Innovative Insights for Establishing a Synbiotic Relationship with Bacillus coagulans: Viability, Bioactivity, and In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
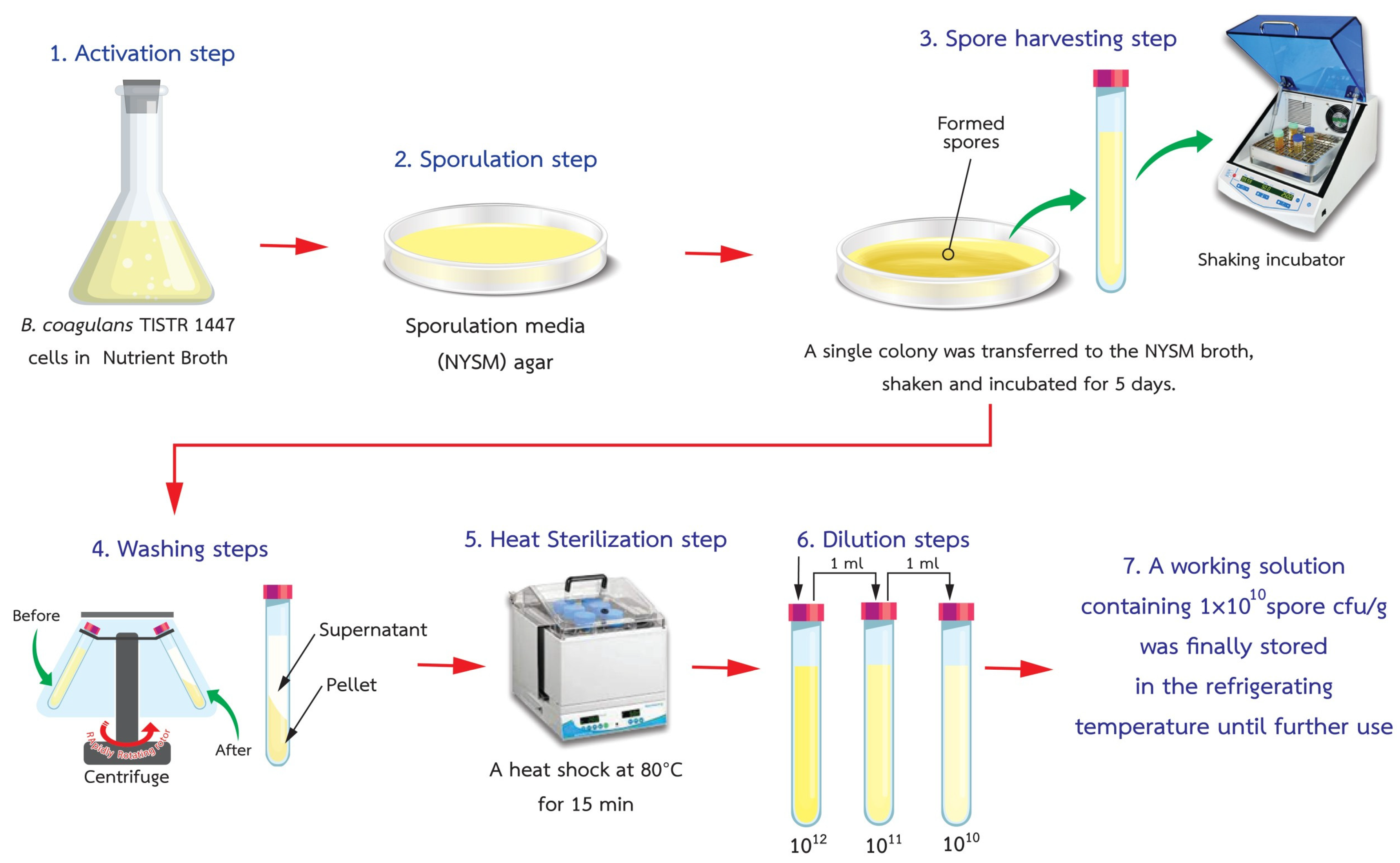
2.2. Production of Spore Suspensions
2.3. Production of Synbiotic Microcapsules by Spray Drying
2.4. In Vitro Bioactive Properties of Synbiotic Microcapsules
2.4.1. 1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Free-Radical Scavenging
2.4.2. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging (HRSA)
2.4.3. Superoxide Radical Scavenging
2.4.4. In Vitro Activities of α-Glucosidase
2.4.5. In Vitro Activities of α-Amylase
2.4.6. Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV (DPP-IV) Inhibition
2.5. In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Digestion
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effects of Microencapsulation and Spray Drying on the Survival Rate
3.2. Bioactivity of the Encapsulated Products
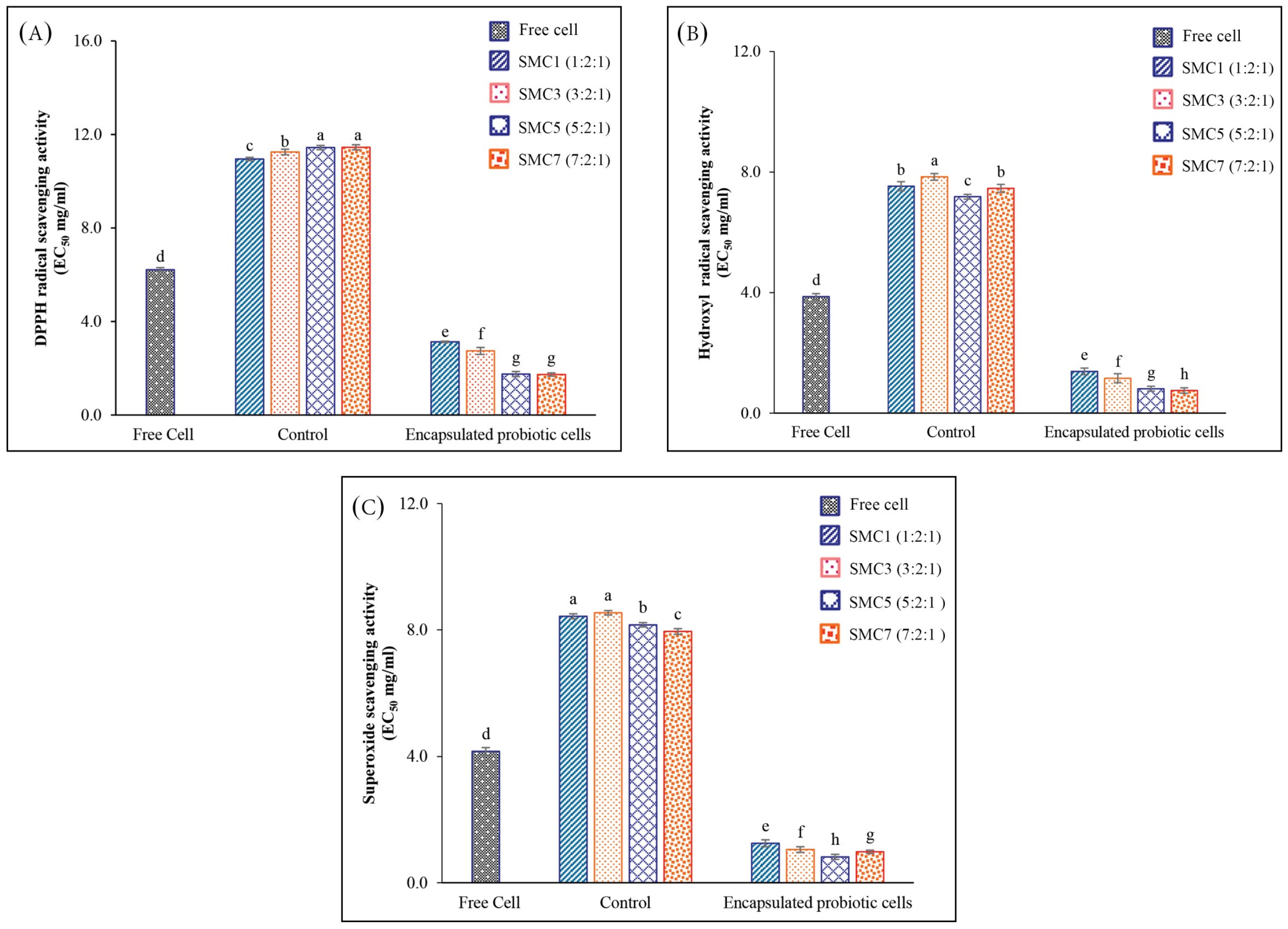
3.2.1. In Vitro Antioxidant Activities
3.2.2. α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities
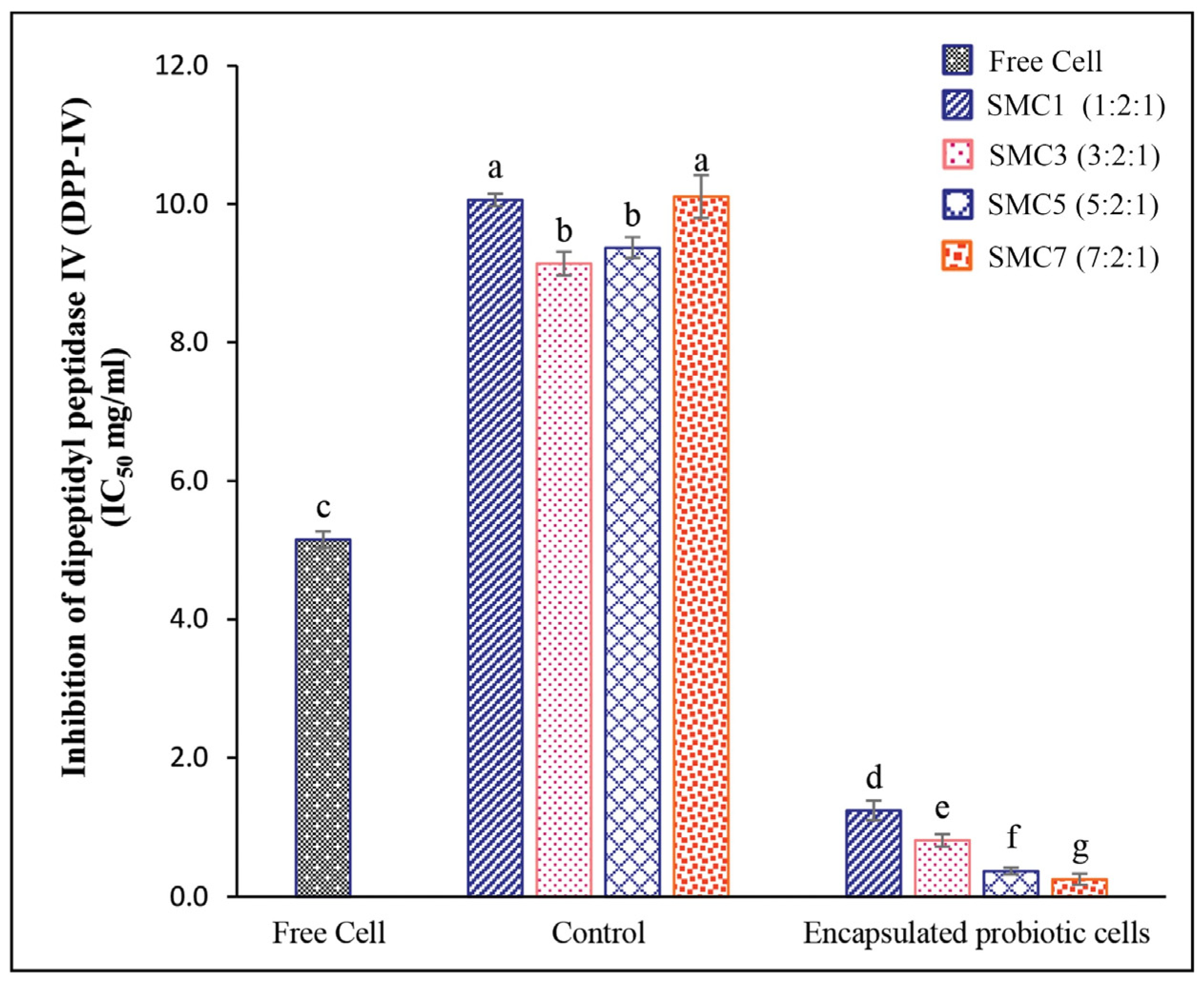
3.2.3. DPP-IV-Inhibitory Activity
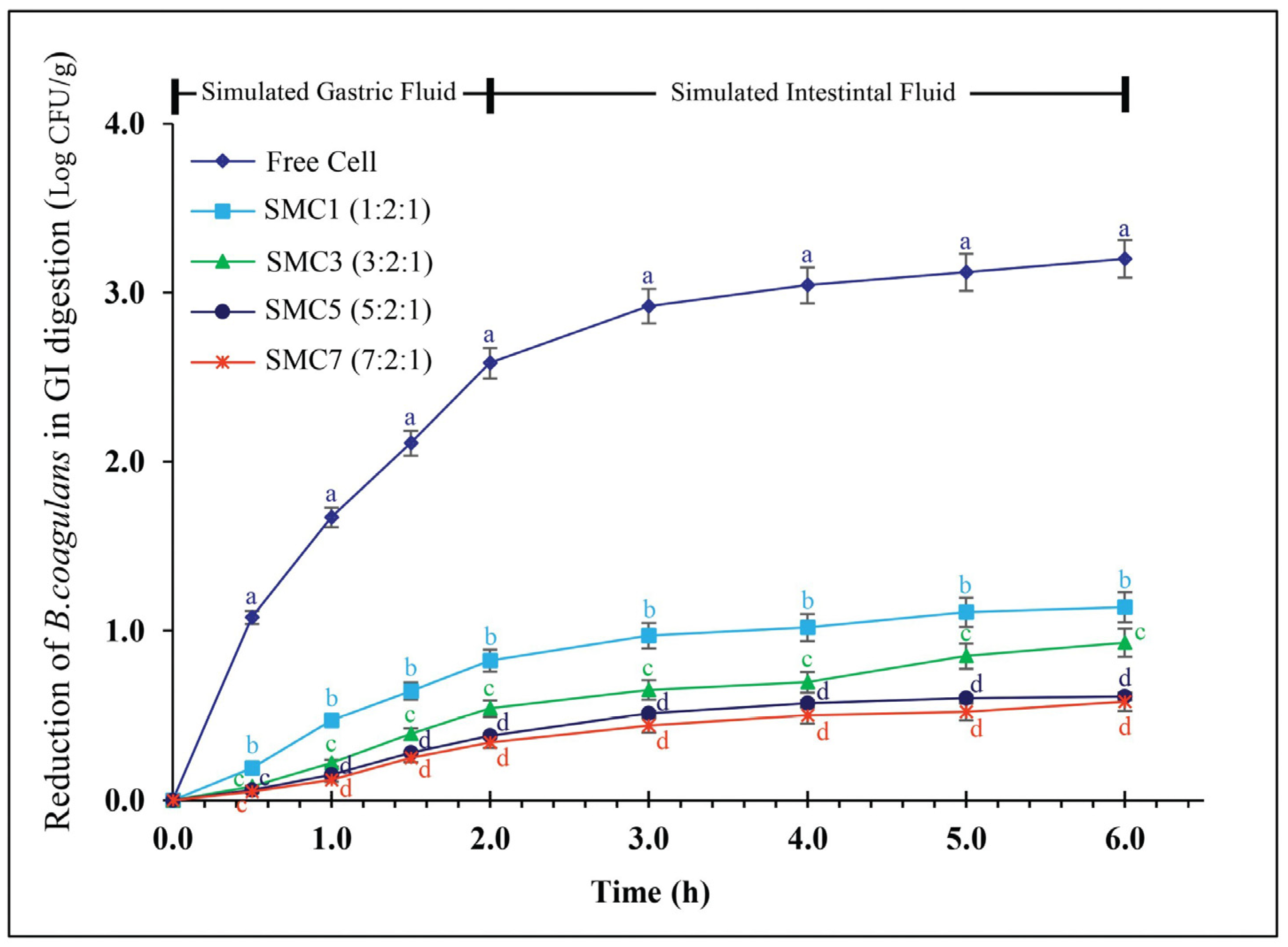
3.3. The Survival Rate during In Vitro Simulation of Gastrointestinal Digestion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poshadri, A.; Deshpande, H.W.; Khodke, U.M.; Katke, S.D. Bacillus coagulans and its Spore as Potential Probiotics in the Production of Novel Shelf-Stable Foods. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. 2022, 10, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedkar, S.; Carraresi, L.; Bröring, S. Food or pharmaceuticals? Consumers’ perception of health-related borderline products. PharmaNutrition 2017, 5, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebeer, S.; Bron, P.A.; Marco, M.L.; Van Pijkeren, J.-P.; Motherway, M.O.C.; Hill, C.; Pot, B.; Roos, S.; Klaenhammer, T. Identification of probiotic effector molecules: Present state and future perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiepś, J.; Dembczyński, R. Current trends in the production of probiotic formulations. Foods 2022, 11, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.; Natarajan, S.; Sivakumar, A.; Ali, F.; Pande, A.; Majeed, S.; Karri, S. Evaluation of anti-diarrhoeal activity of Bacillus coagulans MTCC 5856 and its effect on gastrointestinal motility in Wistar rats. Int. J. Pharma Bio Sci. 2016, 7, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Altun, G.K.; Erginkaya, Z. Identification and characterization of Bacillus coagulans strains for probiotic activity and safety. LWT 2021, 151, 112233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Villeda, B.E.; Falfán-Cortés, R.N.