DPF-Nutrition: Food Nutrition Estimation via Depth Prediction and Fusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We proposed a novel monocular image-based nutrition estimation method based on Depth Prediction and Fusion, referred as DPF-Nutrition. It was the first attempt to incorporate depth prediction and RGB-D fusion techniques in vision-based nutrition estimation.
- We designed an RGB-D fusion module that incorporated the proposed cross-modal attention block (CAB) and multi-scale fusion network to fully exploit the informative image features for nutrition estimation.
- Our proposed DPF-Nutrition demonstrated effectiveness in accurately estimating multiple nutrients, which has been evaluated on the public dataset Nutrition5k.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Methods
- Module1: Depth prediction module aims to reconstruct the 3D depth information based on 2D monocular images. The depth prediction module employs a vision transformer as the encoder which can reduce the loss of granularity and feature resolution for more accurate 3D information recovery.
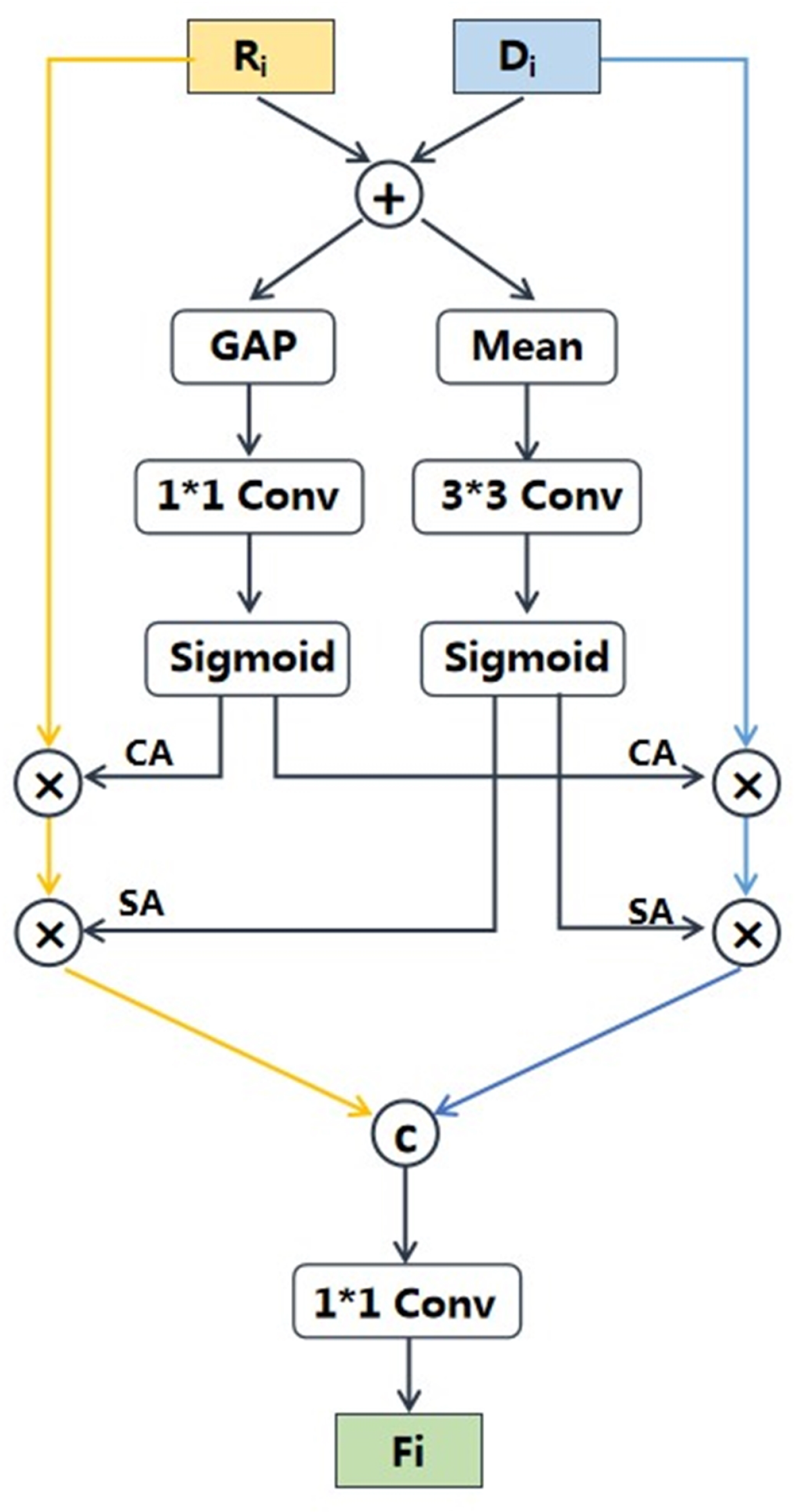
- Module2: RGB-D fusion module is specifically designed to fully leverage the features of RGB and predicted depth images for nutrition estimation. This module integrates the proposed multi-scale fusion network and cross-modal attention block (CAB). The multi-scale fusion network effectively enriches the intricate semantic features of fine-grained food images, while the CAB further enhances the complementarity of RGB and depth features.
