Abstract
The abstract is a crucial component of a research article. Abstracts head the text—and sometimes they can appear alone in separate listings (e.g., conference proceedings). The purpose of the abstract is to inform the reader succinctly what the paper is about, why and how the research was carried out, and what conclusions might be drawn. In this paper we consider the same (or a similar) abstract in 13 different formats to illustrate the strengths and weaknesses of each approach.
1. Introduction
The abstract is a crucial component in a journal article [1]. It heads and summarises the text—and it can appear alone in separate lists of publications. The purpose of the abstract is to inform the reader succinctly of what the paper is about, why the research was carried out, what happened, and what conclusions might be drawn. In this paper, we present the same (or a similar) abstract in different formats to illustrate the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches. These are variations of the block format (version 1) in terms of structure (e.g., version 3: structured abstracts) and contents (e.g., version 8: tweetable abstracts).
Version 1: The Block Format
Here is a typical “informative” abstract found in a recent article [2], set out in the traditional manner.
- Abstract. This paper focuses on the issue of whether or not academic writing changes over time. We examine a selection of book reviews written by five authors over a 20–25 years period. The data show little evidence of change for each of these authors as measured by readability scores and grammatical features. These findings are in line with earlier ones that suggest that academic writing styles are fixed fairly early on and do not alter much with time.
Version 2: Spaced Text
Here line-spacing is used to separate the sections and clarify the same abstract as the one above.
Abstract
- This paper focuses on the issue of whether or not academic writing changes over time.
- We examine a selection of book reviews written by five authors over a 20–25 years period.
- The data show little evidence of change for each of these authors as measured by readability scores and grammatical features.
- These findings are in line with earlier ones that suggest that academic writing styles are fixed fairly early on and do not alter much with time.
By starting each new sentence on a new line we maintain that this version of the abstract is easier to read than the block format. Further, with longer abstracts, one can split each subsection into paragraphs and also start each new paragraph on a new line.
Version 3: Structured Abstracts
Structured abstracts typically use standard sub-headings to clarify the content of the abstract. For example:
- Background. There has been little research examining how academic writing changes with time.
- Aim. The aim of this study was to see whether or not an author’s style when writing an academic book review changes over time.
- Method. We examined a selection of book reviews written by five authors over a 20–25 years period. For each author we recorded the number of words, the number of paragraphs, the average sentence lengths, the use of passive tenses, and reading difficulty, as measured by the Flesch Reading Ease scale and the grade scores.
- Results. The data showed that whilst the individual authors varied in their styles, each was consistent across the 20–25 years period.
- Conclusions. Academic writing styles are fixed fairly early on and do not alter much with time.
Such abstracts can be commonly found in medical journals and in some journals in the social sciences. As shown in the example above, such abstracts usually contain more details than traditional ones. One particular detail not mentioned in the abstract above (because of the nature of the study) is the number of participants involved and their sex (see [3]). More detailed accounts of the development and use of structured abstracts can be found elsewhere [1,4,5]. In some journals, the text is run on continuously, but as shown above, it is easier to read the abstract when it is appropriately spaced.
Version 4: Adding in Key Words
Key words facilitate computer-based search and retrieval for related materials (however, they are often insufficiently precise). In addition, they may be useful for indexing purposes [1].
- Background. There has been little research examining how academic writing changes with time.
- Aim. The aim of this study was to see whether or not an author’s style when writing an academic book review changes over time.
- Method. We examined a selection of book reviews written by five authors over a 20–25 years period. For each author we recorded the number of words, the number of paragraphs, the average sentence lengths, the use of passive tenses, and reading difficulty, as measured by the Flesch Reading Ease scale and the grade scores.
- Results. The data showed that whilst the individual authors varied in their styles, each was consistent across the 20–25 years period.
- Conclusions. Academic writing styles are fixed fairly early on and do not alter much with time.
- Key words. book reviews; readability; age
Version 5: Abstracts Containing Electronic Links to Previous Research
Electronic links can be provided in abstracts that link the reader directly to previous papers related to the current research. For example, in the abstract below, clicking on to these italicised links would take you directly to these papers.
- Background. There has been little research examining how academic writing changes with time.
- Aim. The aim of this study was to see whether or not an author’s style when writing an academic book review changes over time (Hartley & Cabanac, 2015; Hartley, Howe and McKeachie, 2001).
- Method. We examined a selection of book reviews written by five authors over a 20–25 year period. For each author we recorded the number of words, the number of paragraphs, the average sentence lengths, the use of passive tenses, and reading difficulty, as measured by the Flesch Reading Ease scale and the grade scores (Hartley & Cabanac, 2016).
- Results. The data showed that whilst the individual authors varied in their styles, each was consistent across the 20–25 years period.
