Purification and Identification of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bighead Carp Skin Collagen Peptides’ Preparation
2.2.1. Protein Recovery Rate
2.2.2. Preparation of Collagen
2.2.3. SDS-PAGE
2.3. Hydrolysis of Collagen and Measurement of Molecular Weight Distribution
2.3.1. Hydrolysis of Collagen
2.3.2. Measurement of the Molecular Weight Distribution
2.4. Isolation and Purification of Collagen Peptides
2.4.1. Ultrafiltration of Hydrolysates
2.4.2. RP-HPLC Purification
2.5. Determination of DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity
2.6. Identification of Peptide Sequences by Nano-HPLC-MS/MS
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.8. Synthesis of Peptides
2.9. Determination of DPP-IV Inhibition Pattern
2.10. Prediction of Toxicity and Digestibility
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
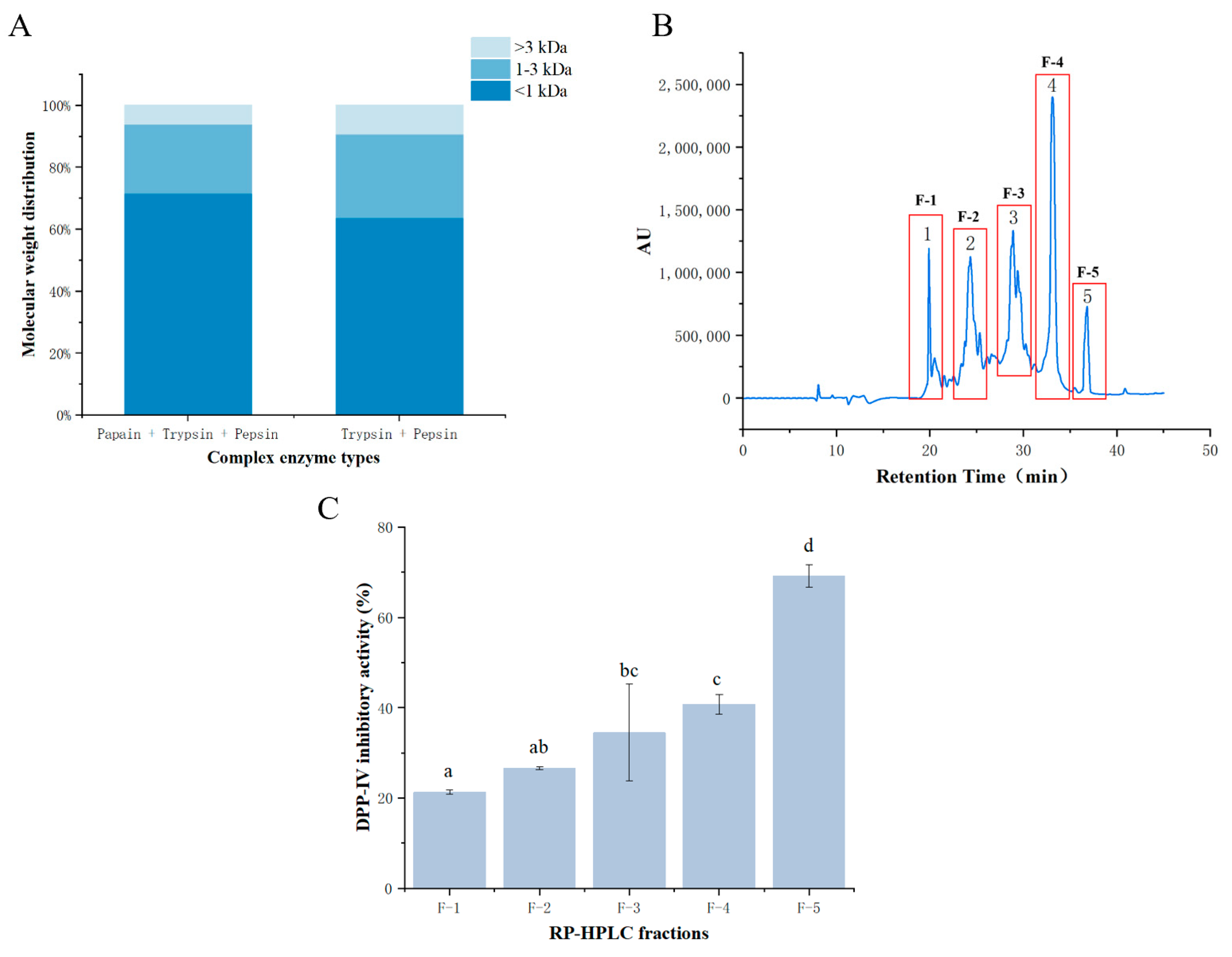
3.1. SDS-PAGE, Recovery Rate, and Molecular Weight Distribution of Prepared Bighead Carp Skin Collagen
3.2. DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of Fractions after Purification
3.2.1. RP-HPLC of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides
