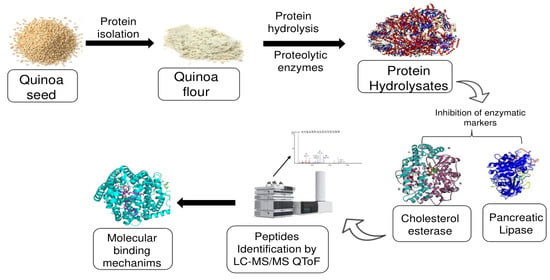
Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials (Quinoa Seeds) and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Quinoa Protein Isolate
2.3. Quinoa Protein Hydrolysate Production
2.4. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH%)
2.5. Anti-hypercholesterolemia Assays
2.5.1. Determination of Pancreatic Lipase (PL) Inhibitory Activity of QPHs
2.5.2. Determination of Cholesterol Esterase Inhibitory Activity of QPHs
2.6. Peptide Identification
2.6.1. Sequencing of Peptides Implied in PL and CEase-Inhibitory Activities Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Quadrupole Time-of-Flight (LC-MS Q T-O-F)
2.6.2. Potential Biologically Active Peptides Selection Using PeptideRanker
2.6.3. Selection of Identified PL and CEase Inhibitory Peptides Using Peptide Ranker
2.7. Molecular Docking
2.7.1. Preparation of Protein Structure
2.7.2. Active Site Identification and Grid Generation
2.7.3. Peptide Docking and Binding Free Energy Calculation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results & Discussion
3.1. Degree of Hydrolysis (DH%)
3.2. Cholesterol Esterase Inhibitory Activity
3.3. Pancreatic Lipase (PL) Inhibitory Activity
3.4. Selection and Identification of Cholesterol Esterase Inhibitory Peptides from Selected QPHs
3.5. Identification of PL Inhibitory Peptides
3.6. Molecular Docking of Shortlisted Peptides in the Active Site of Human and Bovine CEase
3.7. Molecular Docking of Identified Peptides in the Active Site of Human and Porcine PL
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adisakwattana, S.; Moonrat, J.; Srichairat, S.; Chanasit, C.; Tirapongporn, H.; Chanathong, B.; Ngamukote, S.; Mauml, K.; Sapwarobol, S. Lipid-Lowering mechanisms of grape seed extract (Vitis vinifera L.) and its antihyperlidemic activity. J. Med. Plants Res. 2010, 4, 2113–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.M.; Wang, L.; Gandra, S.R.; Quek, R.G.; Li, L.; Baser, O. Clinical and economic burden associated with cardiovascular events among patients with hyperlipidemia: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2016, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, L.; Palaniswamy, D.; Mohankumar, S.K. Targeting obesity with plant-derived pancreatic lipase inhibitors: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 155, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, F.; Pauly, A.; Rombouts, I.; Jansens, K.J.A.; Deleu, L.J.; Delcour, J.A. Proteins of Amaranth (Amaranthus spp.), Buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp.), and Quinoa (Chenopodium spp.): A Food Science and Technology Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Le Maux, S.; Dubrulle, C.; Barre, C.; FitzGerald, R.J. Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) protein hydrolysates with in vitro dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory and antioxidant properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Omar, L.S.; Kamal, H.; Kilari, B.P.; Maqsood, S. Multi-functional bioactive properties of intact and enzymatically hydrolysed quinoa and amaranth proteins. LWT 2019, 110, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hao, Y.; Teng, C.; Yao, Y.; Ren, G. Functional properties and adipogenesis inhibitory activity of protein hydrolysates from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 2103–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boachie, R.; Yao, S.; Udenigwe, C.C. Molecular mechanisms of cholesterol-lowering peptides derived from food proteins. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 20, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Arnoldi, A.; Aiello, G. Soybean peptides exert multifunctional bioactivity modulating 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coa reductase and dipeptidyl peptidase-IV targets in vitro. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 4824–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, H.L.R.; Peralta, J.P.; Tejano, L.A.; Chang, Y.-W. In silico and in vitro assessment of portuguese oyster (Crassostrea angulata) proteins as precursor of bioactive peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awosika, T.O.; Aluko, R.E. Inhibition of the in vitro activities of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase by yellow field pea (Pisum sativum L.) protein hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Shoemaker, C.F. Fractionation and identification of a novel hypocholesterolemic peptide derived from soy protein Alcalase hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2007, 40, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, F.F.; Mudgil, P.