2.2.1. The Depth Prediction Module
2.2.2. RGB-D Fusion Module
2.2.3. Loss Function
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Detail
3.2. Backbone Comparison
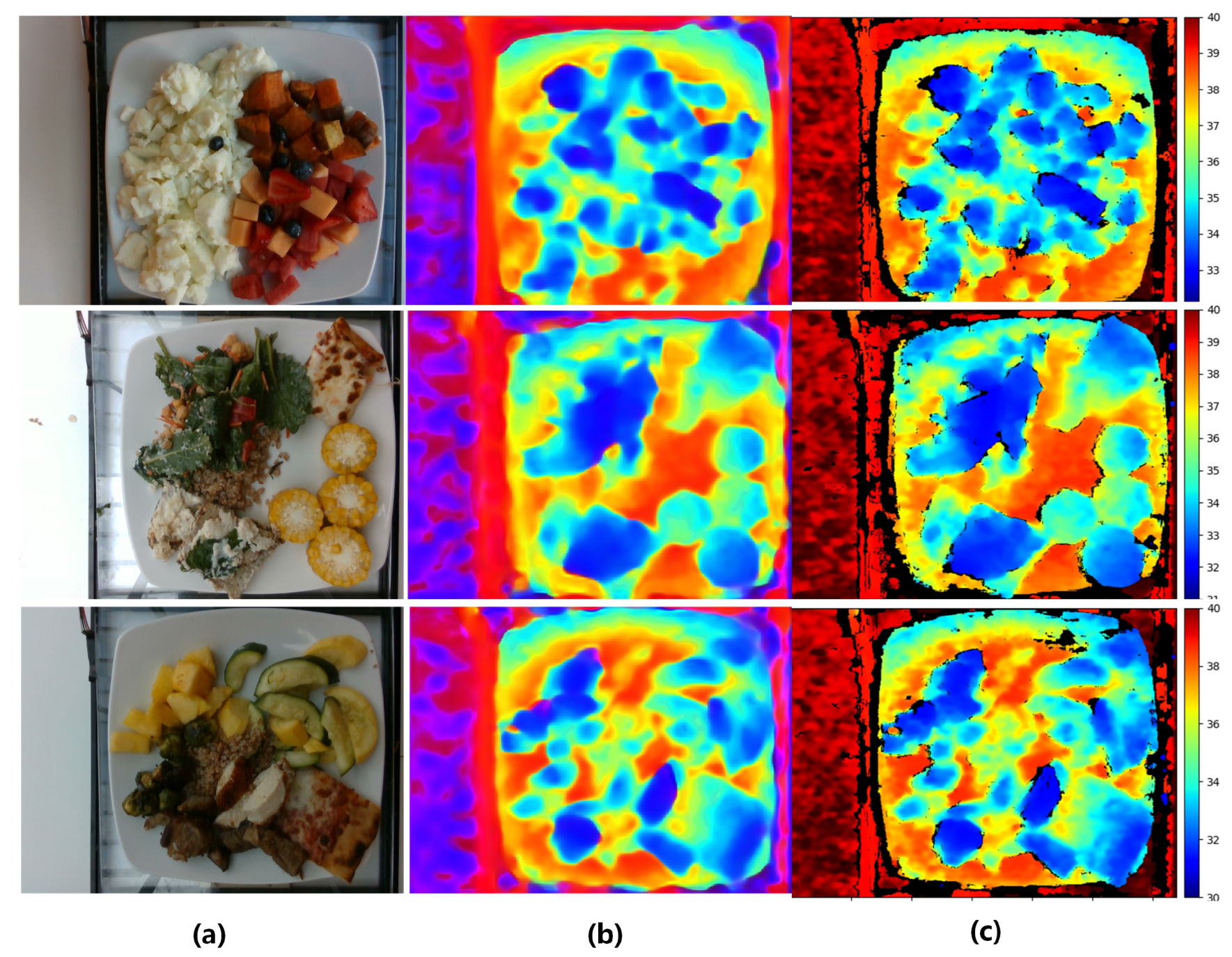
3.3. Depth Prediction Analysis
3.4. Cross-Modal Fusion Analysis
3.5. Method Comparison
3.6. Ablation Study
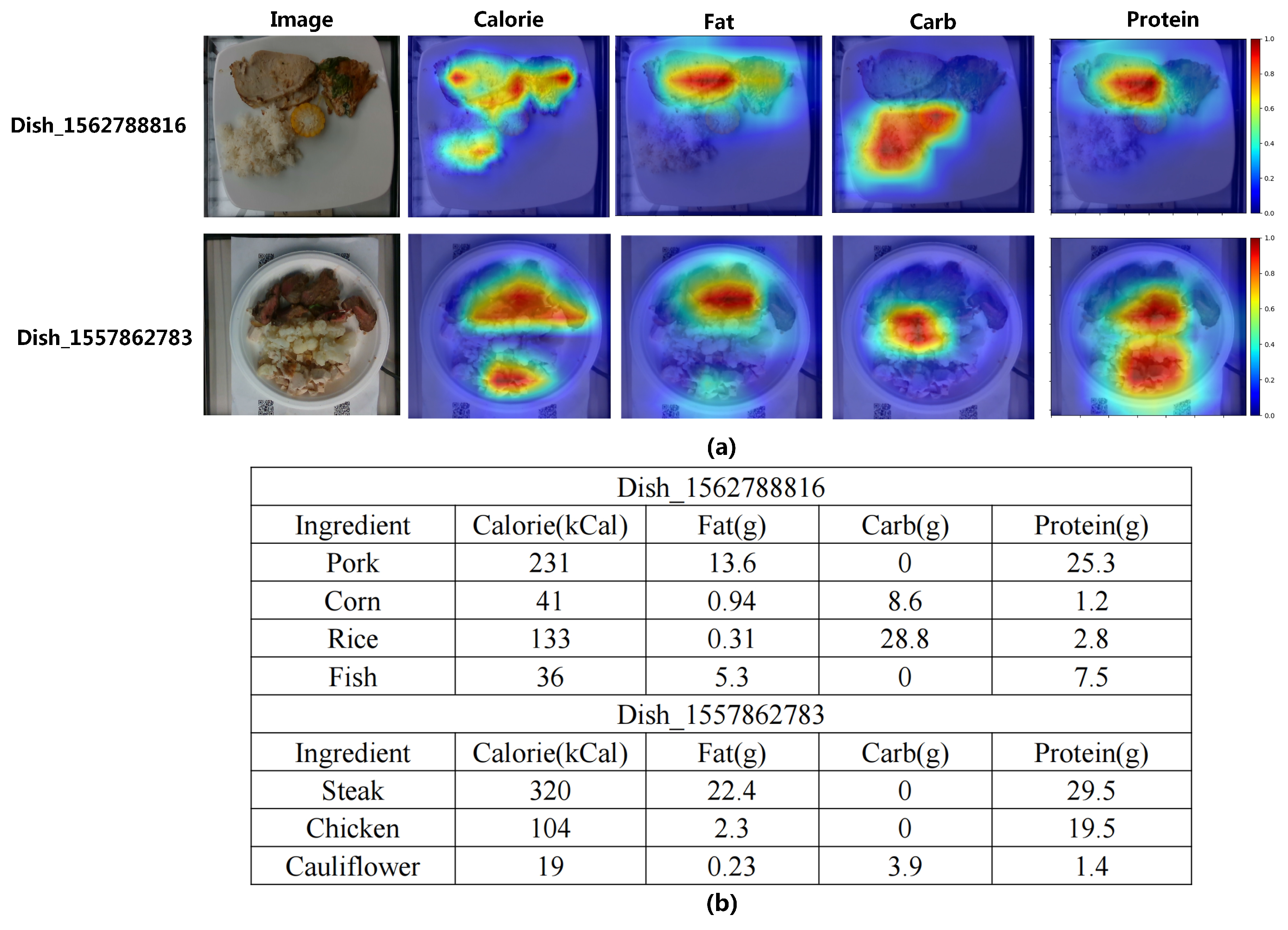
3.7. Visualization Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Greenhalgh, S. Soda industry influence on obesity science and policy in China. J. Public Health Policy 2019, 40, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J. 2011 Food & Health Survey Consumer Attitudes toward Food Safety, Nutrition & Health; International Food Information Council Foundation: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Mittl, B.; Zimmerman, T.P.; Thompson, F.E.; Bingley, C.; Willis, G.; Islam, N.G.; Baranowski, T.; McNutt, S.; et al. The automated self-administered 24-hour dietary recall (ASA24): A resource for researchers, clinicians and educators from the National Cancer Institute. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, A.; Johnston, N.; Rathod, V.; Korattikara, A.; Gorban, A.; Silberman, N.; Guadarrama, S.; Papandreou, G.; Huang, J.; Murphy, K.P. Im2Calories: Towards an automated mobile vision food diary. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1233–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ege, T.; Yanai, K. Image-based food calorie estimation using knowledge on food categories, ingredients and cooking directions. In Proceedings of the on Thematic Workshops of ACM Multimedia 2017, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, F.P.W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, J.; Lo, B. Image-based food classification and volume estimation for dietary assessment: A review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 