3.2.2. DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of Fractions
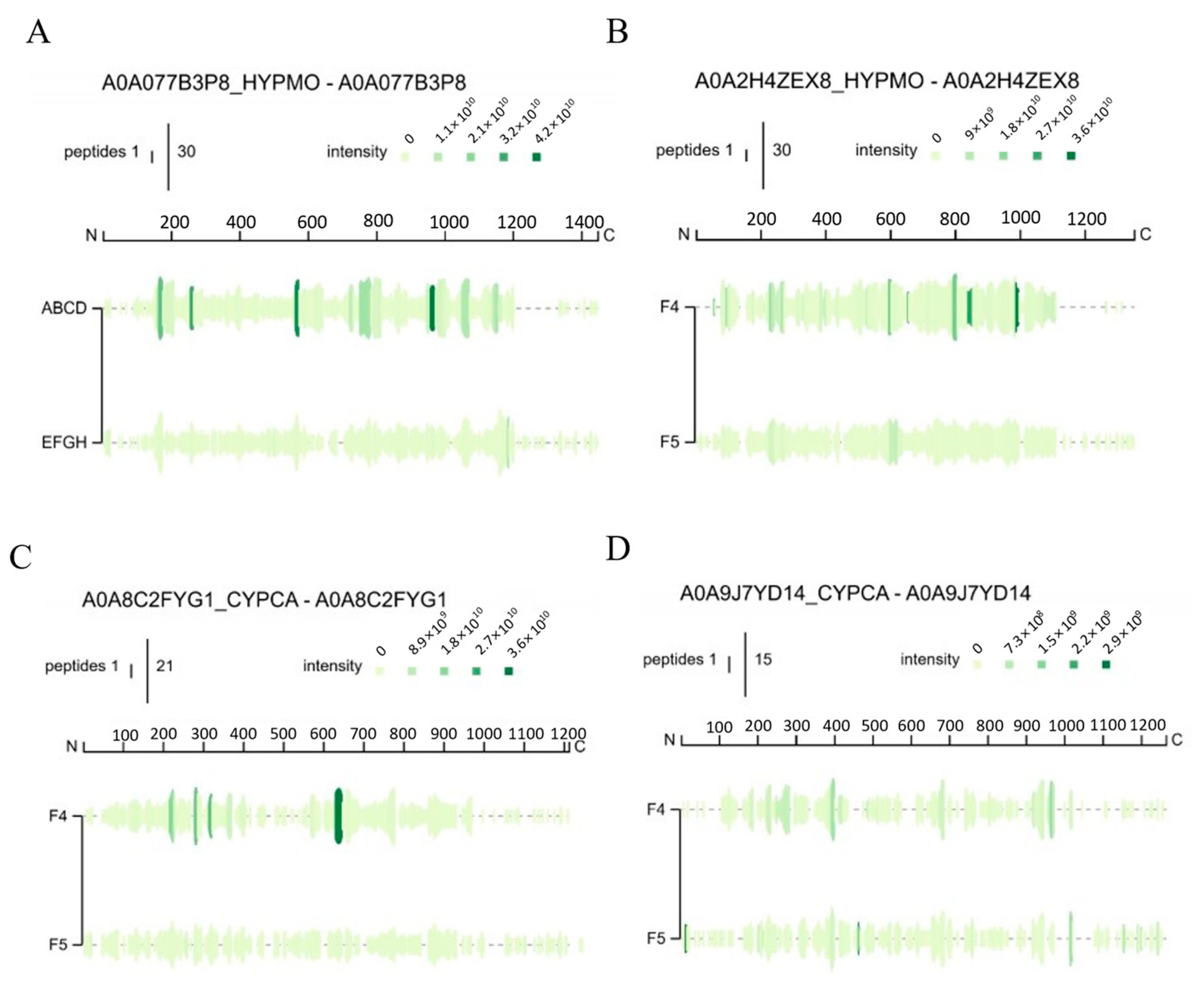
3.3. Identification and Analysis of Peptide Sequences
3.3.1. Nano-HPLC-MS/MS Spectra of Collagen Peptides
3.3.2. Molecular Docking of Collagen Peptides
3.4. DPP-IV Inhibitory Activity of Synthetic Peptides
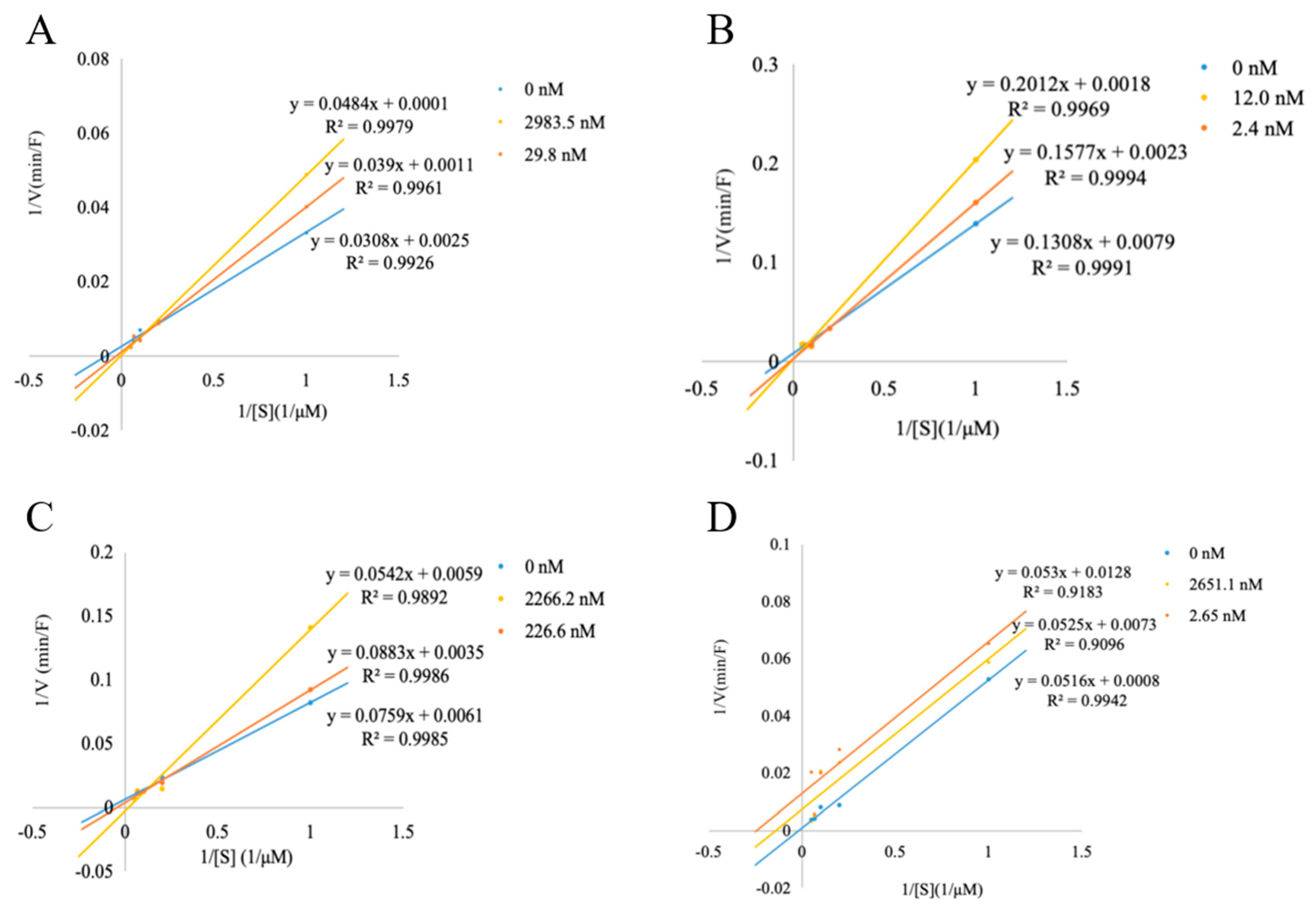
3.5. DPP-IV Inhibitory Pattern
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, X.; Liang, S.; Sun, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Enhancing bighead carp cutting: Chilled storage insights and machine vision-based segmentation algorithm development. Food Chem. 2024, 450, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, H.; Luo, Y.; Shen, H. Lipid Content and Fatty Acid Profile of Muscle, Brain and Eyes of Seven Freshwater Fish: A Comparative Study. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y.; Li, B.; Tan, Y. From formation to solutions: Off-flavors and innovative removal strategies for farmed freshwater fish. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 144, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Fan, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, H.; Luo, Y.; Shen, H. Seasonal variations of fatty