Exploratory Genomic Marker Analysis of Virulence Patterns in Listeria monocytogenes Human and Food Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Whole-Genome Sequencing and in Silico Analysis
2.2. Statistical Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
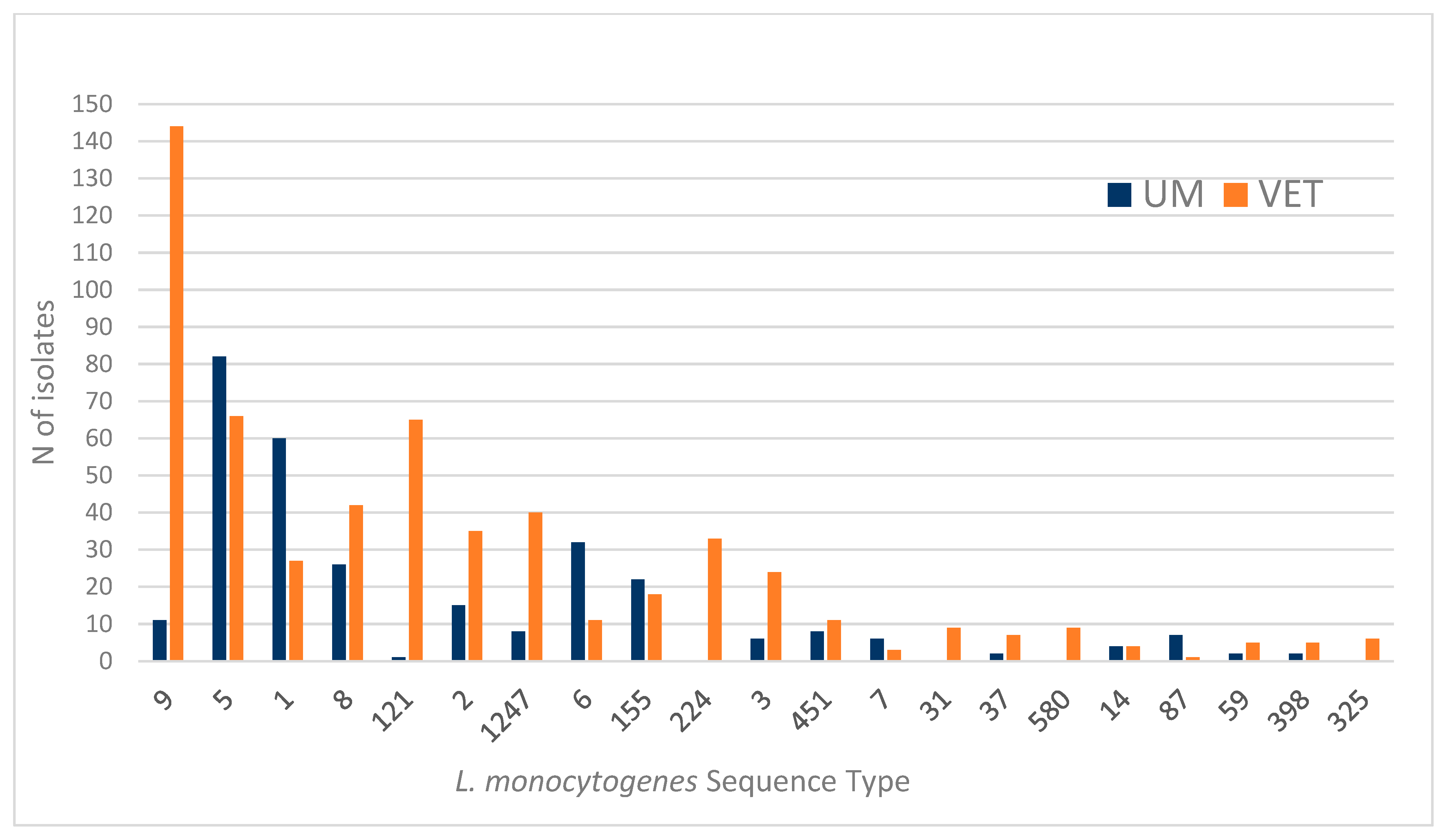
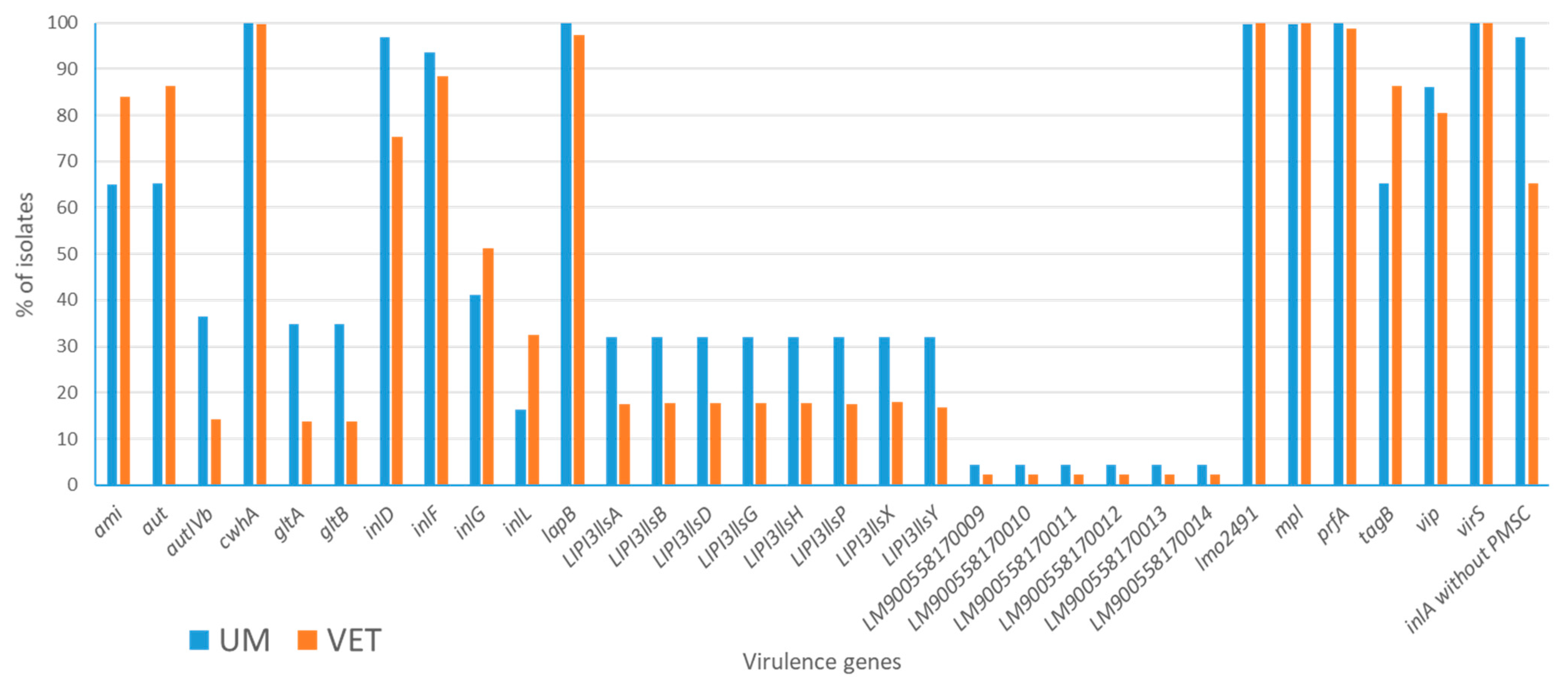
3. Results
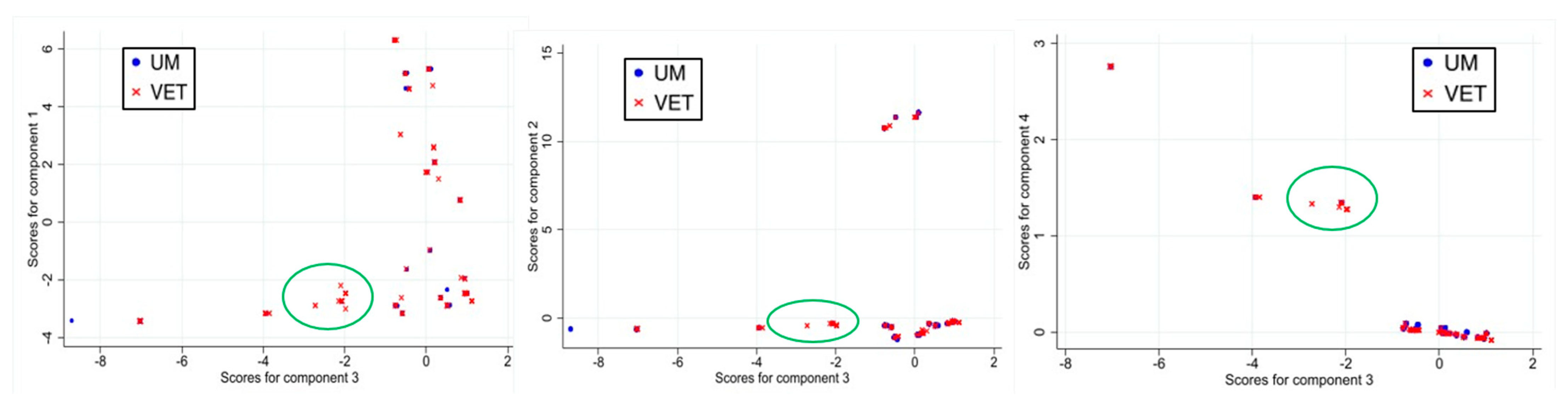
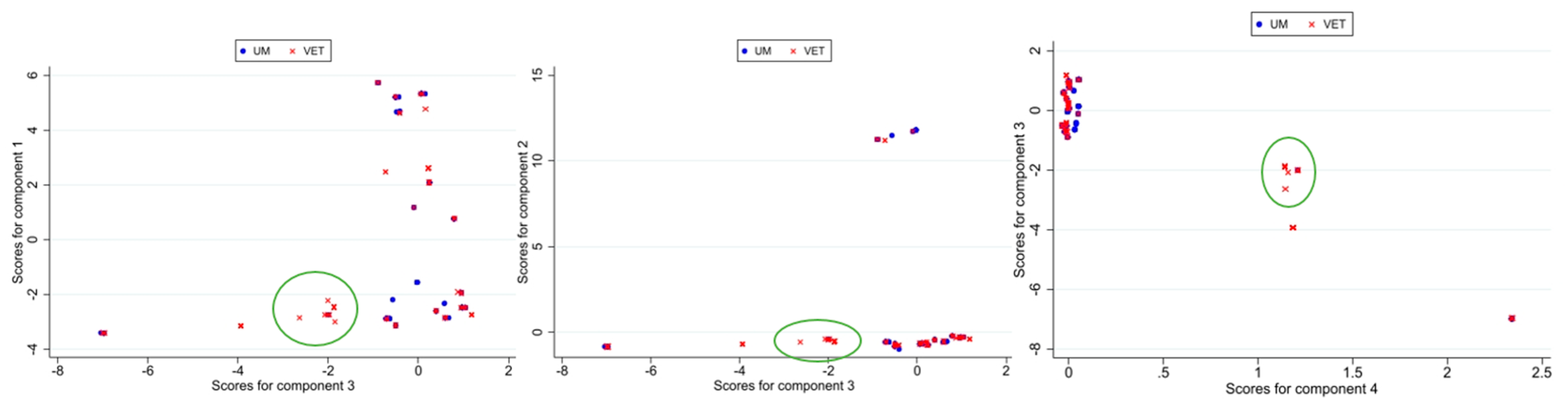
3.1. Principal Component Analysis
3.1.1. Results for First PCA Approach
3.1.2. Results for Second PCA Approach
3.1.3. Focus on 2018–2023 Dataset
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IZSLT | Istituto Zooprofilattico Sperimentale del Lazio e della Toscana “M. Aleandri” |
| UOC | Unità Operativa Complessa—Complex Operational Unit |
| UOT | Unità Operativa Territoriale—Territorial Operational Unit |
| CREP | Regional Reference Center for Pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae |
| LRPTAU | Regional Reference Laboratory for Foodborne Pathogens of Human Origin |
| PMSC | Premature stop codon |
References
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union One Health 2023 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLauchlin, J. The Relationship between Listeria and Listeriosis. Food Control 1996, 7, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.; Hearn, J.; Taylor, C.; Wheelhouse, N.; Kaczmarek, M.; Moorhouse, E.; Singleton, I. Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Ready to Eat Plant Produce Are Diverse and Have Virulence Potential. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 299, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiavano, G.F.; Ateba, C.N.; Petruzzelli, A.; Mele, V.; Amagliani, G.; Guidi, F.; De Santi, M.; Pomilio, F.; Blasi, G.; Gattuso, A.; et al. Whole-genome Sequencing Characterization of Virulence Profiles of Listeria monocytogenes Food and Human Isolates and in Vitro Adhesion/Invasion Assessment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority and European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (EFSA and ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapid Alert System for Food and Feed RASFF NOTIFICATION 2022.4497. Listeria ST155 Outbreak in Italy. Available online: https://webgate.ec.europa.eu/rasff-window/screen/notification/563256 (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Ferreira, V.; Wiedmann, M.; Teixeira, P.; Stasiewicz, M.J. Listeria monocytogenes Persistence in Food-Associated Environments: Epidemiology, Strain Characteristics, and Implications for Public Health. J. Food Prot. 2014, 77, 150–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiwdmann, M.; Sauders, B. Ecology of Listeria Species and L. monocytogenes in the Natural Environment. In Listeria, Listeriosis, and Food Safety; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 39–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bucur, F.I.; Grigore-Gurgu, L.; Crauwels, P.; Riedel, C.U.; Nicolau, A.I. Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes to Stress Conditions Encountered in Food and Food Processing Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.L.; Ricke, S.C.; Donaldson, J.R. Establishment of Listeria monocytogenes in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poimenidou, S.V.; Chrysadakou, M.; Tzakoniati, A.; Bikouli, V.C.; Nychas, G.J.; Skandamis, P.N. Variability of Listeria monocytogenes Strains in Biofilm Formation on Stainless Steel and Polystyrene Materials and Resistance to Peracetic Acid and Quaternary Ammonium Compounds. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 237, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russini, V.; Spaziante, M.; Zottola, T.; Fermani, A.G.; Di Giampietro, G.; Blanco, G.; Fabietti, P.; Marrone, R.; Parisella, R.; Parrocchia, S.; et al. A Nosocomial Outbreak of Invasive Listeriosis in An Italian Hospital: Epidemiological and Genomic Features. Pathogens 2021, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russini, V.; Spaziante, M.; Varcasia, B.M.; Diaconu, E.L.; Paolillo, P.; Picone, S.; Brunetti, G.; Mattia, D.; De Carolis, A.; Vairo, F.; et al. A Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Epidemiological Investigation of a Pregnancy-Related Invasive Listeriosis Case in Central Italy. Pathogens 2022, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EC) No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. O.J. L. 2005, 338, p. 1. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/2073/2020-03-08 (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Seeliger, H.P.R.; Jones, D. Listeria. In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986; Volume 2, pp. 1235–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Doumith, M.; Buchrieser, C.; Glaser, P.; Jacquet, C.; Martin, P. Differentiation of the Major Listeria monocytogenes Serovars by Multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3819–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsi, R.H.; den Bakker, H.C.; Wiedmann, M. Listeria monocytogenes Lineages: Genomics, Evolution, Ecology, and Phenotypic Characteristics. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, B.; Gerner-Smidt, P. The Epidemiology of Human Listeriosis. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragon, M.; Wirth, T.; Hollandt, F.; Lavenir, R.; Lecuit, M.; Le Monnier, A.; Brisse, S. A New Perspective on Listeria monocytogenes Evolution. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Zhu, R.; Lan, R.; Jin, D.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Molecular Typing of Listeria monocytogenes in China. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maury, M.M.; Tsai, Y.H.; Charlier, C.; Touchon, M.; Chenal-Francisque, V.; Leclercq, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Gaultier, C.; Roussel, S.; Brisabois, A.; et al. Uncovering Listeria monocytogenes Hypervirulence by Harnessing Its Biodiversity. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maury, M.M.; Bracq-Dieye, H.; Huang, L.; Vales, G.; Lavina, M.; Thouvenot, P.; Disson, O.; Leclercq, A.; Brisse, S.; Lecuit, M. Hypervirulent Listeria monocytogenes Clones’ Adaption to Mammalian Gut Accounts for Their Association with Dairy Products. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.; Tourdjman, M.; Leclercq, A.; Hamelin, E.; Laurent, E.; Fredriksen, N.; van Cauteren, D.; Bracq-Dieye, H.; Thouvenot, P.; Vales, G.; et al. Real-Time Whole-Genome Sequencing for Surveillance of Listeria monocytogenes, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, G.; Xu, X.; Allard, M.; Li, P.; Brown, E.; Yang, X.; Pan, H.; Meng, J. Evolution and Diversity of Listeria monocytogenes from Clinical and Food Samples in Shanghai, China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, V.; den Bakker, H.C.; Hormazábal, J.C.; González-Rocha, G.; Bello-Toledo, H.; Toro, M.; Moreno-Switt, A.I. Genomic Diversity of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Clinical and Non-Clinical Samples in Chile. Genes 2018, 9, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLauchlin, J.; Mitchell, R.T.; Smerdon, W.J.; Jewell, K. Listeria monocytogenes and Listeriosis: A Review of Hazard Characterisation for Use in Microbiological Risk Assessment of Foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 92, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Pouseele, H.; Maury, M.M.; Leclercq, A.; Tarr, C.; Björkman, J.T.; Dallman, T.; Reimer, A.; Enouf, V.; et al. Whole Genome-Based Population Biology and Epidemiological Surveillance of Listeria monocytogenes. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 2, 16185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonazzi, M.; Lecuit, M.; Cossart, P. Listeria monocytogenes Internalin and E-Cadherin: From Structure to Pathogenesis. Cell Microbiol. 2009, 11, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nightingale, K.K.; Windham, K.; Wiedmann, M. Evolution and Molecular Phylogeny of Listeria monocytogenes Isolated from Human and Animal Listeriosis Cases and Foods. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 5537–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magagna, G.; Gori, M.; Russini, V.; De Angelis, V.; Spinelli, E.; Filipello, V.; Tranquillo, V.M.; De Marchis, M.L.; Bossù, T.; Fappani, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Virulence Potential of Listeria monocytogenes through the Characterization of the Truncated Forms of Internalin A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disson, O.; Moura, A.; Lecuit, M. Making Sense of the Biodiversity and Virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. Trends Microbiol. 