Opening and Reusing Transparent Peer Reviews with Automatic Article Annotation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Open Peer Review
1.2. Problem Statement: Lack of Tool Support
- A pipeline, named AR-Annotator (Article and Review Annotator), to enrich articles and reviews with RDFa data, immediately preparing them for efficient analysis by SPARQL queries, and furthermore providing a way to allow them to be added to the LOD 1 Cloud and scholarly communication knowledge graphs such as SCM-KG knowledge graph [15].
- We support the repeatability and reproducibility of our approach and the empirical evaluation results by providing the source code of the article enriching module and the evaluation procedure under Apache license [16].
2. Use Cases and Derived Requirements
2.1. Use Cases
2.1.1. Soliciting Additional Reviews
2.1.2. Automated Analysis of Reviews
2.1.3. Sharing and Reusing Articles and Reviews
2.1.4. Multi-Device Accessibility of Reviews
2.1.5. Independent Quality (Re-)Assessment
2.2. Requirements
- It should be possible to create initial reviews for an article in a closed submission and review management system.
- The support for comments and annotations is the most requested feature from the reviewing tools [17]. Reviewers should be enabled to attach comments in a fine-grained way to precise structural elements of an article, and these attachments should be preserved in the published document.
- The structure of all parts of an article should be exposed explicitly; each structural component of an article should have a globally unique identifier.
- Not only should the structure of the article from the authoring environment be preserved, but, where possible, structural information implicitly hidden in unstructured text should be extracted, and the text of the published article should be enriched with an explicit representation of such structures.
- In line with the FAIR principles of making data Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable [18], our system should publish reviews in a standard web format, which humans can consume with a browser, but which can also carry semantic metadata enabling queries and other automated analyses.
- For compatibility with post-publication peer review processes, it should be possible to add further reviews to documents once it has been published.
3. Related Work
3.1. Tool Support for Open Peer Review
3.2. Tools for Annotating Articles
4. Implementation
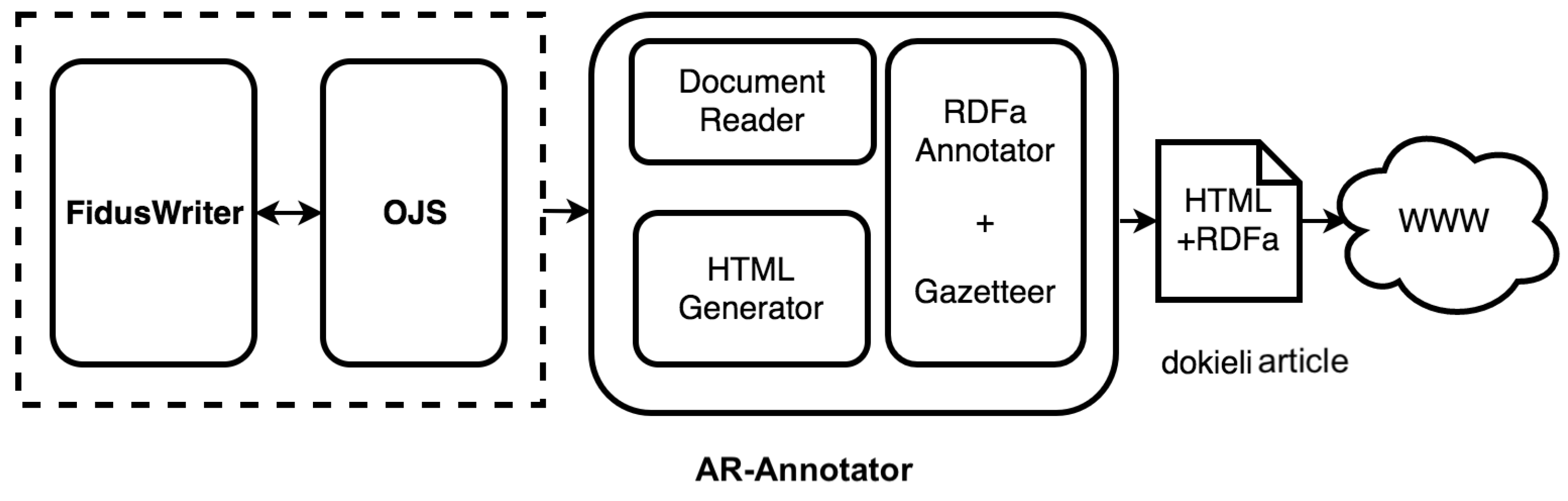
4.1. Architecture
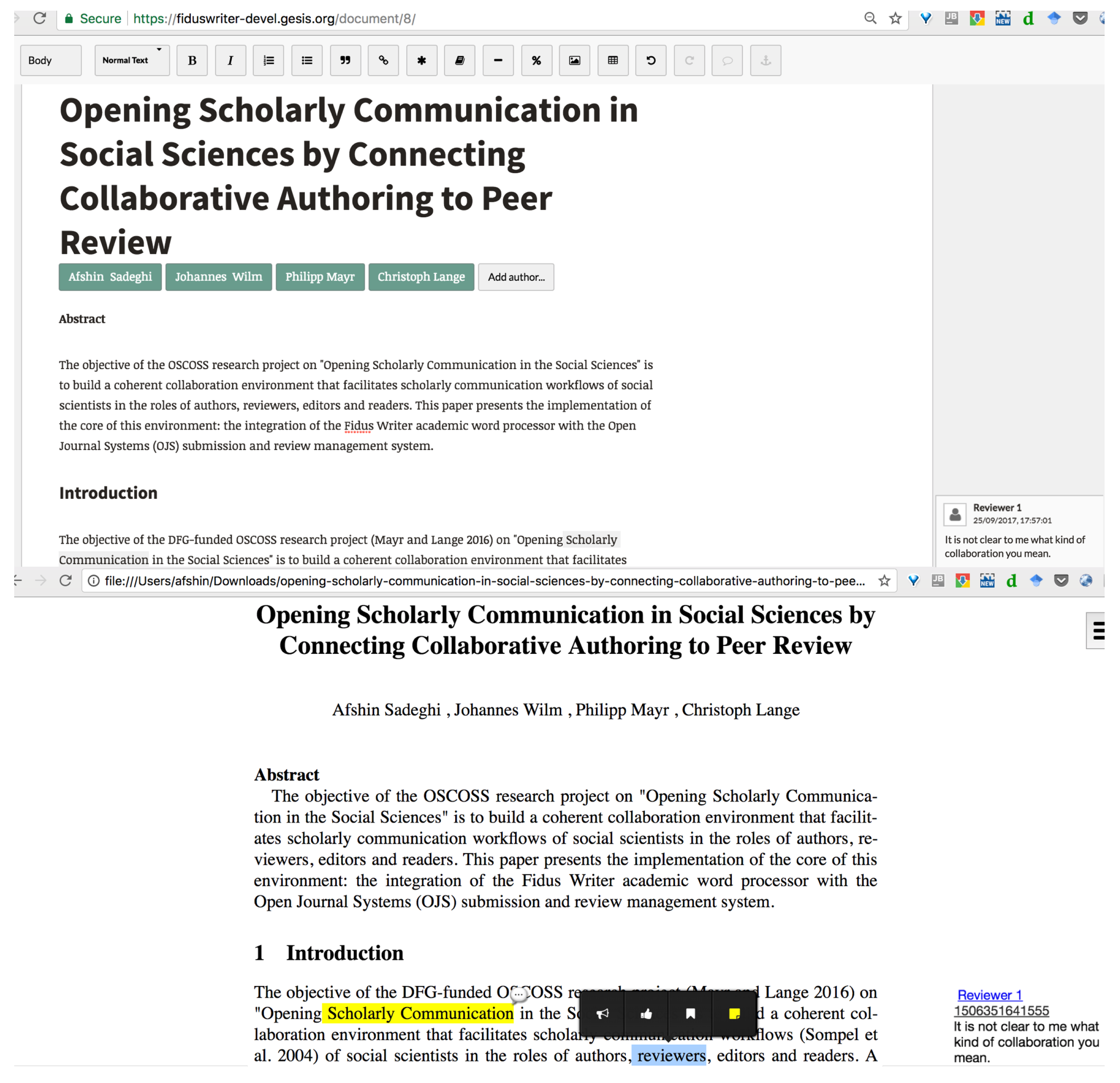
4.2. Integration of Reused Components: Fidus Writer, OJS and dokieli
4.3. The AR-Annotator Article and Review Annotator
- Transformation of the article’s explicit structure, including metadata and comments, to dokieli’s HTML+RDFa format.