acid profile in different tissues of farmed bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roglic, G. WHO Global report on diabetes: A summary. Int. J. Noncommun. Dis. 2016, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetes Basics. (n.d.). International Diabetes Federation. Available online: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/what-is-diabetes/ (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Tatulashvili, S.; Fagherazzi, G.; Dow, C.; Cohen, R.; Fosse, S.; Bihan, H. Socioeconomic inequalities and type 2 diabetes complications: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 46, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, E.; Miles, J. Side Effect Synergism Between Metformin and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Am. Heart J. 2022, 254, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadsby, R. New treatments for type 2 diabetes—The DPP4 inhibitors. Prim. Care Diabetes 2007, 1, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasina, S.V.S.K.; Baradhi, K.M. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP IV) Inhibitors. PubMed; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542331/ (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Salvo, F.; Moore, N.; Arnaud, M.; Robinson, P.; Raschi, E.; De Ponti, F.; Bégaud, B.; Pariente, A. Addition of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors to sulphonylureas and risk of hypoglycaemia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2016, 353, i2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2017, 43, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivero-Pino, F.; Espejo-Carpio, F.J.; Guadix, E.M. Identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from vegetable protein sources. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umezawa, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Ogawa, K.; Naganawa, H.; Hamada, M.; Takeuchi, T. Diprotins A and B, inhibitors of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV, produced by bacteria. J. Antibiot. 1984, 37, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.-C.; Tung, Y.-S.; Huang, S.-L.; Jao, C.-L. Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Activity of Peptides in Porcine Skin Gelatin Hydrolysates. In Bioactive Food Peptides in Health and Disease; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/42418 (accessed on 6 November 2022).
