Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Zein Peptides
2.3. Peptidomics Analysis of Zein Peptides Using LC-MS/MS Analysis
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Effects of Zein Peptides on Proliferation of C2C12 Cells
2.6. Impacts of Zein Peptides on the Cell Cycle of C2C12 Cells
2.7. Impacts of Zein Peptides on Anti-Apoptotic Effect of C2C12 Cells
2.8. Extraction of RNA
2.9. Transcriptomics Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impacts of Zein Peptides on the Proliferation of C2C12 Cells
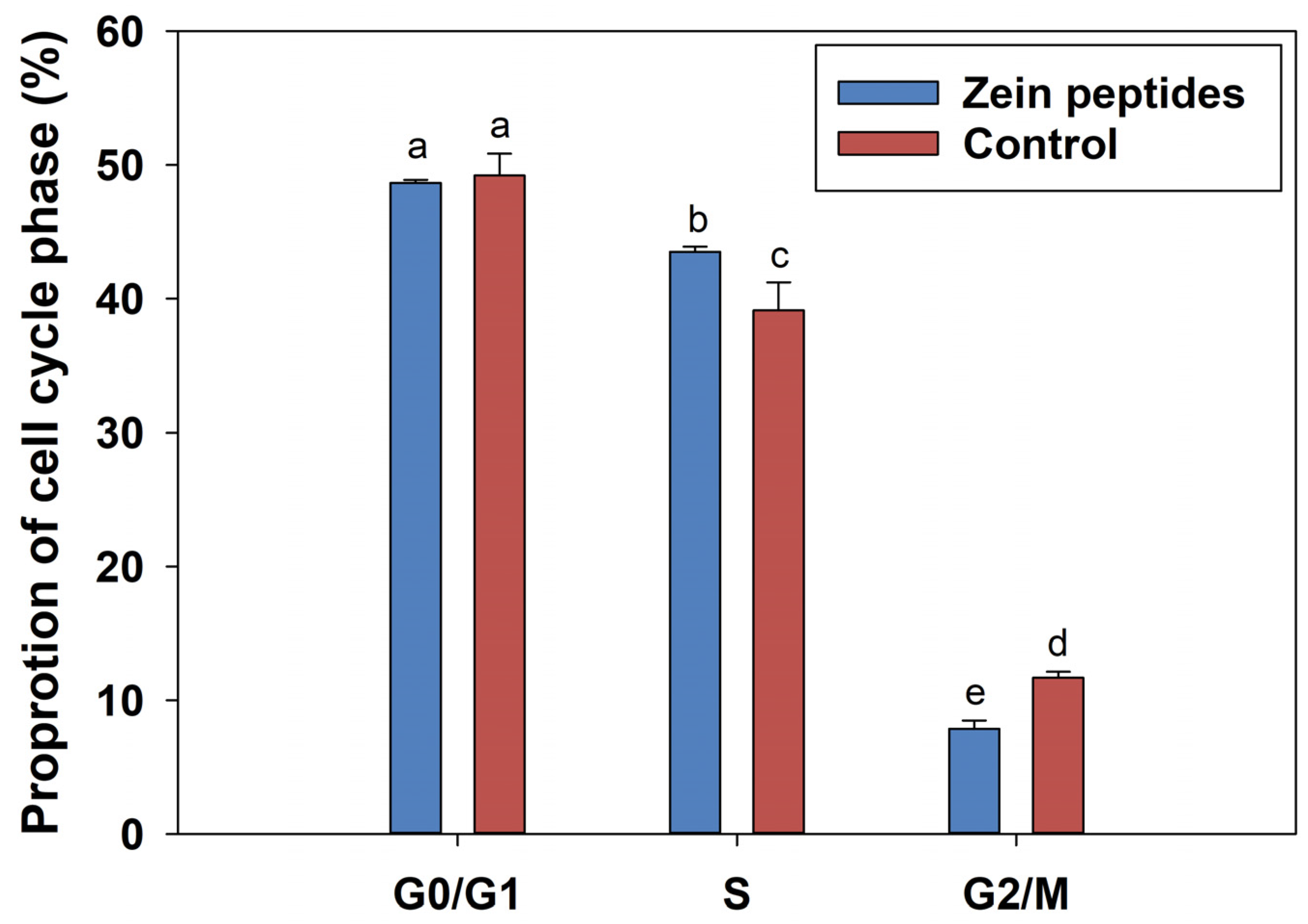
3.2. Impacts of Zein Peptides on the Cycle of C2C12 Cells
3.3. Impacts of Zein Peptides on the Apoptosis of C2C12 Cells
3.4. Identification of Peptide Sequences using Peptidomics Analysis
3.5. Transcriptomics Analysis
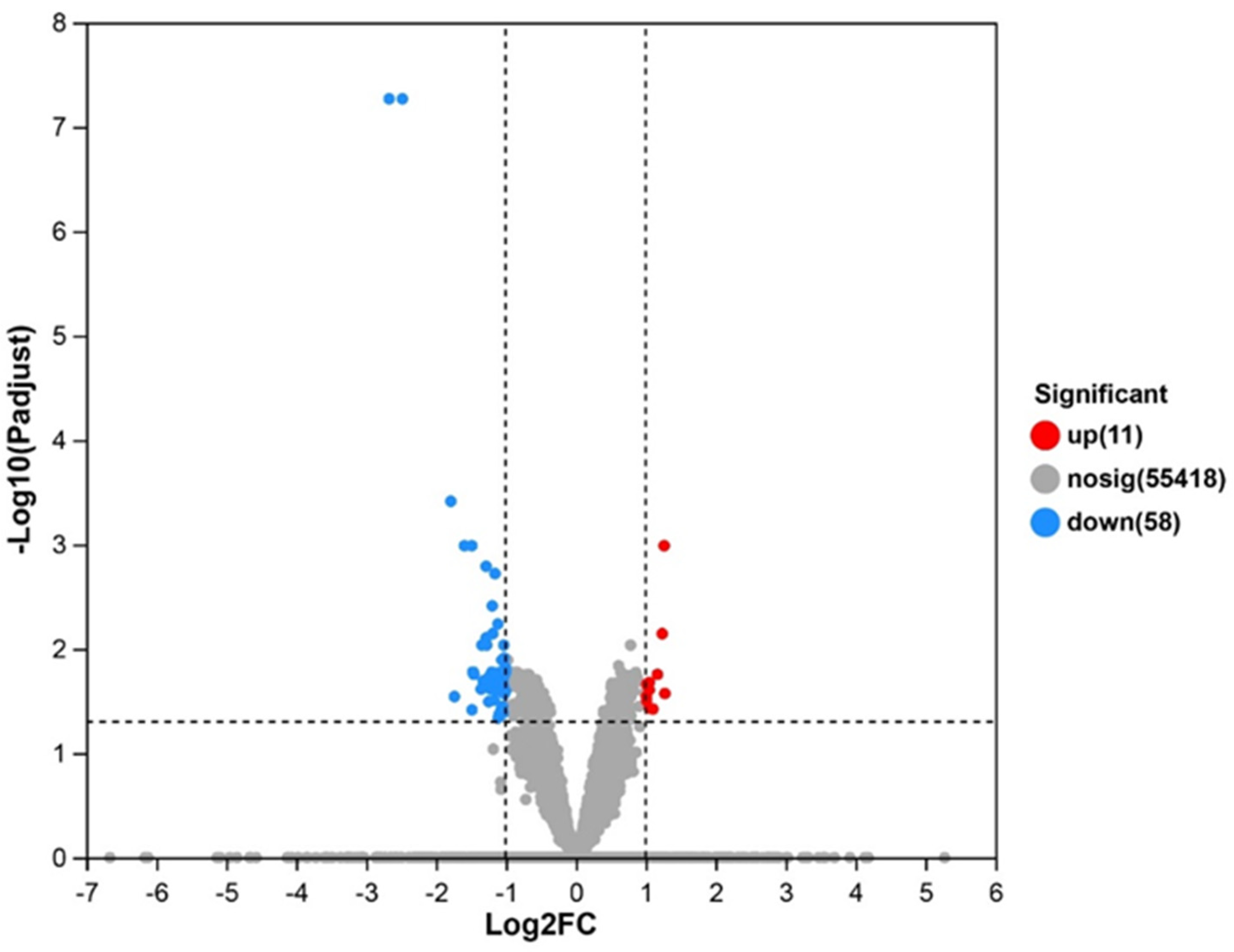
3.5.1. DEGs and Cluster Analysis
3.5.2. GO Analysis
3.5.3. KEGG Analysis
3.6. The Potential Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Zein Peptides on the Cell Proliferation
4.2. Effect of Zein Peptides on Cell Cycle
4.3. Effect of Zein Peptides on Anti-Apoptotic Effect of C2C12 Cells
4.4. Analysis of Zein Peptide Sequences Using LC-MS/MS
4.5. The Potential Molecular Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colleluori, G.; Villareal, D.T. Aging, obesity, sarcopenia and the effect of diet and exercise intervention. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 155, 111561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Ou, H.Y.; Hsu, H.Y.; Cheng, K.P.; Hsieh, T.J.; Yeh, C.H.; Su, F.C.; Kuo, L.C. Beyond sarcopenia: Older adults with type II diabetes mellitus tend to experience an elevated risk of poor dynamic balance-a case-control study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ji, Y.A.; Liu, R.Q.; Zhu, X.C.; Wang, K.X.; Yang, X.M.; Liu, B.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.T.; et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction: Roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmer, P.; Jung, T.; Castro, J.P.; Pomatto, L.C.D.; Sun, P.Y.; Davies, K.J.A.; Grune, T. Sarcopenia–Molecular mechanisms and open questions. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.; Gand, L.V.; Amrute-Nayak, M.; Nayak, A. Emerging mechanisms of skeletal muscle homeostasis and cachexia: The SUMO perspective. Cells 2023, 12, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanova, M.; Kohout, P. Molecular mechanisms underlying intensive care unit-acquired weakness and sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelkar, N. Clinical applications of whey protein. In Nutrition Science, Marketing Nutrition, Health Claims, and Public Policy; Ghosh, D., Bogueva, D., Smarta, R., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Joy, J.M.; Vogel, R.M.; Shane Broughton, K.; Kudla, U.; Kerr, N.Y.; Davison, J.M.; Wildman, R.E.C.; DiMarco, N.M. Daytime and nighttime casein supplements similarly increase muscle size and strength in response to resistance training earlier in the day: A preliminary investigation. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.L.; Chen, X.W.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; An, J.L.; Liu, X.Q. Anti-inflammatory function of plant-derived bioactive peptides: A review. Foods 2022, 11, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathade, V.; Nene, S.; Ratnam, S.; Khatri, D.K.; Raghuvanshi, R.S.; Singh, S.B.; Srivastava, S. Emerging insights of peptide-based nanotherapeutics for effective management of rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci. 2023, 312, 121257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.C.; Zhang, N.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.H.; Fu, Y. Potential of Food Protein-Derived Bioactive Peptides against Sarcopenia: A Comprehensive Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 5419–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Gaine, G.K.; Zhou, L.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, J.; Sun, B.G. The classical and potential novel healthy functions of rice bran protein and its hydrolysates. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 8454–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Jang, G.; Jung, W.K.; Park, Y.H.; Bae, H. Stretchable zein-coated alginate fiber for aligning muscle cells to artificially produce cultivated meat. Npj Sci. Food 2024, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.H.; Wang, A.M.; Dai, W.H.; Chen, S.; Ding, Y.H.; Sun, L.V. Lmod3 promotes myoblast differentiation and proliferation via the AKT and ERK pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, C.; Jia, W. Food-derived bioactive peptides as momentous food components: Can functional peptides passed through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and NF-κB pathway to repair and protect the skeletal muscle injury? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Chen, X.; Zuo, Z.J.; Wang, J.N.; Guo, Y.C. Identification and Characterization of Peptides from Bovine Collagen Hydrolysates that Promote Myogenic Cell Proliferation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4876–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Z.M.; Li, L.L.; Liu, S.; Wu, P.; Zhou, M.; Li, C.W.; Li, X.D.; Luo, G.X.; Zhang, J.X. Stem cell-niche engineering via multifunctional hydrogel potentiates stem cell therapies for inflammatory bone loss. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2209466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.C.L.; Ritso, M.; Nelson, G.M.; Mokhtari, Z.; Nakka, K.; Bandukwala, H.; Goldman, S.R.; Park, P.J.; Mounier, R.; Chazaud, B.; et al. Negative elongation factor regulates muscle progenitor expansion for efficient myofiber repair and stem cell pool repopulation. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1014–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Kwon, E.Y.; Han, Y.A. Collagen hydrolysate containing tripeptides ameliorates sarcopenia in middle-aged mice. Molecules 2022, 27, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devries, M.C.; Chris, M.G.; Bolster, D.R.; Alison, K.; Maike, R.; Laura, H.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Leucine, not total pprotein, content of a supplement is the primary determinant of muscle protein anabolic responses in healthy older women. J. Nutr. 2018, 7, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodan, D.; Filip, M.; Perhaita, I.; Vlassa, M.; Popescu, V.; Marcus, I.; Moldovan, M. The influence of minerals and lactose content on the stability of whey protein powders. Stud. Univ. Babes-Bolyai Chem. 2017, 62, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wroblewski, O.M.; Vega-Soto, E.E.; Nguyen, M.H.; Cederna, P.S.; Larkin, L.M. Impact of human epidermal growth factor on tissue-engineered skeletal muscle structure and function. Tissue Eng. Part A 2021, 27, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.S.Y.; Xing, D.; Zhang, Q.X.; Li, H.; Lin, J.J.; He, Z.H.; Lin, J.H. LncRNAs as a new regulator of chronic musculoskeletal disorder. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.S.; Li, X.; Qian, L.L.; Cai, C.B.; Xiao, G.J.; Jiang, S.W.; Li, B.; Gao, T.; Cui, W.T. An integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA in skeletal muscle from myostatin-edited Meishan pigs. Genome 2019, 62, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supruniuk, E.; Zebrowska, E.; Chabowski, A. Branched chain amino acids-friend or foe in the control of energy substrate turnover and insulin sensitivity? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2559–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijles, D.N.; Fuller, S.J.; Cull, J.J.; Alharbi, H.O.; Cooper, S.T.E.; Sugden, P.H.; Clerk, A. The insulin receptor family and protein kinase B (Akt) are activated in the heart by alkaline pH and α1-adrenergic receptors. Biochem. J. 2021, 478, 2059–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.L.; Qian, Y.; Tang, J.; Yao, C.J.; Yu, S.L.; Qu, J.H.; Wei, H.Y.; Chen, G.; Han, Y. Arsenic trioxide promotes ERK1/2-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of BIMEL to attenuate apoptosis in BEAS-2B cells. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2023, 369, 110304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-López, E.M.; Coronado-Parra, T.; Marín-Vicente, C.; Szallasi, Z.; Gómez-Abellán, V.; López-Andreo, M.J.; Gragera, M.; Gómez-Fernández, J.C.; López-Nicolás, R.; Corbalán-García, S. Deciphering the role and signaling pathways of PKCα in luminal a breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.Q.; Jin, C.J.; Bai, H.X.; Liang, G.F.; Su, X.D.; Wang, D.D.; Yao, J.H. Low rumen degradable starch promotes the growth performance of goats by increasing protein synthesis in skeletal muscle via the AMPK-mTOR pathway. Anim. Nutr. 