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Santos-López, E.M.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Torres-Vitela, M.R.; Villarruel-López, A.; Castro-Rosas, J. Synbiotic Encapsulation: A Trend towards Increasing Viability and Probiotic Effect. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2023, 2023, 7057462. [Google Scholar]
- Inatsu, Y.; Nakamura, N.; Yuriko, Y.; Fushimi, T.; Watanasiritum, L.; Kawamoto, S. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis strains in Thua nao, a traditional fermented soybean food in northern Thailand. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hindi, R.R.; Abd El Ghani, S. Production of functional fermented milk beverages supplemented with pomegranate peel extract and probiotic lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Qual. 2020, 2020, 4710273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Li, N.; Yue, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Evivie, S.E.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Screening for potential novel probiotics with dipeptidyl peptidase IV-inhibiting activity for type 2 diabetes attenuation in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhiainen, T.; Collin, M.; Narva, M.; Cheng, Z.J.; Poussa, T.; Vapaatalo, H.; Korpela, R. Effect of long-term intake of milk peptides and minerals on blood pressure and arterial function in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Milchwiss.—Milk Sci. Int. 2005, 60, 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Razmpoosh, E.; Javadi, A.; Ejtahed, H.S.; Mirmiran, P.; Javadi, M.; Yousefinejad, A. The effect of probiotic supplementation on glycemic control and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized placebo controlled trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, Y. The hypocholesterolaemic effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus American Type Culture Collection 4356 in rats are mediated by the down-regulation of Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Thirabunyanon, M.; Boonprasom, P.; Niamsup, P. Probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented dairy milks on antiproliferation of colon cancer cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.A.; Forsythe, P.; Chew, M.V.; Escaravage, E.; Savignac, H.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Cryan, J.F. Ingestion of Lactobacillus strain regulates emotional behavior and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse via the vagus nerve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16050–16055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’mahony, L. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind comparison of the probiotic bacteria lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjavainen, P.V.; Salminen, S.J.; Isolauri, E. Probiotic bacteria in the management of atopic disease: Underscoring the importance of viability. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2003, 36, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Campos-Soldini, A.; Chel-Guerrero, L.; Drago, S.R.; Betancur-Ancona, D. Bioactive Phaseolus lunatus peptides release from maltodextrin/gum arabic microcapsules obtained by spray drying after simulated gastrointestinal digestion. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Campaniello, D.; Speranza, B.; Racioppo, A.; Altieri, C.; Sinigaglia, M.; Corbo, M.R. Microencapsulation of saccharomyces cerevisiae into alginate beads: A focus on functional properties of released cells. Foods 2020, 9, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, R.; Chawla, S.; Gauba, P.; Singh, M.; Tiwari, R.K.; Upadhyay, S.; Sharma, S.; Chanda, S.; Gaur, S. Natural sources and encapsulating materials for probiotics delivery systems: Recent applications and challenges in functional food development. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 971784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, S.; Pandey, P.; Mishra, H.N. Novel approaches for co-encapsulation of probiotic bacteria with bioactive compounds, their health benefits and functional food product development: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Liu, B.; He, L.; Hu, J.; Liu, H. The incorporation of peach gum polysaccharide into soy protein based microparticles improves probiotic bacterial survival during simulated gastrointestinal digestion and storage. Food Chem. 2023, 413, 135596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramouli, V.; Kailasapathy, K.; Peiris, P.; Jones, M. An improved method of microencapsulation and its evaluation to protect Lactobacillus spp. in simulated gastric conditions. J. Microbiol. Methods 2004, 56, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi, S.; Janfaza, S.; Tasnim, N.; Gibson, D.L.; Hoorfar, M. Microencapsulating polymers for probiotics delivery systems: Preparation, characterization, and applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 120, 106882. [Google Scholar]
- Kothakota, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, M.; Juvvi, P.; Rao, S.; Kautkar, S. Characteristics of spray dried dahi powder with maltodextrin as an adjunct. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 7, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.; Sheskey, P.; Quinn, M. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; American Pharmacists Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; 917p. [Google Scholar]
- Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S.; Soukoulis, C.; Yonekura, L.; Fisk, I. Optimization of spray-drying process conditions for the production of maximally viable microencapsulated L. acidophilus NCIMB 701748. Dry. Technol. 2013, 31, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Tao, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, B. Positive effects of a Clostridium butyricum-based compound probiotic on growth performance, immune responses, intestinal morphology, hypothalamic neurotransmitters, and colonic microbiota in weaned piglets. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 2926–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, B.; Jelley, S.; Yousten, A. Selective medium for mosquito pathogenic strains of Bacillus sphaericus 2362. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1989, 55, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan-Tontul, S.; Erbas, M. Single and double layered microencapsulation of probiotics by spray drying and spray chilling. Lwt—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Morfin, R.C.; Pérez-Masiá, R.; Sanchez, G.; Lopez-Rubio, A. Optimization of electrospraying conditions for the microencapsulation of probiotics and evaluation of their resistance during storage and in-vitro digestion. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanangul, S.; Sangsawad, P.; Alashi, M.A.; Aluko, R.E.; Tochampa, W.; Chittrakorn, S.; Ruttarattanamongkol, K. Antioxidant activities of sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.) protein isolate and its hydrolysates produced with different proteases. Maejo Int. J. Sci. Technol. 2021, 15, 48–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Deng, Z.; Ramdath, D.D.; Tang, Y.; Chen, P.X.; Liu, R.; Liu, Q.; Tsao, R. Phenolic profiles of 20 Canadian lentil cultivars and their contribution to antioxidant activity and inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudgil, P.; Jobe, B.; Kamal, H.; Alameri, M.; Al Ahbabi, N.; Maqsood, S. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV, α-amylase, and angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitory properties of novel camel skin gelatin hydrolysates. LWT 2019, 101, 251–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sangsawad, P.; Katemala, S.; Pao, D.; Suwanangul, S.; Jeencham, R.; Sutheerawattananonda, M. Integrated Evaluation of Dual-Functional DPP-IV and ACE Inhibitory Effects of Peptides Derived from Sericin Hydrolysis and Their Stabilities during In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal and Plasmin Digestions. Foods 2022, 11, 3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Qu, P.; Luo, S.; Wang, C. Potential uses of milk proteins as encapsulation walls for bioactive compounds: A review. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 7959–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, F.; Santos, L. Microencapsulation of caffeic acid and its release using aw/o/w double emulsion method: Assessment of formulation parameters. Dry. Technol. 2019, 37, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukoulis, C.; Behboudi-Jobbehdar, S.; Yonekura, L.; Parmenter, C.; Fisk, I. Impact of milk protein type on the viability and storage stability of microencapsulated Lactobacillus acidophilus NCIMB 701748 using spray drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Anil Kumar, N.V.; Zucca, P.; Varoni, E.M.; Dini, L.; Panzarini, E.; Rajkovic, J.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Azzini, E.; Peluso, I. Lifestyle, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Back and forth in the pathophysiology of chronic diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 694. [Google Scholar]
- Kodali, V.P.; Sen, R. Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of an exopolysaccharide from a probiotic bacterium. Biotechnol. J. Healthc. Nutr. Technol. 2008, 3, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Yue, M.; Yang, C. Effects of Bacillus coagulans on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, immunity function, and gut health in broilers. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Lam, Y.; de Lumen, B.O. Characterization of lunasin isolated from soybean. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7901–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, D.; Ma, T.; Tuo, Y.; Jiang, S.; Qian, F.; Mu, G. In vitro assessment of probiotic and functional properties of Bacillus coagulans T242. Food Biosci. 2020, 36, 100675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Xu, Y.; Dong, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. The effects of microcapsules with different protein matrixes on the viability of probiotics during spray drying, gastrointestinal digestion, thermal treatment, and storage. eFood 2023, 4, e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şengül, N.; Aslím, B.; Uçar, G.; Yücel, N.; Işık, S.; Bozkurt, H.; Sakaoğullarí, Z.; Atalay, F. Effects of exopolysaccharide-producing probiotic strains on experimental colitis in rats. Dis. Colon Rectum 2006, 49, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, K.; Mishra, S.; Pradhan, R.C.; Nagarajan, M.; Kumar, P.K.; Singh, S.S.; Manvi, D.; Gowda, N.N. A comprehensive review on microencapsulation of probiotics: Technology, carriers and current trends. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 3, 100248. [Google Scholar]