2021, 29, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Melo Tavares, R.; Silva, D.A.L.d.; Camargo, A.C.; Yamatogi, R.S.; Nero, L.A. Interference of the Acid Stress on the Expression of LlsX by Listeria monocytogenes Pathogenic Island 3 (LIPI-3) Variants. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilchis-Rangel, R.E.; del Rosario Espinoza-Mellado, M.; Salinas-Jaramillo, I.J.; Martinez-Peña, M.D.; Rodas-Suárez, O.R. Association of Listeria monocytogenes LIPI-1 and LIPI-3 Marker LLsX with Invasiveness. Curr. Microbiol. 2019, 76, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, B.; Liu, H.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, X. 10-Year Molecular Surveillance of Listeria monocytogenes Using Whole-Genome Sequencing in Shanghai, China, 2009–2019. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 551020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Q.; Xue, L.; Zeng, H.; Lei, T.; et al. Heterogeneity, Characteristics, and Public Health Implications of Listeria monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Foods and Pasteurized Milk in China. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Stelten, A.; Simpson, J.M.; Ward, T.J.; Nightingale, K.K. Revelation by Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Genotyping That Mutations Leading to a Premature Stop Codon in InlA Are Common among Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Ready-to-Eat Foods but Not Human Listeriosis Cases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyoui, D.; Takahashi, H.; Miya, S.; Kuda, T.; Kimura, B. Comparison of the Major Virulence-Related Genes of Listeria monocytogenes in Internalin A Truncated Strain 36-25-1 and a Clinical Wild-Type Strain. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nightingale, K.K.; Ivy, R.A.; Ho, A.J.; Fortes, E.D.; Njaa, B.L.; Peters, R.M.; Wiedmann, M. InlA Premature Stop Codons Are Common among Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Foods and Yield Virulence-Attenuated Strains That Confer Protection against Fully Virulent Strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 6570–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painset, A.; Björkman, J.T.; Kiil, K.; Guillier, L.; Mariet, J.F.; Felix, B.; Amar, C.; Rotariu, O.; Roussel, S.; Perez-Reche, F.; et al. Liseq—Whole-Genome Sequencing of a Cross-Sectional Survey of Listeria monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat Foods and Human Clinical Cases in Europe. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.M.; Björkman, J.T.; Kiil, K.; Grant, K.; Dallman, T.; Painset, A.; Amar, C.; Roussel, S.; Guillier, L.; Félix, B.; et al. Closing Gaps for Performing a Risk Assessment on Listeria monocytogenes in Ready-to-Eat (RTE) Foods: Activity 3, the Comparison of Isolates from Different Compartments along the Food Chain, and from Humans Using Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) Analysis. EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 