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Identification and characterization of cholesterol esterase and lipase inhibitory peptides from amaranth protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. X 2021, 12, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, R.; Monu, E. Functional and bioactive properties of quinoa seed protein hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Jobe, B.; Kamal, H.; Alameri, M.; Al Ahbabi, N.; Maqsood, S. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, α-amylase, and angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory properties of novel camel skin gelatin hydrolysates. LWT 2019, 101, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Kilari, B.P.; Kamal, H.; Olalere, O.A.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Multifunctional bioactive peptides derived from quinoa protein hydrolysates: Inhibition of α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-IV and angiotensin I converting enzymes. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 96, 103130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.H.; Qiao, R.; Xin, L.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Shan, B.; Ghodsi, A.; Li, M. Deep learning enables de novo peptide sequencing from data-independent-acquisition mass spectrometry. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooney, C.; Haslam, N.J.; Pollastri, G.; Shields, D.C. Towards the improved discovery and design of functional peptides: Common features of diverse classes permit generalized prediction of bioactivity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabuco, L.G.; Lise, S.; Petsalaki, E.; Russell, R.B. PepSite: Prediction of peptide-binding sites from protein surfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W423–W427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sussman, J.L.; Lin, D.; Jiang, J.; Manning, N.O.; Prilusky, J.; Ritter, O.; Abola, E.E. Protein Data Bank (PDB): Database of three-dimensional structural information of biological macromolecules. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1998, 54, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger-Suite. Protein Preparation Wizard, Prime; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, J.L.; Beard, H.S.; Cao, Y.; Cho, A.E.; Damm, W.; Farid, R.; Felts, A.K.; Halgren, T.A.; Mainz, D.T.; Maple, J.R. Integrated modeling program, applied chemical theory (IMPACT). JCoCh 2005, 26, 1752–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafi, M.A.; Hashim, S.N.; Chay, S.Y.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Zarei, M.; Muhammad, K.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Saari, N. High angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of Alcalase-digested green soybean (Glycine max) hydrolysates. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi-Yekta, M.; Nouri, L.; Azizi, M.H. The effects of hydrolysis condition on antioxidant activity of protein hydrolyzate from quinoa. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambigaipalan, P.; Shahidi, F. Date seed flour and hydrolysates affect physicochemical properties of muffin. Food Biosci. 2015, 12, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Baba, W.N.; Kamal, H.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Hassan, H.M.; Ayoub, M.A.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. A comparative investigation into novel cholesterol esterase and pancreatic lipase inhibitory peptides from cow and camel casein hydrolysates generated upon enzymatic hydrolysis and in-vitro digestion. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, W.N.; Mudgil, P.; Baby, B.; Vijayan, R.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. New insights into the cholesterol esterase-and lipase-inhibiting potential of bioactive peptides from camel whey hydrolysates: Identification, characterization, and molecular interaction. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7393–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-W.; Lin, H.-T.V.; Huang, L.-W.; Lin, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H. Purification and identification of cholesterol micelle formation inhibitory peptides of hydrolysate from high hydrostatic pressure-assisted protease hydrolysis of fermented seabass byproduct. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafar, S.; Kamal, H.; Mudgil, P.; Hassan, H.M.; Maqsood, S. Camel whey protein hydrolysates displayed enhanced cholesteryl esterase and lipase inhibitory, anti-hypertensive and anti-haemolytic properties. LWT 2018, 98, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Baby, B.; Ngoh, Y.-Y.; Vijayan, R.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Identification and molecular docking study of novel cholesterol esterase inhibitory peptides from camel milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 10748–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgil, P.; Kamal, H.; Yuen, G.C.; Maqsood, S. Characterization and identification of novel antidiabetic and anti-obesity peptides from camel milk protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2018, 259, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasko, P.; Barton, H.; Zagrodzki, P.; Izewska, A.; Krosniak, M.; Gawlik, M.; Gawlik, M.; Gorinstein, S. Effect of diet supplemented with quinoa seeds on oxidative status in plasma and selected tissues of high fructose-fed rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2010, 65, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, T.; Watanabe, N.; Yuhara, K.; Itoh, S.; Suda, S.; Tsuruoka, Y.; Nakatsugawa, K.; Konishi, Y. Hypocholesterolemic effect of protein isolated from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) seeds. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2005, 11, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, S.; Futamura, Y.; Miwa, K.; Awano, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Kanamaru, Y.; Tadashi, K.; Kuwata, T. Identification of novel hypocholesterolemic peptides derived from bovine milk beta-lactoglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, H.; Mudgil, P.; Bhaskar, B.; Fisayo, A.F.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Amaranth proteins as potential source of bioactive peptides with enhanced inhibition of enzymatic markers linked with hypertension and diabetes. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 101, 103308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Shieh, C.-T.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Hwang, C.-I.; Lu, C.-P.; Chen, G.-H. Structure-reactivity probes for active site shapes of cholesterol esterase by carbamate inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1999, 1431, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoh, Y.-Y.; Choi, S.B.; Gan, C.-Y. The potential roles of Pinto bean (Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto) bioactive peptides in regulating physiological functions: Protease activating, lipase inhibiting and bile acid binding activities. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siow, H.-L.; Choi, S.-B.; Gan, C.-Y. Structure–activity studies of protease activating, lipase inhibiting, bile acid binding and cholesterol-lowering effects of pre-screened cumin seed bioactive peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 27, 600–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Singh, J.V.; Gupta, M.K.; Singh, P.; Sharma, S.; Nepali, K.; Bedi, P.M.S. Benzoflavones as cholesterol esterase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.-H.; Miercke, L.J.; Krucinski, J.; Starr, J.R.; Saenz, G.; Wang, X.; Spilburg, C.A.; Lange, L.G.; Ellsworth, J.L.; Stroud, R.M. Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 Å: Novel structural features involved in lipase activation. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzyan, S.; Wang, C.-S.; Downs, D.; Hunter, B.; Zhang, X.C. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human bile salt activated lipase. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Fang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Huang, D.; Yang, C. Structure and function of pancreatic lipase-related protein 2 and its relationship with pathological states. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample | DH (%) | CEase (mg/mL) | PL (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| QPI | - | 1.01 ± 0.03 e | 10.4 ± 0.14 d |
| QB-2 | 34.99 ± 0.92 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 c | 1.97 ± 0.03 b |
| QB-4 | 41.91 ± 0.36 b | 0.64 ± 0.02 bc | 1.03 ± 0.01 a |
| QB-6 | 51.91 ± 2.03 c | 0.63 ± 0.01 bc | 0.90 ± 0.00 a |