1926–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M.; Zhu, Z.; Yu, Q.; Divakaran, A.; Sawhney, H. Recognition and volume estimation of food intake using a mobile device. In Proceedings of the 2009 Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Snowbird, UT, USA, 7–8 December 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehais, J.; Anthimopoulos, M.; Shevchik, S.; Mougiakakou, S. Two-view 3D reconstruction for food volume estimation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 19, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Fang, S.; Mao, R.; He, J.; Wright, J.L.; Kerr, D.A.; Boushey, C.J.; Zhu, F. Towards learning food portion from monocular images with cross-domain feature adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 23rd International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing (MMSP), Tampere, Finland, 6–8 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thames, Q.; Karpur, A.; Norris, W.; Xia, F.; Panait, L.; Weyand, T.; Sim, J. Nutrition5k: Towards automatic nutritional understanding of generic food. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8903–8911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Hou, S.; Jia, W.; Zheng, Y. Rapid Non-Destructive Analysis of Food Nutrient Content Using Swin-Nutrition. Foods 2022, 11, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, S.; Shao, Z.; Mao, R.; Fu, C.; Delp, E.J.; Zhu, F.; Kerr, D.A.; Boushey, C.J. Single-view food portion estimation: Learning image-to-energy mappings using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Stathopoulou, T.; Vasiloglou, M.F.; Christodoulidis, S.; Stanga, Z.; Mougiakakou, S. An artificial intelligence-based system to assess nutrient intake for hospitalised patients. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, G.; Shao, Z.; Zhu, F. Image Based Food Energy Estimation With Depth Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 5th International Conference on Multimedia Information Processing and Retrieval (MIPR), Virtual, 2–4 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Min, W.; Hou, S.; Luo, M.; Li, T.