Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
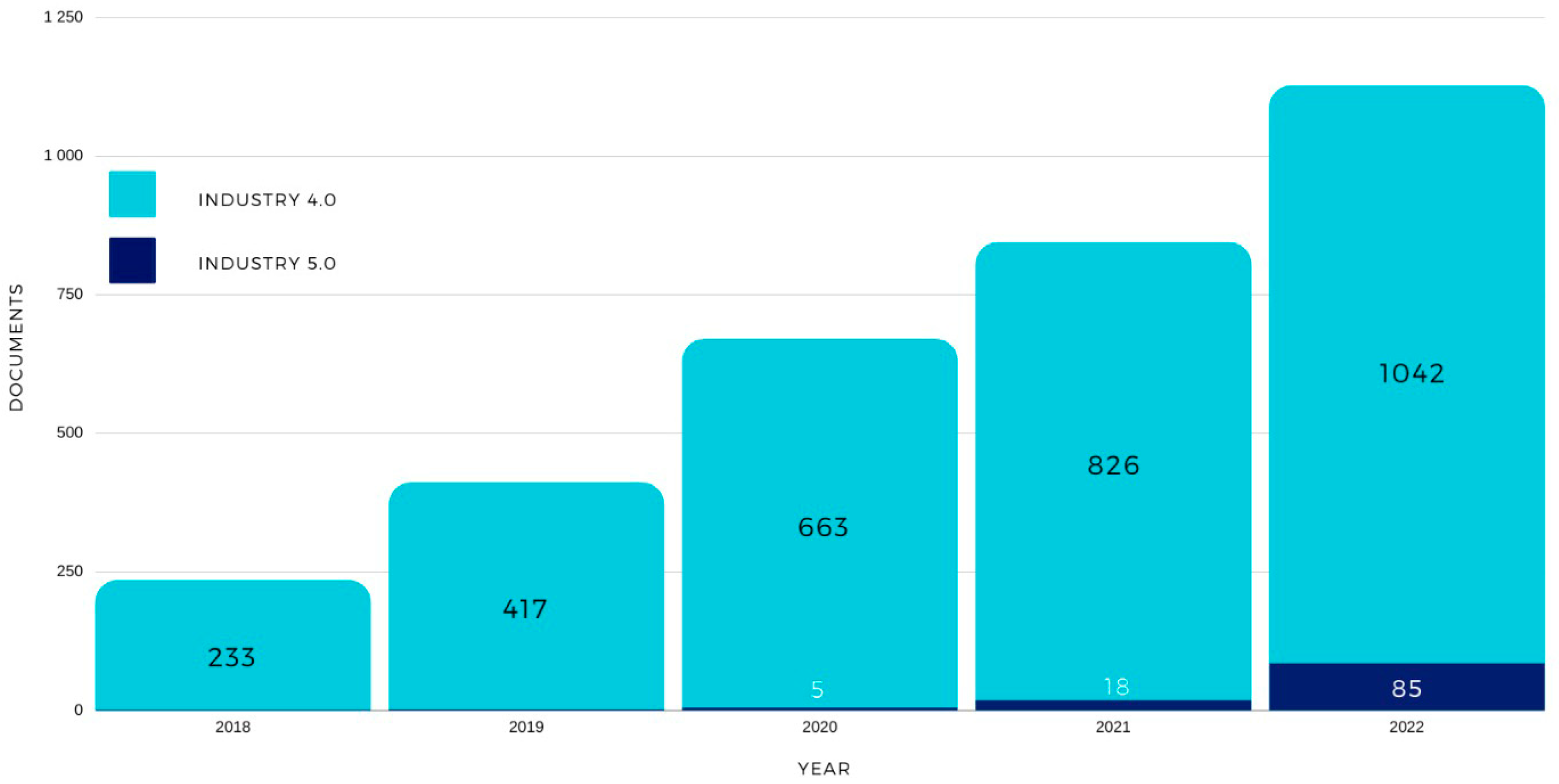
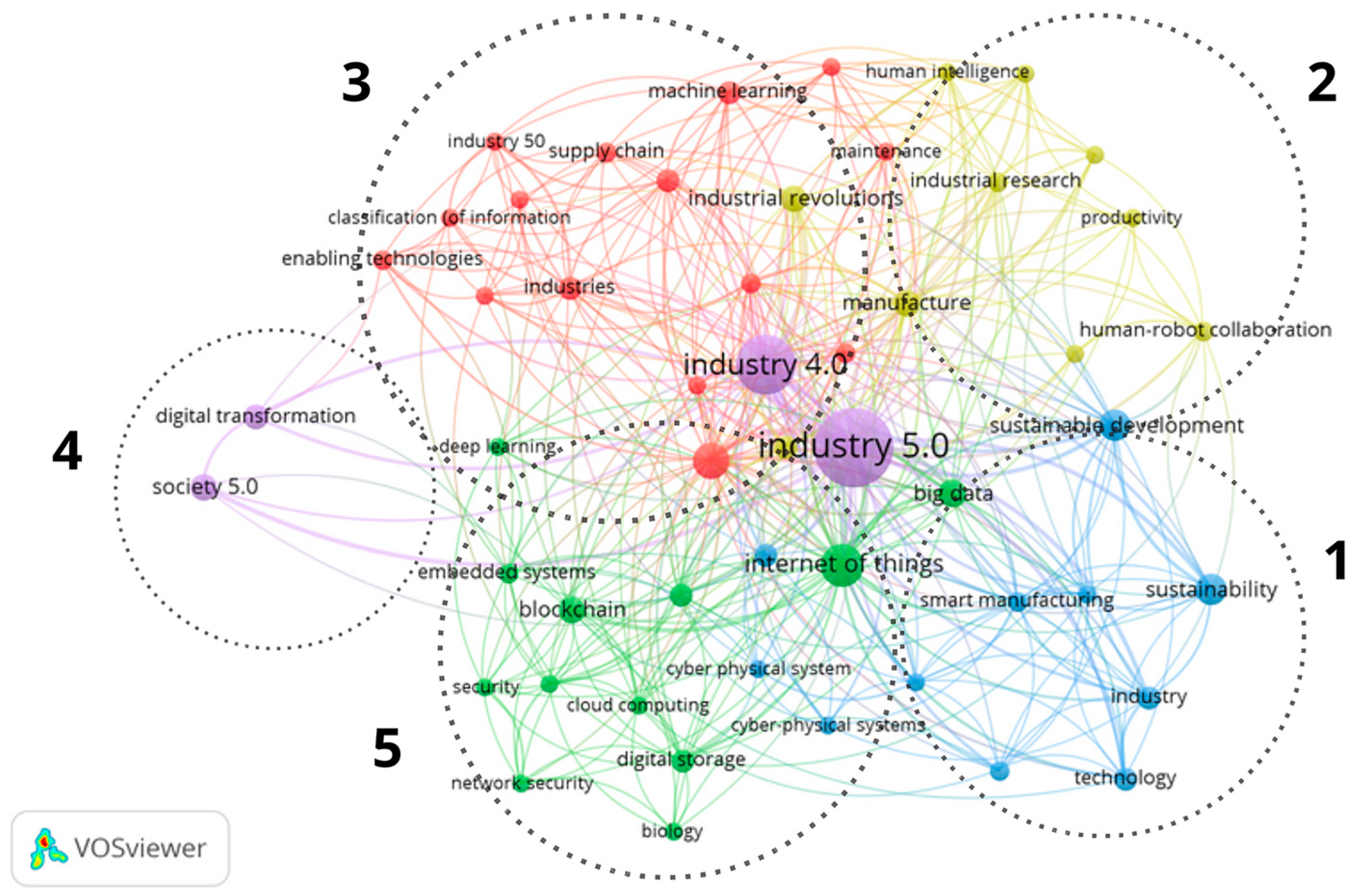
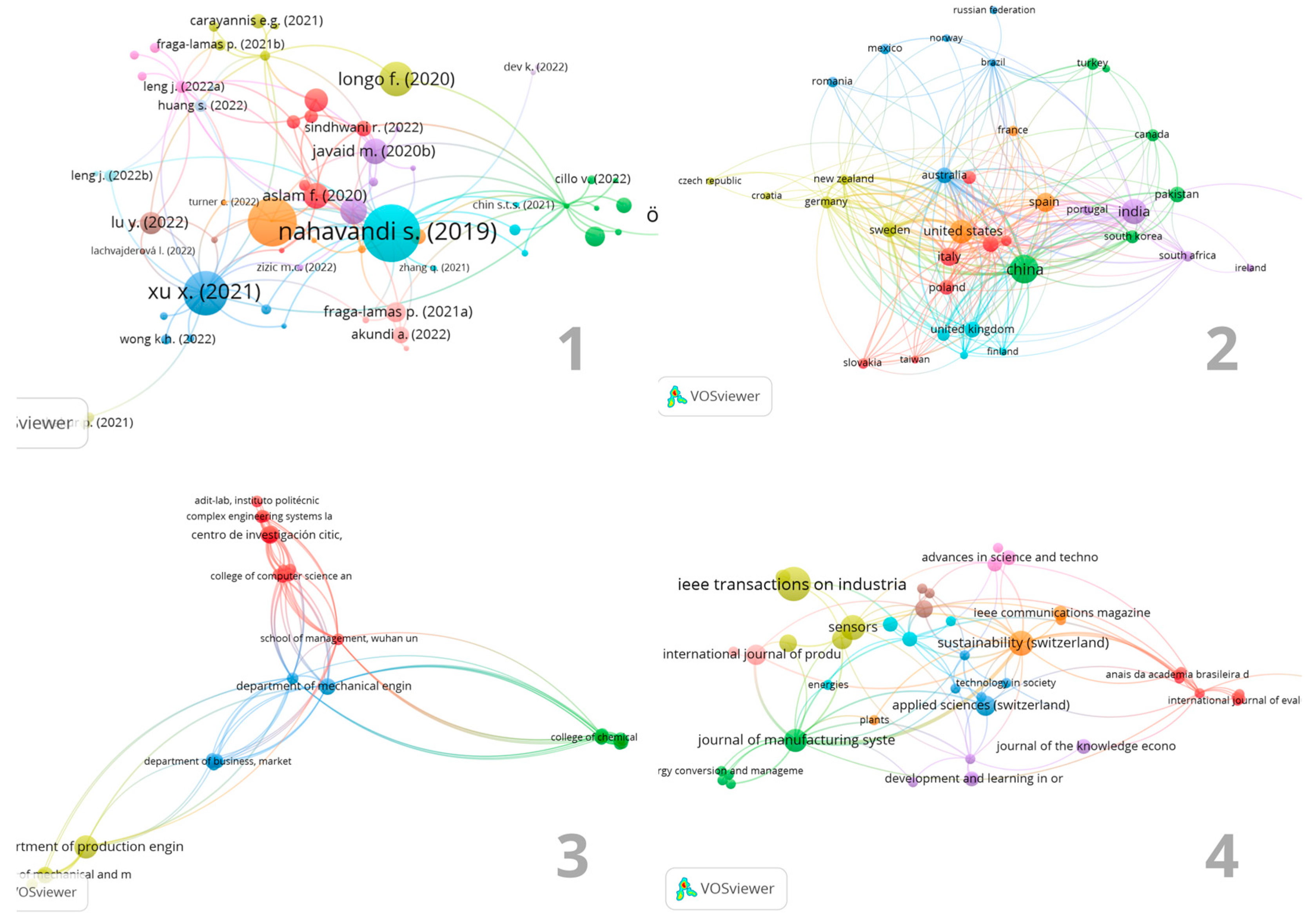
Industry 5.0 in Numbers
- (a)
- Theoretical/conceptual studies or systematic literature reviews/bibliometric analyses that aim to explain/detail/expand the discussion on Industry 5.0 and related topics (I1, I4, I8, I13, I17).
- (b)
- Studies that address the enabling technologies of Industry 5.0 (I2, I3, I6, I7, I12).
- (c)
- Studies that relate Industry 5.0 to its core values, such as sustainability (I12, I19), human-centricity (I1, I2, I3, I5, I10, I18, I20).
- (d)
- Studies that analyze the application of Industry 5.0-related technologies in specific/concrete contexts/cases (I9, I15, I16).