| QC-2 | 36.01 ± 3.08 a | 0.51 ± 0.01 a | 2.90 ± 0.11 c |
| QC-4 | 44.09 ± 0.47 b | 0.55 ± 0.00 ab | 1.51 ± 0.06 ab |
| QC-6 | 66.05 ± 1.60 d | 0.55 ± 0.01 ab | 0.78 ± 0.04 a |
| QP-2 | 45.05 ± 1.00 b | 0.80 ± 0.02 d | 3.32 ± 0.52 c |
| QP-4 | 46.01 ± 0.80 b | 0.88 ± 0.02 d | 1.53 ± 0.03 ab |
| QP-6 | 63.3 ± 2.66 d | 0.87 ± 0.01 d | 1.08 ± 0.02 ab |
| Peptide | p-Value | Peptide Residues | Bound Residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFE | 0.04342 | F1, F2, E3 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| DFTF | 0.03113 | D1, F2, T3, F4 | Phe235, Trp236, Tyr279, His283, Tyr284 |
| DFLM | 0.01757 | D1, F2, L3, M4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| ML | 0.04441 | M1, L2 | Phe235, Trp236, His283 |
| CDCP | 0.04734 | C1, C3, P4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| CYTF | 0.01539 | C1, Y2, T3, F4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| FSAGGLP | 0.3886 | G5, L6, P7 | Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284 |
| MLLL | 0.05859 | M1, L2, L3, L4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| MYLY | 0.1116 | M1, Y2, L3, Y4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| QHPHGLGALCAAPPST | 0.04033 | Q1, H2, P3, G7, L9, C10, P14, S15 | Gy107, Ala108 *, Ser194 *, Ala195 *, Ser220, Trp227 *, Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284, Leu285, Phe324 *, Phe393, His435 * |
| KIVLDSDDPLFGGF | 0.2461 | I2, V3, D7, D8, P9, L10, F11 | Ala108 *, Ser194 *, Trp227 *, Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284, Leu285, Phe324 *, Phe393, His435 * |
| AHCGGLPY | 0.2596 | A1, H2, C3, G4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| LYNDWDLR | 0.379 | W5, D6, L7, R8 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| PGGAR | 0.2249 | G3, A4, R5 | Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284 |
| SGPAR | 0.08677 | P3, A4, R5 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| LPLLR | 0.04626 | P2, L3, L4, R5 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| KPGGTAGSALPRPAHW | 0.3388 | K1, P2, G3, L10 | Phe235, Tyr236, Tyr279, His283, Tyr284, Phe324 * |
| FE | 0.06821 | F1, E2 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| HDSF | 0.09456 | H1, D2, S3, F4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| LR | 0.04441 | L1, R2 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| VYML | 0.08002 | V1, Y2, M3, L4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| RR | 0.02794 | R1, R2 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| LRL | 0.1121 | L1, R2, L3 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| MFVPVPH | 0.3249 | P4, V5, P6 | Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284 |
| HVQGHPALPGVPAHW | 0.02606 | H1, V2, P6, A7, L8, P9, G10, P12, A13, H14 | Ala108 *, Ser194 *, Ala195 *, Ser220, Trp227 *, Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284, Leu285, Phe324 *, Phe393, His435 * |
| AGLR | 0.02471 | A1, G2, L3, R4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| HVASGAGPW | 0.3417 | V2, A3, P8, W9 | Ala108 *, Ser194 *, Ala195 *, Trp227 *, Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284, Phe324 * |
| FTVM | 0.02389 | F1, T2, V3, M4 | Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284 |
| LLPYH | 0.04167 | L2, P3, Y4, H5 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| MVLP | 0.1188 | V2, L3, P4 | Phe235, Trp236, His283 |
| GARR | 0.1087 | G1, A2, R3 | Phe235, Trp236, His283, Tyr284 |
| ASNLDNPSPEGTVM | 0.03203 | D5, N6, P7, S8, E10, T12, V13, M14 | Ala108 *, Ser194 *, Trp227 *, Phe235, Trp236, Arg239, Tyr279, His283, Tyr284, Leu285, Phe324 *, Phe393, His435 * |
| CVLSPL | 0.2097 | V2, S4, P5, L6 | Phe235, Trp236, Tyr279, His283, Tyr284, Val353 |
| HMLH | 0.02838 | H1, M2, L3, H4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| CALVGL | 0.2557 | C1, A2, V4 | Tyr7, Phe12 |
| Peptide | p-Value | Peptide Residues | Bound Residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| FFE | 0.06672 | F1, F2, E3 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Pro181, Phe216 * |
| DFTF | 0.1717 | F2, T3, F4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Pro181, Phe216 * |
| DFLM | 0.08332 | F2, L3, M4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| ML | 0.008899 | M1, L2 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Phe216 * |
| CDCP | 0.2673 | C1, D2, C3 | Lys81, Glu84, Trp253 |