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, S. Vision-based food nutrition estimation via RGB-D fusion network. Food Chem. 2023, 424, 136309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Chen, K.; Shi, J.; Feng, H.; Ouyang, W.; Lin, D. Libra r-cnn: Towards balanced learning for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019; pp. 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montville, J.B.; Ahuja, J.K.; Martin, C.L.; Heendeniya, K.Y.; Omolewa-Tomobi, G.; Steinfeldt, L.C.; Anand, J.; Adler, M.E.; LaComb, R.P.; Moshfegh, A. USDA food and nutrient database for dietary studies (FNDDS), 5.0. Procedia Food Sci. 2013, 2, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijbom, O.; Joshi, N.; Morris, D.; Saponas, S.; Khullar, S. Menu-match: Restaurant-specific food logging from images. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 5–9 January 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, J. Computer vision-based food calorie estimation: Dataset, method, and experiment. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.07632. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, S.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F.; Delp, E.J.; Boushey, C.J. Single-view food portion estimation based on geometric models. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), Miami, FL, USA, 14–16 December 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, Y.; Ege, T.; Cho, J.; Yanai, K. Depthcaloriecam: A mobile application for volume-based foodcalorie estimation using depth cameras. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Multimedia Assisted Dietary Management, Nice, France, 21 October 2019; pp. 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranftl, R.