Effect of Lysosomal Cathepsin L on Proteolysis of Beef Myofibrillar Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vivo Experiments
2.1.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.2. Extraction of MPs
2.2. In Vitro Experiments
2.2.1. Preparation of CAT
2.2.2. Incubation of MPs with Purified CAT
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
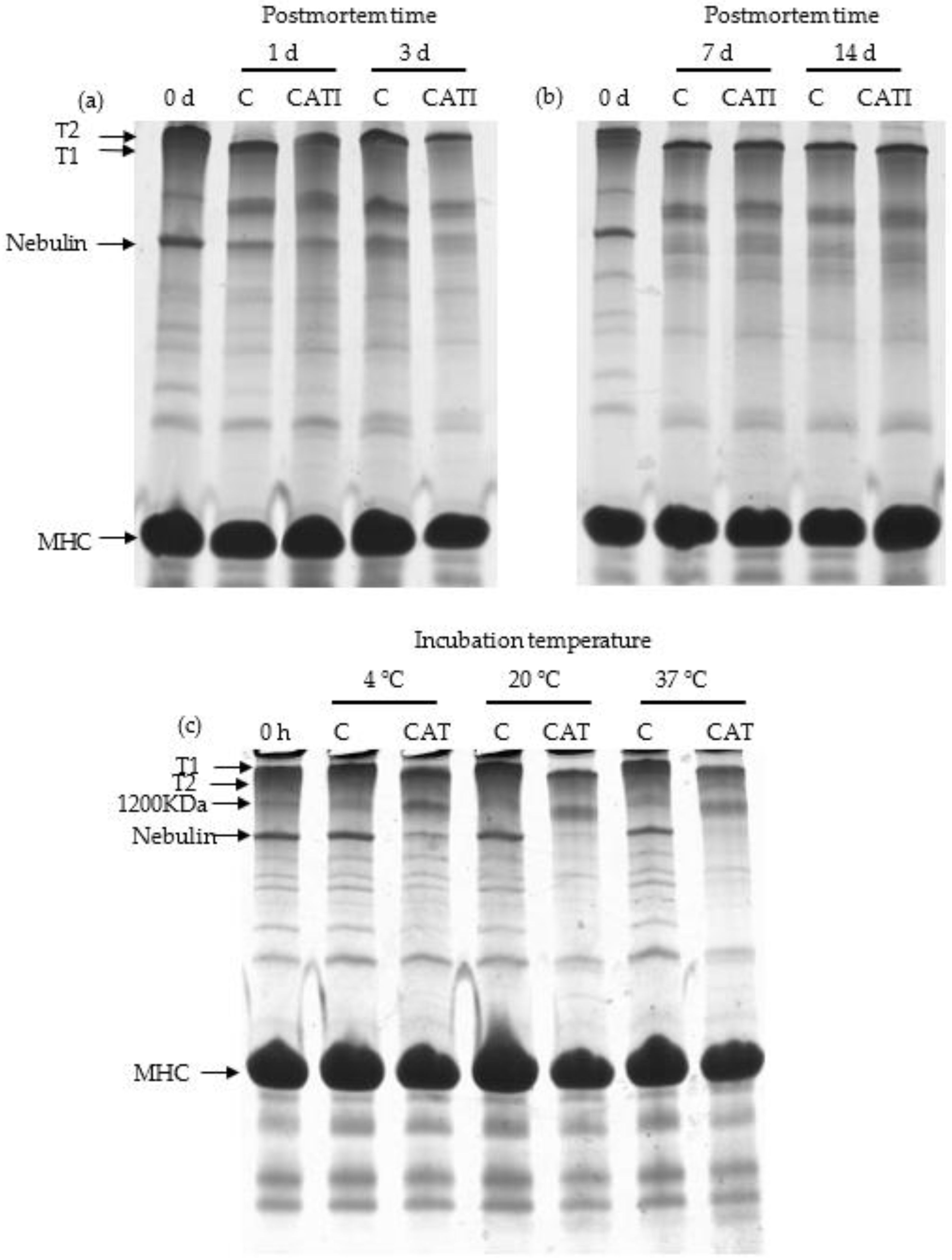
3.1. Titin and Nebulin
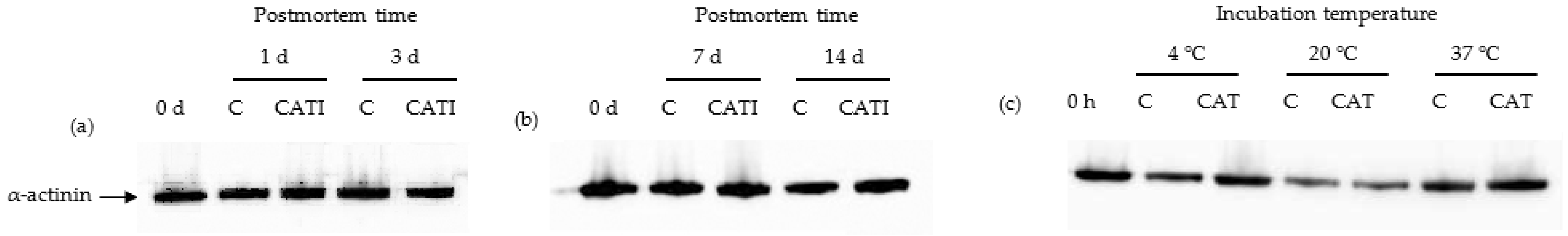
3.2. α-Actinin
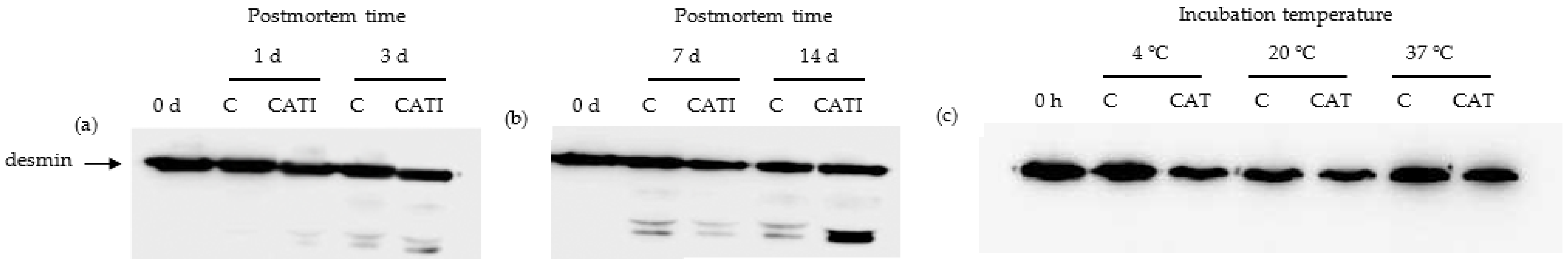
3.3. Desmin
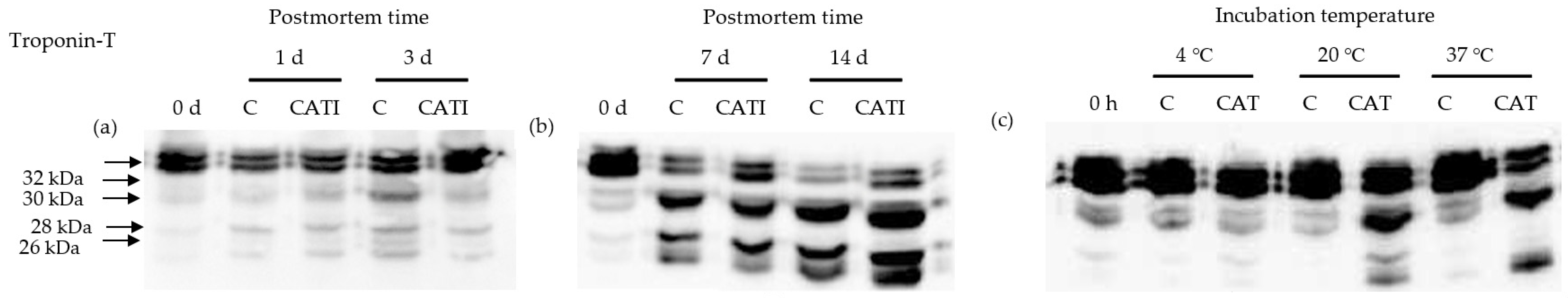
3.4. Troponin-T
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Danga, D.S.; Buhlera, J.F.; Davisa, H.T.; Thornton, K.J.; Schefflerc, T.L.; Matarneh, S.K. Inhibition of mitochondrial calcium uniporter enhances postmortem proteolysis and tenderness in beef cattle. Meat Sci. 2020, 162, 108039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, H.; Elik, S.; Sezer, Y.E. Effect of ultrasonication and vacuum impregnation pretreatments on the quality of beef marinated in onion juice a natural meat tenderizer. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2021, 28, 10820132211012919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, R.; Wheeler, T.L.; Ha, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.G. Meat tenderness: Advances in biology, biochemistry, molecular mechanisms and new technologies. Meat Sci. 2021, 185, 108657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, X.C.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, W.G.; Li, C.B.; Ullah, N.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of ultrasonic processing on caspase-3, calpain expression and myofibrillar structure of chicken during post-mortem ageing. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff-Lonergan, E.; Zhang, W.G.; Lonergan, S.M. Biochemistry of postmortem muscle-lessons on mechanisms of meat tenderization. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohmaraie, M.; Geesink, G.H. Contribution of postmortem muscle biochemistry to the delivery of consistent meat quality with particular focus on the calpain system. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A. Role of calpain system in meat tenderness: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechet, D.; Tassa, A.; Taillandier, D.; Combaret, L.; Attaix, D. Lysosomal proteolysis in skeletal muscle. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 2098–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uytterhaegen, L.; Claeys, E.; Demeyer, D. Effects of exogenous protease effectors on beef tenderness development and myofibrillar degradation and solubility. J. Anim. Sci. 1994, 72, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, A.; Garrel, N.; Obled, A.; Deval, C.; Valin, C.; Penny, I.F. Comparative action of cathepsins D, B, H, L and of a new lysosomal cysteine proteinase on rabbit myofibrils. Meat Sci. 1987, 19, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukura, U.; Okitani, A.; Nishimuro, T.; Kato, H. Mode of degradation of myofibrillar proteins by an endogenous protease, cathepsin L. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1981, 662, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikami, M.; Whiting, A.H.; Taylor, M.A.; Maciewicz, R.A.; Etherington, D.J. Degradation of myofibrils from rabbit, chicken and beef by cathepsin L and lysosomal lysates. Meat Sci. 1987, 21, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohmaraie, M.; Whipple, G.; Kretchmar, D.H.; Crouse, J.D.; Mersmann, H.J. Postmortem proteolysis in longissimus muscle from beef, lamb and pork carcases. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Huang, F.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H. Influence of caspase3 selective inhibitor on proteolysis of chicken skeletal muscle proteins during post mortem aging. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, N.; Liu, H.; Ma, C. Purification and characterisation of cathepsin L2 from dorsal muscle of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix). Food Chem. 2008, 111, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Peng, Z.; Hui, T.; Wang, F.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, G. Potential use of crude extracts from Alaska Pollock muscle as meat tenderizer. CyTA-J. Food 2008, 11, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, K.B.; Prusa, K.J.; Fedler, C.A.; Steadham, E.M.; Lonergan, S.M. Postmortem protein degradation is a key contributor to fresh pork loin tenderness. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 95, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.G.; Geesink, G.H.; Thompson, V.F.; Koohmaraie, M.; Goll, D.E. Is z-disk degradation responsible for postmortem tenderization. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 1351–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Xu, B.C.; Zhu, L.X.; Luo, X. Protein degradation and structure changes of beef muscle during superchilled storage. Meat Sci. 2020, 168, 108180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.D.; Mitchell, M.C.; Marsh, B.B.; Greaser, M.L. Titin content of beef in relation to tenderness. Meat Sci. 1993, 33, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huff-Lonergan, E.; Robson, R.M. Effects of postmortem aging time, animal age, and sex on degradation of titin and nebulin in bovine longissimus muscle. J. Anim. Sci. 1995, 73, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldassarri, V.; Salucci, S.; Ferri, P.; Falcieri, E.; Burattini, S. The role of α-actinin in z-disks assembly: A morphological point of view. Microscopie 