4. Discussion
4.1. Industry 5.0 from a Quadridimensional Perspective: Advancing through a New View of Neoindustrialization
4.2. A New Stage for the Industry: A Revolution or Just Another Number?
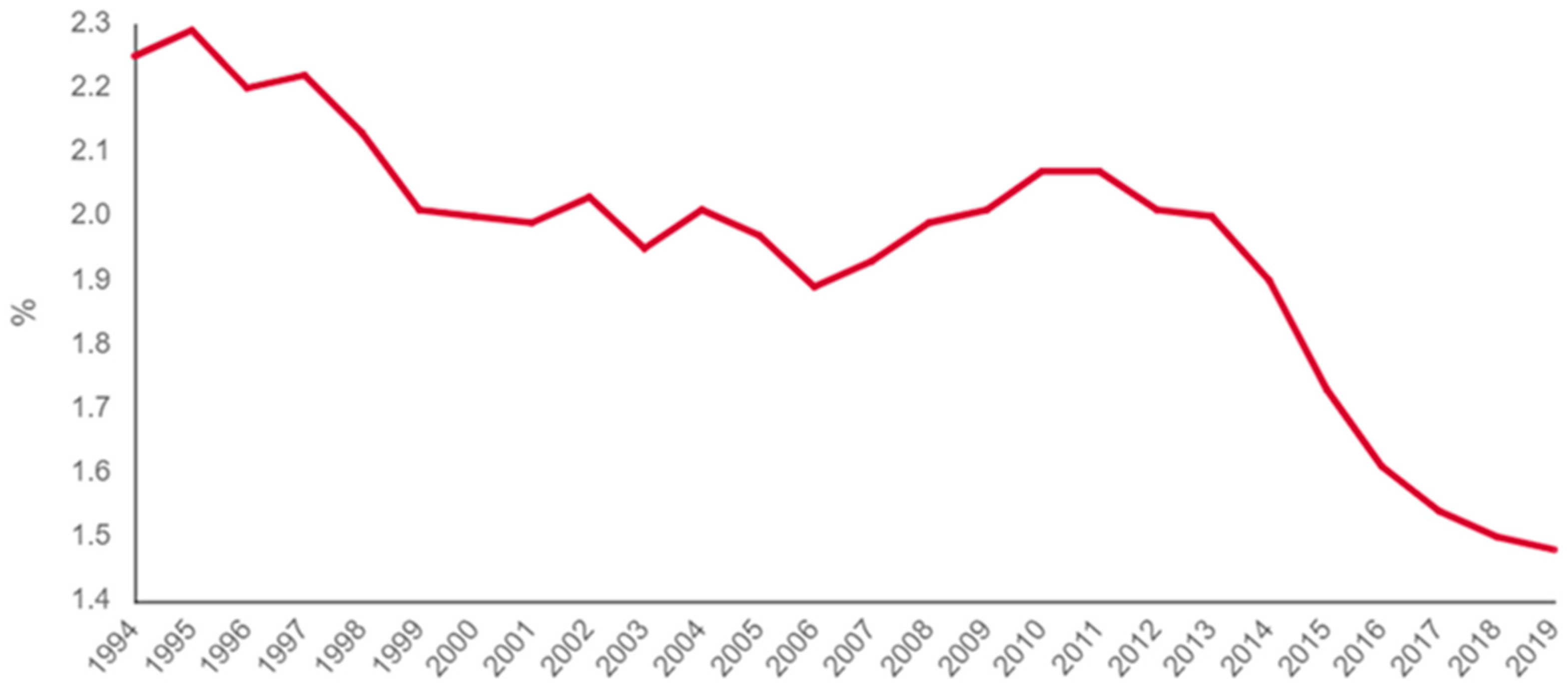
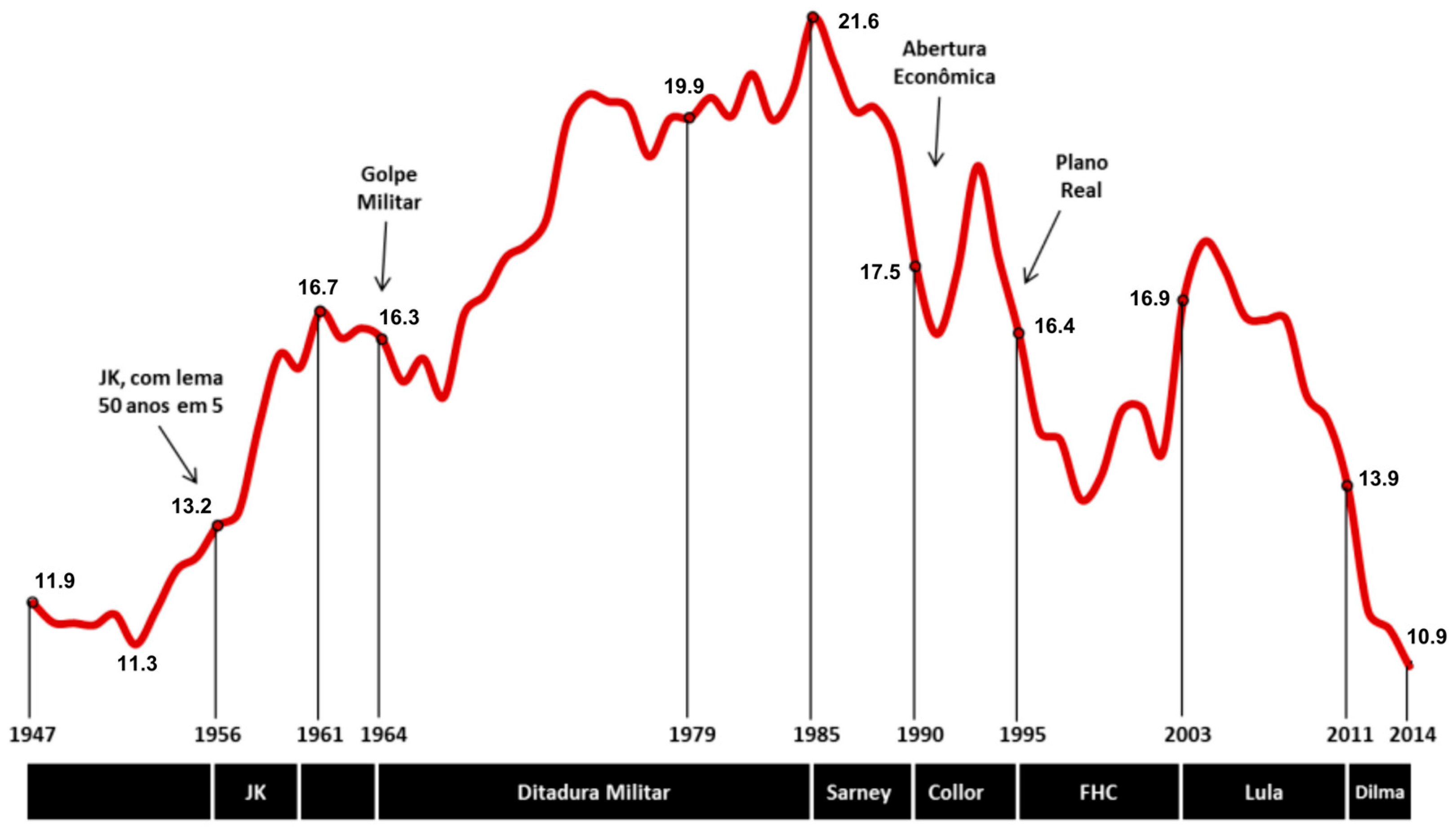
4.3. Neoindustrialization and the Resurgence of Industry’s Protagonism: The Context of the Brazilian Industry
4.4. The Enabling Technologies of Industry 5.0: From Technocentrism to Mass Personalization
4.5. The Human-Machine Relationship in the Industry: A Path to Be Explored
4.6. Study Limitations and Future Research Agenda
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sindhwani, R.; Afridi, S.; Kumar, A.; Banaitis, A.; Luthra, S.; Singh, P.L. Can industry 5.0 revolutionize the wave of resilience and social value creation? A multi-criteria framework to analyze enablers. Technol. Soc. 2022, 68, 101887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, F.; Padovano, A.; Umbrello, S. Value-oriented and ethical technology engineering in industry 5.0: A human-centric perspective for the design of the factory of the future. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, M.; Yu, H. Special Issue. Industry 5.0: The prelude to the sixth industrial revolution. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Industry 5.0: Towards a Sustainable, Human-Centric and Resilient European Industry; European Commission, Directorate-General for Research and Innovation: Luxembourg, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Lu, Y.; Vogel-Heuser, B.; Wang, L. Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0: Inception, conception and perception. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 61, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, D.; Berg, T. An Exploratory Bibliometric Analysis of the Birth and Emergence of Industry 5.0. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’brien, K. Scoping studies: Advancing the methodology. Implement. Sci. 2010, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.; Godfrey, C.; Mcinerney, P.; Munn, Z.; Tricco, A.; Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping Reviews (2020 version). In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; Mcarthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrard, J. Health Sciences Literature Review Made Easy: The Matrix Method, 3rd ed.; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Sudbury, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahavandi, S. Industry 5.0—A Human-Centric Solution. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Pham, Q.-V.; Prabadevi, B.; Deepa, N.; Dev, K.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Liyanage, M. Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 26, 100257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, V.; Hekim, N. Birth of industry 5.0: Making sense of big data with artificial intelligence. The Internet of things and next-generation technology policy. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2018, 22, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A.; Singh, R.P.; Haq, M.I.U.; Raina, A.; Suman, R. Industry 5.0: Potential applications in COVID-19. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2020, 5, 507–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, F.; Aimin, W.; Li, M.; Rehman, K.U. Innovation in the Era of IoT and Industry 5.0: Absolute Innovation Management (AIM) Framework. Information 2020, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A. Critical components of Industry 5.0 towards a successful adoption in the field of manufacturing. J. Ind. Integr. Manag. 2020, 5, 327–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElFar, O.A.; Chang, C.K.; Leong, H.Y.; Peter, A.P.; Chew, K.W.; Show, P.L. Prospects of Industry 5.0 in algae: Customization of production and new advance technology for clean bioenergy generation. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 10, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Chand, S.; Xia, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, X.; Bao, J. Outlook on human-centric manufacturing towards Industry 5.0. J. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 62, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broo, D.G.; Kaynak, O.; Sait, S.M. Rethinking engineering education at the age of industry 5.0. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2022, 25, 100311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Lopes, S.I.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. Green IoT and Edge AI as Key Technological Enablers for a Sustainable Digital Transition towards a Smart Circular Economy: An Industry 5.0 Use Case. Sensors 2021, 21, 5745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akundi, A.; Euresti, D.; Luna, S.; Ankobiah, W.; Lopes, A.; Edinbarough, I. State of Industry 5.0—Analysis and Identification of Current Research Trends. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2022, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Morawska-Jancelewicz, J. The Futures of Europe: Society 5.0 and Industry 5.0 as Driving Forces of Future Universities. J. Knowl. Econ. 2022, 13, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carayannis, E.G.; Draper, J.; Bhaneja, B. Towards Fusion Energy in the Industry 5.0 and Society 5.0 Context: Call for a Global Commission for Urgent Action on Fusion Energy. J. Knowl. Econ. 2021, 12, 1891–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.U.; Ihsan, A.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ali, Z.; Javed, M.A. NOMA-enabled backscatter communications for green transportation in automotive-industry 5.0. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7862–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Yu, Y. An adoption-implementation framework of digital green knowledge to improve the performance of digital green innovation practices for industry 5.0. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniuk, S.; Grabowska, S.; Straka, M. Identification of Social and Economic Expectations: Contextual Reasons for the Transformation Process of Industry 4.0 into the Industry 5.0 Concept. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupic, I.; Čater, T. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organ. Res. Methods 2015, 18, 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.M.; Kiel, D.; Voigt, K.-I. What Drives the Implementation of Industry 4.0? The Role of Opportunities and Challenges in the Context of Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Adrados, J.S.; Chand, S.S.; Wang, L. Humans are not machines—Anthropocentric human–machine symbiosis for ultra-flexible smart manufacturing. Engineering 2021, 7, 734–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschek, D.; Mocan, A.; Draghici, A. Industry 5.0—The expected impact of next industrial revolution. In Proceedings of the Make Learn and TIIM International Conference, Piran, Slovenia, 15–17 May 2019; Thriving on Future Education, Industry, Business and Society. Dermol, V., Ed.; ToKnowPress: Piran, Slovenia, 2019; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Demir, K.A.; Döven, G.; Sezen, B. Industry 5.0 and human-robot Co-working. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2019, 158, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welfare, K.S.; Hallowell, M.R.; Shah, J.A.; Riek, L.D. Consider the Human Work Experience When Integrating Robotics in the Workplace. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction (HRI), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 11–14 March 2019; pp. 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelles, J.; Kuz, S.; Mertens, A.; Schlick, C.M. Human-centered design of assistance systems for production planning and control: The role of the human in Industry 4.0. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Taipei, Taiwan, 14–17 March 2016; pp. 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhardt, D.; Haeusler, M.H.; London, K.; Loke, L.; Feng, Y.; De Oliveira Barata, E.; Firth, C.; Dunn, K.; Khean, N.; Fabbri, A.; et al. CoBuilt 4.0: Investigating the potential of collaborative robotics for subject matter experts. Int. J. Archit. Comput. 2020, 18, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Xu, X.; Klotz, E.; Newman, S. Intelligent Manufacturing in the Context of Industry 4.0: A Review. Engineering 2017, 3, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, S.A. Um modelo evolucionário de busca tecnológica em condições de hipercumulatividade. Rev. Bras. Econ. 2005, 59, 335–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://industriabrasileira.portaldaindustria.com.br/grafico/transformacao/mundo/#/industria-total (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- Departamento de Pesquisas e Estudos Econômicos. Panorama da Indústria Brasileira. FIESP. 2017. Available online: http://www.fiesp.com.br/arquivo-download/?id=236253 (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- Bacha, E. O Futuro da indústria no Brasil: Desindustrialização em Debate; Editora José Olympio: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Federação das Indústrias do Rio de Janeiro—FIRJAN. Panorama da Inovação—Indústria 4.0; FIRJAN: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Firmino, A.S.; Perles, G.X.; Mendes, J.V.; Silva, J.E.A.R.D.; Silva, D.A.L. Towards Industry 4.0: A SWOT-based analysis for companies located in the Sorocaba Metropolitan Region (São Paulo State, Brazil). Gestão Produção 2020, 27, e5622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confederação Nacional de Indústria—C.N.I. Desafios para Indústria 4.0 no Brasil; CNI: Brasília, Brazil, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nardo, M.; Forino, D.; Murino, T. The evolution of man–machine interaction: The role of human in Industry 4.0 paradigm. Prod. Manuf. Res. 2020, 8, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizón, J.; Gola, A. Human–Machine Relationship—Perspective and Future Roadmap for Industry 5.0 Solutions. Machines 2023, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, A. Future of industry 5.0 in society: Human-centric solutions, challenges and prospective research areas. J. Cloud. Comp. 2022, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.; Azarian, M.; Yu, H. Moving from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0: What Are the Implications for Smart Logistics? Logistics 2022, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalba-Diez, J.; Ordieres-Meré, J. Human–Machine Integration in Processes within Industry 4.0 Management. Sensors 2021, 21, 5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Lima, T.M.; Gaspar, P.D. Is Industry 5.0 a Human-Centred Approach? A Systematic Review. Processes 2023, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Id | Year | Author | Title/Source | Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | 2019 | Nahavandi, S. [13] | Industry 5.0-a human-centric solution | 491 |
| I2 | 2022 | Maddikunta, P.K.R., Pham, Q.-V., B, P., (…), Ruby, R., Liyanage, M. [14] | Industry 5.0: A survey on enabling technologies and potential applications | 347 |
| I3 | 2018 | Özdemir, V., Hekim, N. [15] | Birth of Industry 5.0: Making Sense of Big Data with Artificial Intelligence, “the Internet of Things” and Next-Generation Technology Policy | 326 |
| I4 | 2021 | Xu, X., Lu, Y., Vogel-Heuser, B., Wang, L. [5] | Industry 4.0 and Industry 5.0—Inception, conception and perception | 292 |
| I5 | 2020 | Longo, F., Padovano, A., Umbrello, S.. [2] | Value-oriented and ethical technology engineering in industry 5.0: A human-centric perspective for the design of the factory of the future | 181 |
