A Simple High-Throughput Technology for Microorganism Detection and Quantitative Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Optimization of Medium for Three Strains
2.3. Reproducibility, Precision, and Accuracy of the High-Throughput Platform
2.4. Trace Cell Detection
2.5. Cell Viability Detection
2.6. Detection Procedure of the Microplate Reader
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection Principle of High-Throughput Method for Microbial Detection
3.2. Effect of Different Media on the Growth of Microorganisms
3.3. Evaluation of Reproducibility, Precision, and Accuracy of the High-Throughput Method
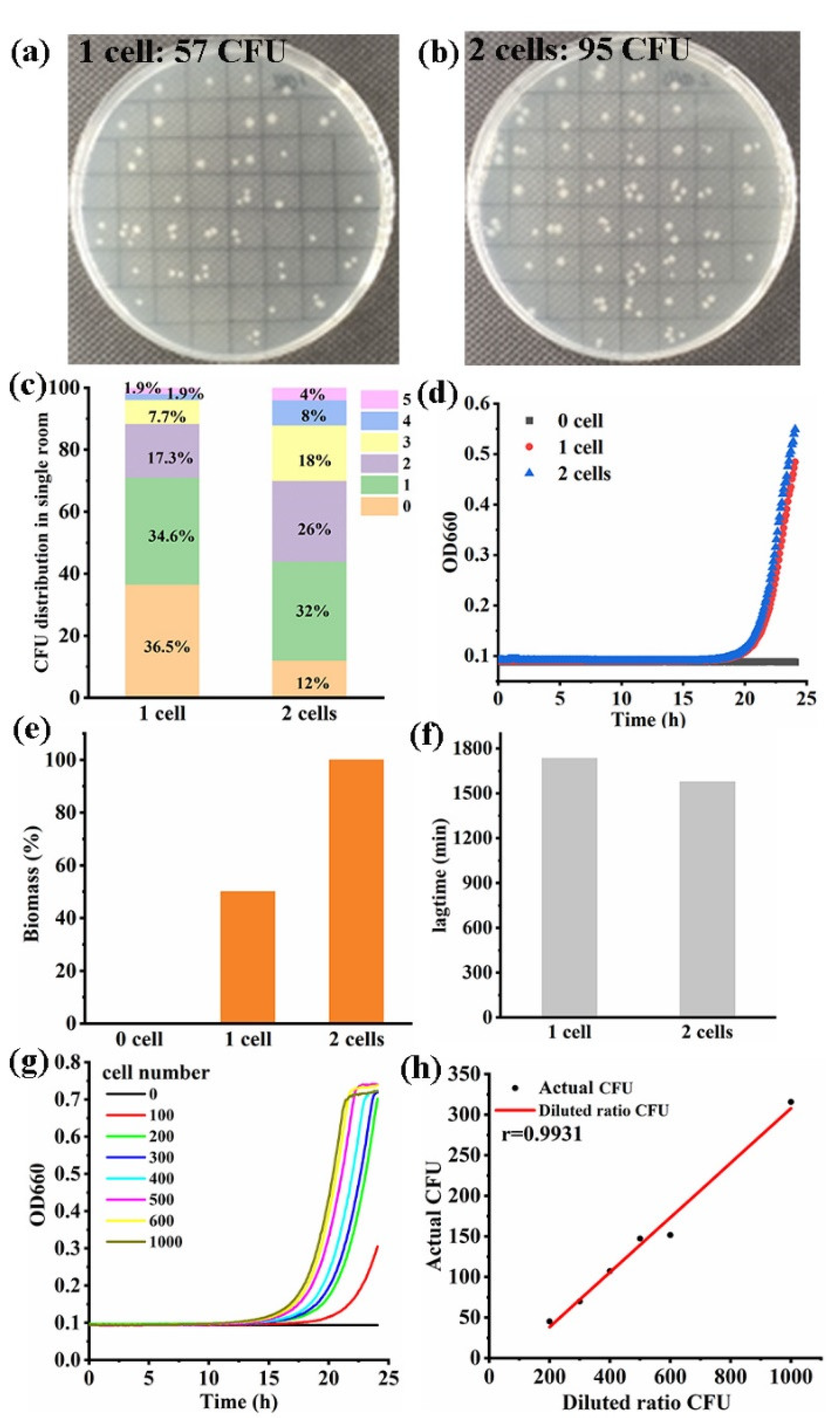
3.4. The High-Throughput Method for Microorganism Detection at Trace Cell Level
3.5. The High-Throughput Method for Cell Viability Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ayrapetyan, M.; Oliver, J.D. The viable but non-culturable state and its relevance in food safety. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 8, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Warden, A.R.; Jiang, H.; Abdullah, A.; Ahmad, M.; Jiang, L.; Ding, X. Time-lapse proteomics unveil constant high exposure of non-antibiotic drug induces synthetic susceptibility towards regular antibiotics. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 269, 127320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic laboratory techniques: Plating methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar]
- Brugger, S.D.; Baumberger, C.; Jost, M.; Jenni, W.; Brugger, U.; Mühlemann, K. Automated counting of bacterial colony forming units on agar plates. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, S.; Yadav, M.; Giri, S.J.; Begum, S.; Das, S.; Phukan, A.; Priyadarshani, P.; Sarkar, S.; Jayswal, A.; Kabyashree, K.; et al. Microliter spotting and micro-colony observation: A rapid and simple approach for counting bacterial colony forming units. J. Microbiol. Methods 2023, 207, 106707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.T.; Lynch, G.K.; Stamo, D.F.; Miller, E.J.; Chatterjee, A.; Kralj, J.M. A high-throughput and low-waste viability assay for microbes. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 2304–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazan, R.; Que, Y.-A.; Maura, D.; Rahme, L.G. A method for high throughput determination of viable bacteria cell counts in 96-well plates. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, N. Sea hedgehog-inspired surface-enhanced Raman scattering biosensor probe for ultrasensitive determination of Staphylococcus aureus in food supplements. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 252, 116146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, G.; Kaur, N.; Singh, N. Pattern-based colorimetric sensor array to monitor food spoilage using automated high-throughput analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 196, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santovito, E.; Elisseeva, S.; Bukulin, A.; Kerry, J.P.; Papkovsky, D.B. Facile biosensor-based system for on-site quantification of total viable counts in food and environmental swabs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 176, 112938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, H.; Song, G.; Huang, K.; Luo, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, X.; Cheng, N. Intelligent biosensing strategies for rapid detection in food safety: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 202, 114003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, C.J.; Burtner, C.R.; Kennedy, B.K.; Kaeberlein, M. A method for high-throughput quantitative analysis of yeast chronological life span. J. Gerontol. Ser. A: Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2008, 63, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Song, L.; Liu, S.Q.; Huang, D. A high throughput screening assay for determination of chronological lifespan of yeast. Exp. Gerontol. 