| CYTF | 0.1707 | C1, Y2, T3, F4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 * |
| FSAGGLP | 0.3038 | F1, S2, A3, G4 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| MLLL | 0.009667 | M1, L2, L3, L4 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 * |
| MYLY | 0.05041 | M1, Y2, L3, Y4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| QHPHGLGALCAAPPST | 0.01253 | Q1, H2, P3, H4, L9, C10, A11, A12, P13, P14, S15 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Lys81, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 *, Trp253 |
| KIVLDSDDPLFGGF | 0.05873 | K1, I2, V3, D5, S6, D7, P9, L10, F11, G13, F14 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Ile79, Asp80, Lys81, Glu84, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Pro181, Phe216 *, Trp253, Arg257, His264 * |
| AHCGGLPY | 0.2518 | G5, L6, P7, Y8 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| LYNDWDLR | 0.5264 | L1, Y2, N3, W5 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| PGGAR | 0.2735 | P1, G2, A4 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Glu180, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| SGPAR | 0.1096 | G2, P3, A4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| LPLLR | 0.01133 | L1, P2, L3, L4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Ala179, Glu180, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| KPGGTAGSALPRPAHW | 0.1243 | K1, P2, G3, A9, L10 | Phe78 *, Lys81, Glu84, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Phe216 *, Trp253, His264 * |
| FE | 0.1965 | F1, E2 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Phe216 * |
| HDSF | 0.2314 | H1, S3, F4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| LR | 0.2794 | L1, R2 | Lys81, Glu84, Trp253 |
| VYML | 0.1071 | V1, Y2, M3, L4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| RR | 0.2074 | R1, R2 | Lys81, Glu84, Trp253 |
| LRL | 0.4811 | L1, L3 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Ala179, Glu180, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| MFVPVPH | 0.01305 | F2, V3, P4, P6, H7 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| HVQGHPALPGVPAHW | 0.02747 | H5, P6, A7, L8, P9, H16 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Lys81, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216 *, Trp253, His264 * |
| AGLR | 0.2014 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * | |
| HVASGAGPW | 0.1145 | H1, A6, G7, P8, W9 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Lys81, Glu84, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Phe216 *, Trp253, His264 * |
| FTVM | 0.02278 | F1, T2, V3, M4 | Phe78 *, Try115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| LLPYH | 0.008942 | L1, L2, P3, H5 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| MVLP | 0.006331 | M1, V2, L3, P4 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Ala179, Glu180, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| GARR | 0.1135 | G1, A2, R3, R4 | Lys81, Glu84, Trp253 |
| ASNLDNPSPEGTVM | 0.08445 | A1, S2, N3, L4, N6, P7, S8, P9, E10, V13, M14 | Phe78 *, Asp80, Lys81, Glu84, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Leu154, Ala179, Phe216 *, Trp253, Arg257, His264 * |
| CVLSPL | 0.1236 | L3, S4, P5, L6 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Ala179, Glu180, Pro181, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| HMLH | 0.008295 | H1, M2, L3, H4 | Gly77, Phe78 *, Tyr115, His152 *, Ser153 *, Leu154, Gly155, Ala179, Phe216 * |
| CALVGL | 0.2596 | A2, L3, V4, L6 | Phe78 *, Tyr115, Ser153 *, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216 *, His264 * |
| Peptide | GlideScore (kcal/mol) | MM-GBSA Based Binding Free Energy (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | Salt-Bridge | π-π Interactions | Cation-π Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEase (Human)—PDB ID: 1F6W | |||||||
| HVASGAGPW | −9.07 | −64.32 | Gly107, Asn121, Asn122, Asp434, His435, Gln440, Lys445 | Ile69, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala117, Phe119, Tyr123, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Ile323, Phe324, Ala436, Ile439, Tyr453 | Asp437 | Arg423 | |
| AHCGGLPY | −8.95 | −55.00 | Ile69, Asn121, Leu274, Asp437 | Ile69, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala117, Leu124, Val272, Pro273, Leu274, Ala275, Met281, Leu282, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327, Ala436, Ile439, Tyr453 | Lys445 | ||