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidative properties of milk protein-derived dipeptides and hydrolysates. Peptides 2013, 39, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Hong, P.; Deng, C. Characterization and comparison of collagen extracted from the skin of the Nile tilapia by fermentation and chemical pretreatment. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 128139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Chang, S.K. Isolation and characterization of collagen extracted from channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) skin. Food Chem. 2018, 242, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Evaluating in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibition by peptides from common carp (Cyprinus carpio) roe in cell culture models. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 246, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Han, L.; Hong, H.; Pan, J.; Liu, H.; Luo, Y. Purification and identification of novel antioxidant peptides from silver carp muscle hydrolysate after simulated gastrointestinal digestion and transepithelial transport. Food Chem. 2021, 342, 128275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.A.; Alkali, I.Y. In silico molecular docking studies of some phytochemicals against peroxisome-proliferator activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ). GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Browne, J.J.; Van Crugten, J.; Hasan, F.; Liu, L.; Barkla, B.J. In Silico, Molecular Docking and In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of the Major Rapeseed Seed Storage Proteins. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 01340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Systèmes, D. Free Download: BIOVIA Discovery Studio Visualizer. Dassault Systèmes. Available online: https://discover.3ds.com/discovery-studio-visualizer-download (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Huang, S.-Y. HDOCK: A web server for protein–protein and protein–DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W365–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic study of acid soluble collagen and gelatin from skins and bones of young and adult Nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 86, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Nagai, T.; Tanaka, M. Characterisation of acid-soluble collagen from skin and bone of bigeye snapper (Priacanthus tayenus). Food Chem. 2005, 89, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Seasonal variation of acid-soluble collagens extracted from the swim bladders and skins of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) and grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Food Biosci. 2016, 15, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Zhu, X.; Matsui, R.; Shijoh, M.; Takamizawa, S. Characterization of Fish Muscle Type I Collagen. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Mubango, E.