14, 1151E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, R.; Stephan, R.; Althaus, D.; Brisse, S.; Maury, M.; Tasara, T. Phenotypic and Genotypic Characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes Strains Isolated during 2011–2014 from Different Food Matrices in Switzerland. Food Control 2015, 57, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Félix, B.; Feurer, C.; Maillet, A.; Guillier, L.; Boscher, E.; Kerouanton, A.; Denis, M.; Roussel, S. Population Genetic Structure of Listeria monocytogenes Strains Isolated from the Pig and Pork Production Chain in France. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henri, C.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Carleton, H.A.; Radomski, N.; Kaas, R.S.; Mariet, J.F.; Felten, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Smidt, P.G.; Roussel, S.; et al. An Assessment of Different Genomic Approaches for Inferring Phylogeny of Listeria monocytogenes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russini, V.; Corradini, C.; De Marchis, M.L.; Bogdanova, T.; Lovari, S.; De Santis, P.; Migliore, G.; Bilei, S.; Bossù, T. Foodborne Toxigenic Agents Investigated in Central Italy: An Overview of a Three-Year Experience (2018–2020). Toxins 2022, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S. Babraham Bioinformatics—FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 25 January 2021).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality Assessment Tool for Genome Assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA, E.F.S.A.; Costa, G.; Di Piazza, G.; Koevoets, P.; Iacono, G.; Liebana, E.; Pasinato, L.; Rizzi, V.; Rossi, M. Guidelines for Reporting Whole Genome Sequencing-based Typing Data through the EFSA One Health WGS System. EFSA Support. Publ. 2022, 19, 7413E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C.J.; Bygraves, J.A.; Feil, E.; Morelli, G.; Russell, J.E.; Urwin, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zurth, K.; Caugant, D.A.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing: A Portable Approach to the Identification of Clones within Populations of Pathogenic Microorganisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 3140–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salcedo, C.; Arreaza, L.; Alcalá, B.; De la Fuente, L.; Vázquez, J.A. Development of a Multilocus Sequence Typing Method for Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes Clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. GitHub—Tseemann/Mlst: Scan Contig Files Against PubMLST Typing Schemes. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/mlst (accessed on 11 February 2022).
- Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J. BIGSdb: Scalable Analysis of Bacterial Genome Variation at the Population Level. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-Access Bacterial Population Genomics: BIGSdb Software, the PubMLST.Org Website and Their Applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and Applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, P.; Halvorsen, E.M.; Ammendolia, D.A.; Mor-Vaknin, N.; O’Riordan, M.X.D.; Brumell, J.H.; Markovitz, D.M.; Higgins, D.E. Invasion of the Brain by Listeria monocytogenes Is Mediated by InlF and Host Cell Vimentin. mBio 2018, 9, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, N.; Gianfelice, A.; Gray-Owen, S.D.; Ireton, K. Impact of the Listeria monocytogenes Protein InlC on Infection in Mice. Infect. Immun. 2013, 81, 1334–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seveau, S.; Pizarro-Cerda, J.; Cossart, P. Molecular Mechanisms Exploited by Listeria monocytogenes during Host Cell Invasion. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Haendiges, J.; Keller, E.N.; Myers, R.; Kim, A.; Lombard, J.E.; Karns, J.S.; Van Kessel, J.A.S.; Haley, B.J. Genetic Diversity and Virulence Profiles of Listeria monocytogenes Recovered from Bulk Tank Milk, Milk Filters, and Milking Equipment from Dairies in the United States (2002 to 2014). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quereda, J.J.; Nahori, M.A.; Meza-Torres, J.; Sachse, M.; Titos-Jiménez, P.; Gomez-Laguna, J.; Dussurget, O.; Cossart, P.; Pizarro-Cerdá, J. Listeriolysin S Is a Streptolysin S-like Virulence Factor That Targets Exclusively Prokaryotic Cells in Vivo. mBio 2017, 8, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żurawik, A.; Kasperski, T.; Olechowska-Jarząb, A.; Szczesiul-Paszkiewicz, P.; Żak, I.; Wójcicki, M.; Maćkiw, E.; Chmielarczyk, A. Genetic Diversity, Virulence Factors and Antibiotic Resistance of Listeria monocytogenes from Food and Clinical Samples in Southern Poland. Pathogens 2024, 13, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmeiner, A.; Njage, P.M.K.; Hansen, L.T.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Leekitcharoenphon, P. Predicting Listeria monocytogenes Virulence Potential Using Whole Genome Sequencing and Machine Learning. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 410, 110491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Comp1 | Comp2 | Comp3 | Comp4 | Comp5 | Comp6 | Comp7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ami | 0.2554 | 0.0232 | 0.0064 | −0.0002 | 0.051 | 0.2571 | 0.1926 |
| aut | 0.2601 | 0.0236 | 0.012 | −0.0006 | 0.05 | 0.2506 | 0.1836 |
| autIVb | 0.2518 | 0.0612 | −0.0088 | 0.0001 | −0.0588 | −0.2233 | −0.2093 |
| gltA | 0.2601 | −0.0236 | −0.012 | 0.0006 | −0.05 | −0.2506 | -0.1836 |
| gltB | 0.2601 | −0.0236 | −0.012 | 0.0006 | −0.05 | −0.2506 | −0.1836 |
| inlD | 0.0474 | 0.0188 | 0.5649 | −0.2424 | 0.1889 | −0.044 | 0.0657 |
| inlF | 0.0005 | −0.0004 | −0.0133 | −0.0125 | 0.0437 | 0.5997 | −0.7838 |
| inlG | 0.0675 | −0.0693 | −0.2914 | 0.0161 | 0.6334 | −0.1671 | −0.0459 |