| LYNDWDLR | −8.90 | −63.67 | Ile69, Asn121, Pro273, Asp434, Asp437 | Ile69, Ala108, Met111, Ala117, Phe119, Leu124, Val272, Pro273, Leu274, Ala275, Met281, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327, Ala436 | Arg423, Asp437, Lys445 | ||
| MFVPVPH | −8.37 | −94.06 | Asn121, His435 | Tyr105, Ala108, Met111, Ala117, Phe119, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Met281, Leu282, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439, Tyr453 | Lys445 | Trp227 | |
| FSAGGLP | −7.44 | −47.70 | His435, Asp437 | Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Val272, Met281, Leu282, Tyr284, Val285, Phe324, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439 | |||
| HDSF | −7.89 | −44.43 | Gly107, Ala108, Glu193, Asp437, Gln440 | Ala108, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Met281, Leu282, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439, Tyr453 | Asp437 | ||
| LRL | −7.81 | −49.25 | Glu193, Ser194 | Trp103, Tyr105, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Val272, Met281, Leu282, Tyr284, Val285, Phe324, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439 | Glu193 | ||
| LLPYH | −7.57 | −47.61 | Ile69, Glu193, His435, Asp437 | Ile69, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Leu124, Val272, Met281, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327, Ala436, Ile439 | Asp437 | ||
| MYLY | −7.30 | −46.79 | Gly107, His435, Asp437 | Ala108, Met111, Leu124, Ala195, Trp227, Met281, Leu282, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439 | Asp437 | Phe324 | |
| CVLSPL | −7.64 | −65.08 | Gly107, Ser194, Ala436, Asp437 | Ala108, Leu110, Ala117, Leu124, Ala195, Trp227, Val272, Met281, Leu282, Val285, Ile323, Phe324, Ile327Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Ile439 | |||
| CEase (Bovine)—PDB ID: 1AQL | |||||||
| AHCGGLPY | −10.05 | −72.14 | Ser194, Asp434, Asp437 | Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Tyr427, Ala436, Leu439, Tyr453 | Asp434, Asp437 | ||
| MFVPVPH | −9.828 | −87.97 | Thr68 | Ala67, Leu69, Tyr75, Tyr105, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala113, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Trp227 | Arg63 | ||
| Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | |||||||
| LPLLR | −9.218 | −78.64 | Glu193 | Leu69, Trp103, Tyr105, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | Glu193 | ||
| CYTF | −8.261 | −62.93 | Glu193, Ser194, His435 | Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | Glu193 | ||
| FSAGGLP | −8.861 | −73.84 | Ala117 | Tyr75, Tyr105, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala113, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Leu439 | Trp227 | ||
| LLPYH | −8.437 | −76.32 | Gly106, Glu193 | Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | His435 | Phe324, His435 | |
| CVLSPL | −8.980 | −71.06 | Ala113, Ala117, His435 | Tyr75, Tyr105, Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Ala113, Ala117, Leu124, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | Trp227, Phe324 | ||
| PGGAR | −8.680 | −72.64 | Glu193 | Ala108, Leu110, Met111, Tyr125, Ala195, Trp227, Leu272, Leu274, Leu282, Leu285 | Glu193 | Trp227 | |
| Leu323, Phe324, Met327, Leu392, Phe393, Ala436, Leu439 | |||||||
| HDSF | −8.348 | −33.84 | Ala108, Ser194, Ala436 | Ala108, Leu124, Ala195, Trp227, Leu272, Leu282, Leu285, Leu323, Phe324, Leu392, Phe393, Tyr427, Ala436, Leu439 | Asp434, His435 | ||
| HVASGAGPW | −8.884 | −67.55 | Arg63, Gly106, Asn118, Asn122, Asp434, His435, Ala436 | Tyr75, Trp103, Met111, Ala113, Ala117, Phe119, Tyr123, Leu124, Tyr125, Leu323, Met424, Tyr427, Ala436, Leu439, Tyr453 | Asp434, Asp437 | ||
| Peptide | GlideScore (kcal/mol) | MM-GBSA Based Binding Free Energy (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonds | Hydrophobic Interactions | Salt Bridge | π-π Interactions | Cation-π Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LIP (Human)—PDB ID: 1LPB | |||||||
| HVASGAGPW | −11.74 | −46.02 | Phe77, Asp79, Glu233, Lys238, Ala259, His263 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ala207, Ile209, Leu213, Phe215 Val232, Cys237, Trp252, Phe258, Ala259, Ala260, Cys261, Leu264 | Glu233 | ||
| AHCGGLPY | −11.73 | −61.96 | Phe77, Ser152, Asp205, Cys237 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ala207, Ile209, Leu213, Phe215, Trp252, Phe258, Ala259, Ala260, Cys261, Leu264 | Asp205 | Phe215, Lys238 | |
