Abrasion Behaviour of Different Charcoal Toothpastes When Using Electric Toothbrushes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
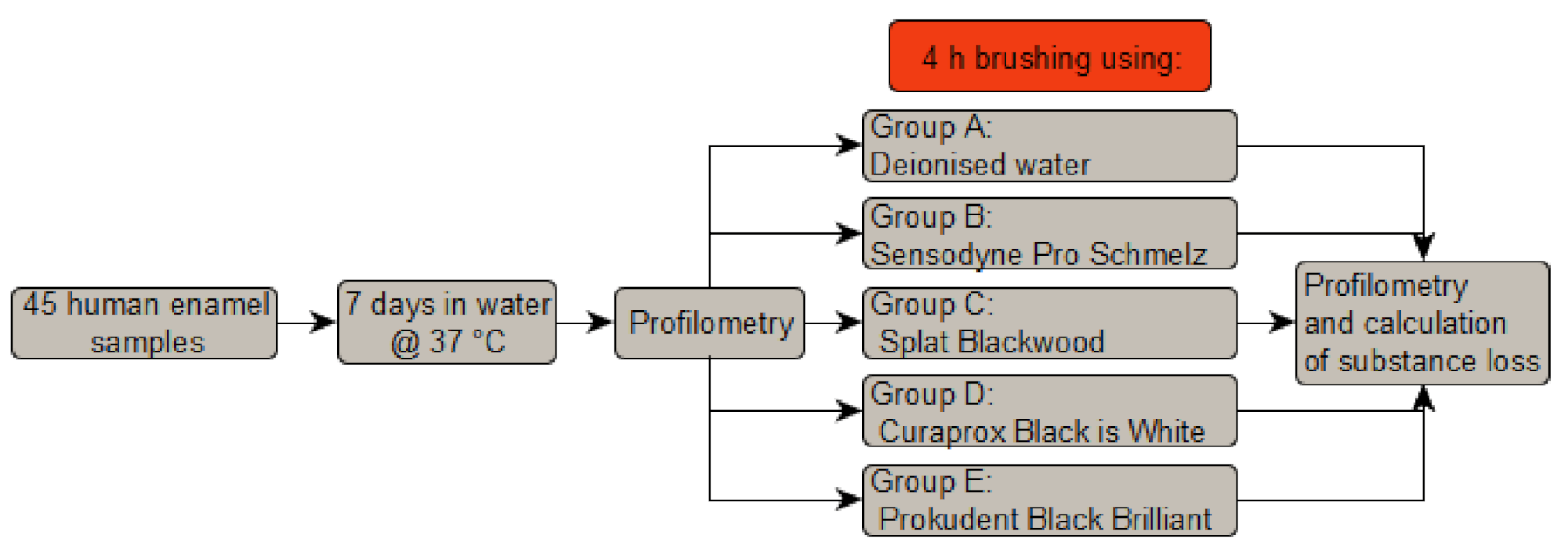
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Toothbrushing Machine
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Profilometry and Calculation of Substance Loss
2.4. Brushing
2.5. Statistics
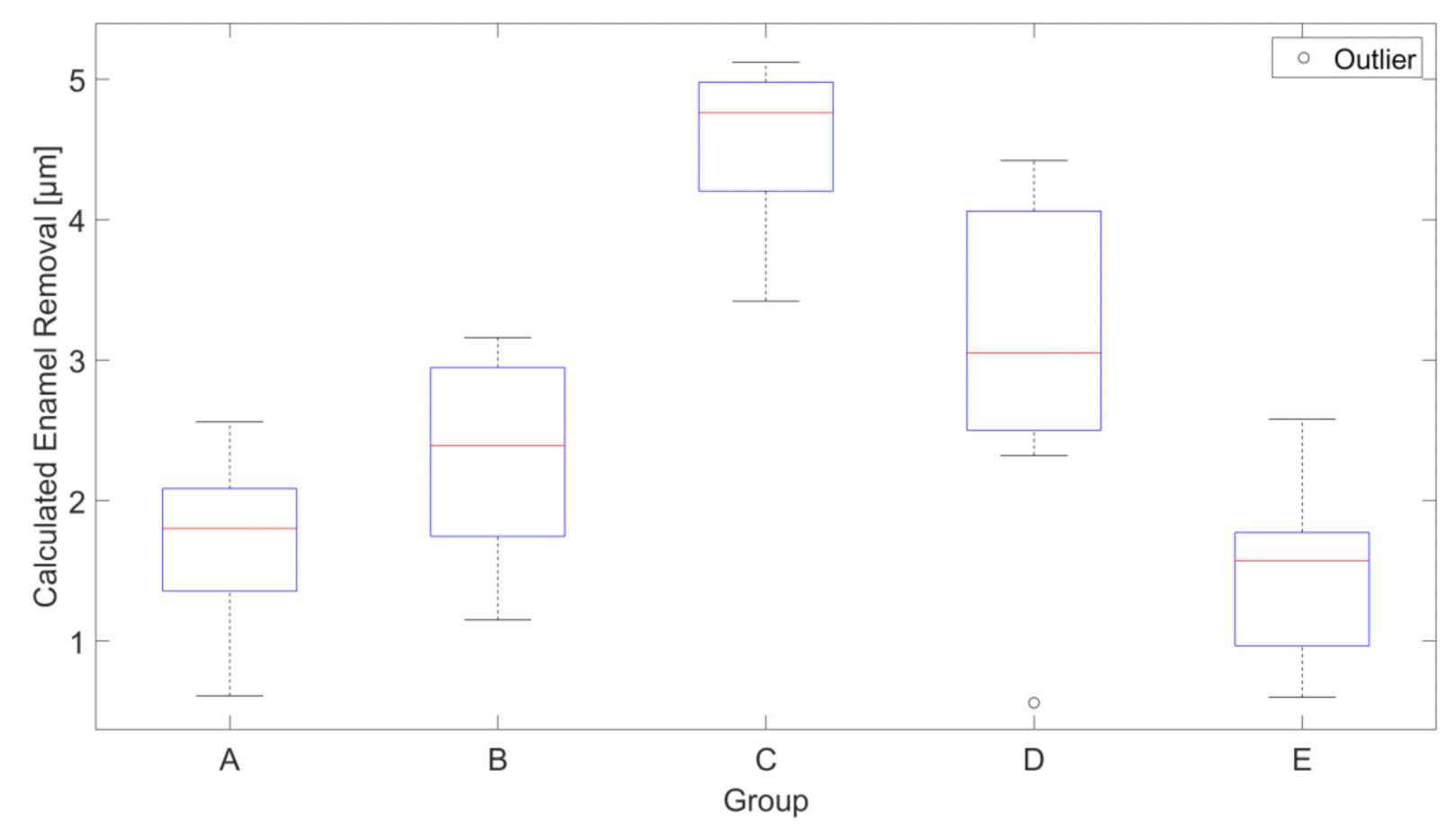
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, J.K.; Bashirelahi, N.; Reynolds, M.A. Charcoal and charcoal-based dentifrices: A literature review. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2017, 148, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwall, L.H.; Greenwall-Cohen, J.; Wilson, N.H.F. Charcoal-containing dentifrices. Br. Dent. J. 2019, 226, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhana, C.; Rao, G.N.; Sathish, R.S.; Kumar, P.S.; Kumar, V.A.; Madhav, M.V. Study on defluoridation of drinking water using zirconium ion impregnated activated charcoals. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 2007, 14, 350–354. [Google Scholar]
- Pertiwi, U.; Eriwati, Y.K.; Irawan, B. Surface changes of enamel after brushing with charcoal toothpaste. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; p. 12002. [Google Scholar]
- Palandi, S.D.; Kury, M.; Picolo, M.Z.D.; Coelho, C.S.S.; Cavalli, V. Effects of activated charcoal powder combined with toothpastes on enamel color change and surface properties. J. Esthet. Restor. Dent. 2020, 32, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, A.; Attin, T. Design of Erosion/Abrasion Studies—Insights and Rational Concepts. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Philpotts, C.J.; Weader, E.; Joiner, A. The measurement in vitro of enamel and dentine wear by toothpastes of different abrasivity. Int. Dent. J. 2005, 55, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagger, D.C.; Harrison, A. An In-Vitro Investigation into the Wear Effects of Selected Restorative Materials on Enamel. J. Oral Rehabil. 1995, 22, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.; Addy, M. Wear of dentine in vitro by toothpaste abrasives and detergents alone and combined. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2005, 32, 1242–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiner, A.; Philpotts, C.J.; Ashcroft, A.T.; Laucello, M.; Salvaderi, A. In vitro cleaning, abrasion and fluoride efficacy of a new silica based whitening toothpaste containing blue covarine. J. Dent. 2008, 36, S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeggi, T.; Lussi, A. Toothbrush abrasion of erosively altered enamel after intraoral exposure to saliva: An in situ study. Caries Res. 1999, 33, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, S.; West, N.X.; Pickles, M.J.; Joiner, A.; Newcombe, R.G.; Addy, M. Investigation of erosion and abrasion on enamel and dentine: A model in situ using toothpastes of different abrasivity. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2003, 30, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attin, T.; Buchalla, W.; Gollner, M.; Hellwig, E. Use of variable remineralization periods to improve the abrasion resistance of previously eroded enamel. Caries Res. 2000, 34, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganss, C.; Marten, J.; Hara, A.T.; Schlueter, N. Toothpastes and enamel erosion/abrasion—Impact of active ingredients and the particulate fraction. J. Dent. 2016, 54, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GSK Customer Support by Email Inquiry. Available online: https://www.gsk.com (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Coldmooncosmetics. Available online: https://www.coldmooncosmetics.de/marken/splat/ (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Curaprox. Available online: https://www.curaprox.com/data/downloads/81427791789Black_Is_White_d.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Rossmann Customer Support by Email Inquiry. Available online: https://business.rossmann.de (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Nečas, D.; Klapetek, P. Gwyddion: An open-source software for SPM data analysis. Open Phys. 2012, 10, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickles, M.; Joiner, A.; Weader, E.; Cooper, Y.; Cox, T. Abrasion of human enamel and dentine caused by toothpastes of differing abrasivity determined using an in situ wear model. Int. Dent. J. 2005, 55, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzo, D.; Philpotts, C.J.; Cox, T.F.; Joiner, A. The effect of toothpaste concentration on enamel and dentine wear in vitro. J. Dent. 2010, 38, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prencipe, M.; Vandeven, M.; Feldman, B.N.; Schemehorn, B.R. A Comparative Study of Laboratory Dentifrice Abrasion Measuring