Effect of Addition Amount on Rheological, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Whole-Grain Sweet Potato Noodles Using Extrusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Determination of Amylose Content in WSPF and WF
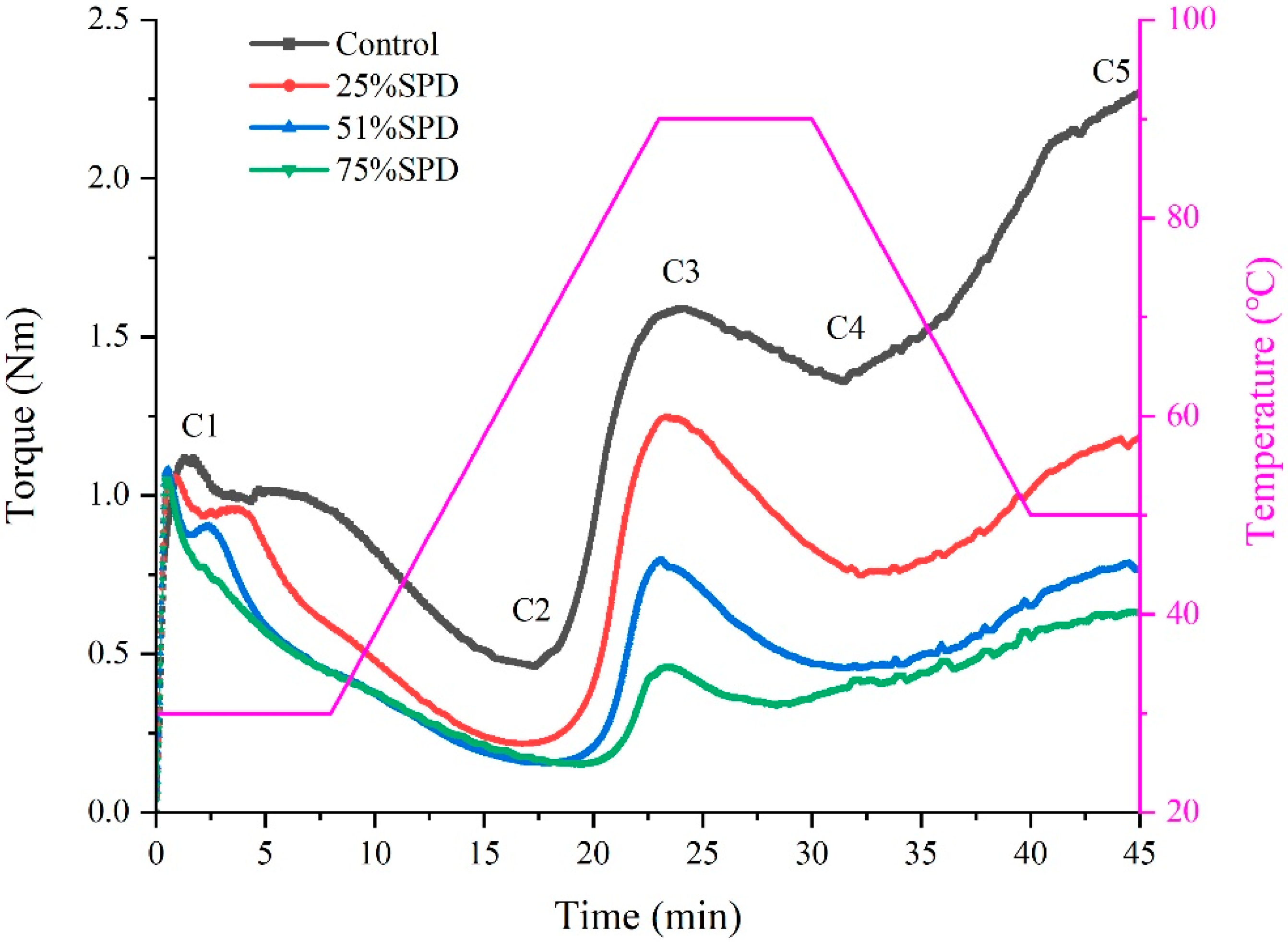
2.3. Mixolab Measurement of SPDs
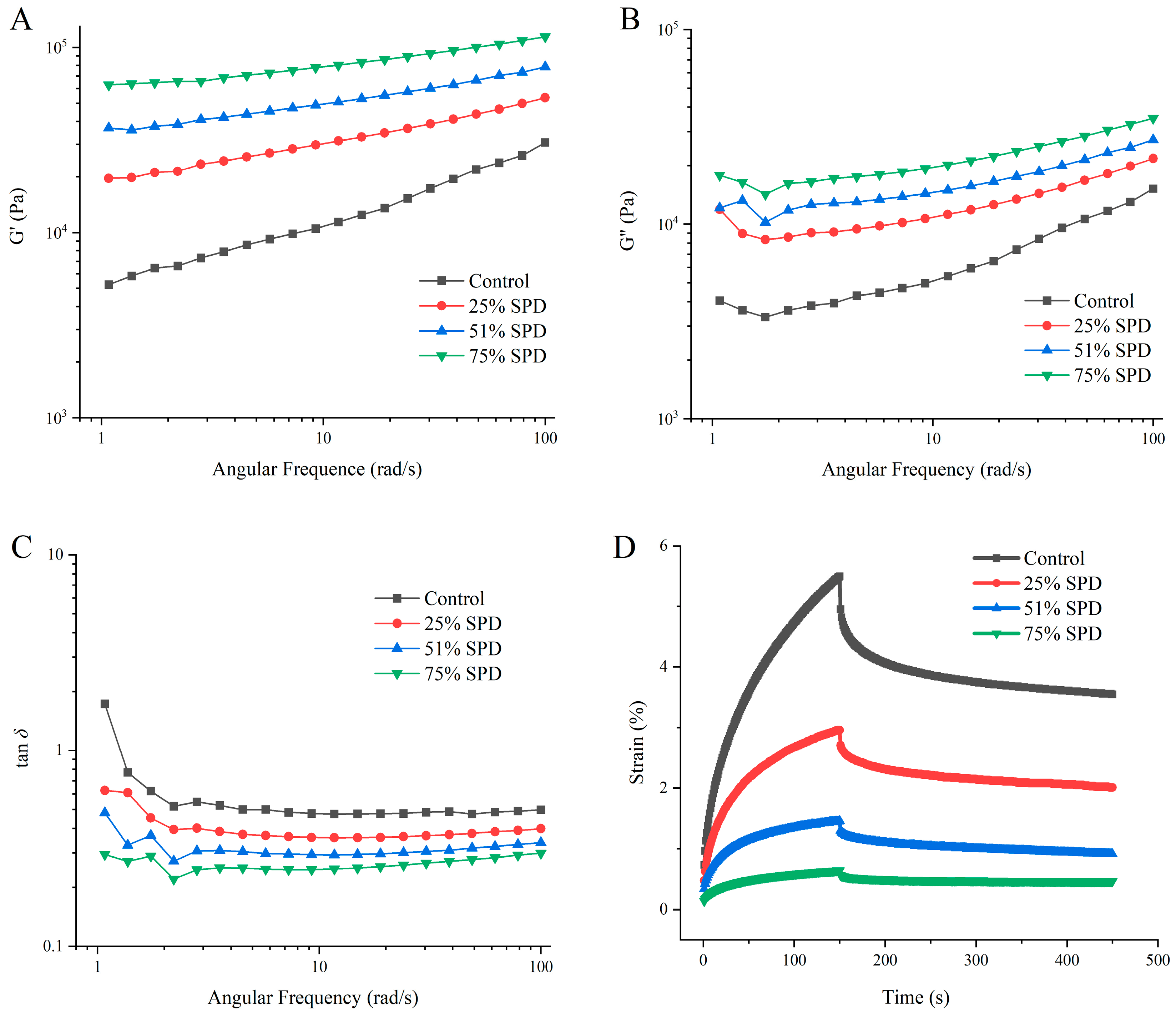
2.4. Rheological Measurements of SPDs
2.4.1. Dynamic Frequency Sweep Test
2.4.2. Creep Recovery Scanning Test
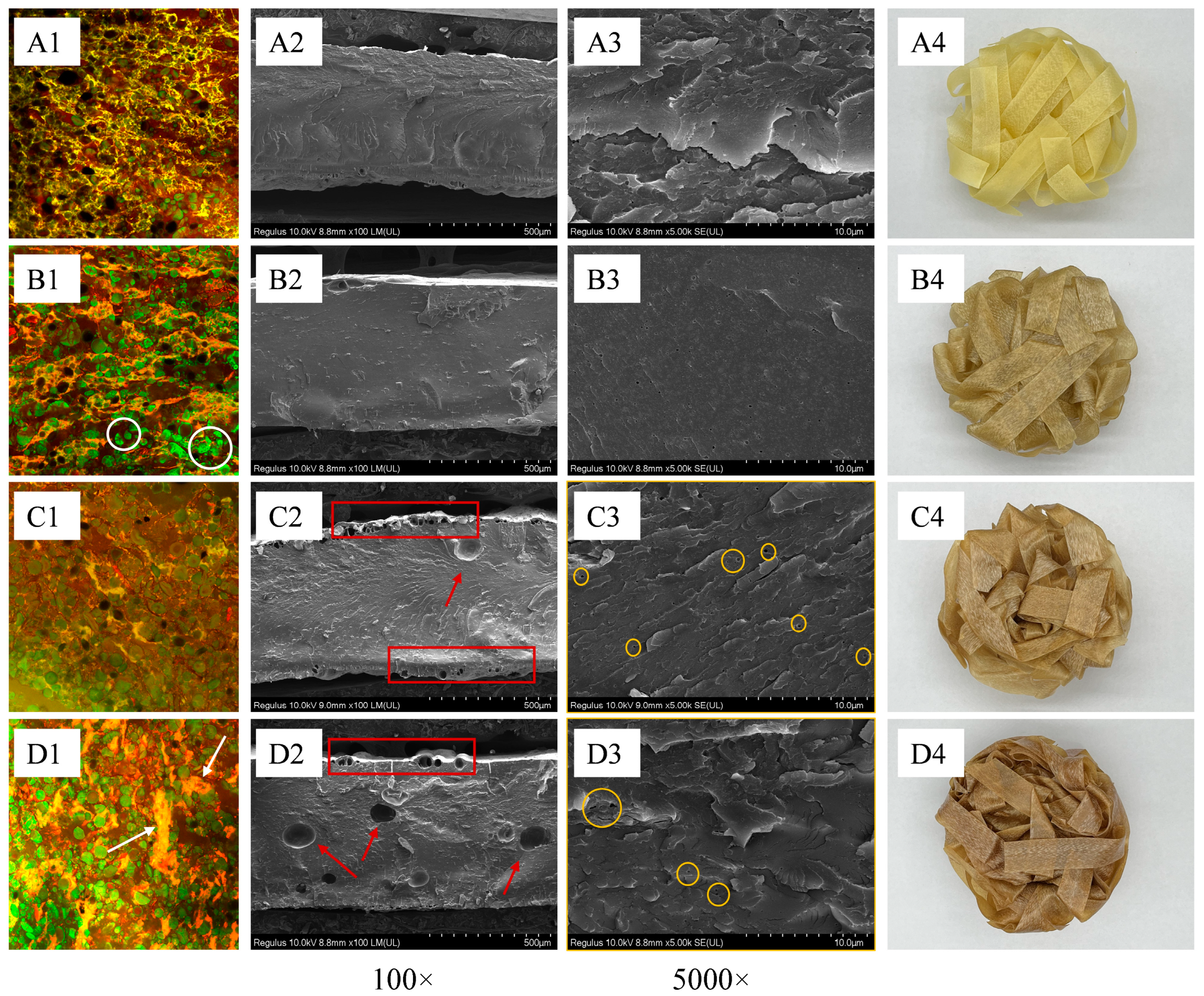
2.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM) of SPDs
2.6. Preparation of ESPNs
2.7. Determination of Cooking Characteristics of ESPNs
2.8. Determination of Expansion Capacity of ESPNs
2.9. Texture Properties of Cooked ESPNs
2.10. Sensory Evaluation ESPNs
2.11. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) of ESPNs
2.12. Thermal Properties of ESPNs
2.13. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) of ESPNs
2.14. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of ESPNs
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Starch Content of WSPF and WF
3.2. The Mixing Behavioral Characteristics Analysis of Doughs
3.3. Rheological Properties Analysis of Doughs
3.4. CLSM Analysis of Doughs
3.5. Cooking Characteristics of Noodles
3.6. Expansion Capacity of ESPNs
3.7. Texture Properties of Noodles
3.8. Sensory Analysis
3.9. Microstructure of Different Noodles
3.10. Thermal Properties of Noodles
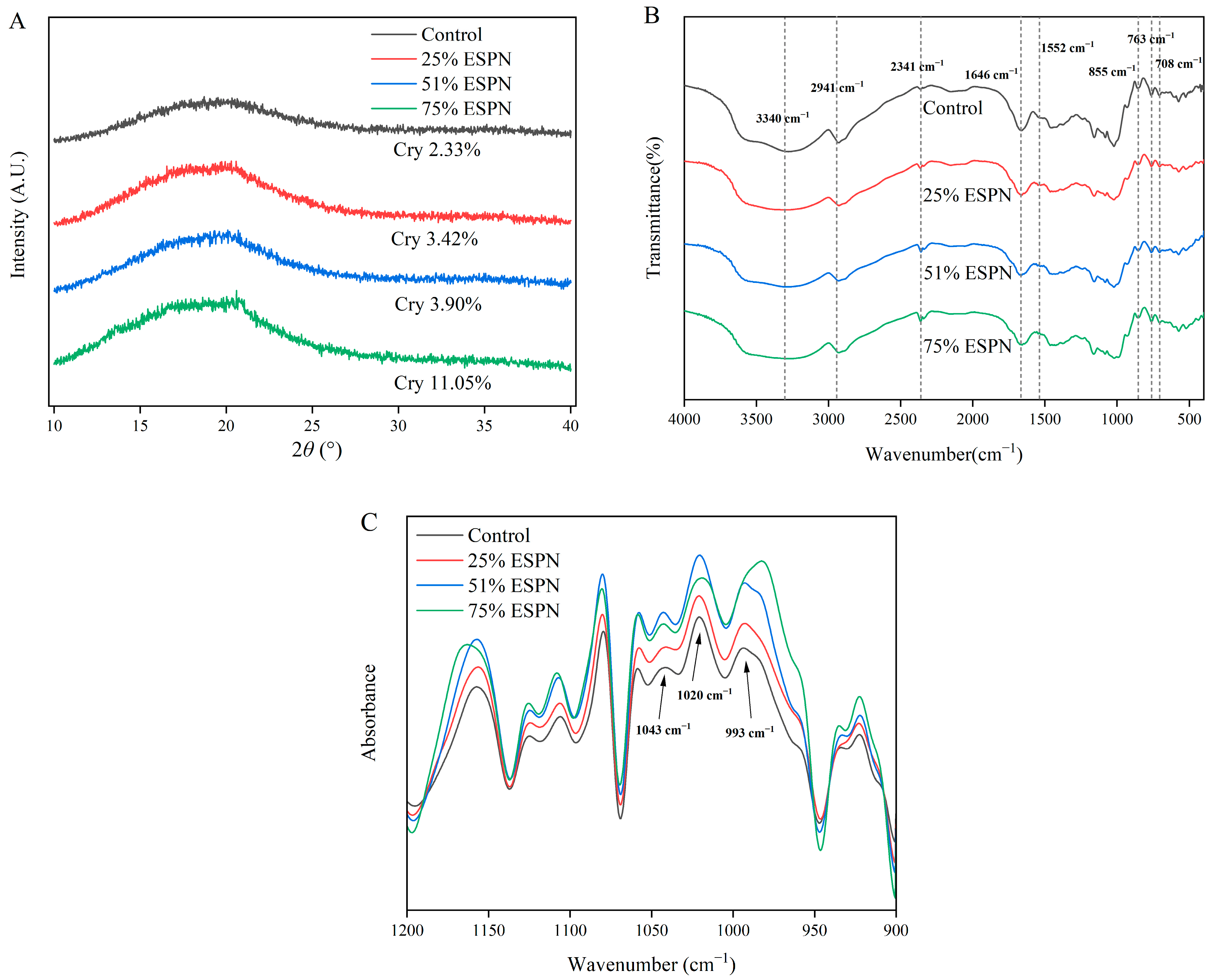
3.11. XRD Analysis of Noodles
3.12. Analysis of FTIR Experiment Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Y.; Naumovski, N.; Ranadheera, C.S.; D’Cunha, N.M. Nutrition-Related Health Outcomes of Sweet Potato (Ipomoea batatas) Consumption: A Systematic Review. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Bourke, P.; Frias, J.M.; Tiwari, B.K.; Cullen, P.J. Inactivation of Escherichia coli in Orange Juice Using Ozone. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Tobias, D.K.; Malik, V.S.; Pan, A.; Hruby, A.