| I6 | 2020 | Javaid, M., Haleem, A., Singh, R.P., (…), Raina, A., Suman, R. [16] | Industry 5.0: Potential applications in COVID-19 | 119 |
| I7 | 2020 | Aslam, F., Aimin, W., Li, M., Rehman, K.U. [17] | Innovation in the era of IoT and industry 5.0: Absolute innovation management (AIM) framework | 106 |
| I8 | 2020 | Javaid, M., Haleem, A. [18] | Critical components of industry 5.0 towards a successful adoption in the field of manufacturing | 103 |
| I9 | 2021 | ElFar, O.A., Chang, C.-K., Leong, H.Y., (…), Chew, K.W., Show, P.L. [19] | Prospects of Industry 5.0 in algae: Customization of production and new advance technology for clean bioenergy generation | 89 |
| I10 | 2022 | Lu, YQ; Zheng, H; (…); Bao, JS [20] | Outlook on human-centric manufacturing towards Industry 5.0 | 64 |
| I11 | 2022 | Gürdür Broo, D., Kaynak, O., Sait, S.M. [21] | Rethinking engineering education at the age of industry 5.0 | 58 |
| I12 | 2021 | Fraga-Lamas, P., Lopes, S.I., Fernández-Caramés, T.M. [22] | Green iot and edge AI as key technological enablers for a sustainable digital transition towards a smart circular economy: An industry 5.0 use case | 57 |
| I13 | 2022 | Akundi, A., Euresti, D., Luna, S., (…), Lopes, A., Edinbarough, I. [23] | State of Industry 5.0—Analysis and Identification of Current Research Trend | 46 |
| I14 | 2022 | Carayannis, E.G., Morawska-Jancelewicz, J. [24] | The Futures of Europe: Society 5.0 and Industry 5.0 as Driving Forces of Future Universities | 42 |
| I15 | 2021 | Carayannis, E.G., Draper, J., Bhaneja, B. [25] | Towards Fusion Energy in the Industry 5.0 and Society 5.0 Context: Call for a Global Commission for Urgent Action on Fusion Energy | 40 |
| I16 | 2022 | Khan, W.U., Ihsan, A., Nguyen, T.N., Ali, Z., Javed, M.A. [26] | NOMA-Enabled Backscatter Communications for Green Transportation in Automotive-Industry 5.0 | 38 |
| I17 | 2021 | Madsen, D.Ø., Berg, T. [6] | An exploratory bibliometric analysis of the birth and emergence of industry 5.0 | 35 |
| I18 | 2022 | Sindhwani, R., Afridi, S., Kumar, A., (…), Luthra, S., Singh, P.L. [1] | Can industry 5.0 revolutionize the wave of resilience and social value creation? A multi-criteria framework to analyze enablers | 34 |
| I19 | 2022 | Yin, S., Yu, Y. [27] | An adoption-implementation framework of digital green knowledge to improve the performance of digital green innovation practices for industry 5.0 | 31 |
| I20 | 2022 | Saniuk, S., Grabowska, S., Straka, M [28] | Identification of Social and Economic Expectations: Contextual Reasons for the Transformation Process of Industry 4.0 into the Industry 5.0 Concept | 30 |
| Critical Success Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Technological Infrastructure |
|
| Qualified Human Capital |
|
| Innovation and Technological Development |
|
| Favorable Business Environment |
|
| Sustainability and Social Responsibility |
|
| Technologies | Definition |
|---|---|
| Edge Computing | Edge Computing (EC) is a data processing approach at the network edge that offers benefits such as low latency, increased energy efficiency, and enhanced security. Industries can access local data and minimize the volume sent to centralized servers, enabling proactive analytics and smarter decision-making. |
| Digital Twins | Digital Twins (DT) are digital replicas that enable mass customization, and the seamless flow of data between the physical, digital, and cyber space is necessary for their application. In Industry 5.0, DT enables analysis, monitoring, and prevention of issues before they occur in the real world, offering significant value for the development of personalized products and innovative business models. With IoT and advancements in AI, ML, and big data analytics, DT reduces maintenance costs, improves system performance, and helps prevent major financial losses. |