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Koltun, V. Vision transformers for dense prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 12179–12188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5583–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Bahador, N.; Ferreira, D.; Tamminen, S.; Kortelainen, J. Deep learning–based multimodal data fusion: Case study in food intake episodes detection using wearable sensors. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2021, 9, e21926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chennupati, S.; Sistu, G.; Yogamani, S.; A Rawashdeh, S. Multinet++: Multi-stream feature aggregation and geometric loss strategy for multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–17 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Min, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Kang, L.; Wei, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, S. Large scale visual food recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 9932–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laina, I.; Rupprecht, C.; Belagiannis, V.; Tombari, F.; Navab, N. Deeper depth prediction with fully convolutional residual networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, K.; Cheng, T.; Jiang, B.; Deng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Mu, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, X.; et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucott, L.; Poobalan, A.; Smith, W.C.S.; Avenell, A.; Jung, R.; Broom, J. Effects of weight loss in overweight/obese individuals and long-term hypertension outcomes: A systematic review. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Miura, J.; Lu, L.X.; Bernier, M.; DeCabo, R.; Lane, M.A.; Roth, G.S.; Ingram, D.K. Circulating adiponectin levels increase in rats on caloric restriction: The potential for insulin sensitization. Exp. Gerontol. 2004, 39, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poli, V.F.S.; Sanches, R.B.; dos Santos Moraes, A.; Fidalgo, J.P.N.; Nascimento, M.A.; Bresciani, P.; Andrade-Silva, S.G.; Cipullo, M.A.T.; Clemente, J.C.; Caranti, D.A. The excessive caloric intake and micronutrient deficiencies related to obesity after a long-term interdisciplinary therapy. Nutrition 2017, 38, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
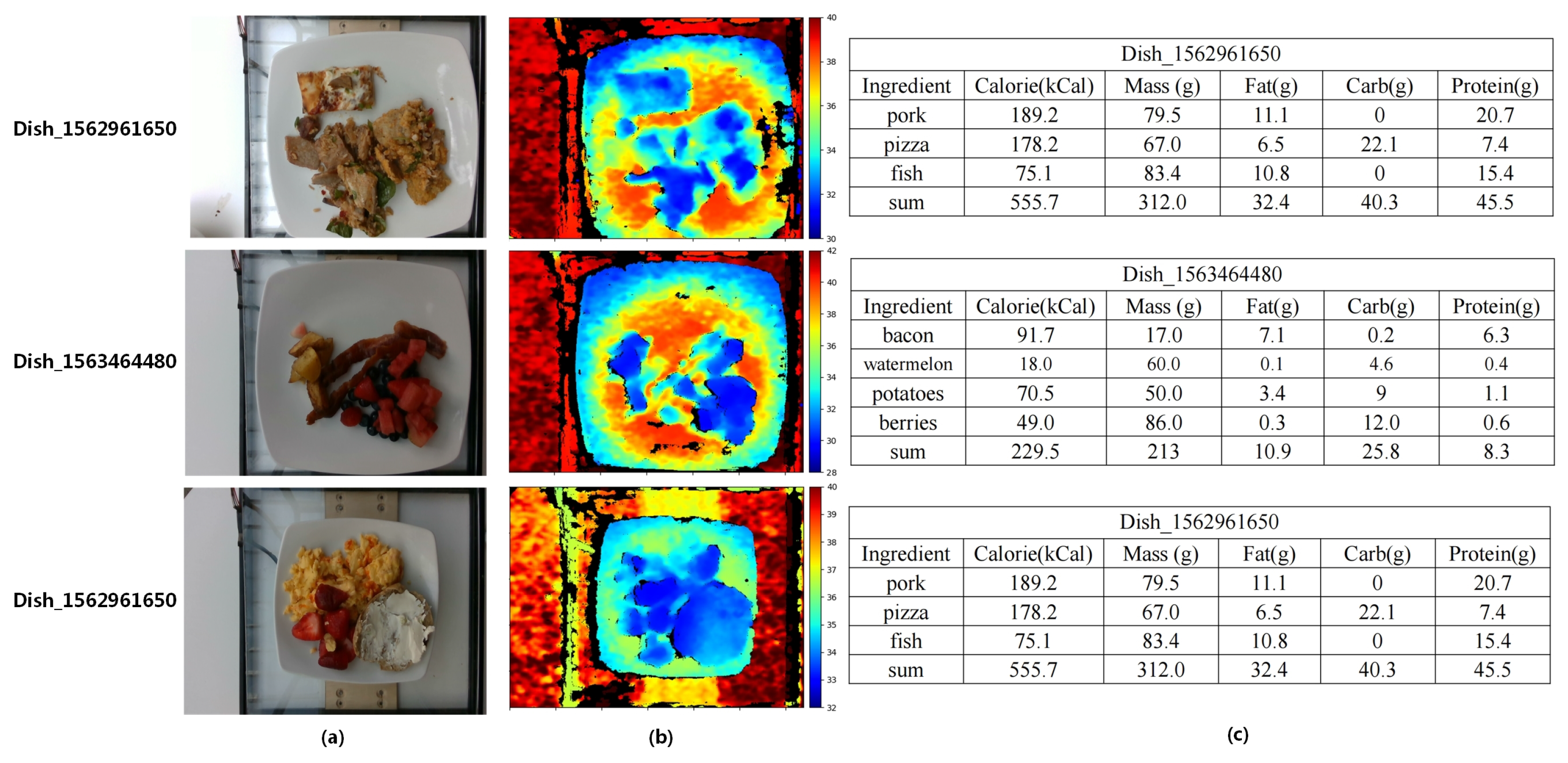

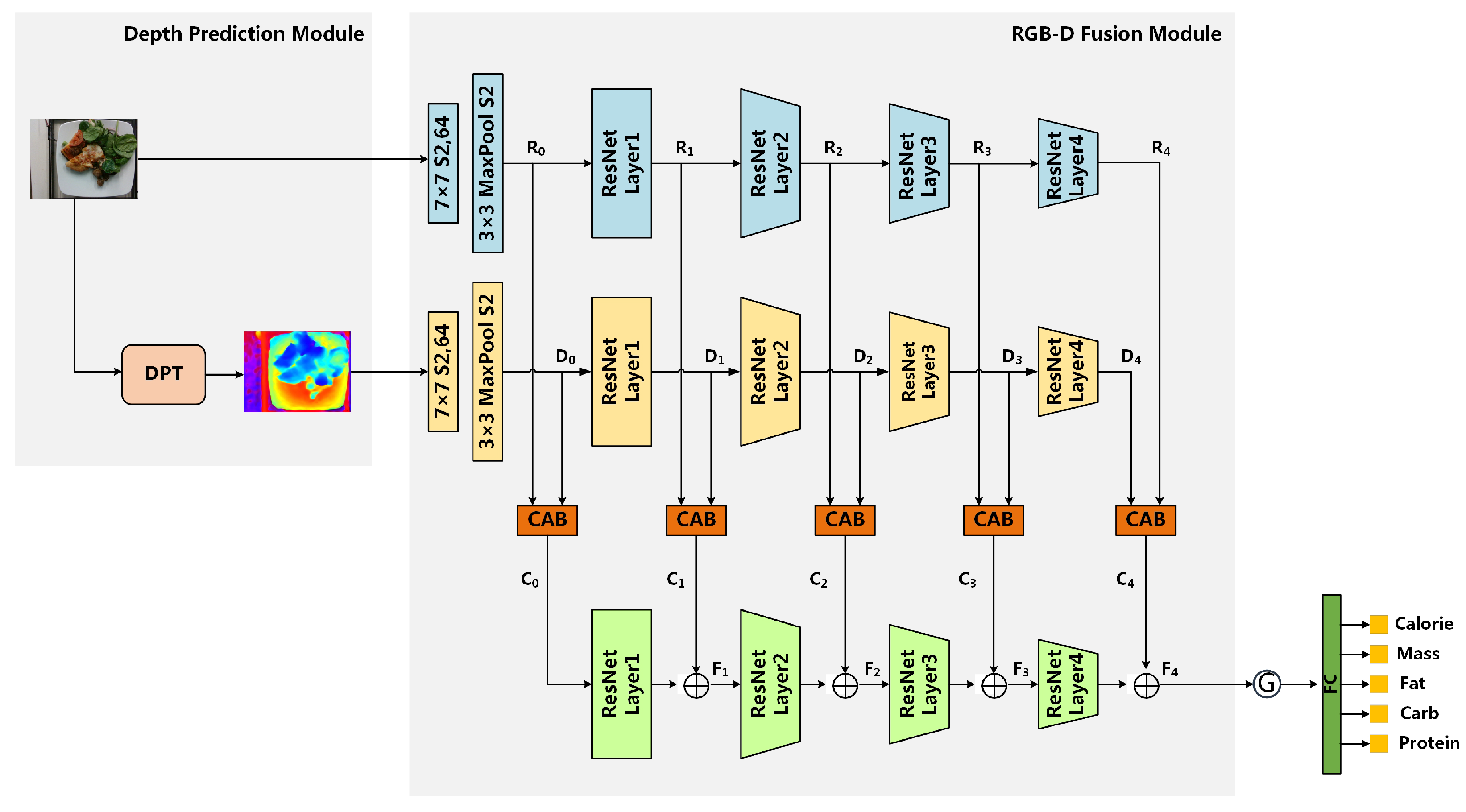
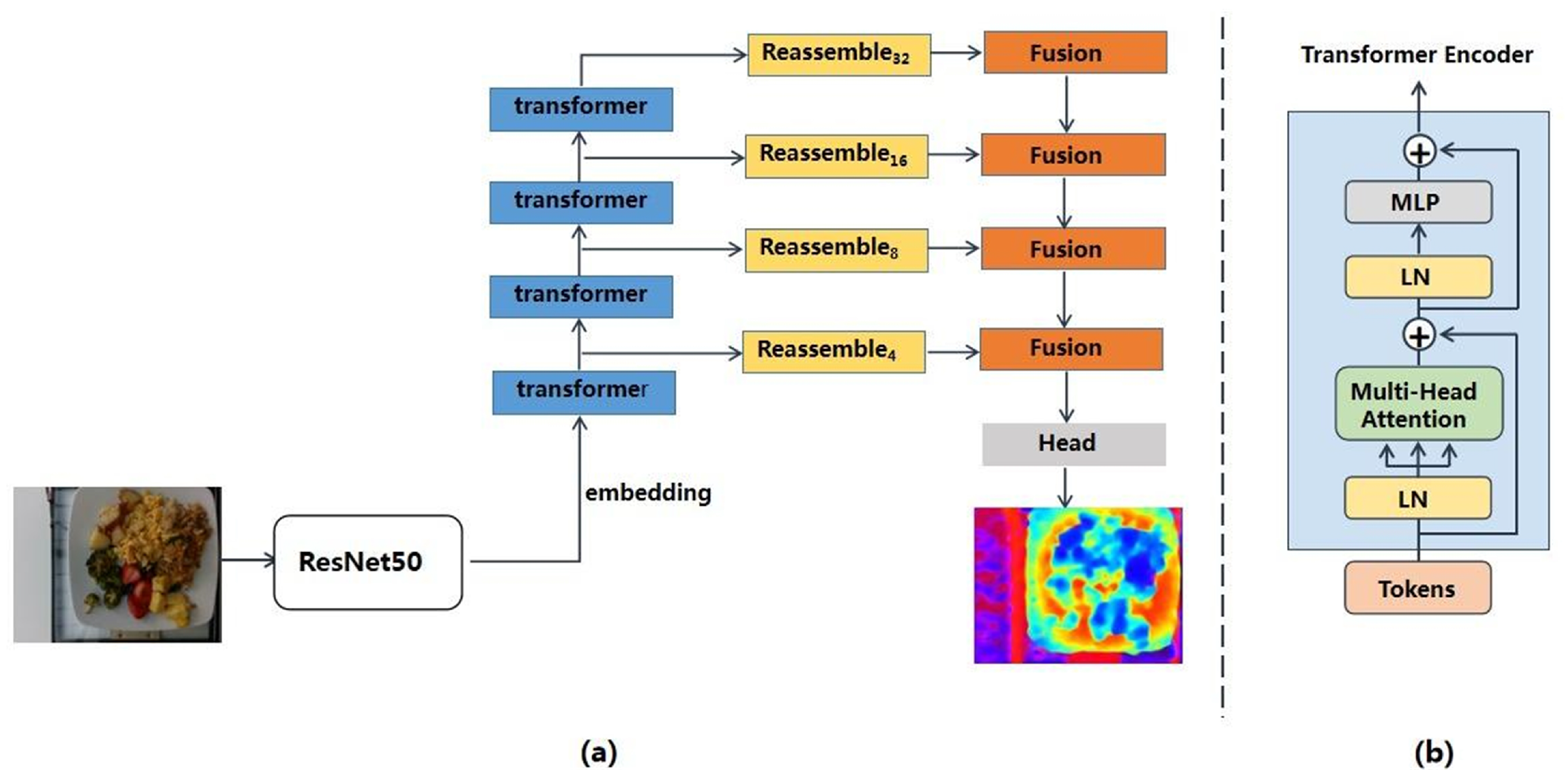
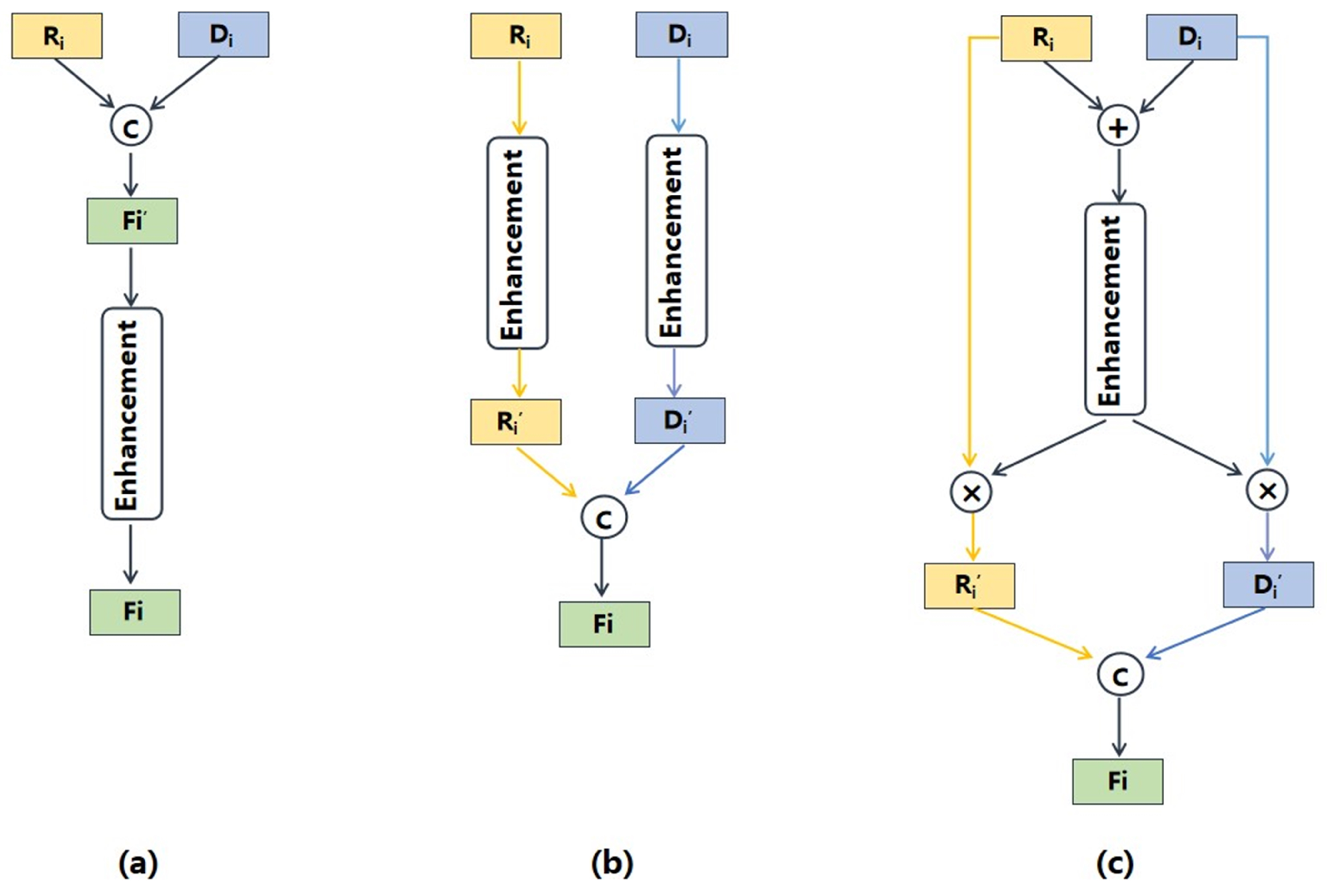
| Dataset | Diversity | Size | Annotation | Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MenuMatch [19] | 41 | 646 | Calories | N |
| ECUSTFD [20] | 160 | 2978 | Volume and Mass | N |
| Fang et al. [21] | 3 | 45 | Calories | N |
| Ando et al. [22] | 3 | 270 | Calories | Y |
| Nutrition5k [10] | 5066 | 3490 | Calories, Mass and Macronutrients | Y |
| Methods | Calories MAE (kCal)/PMAE (%) | Mass MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Fat MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Carb MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Protein MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Mean PMAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ViT [29] | 52.4/20.4 | 32.5/16.3 | 3.78/29.4 | 5.72/28.9 | 5.72/28.9 | 24.6 |
| VGG16 [28] | 47.9/18.6 | 29.2/14.6 | 3.61/28.0 | 5.18/26.2 | 4.71/26.8 | 22.8 |
| InceptionV3 [36] | 46.2/18.0 | 28.4/14.2 | 3.24/25.1 | 5.1/25.8 | 4.37/24.8 | 21.6 |
| ResNet50 [23] | 46.9/18.2 | 27.7/13.8 | 3.61/28.0 | 4.51/22.8 | 4.56/25.9 | 21.7 |
| ResNet101 [23] | 46.0/17.9 | 27.2/13.6 | 3.42/26.5 | 4.56/23.0 | 4.31/24.5 | 21.1 |
| Method | AbsRel | RMSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet [26] | 0.573 | 0.771 | 0.860 | 0.661 | 0.211 |
| FCRN [37] | 0.634 | 0.799 | 0.877 | 0.529 | 0.189 |
| HRNet [38] | 0.692 | 0.864 | 0.906 | 0.387 | 0.162 |
| DPT [24] | 0.743 | 0.893 | 0.942 | 0.322 | 0.128 |