- Suetsuna, K.; Ukeda, H.; Ochi, H. Isolation and characterization of free radical scavenging activities peptides derived from casein. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2000, 11, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awosika, T.O.; Aluko, R.E. Inhibition of the in vitro activities of α-amylase, α-glucosidase and pancreatic lipase by yellow field pea (Pisum sativum L.) protein hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2021–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.; Huligere, S.S.; Ramu, R.; Naik Bajpe, S.; Sreenivasa, M.; Silina, E.; Stupin, V.; Achar, R.R. Evaluation of probiotic and antidiabetic attributes of lactobacillus strains isolated from fermented beetroot. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 911243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ke, W.; Zhang, Q.; Undersander, D.; Zhang, G. Effects of Bacillus coagulans and Lactobacillus plantarum on the Fermentation Quality, Aerobic Stability and Microbial Community of Triticale Silage. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, D.-C.; Rhee, H.-I. Intestinal Production of Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitor by Bacillus coagulans Spores. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X.; Teng, C.; Sun, B. Enhanced production of α-glucosidase inhibitor by a newly isolated strain of Bacillus subtilis B2 using response surface methodology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieco-Saiz, N.; Belguesmia, Y.; Raspoet, R.; Auclair, E.; Gancel, F.; Kempf, I.; Drider, D. Benefits and inputs from lactic acid bacteria and their bacteriocins as alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters during food-animal production. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12451. [Google Scholar]
- Tidona, F.; Criscione, A.; Guastella, A.M.; Zuccaro, A.; Bordonaro, S.; Marletta, D. Bioactive peptides in dairy products. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 8, 315–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.; Lu, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Yan, Q.; Jiang, Z. Physicochemical properties and bioactivities of rice beans fermented by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Engineering 2021, 7, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudgil, P.; Aldhaheri, F.; Hamdi, M.; Punia, S.; Maqsood, S. Fortification