| inlL | 0.1021 | −0.0349 | −0.4174 | 0.026 | 0.1763 | −0.1009 | 0.0537 |
| LIPI3-llsA | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsB | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsD | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsG | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsH | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsP | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsX | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI3-llsY | 0.266 | −0.0374 | −0.044 | 0.0029 | 0.0797 | 0.1654 | 0.1291 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170009 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170010 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170011 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170012 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170013 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| LIPI4-LM900558170014 | 0.0339 | 0.4031 | −0.029 | 0.0017 | 0.0337 | 0.0068 | 0.0091 |
| lmo2491 | 0.0141 | 0.0057 | 0.2163 | 0.6639 | 0.0644 | −0.0034 | 0.0029 |
| mpl | 0.0141 | 0.0057 | 0.2163 | 0.6639 | 0.0644 | −0.0034 | 0.0029 |
| tagB | 0.2601 | 0.0236 | 0.012 | −0.0006 | 0.05 | 0.2506 | 0.1836 |
| vip | 0.0891 | 0.0284 | −0.0581 | 0.0067 | −0.6343 | 0.1177 | 0.1636 |
| inlA without PMSCs | 0.0469 | 0.0181 | 0.5508 | −0.2419 | 0.2141 | −0.0109 | 0.0087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russini, V.; De Marchis, M.L.; Sampieri, C.; Onorati, C.; Zucchitta, P.; De Santis, P.; Varcasia, B.M.; De Santis, L.; Chiaverini, A.; Gattuso, A.; et al. Exploratory Genomic Marker Analysis of Virulence Patterns in Listeria monocytogenes Human and Food Isolates. Foods 2025, 14, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101669
Russini V, De Marchis ML, Sampieri C, Onorati C, Zucchitta P, De Santis P, Varcasia BM, De Santis L, Chiaverini A, Gattuso A, et al. Exploratory Genomic Marker Analysis of Virulence Patterns in Listeria monocytogenes Human and Food Isolates. Foods. 2025; 14(10):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101669
Chicago/Turabian StyleRussini, Valeria, Maria Laura De Marchis, Cinzia Sampieri, Cinzia Onorati, Piero Zucchitta, Paola De Santis, Bianca Maria Varcasia, Laura De Santis, Alexandra Chiaverini, Antonietta Gattuso, and et al. 2025. "Exploratory Genomic Marker Analysis of Virulence Patterns in Listeria monocytogenes Human and Food Isolates" Foods 14, no. 10: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101669
APA StyleRussini, V., De Marchis, M. L., Sampieri, C., Onorati, C., Zucchitta, P., De Santis, P., Varcasia, B. M., De Santis, L., Chiaverini, A., Gattuso, A., Vestri, A., Gasperetti, L., Condoleo, R., Palla, L., & Bossù, T. (2025). Exploratory Genomic Marker Analysis of Virulence Patterns in Listeria monocytogenes Human and Food Isolates. Foods, 14(10), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14101669