| Depth Source | Calories MAE (kCal)/PMAE (%) | Mass MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Fat MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Carb MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Protein MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Mean PMAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UNet [26] | 41.6/16.2 | 22.6/11.3 | 3.29/25.5 | 4.43/22.4 | 4.01/22.8 | 19.6 |
| FRCN [37] | 40.7/15.8 | 22.7/11.3 | 3.17/24.6 | 4.28/21.6 | 3.87/22.0 | 19.1 |
| HRNet [38] | 39.3/15.3 | 21.6/10.8 | 3.01/23.3 | 4.13/20.9 | 3.72/21.2 | 18.3 |
| DPT [24] | 37.9/14.7 | 21.2/10.6 | 2.92/22.6 | 4.09/20.7 | 3.56/20.2 | 17.8 |
| Depth sensor | 36.5/14.2 | 20.4/10.2 | 2.76/21.4 | 4.08/20.6 | 3.48/19.8 | 17.2 |
| Method | Calories MAE (kCal)/PMAE (%) | Mass MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Fat MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Carb MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Protein MAE (g)/PMAE (%) | Mean PMAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancement–Fusion | 39.1/15.2 | 22.6/11.3 | 3.03/23.5 | 4.14/20.9 | 3.80/21.6 | 18.5 |
| Fusion–Enhancement | 39.3/15.3 | 21.6/10.8 | 3.01/23.3 | 4.13/20.9 | 3.72/21.2 | 18.3 |
| CAB | 37.9/14.7 | 21.2/10.6 | 2.92/22.6 | 4.09/20.7 | 3.56/20.2 | 17.8 |
| Input | Methods | Calories MAE (kCal)/ PMAE (%) | Mass MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Fat MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Carb MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Protein MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Mean PMAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGB-D images | Google-Nutrition-depth [10] | 47.6/18.8 | 40.7/18.9 | 2.27/18.1 | 4.6/23.8 | 3.7/20.9 | 20.1 |
| RGB-D Nutrition [15] | 38.5/15.0 | 21.6/10.8 | 3.0/23.5 | 4.43/22.4 | 3.69/21.0 | 18.5 | |