- Conclusions. Academic writing styles are fixed fairly early on and do not alter much with time.
- Key words. book reviews; readability; age
Version 6: Abstracts with Highlights
Currently, especially in journals published by Elsevier, it is fashionable to include the highlights of a paper either before, or more frequently, after the abstract. Sometimes these highlights accompany the abstract, but it is more common to find them on their own after the titles of the articles. For the abstract under discussion, a highlight might appear thus:
Highlights
- Academic writing styles change little with age when writing book reviews
- …
But there are usually three or four highlights per paper.
Version 7. Readable Abstracts
Readable abstracts are typically added to an article (at the beginning or the end) in addition to the more technical one, and they provide a lay person’s account of the content of the paper [6,7]. A related approach is to provide information under headings—such as “What is already known about this topic?” “What this study adds”, and “What are the implications of this study for practice and/or policy?” Examples can be found in the British Medical Journal, and the British Journal of Educational Technology. Here we might find:
- What is already known about this topic?There are few studies of academic writing over time, but most assume that writing improves with practice.
- What are the implications of this study for practice and/or policy?None.
Version 8: Tweetable Abstracts
Some journals (e.g., Methods in Ecology and Evolution and BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology) now require authors to produce a tweetable abstract as well as a traditional one. The aim being, presumably, to facilitate rapid dissemination of the contents (e.g., [8]). Tweetable abstracts contain the essence of a study and a hyperlink with the paper’s DOI or URL in no more than 140 characters.
In our case, this might read:
- Academic writing styles change little with age when writing book reviews—study finds.
However, the little research that we have found so far on this topic does not suggest that tweeting an abstract leads to significantly greater downloads of the related papers [9].
Version 9: One-Sentence Abstracts
Some platforms, like OpenReview1 used by the International Conference on Learning Representations (in the Machine Learning community) display an abstract in block format and a TL; DR section. This acronym introduced in the Oxford dictionaries2 in 2013 means: “TL;DR, abbrev.: ‘too long didn’t read’: used as a dismissive response to a lengthy online post, or to introduce a summary of a lengthy post.”
In our case, the TL;DR version of the abstract might read:
- TL;DR: Academic writing styles change little with age when writing book reviews.
Version 10: One-Word Abstracts
Even shorter than tweetable abstracts are one-word abstracts. Such abstracts can occur when the title of an article is phrased in the form of a question. So, if the title of our paper had been “Does academic writing change with age?” a one-word abstract would say “No”.
One word abstracts are rare, and are probably meant to be witty. Here are some examples:
- Title: Can apparent superluminal neutrino speeds be explained as a quantum weak measurement?Abstract: Probably not in [10].
- Title: Is the sequence of earthquakes in Southern California, with aftershocks removed, Poissonian?Abstract: Yes in [11].
- Title: Do users verify SSH keys?Abstract: No in [12].
Version 11: Graphical Abstracts
A number of journals now ask authors to provide a graphical abstract in addition to a normal one [13]. Such abstracts are supposed to provide “a single, concise pictorial and visual summary of the main findings of an article”3. However, to our knowledge, there has so far been little assessment of papers with graphical abstracts. Indeed, Pferschy-Wenzig et al. [14] found that manuscripts published in the Molecules journal without graphical abstracts performed better in terms of downloads, abstract views, and total citations than manuscripts with them.
Sometimes these graphical abstracts stand alone, but they often accompany a traditional verbal one. A graphical abstract for this current paper might look as in Figure 1, but it would be difficult for readers to understand it without reading the paper first.
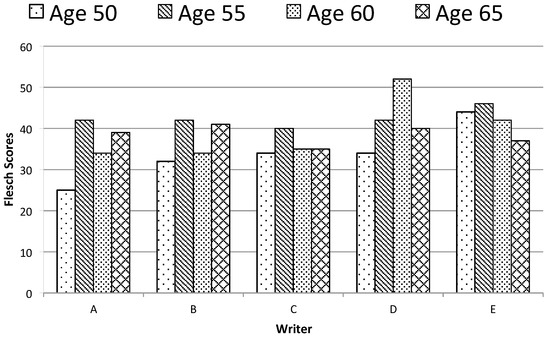
Figure 1.
Potential graphical abstract for paper [2].
Version 12: Video Abstracts
Video abstracts normally consist of brief interviews with the author(s) explaining what they did, why, and what happened. It might be possible to include one here, but we have not been asked to do so. Video abstracts are usually created after the paper under consideration has been accepted, and they are linked to the paper upon publication. Examples can be found in electronic versions of papers published in Nature Chemistry, The New Journal of Physics, and the British Medical Journal (after 2015). Spicer [15] maintains that video abstracts allow authors to communicate their research through a personalized media-rich environment in ways that are impossible in print. Details of how to create and submit video abstracts can be found at http://authorservices.taylorandfrancis.com.
