulation-Based Training and Education. Available online: http://www.msc-les.org/proceedings/hms/2011/HMS2011_221.pdf (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Merkuryev, Y.; Bikovska, J. Business Simulation Game Development for Education and Training in Supply Chain Management. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6243943 (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Titton, L.A. Parameterised Business Simulation Game Development for Education in Supply Chain Management and Logistics. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-319-04954-0_27 (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Stiller, S.; Falk, B.; Philipsen, R.; Brauner, P.; Schmitt, R.; Ziefle, M. A Game-Based Approach to Understand Human Factors in Supply Chains and Quality Management. Procedia CIRP 2014, 20, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hauge, J.; Duin, H.; Thoben, K.-D. Increasing the Resiliency of Global Supply Networks by Using Games. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269809342_Increasing_the_Resiliency_of_Global_Supply_Network_by_Using_Games (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Gonzalez-Feliu, J.; Chong, M.; Vargas Florez, J.; Padilla Solis, J. Handbook of Research on Urban and Humanitarian Logistics; IGI Global: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2019; ISBN 1-5225-8161-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hidayatno, A.; Zulkarnain; Hasibuan, R.G.; Wardana Nimpuno, G.C.; Destyanto, A.R. Designing a Serious Simulation Game as a Learning Media of Sustainable Supply Chain Management for Biofuel Production. In Energy Procedia; Bevrani, H., Ed.; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 156, pp. 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, V.A.C.; Rosly, M.M.; Nakano, M. A Single Player Serious Game for Sustainable Supply Chain Management. Stud. Simul. Gaming 2018, 28, 60–72. [Google Scholar]
- Salman, S.; Alaswad, S. The X-Supply Game. Available online: https://sinansalman.github.io/xsg/docs/2018IISE_XSG_Presentation.pdf (accessed on 22 November 2023).
- Ansari, Z.N.; Kant, R. Exploring the Framework Development Status for Sustainability in Supply Chain Management: A Systematic Literature Synthesis and Future Research Directions. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 873–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stindt, D. A Generic Planning Approach for Sustainable Supply Chain Management-How to Integrate Concepts and Methods to Address the Issues of Sustainability? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 153, 146–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.M.C.; Ruel, S. What Does “Sustainable Supply Chain Management” Really Mean? A Contribution to Bridging the Gap between Research, Education and Practice. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2024, 35, 332–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassaneh, T.C.; Bolisani, E.; Cegarra-Navarro, J.-G. Knowledge Management Practices for Sustainable Supply Chain Management: A Challenge for Business Education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, T. Play with Purpose-Lego Serious Play: Methods for Understanding and Researching Complex Systems Such as Supply Chains and Supply Chain Management. In Handbook of Research Methods for Supply Chain Management; Childe, S., Soares, A., Eds.; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2022; pp. 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Katsaliaki, K.; Mustafee, N.; Kumar, S. A Game-Based Approach towards Facilitating Decision Making for Perishable Products: An Example of Blood Supply Chain. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 4043–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destyanto, A.R.; Fajar, N.F.; Ardi, R. Serious Simulation Game Design to Support Extensive Understanding of Closed-Loop Supply Chain Concept in E-Waste Management Context. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Industrial and Business Engineering, Hon Kong, China, 27–29 September 2019; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kavota, J.K.; Kamdjoug, J.R.K.; Wamba, S.F. Social Media and Disaster Management: Case of the North and South Kivu Regions in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Jaller, M.; Wassenhove, L.N.V.; Pérez, N.; Wachtendorf, T. On the Unique Features of Post-Disaster Humanitarian Logistics. J. Oper. Manag. 2012, 30, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
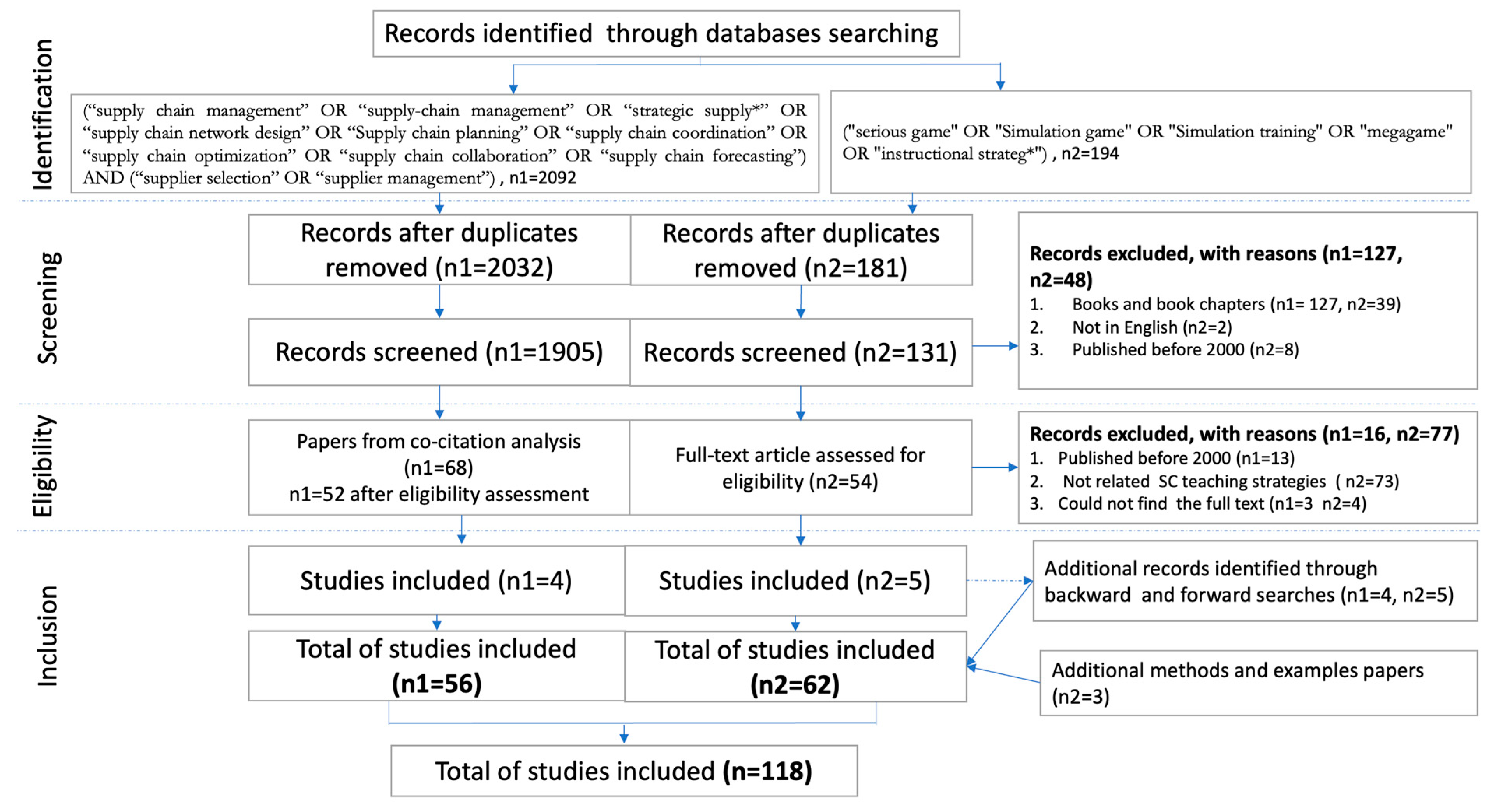
| Database | Query 1 | Number of Papers |
|---|---|---|
| ABI-Inform | NOFT ((“supply chain management” OR “supply-chain management” OR “strategic suppl*” OR “supply chain network design” OR “Supply chain planning” OR “supply chain coordination” OR “supply chain optimization” OR “supply chain collaboration” OR “supply chain forecasting”) AND (“supplier selection” OR “supplier management”)) | 358 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“supply chain management” OR “supply-chain management” OR “strategic suppl*” OR “supply chain network design” OR “supply chain planning” OR “supply chain coordination” OR “supply chain optimization” OR “supply chain collaboration” OR “supply chain forecasting”) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (“supplier selection” OR “supplier management”)) | 1734 |
| Total | 2092 |
| Database | Query 2 | Number of Papers |
|---|---|---|
| ABI-Inform | MAIN SUBJECT.EXACT (“supply chains”) AND NOFT (serious game” OR “simulation game” OR “simulation training” OR “megagame” OR “instructional strateg*”) | 12 |
| Scopus | TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“strategic supply chain” OR “collaborative supply chain” OR “supply chain management”) AND (“serious game” OR “simulation game” OR “simulation training” OR “megagame” OR “instructional strateg*”)) | 108 |
| ACM-library | [[All: “strategic supply chain”] OR [All: “collaborative supply chain”] OR [All: “supply chain management”]] AND [[All: “serious game”] OR [All: “simulation game”] OR [All: “simulation training”] OR [All: “megagame”] OR [All: “ instructional strateg*”]] | 49 |
| Business source complete | TI ((“strategic supply chain” OR “collaborative supply chain” OR “supply chain management”) AND TI (“serious game” OR “simulation game” OR “simulation training” OR “megagame” OR “instructional strateg*”)) | 3 |
| ABSL | Supply chain | 22 |
| Total | 194 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kavota, J.K.; Cassivi, L.; Léger, P.-M. A Systematic Review of Strategic Supply Chain Challenges and Teaching Strategies. Logistics 2024, 8, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010019
Kavota JK, Cassivi L, Léger P-M. A Systematic Review of Strategic Supply Chain Challenges and Teaching Strategies. Logistics. 2024; 8(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKavota, Jérémie Katembo, Luc Cassivi, and Pierre-Majorique Léger. 2024. "A Systematic Review of Strategic Supply Chain Challenges and Teaching Strategies" Logistics 8, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010019
APA StyleKavota, J. K., Cassivi, L., & Léger, P.-M. (2024). A Systematic Review of Strategic Supply Chain Challenges and Teaching Strategies. Logistics, 8(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics8010019