| Collaborative Robots | Cobots are robots designed to work alongside humans, providing increased efficiency and safety in the work environment. They have the ability to detect unforeseen impacts and immediately stop when they detect objects in their path. While efficient in large-scale production, managing human connections remains important in tasks that require critical thinking and customization. |
| Internet of Everything | Internet of Everything (IoE) connects people, processes, information, and objects, offering benefits for Industry 5.0 such as enhancing customer experience and reducing operational costs. IoE can optimize the supply chain, reduce waste, and improve production processes. Wireless technology and sensors are used for information exchange, such as in the Internet of Medical Things. |
| Big Data | Big Data is a technology that stores large amounts of complex data using IoT devices and provides significant services to manufacturers and service providers. Big Data Analytics enables the analysis of large volumes of data, allowing for mass customization and a better understanding of consumer behavior in Industry 5.0. With the integration of Big Data and IoT, real-time information can be collected to optimize production, reduce costs, and make more informed decisions. |
| Blockchain | Blockchain is a secure and decentralized technology that protects customer data against deletion, tampering, and revision, making it suitable for handling data privacy and traceability. It can be used to create distributed management platforms, providing transparency and immutability for significant event records in Industry 5.0. Additionally, it enables the execution of smart contracts to enforce security measures and automate processes. |
| 6G | The 6G technology can offer valuable services for Industry 5.0, with dense infrastructure, reduced latency, and integrated AI capabilities. 6G networks can enhance the performance of Industry 5.0 applications, but energy efficiency needs to be ensured. Quantum and free-space optical communication can help address high data rate challenges. |
| Artificial Intelligence | Artificial intelligence provides human-like capabilities to perform tasks in the manufacturing field, enabling the solution of complex problems in a faster and more cost-effective manner. Additionally, AI is capable of understanding the functioning of the human brain and efficiently executing high-level tasks, enhancing the thinking process and directing the system towards powerful and predictive intelligence. |
| Benefits/Advantages/Opportunities | Challenges/Threats |
|---|---|
| Human well-being | Lack of skills and training |
| Manufacturing flexibility | Resistance to change |
| Development of human and machine capabilities | Privacy and security concerns |
| Increased efficiency and productivity | Accountability in case of failures |
| Improved product quality | High cost |
| Improved workplace safety | Excessive dependence |
| Higher worker satisfaction | |
| Cost reduction | |
| Improved decision-making |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pereira, R.; dos Santos, N. Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0. Logistics 2023, 7, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7030043
Pereira R, dos Santos N. Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0. Logistics. 2023; 7(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7030043
Chicago/Turabian StylePereira, Ricardo, and Neri dos Santos. 2023. "Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0" Logistics 7, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7030043
APA StylePereira, R., & dos Santos, N. (2023). Neoindustrialization—Reflections on a New Paradigmatic Approach for the Industry: A Scoping Review on Industry 5.0. Logistics, 7(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/logistics7030043