Version 13: Computer-Generated Abstracts
We do not know whether or not we have read any computer-generated abstracts, nor indeed what it would be like to create one. Nonetheless, the possibilities in this respect have been discussed since the 1960s (e.g., [16,17]). It should not be beyond the bounds of possibility to expect that computer-assisted abstracts will soon become the norm.
2. Concluding Remarks
In this paper, we have tried to show that there is more than one way of writing an abstract. Normally, of course, authors follow the styles used in the journals they are submitting their articles to. However, some journals seem to be more ambitious than others in this respect. Readers may be interested to know that the wording for Publications in this respect reads:
- “We strongly encourage authors to use the … style of structured abstracts, but without the headings.”
In the same line and as part as its Manuscript Formatting Guide, the flagship Nature journal provides an example of abstract in block format with annotations explaining the sequence of information that authors are requested to provide in writing the abstract (see Figure 2).

Figure 2.
“How to construct a Nature summary paragraph” as provided in the Manuscript formatting guide at https://www.nature.com/nature/authors/gta.
Perhaps the most important consideration is who the article is for. Scholarly readers might like a structured abstract with links to the previous research and key words. Others are perhaps satisfied with a less-detailed approach. We would probably all enjoy a one-word abstract.
Different aims and purposes imply that there may be different (but overlapping) ways of evaluating abstracts. Some authors, for instance, have evaluated abstracts using checklists, others rating scales, and others readability measures (and some all three—e.g., [4,18]). Some others have employed appropriate readers, whereas others have used some students, writers, and subject matter experts (e.g., [19]). Perhaps current authors might like to employ some of these methods for assessing the efficiency of their abstracts before finalising them.
Acknowledgments
This article was not funded by any external sources of funding to the authors.
Author Contributions
J.H. and G.C. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hartley, J. Academic Writing and Publishing: A Practical Handbook; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, J.; Cowan, J.; Deeson, C.; Thomas, P. Book reviews in time. Scientometrics 2016, 109, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J. More sex please, we’re psychologists. Psychologist 2004, 17, 80–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, J.; Betts, L. Common weaknesses in traditional abstracts in the social sciences. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 60, 2010–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J. Current findings from research on structured abstracts: An update. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2014, 102, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, J. What’s new in abstracts of science articles? J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 2016, 104, 235–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehne, L.M.; Olden, J.D. Lay summaries needed to enhance science communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3585–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Else, H. Tell us about your paper—And make it short and tweet. Times Higher Education, 9 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tonia, T.; Van Oyen, H.; Berger, A.; Schindler, C.; Künzli, N. If I tweet will you cite? The effect of social media exposure of articles on downloads and citations. Int. J. Public Health 2016, 61, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, M.V.; Brunner, N.; Popescu, S.; Shukla, P. Can apparent superluminal neutrino speeds be explained as a quantum weak measurement? J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2011, 44, 492001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.K.; Knopoff, L. Is the sequence of earthquakes in Southern California, with aftershocks removed, Poissonian? Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1974, 64, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, P. Do Users Verify SSH keys? Login 2011, 36, 35–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gilaberte, Y.; Nagore, E.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Moreno, D. Is a Picture Worth a Thousand Words? The Graphical Abstract. Actas Dermo-Sifiliogr. 2016, 107, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pferschy-Wenzig, E.M.; Pferschy, U.; Wang, D.; Mocan, A.; Atanasov, A. Does a Graphical Abstract Bring More Visibility to Your Paper? Molecules 2016, 21, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, S. Video abstracts are a low-barrier means for publishers to extend the shelf life of research. London School of Economics—Impact of the Social Sciences Blog, 2 May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Luhn, H.P. The automatic creation of literature abstracts. IBM J. Res. Dev. 1958, 2, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggion, H.; Poibeau, T. Automatic text summarization: Past, present and future. In Multi-Source, Multilingual Information Extraction and Summarization; Poibeau, T., Saggion, H., Piskorski, J., Yangarber, R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 3–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ufnalska, S.; Hartley, J. How can we evaluate the quality of abstracts. Eur. Sci. Ed. 2009, 35, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hartley, J. Improving the clarity of journal abstracts in Psychology. Sci. Commun. 2003, 24, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1 | See, e.g., https://openreview.net/forum?id=rJY0-Kcll |
| 2 | |
| 3 | Elsevier’s web page “Graphical Abstracts” at https://www.elsevier.com/authors/journal-authors/graphical-abstract provides several examples taken from published articles in a variety of disciplines. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).