2011, 46, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, L.W. Growth and maintenance of yeast. In Two-Hybrid Systems: Methods and Protocols; MacDonald, P.N., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Freyre-González, J.A.; Treviño-Quintanilla, L.G.; Valtierra-Gutiérrez, I.A.; Gutiérrez-Ríos, R.M.; Alonso-Pavón, J.A. Prokaryotic regulatory systems biology: Common principles governing the functional architectures of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli unveiled by the natural decomposition approach. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 161, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Guan, X.; Zhou, Z. The anti-aging potential of neohesperidin and its synergistic effects with other citrus flavonoids in extending chronological lifespan of Saccharomyces Cerevisiae BY4742. Molecules 2019, 24, 4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, G.; Leng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, X.; Feng, Z. The nutrient requirements of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and their application to fermented milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5971–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, K. Preparing spread plates protocols. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2006, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bauchop, T.; Elsden, S.R. The growth of micro-organisms in relation to their energy supply. Microbiology 1960, 23, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountcastle, S.E.; Vyas, N.; Villapun, V.M.; Cox, S.C.; Jabbari, S.; Sammons, R.L.; Shelton, R.M.; Walmsley, A.D.; Kuehne, S.A. Biofilm viability checker: An open-source tool for automated biofilm viability analysis from confocal microscopy images. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.; Sargison, F.A.; Stawarz, H.; Fox, W.B.; Huete, S.G.; Hassan, A.; McTeir, B.; Pickering, A.C. A case report: Insights into reducing plastic waste in a microbiology laboratory. Access Microbiol. 2021, 3, 000173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CODEX Alimentarius Commission. Draft Principles and Guidelines for the Conduct of Microbiological Risk Assessment; Alinorm 99/13A; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, T.; McMeekin, T.A. Modeling microbial growth within food safety risk assessments. Risk Anal. 2003, 23, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey Hazel, M. Life, death, and in-between: Meanings and methods in microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2011, 77, 5571–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azinheiro, S.; Ghimire, D.; Carvalho, J.; Prado, M.; Garrido-Maestu, A. Next-day detection of viable Listeria monocytogenes by multiplex reverse transcriptase real-time PCR. Food Control 2022, 133, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Spread Plate Method | High-Throughput Method | |
|---|---|---|
 |  | |
| dish | 288 culture dishes | one 96-well plate |
| volume of medium | 5760 mL | 9.6 mL |
| preparation time | 5 h | 2 h |
| incubation | 48 h | 24 h |
| count method | Manual count | Plate reader |
| experimental time | 26 h | 1.25 h |
| US$ per sample | 0.9 | 0.08 |
| result | CFU | lag time, doubling time, survival, CFU |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wu, Z. A Simple High-Throughput Technology for Microorganism Detection and Quantitative Analysis. Foods 2024, 13, 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182954
Wang L, Wu Z. A Simple High-Throughput Technology for Microorganism Detection and Quantitative Analysis. Foods. 2024; 13(18):2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182954
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liping, and Ziyun Wu. 2024. "A Simple High-Throughput Technology for Microorganism Detection and Quantitative Analysis" Foods 13, no. 18: 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182954
APA StyleWang, L., & Wu, Z. (2024). A Simple High-Throughput Technology for Microorganism Detection and Quantitative Analysis. Foods, 13(18), 2954. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13182954