of Chami (traditional soft cheese) with probiotic-loaded protein and starch microparticles: Characterization, bioactive properties, and storage stability. LWT 2022, 158, 113036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoha, K.; Moses, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Effect of different drying methods on the functional properties of probiotics encapsulated using prebiotic substances. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Kil, B.J.; Yoon, S.J.; Yun, C.-H.; Huh, C.-S. The effect of milk protein on the biological and rheological properties of probiotic capsules. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | Viable Cells (log CFU/g) | Survival Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Spray Drying | After Spray Drying | ||
| Free Cell | 10.35 ± 0.15 a | 4.67 ± 0.26 d | 45.12 ± 0.25 d |
| SMC1 (1:2:1) | 10.91 ± 0.29 a | 7.28 ± 0.37 c | 66.73 ± 0.73 c |
| SMC3 (3:2:1) | 10.61 ± 0.93 a | 8.35 ± 0.20 b | 78.70 ± 0.18 b |
| SMC5 (5:2:1) | 10.75 ± 0.06 a | 9.93 ± 0.53 a | 92.37 ± 0.36 a |
| SMC7 (7:2:1) | 10.58 ± 0.11 a | 9.77 ± 0.94 a | 92.34 ± 0.27 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suwanangul, S.; Jaichakan, P.; Narkprasom, N.; Kraithong, S.; Narkprasom, K.; Sangsawad, P. Innovative Insights for Establishing a Synbiotic Relationship with Bacillus coagulans: Viability, Bioactivity, and In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Foods 2023, 12, 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193692
Suwanangul S, Jaichakan P, Narkprasom N, Kraithong S, Narkprasom K, Sangsawad P. Innovative Insights for Establishing a Synbiotic Relationship with Bacillus coagulans: Viability, Bioactivity, and In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Foods. 2023; 12(19):3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193692
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuwanangul, Saranya, Pannapapol Jaichakan, Nukrob Narkprasom, Supaluck Kraithong, Kanjana Narkprasom, and Papungkorn Sangsawad. 2023. "Innovative Insights for Establishing a Synbiotic Relationship with Bacillus coagulans: Viability, Bioactivity, and In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion" Foods 12, no. 19: 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193692
APA StyleSuwanangul, S., Jaichakan, P., Narkprasom, N., Kraithong, S., Narkprasom, K., & Sangsawad, P. (2023). Innovative Insights for Establishing a Synbiotic Relationship with Bacillus coagulans: Viability, Bioactivity, and In Vitro-Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Foods, 12(19), 3692. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12193692