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Glycemic Index, Glycemic Load, and Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Results from 3 Large US Cohorts and an Updated Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 218–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L. Influences of Particle Size and Addition Level on the Rheological Properties and Water Mobility of Purple Sweet Potato Dough. Foods 2023, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, C.; Fu, M.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.; Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Shen, X.; Tang, X. Extruded Whole Buckwheat Noodles: Effects of Processing Variables on the Degree of Starch Gelatinization, Changes of Nutritional Components, Cooking Characteristics and in Vitro Starch Digestibility. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6362–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Blecker, C. Prediction of the Rheological Properties of Wheat Dough by Starch-gluten Model Dough Systems: Effect of Gluten Fraction and Starch Variety. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2022, 57, 2126–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kamp, J.-W.; Jones, J.M.; Miller, K.B.; Ross, A.B.; Seal, C.J.; Tan, B.; Beck, E.J. Consensus, Global Definitions of Whole Grain as a Food Ingredient and of Whole-Grain Foods Presented on Behalf of the Whole Grain Initiative. Nutrients 2022, 14, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T/CNSS 008-2021; General Rules for Identification and Labeling of Whole Grain and Whole Grain Food [Group standards]. Chinese Nutrition Association: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Z. Changes in Cooking Characteristics, Structural Properties and Bioactive Components of Wheat Flour Noodles Partially Substituted with Whole-Grain Hulled Tartary Buckwheat Flour. Foods 2024, 13, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, M.; Califano, A.; Lorenzo, G. Influence of Quinoa and Zein Content on the Structural, Rheological, and Textural Properties of Gluten-Free Pasta. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Xiong, X. Effect of Extrusion Feeding Moisture on Dough, Nutritional, and Texture Properties of Noodles Fortified with Extruded Buckwheat Flour. J. Food Process Preserv. 2020, 44, e14978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T 3611-2020; Sweet Potato Powder [Industry standard]. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Ma, Y.; Hong, T.; Xu, D.; Wu, F.; Xu, X. Inhibition of PPO-Related Browning in Fresh Noodles: A Combination of Chemical and Heat Treatment. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Pei, F.; Fang, Y. The Effects of Hydrocolloids on the Thermomechanical, Viscoelastic and Microstructural Properties of Whole Wheat Flour Dough. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Ma, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, X.; Xu, B.; Hu, X. Effect of Sheeting Thickness on the Processing Quality of Wheat-Oat Blended Flour Noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 99, 103223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Li, Z.; Tang, N.; Li, H.; Suo, B.; Fan, H.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.; Ai, Z. Effects of Yeast Fermentation on the Quality Characteristics and in Vitro Starch Digestibility of Fried-Free Instant Noodles with Rapid Rehydration. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 191, 115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraithong, S.; Rawdkuen, S. Effects of Food Hydrocolloids on Quality Attributes of Extruded Red Jasmine Rice Noodle. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Li, M.; Dhital, S.; Tian, Y.; Guo, B. Texture and Digestion of Noodles with Varied Gluten Contents and Cooking Time: The View from Protein Matrix and Inner Structure. Food Chem. 2020, 315, 126230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, C.; Gu, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hong, Y.; Li, Z. Retrogradation Behavior of Corn Starch Treated with 1,4-α-Glucan Branching Enzyme. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, L.; Xu, P.; Deng, X.; Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y. Study on the Quality Characteristics of Hot-Dry Noodles by Microbial Polysaccharides. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-Y.; Guo, X.-N.; Xing, J.-J.; Zhu, K.-X. Effect of Thermal Treatments on in Vitro Starch Digestibility of Sorghum Dried Noodles. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3420–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dhital, S.; Shan, C.-S.; Zhang, M.-N.; Chen, Z.