Methods. J. Clin. Dent. 2016, 27, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Lima, L.C.; Viana, I.E.L.; da Paz, S.L.P.; Bezerra, S.J.C.; Joao-Souza, S.H.; Carvalho, T.S.; Scaramucci, T. Role of desensitizing/whitening dentifrices in enamel wear. J. Dent. 2020, 99, 103390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner, A.; Weader, E.; Cox, T.F. The Measurement of Enamel Wear of Two Tooth pastes. Oral Health Prev. Dent. 2004, 2, 383–388. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenburger, M.; Shellis, R.; Addy, M. Comparative study of wear of enamel induced by alternating and simultaneous combinations of abrasion and erosion in vitro. Caries Res. 2003, 37, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios, D.; Honorio, H.M.; Magalhaes, A.C.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Machado, M.; Silva, S.M.B.; Buzalaf, M.A.R. Effect of salivary stimulation on erosion of human and bovine enamel subjected or not to subsequent abrasion: An in situ/ex vivo study. Caries Res. 2006, 40, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenburger, M.; Addy, M.; Hughes, J.A.; Shellis, R.P. Effect of time on the remineralisation of enamel by synthetic saliva after citric acid erosion. Caries Res. 2001, 35, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhaes, A.C.; Rios, D.; Delbem, A.C.B.; Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Machado, M. Influence of fluoride dentifrice on brushing abrasion of eroded human enamel: An in situ/ex vivo study. Caries Res. 2007, 41, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | Commercial Brand | Ingredients | RDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | - | Aqua | - |
| B | Sensodyne Pro Schmelz Repair Zahnschmelz, conventional (no charcoal) | Hydrated Silica, Aqua, Sorbitol, Glycerin, Potassium Nitrate, PEG-6, Sodium Lactate, Cocamidopropyl Betaine, Aroma, Titanium Dioxide, Xanthan Gum, Sodium Saccharin, Sodium Fluoride (1450 ppm F−), PVM/MA Copolymer, Sodium Hydroxide, Limonene | 35 (±15%) [15] |
| C | Splat Blackwood | Hydrated Silica, Charcoal Powder, Aqua, Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, Glycerin, Maltooligosyl Glucoside, Sodium Lauroyl Sarcosinate, Cellulose Gum, Aroma, Capryloyl/Caproyl Methyl Glucamide, Lauroyl/Myristoyl Methyl Glucamide, Sodium Benzoate, Stevia Rebaudiana Leaf Extract, Potassium Sorbate, Menthol o-Cymen-5-ol, Juniperus Communis Sprout Extract, Limonene | 75 [16] |