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hong, H. Effects of protein and lipid oxidation on the water holding capacity of different parts of bighead carp: Eye, dorsal, belly and tail muscles. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapsongphon, N.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Production and purification of antioxidant peptides from a mungbean meal hydrolysate by Virgibacillus sp. SK37 proteinase. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, L.; Wu, G.; Liu, T.; Qi, X.; Zhang, H. Food-derived dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides: Production, identification, structure-activity relationship, and their potential role in glycemic regulation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 64, 2053–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Wang, R.; Cheng, C.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W. Preparation, structural properties, and in vitro and in vivo activities of peptides against dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) and α-glucosidase: A general review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M. Exploring structural features of potent dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides derived from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin gelatin by an integrated approach of multivariate analysis and Gly-Pro-based peptide library. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Gao, J.; Shen, Q.; Gao, D.; Wang, Q.; Tangyu, M.; Mao, X. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of millet protein peptides and the related mechanisms revealed by molecular docking. LWT 2021, 138, 110587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.; Li-Chan, E.C. Food-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors as a potential approach for glycemic regulation—Current knowledge and future research considerations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Huang, X.; Guyonnet, V.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Huang, X.; et al. Exploration of novel DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from discarded eggshell membrane: An integrated in silico and in vitro study. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchese, G.; Stufano, A.; Trost, B.; Kusalik, A.; Kanduc, D. Peptidology: Short amino acid modules in cell biology and immunology. Amino Acids 2006, 33, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, T. Recent Advances in Non-Peptidomimetic Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors: Medicinal Chemistry and Preclinical Aspects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3982–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gong, J.; Peng, C. Two novel dipeptidyl peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides identified from truffle (Tuber sinense) by peptidomics, in silico, and molecular docking analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 121, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yan, J.; Yu, Y.; Qi, Y. Screening and identification of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from deer skin hydrolysates by an integrated approach of LC–MS/MS and in silico analysis. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Structure activity relationship modelling of milk protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity. Peptides 2016, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Nardo, A.E.; Garzón, A.G.; Añon, M.C.; Drago, S.R. Identification and in silico study of a novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptide derived from green seaweed Ulva spp. hydrolysates. LWT 2022, 154, 112738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermeño, M.; Stack, J.; Tobin, P.R.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Harnedy, P.A.; Stengel, D.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Peptide identification from a Porphyra dioica protein hydrolysate with antioxidant, angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory activities. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 3421–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Teng, X.; Shang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, N. Identification of novel DPP–IV inhibitory peptides from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) skin. Food Res. Int. 2020, 133, 109161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.; Zheng, Y.; Song, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y. Identification and characterization of DPP-IV inhibitory peptides from silver carp swim bladder hydrolysates. Food Biosci. 2020, 38, 100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduc, D. Correlating Low-Similarity Peptide Sequences and Allergenic Epitopes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.; Wal, J.-M.; Bernard, H.; Pentzien, A.-K. Cytotoxic and Allergenic Potential of Bioactive Proteins and Peptides. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 897–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Huang, M.; Zhao, M. Collagen derived Gly-Pro-type DPP-IV inhibitory peptides: Structure-activity relationship, inhibition kinetics and inhibition mechanism. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, G.; Han, L.; Yu, Q. Production and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from discarded cowhide collagen. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Xu, Q.; Lin, L.; Zeng, X.-A.; Sun, B.; Zhao, M. In Vitro Metabolic Stability of a Casein-Derived Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV (DPP-IV) Inhibitory Peptide VPYPQ and Its Controlled Release from Casein by Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10604–10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
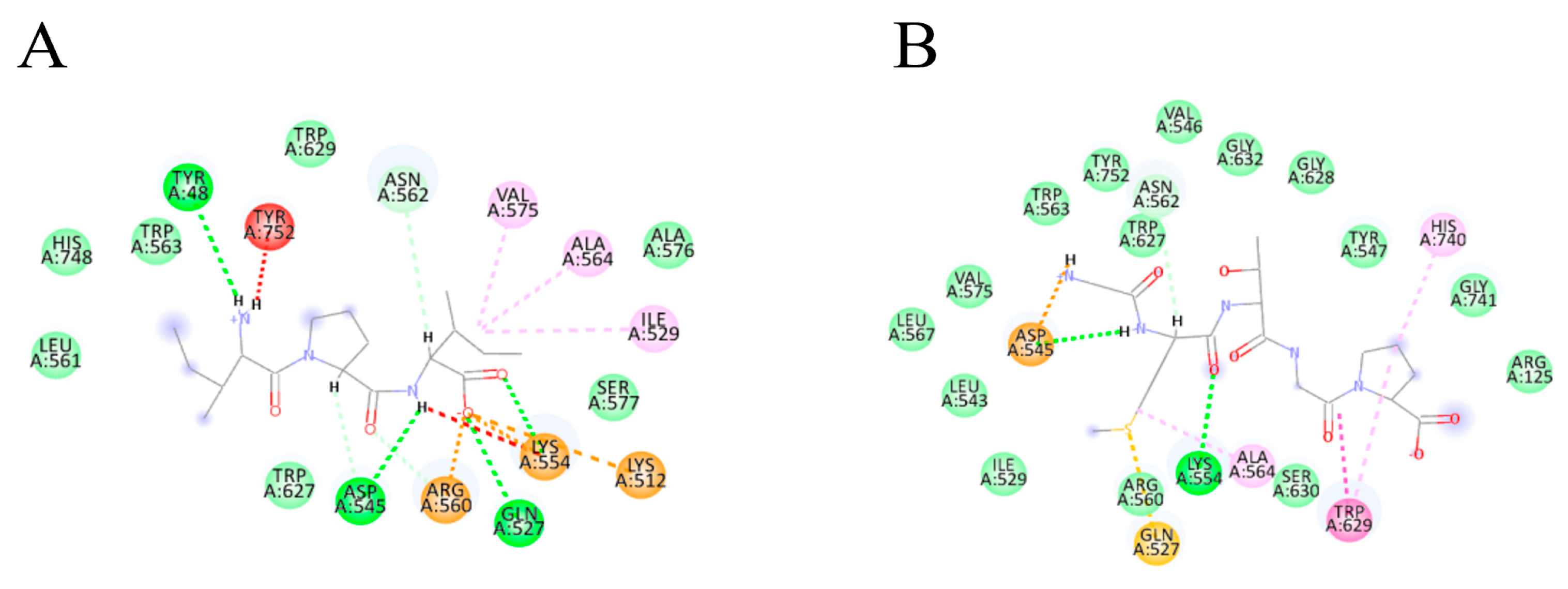
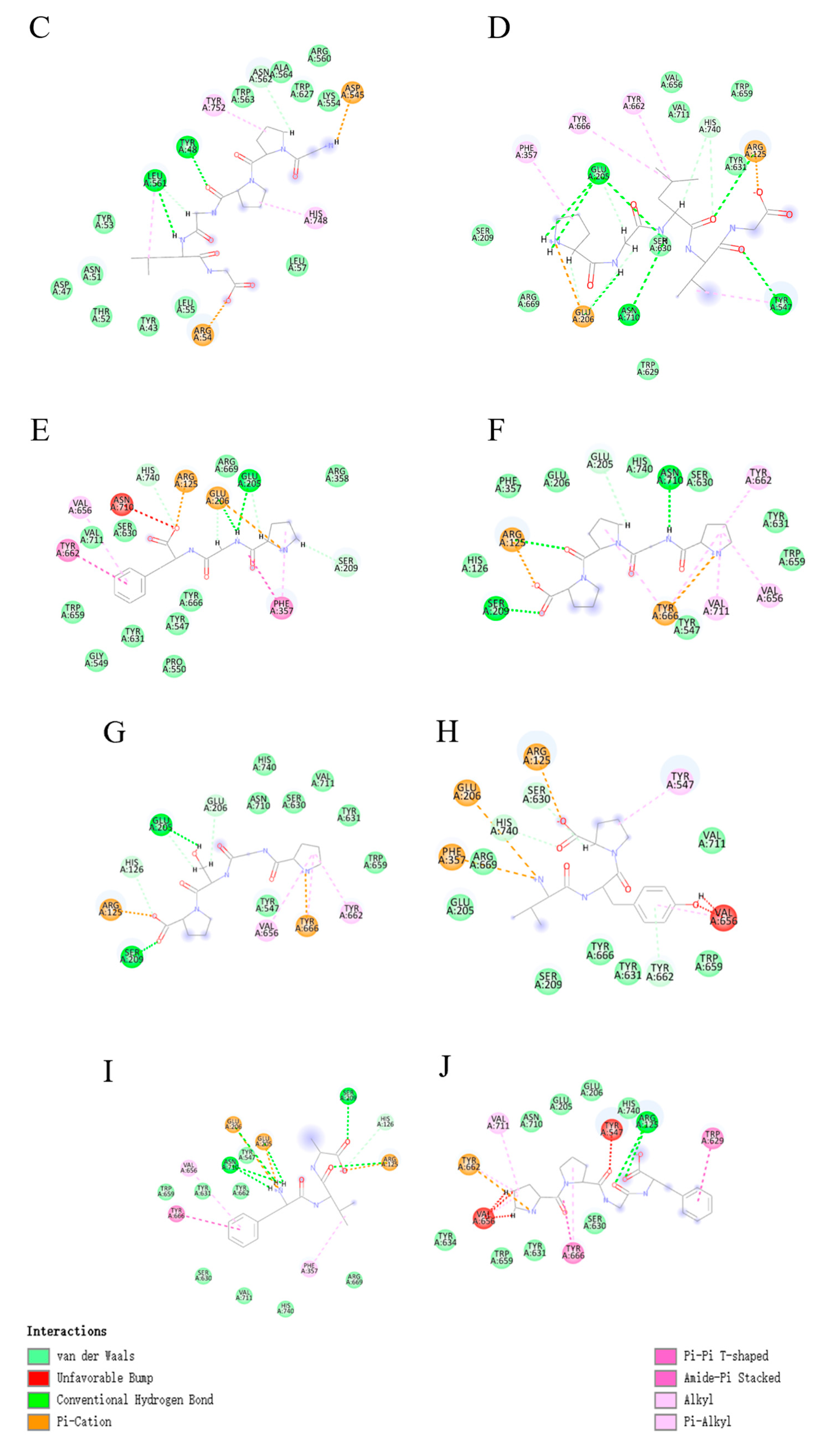