-G. Ordered Structural Changes of Retrograded Starch Gel over Long-Term Storage in Wet Starch Noodles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 270, 118367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksel, H.; Kahraman, K.; Sanal, T.; Ozay, D.S.; Dubat, A. Potential Utilization of Mixolab for Quality Evaluation of Bread Wheat Genotypes. Cereal Chem. 2009, 86, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Mu, T.; Sun, H. Comparative Study of the Effect of Starches from Five Different Sources on the Rheological Properties of Gluten-Free Model Doughs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacón-Vera, E.F.; Bernal-Bailón, I.I.; Dueñas-Rivadeneira, A.A.; Cobeña-Ruíz, G.A.; López-Bello, N. Rheology of Potato flour Mixes and Wheat to Make Bread. Tecnol. Química 2016, 36, 384–394. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridou, A.; Marinopoulou, A.; Biliaderis, C.G. Impact of Flour Particle Size and Hydrothermal Treatment on Dough Rheology and Quality of Barley Rusks. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, M.; De Lamo, B.; Harasym, J.; Ronda, F. Microwave Radiation and Protein Addition Modulate Hydration, Pasting and Gel Rheological Characteristics of Rice and Potato Starches. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zha, X.-Q.; Li, Q.-M.; Pan, L.-H.; Luo, J.-P. Hydrophobic Interaction and Hydrogen Bonding Driving the Self-Assembling of Quinoa Protein and Flavonoids. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Pagani, M.A.; Lucisano, M. The Role of Buckwheat and HPMC on the Breadmaking Properties of Some Commercial Gluten-Free Bread Mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerts, M.; Cardinaels, R.; Oosterlinck, F.; Courtin, C.M.; Moldenaers, P. The Interplay Between the Main Flour Constituents in the Rheological Behaviour of Wheat Flour Dough. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2017, 10, 249–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.-B.; Yu, C.; Yang, Z.; Xing, J.-J.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. Impact of Gluten Quality on Textural Stability of Cooked Noodles and the Underlying Mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, M.; Mu, T.; Sun, H. Influence of Sweet Potato Flour on the Microstructure and Nutritional Quality of Gluten-Free Fresh Noodles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 3938–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia, N.; Dhaka, V.; Khatkar, B.S. Instant Noodles: Processing, Quality, and Nutritional Aspects. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Jin, L.; Xu, X.-H.; Shan, C.-S.; Chen, Z.-G. Long-Term Storage and Temperature Induced Quality Changes of Industrial-Scale Wet Starch Noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 153, 112504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, E.; Tuncel, N.Y.; Tuncel, N.B. Utilization of Lentil, Pea, and Faba Bean Hulls in Turkish Noodle Production. J. Food Sci. Technol.-Mysore 2018, 55, 1734–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Sun, X.; Wu, D.; Meng, L.; Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Shen, X.; Tang, X. Effect of Partial Substitution of Buckwheat on Cooking Characteristics, Nutritional Composition, and in Vitro Starch Digestibility of Extruded Gluten-Free Rice Noodles. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 126, 109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Wang, J.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, W.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. Investigating Changes in the Physicochemical and Structural–Functional Properties of Soybean Milk Under an Industry-Scale Microfluidization System. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Rayas-Duarte, P. The Effect of Mixing and Wheat Protein/Gluten on the Gelatinization of Wheat Starch☆. Food Chem. 2003, 81, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basman, A.; Yalcin, S. Quick-Boiling Noodle Production by Using Infrared Drying. J. Food Eng. 2011, 106, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheetham, N.W.H.; Tao, L.P. Variation in Crystalline Type with Amylose Content in Maize Starch Granules: An X-Ray Powder Diffraction Study. Carbohydr. Polym. 1998, 36, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R.; Hadziyev, D. Characterization of Potato Starch and Its Monoglyceride Complexes. Starch—Stärke 1981, 33, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, K.-X.; Sun, Q.-J.; Amza, T.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhou, H.