| Monocular images | Google-Nutrition-monocular [10] | 70.6/26.1 | 40.4/18.8 | 5.0/34.2 | 6.1/31.9 | 5.5/29.5 | 29.1 |
| Swin-Nutrition [11] | 41.5/16.2 | 27.5/13.7 | 3.21/24.9 | 4.32/21.8 | 4.47/25.4 | 20.4 | |
| DPF-Nutrition (ours) | 37.9/14.7 | 21.2/10.6 | 2.92/22.6 | 4.09/20.7 | 3.56/20.2 | 17.8 |
| Index | Model | Calories MAE (kCal)/ PMAE (%) | Mass MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Fat MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Carb MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Protein MAE (g)/ PMAE (%) | Mean PMAE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) | RGB Stream | 46.0/17.9 | 27.2/13.6 | 3.42/26.5 | 4.56/23.0 | 4.31/24.5 | 21.1 |
| (b) | Depth Stream | 83.5/32.5 | 44.7/22.3 | 6.29/48.8 | 8.08/40.8 | 8.53/ 8.5 | 38.6 |
| (c) | (a) + (b) + direct fusion | 42.7/16.7 | 25.0/12.5 | 3.17/24.6 | 4.31/21.8 | 3.97/22.6 | 19.6 |
| (d) | (a) + (b) + multi-scale fusion | 40.7/15.8 | 24.8/12.4 | 3.01/23.3 | 4.13/20.9 | 3.88/22.1 | 18.9 |
| (e) | (d) + CAB | 37.9/14.7 | 21.2/10.6 | 2.92/22.6 | 4.09/20.7 | 3.56/20.2 | 17.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, W.; Huang, Z. DPF-Nutrition: Food Nutrition Estimation via Depth Prediction and Fusion. Foods 2023, 12, 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234293
Han Y, Cheng Q, Wu W, Huang Z. DPF-Nutrition: Food Nutrition Estimation via Depth Prediction and Fusion. Foods. 2023; 12(23):4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234293
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yuzhe, Qimin Cheng, Wenjin Wu, and Ziyang Huang. 2023. "DPF-Nutrition: Food Nutrition Estimation via Depth Prediction and Fusion" Foods 12, no. 23: 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234293
APA StyleHan, Y., Cheng, Q., Wu, W., & Huang, Z. (2023). DPF-Nutrition: Food Nutrition Estimation via Depth Prediction and Fusion. Foods, 12(23), 4293. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12234293