| Peptide | Docking Score | Hydrophobicity (kcal/mol) | Binding Atoms | Distance (Å) | Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPI (control) | −105.877 | +5.80 | TYR48 ASP545 GLN527 LYS544 | 2.75 2.31 2.23 2.50 | Hydrogen bond |
| N/A | N/A | alkyl bonds | |||
| GMTGP | −146.637 | +9.92 | ASP545 LYS544 | 2.93 2.10 | Hydrogen bond |
| TRP629 TRP629 HIS740 | 4.60 5.26 5.27 | alkyl bonds | |||
| GPPGLG | −131.363 | +10.38 | LEU561 TYR48 | 2.83 2.08 | Hydrogen bond |
| LEU561 HIS748 TYR752 | 4.63 4.62 5.27 | alkyl bonds | |||
| PGLVG | −153.308 | +8.63 | GLU205 GLU205 GLU205 GLU206 ASN710 TYR547 ARG125 | 2.88 2.90 3.07 1.98 2.20 2.73 2.19 | Hydrogen bond |
| PHE357 TYR666 TYR662 TYR547 | 4.07 5.18 4.90 4.01 | alkyl bonds | |||
| PGF | −149.957 | +7.48 | GLU206 GLU205 | 1.66 2.56 | Hydrogen bond |
| VAL656 PHE357 | 5.22 4.68 | alkyl bonds | |||
| PGPP | −138.128 | +9.47 | SER209 ARG125 ASN710 | 1.90 2.76 2.75 | Hydrogen bond |
| TYR666 TYR666 VAL711 VAL656 TYR662 | 4.91 5.37 5.23 4.34 4.26 | alkyl bonds | |||
| PGSP | −137.463 | +9.79 | SER209 GLU205 | 1.28 2.05 | Hydrogen bond |
| VAL656 TYR666 TYR662 | 4.88 4.91 4.38 | alkyl bonds | |||
| VYP | −143.971 | +6.87 | TYR662 HIS740 SER630 | 6.77 4.72 4.25 | Hydrogen bond |
| VAL656 TYR547 | 7.25 6.10 | alkyl bonds | |||
| FVA | −154.863 | +6.23 | ASN710 ASN710 GLU206 GLU205 SER209 ARG125 | 4.79 5.27 5.21 4.82 3.99 4.84 | Hydrogen bond |
| TYR666 PHE357 VAL656 | 5.21 5.89 6.96 | alkyl bonds | |||
| PPGF | −154.322 | +7.62 | ARG125 ARG125 | 5.75 5.91 | Hydrogen bond |
| VAL711 TYR666 TYR662 | 6.24 5.88 5.58 | alkyl bonds |
| Peptide Sequences | Allergen FP | ToxinPred | Peptide Cutter | Molecular Weight (Da) | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VYP | Probable allergen | Non-toxin | 2 | 377.19 | 398.87 ± 47.43 a |
| FVA | Probable non-allergen | Non-toxin | 1 | 335.18 | 402.02 ± 5.28 a |
| PPGF | Probable non-allergen | Non-toxin | 4 | 416.21 | 4.63 ± 1.56 b |
| PGLVG | Probable non-allergen | Non-toxin | 3 | 441.26 | 110.20 ± 43.06 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Zhao, L.; Xie, Y.; Tan, Y. Purification and Identification of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Foods 2024, 13, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172644
Zheng H, Zhao L, Xie Y, Tan Y. Purification and Identification of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Foods. 2024; 13(17):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172644
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Hanzhi, Leyan Zhao, Yushuo Xie, and Yuqing Tan. 2024. "Purification and Identification of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis)" Foods 13, no. 17: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172644
APA StyleZheng, H., Zhao, L., Xie, Y., & Tan, Y. (2024). Purification and Identification of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bighead Carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis). Foods, 13(17), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13172644