-M. Quality Characteristics, Structural Changes, and Storage Stability of Semi-Dried Noodles Induced by Moderate Dehydration Understanding the Quality Changes in Semi-Dried Noodles. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Dhital, S.; Zhang, M.-N.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.-G. Structural, Gelatinization, and Rheological Properties of Heat-Moisture Treated Potato Starch with Added Salt and Its Application in Potato Starch Noodles. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, M.Z.; Deepika, K.; Jan, K.; Swer, T.L.; Kumar, P.; Verma, R.; Verma, K.; Prakash, K.S.; Jan, S.; Bashir, K. Modification of Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Buckwheat and Oat Starch by γ-Irradiation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, J.J.G.; Tournois, H.; de Wit, D.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Short-Range Structure in (Partially) Crystalline Potato Starch Determined with Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier-Transform IR Spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 279, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, R.; Zhang, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Qiu, L.; Jin, Z.; Tian, Y. Impact of Frying Conditions on Hierarchical Structures and Oil Absorption of Normal Maize Starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, B. Hierarchical Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Highland Barley Starch Following Heat Moisture Treatment. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capron, I.; Robert, P.; Colonna, P.; Brogly, M.; Planchot, V. Starch in Rubbery and Glassy States by FTIR Spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 68, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
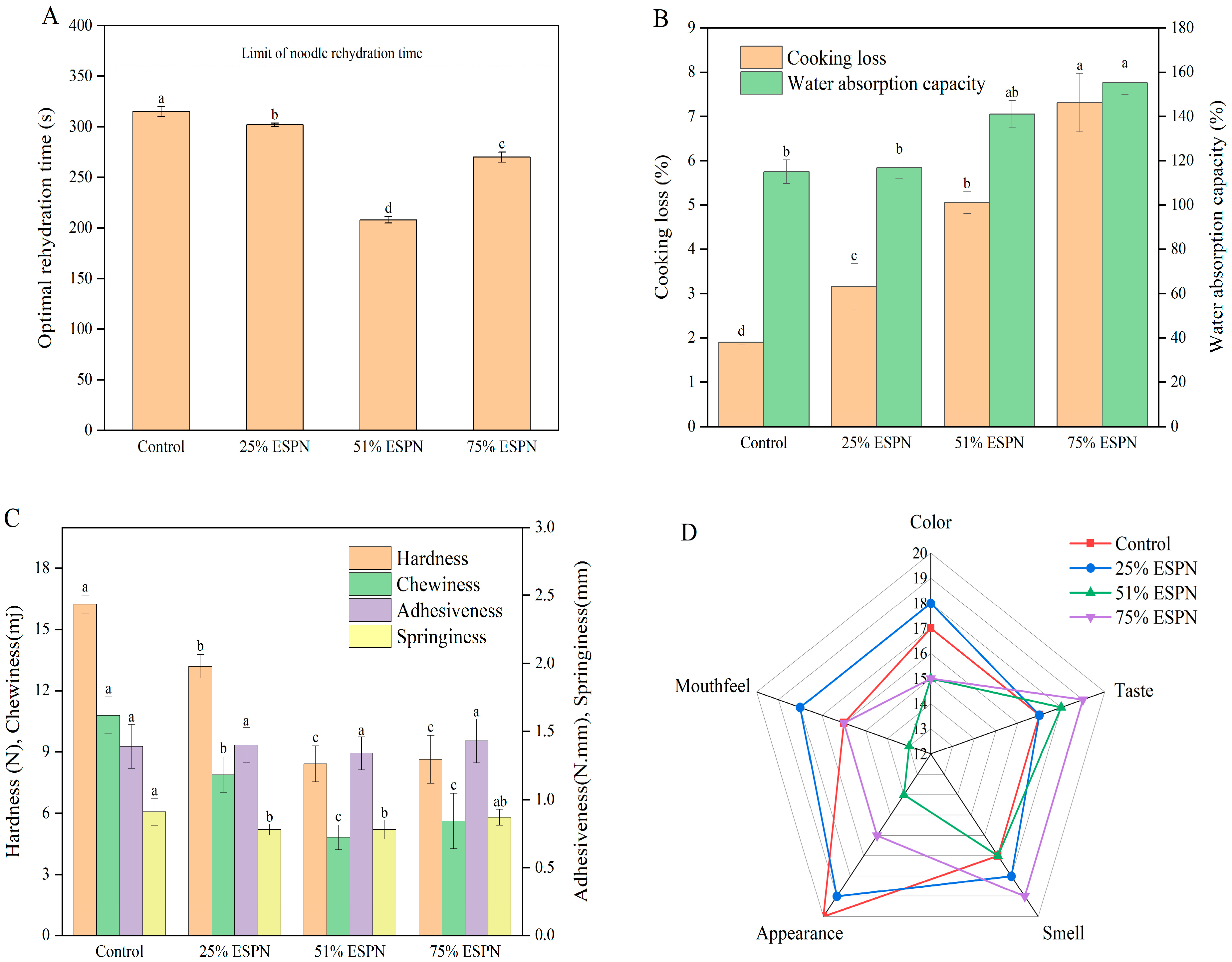
| Evaluation Index | Scoring Criteria | Score (Points) |
|---|---|---|
| Color (20 points) | The bright yellow color is uniform throughout. | 17–20 |
| The color is fairly bright but uneven. | 12–16 | |
| The dull yellow color exhibits poor saturation. | 1–11 | |
| Appearance (20 points) | The surface structure is finely organized, smooth, and flat. | 17–20 |
| The surface structure is more finely organized. | 12–16 | |