| D | Curaprox Black is White | Hydrated Silica, Charcoal Powder, Aqua, Sorbitol, Glycerin, Aroma, Decyl Glucoside, Cocamidropropyl Betaine, Sodium Monofluorophosphate 950 ppm F-, Tocopherol, Xanthan Gum, Maltodextrin, Mica, Hydroxylapatite (Nano), Potassium Acesulfame, Titanium Dioxide, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Chloride, Citrus Limon Peel Oil, Sodium Hydroxide, Zea Mays Starch, Amyloglucosidase, Glucose Oxidase, Urtica Dioca Leaf Extract, Potassium Thiocyanate, Cetearyl Alcohol, Hydrogenated Lecithin, Menthyl Lactate, Methyl Diisopropyl Propionamide, Ethyl Menthane Carboxamide, Stearic Acid, Mannitol, Sodium Bisulfite, Tin Oxide, Lactoperoxidase, Limonene | 50 [17] |
| E | Prokudent Black Brilliant | Hydrated Silica, Charcoal Powder, Aqua, Sorbitol, Propylene Glycol, Pentasodium Triposphate, Tetrapotassium Pyrophosphate, Sodium C14-16 Olefin Sulfonate, Aroma, Disodium Pyrophosphate, Xanthan Gum, Menthol, Sodium Fluoride (1450 ppm F−), Sodium Saccharin | 120 [18] |
| Group | Commercial Brand | Mean Removal [µm] | Standard Deviation [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Water | 1.7 | 0.6 |
| B | Sensodyne Pro Schmelz Repair Zahnschmelz, conventional (no charcoal) | 2.3 | 0.7 |
| C | Splat Blackwood | 4.6 | 0.6 |
| D | Curaprox Black is White | 3.2 | 0.9 |
| E | Prokudent Black Brilliant | 1.4 | 0.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greuling, A.; Emke, J.M.; Eisenburger, M. Abrasion Behaviour of Different Charcoal Toothpastes When Using Electric Toothbrushes. Dent. J. 2021, 9, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9080097
Greuling A, Emke JM, Eisenburger M. Abrasion Behaviour of Different Charcoal Toothpastes When Using Electric Toothbrushes. Dentistry Journal. 2021; 9(8):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9080097
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreuling, Andreas, Johanna Maria Emke, and Michael Eisenburger. 2021. "Abrasion Behaviour of Different Charcoal Toothpastes When Using Electric Toothbrushes" Dentistry Journal 9, no. 8: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9080097
APA StyleGreuling, A., Emke, J. M., & Eisenburger, M. (2021). Abrasion Behaviour of Different Charcoal Toothpastes When Using Electric Toothbrushes. Dentistry Journal, 9(8), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/dj9080097