2012, 18, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.Y.; Stromer, M.H.; Robson, R.M. Effect of electrical stimulation on postmortem titin, nebulin, desmin, and troponin-t degradation and ultrastructural changes in bovine longissimus muscle. J. Anim. Sci. 1996, 74, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwan, S.; Bandman, E. Studies of desmin and α-actinin degradation in bovine semitendinosus muscle. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 1426–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaser, M.L.; Gergely, J. Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 4226–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, I.F.; Nsfield, E. Relationship between toughness and troponin t in conditioned beef. Meat Sci. 1979, 3, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.E.; Huff-Lonergan, E.; Lonergan, S.M.; Jones, W.R.; Rankins, D. Antioxidant status affects color stability and tenderness of calcium chloride-injected beef. J. Anim. Sci. 2001, 79, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.Y.; Stromer, M.H.; Robson, R.M. Identification of the 30 kDa polypeptide in post mortem skeletal muscle as a degradation product of troponin-T. Biochimie 1994, 76, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Feng, H.; Mei, X.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. The effect of active caspase-3 on degradation of chicken myofibrillar proteins and structure of myofibrils. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, M.; Konagaya, S. Hydrolytic action of salmon cathepsins B and L to muscle structural proteins in respect of muscle softening. Nippon. Suisan Gakkaishi 1991, 57, 1917–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, B.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X. Effect of Lysosomal Cathepsin L on Proteolysis of Beef Myofibrillar Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro. Foods 2022, 11, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040613
Cui B, Guo X, Zhang Y, Meng X. Effect of Lysosomal Cathepsin L on Proteolysis of Beef Myofibrillar Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro. Foods. 2022; 11(4):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040613
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Baowei, Xiuyun Guo, Yawei Zhang, and Xiangren Meng. 2022. "Effect of Lysosomal Cathepsin L on Proteolysis of Beef Myofibrillar Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro" Foods 11, no. 4: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040613
APA StyleCui, B., Guo, X., Zhang, Y., & Meng, X. (2022). Effect of Lysosomal Cathepsin L on Proteolysis of Beef Myofibrillar Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro. Foods, 11(4), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11040613