| Surface roughness, swelling, and severe deformation. | 1–11 | |
| Smell (20 points) | The rich flavor of wheat and potatoes | 17–20 |
| There is no noticeable taste or odor. | 12–16 | |
| Offensive odor. | 1–11 | |
| Taste (20 points) | Sweet mouthfeel and aftertaste. | 17–20 |
| There is no off-flavor or faintly sweet aroma. | 12–16 | |
| Sour, bitter, or other undesirable flavors. | 1–11 | |
| Mouthfeel (20 points) | Moderate bite strength. | 17–20 |
| Slightly soft or slightly hard. | 12–16 | |
| The balance between softness and hardness is crucial. | 1–11 |
| Samples | DDT (min) | DST (min) | Wabs (%) | C1–C2 (Nm) | C3 (Nm) | C4/C3 | C5–C4 (Nm) | α (Nm.min−1) | β (Nm.min−1) | γ (Nm.min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.290 ± 0.020 a | 6.700 ± 0.020 a | 58.970 ± 0.060 d | 0.650 ± 0.020 c | 1.630 ± 0.040 a | 0.863 ± 0.012 a | 0.860 ± 0.050 a | −0.073 ± 0.002 d | 0.332 ± 0.004 a | −0.052 ± 0.002 b |
| 25%SPD | 0.870 ± 0.010 b | 4.120 ± 0.030 b | 63.500 ± 0.100 c | 0.830 ± 0.020 b | 1.260 ± 0.030 b | 0.601 ± 0.042 c | 0.460 ± 0.030 b | −0.042 ± 0.002 c | 0.215 ± 0.004 b | −0.085 ± 0.001 c |
| 51%SPD | 0.550 ± 0.020 c | 0.720 ± 0.020 c | 69.030 ± 0.060 b | 0.930 ± 0.020 a | 0.810 ± 0.020 c | 0.559 ± 0.021 c | 0.320 ± 0.010 c | −0.034 ± 0.002 a | 0.120 ± 0.002 c | −0.051 ± 0.001 b |
| 75%SPD | 0.490 ± 0.010 d | 0.580 ± 0.010 d | 72.070 ± 0.120 a | 0.910 ± 0.010 a | 0.470 ± 0.020 d | 0.754 ± 0.042 b | 0.280 ± 0.020 c | −0.038 ± 0.001 b | 0.078 ± 0.002 d | −0.023 ± 0.003 a |
| Samples | z | K × 103 (Pa·sz) | Creep | Recovery | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jmax × 10−2 (Pa−1) | η0 × 103 (Pa·s) | Je × 10−2 (Pa−1) | Je/Jmax (%) | Jv/Jmax (%) | |||
| Control | 0.40 ± 0.02 a | 2.26 ± 0.17 d | 8.39 ± 0.11 a | 12.45 ± 0.07 d | 2.99 ± 0.02 a | 35.60 ± 0.00 b | 64.40 ± 0.00 a |
| 25%SPD | 0.22 ± 0.02 b | 7.09 ± 0.47 c | 3.04 ± 0.03 b | 43.50 ± 0.14 c | 1.42 ± 0.07 b | 46.60 ± 0.01 a | 53.40 ± 0.01 b |
| 51%SPD | 0.21 ± 0.01 c | 9.65 ± 0.43 b | 2.21 ± 0.05 c | 61.50 ± 0.14 b | 0.77 ± 0.11 c | 34.62 ± 0.01 b | 65.38 ± 0.03 a |
| 75%SPD | 0.20 ± 0.01 d | 13.30 ± 0.53 a | 0.98 ± 0.02 d | 165.50 ± 0.21 a | 0.27 ± 0.01 d | 27.44 ± 0.00 b | 72.56 ± 0.00 a |