- Identification of structure (discourse elements) in the unstructured text of the article, and enrichment of the article by an explicit representation of this structure.
5. Usefulness of Publishing Fine-Grained Review Comments
5.1. Study Participants
5.2. Study Design
5.3. Evaluation Result
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross-Hellauer, T. What is open peer review? A systematic review [version 2; referees: 4 approved]. F1000Research 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowicz, K.; Hitzler, P. Open and transparent: The review process of the Semantic Web journal. Learn. Publ. 2012, 25, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BMJ Open. Available online: http://bmjopen.bmj.com/pages/reviewerguidelines (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Data Science Journal. Available online: https://datasciencehub.net (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Walker, R.; Da Silva, P.R. Emerging trends in peer review—A survey. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.; Rooney, M.; Appleby, L.; Wilkinson, G. Open peer review: A randomised controlled trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2000, 176, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R. Opening up BMJ peer review. BMJ 1999, 318, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R. Peer Review: A Flawed Process at the Heart of Science and Journals. J. R. Soc. Med. 2006, 99, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöschl, U. Multi-Stage Open Peer Review: Scientific Evaluation Integrating the Strengths of Traditional Peer Review with the Virtues of Transparency and Self-Regulation. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EasyChair. Available online: http://www.easychair.org (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Open Journal Systems. Available online: https://pkp.sfu.ca/ojs (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- W3 RDFa Syntax. Available online: http://www.w3.org/TR/rdfa-syntax (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- SPAR Ontologies. Available online: http://www.sparontologies.net (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Web Annotation Vocabulary. Available online: https://www.w3.org/TR/annotation-vocab/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Sadeghi, A.; Lange, C.; Vidal, M.E.; Auer, S. Integration of Scholarly Communication Metadata Using Knowledge Graphs. In Research and Advanced Technology for Digital Libraries; Kamps, J., Tsakonas, G., Manolopoulos, Y., Iliadis, L., Karydis, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 328–341. [Google Scholar]
- HTML-RDFa Exporter an Application of AR-Annotator. Available online: https://github.com/OSCOSS/fiduswriter-htmlrdfa (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Sadeghi, A.; Ansari, M.J.; Wilm, J.; Lange, C. A Survey of User Expectations and Tool Limitations in Collaborative Scientific Authoring and Reviewing. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1804.07708. [Google Scholar]
- FAIR Principles. Available online: https://www.force11.org/group/fairgroup/fairprinciples (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Kriegeskorte, N. Open evaluation: A vision for entirely transparent post-publication peer review and rating for science. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Google Docs. Available online: https://docs.google.com/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Fidus Writer. Available online: https://www.fiduswriter.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Sadeghi, A.; Wilm, J.; Mayr, P.; Lange, C. Opening Scholarly Communication in Social Sciences by Connecting Collaborative Authoring to Peer Review. Inf. Wiss. Praxis 2017, 68, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokieli Website. Available online: https://dokie.li/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Capadisli, S.; Guy, A.; Verborgh, R.; Lange, C.; Auer, S.; Berners-Lee, T. Decentralised Authoring, Annotations and Notifications for a Read-Write-Web with dokieli. In Web Engineering; Cabot, J., de Virgilio, R., Torlone, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Available online: http://csarven.ca/dokieli-rww (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Luczak-Rösch, M.; Heese, R. Linked Data Authoring for Non-Experts. In Proceedings of the 18th International World Wide Web Conference, Madrid, Spain, 20–24 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Khalili, A.; Auer, S.; Hladky, D. The RDFa content editor-from WYSIWYG to WYSIWYM. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 36th Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference, Izmir, Turkey, 16–20 July 2012; pp. 531–540. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarese, P.; Ocana, M.; Clark, T. Open semantic annotation of scientific publications using DOMEO. J. Biomed. Semant. 2012, 3, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comeau, D.C.; Islamaj Doğan, R.; Ciccarese, P.; Cohen, K.B.; Krallinger, M.; Leitner, F.; Lu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Rinaldi, F.; Torii, M.; et al. BioC: A minimalist approach to interoperability for biomedical text processing. Database 2013, 2013, 064. [Google Scholar]
- Suhrbier, L.; Kusber, W.H.; Tschöpe, O.; Güntsch, A.; Berendsohn, W.G. AnnoSys—Implementation of a generic annotation system for schema-based data using the example of biodiversity collection data. Database 2017, 2017, 018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzolese, A.G.; Peroni, S.; Recupero, D.R. ACM: Article content miner for assessing the quality of scientific output. In Semantic Web Evaluation Challenge; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Capadisli, S.; Guy, A.; Lange, C.; Auer, S.; Sambra, A.; Berners-Lee, T. Linked Data Notifications: A Resource-Centric Communication Protocol. In The Semantic Web; Blomqvist, E., Maynard, D., Gangemi, A., Hoekstra, R., Hitzler, P., Hartig, O., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; Available online: http://csarven.ca/linked-data-notifications (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- W3C Schema.org. Available online: http://schema.org/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Discourse Elements Ontology. Available online: http://purl.org/spar/deo/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- SWRC Ontology. Available online: http://ontoware.org/swrc/ (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Sample Article Made by AR-Annotator Method. Available online: https://goo.gl/9Bm2yi (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- Semantic Web Journal. Available online: http://www.semantic-web-journal.net (accessed on 30 January 2019).
- AR-Annotator Evaluation Data. Available online: https://github.com/OSCOSS/AR-Annotator/tree/master/Evaluation (accessed on 30 January 2019).
| 1 | LOD here means linked open data. |

| Criterion/Corresponding req. | Fidus Writer | dokieli |
|---|---|---|
| Discoverability of reviews (2, 3, 4, 5) | N/A | Yes (RDFa) |
| Machine-comprehensible representation (3, 4) | N/A | Yes |
| Creation and access to reviews (1) | post publication on article snapshot | pre or post publication (optionally on snapshots) |
| Systematic traditional reviewing workflow (1) | Yes, by OJS integration, a closed review phase is supported | N/A |
| Multiple reviewing rounds (1) | Yes, by OJS integration | N/A |
| User-centered publishing possibility (5) | Restricted to PDF | web-based adaptive rendering |
| Publishing reviews with articles (5) | N/A | Yes, over the Web |
| Post-publication reviews (6) | not currently supported | Yes |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadeghi, A.; Capadisli, S.; Wilm, J.; Lange, C.; Mayr, P. Opening and Reusing Transparent Peer Reviews with Automatic Article Annotation. Publications 2019, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications7010013
Sadeghi A, Capadisli S, Wilm J, Lange C, Mayr P. Opening and Reusing Transparent Peer Reviews with Automatic Article Annotation. Publications. 2019; 7(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications7010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadeghi, Afshin, Sarven Capadisli, Johannes Wilm, Christoph Lange, and Philipp Mayr. 2019. "Opening and Reusing Transparent Peer Reviews with Automatic Article Annotation" Publications 7, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications7010013
APA StyleSadeghi, A., Capadisli, S., Wilm, J., Lange, C., & Mayr, P. (2019). Opening and Reusing Transparent Peer Reviews with Automatic Article Annotation. Publications, 7(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications7010013