| FSAGGLP | −9.726 | −79.39 | Phe77, Asp79, Tyr114, Thr115, Ser152 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Phe215, Trp252, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264 | Asp79 | ||
| LLPYH | −9.716 | −77.18 | Asp79, Tyr114 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Leu213, Phe215, Trp252, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264, Tyr267 | Asp79 | Tyr114, Phe215 | |
| MFVPVPH | −8.824 | −70.12 | Phe77, Lys238, Ala259, Asp205 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ala207, Leu213, Phe215, Val232, Trp252, Phe258, Ala259, Ala260, Cys261, Leu264 | Asp79 | Phe215, His263 | |
| HDSF | −8.305 | −45.69 | Asp79, Phe77 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Leu213, Phe215, Trp252, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264 | Asp79 | Phe215 | |
| CVLSPL | −8.170 | −68.48 | Phe77 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Leu213, Phe215, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264 | Asp79 | ||
| CYTF | −8.353 | −74.89 | Phe77, Asp79 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Val210, Leu213, Phe215, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264, Tyr267 | Asp79 | ||
| DFTF | −7.716 | −55.27 | Phe77, Asp79, Ser152 | Phe77, Ile78, Trp85, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Phe215, Trp252, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264, Tyr267 | Asp79 | ||
| MYLY | −8.085 | −95.47 | Phe77, Asp79 | Phe77, Ile78, Tyr114, Leu153, Ala178, Pro180, Ile209, Val210, Leu213, Phe215, Trp252, Ala259, Ala260, Leu264 | Asp79 | ||
| LIP (Porcine)—PDB ID: 1ETH | |||||||
| AHCGGLPY | −10.95 | −53.03 | Gly77, Asp80, Asn213, Cys238 | Phe78, Ile79, Trp86, Tyr115, Leu154, Leu214, Phe216, Cys238, Ile242, Phe259 | |||
| Gln239, Lys240, Val260, Asn263 | Val260, Ala261, Cys262, Leu265 | ||||||
| MFVPVPH | −8.583 | −67.89 | Val260, Cys262 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Leu214, Phe216, Cys238, Ile242, Phe259, Val260, Ala261, Cys262, Leu265 | |||
| HVASGAGPW | −10.19 | −80.44 | Phe78, Asn213, Gln234, Gln239 Phe259, Cys262 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Pro212, Leu214, Phe216, Trp253, Phe259, Val260, Ala261, Cys262, Leu265 | Asp80 | Trp253 | |
| LPLLR | −8.602 | −77.53 | Phe78, Asp206 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Ile210, Leu214, Phe216, Trp253, Phe259, Val260, Ala261, Cys262, Leu265 | Asp80, Asp206 | Phe216 | |
| CYTF | −8.164 | −75.32 | Phe78, Asp80 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216, Val260, Ala261, Leu265 | Asp80 | Phe78, Tyr115 | |
| FSAGGLP | −8.144 | −72.31 | Asp206, Leu214, Phe259, Val260 | Phe78, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Leu214, Phe216, Cys238, Phe259, Val260, Ala261, Cys262 | Asp206 | ||
| FFE | −8.202 | −58.14 | Phe78, Asp80 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Phe216, Trp253, Val260, Ala261, Leu265 | Asp80 | Phe216, Trp253 | |
| CDCP | −8.166 | −57.75 | Phe78, Asp80 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216, Trp253, Val260, Ala261, Leu265 | Asp80 | ||
| HDSF | −7.751 | −58.29 | Phe78, Asp80 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Ile210, Phe216, Trp253, Val260, Ala261, Leu265 | Asp80 | ||
| MYLY | −8.308 | −76.41 | Phe78, Asp80, Phe259 | Phe78, Ile79, Tyr115, Leu154, Ala179, Pro181, Leu214, Phe216, Trp253, Phe259, Val260, Ala261, Leu265 | Asp80 | Phe216, His264 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ajayi, F.F.; Mudgil, P.; Jobe, A.; Antony, P.; Vijayan, R.; Gan, C.-Y.; Maqsood, S. Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides. Foods 2023, 12, 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061327
Ajayi FF, Mudgil P, Jobe A, Antony P, Vijayan R, Gan C-Y, Maqsood S. Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides. Foods. 2023; 12(6):1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061327
Chicago/Turabian StyleAjayi, Feyisola Fisayo, Priti Mudgil, Amie Jobe, Priya Antony, Ranjit Vijayan, Chee-Yuen Gan, and Sajid Maqsood. 2023. "Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides" Foods 12, no. 6: 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061327
APA StyleAjayi, F. F., Mudgil, P., Jobe, A., Antony, P., Vijayan, R., Gan, C.-Y., & Maqsood, S. (2023). Novel Plant-Protein (Quinoa) Derived Bioactive Peptides with Potential Anti-Hypercholesterolemic Activities: Identification, Characterization and Molecular Docking of Bioactive Peptides. Foods, 12(6), 1327. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12061327