| Samples | ER | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | WAER |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.08 ± 0.02 b | 50.78 ± 0.57 c | 18.44 ± 0.67 b | 1.02 ± 0.02 c | 1.35 ± 0.01 d |
| 25%ESPN | 1.04 ± 0.03 c | 50.98 ± 0.74 c | 18.86 ± 0.45 b | 1.04 ± 0.03 b | 1.56 ± 0.04 c |
| 51%ESPN | 1.00 ± 0.00 d | 51.14 ± 0.46 b | 18.20 ± 0.54 b | 1.08 ± 0.07 b | 1.78 ± 0.02 b |
| 75%ESPN | 1.20 ± 0.02 a | 52.78 ± 0.12 a | 19.84 ± 0.76 a | 1.22 ± 0.020 a | 1.83 ± 0.04 a |
| Samples | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | R1043/1020 | R1020/993 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 117.32 ± 0.20 c | 117.49 ± 0.25 c | 122.9 ± 0.27 c | 0.57 ± 0.01 c | 0.70 ± 0.03 c | 1.22 ± 0.05 a |
| 25%ESPN | 123.38 ± 0.64 b | 123.66 ± 0.35 b | 124.59 ± 0.52 b | 0.77 ± 0.02 c | 0.73 ± 0.02 b | 1.16 ± 0.03 b |
| 51%ESPN | 132.13 ± 0.32 a | 141.42 ± 0.16 a | 148.22 ± 0.29 a | 19.04 ± 0.5 b | 0.75 ± 0.02 b | 1.13 ± 0.02 c |
| 75%ESPN | 131.12 ± 0.79 a | 141.2 ± 0.28 a | 148.01 ± 0.58 a | 22.6 ± 0.12 a | 0.78 ± 0.01 a | 1.01 ± 0.05 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bao, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z. Effect of Addition Amount on Rheological, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Whole-Grain Sweet Potato Noodles Using Extrusion. Foods 2025, 14, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061040
Zeng Y, Wang J, Bao M, Wu Y, Chen Z. Effect of Addition Amount on Rheological, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Whole-Grain Sweet Potato Noodles Using Extrusion. Foods. 2025; 14(6):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061040
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Yan, Jie Wang, Mengxiao Bao, Yue Wu, and Zhigang Chen. 2025. "Effect of Addition Amount on Rheological, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Whole-Grain Sweet Potato Noodles Using Extrusion" Foods 14, no. 6: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061040
APA StyleZeng, Y., Wang, J., Bao, M., Wu, Y., & Chen, Z. (2025). Effect of Addition Amount on Rheological, Structural, and Sensory Properties of Whole-Grain Sweet Potato Noodles Using Extrusion. Foods, 14(6), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14061040