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-García, C.; Hernández-Camacho, J.D.; Carvajal, J.J. Regulation of myogenic gene expression. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 419, 113299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manole, E.; Gaina, G.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Hinescu, M.E. Skeletal muscle stem cells in aging: Asymmetric/Symmetric division switching. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakale, S.; Wu, X.X.; Sonar, Y.; Sun, A.; Fan, X.W.; Crawford, R.; Prasadam, I. How are aging and osteoarthritis related? Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.F.; Gao, F.; Wen, L.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.P.; Jian, Z.J. Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/Akt, P38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Liao, Y.L.; Zheng, X.; Zhuang, X.H.; Gao, C.J.; Zhou, J. Shedding light on the role of phosphorylation in plant autophagy. FEBS Lett. 2022, 596, 2172–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, H.X.Y.; Qian, D.; Yang, F.; Xia, J. Alpiniae oxyphyllae fructus possesses neuroprotective effects on H2O2 stimulated PC12 cells via regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 966348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabulea, A.L.; Janeski, J.D.; Naik, V.D.; Chen, K.; Mor, G.; Ramadoss, J. A multi-organ analysis of the role of mTOR in fetal alcohol spectrum disorders. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.; Mei, W.X.; Zeng, C.C. PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and its role in cancer therapeutics: Are we making headway? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 819128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.N.; Wang, H.H.; Qu, T.Q.; Luo, J.J.; An, P.; Ren, F.Z.; Luo, Y.T.; Li, Y.X. mTORC2: A multifaceted regulator of autophagy. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, M.S.; Yu, B.; Wu, D.; Lu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y. Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways. Foods 2024, 13, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060919
Amin MS, Yu B, Wu D, Lu Y, Wu W, Wang J, Zhang Y, Fu Y. Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways. Foods. 2024; 13(6):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060919
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Mohammad Sadiq, Binbin Yu, Dongjing Wu, Yujia Lu, Wei Wu, Jing Wang, Yuhao Zhang, and Yu Fu. 2024. "Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways" Foods 13, no. 6: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060919
APA StyleAmin, M. S., Yu, B., Wu, D., Lu, Y., Wu, W., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., & Fu, Y. (2024). Zein-Derived Peptides from Corn Promote the Proliferation of C2C12 Myoblasts via Crosstalk of mTORC1 and mTORC2 Signaling Pathways. Foods, 13(6), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13060919







